oil type FIAT PUNTO 1995 176 / 1.G User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: FIAT, Model Year: 1995, Model line: PUNTO, Model: FIAT PUNTO 1995 176 / 1.GPages: 225, PDF Size: 18.54 MB
Page 61 of 225

2B»1
Chapter 2 Part B:
DOHC (16-valve) petrol
engine in-car repair procedures
Contents
Auxiliary drlvebelts - removal and refitting See Chapter 1A Camshaft oil seal - renewal 6 Camshafts and cam followers - removal, inspection and refitting .. 9 Crankshaft oil seals • renewal 7 Cylinder compression test 3 Cylinder head - dismantling and overhaul See Chapter 2D Cylinder head • removal and refitting 10 Cylinder head extension • removal and refitting 8 Engine assembly/Valve timing holes - general information and usage 2
Engine mountings - inspection and renewal 12 Engine oil and filter - renewal See Chapter 1A Engine oil level - check See Weekly checks Flywheel - removal, Inspection and refitting 11 General Information 1 Oil pump and pick-up tube - removal, inspection and refitting 14 Sump - removal and refitting 13 Timing belt and covers - removal and refitting 4 Timing belt tensioner and sprockets • removal and refitting 5
Degrees of difficulty
Easy,
sitable
for
J; Fairly
easy,
suitable Fairtydifflcutt, ^
Difficult,
aitabtefcr Very
difficult,
^ nwice
wim
(ttls for beginner with £
suitable
for competent KYmechanic ^ experienced DIY > suitable
for
expert DIY« experience
some
experience £
suitable
for competent KYmechanic ^ mechanic > or professional ^
Specifications
General Engine code* 176.09.000 •Note: See Vehicle Identification for the location of code marking on the engine. Bore 70.8 mm Stroke 78.86 mm Capacity 1242 cc Compression ratio 10.2:1 Firing order 1-3-4-2 No
1
cylinder location Timing belt end of engine Timing belt tension See text
Camshaft Orlve Toothed belt
No
of bearings 3 Camshaft bearing journal diameters: Ho
1
bearing 35.000 to 35.015 mm
Mo
2 bearing 48.000 to 48.015 mm No 3 bearing 49.000 to 49.015 mm Camshaft bearing Journal running clearance 0.030 to 0.070 mm Camshaft endfloat 0.15 to 0.34 mm
Cylinder head extension Camshaft bearing diamelers: No
1
bearing 35.045 to 35.070 mm No 2 bearing 48,045 to 48.070 mm No 3 bearing 49.045 to 49.070 mm
Cam
follower (tappet) type Hydraulic
Cam
follower (tappet) diameter 28.353 to 28.370 mm
Cam
follower (tappet) bore diameter in cylinder head extension 28.400 to 28.421 mm
Cam
follower (tappet) running clearance 0.046 to
0.051
mm
Page 62 of 225

2A*10 SOHC (8-valve) petrol engine in-car repair procedures
Lubrication system Oil pump type By-rotor driven from front of crankshaft Outer rotor-io-houslng clearance 0.100 to 0.210 mm Axial clearance 0.025 to 0.070 mm
Torque wrench settings Nm itrf ft Camshaft driven gears 120 89 Camshaft sprocket 120 89 Crankshaft sprocket centre bolt: Stage
1
20 15 Stage 2 Angle-tighten a further 90® Cylinder head: Stage
1
30 22 Stage 2 Angle-tighten a further 90" Stage 3 Angle-tighten a further 90° Cylinder head extension to cylinder head 15 11 Engine mounting bolt: M10
x
1.25 59 44 M8 25 18 Engine mounting nut (MlOx 1.25) 60 44 Flywheel 44 32 Timing belt tensioner 25 18 Sump 10 7
1 General information
Using this Chapter Chapter 2 is divided into four Parts; A, B. C and O. Repair operations that can be carried out with the engine hi the vehicle are described in Part A. SOHC (8-valve) petrol engines. Part B, DOHC (16-valve) petrol engines and Pari C, dlesei engines. Part D covers the removal of the engine/transmission as a unit, and describes the engine dismantling and overhaul procedures. In Parts A, B and C, the assumption Is made that the engine is Installed In the vehicle, with all ancillaries connected. If the engine has been removed for overhaul, the preliminary dismantling information which precedes each operation may be ignored.
Engine description Throughout this Chapter, engines are identified by their capacities. A listing of all engines covered, together with their code letters, Is given in the Specifications. The engine covered in this Part of Chapter 2 is a water-cooled, double overhead camshaft, in-line four-cylinder unit, with cast iron cylinder block and aluminium-alloy cylinder head. The unit is mounted transversely at the front of the vehicle, with the transmission bolted to the left-hand side of the engine. The cylinder head houses the eight inlet and eight exhaust valves, which are closed by single coil springs, and which run in guides pressed Into the cylinder head. The two camshafts are housed in 8 cylinder head extension which is bolted to the top of the cylinder head. The exhaust camshaft is driven by a toothed timing belt and In turn drives the inlet camshaft via a pair of gears located at the left-hand end of the cylinder head extension.
The camshafts actuate the valves directly via self-adjusting hydraulic cam followers mounted in the cylinder head extension. The crankshaft is supported by five main bearings, and endfioat is controlled by a thrust bearing fitted to (he upper section of the centre main bearing. Engine coolanl is circulated by a pump, driven by the timing belt. For details of the cooling system, refer to Chapter 3. Lubricant is circulated under pressure by a pump, driven from the front of the crankshaft. Oil is drawn from Ihe sump through a strainer, and then forced through an externally-mounted, replaceable screw-on filter. From there, It is distributed to the cylinder head and cylinder head extension, where it lubricates the camshaft journals and cam followers, and also to the crankcase, where it lubricates the main bearings, connecting rod big and small-ends. gudgeon pins and cylinder bores. Oil Jets are fitted to the base of each cylinder bore - these spray oil onto the underside of the pistons, to improve cooling.
Repair operations possible with the engine in the car The following work can be carried out with the engine in the car: a) Auxiliary drivebett - removal and refitting (refer to Chapter 1A) b) Oil pump and pick-up tube assembly -removal, Inspection and refitting c) Timing belt and covers • removal and refitting d) Timing belt tensioner and sprockets -removal and refitting e) Cylinder head - removal and refitting' f) Cylinder hoad extension - removal and refitting g) Camshaft and cam followers - removal and refitting h) Camshaft oil seal - renewal i) Crankshaft oil seals • renewal
f) Flywheel - removal, inspection and
refitting
k) Engine mountings - Inspection and
renews'
f) Sump • removal and refitting 'Cylinder head dismantling procedures are detailed In Chapter 2D. Note 1: It is possible to remove the
pistons
and connecting rods (after removing (to cylinder head and sump) without removing
tt*»
engine. However, this Is not recommended. Work of this nature is more easily and thoroughly completed with the engine on fix bench, as described in Chapter 20. Note
2x
Many of the procedures in this Ctopfer entail the use of numerous special tools. Whet possible, suitable alternatives are descnbei with details of their fabrication. Before starring any operations on the engine, read through
tto
entire procedure first to familiarise yourself
wft
the work involved, tools to be obtained mi new parts that may be necessary.
2 Engine assembly/ valve timing holes -genera! information
and
usage
Note: Do not attempt to rotate the angint whilst the camshafts are locked In position,
il
the engine is to be left in this state foratofi$ period of time. It Is a good idea to plect suitable warning notices inside the vehicle, and in the engine compartment. This wfl reduce the possibility of the engine being accidentally cranked on the starter motor, which is likely to cause damage with the locking tools In place. 1 To accurately set the valve timing for ell operations requiring removal and refitting of
the
timing belt, liming holes are drilled in ihe camshafts and cylinder head extension. Ihe holes are used In conjunction with camshaft locking tools and crankshaft positioning
rods w
lock the camshafts when all the pistons me positioned at the mid-point of their stroke. Ths
Page 64 of 225

2B*4 DOHC (16-valve) petrol engine in-car repair procedures
4.8 Undo three bolts and romove tho crankshaft pulley from the sprocket
Crankshaft setting toot fabrication 7 To make Ihe crankshafl setting tools, four old spark plugs will be required, together with four lengths of dowel rod. The length of each dowel rod is not critical, bul It must be long enough to protrude about 100 mm above the top of the cylinder head extension when resting on top of a piston located half way down its bore. What is critical, however, is that all four do wo I rods must be exactly the same length. 8 Break off the ceramic upper section of each plug and remove the centre electrode and earth tip. The easiest way to do this is to mount each spark plug in a vice (attar removing the ceramic uppor plug section) and drill a hole down through ihe centre of the plug. The diameter of Ihe drill bit should be the same as Ihe diameter of Ihe dowol rod to be used. When finished you should have four spark plug bodies and four equal length dowel rods which will slide through the centre of the spark plugs.
3 Cylinder compression test
1 When engine performance is down, or it misfiring occurs which cannot be attnbuted to the Ignition or fuel systems, a compression test can provide diagnostic clues as to the engine's condition. If the lest is performed regularly, it can give warning of trouble bofore any other symptoms become apparent.
4.10 Undo the upper timing cover upper retaining bolt, and the rear retaining boll
4.9 Undo the retaining bolt in the centre of the lower timing cover
2 The engine must be fully warmed-up to normal operxrtrfjg temperature, the battery must be fully charged, and all the spark plugs muse be removed (Chapter 1A>. The aid of an assistant wilt also be required. 3 Disable the ignition system by discon-necting the LT wiring plugs to the Ignition coils. 4 Fit a compression tester to the No t cylinder spark plug hole • the type of tester which screws into the plug thread is to be preferred. 5 Have the assistant hold the throttle wide open, and crank the engine on the starter motor; after one or two revolutions, the compression pressure should build up to a maximum figure, and then stabilise. Record the h.ghest reading obtained 6 Repeat the test on the remaining cylinders, recording Ihe pressure in each. 7 All cylinders should produce very similar pressures; any excessive difference indicates Ihe existence of a fault. Note that the compression should build up quickly in a healthy engine; low compression on (he first stroke, followed by gradually increasing pressure on successive strokes, indicates worn piston rings. A low compression reading on the first stroke, which does not build up during successive strokes, indicates leaking valves or a blown head gasket (a cracked head could also be tho cause). 6 If the pressure in any cylinder is very low, carry out the following test to isolate the cause. Introduce a teaspoonful of dean oil into that cylinder through its spark plug hole and repeal the lest. 9 If the addition of oil temporarily improves the compression pressure, this indicates that bore or piston wear is responsible for the pressure loss. No improvement suggests that leaking or burnt valves, or a blown head gasket, may be to blame. 10 A low reading from two adjacent cylinders is almost certainly due to the head gasket having blown between Ihem; the presence of coolant in the engine oil will confirm this. 11 If one cylinder is about 20 percent lower than the others and the engine has a slightly rough idle, a worn camshaft lobe could be the cause. 12 On completion of the test, refit the spark plugs and reconnect the ignition LT wiring plug.
4 Timing belt and covers -removal and refitting §
General information 1 The luncUon of the timing belt Is to drive the camshafts and coolant pump. Should the bell slip or creak in service, the valve timing will be disturbed and piston-to-valve contact wiu occur, resulting in serious engine damage. 2 The timing belt should be renewed at the specified Intervals (see Chapter 1A), or earlier If It is contaminated with oil, or if it is at all noisy In operation (a scraping noise due to uneven wear}. 3 If the timing belt is being removed, it is
a
wise precaution to check the condition of the coolam pump at the same time (oheck for signs of coolant leakage). This may avoid the need to remove the timing belt again at a later stage, should the coolant pump fail. 4 Before carrying out this procedure, it will be necessary to obtain or fabricate suitable camshaft locking tools and piston positioning tools as described in Section 2. The procedures contained In this Section depict the use of the home-made alternative tools described in Section 2. which were fabricated In the Haynes workshop. If the manufacturers tools are being used instead, the procedures are virtually identical. Oo not attempt to remove the timing bell unless the special totfs or their alternatives are available.
Removal 5 Disconnect the battery negative terminal (refer to Disconnecting the battery in the Reference Section of Ihis manual). 6 Remove the auxiliary drivebelt(s) as described In Chapter 1A. 7 Remove the air cleaner, Inlet air duct and resonator as desenbed In Chapter 4B. 8 Undo the three bolts and remove the crankshaft pulley from the sprocket (see illustration). 9 Undo the retaining bolt In the centre of the lower liming cover (see illustration). 10 Undo tho uppor timing cover upper retaining bolt, and the rear retaining bolt located above the alternator (see illustration). 11 Release the crankshaft TDC sensor wiring from the clip on the upper timing cover, then withdraw the cover slightly and slide Ihe wiring plug and socket from the liming cover slot (see illustrations). 12 Release the TDC sensor wiring from the periphery ol the upper and fower timing covers and remove both covers (see Illustrations). 13 Free the accelerator inner cable from the throttle cam, remove the outer cable spring dip, then pull the outer cable out from its mounting bracket rubber grommet. 14 From the side of the throttle body, disconnect the wiring connectors from the
Page 73 of 225

2C«1
Chapter 2 PartC:
Diesel engine in-car repair procedures
Contents
Auxiliary drivebelts - removal and refitting See Chapter 1B Camshaft cover - removal and refitting 6 Camshaft oil seal - renewal 7 Camshaft - removal and refitting See Chapter 20 Crankshaft oil seats - renewal 8 Cylinder compression test « 3 Cylinder head - dismantling and overhaul See Chapter 20 Cylinder head - removal and refitting 9 Engine mountings - inspection and renewal 11 Engine oil and fitter - renewal See Chapter 18 Engine oil level check See Weekly checks
Degrees of difficulty
Flywheel * removal, inspection and refitting 10 General information 1 Location of TDC on No 1 cylinder 2 Oil cooler - removal and refitting 14 Oil pump and pick-up tube • removal, Inspection and refitting 13 Sump • removal and refitting 12 Timing belt and covers • removal and refitting 4 Timing belt tensioner and sprockets - removal, Inspection and refitting 5 Valve clearance check and adjustment See Chapter 1B
Easy,
suitable for novice
with Irttle
|| experience g^
FaMy
eesy,
suitable ^
forbeglnnerwilti
some experience ^
Falrtydfficult, ^ suitable
for
competent DIYmechanic ^
Difficult, suitable
for & experienced DIY mechanic ^
Very
difficult,
^ suitable
for
expert
DfY
jR or professional ^
Specifications
General Engine code:' 1698 cc non-turbo engine 176.B3.000 1698 cc turbo engine: Up to 1997 t76.A3.00aor176.A5.000 1997 onward 176.A3.000or176.B7.000 •Note: See Vehicle Identification for the location of the code marking on the engine. Bore 82.6 mm Stroke 79.2 mm Compression ratio: Non-turbo engine 20.5:1 Turbo engine 19:1 Firing order 1-3-4-2
No 1
cylinder location Timing belt end of engine Titling belt tension See text
Lubrication system Oi pump type By-rotor driven from front of crankshaft Outer rotor-to-houslng clearance 0.080 to 0.186 mm Axial clearance 0.025 to 0.056 mm
Torque wrench settings Nm ibf ft Camshaft cover 10 7 Camshaft sprocket 11B 87 Crankshaft sprocket centre bolt 190 140 Cylinder head: Stage 1 50 37 Stage 2 100 74 StageS Angle-tighten a furtfier 90" Stage 4 Angle-tighten a further 90° CySnder head front bolts 30 22 Flywheel 142 105
Fuel
injection pump sprocket 49 36 Inlet and exhaust manifolds 25 18 Sump 10 7 Timing belt tensioner and idler 44 32
Page 78 of 225

2C*2 Diesel engine in-car repair procedures
5.11 Special Fiat tool necessary to accurately position the camshaft before fitting the sprocket
Camshaft sprocket Removal 11 Remove the timing belt as descnbed in Section 4. A special Rat tool (see illustration) is necessary to position the camshaft before refitting the sprocket, however il the original camshafl Is being re-used, use of the special tool can be ovoided by accurately marking the camshaft position before removing the sprocket. Caution: On later 1996 models the camshaft sprocket can be moved In either direction on tho camshaft location dowel. 12 The camshaft sprocket must now oe held stationary whilst the retaining bolt is loosened. This is no problem on later models where the sprocket incorporates holes, however some early models have a sprocket without holes • on this type Fiat technicians use a special tool
V*— r^r
To make a camshaft sprocket holding tool, obtain two lengths of steel strip about 6 mm thick by 30 mm wide or simllar, one 600 mm long, the other 200 mm long (all dimensions approximate). Bolt the two strips together to form a forked end, leaving tho bolt slack so that the shorter strip can pivot freely. At the end of each 'prong' of the fork, secure a bolt with a nut and a locknut, to act as the futcrums; theso will engage with the cut'Outs In the sprocket, and should protrude by about 30 mm
which clamps on the sprockot teeth. If this tool is not available, it may be possible to make up a similar tool. On later models a sprocket holding tool can easily be made (see Toot Tip). 13 On 1996-on models mark the position of the camshaft in relation to the cylinder head.
5.14a Unscrew and remove the bolt and washer...
This is best achieved by removing tho vacuum pump from the flywheel end of the head and marking the head in relation to Ihe drive slot in ihe end of the camshaft. Note the location of the hose and bracket when removing tha vacuum pump (seo illustration). 14 Unscrew and remove tho boll and v/ashof and withdraw the sprocket from the end of tha camshaft (see Illustrations). Note tha location peg on the camshafl. Inspection 15 With the sprocket removed, examine the camshaft oil seal for signs of leaking. If necessary, rater to Section 7 and renew it 16 Check the sprocket teeth for damage. 17 Wipe clean the sprocket and camshaft mating surfaces-Refitting 18 Locate the sprocket on the end of the camshaft. On J996-on models chock that the camshaft is positioned accurately to tho previously made marks and also make sura thai the TOC mark on Ihe sprocket Is aligned with the mark on the Inner timing cover. If avoiiablo use the special Fiat toot to locate the camshaft correctly. Rofil the bolt and washer and tighten lo the specified torque while holding the camshalt sprocket stationary using the method descnbed previously. Recheck all alignment marks. 19 Refit the timing belt as described in Section 4.
Crankshaft sprocket Caution: The crankshaft sprockot retaining bolt has a left-hand thread. Removal 20 Remove the timing belt as described in Section 4. 21 Working beneath the engine unbolt and remove the flywheel lower cover, than hold the flywheel stationary preferably using a tool which engages the flywheel starter ring gear (see Section 10). Alternatively have an assistant engage a wide-bladed screwdriver with the starter ring gear 22 Unscrew and remove (he crankshaft sprocket retaining bolt (left-hand thread), washer and spacer and slide the sprocket off the end of the crankshaft (see illustrations). It is quite tight and il will be necessary to use a
5.14b ... and remove the sprocket from tho end of the camshaft 5.22a Unscrew and remove the bolt, washer and spacer... 5.22b ... and remove the crankshaft sprocket
Page 105 of 225
2D*10 Engine removal and overhaul procedures
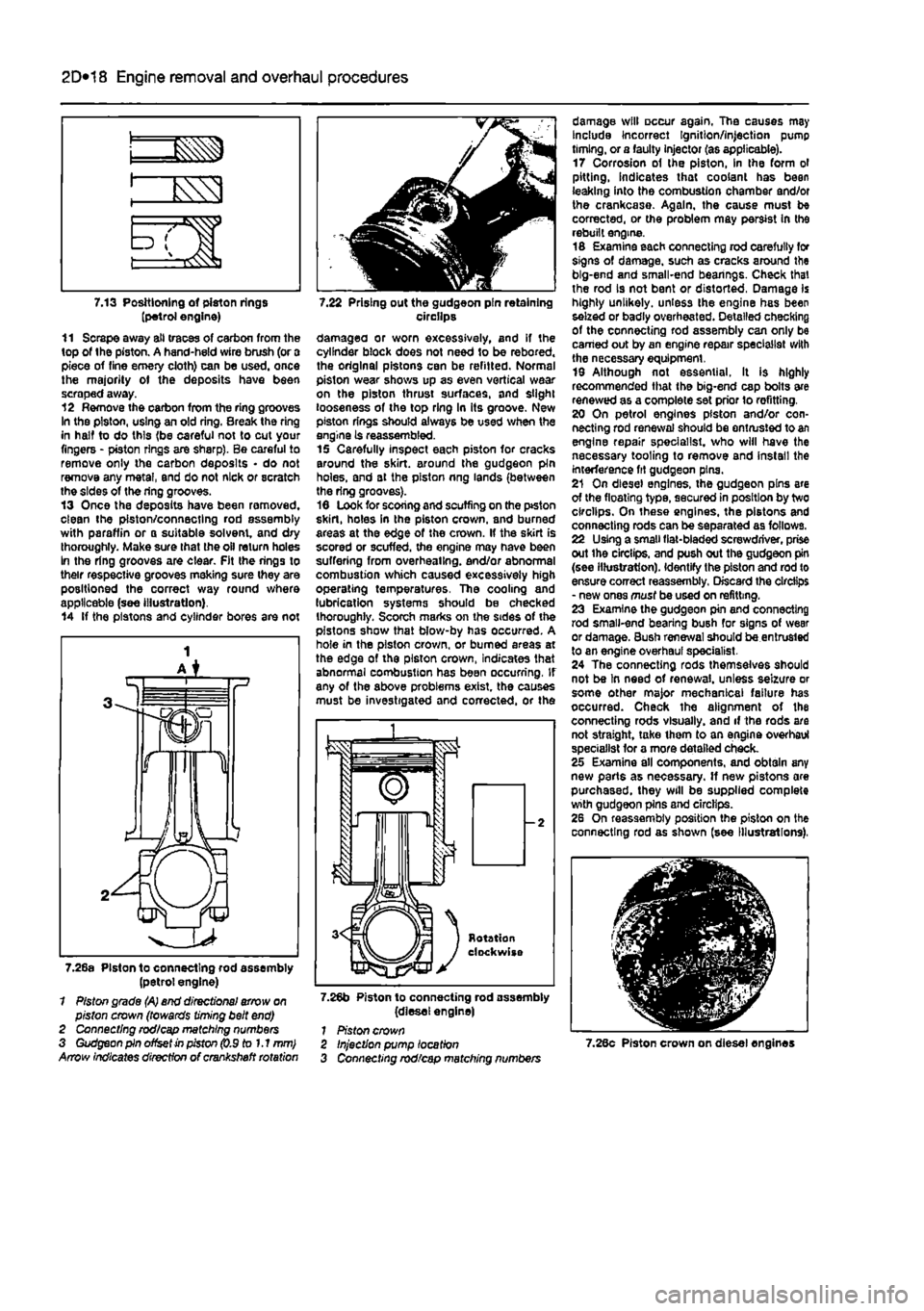
7.13 Positioning of piston rings (petrol engine) 11 Scrape away all traces of carbon from the top of the piston. A hand-held wire brush (or a piece of fine emery cloth) can be used, once the majority ot the deposits have been scraped away. 12 Remove the carbon from the ring grooves In the piston, using an old ring. Break the ring in half to do this (be careful not to cut your fingers - piston rings are sharp). Be careful to remove only the carbon deposits • do not remove any metal, end do not nick or scratch the sides of the ring grooves. 13 Once the deposits have been removed, clean the piston/connecting rod assembly with paraffin or o suitable solvent, and dry thoroughly. Make sure that the oil return holes In the ring grooves are clear. Fit the rings to their respective grooves meking sure they are positioned the correct way round where applicable (see illustration). 14 If the pistons and cylinder bores are not
7.22 Prising out the gudgeon pin retaining circilps damagea or worn excessively, and if the cylinder block does not need to be rebored. the original pistons can be refitted. Normal piston wear shows up as even vertical wear on the piston thrust surfaces, and slight looseness of the top ring In its groove. New piston rings should always be used when the engine is reassembled. 15 Carefully inspect each piston for cracks around the skirt, around the gudgeon pin holes, and at the piston nng lands (between the ring grooves). 16 Look for scoring and scuffing on the ptston skirt, holes in the piston crown, and burned areas at the edge of the crown. If the skirt is scored or scuffed, the engine may have been suffering from overheating, end/or abnormal combustion which caused excessively high operating temperatures. The cooling and lubrication systems should be checked thoroughly. Scorch marks on the sides of the pistons show that blow-by has occurred. A hole in the piston crown, or burned areas at the edge of the piston crown, Indicates that abnormal combustion has been occurring. If any of the above problems exist, the causes must be investigated and corrected, or the
7.26a Piston to connecting rod assembly (petrol engine) 1 Piston grade (A) end directional arrow on piston crown (towards timing belt end) 2 Connecting rod/cap matching numbers 3 Gudgeon pin offset in piston (0.9 to 1.1 mm) Arrow indicates direction of crankshaft rotation
7.26b Piston to connecting rod assembly (diesel engine) 1 Piston crown
damage will occur again. The causes may Include Incorrect Ignition/injection pump timing, or a faulty injector (as applicable). 17 Corrosion of the piston, in the form ol pitting, indicates that coolant has been leaking into the combustion chamber and/or the crankcase. Again, the cause must be corrected, or the problem may persist In the rebuilt engine. 16 Examine each connecting rod carefully for signs of damage, such as cracks around the big-end and small-end bearings. Check that the rod is not bent or distorted, Damage is highly unlikely, unless the engine has been seized or badly overheated. Detailed checking of the connecting rod assembly can only be earned out by an engine repair specialist with the necessary equipment. 19 Although not essential. It is highly recommended that the big-end cap bolts are renewed as a complete set prior lo refitting. 20 On petrol engines piston and/or con-necting rod renewal should be entrusted to an engine repair specialist, who will have the necessary tooling to remove and install the interference fit gudgeon pins. 21 On diesel engines, the gudgeon pins are of the floating type, secured in position by two circlips. On these engines, the pistons and connecting rods can be separated as follows. 22 Using a small fiat-bladed screwdriver, prise out ihe circlips, and push out the gudgeon pin (see illustration). Identify the piston and rod to ensure correct reassembly. Discard the circlips - new ones must be used on refitting. 23 Examine the gudgeon pin and connecting rod small-end bearing bush for signs of wear or damage. Bush renewal should be entrusted to an engine overhaul specialist. 24 The connecting rods themselves should not be In need of renewal, unless seizure or some other major mechanical failure has occurred. Check the alignment of the connecting rods visually, and if the rods are not straight, take ihem to an engine overhaul specialist for a more detailed check. 25 Examine all components, and obtain any new parts as necessary. If new pistons are purchased, they will be supplied complete with gudgeon pins and circlips. 26 On reassembly position the piston on the connecting rod as shown (see Illustrations),
Injection pump location Connecting rod/cap matching numbers 7.28c Piston crown on diesel engines
Page 107 of 225

2D*10 Engine removal and overhaul procedures
8.4 Using a dial gauge to check the crankshaft endfloat 2 Remove the pistons and connecting rods, as described in Section 7. However, If no work fs to be done on the pistons and connecting rods there is no need to remove the cylinder head, or to push the pistons out of the cylinder bores. The pistons should just be pushed far enough up the bores that they are positioned clear of the crankshaft Journals. 3 Unbolt the crankshaft rear oil seal housing from the cylinder block and recover the gasket where fitted. 4 Before removing the crankshaft, check the endfloat using a dial gauge. Push the crankshaft fully one way, and then zero Ihe gauge. Push the crankshaft fully the other way, and check tho endfloat (see Illustration). The result can be compared with the specified amount, and will give an indication as to whether new thrustwashers are required. 6 If a dial gauge is not available, feeler blades can be used. First push the crankshaft fully towards the flywheel end of the engine, then use feeler blades to measure the gap - on petrol engines measure between the centre main bearing thrust washer and the crankshaft web. and on diesel engines measure between the rear main bearing and tha crankshaft web. 6 Note the markings on the main bearing caps which vary according to type. On 8-valve petrol engines there is one line on Ihe cap nearest the timing belt end, two on the second cap, C on the centre cap, then three and four lines on the remaining caps (soo illustration). On 16-valve petrol engines, the caps are marked one to five with a series of lines (one line for the cap nearest the timing
8.6 Main bearing markings (petrol engine)
belt end, two for tho next cap and so on). On diesel engines the caps are marked one to live In the same way but with notches instead ol lines. Note also that on some diesel engines the cap nearest the timing belt end Is not marked and the notches therefore start with No 2 cap. 7 Loosen and remove the main bearing cop retaining bolts, and lift off each bearing cap. Recover the lower bearing shells, and tape them to their respective caps for safe-keeping. On some diesel engines note that the centre main bearing cap botts are longer than the other bolls. 8 Lift the crankshaft Irom the crankcase and remove the upper bearing shells from the crankcase. If the shells are 1o be used again, keep them identified for position. Also remove the thrustwashers from their position either side of the centre main bearing (petrol engines) or rear main bearing (diesel engines) (see illustrations)
Inspection 9 Wash the crankshaft in a suitable solvent and allow It to dry. Flush the oil holes thoroughly, to ensure that ihey are not blocked - use a pipe cleaner or a needle brush il necessary. Remove any sharp edges from the edge of the holes which may damage the new bearings when they are installed. 10 Inspect the main searing and crankpin journals carefully; if uneven wear, cracking, scoring or pitting are evident then the crankshaft should be reground by an engineering workshop, and refitted to the engine with underslze bearings.
11 Use a micrometer to measure the diameter of each main bearing journal. Taking a number of measurements on the surface of each journal will reveal if it Is worn unevenly. Differences in diameter measured at 90" intervals Indicate that the journal is out of round. Differences In diameter measured aiong the length of the journal, indicate that the journal is tapered. Again. If wear is detected, the crankshaft can be reground by an engineering workshop and refitted with undersize bearings. 12 Check the oil seal journals at either end of the crankshaft. If they appear excessively scored or damaged, they may cause the new seals to leak when the engine is reassembled. It may be possible to repair the |ournal; seek the advice of an engmeenng workshop. 13 Measure the crankshaft runoul by setting up a DTI gauge on the centre main bearing journal and rotating the shaft In V - blocks. The maximum deflection of the gauge will indicate Ihe runout. Take precautions to protect the bearing journals and oil seal mating surfaces from damage during this procedure. A maximum runout figure Is not quoted by the manufacturer, but use the figure of 0.05 mm
a»
a rough guido. If the runoul exceeds this figure, crankshaft renewal should be considered • consult your Flat dealer or an engine rebuilding specialist for advico. 14 Refer to Section 10 for details of main and big-end bearing inspection.
9 Cylinder block/crankcase - % cleaning and inspection Sk
Cleaning 1 Remove all external components, brackets and electrical switches/sensors from the block Including the rear engine plate, injection pump/oil filter bracket and gasket, Intermediate shaft bracket, oH vapour breather casing, and coolant pump. Also unboit and remove the ol return tube from the crankcase (see illustrations). For complete cleaning, the core plugs should Ideally be removed. Drill a small hole in the plugs, then insert a self-tapping screw into the hole. Pull out the plugs by
8.8a Removing the thrustwashers.. ... and upper bearing shells (diesel engine) 8.8o Thrustwashers located on the centre main bearing (petrol engine)
Page 114 of 225

3*2 Cooling, heating and ventilation systems
1 General information and precautions
Genera/ Information The engine cooling/cabin heating system is ol pressurised type, comprising a coolant pump driven by the camshaft timing belt (petrol engine models) or auxiliary drlvebelt (diesel engine models), a crossllow radiator, a coolant expansion tank, an electric cooling fan, a thermostat, heater matrix, and all associated hoses and switches. The system functions as follows: Ihe coolant pump circulates cold water around the cylinder block and head passages, and through the Inlet manifold, heater matrix and throttle body to the thermostat housing. When the engine Is cold, the thermostat remains closed and prevents coolant from circulating through the radiator. When the coolant reaches a predetermined temperature, the thermostat opens, and the coolant passes through the top hose to the radiator. As the coolant circulates through the radiator, it is cooled by the in-rush of air when the car is in forward motion. The airllow is supplemented by the action of the electric cooling fan. when necessary, As the temperature of the coolant in the radiator drops, it flows to the bottom of the radiator by convection, and passes out through the bottom hose to the coolant pump - the cycle is then repeatod, When the engine is at normal operating temperature, the coolant expands, and some of It is displaced into the expansion tank. Coolant collects In the tank, and ts returned to Ihe radiator when the system cools. On petrol engine models, the expansion tank is integrated into the side of the radiator. On diesel engine models, and certain petrol engine models with air conditioning, the tank is a separate unit, mounted on the right hand side of the engine compartment. On turbo diesel engine models, the coolant is also passed through a supplementary engine oil cooler, to assist In controlling the engine lubricant temperature. Tho electric cooling fan mounted in front of the radiator is controlled by a thermostatic switch. At a predetermined coolant temperature, the swilch/sensor actuates the tan lo provide additional airflow through the radiator, The switch cuts the electrical supply to the Ion when the coolant temperature has dropped below a preset threshold (see Specifications).
Precautions
A
Warning: Do not attempt to remove the expansion tank pressure cap, or to disturb any part of the cooling system, whlio the engine is hot, as then is a high risk of scalding, tf the expansion tank pressure cap must be removed before the
engine and radiator have fulty cooled (even though this is not recommended?, the pressure in the cooling system must first be relieved. Cover the cap with a thick layer of cloth, to avoid scalding, and slowly unscrew the pressuro cap until a hissing sound Is heard. When the hissing stops, indicating that the pressure has reduced, slowly unscrew the pressure cap until it can be removed; If more hissing sounds are heard, wait until they have stopped before unscrewing the cap completely. At all times, keep your face well away from the pressure cap opening, and protect your hands.
A
Warning: Do not allow antifreeze to come into contact with your skin, or with the painted surfaces of the vehicle. Rinse off spills immediately, with plenty of water. Never leave antifreeze lying around in an open container, or In a puddle In the driveway or on the garage floor. Children and pets are attracted by its sweet smell, but antifreeze can be fatal tf ingested.
A
Warning: If the engine is hot, the electric cooling fan may start rotating even if the engine and ignition are switched off. Be careful to keep your hands, hair, and any loose clothing well clear when working In the engine compartment.
2 Cooling system hoses - f&> disconnection and renewal ^
1 The number, routing and pattern of hoses will vary according to model, but the same basic procedure applies. Before commencing work, make sure that the new hoses are to hand, along wilh new hose clips if needed, it is good practice to renew the hose clips at the same time as the hoses. 2 Drain the cooling system, as described in Chapter 1A or 18, saving the coolant if it is fit for re-use. Apply a little penetrating oil onto the hose clips if they are corroded. 3 Release the hose clips from the hose concerned. Three types of clip are used; worm-drive. spring and 'sardine-can'. The worm-drive clip is released by turning its screw anti-clockwise. The spring clip Is released by squeezing Its tags together with pliers, at the same time working the cbp away from the hose stub. The sardine-can clips are not re-usable, and are best cut off with snips or side cutters. 4 Unclip any wires, cables or other hoses which may be attached to the hose being removed. Make notes for reference when reassembling If necessary. 5 Release the hose from its stubs with a twisting motion. Be careful not to damage the stubs on deltcate components such as the radiator, or thermostat housings. If the hose Is stuck fast, the best course is often to cut it off using a sharp knife, but again be careful not to damage the stubs.
6 Before fitting the new hose, smear the stubs with washing-up liquid or a suitable rubber lubricant to aid fitting. Do not use oil or grease, which may attack the rubber. 7 Fit the hose clips over the ends of the hose, then fit the hose over its stubs. Work the hose Into position. When satisfied, locate and tighten the hose dips. 6 Refill the cooling system as described In Chapter 1A or 1B. Run the engine, and chock that there are no leaks. 9 Recheck the tightness of Ihe hose clips on any new hoses after a few hundred miles. 10 Top-up the coolant level if necessary.
3 Radiator -
removal,
inspection and refitting
Removal Note: If leakage is the reason for removing
the
radiator, bear In mind that minor leaks can often be cured using proprietary radiator sealing compound, with the radiator in situ. 1 Disconnect the battery negative terminal (refer to Disconnecting the battery In the Reference Section of this manual). On diesel engine models, unbolt the relay bracket from the side of the battery tray. 2 Drain the cooling system as described In Chapter 1A or 1B. 3 On 1242 cc (16-valve) petrol engine models, remove the air cleaner and Inlet ducts as desenbed In Chapter 4B, 4 Slacken the clips and disconnect Ihe (op and bottom coolant hoses from the radiator. In addition on diesel engine models, and petrol engine models with a remotely-sited expansion tank, disconnect the expansion tank coolant hose from the right hand side ol the radiator (see Illustrations), 5 Unscrew the fixings and lift the plastic trim panel from above the front bumper Unscrew the bolt(s) securing tho radiator to the upper body panel (see Illustration). Note that the radiator and cooling fan assembly share the same upper mounting bolt. 6 Unbolt the cooling fan(e) and shroud assembly from Ihe rear ot the radiator, as described in Section 5.
3.4a Slacken the clip and disconnect the radiator bottom hose
Page 137 of 225

Fuel system - diesel models 4C*3
Torque wrench settings Nm Ibfft Fuel injection pump roar bracket .. . 29 21 Fuel Injection pump .... 25 18 Fuel Injectors 41 Fuel pipe union nuts .... 30 22 Inlet manifold .... 24 18 Lower oil tiller mounting and injection pump mounting nut ..... .... 71 S2 Turbocnarger to exhaust manifold .... <10 30 Upper Dtl filter mounting end injection pump mounting nut 98 72
1 General information and precautions
General information The fuel system consists of a rear-mounted fust tank, a fuel filter with integral water separator, a fuel injection pump, in|eciors and associated components. A turbocharger is fitted to TDS, TD and TDSX models. Fuel Is drawn from the fuel tank to the fuel Injection pump by a vane-type transfer pump Incorporated in the fuel injection pump. Before reaching tho pump, the fuel passes through a fuel filter, where foreign matter and water aro removed. Excess fuel lubricates the moving components of the pump, and Is then returned to the tank. On turbo models with the Bosch fuel Injection systom, an eiectncally operated heater is incorporated In the fuel filter housing. The fuel injection pump is driven at half-crankshaft speed by the timing belt. The nigh pressure required to inject tho fuel into the compressed air in the swirl chambers Is achlovod by a cam plate acting on a single piston on the Bosch pumo, or by two opposed pistons forced together by rollers running in a cam ring on the Lucas (CAV) pump. Tlie fuel passes through acentral rotor with a single outlet drilling which aligns With ports leading to the Injector pipes. Fuel metering is controlled by a centrifugal governor, which reacts to accelerator pedal
position end engine speed. The governor is linked lo a metering valve, which increases or decreases the amount of fuel delivered at each pumping stroke. On turbocharged models, a separate device also Increases luel delivery with increasing boost pressure. Basic injection timing is determined when the pump is fitted. When the engine is running, it Is varied automatically to suit the prevailing engine speed by a mechanism which turns the cam plate or ring, Tho four fuel injectors proouco a homogeneous spray of fuel Into the swirl chambers located In the cylinder head. The Injectors are calibrated to open end close at critical pressures lo provide efficient and even combustion. Each injector needle is lubricated by fuel, which accumulates In the spring chamber and is channelled to the injection pump return hose by loak-off pipes Bosch or Lucas fuel system components mBy be fitted, depending on the model. Components from the latter manufacturer are marked either CAV. Roto-dlesel or Con-diesel. depending on their date and place of manufacture. With the exception of the fuel filter assembly, replacement components must be of tho same make as those originally fitted. Cold starting is assisted by preheater or glow plugs fitted to each swirl chamber. On the Bosch injection pump, an automatic cold Injection advance device operated through a thermal switch, advances the injection timing by Increasing the fuel pressure. The device operates at coolant temperatures below 55° C,
A stop solenoid cuts the fuel supply to V* Injection pump rotor when the ignition i switched off (see illustration) Provided that the specified maintenance* earned out. the fuel injection equipment #» give long and trouble-free service, ft* j injection pump itself may well outlast tlx ' engine, The main potential cause of damage j to the injection pump and injectors is dirt e water in the fuel. 1 Servicing of the injection pump and injectwi: j, is very limited for tho home mechanic, antf dismantling or adjustment other than thtf described In this Chapter must be entrusted to ' a Rat dealer or fuel Injection specialist.
Precautions
A
Warning: It Is necessary to takt I certain precautions when woriong , on the fuel system component^ particularly the fuel Injectors. Befon carrying out any operations on tho fuel system, refer to the precautions given* Safety first! at the beginning of Mis manual, and to any additional wamlrq notes at the start of the relevant
Sections.
2 Air cleaner and inlet system ^ • removal and refitting S
Removal 1 Remove the air cleaner element u described In Chapter 1B (see illustration).
1.9 Stop solenoid on the injection pump 2.1 Releasing the air cleaner cover clips
Page 144 of 225

4D«1
Chapter 4 Part D:
Exhaust and emission control systems
Contents
Catalytic converter - general Information and precautions 7 Crankcase emission system • general information 3 Evaporative loss emission control system • information and component renewal 2
Degrees of difficulty
Exhaust manifold - removal and refitting 5 Exhaust system - general information and component renewal .... 6 General information 1 Lambda oxygen sensor - removal and refitting 4
Easy, suitable
tor novice with fittie ^
1 experience
Fairly easy, suitable for beginner with ^ some experience ^
Fairiy dfficult, lb suitable for competent ^ DIY mechanic ^
Difficult, suitable for experienced DIY ^ mechanic
Very difficult, ^ suitable far expert DIY or professional
Specifications
Torque wrench settings Exhaust down pipe to manifold Exhaust manifold Exhaust system mounting Exhaust to catalytic converter: M8 M10x1.25
Nm Ibfft 24 18 24 18 27 20
24 18 40 30 53 39
1 General information
Emission control systems All petrol engine models use unleaded petrol and are controlled by engine management systems that are 'tuned' to give the best compromise between driveability. luel consumption and exhaust emission production. In addition, a number of systems are fitted that help to minimise other harmful emissions: a crankcase emission-control system (petrol models only) that reduces the release of pollutants from the crankcase, an evaporative loss emission control system (petrol models only) to reduce the release of hydrocarbons from the fuel tank, a catalytic converter (petrol and diesel models) to reduce exhaust gas pollutants, and an Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) system (turbo diesel models only) to reduce exhaust emissions. Crankcase emission control To reduce the emission of unburned hydrocarbons from the crankcase Into the atmosphere, the engine is sealed and the blow-by gases and oil vapour are drawn from inside the crankcase, through a flame trap.
into the inlet tract to be burned by the engine during normal combustion. Under conditions of high manifold depression (idling, deceleration) the gases will by sucked positively out of the crankcase. Under conditions of low manifold depression (acceleration, full-throttle running) ihe gases are forced out of the crankcase by the (relatively) higher crankcase pressure: if the engine is worn, the raised crankcase pressure (due to increased blow-by) will cause some of the flow to return under all manifold conditions. Exhaust emission control -petrol models To minimise the amount of pollutants which escape Into the atmosphere, a catalytic converter is fitted In the exhaust system. The fuel system is of the closed-loop type, in which a Lambda (or oxygen) sensor In the exhaust system provides the engine management system ECU with constant feedback, enabling the ECU to adjust the air/fuel mixture to optimise combustion. The Lambda sensor has a heating element built-in that Is controlled by the ECU through the Lambda sensor relay to quickly bring the sensor's tip to Its optimum operating temperature. The sensor's tip Is sensitive to oxygen and relays a voltage signal to the ECU
that varies according on the amount of oxygen In the exhaust gas. If the inlet air/fuel mixture is too rich, the exhaust gases are low in oxygen so the sensor sends a low-voltage signal, the voltage rising as the mixture weakens and the amount of oxygen rises In the exhaust gases. Peak conversion efficiency of all major pollutants occurs if the inlet air/fuel mixture Is maintained at the chemlcally-con*ect ratio for the complete combustion of petrol of 14.7 parts (by weight) of air to
1
part of fuel (the stoichiometric ratio). The sensor output voltage alters in a large step at this point, the ECU using the signal change as a reference point and correcting the Inlet air/fuel mixture accordingly by altering the fuel Injector pulse width. Exhaust emission control -diesel models An oxidation catalyst is fitted in the exhaust system of all diesel engine models. This has the effect of removing a large proportion of the gaseous hydrocarbons, carbon monoxide and particulates present in the exhaust gas. An Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) system Is fitted to all turbo diesel engine models. This reduces the level of nitrogen oxides produced during combustion by Introducing a proportion of the exhaust gas back into the inlet manifold, under certain engine operating