Vacuum line CHRYSLER VOYAGER 2004 Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: CHRYSLER, Model Year: 2004, Model line: VOYAGER, Model: CHRYSLER VOYAGER 2004Pages: 2585, PDF Size: 62.54 MB
Page 1387 of 2585

(8) Install the generator and wiring harness (Refer
to 8 - ELECTRICAL/CHARGING/GENERATOR -
INSTALLATION).
(9) Raise vehicle.
(10) Attach wiring harness support clip to the
engine oil dipstick tube.
(11) Connect oil pressure switch electrical connec-
tor.
(12) Install the A/C compressor.
(13) Install the water pump pulley.
(14) Connect the radiator lower hose.(15) Install the accessory drive belt and splash
shield (Refer to 7 - COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/
DRIVE BELTS - INSTALLATION).
(16) Connect the engine block heater electrical con-
nector (if equipped).
(17) Connect the knock sensor electrical connector
(3.8L only).
(18) Install the torque converter to flex plate bolts.
(19) Install the transaxle case cover (Fig. 8).
(20) Install the powertrain struts (Fig. 8).
(21) Install the engine rear mount bracket.
(22) Install the engine front mount and bracket
assembly.
(23)AWD equipped;Install the power transfer
unit (PTU) (Refer to 21 - TRANSMISSION/TRANS-
AXLE/POWER TRANSFER UNIT - INSTALLA-
TION).
(24) Install the axle shafts (Refer to 3 - DIFFER-
ENTIAL & DRIVELINE/HALF SHAFT - INSTALLA-
TION).
(25) Connect exhaust pipe to manifold (Fig. 7).
(26) Install crossmember cradle plate (Fig. 6).
(27) Lower vehicle.
(28) Connect transaxle shift linkage.
(29) Connect transaxle electrical connectors.
(30) Remove plugs from transmission cooler hoses
and install transaxle oil cooler line service splice kit.
Refer to instructions included with kit.
(31) Install transaxle dipstick tube and attach
electrical harness clip.
(32) Connect the A/C lines to compressor.
(33) Connect the A/C compressor electrical connec-
tor.
(34) Evacuate and recharge A/C system.
(35) Connect crankshaft and camshaft position
sensors.
(36) Connect the fuel injector electrical harness
connector and engage clip to support bracket.
(37) Connect engine coolant temperature (ECT)
sensor and ignition coil electrical connectors.
(38) Connect the ground strap to rear of cylinder
head.
(39) Install power steering reservoir.
(40) Engage wire harness clip to engine right side
mount.
(41) Connect the brake booster and speed control
vacuum hoses.
(42) Connect the vacuum hoses to the throttle
body.
(43) Connect the EGR transducer electrical connec-
tor (if equipped).
(44) Connect the TPS, IAC, and MAP sensor elec-
trical connectors.
(45) Connect throttle cables to throttle body.
(46) Install the radiator fans (Refer to 7 - COOL-
ING/ENGINE/RADIATOR FAN - INSTALLATION).
Fig. 13 Right Mount to Engine
1 - BOLT
2 - MOUNT BRACKET
3 - ENGINE RIGHT MOUNT ASSEMBLY
Fig. 14 LEFT MOUNT TO FRAME BRACKET
1 - FRAME BRACKET
2 - FRAME RAIL - LEFT
3 - BOLT
4 - TRANSAXLE MOUNT
9 - 90 ENGINE 3.3/3.8LRS
ENGINE 3.3/3.8L (Continued)
Page 1442 of 2585

DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - INTAKE
MANIFOLD LEAKS
An intake manifold air leak is characterized by
lower than normal manifold vacuum. Also, one or
more cylinders may not be functioning.
WARNING: USE EXTREME CAUTION WHEN THE
ENGINE IS OPERATING. DO NOT STAND IN A
DIRECT LINE WITH THE FAN. DO NOT PUT YOUR
HANDS NEAR THE PULLEYS, BELTS OR THE FAN.
DO NOT WEAR LOOSE CLOTHING.
(1) Start the engine.
(2) Spray a small stream of water (Spray Bottle) at
the suspected leak area.
(3) If engine RPM'S change, the area of the sus-
pected leak has been found.
(4) Repair as required.
INTAKE MANIFOLD - UPPER
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - MANIFOLD
STRIPPED THREAD REPAIR
The composite upper intake manifold thread
bosses, if stripped out, can be repaired by utilizing a
repair screw available through Mopartparts. Repair
screws are available for the following manifold
attached components:
²MAP sensor
²Power steering reservoir
²EGR tube
²Throttle cable bracket
The repair screws require a unique tightening
torque specification from the original screw. Refer to
the following chart for specification.
DESCRIPTION TORQUE*
STRIP-OUT REPAIR SCREWS ONLY
MAP Sensor Repair
Screw4 N´m (35 in. lbs.)
Power Steering Reservoir
Repair Screw9 N´m (80 in. lbs.)
EGR Tube Attaching
Repair Screw9 N´m (80 in. lbs.)
Throttle Cable Bracket
Repair Screw9 N´m (80 in. lbs.)
*Install Slowly Using Hand Tools Only
STANDARD PROCEDURE - INTAKE MANIFOLD
VACUUM PORT REPAIR
The composite intake manifold vacuum ports can
be repaired. Although, if the manifold plenum cham-
ber is damaged or cracked, the manifold must be
replaced.
To repair a broken or damaged vacuum nipple
(port) on the composite intake manifold, perform the
following procedure:
PARTS REQUIRED TOOLS REQUIRED
´ Brass Nipple ± 1/49
O.D. x 1/89pipe thread
(LDP/Speed Control Port)´ Pipe Tap ± 1/89-18
NPT
´ Drill Bit ± 11/329
´ File/Sandpaper
´ Brass Nipple ± 1/29
O.D. x 1/49pipe thread
(Brake Booster Port)´ Pipe Tap ± 1/49-18
NPT
´ Drill Bit ± 7/169
´ File/Sandpaper
NOTE: While performing this procedure, avoid get-
ting the manifold material residue into the plenum
chamber.
(1) File or sand the remaining port back until a
flat surface is obtained (plane normal to nipple (port)
axis).
(2) Drill out the nipple (port) base using a 7/16º
(brake booster port) or 11/32º (LDP/speed control port
) drill bit (Fig. 113).
(3) Using a 1/4º±18 NPT (brake booster port) or
1/8º±18 NPT (LDP/speed control port ) pipe tap, cut
internal threads (Fig. 113). Use caution to start tap
in a axis same as original nipple.
(4) Apply MopartThread Sealant to threads of
repair nipple(s).
(5) Install repair nipple(s). Do not over torque
repair nipple(s).
REMOVAL - UPPER INTAKE MANIFOLD
(1) Disconnect battery negative cable.
(2) Disconnect inlet air temperature (IAT) sensor
electrical connector.
(3) Remove air inlet resonator to throttle body
hose assembly.
(4) Disconnect throttle and speed control cables
from throttle body (Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/
FUEL INJECTION/THROTTLE CONTROL CABLE -
REMOVAL).
(5) Disconnect make-up air hose support clip from
throttle cable bracket.
(6) Disconnect the automatic idle speed (AIS)
motor and throttle position sensor (TPS) wiring con-
nectors from throttle body.
RSENGINE 3.3/3.8L9 - 145
INTAKE MANIFOLD (Continued)
Page 1514 of 2585
nated fuel in this system. If it is necessary to replace
these lines/tubes/hoses, use new original equipment
lines/tubes/hoses.
If equipped:The hose clamps used to secure rub-
ber hoses on vehicles are of a special rolled edge con-
struction. This construction is used to prevent the
edge of the clamp from cutting into the hose. Only
these rolled edge type clamps may be used in this
system. All other types of clamps may cut into the
hoses and cause leaks.
Use new original equipment type hose clamps.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - HOSES AND CLAMP
Inspect all hose connections (clamps and quick con-
nect fittings) for completeness and leaks. Replace
cracked, scuffed, or swelled hoses. Replace hoses that
rub against other vehicle components or show sign of
wear.
Fuel injected vehicles use specially constructed
hoses. When replacing hoses, only use hoses marked
EFM/EFI.
When installing hoses, ensure that they are routed
away from contact with other vehicle components
that could rub against them and cause failure. Avoid
contact with clamps or other components that cause
abrasions or scuffing. Ensure that rubber hoses are
properly routed and avoid heat sources.
The hose clamps have rolled edges to prevent the
clamp from cutting into the hose. Only use clamps
that are original equipment or equivalent. Other
types of clamps may cut into the hoses and cause
high pressure fuel leaks. Tighten hose clamps to 1
N´m (9 in. lbs.) torque.
Inspect all hose connections such as clamps, cou-
plings and fittings to make sure they are secure and
leaks are not present. The component should be
replaced immediately if there is any evidence of deg-
radation that could result in failure.
Never attempt to repair a plastic fuel line/tube.
Replace as necessary.
Avoid contact of any fuel tubes/hoses with other
vehicle components that could cause abrasions or
scuffing. Be sure that the plastic fuel lines/tubes are
properly routed to prevent pinching and to avoid heat
sources.
FUEL PRESSURE REGULATOR
OPERATION
The fuel system uses a nonadjustable pressure reg-
ulator that maintains fuel system pressure at
approximately 400 34 kPa (58 5 psi). The fuel
pressure regulator contains a diaphragm, calibrated
spring and a fuel return valve. The spring pushes
down on the diaphragm and closes off the fuel returnport. System fuel pressure reflects the amount of fuel
pressure required to open the return port.
The pressure regulator is a mechanical device that
is NOT controlled by the PCM or engine vacuum.
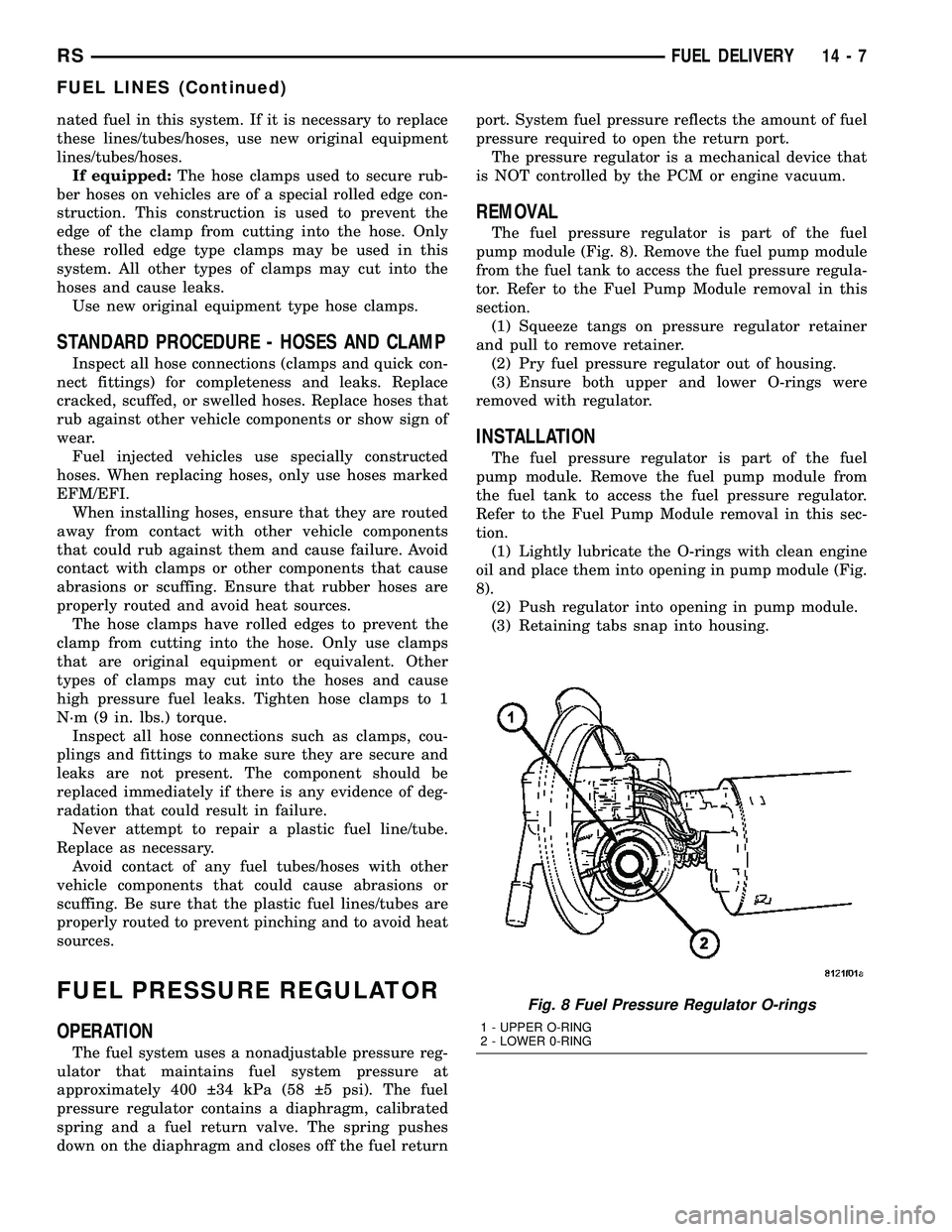
REMOVAL
The fuel pressure regulator is part of the fuel
pump module (Fig. 8). Remove the fuel pump module
from the fuel tank to access the fuel pressure regula-
tor. Refer to the Fuel Pump Module removal in this
section.
(1) Squeeze tangs on pressure regulator retainer
and pull to remove retainer.
(2) Pry fuel pressure regulator out of housing.
(3) Ensure both upper and lower O-rings were
removed with regulator.
INSTALLATION
The fuel pressure regulator is part of the fuel
pump module. Remove the fuel pump module from
the fuel tank to access the fuel pressure regulator.
Refer to the Fuel Pump Module removal in this sec-
tion.
(1) Lightly lubricate the O-rings with clean engine
oil and place them into opening in pump module (Fig.
8).
(2) Push regulator into opening in pump module.
(3) Retaining tabs snap into housing.
Fig. 8 Fuel Pressure Regulator O-rings
1 - UPPER O-RING
2 - LOWER 0-RING
RSFUEL DELIVERY14-7
FUEL LINES (Continued)
Page 1518 of 2585
OPERATION
All models pass a full 360 degree rollover test
without fuel leakage. To accomplish this, fuel and
vapor flow controls are required for all fuel tank con-
nections.
All models are equipped with either one or two
check valves mounted into the top of the fuel tank (or
pump module).
An evaporation control system is connected to the
check valve(s)/control valve(Refer to 25 - EMIS-
SIONS CONTROL/EVAPORATIVE EMISSIONS/
ORVR - OPERATION) to reduce emissions of fuel
vapors into the atmosphere, when the tank is vented
due to vapor expansion in the tank. When fuel evap-
orates from the fuel tank, vapors pass through vent
hoses or tubes to a charcoal canister where they are
temporarily held. When the engine is running, the
vapors are drawn into the intake manifold. In addi-
tion, fuel vapors produced during vehicle refueling
are allowed to pass through the vent hoses/tubes to
the charcoal canister(s) for temporary storage (prior
to being drawn into the intake manifold). All models
are equipped with a self-diagnosing system using a
Leak Detection Pump (LDP) or Natural Vacuum
Leak Detection (NVLD). Refer to the Emission Con-
trol System for additional information.
INLET CHECK VALVE
All vehicles have an inlet check valve on the inside
of the fuel tank at the filler inlet
The valve prevents fuel from splashing back on
customer during vehicle refueling. The valve is a
non-serviceable item.
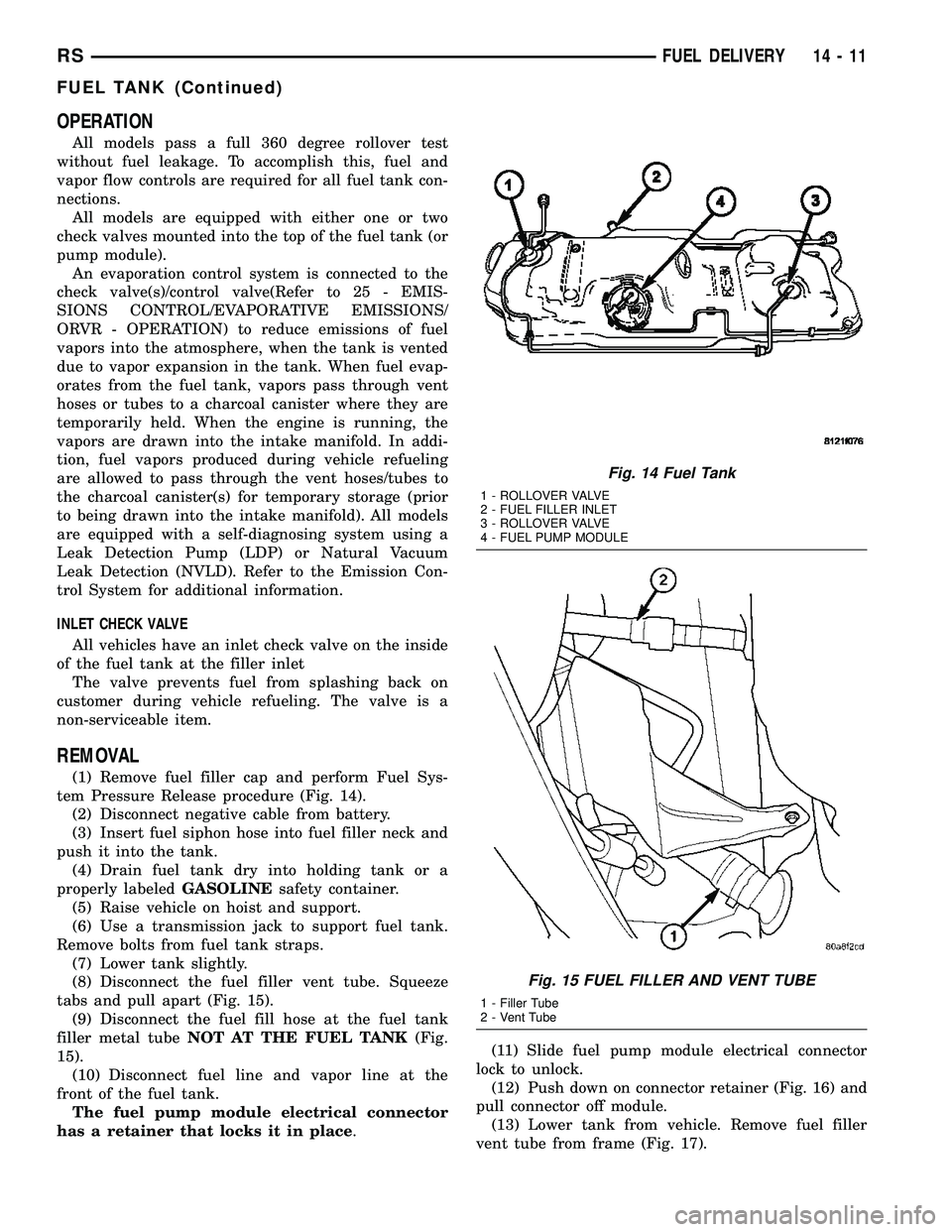
REMOVAL
(1) Remove fuel filler cap and perform Fuel Sys-
tem Pressure Release procedure (Fig. 14).
(2) Disconnect negative cable from battery.
(3) Insert fuel siphon hose into fuel filler neck and
push it into the tank.
(4) Drain fuel tank dry into holding tank or a
properly labeledGASOLINEsafety container.
(5) Raise vehicle on hoist and support.
(6) Use a transmission jack to support fuel tank.
Remove bolts from fuel tank straps.
(7) Lower tank slightly.
(8) Disconnect the fuel filler vent tube. Squeeze
tabs and pull apart (Fig. 15).
(9) Disconnect the fuel fill hose at the fuel tank
filler metal tubeNOT AT THE FUEL TANK(Fig.
15).
(10) Disconnect fuel line and vapor line at the
front of the fuel tank.
The fuel pump module electrical connector
has a retainer that locks it in place.(11) Slide fuel pump module electrical connector
lock to unlock.
(12) Push down on connector retainer (Fig. 16) and
pull connector off module.
(13) Lower tank from vehicle. Remove fuel filler
vent tube from frame (Fig. 17).
Fig. 14 Fuel Tank
1 - ROLLOVER VALVE
2 - FUEL FILLER INLET
3 - ROLLOVER VALVE
4 - FUEL PUMP MODULE
Fig. 15 FUEL FILLER AND VENT TUBE
1 - Filler Tube
2 - Vent Tube
RSFUEL DELIVERY14-11
FUEL TANK (Continued)
Page 1538 of 2585

weather, high pressure area. This is important
because as air pressure changes the barometric pres-
sure changes. Barometric pressure and altitude have
a direct inverse correlation, as altitude goes up baro-
metric goes down. The first thing that happens as
the key is rolled on, before reaching the crank posi-
tion, the PCM powers up, comes around and looks at
the MAP voltage, and based upon the voltage it sees,
it knows the current barometric pressure relative to
altitude. Once the engine starts, the PCM looks at
the voltage again, continuously every 12 milliseconds,
and compares the current voltage to what it was at
key on. The difference between current and what it
was at key on is manifold vacuum.
During key On (engine not running) the sensor
reads (updates) barometric pressure. A normal range
can be obtained by monitoring known good sensor in
you work area.
As the altitude increases the air becomes thinner
(less oxygen). If a vehicle is started and driven to a
very different altitude than where it was at key On
the barometric pressure needs to be updated. Any
time the PCM sees Wide Open throttle, based upon
TPS angle and RPM it will update barometric pres-
sure in the MAP memory cell. With periodic updates,
the PCM can make its calculations more effectively.
The PCM uses the MAP sensor to aid in calculat-
ing the following:
²Barometric pressure
²Engine load
²Manifold pressure
²Injector pulse-width
²Spark-advance programs
²Shift-point strategies (F4AC1 transmissions
only, via the PCI bus)
²Idle speed²Decel fuel shutoff
The PCM recognizes a decrease in manifold pres-
sure by monitoring a decrease in voltage from the
reading stored in the barometric pressure memory
cell. The MAP sensor is a linear sensor; as pressure
changes, voltage changes proportionately. The range
of voltage output from the sensor is usually between
4.6 volts at sea level to as low as 0.3 volts at 26 in. of
Hg. Barometric pressure is the pressure exerted by
the atmosphere upon an object. At sea level on a
standard day, no storm, barometric pressure is 29.92
in Hg. For every 100 feet of altitude barometric pres-
sure drops .10 in. Hg. If a storm goes through it can
either add, high pressure, or decrease, low pressure,
from what should be present for that altitude. You
should make a habit of knowing what the average
pressure and corresponding barometric pressure is
for your area.REMOVAL
REMOVAL - 2.4L
(1) Disconnect the negative battery cable.
(2) Disconnect electrical connector and vacuum
hose from MAP sensor (Fig. 20).
(3) Remove two screws holding sensor to the
intake manifold.
REMOVAL - 3.3/3.8L
(1) Disconnect the negative battery cable.
(2) Remove vacuum hose and mounting screws
from manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor (Fig.
21).
(3) Disconnect electrical connector from sensor.
Remove sensor.
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - 2.4L
(1) Install sensor.
(2) Install two screws and tighten.
(3) Connect the electrical connector and vacuum
hose to the MAP sensor (Fig. 20).
(4) Connect the negative battery cable.
INSTALLATION - 3.3/3.8L
(1) Install sensor (Fig. 21).
(2) Install screws and tighten toPLASTIC MAN-
IFOLD 1.7 N´m (15 in. lbs.) ALUMINUM MANI-
FOLD 3.3 N´m (30 in. lbs.).
(3) Connect the electrical connector to the sensor.
Install vacuum hose.
(4) Connect the negative battery cable.
Fig. 21 MAP SENSOR - 3.3/3.8L
RSFUEL INJECTION14-31
MAP SENSOR (Continued)
Page 1543 of 2585

neously then gently pull the throttle cable from
throttle bracket or if it is the slide snap design you
have to slide the locking tab out of the hole and then
slide the cable assembly out of the bracket.
INSTALLATION
(1) From the engine compartment, push the hous-
ing end fitting and grommet into the dash panel.In-
stall gromment into the dash panel.
(2) Install the cable housing (throttle body end)
into the cable mounting bracket on the engine.
(3) From inside the vehicle, hold up the pedal and
install throttle cable and cable retainer in the upper
end of the pedal shaft.
(4) At the dash panel, install the cable retainer
clip between the end of the throttle cable fitting and
grommet
(5) From the engine compartment, rotate the
throttle lever wide open and install the throttle
cable.
THROTTLE POSITION SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
The throttle position sensor mounts to the side of
the throttle body (Fig. 30) or (Fig. 31).The sensor
connects to the throttle blade shaft. The TPS is a
variable resistor that provides the Powertrain Con-
trol Module (PCM) with an input signal (voltage).
OPERATION
The signal represents throttle blade position. As
the position of the throttle blade changes, the resis-
tance of the TPS changes.
The PCM supplies approximately 5 volts to the
TPS. The TPS output voltage (input signal to the
powertrain control module) represents throttle blade
position. The TPS output voltage to the PCM varies
from approximately 0.6 volt at minimum throttle
opening (idle) to a maximum of 4.5 volts at wide open
throttle.
Along with inputs from other sensors, the PCM
uses the TPS input to determine current engine oper-
ating conditions. The PCM also adjusts fuel injector
pulse width and ignition timing based on these
inputs.
REMOVAL - 3.3/3.8L
(1) Disconnect the negative battery cable.
(2) Remove the electrical connector from the Inlet
Air Temperature sensor.
(3) Remove the air cleaner box lid. Remove hose
from throttle body.
(4) Disconnect the electrical connector at TPS.
(5) Disconnect the electrical connector at IAC.
(6) Remove the throttle and speed control cables
from throttle body.
(7) Remove 3 mounting bolts from throttle body.
(8) Remove throttle body.
(9) Disconnect the purge vacuum line from the
throttle body.
(10) Remove TPS from throttle body.
Fig. 30 Throttle Position SensorÐ2.4L Engine
1 - Idle Air Control Valve
2 - Throttle Position Sensor
Fig. 31 Throttle Position SensorÐ3.3/3.8L Engine
1 - Idle Air Control Valve
2 - Throttle Position Sensor
14 - 36 FUEL INJECTIONRS
THROTTLE CONTROL CABLE (Continued)
Page 1544 of 2585

INSTALLATION - 3.3/3.8L
(1) Install TPS to throttle body.
(2) Disconnect the purge vacuum line from the
throttle body.
(3) Install throttle body.
(4) Install 3 mounting bolts from throttle body.
Tighten bolts.
(5) Install the throttle and speed control cables to
throttle body.(6) Connect the electrical connector at TPS.
(7) Connect the electrical connector at IAC.
(8) Install the air cleaner box lid. Install hose to
throttle body.
(9) Install the electrical connector to the Inlet Air
Temperature sensor.
(10) Connect the negative battery cable.
RSFUEL INJECTION14-37
THROTTLE POSITION SENSOR (Continued)
Page 2398 of 2585

REAR CONTROL PANEL
The rear A/C-heater control centrally mounted in
the headliner allows intermediate seat passengers to
adjust rear air distribution, temperature and blower
motor speed when the center knob on the front A/C-
heater control is set to the Rear position. The rear
A/C-heater control contains:
²a rotary adjustment knob for temperature.
²a rotary adjustment for fan speed control.
DESCRIPTION - AUTOMATIC THREE ZONE
The automatic temperature control (ATC), three
zone, front and rear heating and air conditioning sys-
tem allows both the driver and front occupants and
the rear intermediate occupants to select individual
comfort temperatures.
NOTE: Individual comfort temperatures are the per-
ceived temperature level at the individual seating
areas, NOT the actual passenger compartment air
temperature.
The ATC system includes a particulate air filter.
The filter element is the same size as the air condi-
tioning evaporator to ensure ample capacity. A door
at the base of the HVAC housing below the glove box
provides easy access to the filter element.
The ATC computer utilizes integrated circuitry and
information carried on the programmable communi-
cations interface (PCI) data bus network to monitor
many sensors and switch inputs throughout the vehi-
cle. In response to those inputs, the internal circuitry
and programming of the ATC computer allow it to
control electronic functions and features of the ATC
system. The inputs to the ATC computer are:
²Vehicle Speed/Engine RPM± The ATC com-
puter monitors engine rpm, vehicle speed and mani-
fold absolute pressure information from the
powertrain control module (PCM).
²Coolant Temperature± ATC computer moni-
tors coolant temperature received from the PCM and
converts it to degrees Fahrenheit.
²Ambient Temperature± ATC computer moni-
tors ambient temperature from the compass mini trip
computer (CMTC) and converts it to degrees Fahren-
heit.
²Engine Miscellaneous Sensor Status±ATC
computer monitors A/C disable information from the
PCM.
²Refrigerant Pressure± ATC computer moni-
tors barometric pressure, intake air temperature,
high side pressure and methanol content as broad-
cast by the PCM.
²Door Ajar Status± The ATC computer moni-
tors driver front door, passenger front door, left rear
door, right rear door and liftgate ajar information, asidentified by the body control module (BCM), to
determine if all in-car temperatures should be main-
tained.
²Dimming± The ATC computer monitors dim-
ming status from the BCM to determine the required
level of brightness and will dim accordingly.
²Vehicle Odometer± The ATC computer moni-
tors the vehicle odometer information from the BCM
to prevent flashing the vacuum-flourescent (VF) dig-
ital display icons if the manual motor calibration or
manual cool down tests have failed. Flashing of the
display icons will cease when the vehicle odometer is
greater than 3 miles.
²English/Metric± The ATC computer monitors
the English/Metric information broadcast by the
CMTC. The set temp displays for both the front and
rear control heads will be set accordingly.
²Vehicle Identification Number± The ATC
computer monitors the last eight characters of the
VIN broadcast by the PCM and compares it to the
information stored in EEPROM. If it is different, the
new number will be stored over the old one and a
motor calibration shall be initiated.
²A/C System Information± The ATC computer
will send a message for evaporator temperature too
low, fan blower relay status, evaporator sensor fail-
ure, rear window defogger relay and A/C select.
FRONT CONTROL PANEL
The front A/C-heater control and integral computer
is mounted in the instrument panel and contains:
²a power button which allows the system to be
completely turned off. The display is blank when the
system is off.
²a rocker switch that selects a cool-down rate.
LO-AUTO or HI-AUTO are displayed when the sys-
tem is in automatic operation.
²three rocker switches that select comfort temper-
atures from 15É to 30É C (59É to 85É F), which are
shown in the VF digital display. If the set temp is 15É
C (59É F) and the down button is pressed, the set
temp value will become 13É C (55É F) but the display
will show LO. If the set temp is 29É C (85É F) and the
up button is pressed, the set temp value will become
32É C (90É F) but the display will show HIGH. Tem-
peratures can be displayed in either metric or Fahr-
enheit, which is controlled from the overhead console.
²an air conditioning button that allows the com-
pressor to be turned off. A Snowflake symbol is illu-
minated when air conditioning is on, whether under
manual or automatic control.
²an air recirculation button. A Recirculation sym-
bol appears in the display when the button is
pressed, or when the system exceeds 80 percent cir-
culated air under automatic control due to high air
conditioning demand.
RSHEATING & AIR CONDITIONING24-3
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING (Continued)
Page 2461 of 2585

CAUTION
A/C SYSTEM
CAUTION: Liquid refrigerant is corrosive to metal
surfaces. Follow the operating instructions supplied
with the service equipment being used.
Never add R-12 to a refrigerant system designed to
use R-134a and do not use R-12 equipment or parts
on the R-134a system. Damage to the system will
result.
R-12 refrigerant oil must not be mixed with R-134a
refrigerant oil. They are not compatible and damage
to the system will result.
Do not overcharge the refrigerant system. Over-
charging will cause excessive compressor head
pressure and can cause noise and system failure.
Recover the refrigerant before opening any fitting
or connection. Open the fittings with caution, even
after the system has been discharged. Never open
or loosen a connection before recovering the refrig-
erant.
If equipped, do not remove the secondary retention
clip from any spring-lock coupler connection while
the refrigerant system is under pressure. Recover
the refrigerant before removing the secondary
retention clip. Open the fittings with caution, even
after the system has been discharged. Never open
or loosen a connection before recovering the refrig-
erant.
Do not open the refrigerant system or uncap a
replacement component until you are ready to ser-
vice the system. This will prevent contamination in
the system. Before disconnecting a component,
clean the outside of the fittings thoroughly to pre-
vent contamination from entering the refrigerant
system. Immediately after disconnecting a compo-
nent from the refrigerant system, seal the open fit-
tings with a cap or plug.
Refrigerant oil will absorb moisture from the atmo-
sphere if left uncapped. Do not open a container of
refrigerant oil until you are ready to use it. Replace
the cap on the oil container immediately after using.
Store refrigerant oil only in a clean, airtight, and
moisture-free container.
Keep service tools and the work area clean. Con-
tamination of the refrigerant system must be
avoided.
CAUTION: The use of A/C system sealers may
result in damage to A/C refrigerant recovery/evacu-
ation/recharging equipment and/or A/C systems.
Many federal, state/provincial and local regulations
prohibit the recharge of A/C systems with known
leaks. DaimlerChrysler recommends the detection
of A/C system leaks through the use of approvedleak detectors and fluorescent leak detection dyes.
Vehicles found with A/C system sealers should be
treated as contaminated and replacement of the
entire A/C refrigerant system is recommended. A/C
systems found to be contaminated with A/C system
sealers, A/C stop-leak products or seal conditioners
voids the warranty for the A/C system.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - REFRIGERANT
SYSTEM LEAKS
WARNING: R-134a SERVICE EQUIPMENT OR VEHI-
CLE A/C SYSTEM SHOULD NOT BE PRESSURE
TESTED OR LEAK TESTED WITH COMPRESSED
AIR. MIXTURE OF AIR and R-134a CAN BE COM-
BUSTIBLE AT ELEVATED PRESSURES. THESE MIX-
TURES ARE POTENTIALLY DANGEROUS AND MAY
RESULT IN FIRE OR EXPLOSION CAUSING INJURY
OR PROPERTY DAMAGE.
AVOID BREATHING A/C REFRIGERANT AND LUBRI-
CANT VAPOR OR MIST. EXPOSURE MAY IRRITATE
EYES, NOSE AND THROAT. USE ONLY APPROVED
SERVICE EQUIPMENT MEETING SAE REQUIRE-
MENTS TO DISCHARGE R-134a SYSTEM. IF ACCI-
DENTAL SYSTEM DISCHARGE OCCURS,
VENTILATE WORK AREA BEFORE RESUMING SER-
VICE.
If the A/C system is not cooling properly, determine
if the refrigerant system is fully charged with R-134a
(Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/
PLUMBING - FRONT/REFRIGERANT - DIAGNO-
SIS AND TESTING - REFRIGERANT SYSTEM
CHARGE LEVEL). If while performing this test A/C
liquid line pressure is less than 345 kPa (50 psi) pro-
ceed to System Empty procedure. If liquid line pres-
sure is greater than 345 kPa (50 psi) proceed to
System Low procedure. If the refrigerant system is
empty or low in refrigerant charge, a leak at any line
fitting or component seal is likely. A review of the fit-
tings, lines and components for oily residue is an
indication of the leak location.
To detect a leak in the refrigerant system, perform
one of the following procedures as indicated by the
results of the refrigerant system charge level test.
SYSTEM EMPTY
(1) Evacuate the refrigerant system to the lowest
degree of vacuum possible (approx. 28 in Hg.) (Refer
to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMB-
ING - FRONT/REFRIGERANT - STANDARD PRO-
CEDURE - REFRIGERANT SYSTEM EVACUATE).
Determine if the system holds a vacuum for 15 min-
utes. If vacuum is held, a leak is probably not
24 - 66 PLUMBING - FRONTRS
PLUMBING - FRONT (Continued)
Page 2462 of 2585

present. If system will not maintain vacuum level,
proceed with this procedure.
(2) Prepare a 0.284 Kg. (10 oz.) refrigerant charge
to be injected into the system.
(3) Connect and dispense 0.284 Kg. (10 oz.) of
refrigerant into the evacuated refrigerant system
(Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/
PLUMBING - FRONT/REFRIGERANT - STANDARD
PROCEDURE - REFRIGERANT SYSTEM
CHARGE).
(4) Proceed to the SYSTEM LOW procedures.
SYSTEM LOW
(1) Position the vehicle in a wind-free work area.
This will aid in detecting small leaks.
(2) Bring the refrigerant system up to operating
temperature and pressure. This is done by allowing
the engine to run for five minutes with the system
set to the following:
²Transaxle in Park
²Engine idling
²Rear A/C Off (if equipped)
²A/C controls set to 100 percent outside air
²Blower switch in the highest speed position
²A/C in the ON position
²Front windows open
CAUTION: A leak detector designed for R-12 refrig-
erant (only) will not detect leaks in a R-134a refrig-
erant system.
(3) Shut off the vehicle and wait 2 to 7 minutes.
Then use an Electronic Leak Detector that is
designed to detect R-134a type refrigerant and search
for leaks. Fittings, lines, or components that appear
to be oily usually indicates a refrigerant leak. To
inspect the evaporator core for leaks, insert the leak
detector probe into the drain tube opening or a heat
duct. A R-134a dye is available to aid in leak detec-
tion, use only DaimlerChrysler approved refrigerant
dye.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - SYSTEM CHARGE
LEVEL TEST - GASOLINE ENGINES
WARNING: REFER TO THE APPLICABLE WARN-
INGS AND CAUTIONS FOR THIS SYSTEM BEFORE
PERFORMING THE FOLLOWING OPERATION (Refer
to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING -
FRONT - WARNING - A/C PLUMBING) and (Refer to
24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING -
FRONT - CAUTION - A/C PLUMBING).
NOTE: The proper amount of R-134a refrigerant for
the refrigerant system in this model is:²Single or Dual Zone (Front Unit Only) - 0.96
kilograms (2.13 pounds or 34 ounces)
²Three Zone (Front and Rear Units) - 1.31 kilo-
grams (2.88 pounds or 46 ounces)
The procedure that follows should be used to deter-
mine whether the refrigerant system contains the
proper refrigerant charge. Symptoms of an improper
refrigerant charge (low) include: poor air conditioner
performance, fog emitted from the air conditioner
outlets, a hissing sound from the expansion valve/
evaporator area. There are two different methods
with which the refrigerant charge level may be
tested:
1. Using a DRBIIItscan tool, a thermocouple and
the Charge Determination Chart (Fig. 1). Refer to
the appropriate diagnostic information.
2. Using a manifold gauge set, a thermocouple and
the Charge Determination Chart (Fig. 1).
A temperature probe is required to measure liquid
line temperature. The clamp-on, Type K thermocou-
ple temperature probe used in this procedure is
available through the DaimlerChrysler Professional
Service Equipment (PSE) program. This probe (PSE
#66-324-0014 or #80PK-1A) is compatible with tem-
perature-measuring instruments that accept Type K
thermocouples, and have a miniature connector
input. Other temperature probes are available
through aftermarket sources; however, all references
in this procedure will reflect the use of the probe
made available through the PSE program.
In order to use the temperature probe, a digital
thermometer will also be required. If a digital ther-
mometer is not available, an adapter is available
through the PSE program that will convert any stan-
dard digital multimeter into a digital thermometer.
This adapter is designed to accept any standard Type
K thermocouple. If a digital multimeter is not avail-
able, this tool is also available through the PSE pro-
gram.
NOTE: When connecting the service equipment
couplings to the refrigerant system service ports,
be certain that the valve of each coupling is fully
closed. This will reduce the amount of effort
required to make the connection.
(1) Remove the caps from the refrigerant system
service ports and attach a manifold gauge set or a
R-134a refrigerant recovery/recycling/charging sta-
tion that meets SAE Standard J2210 to the refriger-
ant system.
(2) Attach a clamp-on thermocouple to the liquid
line. The thermocouple must be placed as close to the
A/C pressure transducer as possible to accurately
observe liquid line temperature.
(3) Bring the refrigerant system up to operating
temperature and pressure. This is done by allowing
RSPLUMBING - FRONT24-67
PLUMBING - FRONT (Continued)