oil pressure DAEWOO NUBIRA 2004 Service Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DAEWOO, Model Year: 2004, Model line: NUBIRA, Model: DAEWOO NUBIRA 2004Pages: 2643, PDF Size: 80.54 MB
Page 358 of 2643
1F – 112IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
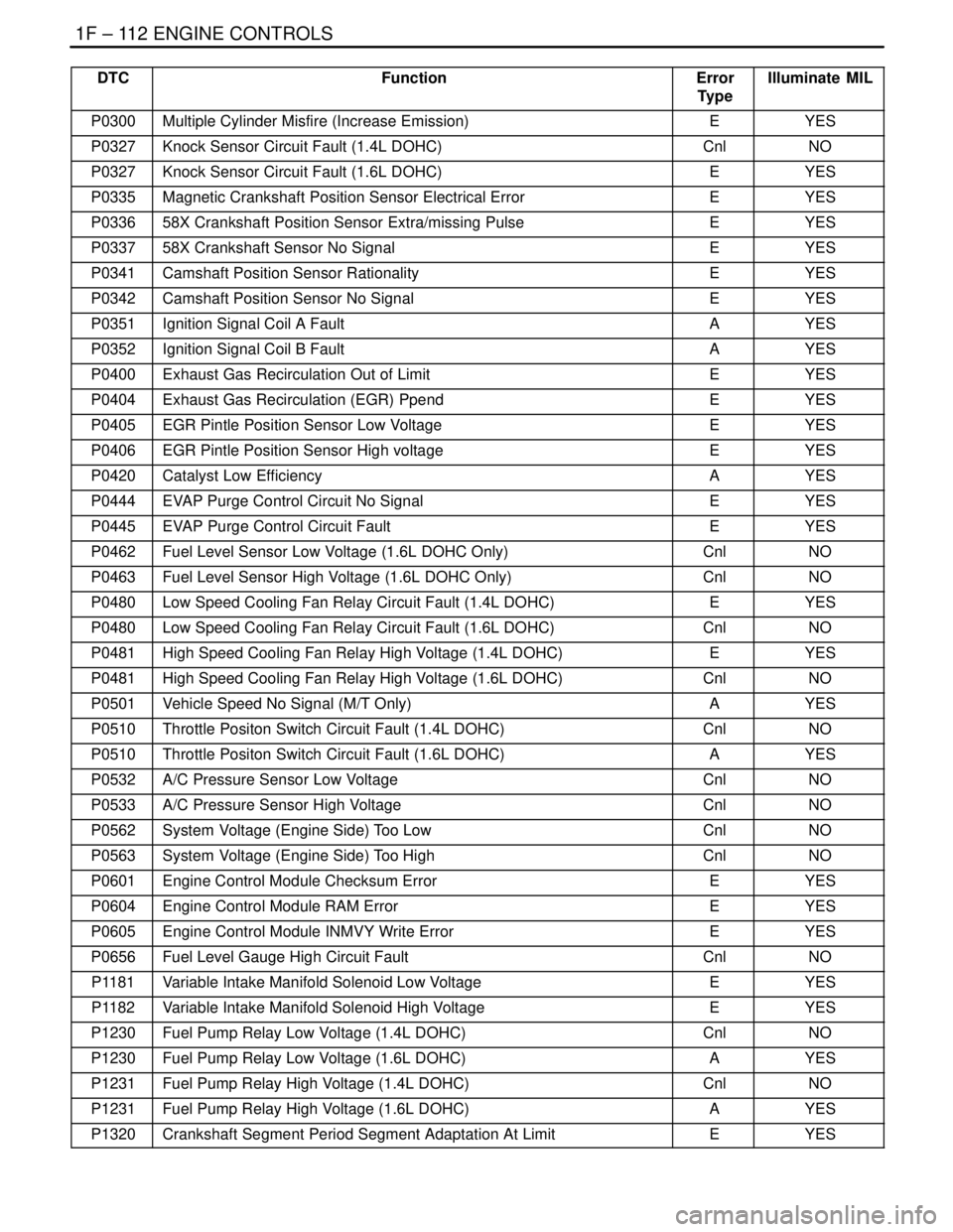
DTCIlluminate MIL Error
Type Function
P0300Multiple Cylinder Misfire (Increase Emission)EYES
P0327Knock Sensor Circuit Fault (1.4L DOHC)CnlNO
P0327Knock Sensor Circuit Fault (1.6L DOHC)EYES
P0335Magnetic Crankshaft Position Sensor Electrical ErrorEYES
P033658X Crankshaft Position Sensor Extra/missing PulseEYES
P033758X Crankshaft Sensor No SignalEYES
P0341Camshaft Position Sensor RationalityEYES
P0342Camshaft Position Sensor No SignalEYES
P0351Ignition Signal Coil A FaultAYES
P0352Ignition Signal Coil B FaultAYES
P0400Exhaust Gas Recirculation Out of LimitEYES
P0404Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) PpendEYES
P0405EGR Pintle Position Sensor Low VoltageEYES
P0406EGR Pintle Position Sensor High voltageEYES
P0420Catalyst Low EfficiencyAYES
P0444EVAP Purge Control Circuit No SignalEYES
P0445EVAP Purge Control Circuit FaultEYES
P0462Fuel Level Sensor Low Voltage (1.6L DOHC Only)CnlNO
P0463Fuel Level Sensor High Voltage (1.6L DOHC Only)CnlNO
P0480Low Speed Cooling Fan Relay Circuit Fault (1.4L DOHC)EYES
P0480Low Speed Cooling Fan Relay Circuit Fault (1.6L DOHC)CnlNO
P0481High Speed Cooling Fan Relay High Voltage (1.4L DOHC)EYES
P0481High Speed Cooling Fan Relay High Voltage (1.6L DOHC)CnlNO
P0501Vehicle Speed No Signal (M/T Only)AYES
P0510Throttle Positon Switch Circuit Fault (1.4L DOHC)CnlNO
P0510Throttle Positon Switch Circuit Fault (1.6L DOHC)AYES
P0532A/C Pressure Sensor Low VoltageCnlNO
P0533A/C Pressure Sensor High VoltageCnlNO
P0562System Voltage (Engine Side) Too LowCnlNO
P0563System Voltage (Engine Side) Too HighCnlNO
P0601Engine Control Module Checksum ErrorEYES
P0604Engine Control Module RAM ErrorEYES
P0605Engine Control Module INMVY Write ErrorEYES
P0656Fuel Level Gauge High Circuit FaultCnlNO
P1181Variable Intake Manifold Solenoid Low VoltageEYES
P1182Variable Intake Manifold Solenoid High VoltageEYES
P1230Fuel Pump Relay Low Voltage (1.4L DOHC)CnlNO
P1230Fuel Pump Relay Low Voltage (1.6L DOHC)AYES
P1231Fuel Pump Relay High Voltage (1.4L DOHC)CnlNO
P1231Fuel Pump Relay High Voltage (1.6L DOHC)AYES
P1320Crankshaft Segment Period Segment Adaptation At LimitEYES
Page 405 of 2643
ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 159
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
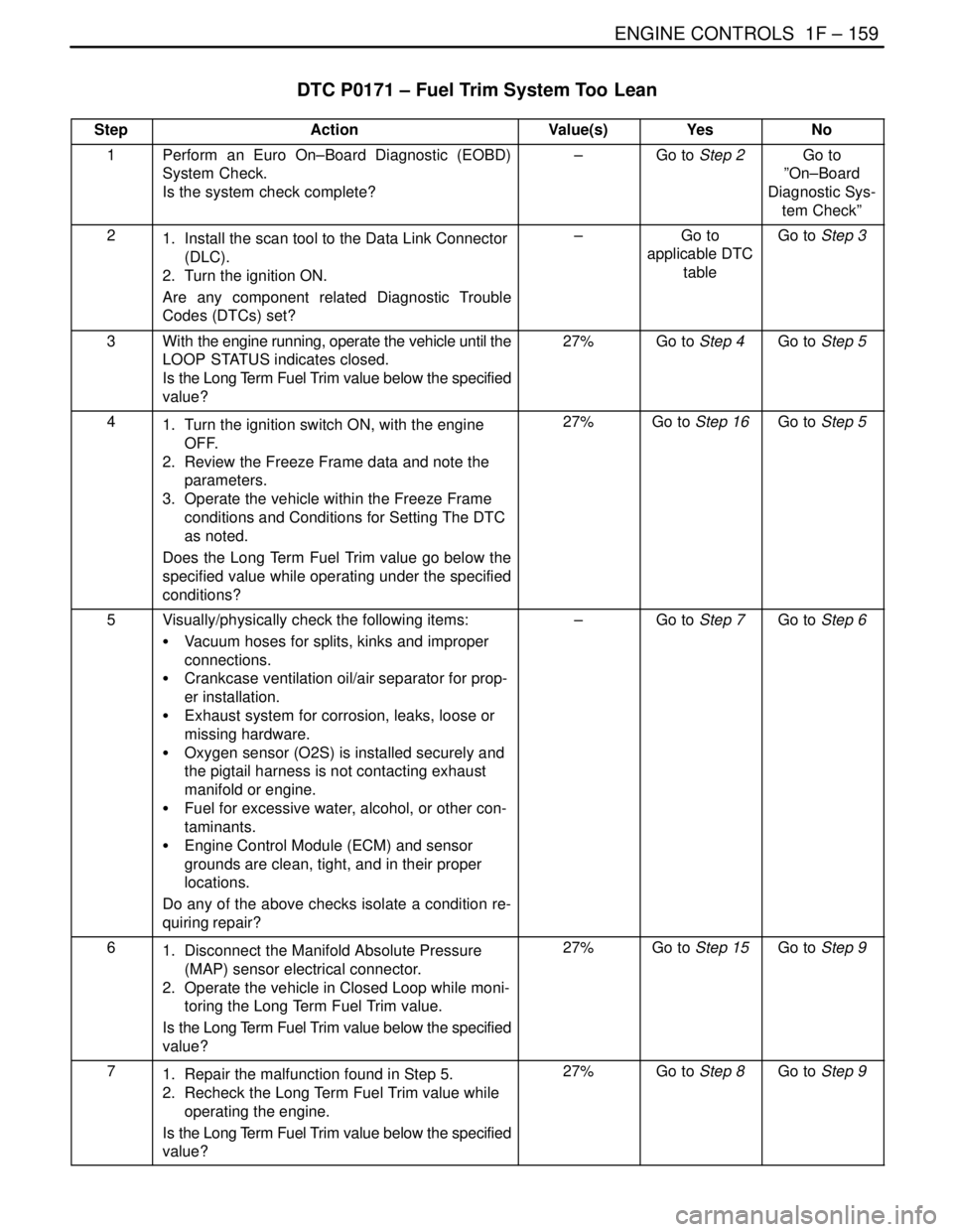
DTC P0171 – Fuel Trim System Too Lean
StepActionValue(s)YesNo
1Perform an Euro On–Board Diagnostic (EOBD)
System Check.
Is the system check complete?–Go to Step 2Go to
”On–Board
Diagnostic Sys-
tem Check”
21. Install the scan tool to the Data Link Connector
(DLC).
2. Turn the ignition ON.
Are any component related Diagnostic Trouble
Codes (DTCs) set?–Go to
applicable DTC
tableGo to Step 3
3With the engine running, operate the vehicle until the
LOOP STATUS indicates closed.
Is the Long Term Fuel Trim value below the specified
value?27%Go to Step 4Go to Step 5
41. Turn the ignition switch ON, with the engine
OFF.
2. Review the Freeze Frame data and note the
parameters.
3. Operate the vehicle within the Freeze Frame
conditions and Conditions for Setting The DTC
as noted.
Does the Long Term Fuel Trim value go below the
specified value while operating under the specified
conditions?27%Go to Step 16Go to Step 5
5Visually/physically check the following items:
S Vacuum hoses for splits, kinks and improper
connections.
S Crankcase ventilation oil/air separator for prop-
er installation.
S Exhaust system for corrosion, leaks, loose or
missing hardware.
S Oxygen sensor (O2S) is installed securely and
the pigtail harness is not contacting exhaust
manifold or engine.
S Fuel for excessive water, alcohol, or other con-
taminants.
S Engine Control Module (ECM) and sensor
grounds are clean, tight, and in their proper
locations.
Do any of the above checks isolate a condition re-
quiring repair?–Go to Step 7Go to Step 6
61. Disconnect the Manifold Absolute Pressure
(MAP) sensor electrical connector.
2. Operate the vehicle in Closed Loop while moni-
toring the Long Term Fuel Trim value.
Is the Long Term Fuel Trim value below the specified
value?27%Go to Step 15Go to Step 9
71. Repair the malfunction found in Step 5.
2. Recheck the Long Term Fuel Trim value while
operating the engine.
Is the Long Term Fuel Trim value below the specified
value?27%Go to Step 8Go to Step 9
Page 747 of 2643

ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 501
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0506
IDLE SPEED RPM LOWER THAN DESIRED IDLE SPEED
Circuit Description
The Engine Control Module (ECM) controls the air enter-
ing into the engine with an Idle Air Control (IAC) Valve. To
increase the idle rpm, the ECM commands the pintle in-
side the IAC valve away from the throttle body seat. This
allows more air to bypass through the throttle blade. To de-
crease the rpm the ECM commands the pintle towards the
throttle body seat. This reduces the amount of air bypass-
ing the throttle blade. A scan tool will read the IAC valve
pintle position in counts. The higher the counts, the more
air that is allowed to bypass the throttle blade. This Diag-
nostic Trouble Code (DTC) determines if a low idle condi-
tion exists as defined as 100 rpm below the desired idle
rpm.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
S No intrusive tests are active.
S DTC(s) P0106, P0107, P0108, P0112, P0113,
P0117, P0118, P0122, P0123, P0131, P0132,
P0133, P0135, P0141, P1133, P1134, P0171,
P01167, P1171, P0172, P0201, P0202, P0203,
P0204, P0300, P0336, P0337, P0341, P0342,
P0351, P0352, P0402, P0404, P1404, P0405,
P0406, P0443, and P0502 are not set.
S Engine is running more than 60 seconds.
S Barometric Pressure (BARO) is greater than 72
kPa (10.4 psi).
S Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) is greater than
60°C (140°F).
S Ignition voltage is between 11 and 16 volts.
S Manifold Absolute Pressure is less than 60 kPa (8.7
psi).
S IAC valve is controlled fully opened.
S All of the above must be met for greater than 5 sec-
onds.Action Taken When the DTC Sets
S The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) will illuminate
after three consecutive ignition cycle with a fail.
S The ECM will record operating conditions at the
time the diagnostic fails. This information will be
stored in the Freeze Frame and Failure Records
buffers.
S A history DTC is stored.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
S The MIL will turn off after four consecutive ignition
cycles in which the diagnostic runs without a fault.
S A history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm–
up cycles without a fault.
S DTC(s) can be cleared by using the scan tool.
S Disconnecting the ECM battery feed for more than
10 seconds.
Diagnostic Aids
Inspect the IAC valve electrical connection for proper mat-
ing.
Inspect the wiring harness for damage.
Inspect the throttle stop screw for signs of tampering.
Inspect the throttle linkage for signs of binding or exces-
sive wear.
A slow or unstable idle may be caused by one of the follow-
ing conditions:
S Fuel system too rich or too lean.
S Foreign material in the throttle body bore or in the
air induction system.
S A leaking or restricted intake manifold.
S Excessive engine overloading. Check for seized
pulleys, pumps, or motors on the accessory drive.
S Overweight engine oil.
Page 848 of 2643

1F – 602IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
9. Connect the PCV hose to the valve cover.
10. Connect the breather hose to the valve cover.
11. Connect the IAT sensor connector.
12. Connect the negative battery cable.
13. Perform a leak check of the fuel rail and fuel injec-
tors.
ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE
SENSOR (1.4L/1.6L DOHC)
Removal Procedure
1. Relieve the coolant system pressure.
2. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
3. Disconnect the engine coolant temperature (ECT)
sensor connector.
Notice : Take care when handling the engine coolant tem-
perature sensor. Damage to the sensor will affect the prop-
er operation of the fuel injection system.
4. Remove the ECT sensor
Installation Procedure
1. Install the engine coolant temperature (ECT) sen-
sor.
Tighten
Tighten the engine coolant temperature (ECT) sensor
to 17.5 NSm (13 lb–ft).
2. Connect the ECT sensor connector.
3. Connect the negative battery cable.
ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE
SENSOR (1.8L DOHC)
Removal Procedure
1. Relieve the coolant system pressure.
2. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
3. Disconnect the engine coolant temperature (ECT)
sensor connector.
Notice : Take care when handling the engine coolant tem-
perature sensor. Damage to the sensor will affect the prop-
er operation of the fuel injection system.
4. Remove the ECT sensor from the electronic ignition
(EI) system ignition coil adapter.
Page 856 of 2643
1F – 610IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
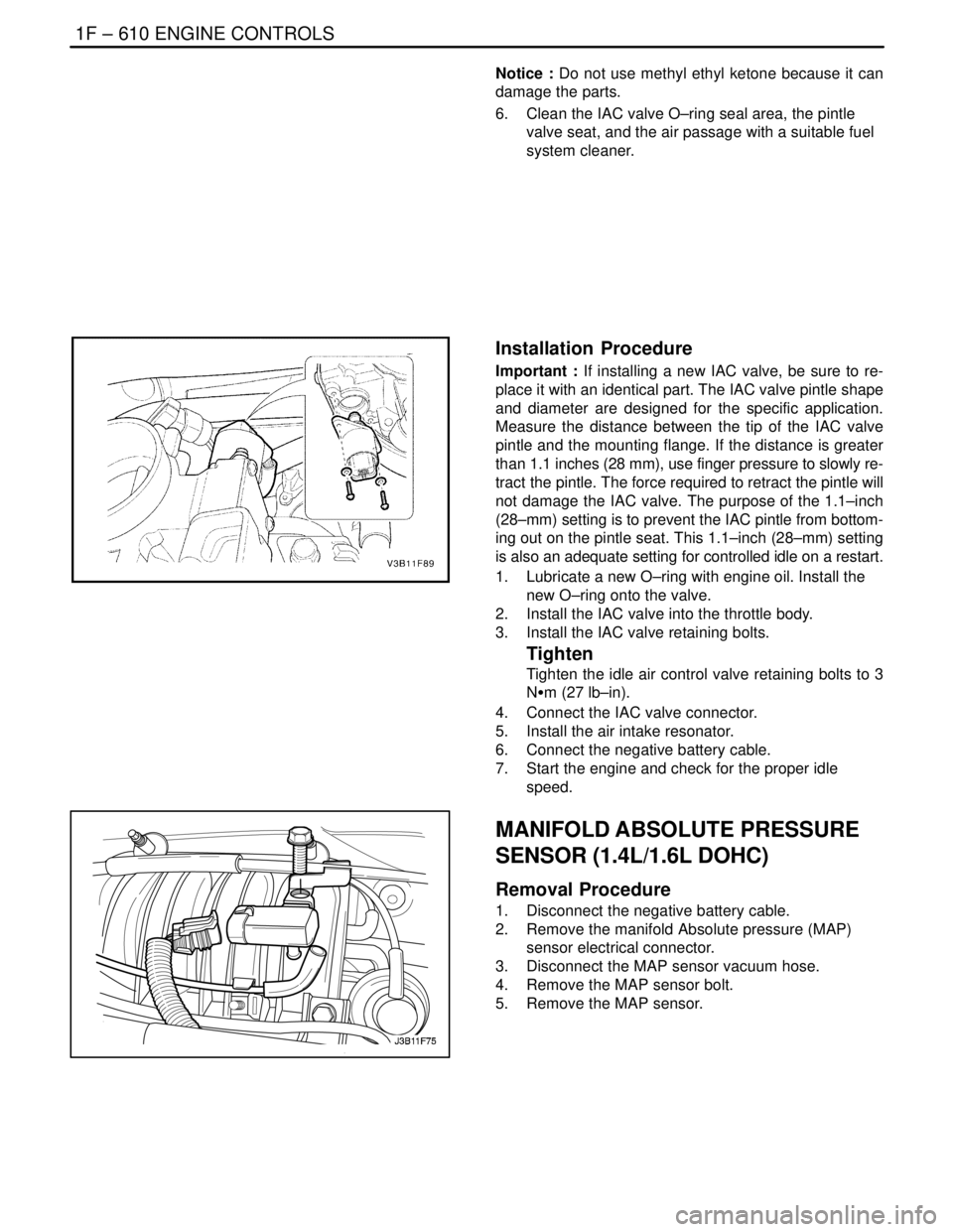
Notice : Do not use methyl ethyl ketone because it can
damage the parts.
6. Clean the IAC valve O–ring seal area, the pintle
valve seat, and the air passage with a suitable fuel
system cleaner.
Installation Procedure
Important : If installing a new IAC valve, be sure to re-
place it with an identical part. The IAC valve pintle shape
and diameter are designed for the specific application.
Measure the distance between the tip of the IAC valve
pintle and the mounting flange. If the distance is greater
than 1.1 inches (28 mm), use finger pressure to slowly re-
tract the pintle. The force required to retract the pintle will
not damage the IAC valve. The purpose of the 1.1–inch
(28–mm) setting is to prevent the IAC pintle from bottom-
ing out on the pintle seat. This 1.1–inch (28–mm) setting
is also an adequate setting for controlled idle on a restart.
1. Lubricate a new O–ring with engine oil. Install the
new O–ring onto the valve.
2. Install the IAC valve into the throttle body.
3. Install the IAC valve retaining bolts.
Tighten
Tighten the idle air control valve retaining bolts to 3
NSm (27 lb–in).
4. Connect the IAC valve connector.
5. Install the air intake resonator.
6. Connect the negative battery cable.
7. Start the engine and check for the proper idle
speed.
MANIFOLD ABSOLUTE PRESSURE
SENSOR (1.4L/1.6L DOHC)
Removal Procedure
1. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
2. Remove the manifold Absolute pressure (MAP)
sensor electrical connector.
3. Disconnect the MAP sensor vacuum hose.
4. Remove the MAP sensor bolt.
5. Remove the MAP sensor.
Page 869 of 2643

ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 623
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
AND SYSTEM OPERATION
IGNITION SYSTEM OPERATION
This ignition system does not use a conventional distribu-
tor and coil. It uses a crankshaft position sensor input to
the engine control module (ECM). The ECM then deter-
mines Electronic Spark Timing (EST) and triggers the di-
rect ignition system ignition coil.
This type of distributorless ignition system uses a ”waste
spark” method of spark distribution. Each cylinder is
paired with the cylinder that is opposite it (1–4 or 2–3). The
spark occurs simultaneously in the cylinder coming up on
the compression stroke and in the cylinder coming up on
the exhaust stroke. The cylinder on the exhaust stroke re-
quires very little of the available energy to fire the spark
plug. The remaining energy is available to the spark plug
in the cylinder on the compression stroke.
These systems use the EST signal from the ECM to con-
trol the electronic spark timing. The ECM uses the follow-
ing information:
S Engine load (manifold pressure or vacuum).
S Atmospheric (barometric) pressure.
S Engine temperature.
S Intake air temperature.
S Crankshaft position.
S Engine speed (rpm).
ELECTRONIC IGNITION SYSTEM
IGNITION COIL
The Electronic Ignition (EI) system ignition coil provides
the spark for two spark plugs simultaneously. The EI sys-
tem ignition coil is not serviceable and must be replaced
as an assembly.
CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR
This direct ignition system uses a magnetic crankshaft
position sensor. This sensor protrudes through its mount
to within approximately 0.05 inch (1.3 mm) of the crank-
shaft reluctor. The reluctor is a special wheel attached to
the crankshaft or crankshaft pulley with 58 slots machined
into it, 57 of which are equally spaced in 6 degree intervals.
The last slot is wider and serves to generate a ”sync
pulse.” As the crankshaft rotates, the slots in the reluctor
change the magnetic field of the sensor, creating an in-
duced voltage pulse. The longer pulse of the 58th slot
identifies a specific orientation of the crankshaft and al-
lows the engine control module (ECM) to determine the
crankshaft orientation at all times. The ECM uses this in-
formation to generate timed ignition and injection pulses
that it sends to the ignition coils and to the fuel injectors.
CAMAHAFT POSITION SENSOR
The Camshaft Position (CMP) sensor sends a CMP sen-
sor signal to the engine control module (ECM). The ECM
uses this signal as a ”sync pulse” to trigger the injectors in
the proper sequence. The ECM uses the CMP sensor sig-
nal to indicate the position of the #1 piston during its power
stroke. This allows the ECM to calculate true sequential
fuel injection mode of operation. If the ECM detects an in-
correct CMP sensor signal while the engine is running,
DTC P0341 will set. If the CMP sensor signal is lost while
the engine is running, the fuel injection system will shift to
a calculated sequential fuel injection mode based on the
last fuel injection pulse, and the engine will continue to run.
As long as the fault is present, the engine can be restarted.
It will run in the calculated sequential mode with a 1–in–6
chance of the injector sequence being correct.
IDLE AIR SYSTEM OPERATION
The idle air system operation is controlled by the base idle
setting of the throttle body and the Idle Air Control (IAC)
valve.
The engine control module (ECM) uses the IAC valve to
set the idle speed dependent on conditions. The ECM
uses information from various inputs, such as coolant tem-
perature, manifold vacuum, etc., for the effective control
of the idle speed.
FUEL CONTROL SYSTEM
OPERATION
The function of the fuel metering system is to deliver the
correct amount of fuel to the engine under all operating
conditions. The fuel is delivered to the engine by the indi-
vidual fuel injectors mounted into the intake manifold near
each cylinder.
The two main fuel control sensors are the Manifold Abso-
lute Pressure (MAP) sensor, the Front Heated Oxygen
Sensor (HO2S1) and the Rear Heated Oxygen Sensor
(HO2S2).
The MAP sensor measures or senses the intake manifold
vacuum. Under high fuel demands the MAP sensor reads
a low vacuum condition, such as wide open throttle. The
engine control module (ECM) uses this information to ri-
chen the mixture, thus increasing the fuel injector on–time,
to provide the correct amount of fuel. When decelerating,
the vacuum increases. This vacuum change is sensed by
the MAP sensor and read by the ECM, which then de-
creases the fuel injector on–time due to the low fuel de-
mand conditions.
HO2S Sensors
The HO2S sensor is located in the exhaust manifold. The
HO2S sensor indicates to the ECM the amount of oxygen
in the exhaust gas and the ECM changes the air/fuel ratio
to the engine by controlling the fuel injectors. The best air/
fuel ratio to minimize exhaust emissions is 14.7 to 1, which
allows the catalytic converter to operate most efficiently.
Page 1021 of 2643

HYDRAULIC BRAKES 4A – 5
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DIAGNOSIS
BRAKE SYSTEM TESTING
Brakes should be tested on a dry, clean, reasonably
smooth and level roadway. A true test of brake perfor-
mance cannot be made if the roadway is wet, greasy, or
covered with loose dirt whereby all tires do not grip the
road equally. Testing will also be adversely affected if the
roadway is crowned so as to throw the weight so roughly
that the wheels tend to bounce.
Test the brakes at different vehicle speeds with both light
and heavy pedal pressure; however, avoid locking the
brakes and sliding the tires. Locked brakes and sliding
tires do not indicate brake efficiency since heavily braked,
but turning, wheels will stop the vehicle in less distance
than locked brakes. More tire–to–road friction is present
with a heavily–braked, turning tire than with a sliding tire.
Because of the high deceleration capability, a firmer pedal
may be felt at higher deceleration levels.
There are three major external conditions that affect brake
performance:
S Tires having unequal contact and grip of the road
will cause unequal braking. Tires must be equally
inflated, and the tread pattern of the right and the
left tires must be approximately equal.
S Unequal loading of the vehicle can affect the brake
performance since the most heavily loaded wheels
require more braking power, and thus more braking
effort, than the others.
S Misalignment of the wheels, particularly conditions
of excessive camber and caster, will cause the
brakes to pull to one side.
To check for brake fluid leaks, hold constant foot pressure
on the pedal with the engine running at idle and the shift
lever in NEUTRAL. If the pedal gradually falls away with
the constant pressure, the hydraulic system may be leak-
ing. Perform a visual check to confirm any suspected
leaks.
Check the master cylinder fluid level. While a slight drop
in the reservoir level results from normal lining wear, an ab-
normally low level indicates a leak in the system. The hy-
draulic system may be leaking either internally or external-
ly. Refer to the procedure below to check the master
cylinder. Also, the system may appear to pass this test
while still having a slight leak. If the fluid level is normal,
check the vacuum booster pushrod length. If an incorrect
pushrod length is found, adjust or replace the rod.
Check the master cylinder using the following procedure:
S Check for a cracked master cylinder casting or
brake fluid leaking around the master cylinder.
Leaks are indicated only if there is at least one drop
of fluid. A damp condition is not abnormal.S Check for a binding pedal linkage and for an incor-
rect pushrod length. If both of these parts are in
satisfactory condition, disassemble the master cyl-
inder and check for an elongated or swollen primary
cylinder or piston seals. If swollen seals are found,
substandard or contaminated brake fluid should be
suspected. If contaminated brake fluid is found, all
the components should be disassembled and
cleaned, and all the rubber components should be
replaced. All of the pipes must also be flushed.
Improper brake fluid, or mineral oil or water in the fluid,
may cause the brake fluid to boil or cause deterioration of
the rubber components. If the primary piston cups in the
master cylinder are swollen, then the rubber parts have
deteriorated. This deterioration may also be evidenced by
swollen wheel cylinder piston seals on the drum brake
wheels.
If deterioration of rubber is evident, disassemble all the hy-
draulic parts and wash the parts with alcohol. Dry these
parts with compressed air before reassembly to keep alco-
hol out of the system. Replace all the rubber parts in the
system, including the hoses. Also, when working on the
brake mechanisms, check for fluid on the linings. If exces-
sive fluid is found, replace the linings.
If the master cylinder piston seals are in satisfactory condi-
tion, check for leaks or excessive heat conditions. If these
conditions are not found, drain the fluid, flush the master
cylinder with brake fluid, refill the master cylinder, and
bleed the system. Refer to ”Manual Bleeding the Brakes”
or”Pressure Bleeding the Brakes” in this section.
BRAKE HOSE INSPECTION
The hydraulic brake hoses should be inspected at least
twice a year. The brake hose assembly should be checked
for road hazard damage, cracks, chafing of the outer cov-
er, and for leaks or blisters. Inspect the hoses for proper
routing and mounting. A brake hose that rubs on a suspen-
sion component will wear and eventually fail. A light and
a mirror may be needed for an adequate inspection. If any
of the above conditions are observed on the brake hose,
adjust or replace the hose as necessary.
WARNING LAMP OPERATION
This brake system uses a BRAKE warning lamp located
in the instrument panel cluster. When the ignition switch
is in the START position, the BRAKE warning lamp should
glow and go OFF when the ignition switch returns to the
RUN position.
The following conditions will activate the BRAKE lamp:
S Parking brake applied. The light should be ON
whenever the parking brake is applied and the igni-
tion switch is ON.
S Low fluid level. A low fluid level in the master cylin-
der will turn the BRAKE lamp ON.
S EBD system is disabled. The light should be ON
when the EBD system is malfunctioning.
Page 1028 of 2643
4A – 12IHYDRAULIC BRAKES
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
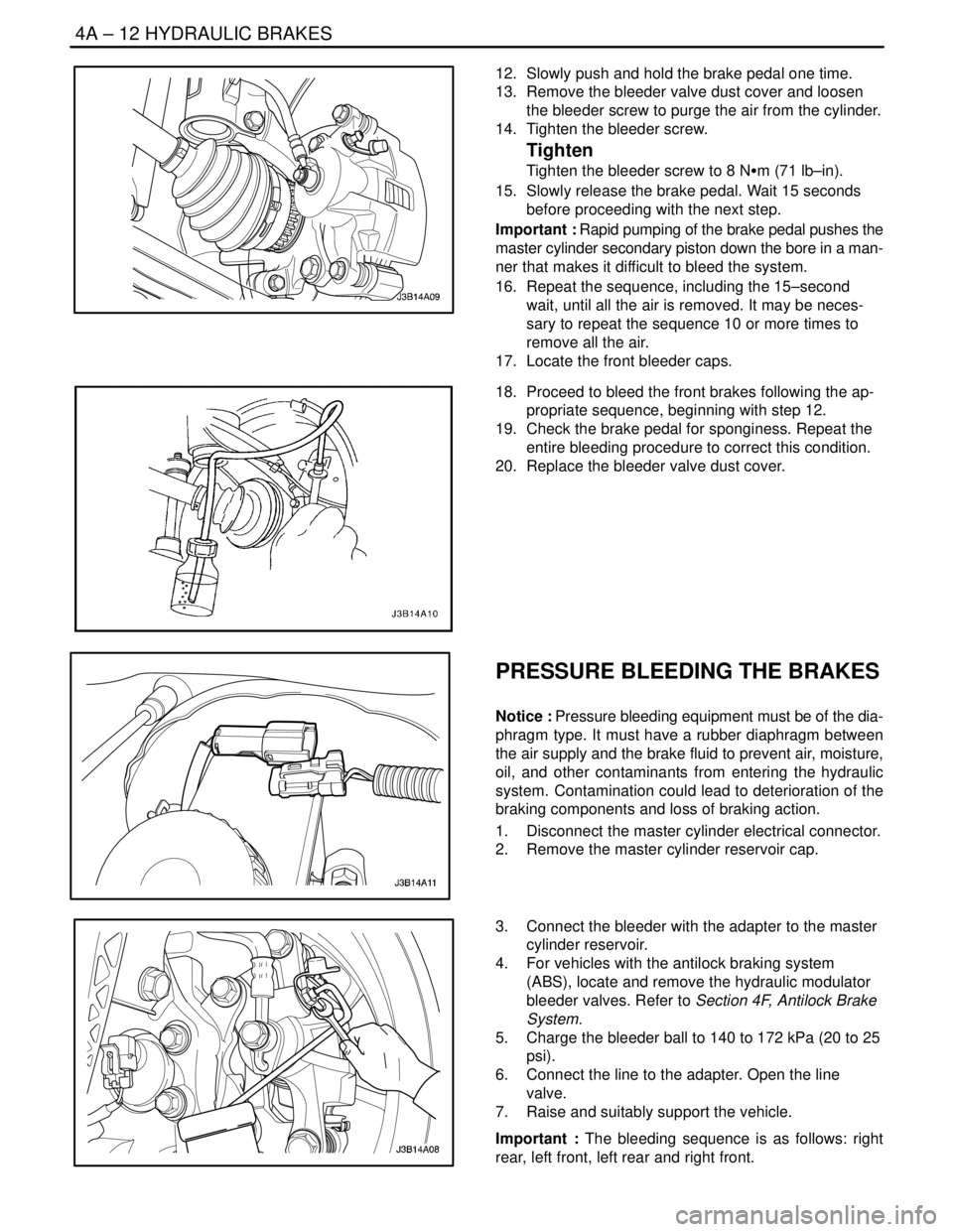
12. Slowly push and hold the brake pedal one time.
13. Remove the bleeder valve dust cover and loosen
the bleeder screw to purge the air from the cylinder.
14. Tighten the bleeder screw.
Tighten
Tighten the bleeder screw to 8 NSm (71 lb–in).
15. Slowly release the brake pedal. Wait 15 seconds
before proceeding with the next step.
Important : Rapid pumping of the brake pedal pushes the
master cylinder secondary piston down the bore in a man-
ner that makes it difficult to bleed the system.
16. Repeat the sequence, including the 15–second
wait, until all the air is removed. It may be neces-
sary to repeat the sequence 10 or more times to
remove all the air.
17. Locate the front bleeder caps.
18. Proceed to bleed the front brakes following the ap-
propriate sequence, beginning with step 12.
19. Check the brake pedal for sponginess. Repeat the
entire bleeding procedure to correct this condition.
20. Replace the bleeder valve dust cover.
PRESSURE BLEEDING THE BRAKES
Notice : Pressure bleeding equipment must be of the dia-
phragm type. It must have a rubber diaphragm between
the air supply and the brake fluid to prevent air, moisture,
oil, and other contaminants from entering the hydraulic
system. Contamination could lead to deterioration of the
braking components and loss of braking action.
1. Disconnect the master cylinder electrical connector.
2. Remove the master cylinder reservoir cap.
3. Connect the bleeder with the adapter to the master
cylinder reservoir.
4. For vehicles with the antilock braking system
(ABS), locate and remove the hydraulic modulator
bleeder valves. Refer to Section 4F, Antilock Brake
System.
5. Charge the bleeder ball to 140 to 172 kPa (20 to 25
psi).
6. Connect the line to the adapter. Open the line
valve.
7. Raise and suitably support the vehicle.
Important : The bleeding sequence is as follows: right
rear, left front, left rear and right front.
Page 1042 of 2643

MASTER CYLINDER 4B – 9
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
AND SYSTEM OPERATION
MASTER CYLINDER
The master cylinder is designed for use in a diagonal–split
system. One front and one diagonally opposite rear brake
are served by the primary piston. The opposite front and
rear brakes are served by the secondary piston. The mas-
ter cylinder incorporates the functions of the standard dual
master cylinder, plus a low fluid level indicator and the pro-
portioning valves in the non–antilock braking system. The
proportioning valves limit the outlet pressure to the rear
brakes after a predetermined master cylinder pressure
has been reached.
Important :
S Replace all the components included in the repair
kits used to service this master cylinder.S Lubricate rubber parts with clean brake fluid to ease
assembly.
S Do not use lubricated shop air on brake parts, as
this may damage rubber components.
S If any hydraulic component is removed or discon-
nected, it may be necessary to bleed all or part of
the brake system.
S The torque values specified are for dry, unlubri-
cated fasteners.
S Perform all service operations on a clean bench,
free from all traces of mineral oil.
FLUID LEVEL SENSOR
The master cylinder is equipped with a fluid level sensor.
This sensor will activate the BRAKE light if a low fluid level
condition is detected. Once the fluid level is corrected, the
BRAKE light will go out.
Page 1057 of 2643

FRONT DISC BRAKES 4D – 9
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
AND SYSTEM OPERATION
DISC BRAKE CALIPER ASSEMBLY
This caliper has a single bore and is mounted to the steer-
ing knuckle with two mounting bolts. Hydraulic pressure,
created by applying the brake pedal, is converted by the
caliper to a stopping force. This force acts equally against
the piston and the bottom of the caliper bore to move the
piston outward and to slide the caliper inward, resulting in
a clamping action on the rotor. This clamping action forces
the linings against the rotor, creating friction to stop the ve-
hicle.Important :
S Replace all components included in the repair kits
used to service this caliper.
S Lubricate the rubber parts with clean brake fluid to
ease assembly.
S Do not use lubricated shop air on brake parts, as
damage to the rubber components may result.
S If any hydraulic component is removed or discon-
nected, it may be necessary to bleed all or part of
the brake system.
S Replace the pads in axle sets only.
S The torque values specified are for dry, unlubri-
cated fasteners.
S Perform the service operations on a clean bench,
free from all mineral oil materials.