oil dipstick CHEVROLET DYNASTY 1993 User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: CHEVROLET, Model Year: 1993, Model line: DYNASTY, Model: CHEVROLET DYNASTY 1993Pages: 2438, PDF Size: 74.98 MB
Page 1920 of 2438

cle and or engine application the Saginaw T/C style
power steering pump is used on, it will be equipped
with a plastic integral or remote mounted power
steering fluid reservoir. Drive tangs on the power steering gear pinion, mate
loosely with the stub shaft of the steering gear. This
will allow manual steering control to be maintained, if
the drive belt on the power steering pump should
break. However, under these conditions, steering effort
will significantly increase.
STEERING COMPONENTS SERVICE DIAGNOSIS
POWER STEERING PUMP SERVICE
The service procedures for the Saginaw power steer-
ing pump are limited to the areas and components
listed below. No repair procedures are to be done
on internal components of the Saginaw power
steering pumps.
² Repair of power steering fluid leaks from areas of
the power steering pump sealed by O-rings is allowed
(See Pump Leak Diagnosis). However power steering
pump shaft seal leakage will require replacement of
the pump.
² Power steering fluid reservoirs, related components
and attaching hardware.
² Power steering fluid reservoir filler cap/dipstick as-
semblies. Because of unique shaft bearings, flow control levels
or pump displacements, power steering pumps may be
used only on specific vehicle applications. Be sure that
all power steering pumps are only replaced with a
pump that is the correct replacement for that specific
application. Hydraulic pressure is provided for operation of the
power steering gear by the belt driven power steering
pumps (Fig . 1 & 2). It is a constant displacement, vane
type pump. The power steering pump is connected to
the steering gear by a power steering fluid pressure
hose and return hose.
Rectangular pumping vanes in the shaft driven rotor,
move power steering fluid from the intake to the cam ring
pressure cavities of the power steering pump. As the rotor
begins to turn, centrifugal force throws the vanes against
the inside surface of the cam ring to pickup residual oil.
This oil is then forced into the high pressure area. As more
oil is picked up by the vanes. That additional oil is forced
into the cavities of the thrust plate through two crossover
holes in the cam ring and pressure plate. The crossover
holes empty into the high pressure area between the
pressure plate and the housing end cover.
As the high pressure area is filled, oil flows under
the vanes in the rotor slots, forcing the vanes to follow
the inside surface of the cam ring. As the vanes
reach the restricted area of the cam ring, oil is
forced out from between the vanes. When excess oil
flow is generated during high-speed operation, a regu-
lated amount of oil returns to the pump intake side
through a flow control valve. The flow control valve
reduces the power required to drive the pump
and holds down temperature build-up.
Fig. 1 Saginaw Ham Can Power Steering Pump
Fig. 2 Saginaw T/C Style Power Steering Pump
19 - 2 STEERING Ä
Page 1927 of 2438

When steering conditions exceed maximum pres-
sure requirements, such as when the wheels are
turned against the stops. The pressure built up in
the steering gear exerts pressure on the spring end of
the flow control valve. The high pressure lifts the re-
lief valve ball from its seat and allows oil to flow
through a trigger orifice located in the outlet fitting.
This reduces pressure on the spring end of the flow
control valve which then opens and allows the oil to
return to the intake side of the pump. This action
limits maximum pressure output of the pump to a
safe level. Under normal power steering pump operating con-
ditions, pressure requirements of the pump are below
maximum, causing the pressure relief valve to re-
main closed.
CHECKING POWER STEERING FLUID LEVEL
WARNING: FLUID LEVEL SHOULD BE CHECKED
WITH ENGINE OFF TO PREVENT INJURY FROM
MOVING PARTS. DO NOT USE AUTOMATIC TRANS-
MISSION FLUID IN THE POWER STEERING SYS-
TEM. DO NOT OVERFILL THE POWER STEERING
SYSTEM.
Wipe reservoir filler cap free of dirt, before check-
ing power steering fluid level. The dipstick should in- dicate FULL COLD when fluid is at normal ambient
temperature, approximately 21ÉC to 27ÉC (70ÉF to
80ÉF). In all pumps add fluid as necessary to obtain
proper level, using only MopartPower Steering
Fluid, or equivalent. DO NOT USE ANY TYPE
OF AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION FLUID.
POWER STEERING PUMP PRESSURE TEST
The following procedure can be used to test the op-
eration of the power steering system on the vehicle. (1) Check power steering pump drive belt tension
and adjust as necessary. (2) Disconnect power steering fluid pressure hose,
at steering gear or power steering pump. Use a con-
tainer for dripping fluid. (3) Connect Pressure Gauge, Special Tool C-3309-E
(Fig. 1) to both hoses using adapter fittings. Connect
spare pressure hose to gear or pump. (4) Completely open valve on Special Tool
C-3309-E (Fig. 1). (5) Start engine and let idle.
(6) Check power steering fluid level, and add fluid
as necessary. (7) Gauge should read below 862 kPa (125 psi), if
above, inspect the hoses for restrictions and repair as
necessary. The initial pressure should be in the
range of 345-552 kPa (50-80 psi).
PUMP LEAKAGE DIAGNOSIS
Ä STEERING 19 - 9
Page 1932 of 2438

(10) Connect negative cable back on negative post
of battery. (11) Start engine and turn steering wheel several
times from stop to stop to bleed air from fluid in sys-
tem. Stop engine, check fluid level, and inspect sys-
tem for leaks. See Checking Fluid Level.
3.0 LITER
REMOVE
(1) REMOVE THE (-) NEGATIVE BATTERY CA-
BLE FROM THE BATTERY AND ISOLATE CA-
BLE. (2) Remove the serpentine accessory drive belt
from engine (Fig. 4). See Cooling, Group 7 for de-
tailed removal procedure.
(3) Remove the hose clamp and bolt mounting the
power steering pump filler tube and dipstick assem-
bly (Fig. 5) to power steering pump and generator
bracket. Remove filler tube and dipstick assembly
from power steering pump. (4) Raise vehicle See Hoisting, Group 0.
(5) Remove the 2 nut, bolt and spring assemblies
attaching the exhaust pipe to exhaust manifold. Re-
move exhaust pipe from exhaust manifold and move
to left side of vehicle. This is required for clear-
ance to remove power steering pump from vehi-
cle. (6) Remove vehicle's wiring harness connector (if
applicable to vehicle being serviced) from the power
steering pressure switch (Fig. 6). (7) Put oil drain pan under vehicle to catch power
steering fluid. Remove hose clamp and low pressure
fluid hose, from power steering gear fluid tube (Fig.
7). Allow excess power steering fluid to drain from
power steering pump and hose. (8) Loosen the high pressure power steering fluid
line fitting at the power steering pump (Fig. 7). Then
remove high pressure power steering fluid line from
power steering pump. (9) Remove nut holding the power steering pump
rear support bracket to pump (Fig. 8). Then remove
the 2 bolts (Fig. 7) mounting the power steering
pump support bracket to engine and remove bracket
from vehicle. (10) Remove the 2 bolts that mount the front of
the power steering pump to the mounting plate (Fig.
9). Access to the mounting bolts is through the holes
in power steering pump pulley using a deep well
socket. (11) Remove the power steering pump and pulley
assembly from vehicle. Remove pump assembly from
vehicle in area between floor pan and front suspen-
sion crossmember. Pump will fit through area of ex-
haust pipe tunnel in floor pan.
Fig. 4 3.0L Serpentine Drive Belt Routing
Fig. 5 Power Steering Pump Filler Tube/Dipstick Assembly
Fig. 6 Power Steering Pressure Switch Location 3.0L
19 - 14 STEERING Ä
Page 1995 of 2438

THREE SPEED TORQUEFLITE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE INDEX
page page
Accumulator-Recondition ................... 67
Aluminum Thread Repair ................... 48
Assembly Subassembly Installation ........... 57
Band Adjustment ......................... 47
Bearing Adjustment Procedures .............. 81
Clutch and Servo Air Pressure Tests .......... 43
Differential Repair ........................ 76
Disassembly Subassembly Removal .......... 50
Fluid and Filter Change .................... 40
Fluid Drain and Refill ..................... 40
Fluid Leakage-Transaxle Torque Converter Housing Area .......................... 44
Fluid Level and Condition .................. 40
Front Clutch-Recondition ................... 62
Front Planetary & Annulus Gear-Recondition .... 65
Gearshift Linkage Adjustment ............... 46
General Information ....................... 35
Governor ............................... 48
Hydraulic Control Pressure Adjustments ....... 47
Hydraulic Pressure Tests ................... 42
Kickdown Servo (Controlled Load)-Recondition . . 67 Low/Reverse Servo-Recondition
.............. 66
Oil Cooler Flow Check .................... 48
Oil Coolers and Tubes Reverse Flushing ...... 48
Oil Pump-Recondition ..................... 62
Output Shaft Repair ...................... 71
Park/Neutral Position and Back-Up Lamp Switch . 47
Parking Pawl ............................ 71
Pump Oil Seal-Replacement ................ 61
Rear Clutch-Recondition ................... 64
Road Test .............................. 40
Selection of Lubricant ..................... 40
Special Additives ......................... 40
Three Speed Torqueflite General Diagnosis ..... 36
Throttle Pressure Linkage Adjustment ......... 46
Torque Converter Clutch Solenoid Wiring Connector ............................ 40
Transaxle and Torque Converter Removal ...... 48
Transfer Shaft Repair ..................... 68
Valve Body-Recondition .................... 57
Vehicle Speed Sensor Pinion Gear ........... 47
GENERAL INFORMATION
Safety goggles should be worn at all times
when working on these transaxles. This transaxle combines a fully automatic 3 speed
transmission, final drive gearing, and differential into
a front wheel drive system. The unit is a Metric
design. The identification markings and usage of the
transaxle are charted in Diagnosis and Tests. Transaxle operation requirements are differ-
ent for each vehicle and engine combination and
some internal parts will be different to provide
for this. Therefore, when replacing parts, refer to
the seven digit part number stamped on rear of
the transaxle oil pan flange. Within this transaxle, there are 3 primary areas:
(1) Main center line plus valve body.
(2) Transfer shaft center line (includes governor and
parking sprag). (3) Differential center line. Center distances be-
tween the main rotating parts in these 3 areas are held
precise. This maintains a low noise level through
smooth accurate mesh of the gears. The torque converter, transaxle area, and differential
are housed in an integral aluminum die casting. The
differential oil sump is common with thetransaxle
sump. Separate filling of the differential is NOT nec-
essary. The torque converter is attached to the crankshaft
through a flexible driving plate. Cooling of the con-
verter is accomplished by circulating the transaxle
fluid through an oil-to-water type cooler located in the
radiator side tank and/or an oil-to air heat ex- changer. The torque converter assembly is a sealed
unit that cannot be disassembled.
The transaxle fluid is filtered by an internal filter
attached to the lower side of the valve body assem-
bly. Engine torque is transmitted to the torque con-
verter then, through the input shaft to multiple-disc
clutches in the transaxle. The power flow depends on
the application of the clutches and bands. Refer to
Elements in Use Chart in Diagnosis and Tests sec-
tion. The transaxle consists of two multiple-disc
clutches, an overrunning clutch, two servos, a hy-
draulic accumulator, two bands, and two planetary
gear sets. They provide three forward ratios and a re-
verse ratio. The common sun gear of the planetary
gear sets is connected to the front clutch by a driving
shell. The drive shell is splined to the sun gear and
to the front clutch retainer. The hydraulic system
consists of an oil pump, and a single valve body
which contains all of the valves except the governor
valves. The transaxle sump and differential sump are
both vented through the dipstick.Output torque
from the main center line is delivered through heli-
cal gears to the transfer shaft.This gear set is a
factor of the final drive (axle) ratio. The shaft also
carries the governor and parking sprag. An integral
helical gear on the transfer shaft drives the differen-
tial ring gear. The final drive gearing is completed
with one of three gear sets producing overall top gear
ratios of 2.78, 3.02, or 3.22 depending on model and
application.
Ä TRANSAXLE 21 - 35
Page 2000 of 2438

FLUID LEVEL AND CONDITION
The transmission and differential sump have a
common oil sump with a communicating opening
between the two. Before removing the dipstick, wipe all dirt off of the
protective disc and the dipstick handle. The torque converter will fill in both the PPark or N
Neutral positions. Place the selector lever in PPark to
check fluid level. Inspect fluid level on dipstick every six months.
Allow the engine to idle for at least one minute
with vehicle on level ground. This will assure
complete oil level stabilization between differen-
tial and transmission. A properly filled transaxle
will read near the addmark when fluid temperature is
21 degrees Celsius (70 degrees Fahrenheit). When the
transaxle reaches operating temperature the fluid
should be in the HOTregion.
Low fluid level can cause a variety of conditions
because it allows the pump to take in air along with the
fluid. As in any hydraulic system, air bubbles make the
fluid spongy, therefore, pressures will be low and build
up slowly. Improper filling can also raise the fluid level too
high. When the transaxle has too much fluid, the gears
churn up foam and cause the same conditions which
occur with a low fluid level. In either case, the air bubbles can cause overheating,
fluid oxidation, and varnishing, which can interfere
with normal valve, clutch, and servo operation. Foam-
ing can also result in fluid escaping from the transaxle
vent (dipstick handle) where it may be mistaken for a
leak. Along with fluid level, it is important to check the
condition of the fluid. When the fluid smells burned,
and is contaminated with metal or friction material
particles, a complete transaxle overhaul is needed. Be
sure to examine the fluid on the dipstick closely. If
there is any doubt about its condition, drain out a
sample for a double check. After the fluid has been checked, seat the dipstick
fully to seal out water and dirt.
SELECTION OF LUBRICANT
It is important that the proper lubricant be used in
these transmissions. MOPAR tATF PLUS (Automatic
Transmission Fluid-Type 7176) should be used to aid in
assuring optimum transmission performance. Fluids of
the type labeled DEXRON II Automatic Transmission
Fluid should be used only if the recommended fluid is
not available. It is important that the transmission
fluid be maintained at the prescribed level using the
recommended fluids.
SPECIAL ADDITIVES
Chrysler Corporation does not recommend the addi-
tion of any fluids to the transmission, other than the
automatic transmission fluid listed above. An ex- ception to this policy is the use of special dyes to aid in
detecting fluid leaks. The use of transmission sealers
should be avoided, since they may adversely affect
seals.
FLUID AND FILTER CHANGE
When the factory fill fluid is changed, only
fluids of the type labeled MOPAR tATF PLUS
(Automatic Transmission fluid) Type 7176 should
be used. A band adjustment and filter change
should be made at the time of the oil change. The
magnet (on the inside of the oil pan) should also
be cleaned with a clean, dry cloth. If the transaxle is disassembled for any reason,
the fluid and filter should be changed, and the
band(s) adjusted.
FLUID DRAIN AND REFILL
(1) Raise vehicle on a hoist (See Lubrication, Group
0). Place a drain container with a large opening, under
transaxle oil pan. (2) Loosen pan bolts and tap the pan at one corner to
break it loose allowing fluid to drain, then remove the
oil pan. (3) Install a new filter and gasket on bottom of the
valve body and tighten retaining screws to 5 N Im (40
in. lbs.). (4) Clean the oil pan and magnet. Reinstall pan
using new MOPAR tAdhesive sealant. Tighten oil pan
bolts to 19 N Im (165 in. lbs.).
(5) Pour four quarts of MOPAR tATF PLUS (Auto-
matic Transmission Fluid) Type 7176 through the
dipstick opening. (6) Start engine and allow to idle for at least one
minute. Then, with parking and service brakes ap-
plied, move selector lever momentarily to each posi-
tion, ending in the park or neutral position. (7) Add sufficient fluid to bring level to 1/8 inch
below the ADD mark. Recheck fluid level after transaxle is at normal
operating temperature. The level should be in the HOT
region (Fig. 1). To prevent dirt from entering transaxle, make cer-
tain that dipstick is full seated into the dipstick open-
ing.
TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH SOLENOID WIRING
CONNECTOR
If wiring connector is unplugged, the torque con-
verter clutch will not operate (Fig. 2).
ROAD TEST
Prior to performing a road test, be certain that the
fluid level and condition, and control cable adjustments
have been checked and approved. During the road test, the transaxle should be oper-
ated in each position to check for slipping and any
variation in shifting.
21 - 40 TRANSAXLE Ä
Page 2004 of 2438

clutch is operating. Hold air pressure on for a few
seconds and inspect system for excessive oil leaks.
REAR CLUTCH
Apply air pressure to rear clutch applypassage
and listen for a dull thudwhich indicates that rear
clutch is operating. Also inspect for excessive oil
leaks. If a dull thudcannot be heard in the clutches,
place finger tips on clutch housing and again apply
air pressure. Movement of piston can be felt as the
clutch is applied.
KICKDOWN SERVO (FRONT)
Direct air pressure into kickdown servo ONpas-
sage. Operation of servo is indicated by a tightening
of front band. Spring tension on servo piston should
release the band.
LOW AND REVERSE SERVO (REAR)
Direct air pressure into LOW-REVERSE SERVO
APPLY passage. Operation of servo is indicated by a
tightening of rear band. Spring tension on servo pis-
ton should release the band. If clutches and servos operate properly, no upshift
or erratic shift conditions indicate that malfunctions
exist in the valve body.
FLUID LEAKAGE-TRANSAXLE TORQUE
CONVERTER HOUSING AREA
(1) Check for Source of Leakage.
Since fluid leakage at or around the torque con-
verter area may originate from an engine oil leak,
the area should be examined closely. Factory fill
fluid is dyed red and, therefore, can be distinguished
from engine oil. (2) Prior to removing the transaxle, perform the
following checks:
² When leakage is determined to originate from the
transaxle, check fluid level prior to removal of the
transaxle and torque converter.
² High oil level can result in oil leakage out the
vent in the dipstick. If the fluid level is high, adjust
to proper level. After performing this operation, inspect for leak-
age. If a leak persists, perform the following opera-
tion on the vehicle to determine if it is the torque
converter or transaxle that is leaking.
LEAKAGE TEST PROBE
(1) Remove torque converter housing dust shield.
(2) Clean the inside of torque converter housing
(lower area) as dry as possible. A solvent spray fol-
lowed by compressed air drying is preferable.
Fig. 4 Air Pressure Tests
21 - 44 TRANSAXLE Ä
Page 2005 of 2438
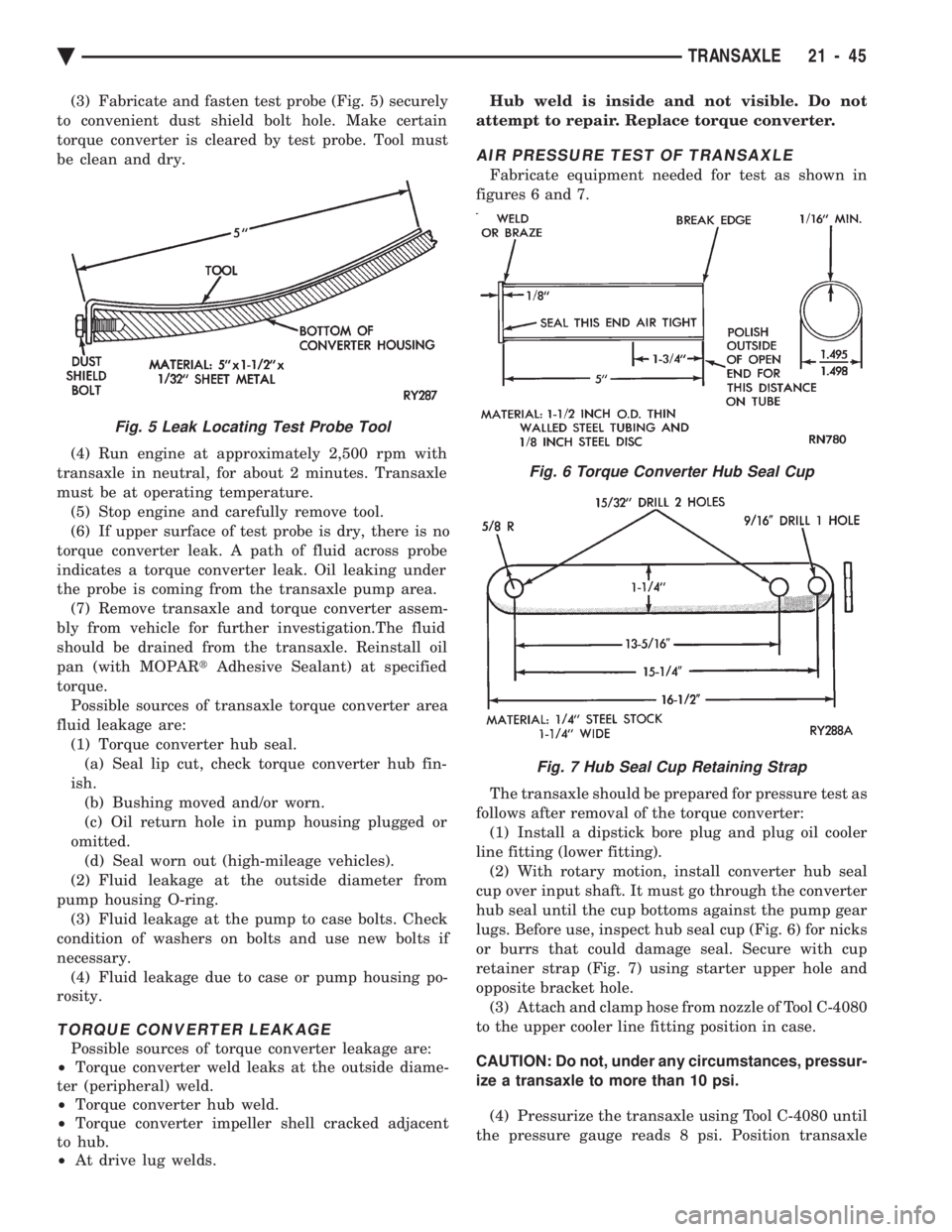
(3) Fabricate and fasten test probe (Fig. 5) securely
to convenient dust shield bolt hole. Make certain
torque converter is cleared by test probe. Tool must
be clean and dry.
(4) Run engine at approximately 2,500 rpm with
transaxle in neutral, for about 2 minutes. Transaxle
must be at operating temperature. (5) Stop engine and carefully remove tool.
(6) If upper surface of test probe is dry, there is no
torque converter leak. A path of fluid across probe
indicates a torque converter leak. Oil leaking under
the probe is coming from the transaxle pump area. (7) Remove transaxle and torque converter assem-
bly from vehicle for further investigation.The fluid
should be drained from the transaxle. Reinstall oil
pan (with MOPAR tAdhesive Sealant) at specified
torque. Possible sources of transaxle torque converter area
fluid leakage are: (1) Torque converter hub seal.(a) Seal lip cut, check torque converter hub fin-
ish. (b) Bushing moved and/or worn.
(c) Oil return hole in pump housing plugged or
omitted. (d) Seal worn out (high-mileage vehicles).
(2) Fluid leakage at the outside diameter from
pump housing O-ring. (3) Fluid leakage at the pump to case bolts. Check
condition of washers on bolts and use new bolts if
necessary. (4) Fluid leakage due to case or pump housing po-
rosity.
TORQUE CONVERTER LEAKAGE
Possible sources of torque converter leakage are:
² Torque converter weld leaks at the outside diame-
ter (peripheral) weld.
² Torque converter hub weld.
² Torque converter impeller shell cracked adjacent
to hub.
² At drive lug welds. Hub weld is inside and not visible. Do not
attempt to repair. Replace torque converter.
AIR PRESSURE TEST OF TRANSAXLE
Fabricate equipment needed for test as shown in
figures 6 and 7.
The transaxle should be prepared for pressure test as
follows after removal of the torque converter: (1) Install a dipstick bore plug and plug oil cooler
line fitting (lower fitting). (2) With rotary motion, install converter hub seal
cup over input shaft. It must go through the converter
hub seal until the cup bottoms against the pump gear
lugs. Before use, inspect hub seal cup (Fig. 6) for nicks
or burrs that could damage seal. Secure with cup
retainer strap (Fig. 7) using starter upper hole and
opposite bracket hole. (3) Attach and clamp hose from nozzle of Tool C-4080
to the upper cooler line fitting position in case.
CAUTION: Do not, under any circumstances, pressur-
ize a transaxle to more than 10 psi. (4) Pressurize the transaxle using Tool C-4080 until
the pressure gauge reads 8 psi. Position transaxle
Fig. 5 Leak Locating Test Probe Tool
Fig. 6 Torque Converter Hub Seal Cup
Fig. 7 Hub Seal Cup Retaining Strap
Ä TRANSAXLE 21 - 45
Page 2009 of 2438

If equipped, unplug torque converter clutch
plug, located near the dipstick.
CAUTION: Raise vehicle. Remove front wheels. Refer
to Suspension, Group 2 to remove or install wheel
hub nut and both drive shafts. Remove torque converter dust cover. Mark
torque converter and drive plate with chalk, for
reassembly. Remove torque converter mounting
bolts.
Fig. 1 Remove Upper and Lower Oil Cooler Hoses
Fig. 2 Engine Support Fixture
Fig. 3 Remove Bell Housing Upper Bolts
Fig. 4 Remove or Install Left Splash Shield
Fig. 5 Remove or Install Access Plug in Right Splash Shield to Rotate Engine Crankshaft
Fig. 6 Remove or Install Wire to Neutral/Park Safety Switch
Ä TRANSAXLE 21 - 49
Page 2053 of 2438

FLUID LEVEL AND CONDITION
The transmission and differential sump have a
common oil sump with a communicating opening
between the two. The torque converter fills in both the PPark and N
Neutral positions. Place the selector lever in PPark to
check the fluid level. The engine should be running
at idle speed for at least one minute, with the
vehicle on level ground. This will assure com-
plete oil level stabilization between differential
and transmission. The fluid should be at normal
operating temperature (approximately 82 C. or 180 F.).
The fluid level is correct if it is in the HOTregion
(cross-hatched area) on the oil level indicator. Low fluid level can cause a variety of conditions
because it allows the pump to take in air along with the
fluid. As in any hydraulic system, air bubbles make the
fluid spongy, therefore, pressures will be low and build
up slowly. Improper filling can also raise the fluid level too
high. When the transaxle has too much fluid, the gears
churn up foam and cause the same conditions which
occur with a low fluid level. In either case, the air bubbles can cause over heat-
ing, fluid oxidation, and varnishing, which can inter-
fere with normal valve, clutch, and accumulator opera-
tion. Foaming can also result in fluid escaping from the
transaxle vent where it may be mistaken for a leak. Along with fluid level, it is important to check the
condition of the fluid. When the fluid smells burned,
and is contaminated with metal or friction material
particles, a complete transaxle overhaul is needed. Be
sure to examine the fluid on the dipstick closely. If
there is any doubt about its condition, drain out a
sample for a double check. After the fluid has been checked, seat the dipstick
fully to seal out water and dirt.
SELECTION OF LUBRICANT
It is important that the proper lubricant be used in
the 41TE transaxle. MOPAR tATF PLUS (Automatic
Transmission FluidÐtype 7176) should be used to aid
in assuring optimum transmission performance. Flu-
ids of the type labeled DEXRON II Automatic Trans-
mission Fluid are not recommended . DEXRON II
can be used only if the recommended fluid is not
available. If more than a small amount of DEXRON II
is used shudder or shift quality problems may result. It
is important that the transmission fluid be maintained
at the prescribed level using the recommended fluids.
SPECIAL ADDITIVES
Chrysler Corporation does not recommend the addi-
tion of any fluids to the transaxle, other than the
automatic transmission fluid listed above. An excep- tion to this policy is the use of special dyes to aid in
detecting fluid leaks. The use of transmission sealers
should be avoided, since they may adversely affect
seals.
FLUID AND FILTER CHANGES
When the factory fill fluid is changed, only fluids
labeled MOPAR tATF PLUS (Automatic Transmis-
sion fluid) Type 7176 should be used. A filter change
should be made at the time of the oil change. Also
the magnet (on the inside of the oil pan) should be
cleaned with a clean, dry cloth. If the transaxle is disassembled for any reason, the
fluid and filter should be changed.
FLUID DRAIN AND REFILL
(1) Raise vehicle on a hoist (See Lubrication,
Group 0). Place a drain container with a large open-
ing, under transaxle oil pan. (2) Loosen pan bolts and tap the pan at one corner
to break it loose allowing fluid to drain, then remove
the oil pan. (3) Install a new filter and O-ring on bottom of the
valve body. (4) Clean the oil pan and magnet. Reinstall pan
using new MOPAR tAdhesive Sealant. Tighten oil
pan bolts to 19 N Im (165 in. lbs.).
(5) Pour four quarts of MOPAR tATF PLUS (Au-
tomatic Transmission Fluid) Type 7176 through the
fill tube. (6) Start engine and allow to idle for at least one
minute. Then, with parking and service brakes ap-
plied, move selector lever momentarily to each posi-
tion, ending in the park or neutral position. (7) Add sufficient fluid to bring level to 1/8 inch
below the ADD mark. Recheck fluid level after transaxle is at normal op-
erating temperature. The level should be in the HOT
region (Fig. 3).
To prevent dirt from entering transaxle, make cer-
tain that dipstick is seated into the dipstick fill tube
(Fig. 4).
ROAD TEST
Prior to performing a road test, be certain that the
fluid level and condition, and control cable adjust-
ment have been checked and approved.
Fig. 3 Oil Level Indicator
Ä TRANSAXLE 21 - 93
Page 2057 of 2438

first separator plate and watch carefully for the pis-
ton to move forward. The piston should return to its
original position after the air pressure is removed.
UNDERDRIVE CLUTCH
Because this clutch piston cannot be seen, its oper-
ation is checked by function. Air pressure is applied
to the low/reverse and the 2/4 clutches. This locks
the output shaft. Use a piece of rubber hose wrapped
around the input shaft and a pair of clamp-on pliers
to turn the input shaft. Next apply air pressure to
the underdrive clutch. The input shaft should not ro-
tate with hand torque. Release the air pressure and
confirm that the input shaft will rotate.
FLUID LEAKAGE-TORQUE CONVERTER HOUSING
AREA
(1) Check for source of leakage.
Since fluid leakage at or around the torque con-
verter area may originate from an engine oil leak,
the area should be examined closely. Factory fill
fluid is dyed red and, therefore, can be distinguished
from engine oil. (2) Prior to removing the transaxle, perform the
following checks: When leakage is determined to originate from the
transaxle, check fluid level prior to removal of the
transaxle and torque converter. High oil level can result in oil leakage out the vent
in the manual shaft. If the fluid level is high, adjust
to proper level. After performing this operation, inspect for leak-
age. If a leak persists, perform the following opera-
tion on the vehicle to determine if it is the torque
converter or transaxle that is leaking.
LEAKAGE TEST PROBE
(1) Remove torque converter housing dust shield.
(2) Clean the inside of torque converter housing
(lower area) as dry as possible. A solvent spray fol-
lowed by compressed air drying is preferable. (3) Fabricate and fasten test probe (Fig. 4) securely
to convenient dust shield bolt hole. Make certain
torque converter is cleared by test probe. Tool must be
clean and dry. (4) Run engine at approximately 2,500 rpm with
transaxle in neutral, for about 2 minutes. Transaxle
must be at operating temperature. (5) Stop engine and carefully remove tool.
(6) If upper surface of test probe is dry, there is no
torque converter leak. A path of fluid across probe
indicates a torque converter leak. Oil leaking under the
probe is coming from the transaxle torque converter
area. (7) Remove transaxle and torque converter assembly
from vehicle for further investigation. The fluid should
be drained from the transaxle. Re install oil pan (with
MOPAR tAdhesive Sealant) at specified torque.
Possible sources of transaxle torque converter area
fluid leakage are: (1) Torque converter hub seal.
² Seal lip cut, check torque converter hub finish.
² Bushing moved and/or worn.
² Oil return hole in pump housing plugged or omitted.
² Seal worn out (high-mileage vehicles).
(2) Fluid leakage at the outside diameter from pump
housing O-ring. (3) Fluid leakage at the front pump to case bolts.
Check condition of washers on bolts and use new bolts,
if necessary. (4) Fluid leakage due to case or front pump housing
porosity.
TORQUE CONVERTER LEAKAGE
Possible sources of torque converter leakage are:
² Torque converter weld leaks at the out side (periph-
eral) weld.
² Torque converter hub weld.
Hub weld is inside and not visible. Do not
attempt to repair. Replace torque converter. If the torque converter must be replaced, refer
to Torque Converter Clutch Break-in Procedure
in this section. This procedure will reset the
transmission control module break-in status.
Failure to perform this procedure may cause
transaxle shutter.
AIR PRESSURE TEST OF TRANSAXLE
Fabricate equipment needed for test as shown in
Figures 5 and 6. The transaxle should be prepared for pressure test as
follows after removal of the torque converter: (1) Plug dipstick tube and plug oil cooler line fitting.
Remove vent from manual shaft and in stall a 1/8 inch
pipe plug.Fig. 4 Leak Locating Test Probe Tool
Ä TRANSAXLE 21 - 97