automatic transmission CHEVROLET CAMARO 1967 1.G Chassis Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: CHEVROLET, Model Year: 1967, Model line: CAMARO, Model: CHEVROLET CAMARO 1967 1.GPages: 659, PDF Size: 114.24 MB
Page 311 of 659

ENGINE FUEL 6M-3
Idle Speed and Mixture Adjustment (With Air Injection
Reactor System)
The following is the recommended procedure for Air
Injection Reactor System equipped engines.
NOTE: This adjustment should be performed
with engine at operating temperature and parking
brake applied.
1.
Remove air cleaner.
2.
Connect tachometer to engine, then set hand brake
and shift transmission into neutral.
3.
As a preliminary adjustment, turn idle mixture
screws lightly to seat and back out 3 turns.
CAUTION: Do not turn idle mixture screw
tightly against seat or damage may result."
4.
With engine running (choke wide open) adjust idle
speed screw to specified idle speed. (Automatic
transmission in dirve, synchronized transmission in
neutral).
5.
Adjust idle mixture screw (turn in) to "lean roll"
position; then turn screw out 1/4 turn (1/4 turn
rich from "lean roll"). The definition of "lean
roll" point is a 20 to 30 rpm drop in engine speed,
obtained by leaning the idle mixture.
NOTE: On air conditioned vehicles, turn air
conditioning "OFF" on in-line, 283, 327, and'
350 cu. in. engines, and turned "ON" and hot
idle compensator held closed on 396 and 427 cu.
in. engines.
6. Repeat Steps 4 and 5 as needed for final adjustment.
NOTE: If necessary, final adjustment of the
carburetor may be made with air cleaner
installed.
7.
Shut down the engine, remove gauges and install air
cleaner. *
Fast Idle Adjustment
Rochester
4MV and Holley
With fast idle lever on high step of cam and choke valve
open (engine warm) set fast idle to give specified engine
rpm. Adjust sejrew on Rochester 4MV and bend fast
idle lever *pn Holley. .
Choke Adjustment
With Remote Choke (Fig. 2c)
1.
Remove air cleaner and check to see that choke
valve and rod move freely.
2.
Disconnect choke rod at choke lever.
3.
Check choke adjustment as follows:
On all except 275 and 300 h.p. 327 cu. in. engines,
hold choke valve closed and pull.rod up against stop.
The top of choke rod end should be 1/2-1 rod diame-
ter above top of hole in choke valve lever.
On 275 and 300 h.p. 327 cu. in. engines, hold choke
valve closed and push rod down against stop on ther-
mostat bracket. The top of the choke rod should be
1/2-1 rod diameter below the top of the hole in the
choke lever.
4.
If necessary, adjust rod length by bending rod at
offset bend. (Bend must be such that rod enters
choke lever hole freely and squarely).
5.
Connect rod at choke lever and install air cleaner.
With Manual Choke (Carter YF)
1.
Remove air cleaner.
CHOKE VALVE
COMPLETELY
CLOSED
PULL UPWARD ON
ROD TO END OF
TRAVEL
BEND ROD
TO ADJUST
ROD IN BOTTOM
OF SLOT
BOTTOM OF
ROD SHOULD
BE EVEN WITH
TOP OF
HOLE
CHOKE VALVE
CLOSED
BOTTOM OF
ROD SHOULD
BE EVEN WITH
TOP OF HOLE
TOP OF ROD
SHOULD BE EVEN
WITH BOTTOM
OF HOLE (CHOKE
CLOSED)
BEND ROD TO
ADJUST
PULL DOWNWARD'
ON ROD TO CON-
TACT STOP
L6 (TYPICAL)
[
V8 327-275 HP
V8 350-295 HP
BEND ROD
TO ADJUST
PULL UPWARD ON
ROD TO CONTACT
STOP ON BRACKET
ALL V8 (EXCEPT 327-275 HP
AND 350-295 HP)
Fig.
2C—Remote Choke Adjustment
CHEVROLET CHASSIS SERVICE MANUAL
Page 313 of 659

ENGINE FUEL 6M-5
3.
Disconnect choke rod or choke cable.
4.
Disconnect accelerator linkage.
5.
If equipped with Automatic transmission, discon-
nect TV linkage.
6. Remove carburetor attaching nuts and/or bolts and
remove carburetor.
Test Before Installation -
It is good shop practice to fill the carburetor bowl
before installing the carburetor. This reduces the strain
on the starting motor and battery and reduces the pos-
sibility of backfiring while attempting to start the engine.
A fuel pump clamped to the bench, a small supply of fuel
and the necessary fittings enable the carburetor to be
filled1 and the operation of the float and'intake needle and
seat to be checked. Operate the throttle several times
and check the discharge from the pump jets before in-
stalling the carburetor.
Installation
1.
Be certain throttle body and intake manifold sealing
surfaces are clean.
2.
Install new carburetor to manifold flange gasket (if
required).
3.
Install carburetor over manifold studs.
4.
Start vacuum and fuel lines at carburetor.
5.
Install attaching nuts and/or bolts and tighten
securely.
6. Tighten fuel and vacuum lines.
7.
Connect and adjust accelerator and TV linkage.
8. Connect choke tube or choke rod.
9. Adjust idle speed and mixture, then install air
cleaner. #
Fuel Filter Maintenance
1.
Disconnect fuel line connection at inlet fuel filter
nut.
2.
Remove inlet fuel filter nut from carburetor with a
1"
box wrench or socket.
3.
Remove filter element and spring (fig. 4c).
Fig. 5C-Choke Coil-L6 Engine
4.
Fig. 4C-Fuel Filter
Check element for restriction by blowing on cone
end, element should allow air to pass freely.
5.
Clean element by washing in solvent and blowing out.
Blow in opposite direction of fuel flow.
NOTE: Element should be replaced if plugged
or if flooding ocpurs. A plugged filter will
result in a loss of engine power or rough (pul-
sating) engine feel, especially at high engine
speeds.
6. Install element spring, then install element in car-
buretor so small section of cone faces out.
7.
Install new gasket on inlet fitting nut then install
nut in carburetor and tighten securely.
8. Install fuel line and tighten connector.
Choke Coil Replacement
L6 Engines (Fig. 5c)
1.
Remove air cleaner then disconnect choke rod upper
clip.
2.
Remove bolts attaching choke coil to manifold, then
remove choke coil and choke rod as an assembly.
3.
Disconnect choke rod from choke coil.
4.
Connect choke rod to new choke coil and install as-
sembly on manifold.
5.
Install bolts and tighten securely.
6. Adjust and connect choke rod as outlined.
7.
Start and warm-up the engine then check operation
of choke and install air cleaner.
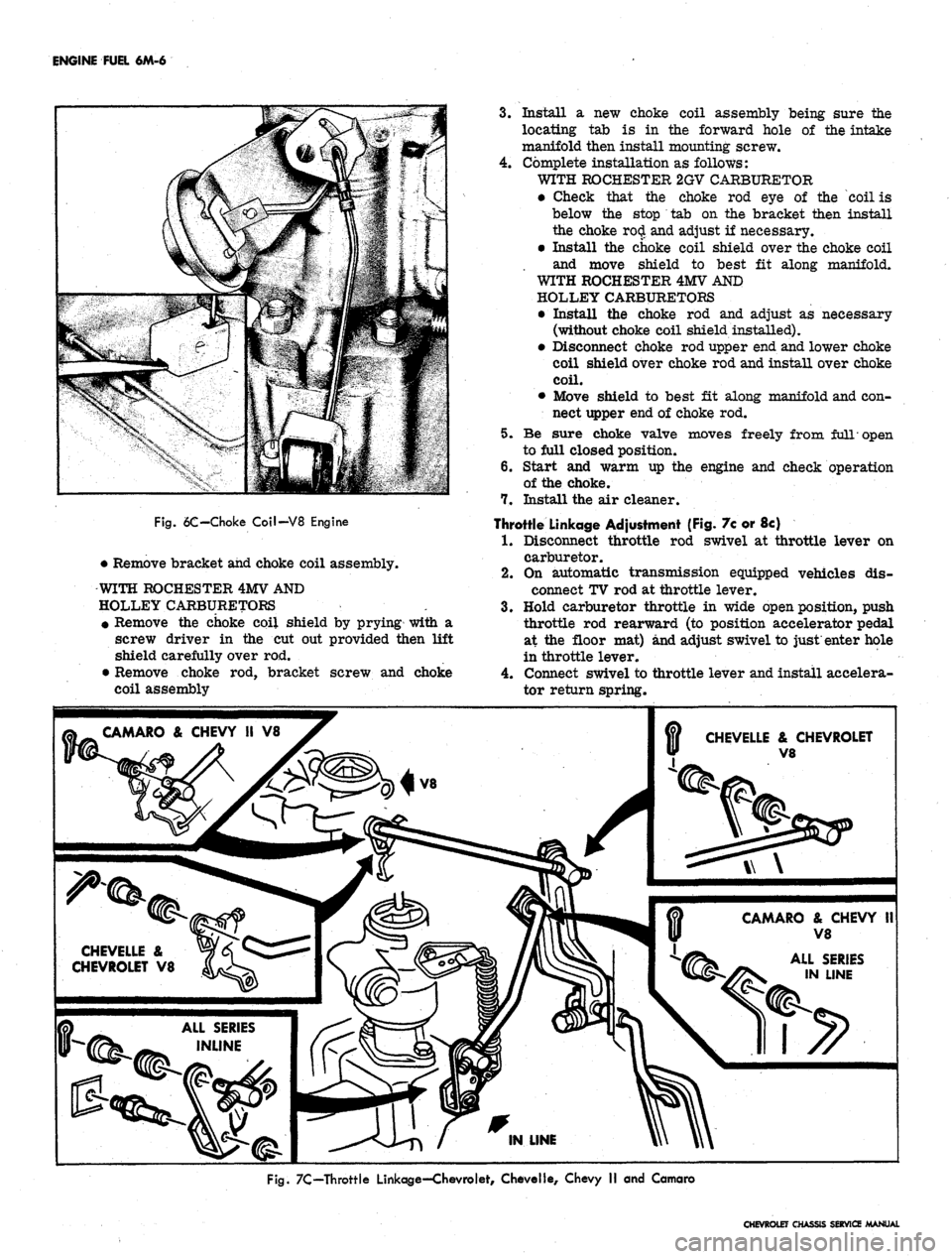
V8 Engines (Fig. 6c)
1.
Remove air cleaner then disconnect choke rod upper
clip.
2.
Remove choke coil as follows:
WITH ROCHESTER 2GV CARBURETOR
• Remove the choke coil shield by prying with a
screw driver in the cut out provided then re-
move the choke rod.
CHEVROLET CHASSIS SERVICE MANUAL
Page 314 of 659
ENGINE FUEL 6M-6
Fig.
6C-Choke Coil-V8 Engine
• Remove bracket and choke coil assembly.
WITH ROCHESTER 4MV AND
HOLLEY CARBURETORS
• Remove the choke coil shield by prying with a
screw driver in the cut out provided then lift
shield carefully over rod.
• Remove choke rod, bracket screw and choke
coil assembly
3.
Install a new choke coil assembly being sure the
locating tab is in the forward hole of the intake
manifold then install mounting screw.
4.
Complete installation as follows:
WITH ROCHESTER 2GV CARBURETOR
• Check that the choke rod eye of the coil is
below the stop tab on the bracket then install
the choke
ro
• Install the choke coil shield over the choke coil
and move shield to best fit along manifold.
WITH ROCHESTER 4MV AND
HOLLEY CARBURETORS
• Install the choke rod and adjust as necessary
(without choke coil shield installed).
• Disconnect choke rod upper end and lower choke
coil shield over choke rod and install over choke
coil.
• Move shield to best fit along manifold and con-
nect upper end of choke rod.
5. Be sure choke valve moves freely from full open
to full closed position.
6. Start and warm up the engine and check operation
of the choke.
7. Install the air cleaner.
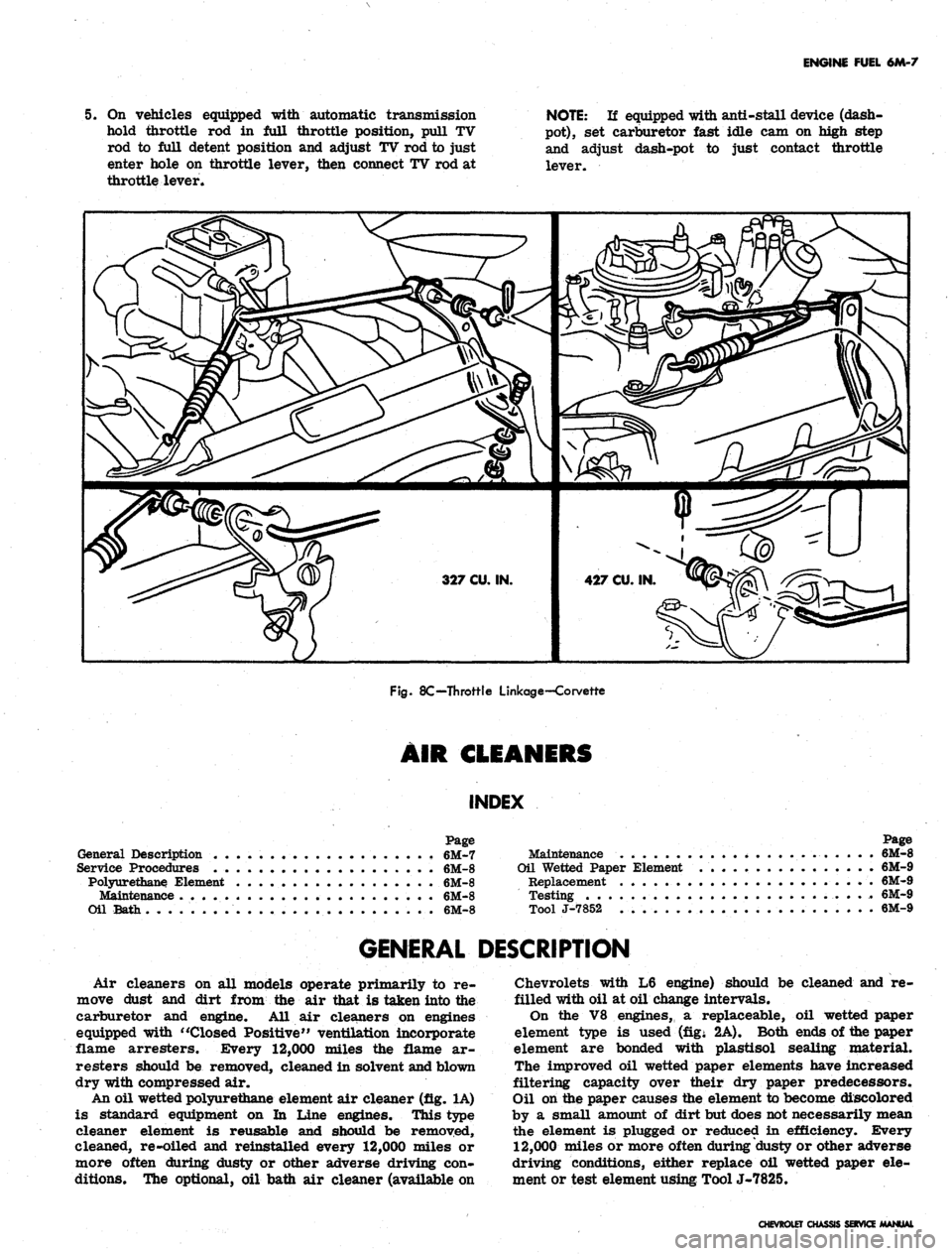
Throttle Linkage Adjustment (Fig. 7c or 8c)
1.
Disconnect throttle rod swivel at throttle lever on
carburetor.
2.
On automatic transmission equipped vehicles dis-
connect TV rod at throttle lever.
3.
Hold carburetor throttle in wide open position, push
throttle rod rearward (to position accelerator pedal
at the floor mat) and adjust swivel to just enter hole
in throttle lever.
4.
Connect swivel to throttle lever and install accelera-
tor return spring.
CAMARO & CHEVY II V8
CHEVELLE & CHEVROLET
V8
CAMARO
&
CHEVY
II
V8
CHEVELLE &
CHEVROLET V8
ALL SERIES
IN LINE
ALL SERIES
INLINE
Fig.
7C—Throttle Linkage—Chevrolet, Chevelle, Chevy II and Camaro
CHEVROLET CHASSIS SERVICE MANUAL
Page 315 of 659
ENGINE FUEL 6M-7
5. On vehicles equipped with automatic transmission
hold throttle rod in full throttle position, pull TV
rod to full detent position and adjust TV rod to just
enter hole on throttle lever, then connect TV rod at
throttle lever.
NOTE:
If equipped with anti-stall device (dash-
pot),
set carburetor fast idle cam on high step
and adjust dash-pot to just contact throttle
lever.
327
CU.
IN.
427
CU.
IN.
Fig.
8C—Throttle Linkage-Corvette
AIR
CLEANERS
INDEX
Page
General Description 6M-7
Service Procedures . . 6M-8
Polyurethane. Element 6M-8
Maintenance 6M-8
Oil Bath 6M-8
Page
Maintenance
...........* 6M-8
Oil
Wetted
Paper
Element
6M-9
Replacement
* . 6M-9
Testing 6M-9
Tool J-7852 . 6M-9
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
Air cleaners on all models operate primarily to re-
move dust and dirt from the air that is taken into the
carburetor and engine. All air cleaners on engines
equipped with "Closed Positive" ventilation incorporate
flame arresters. Every 12,000 miles the flame ar-
resters should be removed, cleaned in solvent and blown
dry with compressed air.
An oil wetted polyurethane element air cleaner (fig. 1A)
is standard equipment on In Line engines. This type
cleaner element is reusable and should be removed,
cleaned, re-oiled and reinstalled every 12,000 miles or
more often during dusty or other adverse driving con-
ditions. The optional, oil bath air cleaner (available on
Chevrolets with L6 engine) should be cleaned and re-
filled with oil at oil change intervals.
On the V8 engines,, a replaceable, oil wetted paper
element type is used (fig; 2A). Both ends of me paper
element are bonded with plastisol sealing material.
The improved oil wetted paper elements have increased
filtering capacity over their dry paper predecessors.
Oil on the paper causes the element to become diBcolored
by a small amount of dirt but does not necessarily mean
the element is plugged or reduced in efficiency. Every
12,000 miles or more often during dusty or other adverse
driving conditions, either replace oil wetted paper ele-
ment or test element using ToolJ-7825.
CHEVROLET CHASSIS SOVICE/MANUAL
Page 369 of 659

CLUTCH AND TRANSMISSIONS 7-10 ,
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The overdrive unit is essentially a two-speed planetary-
transmission attached to the rear of a conventional three-
speed transmission. In overdrive, engine speed is ap-
proximately 30 per cent slower at a given road speed
since the drive train includes planetary gears which pro-
vide a lower overall gear ratio than that obtained in high
gear with the conventional transmission.
The electrical equipment which controls the automatic
action of the mechanical portion of the overdrive unit
consists of a solenoid, a speed-sensitive governor switch,
a relay and a kickdown switch. The circuit including this
equipment makes it possible to operate in overdrive above
a pre-set cut-in speed, or in .conventional drive at any
speed.
With the overdrive unit engaged, the transmission
should not be left in any forward gear with intent of lock-
ing the drive-line as the overrunning clutch is a free-
wheeling condition.
SERVICING THE OVERDRIVE
With the,overdrive assembly removed from the trans-
mission, service operations on the transmission proper
are the same as for the standard three-speed trans-
mission.
Repairs to the overdrive housing, output shaft, ring
gear assembly, clutch cam, roller retainer, pinion cage,
sun gear, shift rail, sun gear control plate, output shaft
bearing, oil seal, speedometer drive gear, solenoid pawl
and interlock plunger may be performed underneath the
car, if so desired, by removing the overdrive housing
without disturbing the transmission. Refer to Overhaul
Manual for Service Procedure.
If the transmission mainshaft, overdrive adapter or
transmission rear bearing which is retained in adapter
require replacement, the entire transmission and over-
drive assembly should be removed and overhauled on the
bench.
MAINTENANCE AND ADJUSTMENTS
Servicing of the overdrive governor switch and pinion,
the sun gear solenoid, oil seal and cable bracket, the out-
put shaft rear oil seal, the control shaft lever, and the
speedometer driven gear may be accomplished without
removing the overdrive from the vehicle, as discussed
in the following paragraphs:
GOVERNOR SWITCH AND PINION
To remove governor switch, disconnect wires at gover-
nor switch and screw governor
out
of housing, using Tool
J-4653 on the flat hexagonal surface of governor case.
The pinion may be separated from the governor by re-
moving the snap ring on the shaft.
SUN GEAR SOLENOID, OIL SEAL AND
CONTROL CABLE BRACKET
Remove the solenoid by taking out the two mounting
bolts and lock washers, removing
the.
cable bracket with
the lower bolt. Turn the solenoid 1/4 turn and
pull,
sole-
noid plunger out of adapter. The oil seal may be pried
out of the adapter.
CASE REAR OIL SEAL
Removal
1.
Remove propeller shaft as outlined in Section 4.
2.
Using a punch against seal in housing, pry out seal
from housing.
Installation
1.
Prelubricate between sealing lips and coat outside of
new oil seal with a suitable sealant, then start seal
into bore in overdrive housing.
2.
Using Tool J-5154 drive oil seal into counterbore.
3.
Install propeller shaft as outlined in Section 4.
CONTROL SHAFT LEVER AND/OR "O" RING
OIL SEALS
To remove- the control shaft, disconnect the cpntrol
cable, remove tapered pin and pull lever out. Replace
the two "0" ring seals on the control shaft. Insert shaft
and new "O" ring seals into housing and install tapered
pin. Connect control wire to lever.
SPEEDOMETER DRIVEN GEAR
Disconnect speedometer cable, remove lock plate to
housing bolt and lock washer and remove lock plate. In-
sert screw driver in lock plate slot in fitting and pry
fitting, gear and shaft from housing. Pry "O" ring from
groove in guide.
Install new "O" ring in groove in fitting and insert
shaft.
Hold the assembly so slot in fitting is toward lock plate
boss on housing and install in housing. Push fitting into
housing until lock plate can be inserted in groove and
attached to housing.
L
dl
ZAIR GAP
km (CHECK WITH
M*= POINTS BARELY
'A
AoWER
|^
POINT
0 ADJUST
=^ i
SUPPORT
Fig. IB - Checking Relay Air Gap
CHEVROLET CHASSIS SERVICE MANUAL
Page 382 of 659

CLUTCH
AND
TRANSMISSIONS
7-23
Assembly (Fig.
4X)
1.
With detent spring tang projecting
up
over
the 3rd
and
4th
shifter shaft cover opening install
the
first
and second detent
cam
onto
the
detent
cam
pivot
pin.
With
the
detent spring tang projecting
up
over
the
first
and
second shifter shaft cover hole install
the
3rd
and 4th
detent
cam,
NOTE:
The 1-2
detent
cam has a
.090" greater
contour
on the
inside detent notch.
2.
3.
Install detent
cam
retaining
"C"
ring
to
pivot shaft,
and hook spring into detent
cam
notches.
Install
1-2 and 3-4
shifter shaft assemblies
in
cover
being careful
not to
damage seals. Install both shift
forks
to
shifter shaft assemblies, lifting
up on
detent
cam
to
allow forks
to
fully seat into position.
4.
Install reverse detent ball
and
spring
to
cover, then
install reverse shifter shaft assembly
to
cover.
5.
Install outer shifter levers, flat washers, lock wash-
ers
and
bolts.
Installation
1.
Shift shifter levers into neutral detent (center) posi-
tion. Position cover gasket
on
case.
2.
Carefully position side cover into place making sure
the shift forks
are
aligned with their respective
mainshaft clutch sliding sleeves.
Install cover attaching bolts
and
tighten evenly
to
specified torque.
Remove filler plug
and add
lubricant specified
in
Section
0, to
level
of
filler plug hole.
3.
4.
ALUMINUM POWERGLIDE
INDEX
Page
General
Description
7-23
Maintenance
and
Adjustments .............. 7—23
Oil
Level Check
7-23
Periodic
Oil
Change
7-24
Periodic
Low
Band Adjustment
7-24
Manual
Shift Linkage Check
and
Adjust
7-24
Floor
Shift Linkage
7-25
Floor
Mounted Control Lever
and
Bracket
Assembly
7-29
Throttle
Valve Linkage
.... 7-29
Neutral
Safety Switch
.. . 7-30
Throttle
Return Check Valve (Dashpot)
7-30
Component
Parts Replacement
7-30
Transmission
Replacement .............. 7—30
Page
Other
Service Operations
7-32
Diagnosis
7-32
Warming
Up
Transmission
7-32
Shop
Warm
Up , 7-32
Road
Warm
Up 7-32
Checking
Fluid Level
and
Condition
7-32
Manual
Linkage
7-32
Oil
Leaks
7-33
Basic
Pressure Checks
7-33
Wide
Open Throttle Upshift Pressure Check
.... 7-33
Idle
Pressure
in
Drive Range
7-33
Manual
"Low"
Range Pressure Check .......
7-33
Drive
Range Overrun (Coast) Pressure
.
.......
7-33
Powerglide
Shift Points
. . 7-35
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The case
and
converter housing
of the two
speed alumi-
num Powerglide Transmission
is a
single case aluminum
unit. When
the
manual control
is
placed
in the
drive
po-
sition,
the
transmission automatically shifts
to low
gear
for initial vehicle movement.
As the car
gains speed
and
depending
on
load
and
throttle position,
an
automatic shift
is made
to
high gear.
A
forced downshift feature
pro-
vides
a
passing gear
by
returning
the
transmission
to low
range.
The
oil
pump assembly
is a
conventional gear type
and
the
oil
pump housing
is of the
large diameter type acting
as
the
front bulkhead
of the
transmission.
The
torque
converter
is a
conventional three element welded design
bolted
to the
engine flywheel which drives through
a
two-
speed planetary gearset.
The
high clutch assembly
is
typical
of the
designs used
in
this type transmission.
The
aluminum Powerglide uses
an
output shaft mounted
gov-
ernor which requires
a
hole through
the
output shaft.
The
reverse clutch assembly
is a
multiple disc type clutch.
The steel plates
are
splined directly
to the
case while
the
face plates
are
splined
to the
internal
or
ring gear.
The
clutch piston operates within
the
rear portion
of the
case.
The internal diameter
of the
pistoh
is
sealed to
an
integral
hub portion
of the
case rear bulkhead.
The
outside
dia-
meter
is
sealed
to a
machined portion
of the
case.
The
piston
is
hydraulically applied
and is
released
by
separate
coil springs.
The
valve body assembly
is
bolted
to the
bottom
of the
transmission case
and is
accessible
for
service
by
removing
the oil pan
assembly.
The
valve
body consists
of an
upper
and
lower body located
on
either
side
of a
transfer plate.
The
vacuum modulator
is lo-
cated
on the
left rear face
of the
transmission case.
The
modulator valve bore
is
located
in the
upper valve body.
MAINTENANCE
AND
ADJUSTMENTS
OIL LEVEL CHECK
The transmission
oil
level should
be
checked period-
ically
as
recommended
in
Section
0. Oil
should
be
added
only when level
is on or
below
the
"ADD" mark
on the dip
stick with
oil hot or at
operating temperature.
The oil
level
dip
stick
is
located
at the
right rear
of the
engine
compartment. Fill with
oil
specified
in
Section
0.
In order
to
check
oil
level accurately,
the
engine should
be idled with
the
transmission
oil hot and the
control
lever
in
neutral (N) position.
It
is
important that
the oil
level
be
maintained
no
higher than
the
"FULL" mark
on the
transmission
oil
level gauge.
DO NOT
OVERFILL,
for
when
the oil
level
CHEVROLET CHASSIS SERVICE MANUAL
Page 395 of 659

CLUTCH AND TRANSMISSIONS 7-36
TURBO HYDRA-MATIC TRANSMISSION
INDEX
Page
General Description . . , . 7-36
Maintenance and Adjustments . 7-37
Transmission Fluid 7-37
Fluid Level Indicator 7-37
Shift Control Linkage Adjustment ........... 7-37
Neutral Safety Switch Adjustment 7-37
Draining and Refilling Transmission . . . 7-37
Pressure Regulator Valve 7-38
Control Valve Body . 7-39
Governor ..'.... 7-40
Modulator and Modulator Valve 7-40
Parking Linkage . . 7-40
Page
Rear Seal -. 7-40
Other Service Operations . . 7-40
Transmission Replacement 7-40
Turbo Hydra-Matic Diagnosis Procedure. ......... 7-41
Sequence . ; ; 7-41
Oil Level and Condition Check 7-41
Manual Linkage 7-41
Oil Leaks .' 7-41
Case Porosity - Repair ................ 7-42
Oil Pressure Check 7-42
Transmission Shift Points 7-42
Special Tools 7-43
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The Turbo Hydra-Matic transmission is a fully auto-
matic unit consisting primarily of a 3-element hydraulic
torque converter and a compound planetary gear set.
Three multiple-disc clutches, one sprag unit, one roller
clutch and two bands provide the friction elements re-
quired to obtain the desired function of the compound
planetary gear set.
The torque converter couples the engine to the plane-
tary gears through oil and provides hydraulic torque
multiplication when required. The compound planetary
gear set produces three forward speeds and reverse.
The
3-
element torque converter consists of a pump or
driving member, a turbine or driven member, and a
stator assembly. The stator is mounted on a one-way
roller clutch which will allow the stator to turn clock-
wise but not counter-clockwise.
The torque converter housing is filled with oil and
is attached to the engine crankshaft by a flex plate and
always rotates at engine speed. The converter pump is
an integral part of the converter housing, therefore the
pump blades, rotating at engine speed, set the oil within
the converter into motion and direct it to the turbine,
causing the turbine to rotate.
As the oil passes through the turbine it is traveling in
such a direction that if it were not re-directed by the
stator it would hit the rear of the converter pump blades
and impede its pumping action. So at low turbine speeds,
the oil is re-directed by the stator to the converter pump
in such a manner that it actually assists the converter
pump to deliver power or multiply engine torque.
As turbine speed increases, the direction of the oil
leaving the turbine changes and flows against the rear
side of the stator vanes in a clockwise direction. Since
the stator is now impeding the smooth flow of oil, its
roller clutch releases and it revolves freely on its shaft.
Once the stator becomes inactive, there is no further
multiplication of engine torque within the converter. At
this point, the converter is merely acting as a fluid
coupling as both the converter pump and turbine are
being driven at approximately the same speed - or at a
one-to-one ratio.
A hydraulic system pressurized by a gear type pump
provides the working pressure required to operate the
friction elements and automatic controls.
External control connections to transmission are:
Manual Linkage
Engine Vacuum
12 Volt Electrical
Signal
To select the desired op-
erating range.
To operate a vacuum mod-
ulator unit.
To operate an electrical
detent solenoid.
A vacuum modulator is used to automatically sense
any change in the torque input to the transmission. The
vacuum, modulator transmits this signal to the pressure
regulator for line pressure control, to the 1-2 accumula-
tor valve, and to the shift valves so that all torque re-
quirements of the transmission are met and smooth
shifts are obtained at all throttle openings.
The detent solenoid is activated by an alectric switch
on the carburetor. When the throttle is fully opened, the
switch on the carburetor is closed, activating the detent
solenoid and. causing the transmission to downshift at
speeds below approximately 70 MPH.
The selector quadrant has six selector positions: P,R,
N,D,
L2,L1.
P.
*
- Park position positively locks the output shaft to
the transmission case by means of a locking pawl
to prevent the vehicle from rolling in either di-
rection. The engine may be started in Park
position.
R. - Reverse enables the vehicle to be operated in a
reverse direction.
N.
- Neutral position enables the engine to be started
and run without driving the vehicle.
D,
- Drive Range is used for all normal driving condi-
tions and maximum economy. Drive Range has
three gear ratios, from the starting ratio to
direct drive. Detent downshifts are available by
depressing the accelerator to the floor.
L2.
- L2 Range has the same starting ratio as Drive
Range, but prevents the transmission from shift-
ing above second speed to retain second speed
acceleration when extra performance is desired.
L2 Range can also be used for engine braking.
L2 Range can be selected at any vehicle speed,
and the transmission will shift to second gear and
remain in second until the vehicle speed or the
throttle are changed to obtain first gear operation
in the same manner as in D Range.
CHIVROLET CHASSIS SERVICE MANUAL
Page 450 of 659

STEERING 9-10
SECTOR SHAFT SEAL REPLACEMENT
A faulty seal may be replaced without removal of
steering gear from car by removing pitman arm as out-
lined under Maintenance and Adjustments--Steering Gear
Adjustments and proceed as follows:
1.
Loose lash adjuster lock nut and turn lash adjuster
screw several turns counterclockwise.
2.
Remove three cap screws holding side cover to gear
bushing.
3.
Pull side cover and sector shaft from gear housing
as a unit. Do not separate side cover from sector
shaft.
4.
Pull sector shaft seal from gear housing using
hooked tool or pliers.
5. Coat new seal with chassis grease and position in
sector shaft bore.
6. Place a socket or piece of pipe of suitable diameter
on top of seal and drive seal into bore by tapping
pipe or socket with soft hammer.
7. Install sector shaft side cover assembly, being care-
ful not to damage new seal with splines on end of
shaft; splines may be wrapped with a few turns of
tape to prevent this.
8. Install new side cover gasket and align side cover on
gear housing and install cap screw.
9. Perform steering gear adjustment and install pitman
arm as outlined under Maintenance and Adjustments.
STEERING COLUMN
All models are equipped with new energy absorbing
steering columns. The columns are of five basic designs
as follows:
1.
Syncromesh. The syncromesh column is used on
models with standard, column mounted, conventional
shift levers. The shift tube, within the outer mast
jacket, includes two lower shift levers for connection
to the transmission control linkage.
2.
Automatic and floor shift. This column is used on
models equipped with column mounted powerglide
shift levers, or models with floor shift. If the ve-
hicle has the column mounted powerglide shift con-
trol, the inner shift tube has a single lower shift
lever for connection to the transmission control
linkage. On floor shift models, no lower shift levers
are present on the shift tube.
3.
Tilt wheel option. The upper end and steering shaft
of this column is specially designed to accommodate
the optional tilt steering wheel.
4.
Standard Corvette Column. The standard Corvette
column is similar in design to the Automatic and
Floor Shift column used on other models, except
no shift tube is used. Other differences are pointed
out in the disassembly and assembly procedures for
Standard Corvette column.
5. Telescopic wheel option. The upper end and steering
shaft of this column is specially designed to ac-
commodate the optional telescoping steering wheel.
To perform service procedures on steering column
upper end components, it is not necessary to remove the
column from the vehicle. The steering wheel, horn com-
ponents, turn signal switch, upper housing with bearing,
shift control lever, hazard warning knob, and upper shift
bowl may all be removed with the column remaining in
the vehicle. When servicing the above components, omit
the removal procedure and proceed with the applicable
disassembly procedures. Because of the numerous dif-
ferences in steering column types, be sure to refer to the
set of instructions below which apply to the exact column
to be serviced:
CAUTION: The outer mast jacket, shift tube, _
steering shaft, and instrument panel column
mounting b
racket
are designed as energy ab-
sorbing units. Because of the design of these
components, it is absolutely necessary to handle
the column with care when performing any serv-
ice operation required. Avoid hammering, jar-
ring, dropping, or leaning on any portion of the
column.
Removal
1.
Disconnect steering column harness at connector.
Disconnect neutral safety switch and back-up lamp
switch connectors if so equipped.
Remove steering wheel as outlined in this section.
Remove nuts and washers securing flanged end of
column to steering gear. On Chevy H models, re-
move nut and clamp bolt securing lower end of steer-
ing column to steering gear.
Disconnect transmission control linkage, if so
equipped, from lower column shift tube, levers.
Chevrolet and Chevy II only: Remove screws at-
taching upper and lower mast jacket covers together.
On Chevrolet, remove screws attaching lower cover
to instrument panel (figs. 15 and 18). Remove lower
cover.
Chevelle only: Remove screws securing mast jacket
trim cover to instrument panel and remove cover
(fig. 15).
Corvette, only: Remove screws securing escutcheon
to instrument panel. Remove screws securing upper
and lower covers together and remove covers.
On Chevrolet and Chevelle columns with Powerglide
shift levers, loosen set screw at six o'clock position
at bottom of column and remove the transmission
shift indicator pointer (fig. 15).
9. Chevrolet only (fig. 19):
a. Remove screws securing cover trim to dash
panel and remove cover trim.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
Fig.
18—Mast Jacket Cover Attachments—Chevy II
CHEVROLET CHASSIS SERVICE MANUAL
Page 463 of 659
STEERING 9-23
Fig.
47—I retaliating Spherical Joint Spring
upper shaft should be on the same side as the
flat on the lower shaft.
d. Install the upper shaft with spheres into the lower
shaft.
e. Insert the joint preload spring through the
spheres into the lower shaft. Using the upper
shaft to hold the spring in place, carefully feed
the spring into the upper shaft joint with a narrow
bladed screwdriver (fig. 47).
17.
Slide the race and bearing over the top of steering
shaft and install shaft in shift tube from upper end.
Carefully guide shaft through shift tube, taking care
not to tear or push out foam seal cemented inside
lower end of shift tube.
18.
Install tilt control lever and, holding lock shoes in
disengaged position, assemble bearing housing on the
shaft over the support until pivot pin holes line up.
19.
Secure bearing housing in position by pressing in the
pivot pins.
20.
Place housing in full up position and install tilt
spring, tapered end first. Install tilt spring retainer
using screwdriver in retainer slot.
21.
Install turn signal switch with three mounting
screws. Place short length screw in top position
above lock shoes.
NOTE:
If the steering shaft, adapter, mast
jacket, support or bearing housing has been,
replaced, the component stack-up in the column
will be different. Replace the lower plastic in-
jected tolerance ring and the lower bearing pre-
load spring with the necessary tolerance ring
kit as described below.
22.
Slide kit spring, tolerance ring kit, washers, and
retaining ring on steering shaft from lower end.
Seat retaining ring in steering shaft groove.
23.
Screw tolerance ring kit sections together leaving
enough inner edge exposed for later adjustment as
shown in Figure 35.
24.
Install inner race, inner race seat, and bearing lock-
nut on end of steering shaft, using locknut wrench
ToolJ-22599 (fig. 39).
25.
Remove any remaining looseness from internal col-
umn stack-up by unscrewing inner tolerance kit ring
section; then screw inner ring section back in 1/8 to
1/4 turn (fig. 36).
26.
Tighten bearing locknut installed in Step 24 above
until the torque required to rotate the steering shaft,
with the housing in the mid position, is 23 lb. in.
27.
Touch the outer surface of the tolerance ring kit at
several locations with a hot soldering iron to melt
the threads of the inner and outer sections together.
28.
Check to insure hazard warning switch is pushed in.
Remove tilt release control lever and install turn
signal switch cover using turn signal cover installer
Tool J-21853 (fig. 48). On automatic column, be sure
key in the cover is aligned with keyway in bearing
housing.
29.
Place turn signal control lever in position and se-
cure with mounting screw. Screw tilt release control
lever in. Screw hazard warning knob in.
30.
On automatic columns, place transmission shift con-
trol lever in position and insert lever retaining pin.
31.
On automatic columns to be installed in a Camaro,
insert the bulb and cap into the turn signal switch
housing (fig. 33). Slide pointer into position in bowl.
Install dial and dial retainer with mounting screws
removed during disassembly.
32.
Install steering shaft flange on bottom of shaft and
secure with flange bolt.
33.
Remove column from vise. Pull wires back against
column leaving a small amount of slack. Snap wiring
protector into position. Be sure enough slack re-
mains in wires to allow column head to tilt to full
up position.
34.
If mesh cover was removed, wrap mesh cover around
mesh portion of jacket and secure with friction or
electricians tape.
35.
Slide cancelling cam and cancelling cam spring on
upper end of shaft.
Disassembly—Standard Corvette Column (Fig. 49)
1.
Place column on a suitable work bench.
2.
Remove upper bearing preload spring and cancelling
cam from end of column.
3.
Slide escutcheon clear of wiring protector and re-
move protector.
4.
Remove turn signal lever retaining screw and re-
move lever. Push hazard warning knob in; unscrew
and remove knob.
Fig.
48—Installing Turn Signal Switch Cover Using
Signal Switch Installer Tool J-21853
CHEVROLET CHASSIS SERVICE MANUAL
Page 513 of 659

SECTION 12
ELECTRICAL-BODY AND CHASSIS
CONTENTS
OF
THIS
SECTION
Page
Page
System 12-1
Instruments and Gauges 12-21
Directional Signal 12r40
Windshield Wipers and Washers 12-44
Wiring Diagrams 12-56
Special Tools 12-60
LIGHTING SYSTEM
INDEX
Page
General Description
!2-i
Maintenance and Adjustments
•.................. 12-2
Headlamp Adjustment......................
12-3
Headlamp Panel Travel Adjustment.
12-5
Service Operations.
. . .. 12-5
Front Lighting
12-5
Headlamp
. 12_5
Parking Lamp
12-5
Fender Lamp
. 12_^
Headlamp Panel
12-8
Headlamp Panel Motor
^2-9
Rear Lighting
l2-10
Tail, Stop and Directional Lamps
12-10
Page
Backing Lamps
12-14
License Plate Lamp
12-14
Automatic Transmission Quadrant Lamp
12-14
Seat Separator Console Lamps
. 12-15
Lighting Switch
. . 12-15
Wiper Switch.
12-15
Stoplight Switch
12-15
Dimmer Switch
12-15
Backing Lamp Switches
12-15
Neutral Safety Switches
12-17
Parking Brake Alarm Switch
................. 12-19
Instrument Panel Compartment Lamp/Switch
12-19
Cirgarette Lighter
12-19
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
.
The lighting system includes: the main lighting switch,
stop light, dimmer, and backing lamp switches, head-
lamps, parking lamps, stop, tail and directional lamps,
instrument illumination and indicator lamps, and the
necessary wiring to complete the various circuits. A
fuse panel provides convenient power take offs and fuse
clips for the appropriate circuits (fig. 1).
Chevrolet and Chevelle headlamp installation is all
new in that the headlamps are located in the radiator
support with adjusting screws and springs. Eliminating
the need for having separate headlamp housings. Chev-
rolet and Chevelle headlamp retainers and springs are
interchangeable.
Chevy n headlamp housings are new because of revised
front end styling and Corvette front end lighting is basi-
cally carryover.
Front fender lamps have been added as an option for
Chevrolet models and as standard equipment on Caprice
series.
Camaro models use single headlamps and the Rally
Sport model headlamps are covered by a retractable
section of the grille when lamps are not used. The sec-
tion of the grille covering the headlamps folds back when
lights are required; the headlamps are stationary. The
covering is retracted by a small electric motor mounted
to the headlamp housing. The headlamps are automat-
ically uncovered when the headlight switch is pulled "ON"
for illumination. If at any time the electrical circuit
becomes inoperative, the lamps can be uncovered manu-
ally. The ignition switch must be
"ON"
in order to close
the headlamp doors.
Parking lamp for Chevelle and Chevrolet models are
new due to revised front end sheet metal and bumper
styling. Parking lamps are located in the bumper on
Chevrolet, Chevelle and Chevy n models
Camaro parking lamps are located in the radiator
grille except for the Rally Sport models on which the
parking lamps are in the valance panel. For styling
reasons, the lens is white and an amber glass bulb is
used. All Camaro parking lamps require a separate
ground wire to assure a good ground contact because of
the plastic grille and painted contact surfaces.
The Chevrolet tail, stop, and directional lamps are in
one housing with a three section lens design on Impala
and Caprice sedans. The center lens for Impala series
is the back-up lamp. The center lens on the Caprice is
a tail lamp with the back-up lamps being located in the
rear bumper. Chevrolet station wagons have three indi-
vidual housings with three lenses, the center lamp being
the back-up. Biscayne and Bel-Air sedans have a single
housing and lens for tail, stop, and directional lamp with
a similarly constructed back-up lamp inboard and adja-
cent to it.
Chevelle tail, stop, and directional lamps are a single
lens design that follows through with the rear fender
styling. The back-up lamp is located in r.ear bumper.
Camaro models except Rally Sport have tail lamps
with integral back-up lamps mounted inboard of the rear
fenders between the trunk opening and bumper. The
Rally Sport model has dual tail lamps in the rear housing
and valance mounted back-up lamps.
Corvette, Chevy n, and Corvair tail and directional
signal lights are carryover. The Corvette has new back-
up lamps center mounted above the license plate opening.
CHEVROLET CHASSIS SERVICE