change wheel CHEVROLET CAMARO 1967 1.G Chassis User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: CHEVROLET, Model Year: 1967, Model line: CAMARO, Model: CHEVROLET CAMARO 1967 1.GPages: 659, PDF Size: 114.24 MB
Page 382 of 659

CLUTCH
AND
TRANSMISSIONS
7-23
Assembly (Fig.
4X)
1.
With detent spring tang projecting
up
over
the 3rd
and
4th
shifter shaft cover opening install
the
first
and second detent
cam
onto
the
detent
cam
pivot
pin.
With
the
detent spring tang projecting
up
over
the
first
and
second shifter shaft cover hole install
the
3rd
and 4th
detent
cam,
NOTE:
The 1-2
detent
cam has a
.090" greater
contour
on the
inside detent notch.
2.
3.
Install detent
cam
retaining
"C"
ring
to
pivot shaft,
and hook spring into detent
cam
notches.
Install
1-2 and 3-4
shifter shaft assemblies
in
cover
being careful
not to
damage seals. Install both shift
forks
to
shifter shaft assemblies, lifting
up on
detent
cam
to
allow forks
to
fully seat into position.
4.
Install reverse detent ball
and
spring
to
cover, then
install reverse shifter shaft assembly
to
cover.
5.
Install outer shifter levers, flat washers, lock wash-
ers
and
bolts.
Installation
1.
Shift shifter levers into neutral detent (center) posi-
tion. Position cover gasket
on
case.
2.
Carefully position side cover into place making sure
the shift forks
are
aligned with their respective
mainshaft clutch sliding sleeves.
Install cover attaching bolts
and
tighten evenly
to
specified torque.
Remove filler plug
and add
lubricant specified
in
Section
0, to
level
of
filler plug hole.
3.
4.
ALUMINUM POWERGLIDE
INDEX
Page
General
Description
7-23
Maintenance
and
Adjustments .............. 7—23
Oil
Level Check
7-23
Periodic
Oil
Change
7-24
Periodic
Low
Band Adjustment
7-24
Manual
Shift Linkage Check
and
Adjust
7-24
Floor
Shift Linkage
7-25
Floor
Mounted Control Lever
and
Bracket
Assembly
7-29
Throttle
Valve Linkage
.... 7-29
Neutral
Safety Switch
.. . 7-30
Throttle
Return Check Valve (Dashpot)
7-30
Component
Parts Replacement
7-30
Transmission
Replacement .............. 7—30
Page
Other
Service Operations
7-32
Diagnosis
7-32
Warming
Up
Transmission
7-32
Shop
Warm
Up , 7-32
Road
Warm
Up 7-32
Checking
Fluid Level
and
Condition
7-32
Manual
Linkage
7-32
Oil
Leaks
7-33
Basic
Pressure Checks
7-33
Wide
Open Throttle Upshift Pressure Check
.... 7-33
Idle
Pressure
in
Drive Range
7-33
Manual
"Low"
Range Pressure Check .......
7-33
Drive
Range Overrun (Coast) Pressure
.
.......
7-33
Powerglide
Shift Points
. . 7-35
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The case
and
converter housing
of the two
speed alumi-
num Powerglide Transmission
is a
single case aluminum
unit. When
the
manual control
is
placed
in the
drive
po-
sition,
the
transmission automatically shifts
to low
gear
for initial vehicle movement.
As the car
gains speed
and
depending
on
load
and
throttle position,
an
automatic shift
is made
to
high gear.
A
forced downshift feature
pro-
vides
a
passing gear
by
returning
the
transmission
to low
range.
The
oil
pump assembly
is a
conventional gear type
and
the
oil
pump housing
is of the
large diameter type acting
as
the
front bulkhead
of the
transmission.
The
torque
converter
is a
conventional three element welded design
bolted
to the
engine flywheel which drives through
a
two-
speed planetary gearset.
The
high clutch assembly
is
typical
of the
designs used
in
this type transmission.
The
aluminum Powerglide uses
an
output shaft mounted
gov-
ernor which requires
a
hole through
the
output shaft.
The
reverse clutch assembly
is a
multiple disc type clutch.
The steel plates
are
splined directly
to the
case while
the
face plates
are
splined
to the
internal
or
ring gear.
The
clutch piston operates within
the
rear portion
of the
case.
The internal diameter
of the
pistoh
is
sealed to
an
integral
hub portion
of the
case rear bulkhead.
The
outside
dia-
meter
is
sealed
to a
machined portion
of the
case.
The
piston
is
hydraulically applied
and is
released
by
separate
coil springs.
The
valve body assembly
is
bolted
to the
bottom
of the
transmission case
and is
accessible
for
service
by
removing
the oil pan
assembly.
The
valve
body consists
of an
upper
and
lower body located
on
either
side
of a
transfer plate.
The
vacuum modulator
is lo-
cated
on the
left rear face
of the
transmission case.
The
modulator valve bore
is
located
in the
upper valve body.
MAINTENANCE
AND
ADJUSTMENTS
OIL LEVEL CHECK
The transmission
oil
level should
be
checked period-
ically
as
recommended
in
Section
0. Oil
should
be
added
only when level
is on or
below
the
"ADD" mark
on the dip
stick with
oil hot or at
operating temperature.
The oil
level
dip
stick
is
located
at the
right rear
of the
engine
compartment. Fill with
oil
specified
in
Section
0.
In order
to
check
oil
level accurately,
the
engine should
be idled with
the
transmission
oil hot and the
control
lever
in
neutral (N) position.
It
is
important that
the oil
level
be
maintained
no
higher than
the
"FULL" mark
on the
transmission
oil
level gauge.
DO NOT
OVERFILL,
for
when
the oil
level
CHEVROLET CHASSIS SERVICE MANUAL
Page 383 of 659
CLUTCH AND TRANSMISSIONS 7-24
is at the full mark on the dip stick, it is just slightly be-
low the planetary gear unit. If additional oil is added,
bringing the oil level above the full mark, the planetary
unit will run in the oil, foaming and aerating the oil. This
aerated oil carried through the various oil pressure pas-
sages (low servo, reverse servo, clutch apply, converter,
etc.) may cause malfunction of the transmission assem-
bly, resulting in cavitation noise in the converter and
improper band or clutch application. Overheating may
also occur.
If the transmission is found consistently low on oil, a
thorough inspection should be made to find and correct
all external oil leaks.
PERIODIC OIL CHANGE
The transmission oil should be changed periodically as
recommended in Section 0, and whenever transmission is
to be removed from the vehicle for repairs.
1.
Run engine for one minute in neutral prior to chang-
ing.
2.
Be sure vehicle is level or raise from the rear only.
3.
Remove the oil pan drain plug and allow oil to drain
thoroughly into a pan or can.
Replace drain plug and refill with approximately two
quarts of oil specified in Section 0.
NOTE: To refill the transmission, remove dip
stick from oil filler tube and refill transmission
with oil specified in Section 0 using filler tube
and funnel J-4264. Then, after shifting into all
ranges at idle speed to fill all oil passages, the
engine should be run at 800-1000 rpm with the
transmission in Neutral until the oil warms up,
then add oil as required to raise the fluid level
to the full mark on the dip stick. Refill capacity
is approximately 2 qts.
4.
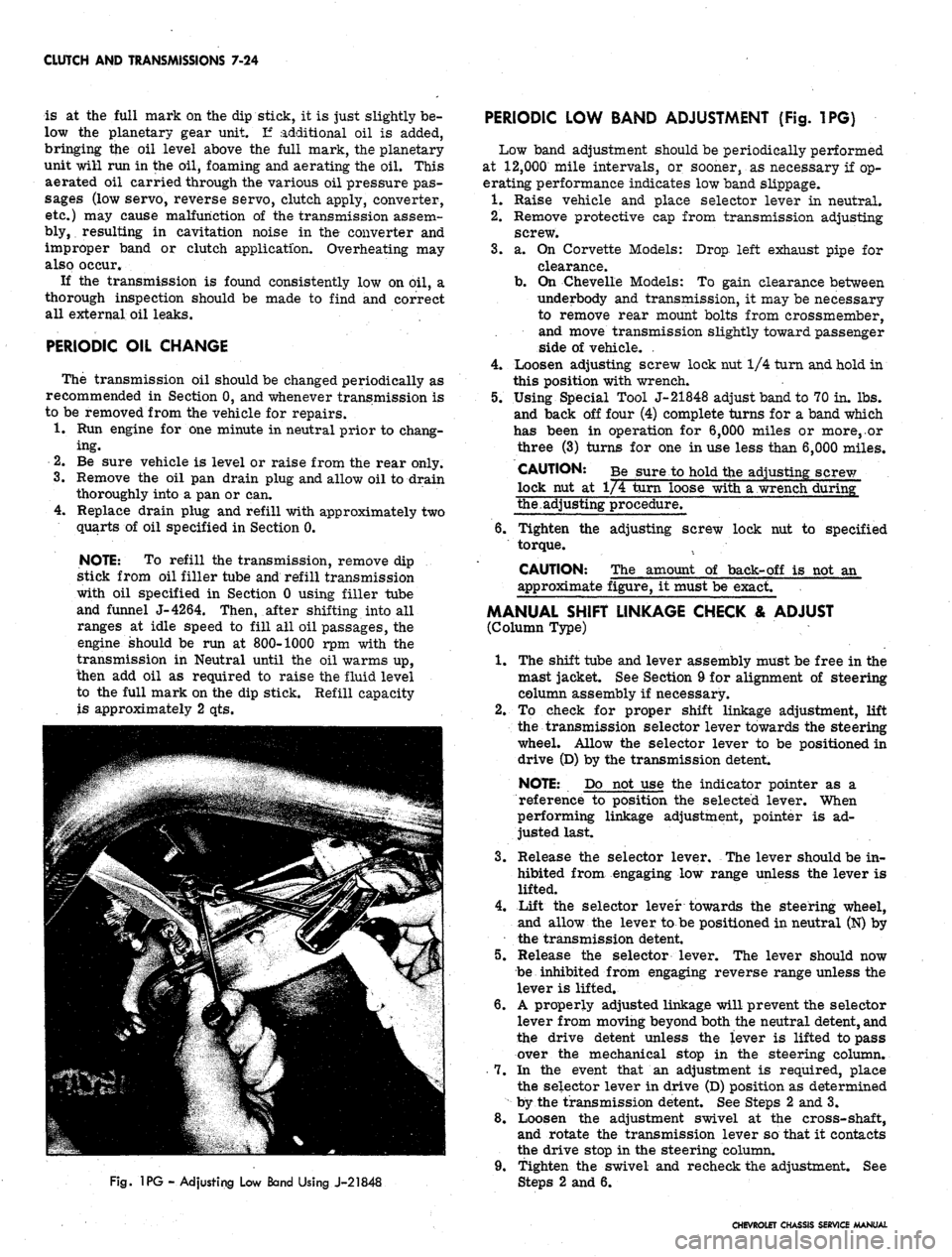
Fig.
1PG - Adjusting Low Band Using J-21848
PERIODIC LOW BAND ADJUSTMENT (Fig. 1PG)
Low band adjustment should be periodically performed
at 12,000 mile intervals, or sooner, as necessary if op-
erating performance indicates low band slippage.
1.
Raise vehicle and place selector lever in neutral.
2.
Remove protective cap from transmission adjusting
screw.
3.
a. On Corvette Models: Drop left exhaust pipe for
clearance.
b.
On Chevelle Models: To gain clearance between
underbody and transmission, it may be necessary
to remove rear mount bolts from crossmember,
and move transmission slightly toward passenger
side of vehicle. .
4.
Loosen adjusting screw lock nut 1/4 turn and hold in
this position with wrench.
5.
Using Special Tool J-21848 adjust band to 70 in. lbs.
and back off four (4) complete turns for a band which
has been in operation for 6,000 miles or more,.or
three (3) turns for one in use less than 6,000 miles.
CAUTION: Be sure to hold the adjusting screw
lock nut at 1/4 turn loose with a wrench during"
the.adjusting procedure.
6. Tighten the adjusting screw lock nut to specified
torque.
CAUTION: The amount of back-off is not an
approximate figure, it must be exact.
MANUAL SHIFT LINKAGE CHECK & ADJUST
(Column Type)
1.
The shift tube and lever assembly must be free in the
mast jacket. See Section 9 for alignment of steering
column assembly if necessary.
2.
To check for proper shift linkage adjustment, lift
the transmission selector lever towards the steering
wheel. Allow the selector lever to be positioned in
drive (D) by the transmission detent.
NOTE: Do not use the indicator pointer as a
reference to position the selected lever. When
performing linkage adjustment, pointer is ad-
justed last.
3.
Release the selector lever. The lever should be in-
hibited from engaging low range unless the lever is
lifted.
4.
Lift the selector lever towards the steering wheel,
and allow the lever to be positioned in neutral (N) by
the transmission detent.
5.
Release the selector lever. The lever should now
be inhibited from engaging reverse range unless the
lever is lifted.
6. A properly adjusted linkage will prevent the selector
lever from moving beyond both the neutral detent, and
the drive detent unless the lever is lifted to pass
over the mechanical stop in the steering column.
7.
In the event that an adjustment is required, place
the selector lever in drive (D) position as determined
by the transmission detent. See Steps 2 and 3.
8. Loosen the adjustment swivel at the cross-shaft,
and rotate the transmission lever so that it contacts
the drive stop in the steering column.
9. Tighten the swivel and recheck the adjustment. See
2 and 6.
CHEVROLET CHASSIS SERVICE MANUAL
Page 396 of 659

CLUTCH AND TRANSMISSIONS 7-37
LI.
- LI Range can be selected at any vehicle speed,
and the transmission will shift to second gear
and remain in second until vehicle speed is re-
duced to approximately 40 MPH, .depending on
axle ratio. LI Range position prevents the trans-
mission from shifting out of first gear.
It is very important that any communication concerning
the Turbo Hydra-Matic always contain the transmission
serial number and that all transmission parts returned
to Chevrolet Motor Division always be tagged with the
transmission serial number.
MAINTENANCE AND ADJUSTMENTS
TRANSMISSION FLUID
Transmission fluid level should be checked with trans-
mission warm and selector lever in "P" Park position,
every time engine oil level is checked or as specified in
Section 0 when engine oil is changed.
CAUTION: Since the Turbo Hydra-Matic trans-
mission is very sensitive to oil level, special
precautions should be taken when checking the
oil level, to insure against an overfifE
Transmission fluid should be changed as specified in
Section 0.
FLUID LEVEL INDICATOR
The fluid level indicator is located in the filler pipe at
the right rear corner of the engine. To bring the fluid
level from the add mark to the full mark add 1 pint.
Fluid level should be to the full mark with transmission
at normal operating temperature. With cold fluid the
level should be at the add mark or slightly below.
SHIFT CONTROL LINKAGE ADJUSTMENT
Adjust linkage as shown below and in Figure 2.
1.
The shift tube and lever assembly must be free in the
mast jacket See Section 9 for alignment of steering
column assembly if necessary.
2.
To check for proper shift linkage adjustment, lift the
transmission selector lever towards the steering
wheel. Allow the selector lever to be positioned in
drive (D) by the transmission detent.
NOTE: Do not use the indicator pointer as a
reference to position the selector lever. When
performing linkage adjustment, pointer is ad-
justed last.
3.
Release the selector lever. The lever should be in-
hibited from engaging low range unless the lever is
lifted.
4.
Lift the selector lever towards the steering wheel,
and allow the lever to be positioned in neutral (N) by
the transmission detent.
5.
Release the selector lever. The lever should now be
inhibited from engaging reverse range unless the
lever is lifted.
6. A properly adjusted linkage will prevent the selector
lever from moving beyond both the neutral detent,
and the drive detent unless the lever is lifted to pass
over the mechanical stop in the steering column.
See schematic diagram.
7.
In the event that an adjustment is required, place the
selector lever in drive (D) position as determined by
the transmission detent. See Steps 2 and 3.
8. Loosen the adjustment swivel at the cross-shaft, and
rotate the transmission lever so that it contacts the
drive stop in the steering column.
9. Tighten the swivel and recheck the adjustment. See
Steps 2 and 6. -
l(h Readjust indicator needle if necessary to agree with
the transmission detent" positions. See Section 9.
11.
Readjust neutral safety switch if necessary to pro-
vide the correct relationship to the transmission de-
tent positions. See Section 12.
12.
When properly adjusted the following conditions must
be met by manual operation of the steering column
shift lever:
a. From reverse to drive position travel, the trans-
mission detent feel must be noted and related to
indicated position on dial.
b.
When in drive and reverse positions, pull lever
rearward (towards steering wheel) and then re-
lease. It must drop back into position with no
restrictions.
NEUTRAL SAFETY SWITCH ADJUSTMENT
The neutral safety switch must be adjusted so that the
car will start in the park or neutral position, but will not
start in the other positions. For replacement refer to
Section 12 of this Manual.
DRAINING AND REFILLING TRANSMISSION
Drain oil immediately after operation before it has had
an opportunity to cool.
To drain oil proceed as follows:
1.
Remove bottom pan attaching screws, pan, and gas-
ket.
2.
Remove oil strainer. Remove "O" ring seal from
pick-up pipe and discard.
3.
Discard strainer if dirty.
4.
Install new "O" ring seal on pick-up pipe and install
strainer and pipe assembly.
5.
Thoroughly clean bottom pan.
6.. Affix new gasket to bottom pan with petroleum jelly.
7.
Install bottom pan with attaching screws and torque
to specifications;
8. If only the pan has been removed, pour approximately
7-1/2 pints of fluid into the transmission. If the
valve body has also been removed use 9-1/2 pints.
After a complete overhaul approximately 19 pints
are required. Be sure container, spout, or funnel is
clean.
9. Start engine and let idle (carburetor off fast idle
step).
Place selector lever in P position and apply
hand brake.
10.
With transmission warm (approximately 150°F), add
fluid to bring level to full mark on indicator.
CAUTION: Do not overfill. Foaming will re-
sult.
CHEVROLET CHASSIS SERVICE MANUAL
Page 441 of 659

SECTION
9
STEERING
CONTENTS
OF
THIS SECTION
Standard Steering
9-1
Power Steering
9-33
Special Tools
9-40
STANDARD STEERING
INDEX
Page
General Description 9.x
Maintenance and Adjustments 9.1
Adjustments
........................
9-2
Steering Gear 9-2
Steering Wheel Alignment and Higji
Point Centering. . . . 9-4
Toe-in Adjustment 9-4
Corvette Steering Ratio . . . . 9-4
Component Replacement and Repairs . . . . 9-4
Steering Wheel . . . 9-4
Regular Production 9-4
Simulated Wood . . . . 9-5
Corvette Telescoping 9-5
Steering Coupling . 9-6
Steering Gear . 9-9
Sector Shaft Seal Replacement 9-10
Steering Column 9-10
Removal 9-10
Disassembly—Syncromesh Column 9-12
Page
Assembly—Syncromesh Column . . 9-14
Disassembly—Column Mounted Powerglide
Lever or Floor Shift Column 9-16
Assembly-^Column Mounted Powerglide
Lever or Floor Shift Column g_x7
Disassembly—Tilt Column 9-19
Assembly—Tilt Column 9-21
Disassembly—Standard Corvette Column 9-23
Assembly—Standard Corvette Column 9-25
Disassembly—Corvette Telescoping Column .... 9.26
Assembly—Corvette Telescoping Column 9-27
Installation 9.27
Steering Linkage 9.29
Tie
Rods.
. 9-29
Relay Rod . . 9-31
Idler Arm . . . . 9-31
Pitman Arm. . 9-32
Steering Arms • • • • 9-32
Steering Damper 9-32
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The regular production steering gear
is the
recirculat-
ing ball type. This gear provides
for
ease
of
handling
by
transmitting forces from worm
to
sector gear through
ball bearings.
The
steering linkage
is of
the relay type,
and extended interval lubrication design, with the pitman
arm connected
to one end of
the relay
rod. The
other
end
of
the
relay
rod is
connected
to an
idler
arm
which
is
connected
to the
frame side rail opposite
the
steering
gear.
Two
adjustable
tie
rods connect
the
relay
rod to
the steering arms.
All passenger
car
models
for 1967 are
equipped with
new energy absorbing steering columns.
The
mast jacket,
shift tube,
and
steering shaft
are
designed
to
collapse
under various front impact conditions.
All new
columns
are
of
this design, including
the
tilt option and telescope
option.
MAINTENANCE
AND
ADJUSTMENTS
The manual steering gear
is
filled
at the
factory with
a
water resistant grease. Seasonal change
of
this lubrica-
tion
is
unnecessary and
the
housing should
not be
drained.
The steering gear lubricant level should
be
checked every
36,000 miles. Whenever required, additions should
be
made using
a
water resistant
EP
chassis lubricant.
Check and fill steering gear
as
follows:
1.
Remove lower
and
outboard cover retaining screws
(fig.
1).
2.
Insert filling device
in
lower screw hole.
3.
Inject lubricant until
it
appears
in
outboard screw
hole; gear
is now
filled
to
correct level.
The steering linkage should
be
lubricated with water
resistant
EP
chassis lubricant every 6,000 miles
or six
months, whichever occurs first. Lubrication points
and
additional information
on the
chassis lubricant
to be
used
can
be
found
in
Section
0 --
General Information
and
Lubrication.
CHEVROLET CHASSIS SERVICE MANUAL
Page 444 of 659

STEERING 9-4
8. Reassemble pitman arm to sector shaft, lining up
marks made during disassembly. Refer to torque
specifications at rear of manual for correct torque
value.
9. Install horn cap or ornament and connect steering
column harness at chassis connector.
NOTE:
Chevy.n models are equipped with a
shim at the frame to steering gear mounting
bolts.
Shims may be removed or installed as
required for proper steering gear alignment.
STEERING WHEEL ALIGNMENT AND
HIGH POINT CENTERING
1.
Set front wheels in straight ahead position. This can
be checked by driving vehicle a short distance on a
flat surface to determine steering wheel position at
which vehicle follows a straight path.
2.
With front wheels set straight ahead, check position
of mark on wormshaft designating steering gear high
point. This mark should be at the top side of the shaft
at 12 o'clock position and lined up with the mark in
the coupling lower clamp.
3.
If gear has been moved off high point when setting
wheels in straight ahead position, loosen adjusting
sleeve clamps on both left and right hand tie rods,
then turn both sleeves an equal number of turns in
the same direction to bring gear back on high point.
CAUTION: Turning the sleeves an unequal
number of turns or in differential directions will
disturb the toe-in setting of the wheels.
4.
Readjust toe-in as outlined in Section 3 (if necessary).
5. With wheels in a straight ahead position and the
steering gear on highpoint, check the steering wheel
alignment by measuring the distance from each hori-
zontal spoke to the horizontal centerline of the
steering wheel (fig. 5). If the horizontal spokes are
over 1-1/8 inches from the horizontal position the
wheel should be removed and centered. (See steering
wheel removal in this section.)
TOE-IN ADJUSTMENT
Adjust the steering linkage for proper toe-in setting as
outlined in Section 3.
CORVETTE STEERING RATIO (Fig. 6)
The Corvette steering ratio may be changed as follows:
CAUTION: Do not use the rearward hole in the
steering arm with power steering equipment or
interference may result.
1.
Remove tie rod ball stud nut at steering arm and
disconnect tie rod from steering arm.
2.
Move tie rod end to forward hole for 17.6:1 ratio
(fast ratio) or rear hole for 20.2:1 ratio (standard
ratio).
3.
Install tie rod stud nut and tighten securely. Repeat
operation on opposite steering arm.
COMPONENT REPLACEMENT AND REPAIRS
STEERING WHEEL
REGULAR PRODUCTION (Fig. 7)
Removal
1.
Disconnect steering column harness from chassis
wiring harness at connector (fig. 8).
2.
Pull out horn button cap or center ornament and
retainer.
3.
Remove three screws from the receiving cup.
4.
Remove the receiving cup, belleville spring, bushing,
and pivot ring.
5. Remove the steering wheel nut and washer.
6. Using Tool J-2927, install centering adapter on
steering shaft, thread puller anchor screws into
threaded holes provided in steering wheel. Turn
center bolt of tool clockwise to remove steering
wheel (fig. 9).
Installation
CAUTION: Direction signal control assembly
must be in "neutral position when assembling
steering wheel to prevent damage to cancelling
cam and control assembly.
1.
With directional cancelling cam and horn contact as-
sembly in place, set wheel onto steering shaft.
Fig. 7—-Regular Wheel and Horn Attachments
CHEVROLET CHASSIS SERVICE MANUAL
Page 475 of 659

STEERING 9-35
Fig.
66—Power Steering Diagnosis
shown in Figure 66. Gauge must be between shut-
off valve and pump. Open shut-off valve,
b.
Remove filler cap from pump reservoir and check
fluid level. Fill pump reservoir to full mark on
dip stick. Start engine and, holding steering
wheel against stop, check connections at Tool
J-5176 for leakage. Bleed system as outlined
under Maintenance and Adjustments. Insert ther-
mometer (Tool J-5421) in reservoir filler open-
ing. Move steering wheel from stop to stop
several times until thermometer indicates that
hydraulic fluid in reservoir has reached tempera-
ture of 150° to 170°F.
CAUTION: To prevent scrubbing flat spots on
tires,
do not turn steering wheel more than five
times without rolling car to change tire-to-floor
contact area.
c. Hold steering wheel against a stop momentarily
and read pressure gauge. If the maximum pres-
sure is below specifications, a faulty hydraulic
circuit is indicated. To determine which part is
faulty, proceed with test number two.
Test Number Two—Oil Circuit Closed
a. Slowly turn shut-off valve on J-5176 to closed
position and read pressure indicated on gauge.
Quickly reopen valve to avoid pump damage, if
indicated pressure is less than specification,
pump output is below requirement and pump may
be considered faulty. If pressure indicated is
within specifications, it may be safely assumed
that the external hoses, connections, valve and
adapter or steering gear is at fault.
NOTE:
If pump proves faulty in test number
two,
test should be repeated after pump is re-
paired and installed in vehicle. This will provide
a means of checking the repairs made to the
pump and the condition of the steering gear or
valve and adapter which may also be faulty.
COMPONENT REPLACEMENT AND REPAIRS
POWER STEERING PUMP
Removal (Fig. 67)
1.
Disconnect hoses at pump. When hoses are discon-
nected, secure ends in raised position to prevent
drainage of oil. Cap or tape the ends of the hoses to
prevent entrance of dirt.
NOTE:
Chevelle with 396 engine uses a remote
reservoir. It is necessary to disconnect the
reservoir to pump hose before removing the
pump.
Hold a 1 qt. container under the reservoir
when the hose is removed to catch the fluid.
2.
Install two caps at pump fittings to prevent drainage
of oil from pump.
3.
Remove pump belt.
4.
On Corvette with 427 engine, loosen alternator ad-
justment and remove pump to alternator belt.
5. Remove pump from attaching parts and remove pump
from vehicle.
NOTE:
On Chevrolet and Chevy II equipped with
283 and 327 engine it may be necessary to re-
move pump brace.
6. Remove drive pulley attaching nut.
7. Remove pulley from shaft with Tool J-21239 (for
stamped pulleys) or Tool J-8433-1 with J-8433-2
adapter (for cast iron pulleys). Do not hammer
pulley off shaft as this will damage the pump.
Fig.
67—Power Steering Pump Mounting
CHEVROLET CHASSIS SERVICE MANUAL
Page 481 of 659

SECTION 10
WHEELS AND TIRES
INDEX
Page
General Description
10-1
Maintenance
and
Adjustments
.............. 10—1
Tires
10-1
Pressures . 10-1
Inspection 10-1
Wear 10-1
Rotation 10-4
Noise 10-4
Cleaning 10-4
Change (W/Wheels) 10-4
Wheels 10-5
Static Balancing (w/Tire) 10-5
Page
Dynamic Balancing (w/Tire) . 10-5
Run Out (w/o Tire) 10-5
Cleaning 10-5
Service Operations 10-5
Tires 10-5
Removal 10-5
Installation 10-5
Repair 10^6
Wheels . 10-6
Valve Assembly 10-6
Repair (Rim) 10-7
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
WHEELS
Chevrolet, Chevelle, Camaro, Chevy n, and Corvette
are base equipped with welded steel wheels. Five studs
with nuts fasten each wheel to the front hub or rear axle
flange. Disc brake equipped vehicles (except Chevrolet
and Corvette) require special 14 inch diameter wheels
with a revised design for clearance, Chevrolet disc brake
equipped vehicles have 15 in. diameter wheels as do all
Corvettes.
Chevrolet station wagons, Chevelle Super Sport 396,
Corvette and Camaro Super Sport 350 are base equipped
with 6 in. width wheels. All other vehicles have 5 in.
width wheels, except Chevy n 100, 300 and 500 Series
Sedans, which have 4 in. width wheels.
Do not install 6 inch width wheels or snow chains on
Chevrolets equipped with rear fender skirts.
TIRES
The factory installed tires on Chevrolet passenger
cars are selected to provide the best all around tire
performance for all normal operation. They are de-
signed to operate satisfactorily with loads up to and in-
cluding the specified full rated load capacity of the
automobile when inflated as recommended in the Vehicle
Capacity Rating and Recommended Tire Inflation Pres-
sures Table (see Specifications).
Optional Oversize and 8-Ply Rating Tires
{Chevrolet and Chevelle Only)
Oversize or 8-ply rating tires are not necessary on
passenger cars for normal requirements. However, an
extra margin of tire service is available when these
options are used at loads up to and including full rated
load.
Optional oversize 4-ply rating and/or 8-ply rating
tires are available on models as indicated in the Tire
Usage Chart (see Specifications). On some models (ex-
ample—Station Wagon), space limitations do not permit
the use of a larger size tire; hence, the 8-ply rating
tire is an available option.
In either case, these tires are applicable to extended
operation at or near full rated load or for trailer towing
when an extra margin of tire service is desired. How-
ever, use of a larger tire or an 8-ply rating tire should
not be construed as permitting an increase in the full
rated vehicle load (see Specifications).
MAINTENANCE AND ADJUSTMENTS
TIRES
Inflation Pressures
To ensure the proper tire inflation pressure for the
owners particular requirements follow the recommenda-
tions in the Vehicle Capacity Rating and Recommended
Tire Inflation Pressures Table (seeSpecifications). Keep
tires properly inflated, and check inflation pressures
periodically. This will ensure the best tire life and riding
comfort, over the full range of driving conditions.
Inspection
Every few thousand miles and at each lubrication, tires
should be checked for sharp objects or stones in the
tread. H tire is punctured, it should be repaired using
one of several repair kits available through tire manu-
facturers1 outlets.
Wear
Misalignment
This is wear due to excessive toe-in or toe-out. In
CHEVROLET CHASSIS SERVICE MANUAL
Page 483 of 659

WHEELS AND TIRES 10-3
Fig.
3 - Spof Wear
to cautioning the owner of his driving habits, is to inter-
change tires regularly.
Side
This may be caused by incorrect wheel camber, under-
inflation, high cambered roads or taking corners at too
high a rate of speed.
The first two causes are the most common. Camber
wear can be readily identified because it occurs only on
one side of the treads, whereas underinflation causes
wear on both sides (fig. 2).
There is, of course, no correction for high cambered
roads.
Cornering wear is discussed further on.
Center
This is caused primarily by overinflation pf the tire
(fig. 2). Invisible fabric damage can also be caused by
overinflation.
Uneven
Uneven or spotty wear (fig. 3) is due to such irregu-
larities as unequal caster or camber, bent front or rear
suspension parts, out-of-balance wheels, brake drums
Fig.
4 - Cornering Wear
out-of-round, brakes out-of-adjustment, or other me-
chanical conditions. The remedy in each case consists
of locating the mechanical defect and correcting it.
Cornering
Since the introduction of independent spring front and
rear wheels, improvements in spring suspension have
enabled drivers to negotiate curves at higher rates of
speed with the same feeling of security that they had
with the older cars at lower speeds. Consequently,
curves are being taken at higher speeds with the result
that a type of tire wear called "Cornering Wear" (fig. 4),
frequently appears.
When a car makes an extremely fast turn, the weight
is shifted from a normal loading on all four wheels to an
abnormal load on the tires on the outside of the curve
and a very light load on the inside tires due to centrifugal
force. This unequal loading may have two unfavorable
results.
First, the rear tire on the inside of the curve may be
relieved of so much load that it is no longer geared to
CHEVROLET CHASSIS SERVICE MANUAL
Page 484 of 659

WHEELS AND TIRES 10-4
the road and it slips, grinding off the tread on the inside
half of the tire at an excessive rate. This type of tire
shows much the same appearance of tread wear as tire
wear caused by negative camber.
Second, the transfer of weight may also over-load the
outside tires so much that they are laterally distorted
resulting in excessive wear on the outside half of the
tire producing a type of wear like that caused by ex-
cessive positive camber.
Cornering wear can be most easily distinguished from
abnormal camber wear by the rounding of the outside
shoulder or edge of the tire and by the roughening of the
tread surface which denotes abrasion.
Cornering wear often produces a fin or raised portion
along the inside edge of each row in the tread pattern.
In some cases this fin is almost as pronounced as a
toe-in fin, and in others, it tapers into a row of tread
blocks to such an extent that the tire has a definite step
wear appearance.
The only remedy for cornering wear is proper in-
struction of owners.
Fig.
5 - Tire Rotatidh
Rotation
To minimize the possibility of tire noise and to equal-
ize tire wear, it is recommended that tires be inter-
changed every 6000 miles as shown in Figure 5 or more
frequently in the case of extremely heavy wear.
NOTE:
Rotate Corvette tires at 4000 miles or
sooner.
Interchanging tires will effectively prevent undue wear
on any particular tire. II tire interchanging is followed
as recommended above, all tires will have the same
number of miles in each wheel position at the end of the
fourth change. When interchanging tires, inspect for
signs of abnormal wear, bulging, etc., stones, glass, and
nails should be removed before reinstallation.
Noise
Noise caused by the normal action of tire treads on
various road surfaces is often confused with rear axle
gears or other noises in the car.
The determination of whether tires are causing the
noise complained of is relatively simple. The car should
be driven at various speeds and note taken of part
throttle, and sudden acceleration and deceleration. Axle
and exhaust noises show definite variations under these
conditions, while tire noise will remain constant. Tire
noise is, however, most pronounced at speeds of approx-
imately twenty or thirty miles per hour.
The tires may be further checked by driving the ear
over smooth pavement with the tires at normal pressure
and again over the same stretch of pavement when the
tires have been inflated to fifty pounds pressure. Reduce
the tires to normal pressure one at a time to determine
the faulty tire or tires. This high inflation pressure
should immediately be reduced to normal after test. If
the noise for which the test is being made is caused by
tires,.
it will noticeably decrease when the tire pressure
is increased, whereas axle noise should show no change
in volume.
If, on inspection, the tires on the front wheels are
found to be creating most of the noise the alignment of
the front wheels should be checked. Excessive tire noise
usually results from lower than recommended tire pres-
sure, incorrect alignment, uneven tire wear, or defective
(thumper) tire.
Cleaning
A great deal of ordinary road dirt which collects on
white sidewall tires may be sponged off with clear water
or a mild soap solution.
A good brand of whitewall tire cleaner, however, is
a quicker and more effective cleaner for removing dirt
and stains from whitewall tires and in many cases it
will remove stains and discoloration that the simpler
method of soap and water will not remove.
Under no circumstances should gasoline, kerosene or
any cleaning fluid containing a solvent derived from oil
be used to clean whitewall tires. Oil in any form is
detrimental to tire rubber and a cleaner with an oil base
will discolor or injure whitewall tires.
Change (W/Wheels)
To change the road wheels using the jack that comes
with the car, observe the following procedure:
1.
Set hand brake and block front wheels if rear wheel
is being changed.
2.
Remove hub cap or wheel disc and break wheel
mounting nuts loose.
3.
Place the jack as directed tinder, General Informa-
tion,
Section 0 and raise car until wheel clears
ground.
4.
Remove wheel mounting nuts and remove wheel from
hub or drum.
5. To replace road wheel, reverse the above instrue-
. tions. Proper torque on nuts is 55-75 ft. lbs.
torque (70-85 ft. lbs. for Corvette aluminum wheel
nuts).
CAUTION: On models equipped with discs, in-
dex the pilot hole in the disc on the valve stem.
(To insure that the anti-rotation notches in wheel
disc register on lugs in wheel rim.)
CHEVROLET CHASSIS SERVICE MANUAL
Page 548 of 659

ELECTRICAL-BODY
AND
CHASSIS
12-36
CAMARO INSTRUMENTS AND GAUGES
INDEX
Page
General Description
12-36
Service Operations
12-36
Instrument Cluster
. . . 12-36
Instrument Lamps
12-36
Printed Circuit
12-36
Fuel Gauge
12-37
Tachometer
. . 12-37
Seat Separator Instrument Console
12-37
Page
Fuel Gauge
12-37
Ammeter
12-37
Temperature Gauge
12-37
Oil Pressure Gauge
. 12-37
Fuel Warning Unit
12-37
Clock.
... 12-37
Oil Pressure Indicator
12-37
Generator Indicator
12-38
Temperature Indicator
12-38
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The standard Camaro instrument cluster assembly con-
sists
of two
circular units which house
the
speedometer
and fuel gauge assemblies.
The oil
pressure, left-hand
directional
and
brake warning indicators
are
located
in
the face
of the
speedometer bezel while generator,
tem-
perature
and
right-hand directional indicators are grouped
with
the
fuel gauge unit.
The
high beam indicator
is
located between
the
cluster bezels.
A special instrumentation package
is
available with
the
eight-cylinder engine
and
center floor console combina-
tion.
The
special cluster includes:
a
clock; coolant
temperature,
oil
pressure, fuel
and
ammeter gauges,
mounted forward
on the
seat separator console;
a ta-
chometer
in the
right circular housing
of the
dash
in-
strument cluster; and
a low
fuel level indicator replacing
the
oil
pressure indicator lamp
in the
instrument cluster.
The instruments
and
gauges,
may be
serviced only
after
the
instrument cluster
is
removed from
the
vehicle.
Indicator
and
cluster lamps except
for the
high beam
indicator
may be
replaced without removing
the
cluster
assembly. Partial cluster removal
is
necessary when
replacing
the
high beam indicator due
to its
proximity
to
the upper brace
rod
anchor plate.
The
bulbs
are in-
stalled
in
plastic sockets which lock into
the
cluster
housing and make contact with
the
printed circuit.
A
low
level fuel warning system
is a
special feature
available with
the
floor console gauge pack. This
sys-
tem includes
an
indicator lamp
in the
dash cluster and
a
semi-conductor unit senses
the
change
in
electrical
re-
sistance
of the
fuel system circuitry
as
variations
in
fuel level occur.
The
sensing device
is
replaced
as a
unit
if
found defective.
The brake warning light serves
a
dual purpose.
It
functions
as an
indicator when
the
parking brake
is ap-
plied
and
also
if
there
is a
malfunction (loss
of
hydraulic
pressure)
in the
brake system. Switches which provide
the signal
to
operate
the
light
are
located
at the
parking
brake assembly
and at the
brake master cylinder
in the
hydraulic lines. Service
of the
brake pressure differ-
ential switch unit
is
covered
in
Section
5 of
this manual.
Regular maintenance
is not
required on
the
instrument
cluster
or its
components other than maintaining clean,
tight electrical connections, replacing defective parts
and keeping
the
speedometer properly lubricated.
SERVICE OPERATIONS
INSTRUMENT CLUSTER (Figs.
50
thru
53)
Removal
and
Installation
1.
Disconnect battery ground cable.
2.
Remove mast jacket lower support screws
at toe
pan.
3.
Remove mast jacket upper support bolts
and
allow
steering wheel
to
rest
on
seat cushion.
CAUTION: Both supports must
be
detached
to
prevent distortion
of
mast jacket.
4.
Remove cluster attaching screws from face
of
panel
and partially remove assembly from console opening.
5. Reaching behind cluster assembly, disconnect speed-
ometer cable, speed warning device
(if so
equipped
-
Fig.
51) and
chassis harness connector
at
rear
of
panel.
6. Remove assembly from console opening to
a
suitable
bench area
for
required service operations.
7.
To
install, reverse removal procedure.
INSTRUMENT CLUSTER LAMP REPLACEMENT
1.
Turn bulb holder counterclockwise
and
pull
out to
remove from
the
cluster housing.
2.
Pull bulb straight out
to
remove from socket.
3.
Press replacement bulb inward
to
lock
in
socket.
4.
Insert lamp assembly into housing, with lugs
on
holder entering notches
in
housing,
and
turn clock-
wise
to
lock
in
place.
PRINTED CIRCUIT REPLACEMENT
1.
Remove instrument cluster
as
previously described
in this section.
2.
Remove
all
cluster illuminating and indicator lamps
from housing.
3.
Remove fuel gauge terminal nuts
or
tachometer
re-
taining nuts securing printed circuit
to
housing.
4.
Remove four
hex
head screws retaining printed
cir-
cuit
to the
cluster housing
and
remove circuit from
housing.
5.
To
install, reverse removal procedure.
CAUTION:
The
retaining screws
are
part
of
the grounding circuit
and
must
be
installed
to
provide proper connections
for the
printed
eir-
cuit.
CHEVROLET CHASSIS SERVICE MANUAL