Engine wiring ISUZU KB P190 2007 Workshop Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: ISUZU, Model Year: 2007, Model line: KB P190, Model: ISUZU KB P190 2007Pages: 6020, PDF Size: 70.23 MB
Page 317 of 6020
3B-56 POWER-ASSISTED STEERING SYSTEM
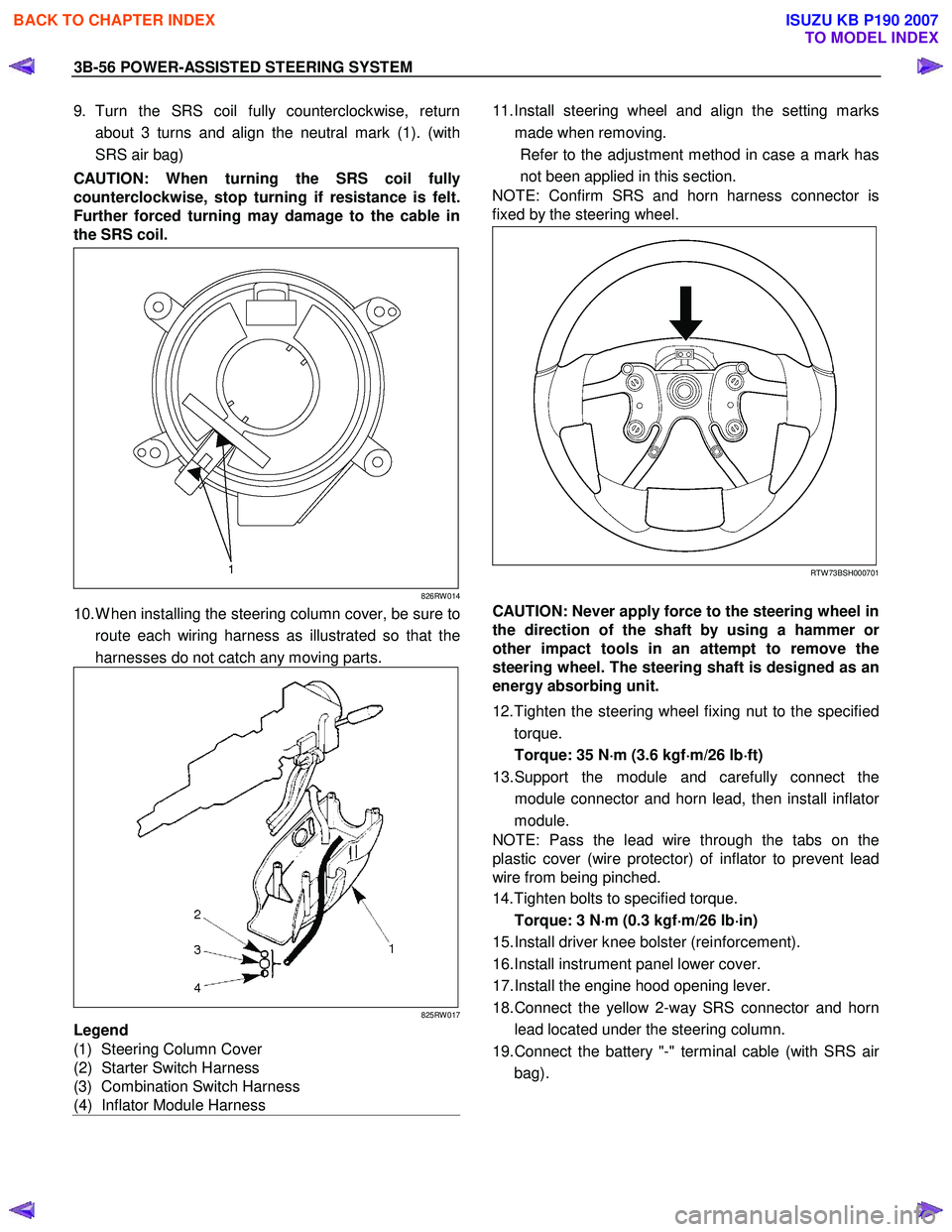
9. Turn the SRS coil fully counterclockwise, return
about 3 turns and align the neutral mark (1). (with
SRS air bag)
CAUTION: When turning the SRS coil fully
counterclockwise, stop turning if resistance is felt.
Further forced turning may damage to the cable in
the SRS coil.
826RW 014
10. W hen installing the steering column cover, be sure to
route each wiring harness as illustrated so that the
harnesses do not catch any moving parts.
825RW 017
Legend
(1) Steering Column Cover
(2) Starter Switch Harness
(3) Combination Switch Harness
(4) Inflator Module Harness
11. Install steering wheel and align the setting marks
made when removing. Refer to the adjustment method in case a mark has
not been applied in this section.
NOTE: Confirm SRS and horn harness connector is
fixed by the steering wheel.
RTW 73BSH000701
CAUTION: Never apply force to the steering wheel in
the direction of the shaft by using a hammer o
r
other impact tools in an attempt to remove the
steering wheel. The steering shaft is designed as an
energy absorbing unit.
12. Tighten the steering wheel fixing nut to the specified torque.
Torque: 35 N ⋅
⋅⋅
⋅
m (3.6 kgf ⋅
⋅⋅
⋅
m/26 lb ⋅
⋅⋅
⋅
ft)
13. Support the module and carefully connect the module connector and horn lead, then install inflato
r
module.
NOTE: Pass the lead wire through the tabs on the
plastic cover (wire protector) of inflator to prevent lead
wire from being pinched.
14. Tighten bolts to specified torque.
Torque: 3 N ⋅
⋅⋅
⋅
m (0.3 kgf ⋅
⋅⋅
⋅
m/26 lb ⋅
⋅⋅
⋅
in)
15. Install driver knee bolster (reinforcement).
16. Install instrument panel lower cover.
17. Install the engine hood opening lever.
18. Connect the yellow 2-way SRS connector and horn lead located under the steering column.
19. Connect the battery "-" terminal cable (with SRS ai
r
bag).
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 617 of 6020

5A-24 BRAKE CONTROL SYSTEM
Computer System Service Precautions
The Anti-lock Brake System and Electronic Brake-force
Distribution interfaces directly with the Electronic
Hydraulic Control Unit (EHCU) which is a control
computer that is similar in some regards to the Engine
Control Module. These modules are designed to
withstand normal current draws associated with vehicle
operation. However, care must be taken to avoid
overloading any of the EHCU circuits. In testing for
opens or shorts, do not ground or apply voltage to any
of the circuits unless instructed to do so by the
appropriate diagnostic procedure. These circuits should
only be tested with a high impedance multimeter
5-8840-0366-0 or special tools as described in this
section. Power should never be removed or applied to
any control module with the ignition in the “ON” position.
Before removing or connecting battery cables, fuses or
connectors, always turn the ignition switch to the “OFF”
position.
General Service Precautions
The following are general precautions which should be
observed when servicing and diagnosing the Anti-lock
Brake System and/or other vehicle systems. Failure to
observe these precautions may result in Anti-lock Brake
System and Electronic Brake-force Distribution
damage.
• If welding work is to be performed on the vehicle using an electric arc welder, the EHCU and valve
block connectors should be disconnected before the
welding operation begins.
• The EHCU and valve block connectors should never be connected or disconnected with the
ignition “ON”.
Note:
• If only rear wheels are rotated using jacks or drum tester, the system will diagnose a speed sensor
malfunction and the “ABS and Brake” warning lamp
will illuminate. But actually no trouble exists. W hen
the DTC is not detected and the ABS and BRAKE
warning lamp is on, “How to erase code” is
performed and an ABS and BRAKE warning lamp
are off.
If the battery has been discharged
The engine may stall if the battery has been completely
discharged and the engine is started via jumper cables.
This is because the Anti-lock Brake System (ABS) and
Electronic Brake-force Distribution (EBD) System
requires a large quantity of electricity. In this case, wait
until the battery is recharged, or set the ABS and EBD
to a non-operative state by removing the fuse for the
ABS. After the battery has been recharged, stop the
engine and install the ABS fuse. Start the engine again,
and confirm that the ABS warning Lamp does not light.
Note on Intermittents
As with virtually any electronic system, it is difficult to
identify an intermittent failure. In such a case duplicating
the system malfunction during a test drive or a good
description of vehicle behavior from the customer may
be helpful in locating a “most likely” failed component or
circuit. The symptom diagnosis chart may also be
useful in isolating the failure. Most intermittent
problems are caused by faulty electrical connections or
wiring. W hen an intermittent failure is encountered,
check suspect circuits for:
• Suspected harness damage.
• Poor mating of connector halves or terminals not fully seated in the connector body (backed out).
• Improperly formed or damaged terminals.
Test Driving ABS Complaint Vehicles
If there has been an abnormality in the lighting pattern
of the “ABS” warning lamp, the fault can be located in
accordance with the “DIAGNOSIS BY “ABS” W ARNING
LAMP ILLUMINATION PATTERN”. Although such
problems can be detected by the driver as a vehicle
symptom, it is still necessary to perform a test drive
following the test procedure mentioned below, in order
to reproduce the symptom for problem diagnosis on a
symptom basis:
1. Start the engine and make sure that the “ABS” W /L
goes OFF. If the W /L remains ON, it means that
the Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) is stored.
Therefore, read the code and locate the fault.
Note: The DTC cannot be cleared if the vehicle speed
does not exceed about 10km/h (6mph) at DTC, even
though the repair operation is completed.
2. Start the vehicle and accelerate to about 30 km/h (19 mph) or more.
3. Slowly brake and stop the vehicle completely.
4. Then restart the vehicle and accelerate to about 40 km/h (25 mph) or more.
5. Brake at a time so as to actuate the ABS and stop the vehicle.
6. Be cautious of abnormality during the test. If the W /L is actuated while driving, read the DTC and
locate the fault.
7. If the abnormality is not reproduced by the test, make best efforts to reproduce the situation
reported by the customer.
8. If the abnormality has been detected, repair in accordance with the “SYMPTOM DIAGNOSIS”.
Note:
• Be sure to perform a test drive on a wide, even road
with light traffic.
• If an abnormality is detected, be sure to suspend the test and start trouble diagnosis at once.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1191 of 6020

Engine Control System (4JH1) 6E-157
DTC P0500 (Symptom Code 1, A) (Flash Code 24)
Circuit Description
The vehicle speed sensor (VSS) is used by the engine
control module (ECM) and speedometer, which
generates a speed signal from the transmission output
shaft. The VSS has the following circuits.
• Ignition voltage feed circuit
• VSS signal circuit
• VSS low reference circuit
The VSS uses a hall effect element. It interacts with the
magnetic field created by the rotating magnet and
outputs square wave pulse signal. The 12 volts
operating supply from the Meter fuse (except 2W D with
A/T) or Back Up fuse (2W D with A/T). The ECM
calculates the vehicle speed by the VSS. If the vehicle
is 2W D with automatic transmission, VSS signals are
sent from the transmission control module (TCM). If the
ECM detects VSS signals are generated with high
frequencies, this DTC will set.
Condition for Running the DTC
• The ignition switch is ON.
Condition for Setting the DTC
• The ECM detects that the vehicle speed is highe
r
than 200 km/h (125 MPH) for 5 seconds.
(Symptom Code 1)
•
The ECM detects that the vehicle speed senso
r
signal frequency is too high for 0.6 seconds.
(Symptom Code A)
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
• The ECM illuminates the malfunction indicato
r
lamp (MIL) when the diagnostic runs and fails.
• The ECM uses a vehicle speed substitution of 5
km/h (3 MPH) for engine control.
Condition for Clearing the MIL/DTC
• The ECM turns OFF the MIL when the diagnostic
runs and does not fail.
• A history DTC clears after 40 consecutive driving
cycles without a fault. Or clear with the scan tool.
Diagnostic Aids
• Electrical or magnetic interference may affect
intermittent condition.
• If an intermittent condition is suspected, refer to
Intermittent Conditions in this section.
DTC P0500 (Symptom Code 1, A) (Flash Code 24)
Schematic Reference: Engine Controls Schematics
Connector End View Reference: Engine Controls
Connector End Views or Engine Control Module (ECM)
Connector End Views
Chart for 2WD with A/T
Step Action Value(s) Yes No
1 Did you perform the Diagnostic System Check-
Engine Controls?
Go to Step 2 Go to Diagnostic
System Check-
Engine Controls
2 1. Inspect all of the circuits going to the automatic transmission (A/T) vehicle speed sensor (VSS)
for the following: • Routed too closely to fuel injection solenoid
wiring or components
• Routed too closely to after-market add-on
electrical equipment
• Routed too closely to solenoids, relays, and
motors
2. If you find incorrect routing, correct the harness routing.
Did you find and correct the condition?
Go to Step 7 Go to Step 3
3 1. Turn OFF the ignition. 2. Disconnect the A/T VSS harness connector.
3. Inspect for an intermittent and for poor connections at the harness connector of the A/T
VSS (pins 1, 2 and 3 of E-30 connector).
4. Repair the connection(s) as necessary.
Did you find and correct the condition?
Go to Step 7 Go to Step 4
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1192 of 6020

6E-158 Engine Control System (4JH1)
Step Action Value(s) Yes No
4 1. Turn OFF the ignition.
2. Disconnect the engine control module (ECM) harness connector.
3. Inspect for an intermittent and for a poor connection on A/T VSS circuit at the harness
connector of the ECM (pin 68 of C-56 connector).
4. Repair the connection(s) as necessary.
Did you find and correct the condition?
Go to Step 7 Go to Step 5
5 1. Remove the A/T VSS. Refer to A/T Speed Sensor Replacement in automatic transmission
section.
2. Visually inspect the A/T VSS for the following conditions: • Physical damage
• Being loose
• Improper installation
3. The following conditions may cause this DTC to set: • Electromagnetic interference in the A/T
VSS circuits
4. Repair or replace as necessary.
Did you find and correct the condition?
Go to Step 7 Go to Step 6
6 Replace the A/T VSS. Refer to A/T Speed Sensor Replacement in automatic transmission section
Did you complete the replacement?
Go to Step 7
7 1. Reconnect all previously disconnected harness
connector(s).
2. Clear the DTCs with the scan tool.
3. Turn OFF the ignition for 30 seconds.
4. Drive the vehicle.
5. Observe the Vehicle Speed parameter with the scan tool.
Does the Vehicle Speed parameter indicate correct
vehicle speed?
Go to Step 8 Go to Step 2
8 Observe the DTC Information with the scan tool. Are there any DTCs that you have not diagnosed? Go to Diagnostic
Trouble Code (DTC) List System OK
Chart for except 2WD with A/T
Step Action Value(s) Yes No
1 Did you perform the Diagnostic System Check-
Engine Controls?
Go to Step 2 Go to Diagnostic
System Check-
Engine Controls
2 1. Inspect all of the circuits going to the vehicle speed sensor (VSS) for the following: • Routed too closely to fuel injection solenoid
wiring or components
• Routed too closely to after-market add-on
electrical equipment
• Routed too closely to solenoids, relays, and
motors
2. If you find incorrect routing, correct the harness routing.
Did you find and correct the condition?
Go to Step 7 Go to Step 3
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1289 of 6020

Engine Control System (4JH1) 6E-255
Symptoms – Engine Controls
Symptoms – Engine Controls
Important Preliminary Inspections Before Starting
Perform Diagnostic System Check – Engine Controls
before using the symptom tables, and verify that all o
f
the following are true:
• The engine control module (ECM) and malfunction
indicator lamp (MIL) are operating correctly.
• There are no diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs)
stored, or a DTC exists but without the MIL.
• The scan tool data is within the normal operating
range. Refer to scan tool Data List in this section.
• Verify the customer concern and locate the correct
symptom in the table of contents. Inspect the items
indicated under that symptom.
Visual and Physical Inspection
Several of the symptom procedures ask for careful
visual and physical inspection. This step is extremel
y
important. The visual and physical inspection can lead
to correcting a problem without further inspections, and
can save valuable time. Ensure that:
• The ECM grounds are clean, tight, and in thei
r
proper location.
• The vacuum hoses are not split or kinked, and
properly connected. Inspect thoroughly for an
y
type of leak or restriction.
• The mass air flow (MAF) sensor is properl
y
installed. The arrows on the plastic portion of the
sensor must point toward the engine.
• The air intake ducts are not collapsed or damaged.
• There are no leaks at the MAF sensor, an
y
connections or intake manifold sealing surfaces.
• The engine harness wiring and terminals are
properly connected and are not pinched or cut.
Intermittent
Important:
Inspect for improper installation of electrical
components if an intermittent condition exists. Inspect
for aftermarket add-on electrical equipment devices,
lights, and cellular phones. Verify that no aftermarket
equipment is connected to the keyword 2000 serial data
circuit. If you cannot locate an intermittent condition, a
cellular phone communication signal may cause the
condition.
Important:
The problem may or may not turn ON the MIL or store a
DTC.
Faulty electrical connections or wiring cause most
intermittent problems. Perform a careful visual and
physical inspection of the suspect connectors for the
following conditions:
• Improperly mated connector halves
• Terminals that are not seated
• Terminals that are damaged or improperly formed
Reform or replace connector terminals in the problem
circuit in order to ensure proper contact tension.
Remove the terminal from the connector body in orde
r
to inspect for poor terminal wire connection.
Road test the vehicle with the DMM connected to the
suspected circuit. An abnormal reading that occurs
when the malfunction occurs is a good indication that
there is a malfunction in the circuit being monitored.
Use the scan tool in order to help detect intermittent
conditions. Useful features of the scan tool include the
following:
• Trigger the Snapshot feature in order to capture
and store engine parameters when the malfunction
occurs. Review this stored information in order to
see the specific running conditions that caused the
malfunction.
• Use the Plot Function on the scan tool in order to
plot selected data parameters. Review this stored
information to aid in locating an intermittent
problem. Refer to the scan tool Users Guide fo
r
more information.
Important:
If the intermittent condition exists as a start and then
stall, test for DTCs relating to the vehicle theft deterrent
system. Test for improper installation of electrical
options such as lights, cellular phones, etc.
Any of the following may cause an intermittent MIL with
no stored DTC:
• The ECM grounds are loose or dirty. Refer to
Engine Controls Schematics.
• The MIL circuit intermittently shorted to ground.
• Electrical system interference caused by a
malfunctioning relay, ECM driven solenoid, o
r
switch. The electrical component can cause a
sharp electrical surge. Normally, the problem will
occur when the malfunctioning component is
operating.
• There is an open diode across the A/C
compressor clutch or any other open diodes.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1290 of 6020
6E-256 Engine Control System (4JH1)
Important:
The following symptom tables contain groups o
f
possible causes for each symptom. The order of these
procedures is not important. If the scan tool readings do
not indicate the problems, then proceed in a logical
order, easiest to check or most likely to cause first. In
order to determine if a specific vehicle is using a
particular system or component, refer to Engine
Controls Schematics for an application.
Use the following tables when diagnosing a symptom
complaint:
• Intermittent Conditions
• Hard Start
• Rough, Unstable, or Incorrect Idle and Stalling
• Cuts Out, Misses
• Surge/Chuggles
• Lack of Power, Sluggishness, or Sponginess
• Hesitation, Sag, Stumble
• Fuel Knock/Combustion Noise
• Poor Fuel Economy
• Excessive Smoke (Black Smoke)
• Excessive Smoke (W hite Smoke)
Intermittent Conditions
Checks Action
DEFINITION:The problem is not currently present but is indicated in DTC History.
OR
There is a customer complaint, but the symptom cannot currently be duplicated, if the problem is not DTC related.
Preliminary Checks • Refer to Symptoms – Engine Controls before starting.
Harness/Connector Many intermittent open or shorted circuits are affected by harness/connector
movement that is caused by vibration, engine torque, bumps/rough pavement, etc.
Test for this type of condition by performing the applicable procedure from the
following list:
• Move related connectors and wiring while monitoring the appropriate scan tool data.
• Move related connectors and wiring with the component commanded ON, and OFF,
with the scan tool. Observe the component operation.
• W ith the engine running, move related connectors and wiring while monitoring
engine operation.
If harness or connector movement affects the data displayed, component/system
operation, or engine operation, inspect and repair the harness/connections as
necessary.
Refer to Electrical Connections or W iring.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1291 of 6020
Engine Control System (4JH1) 6E-257
Checks Action
Electrical Connections or W iring Poor electrical connections, terminal tension or wiring problems cause most intermittent. To perform the following inspections:
• Inspect for poor mating of the connector halves, or terminals improperly seated in the
connector body.
• Inspect for improperly formed or damaged terminals. Test for poor terminal tension.
• Inspect for poor terminal to wire connections including terminals crimped over
insulation. This requires removing the terminal from the connector body.
• Inspect for corrosion/water intrusion. Pierced or damaged insulation can allow
moisture to enter the wiring. The conductor can corrode inside the insulation, with
little visible evidence. Look for swollen and stiff sections of wire in the suspect
circuits.
• Inspect for wires that are broken inside the insulation.
• Inspect the harness for pinched, cut or rubbed through wiring.
• Ensure that the wiring does not come in contact with hot exhaust components.
Control Module Power and Grounds
Component Power and Grounds Poor power or ground connections can cause widely varying symptoms.
• Test all control module power supply circuits. Many vehicles have multiple circuits
supplying power to the control module. Other components in the system may have
separate power supply circuits that may also need to be tested. Inspect connections
at the module/component connectors, fuses, and any intermediate connections
between the power source and the module/component. A test lamp or a DMM may
indicate that voltage is present, but neither tests the ability of the circuit to carry
sufficient current. Ensure that the circuit can carry the current necessary to operate
the component.
• Test all control module ground and system ground circuits. The control module may
have multiple ground circuits. Other components in the system may have separate
grounds that may also need to be tested. Inspect grounds for clean and tight
connections at the grounding point. Inspect the connections at the component and in
splice packs, where applicable. Ensure that the circuit can carry the current
necessary to operate the component.
Temperature Sensitivity • An intermittent condition may occur when a component/connection reaches normal
operating temperature. The condition may occur only when the
component/connection is cold, or only when the component/connection is hot.
• If the intermittent is related to heat, review the data for a relationship with the
following: - High ambient temperatures
- Under hood/engine generated heat
- Circuit generated heat due to a poor connection, or high electrical load
- Higher than normal load conditions, towing, etc.
• If the intermittent is related to cold, review the data for the following:
- Low ambient temperatures–In extremely low temperatures, ice may form in a connection or component. Test for water intrusion.
- The condition only occurs on a cold start.
- The condition goes away when the vehicle warms up.
• Information from the customer may help to determine if the trouble follows a pattern
that is temperature related.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1296 of 6020

6E-262 Engine Control System (4JH1)
Checks Action
Additional Checks •
Electromagnetic interference (EMI) on the reference circuit can cause an engine miss
condition. The scan tool can usually detect EMI by monitoring the engine speed. A
sudden increase in speed with little change in actual engine speed change indicates that
EMI is present. If a problem exists, check routing of high voltage components, such as
fuel injection solenoid valve wiring, near the sensor circuits.
• Inspect for faulty engine mounts.
• Inspect faulty crank pulley.
• Inspect faulty generator & A/C compressor.
• Inspect the generator output voltage. Repair if less than 9 volts or more than 16 volts.
• Inspect the EGR system operating correctly.
• Inspect the A/C operation.
Cut Out, Misses
Checks Action
DEFINITION:A constant jerking that follows the engine speed, usually more pronounced as the engine load increase. The
exhaust has a steady spitting sound at idle, low speed, or hard acceleration for the fuel starvation that can cause the engine to
cut-out.
Preliminary Check • Diagnostic System Check - Engine Controls.
• Inspect that the harness connectors are correctly connected.
• Inspect the engine control module (ECM) and fuel injection pump control unit (PCU)
grounds for being clean, tight, and in their proper locations.
• Inspect the scan tool Data List in this section.
• Inspect the Service Bulletins for ECM software updates.
Sensor Checks Inspect the engine control sensors for the following conditions. Refer to the scan tool
Data List in this section.
• Use the scan tool to observe the Accelerator Pedal Position. Accelerator Pedal
Position indicating angle parameter should change linearly from 0% to 100%
according to the accelerator pedal operation.
• Inspect the crankshaft position (CKP) sensor is tight and the flywheel circumference
is not damaged.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1297 of 6020
Engine Control System (4JH1) 6E-263
Checks Action
Fuel System Checks Inspect the fuel system for the following conditions. Refer to the Fuel System section.
• Inspect for water contamination in the fuel.
• Inspect for external fuel leaks or fuel leakage into the engine oil.
• Inspect the fuel lines between the fuel tank and fuel injection pump for tightness and
all fuel hoses for cuts, cracks and for the use of proper clamps.
Notice: The fuel system from the fuel tank(s) to the fuel injection pump is under a
slight vacuum with the engine running. As a result, air can enter the fuel system if
these connections are not tight. Air in the fuel system will cause fuel injection pump
internal pressure fluctuations especially at high engine speed and load.
• Inspect for air in the fuel system.
Notice: If many air bubbles appear in the fuel, check the fuel system line connections
between the fuel tank and the fuel injection pump for tightness and all fuel hoses for
cuts, cracks and for the use of proper clamps.
a. Remove the fuel hose that connects to the fuel injection pump suction side.
b. Substitute a clear hose.
Notice: A hose must be cleaned.
c. Connect the clear hose to the fuel injection pump.
d. Bleed the fuel system.
e. Let the engine run at idle for at least 2 minutes.
f. Accelerator the engine between idle and W .O.T. (accelerator pedal full travel) many times while observing the clear hose.
• Inspect the fuel tank vent hose for a plugged or kinked.
• Inspect inside the fuel tank for any foreign material that may be getting drawn into
the fuel line pickup causing a blocked condition. Draw fuel from the fuel tank at the
fuel line (as close to the fuel tank as possible) going to the fuel pickup tube to verify a
clean stream of fuel comes out (use the hand-held vacuum pump 5-8840-0279-0/J-
23738-A with a clear hose or equivalent). This will ensure the fuel pickup tube is not
cracked drawing air into the fuel line.
• Inspect the fuel injection pump operation.
Notice: The fuel injection pump must be timed to the engine.
Inspect the eye bolt for any type of restriction or collapsed gauze filter.
Notice: If any type of restriction found, check for a condition that causes contaminated
fuel, such as the customer is using an aftermarket fuel filter or extended maintenance
interval. Also inspect fuel waxing or icing that is caused by an incorrect fuel type used
in winter season or water intrusion in the fuel system.
Air Intake System Checks Inspect the air intake system for the following conditions.
• Inspect the air cleaner and air intake ducts for a restriction, holes, or leaks.
• Inspect for a restriction in the turbocharger inlet duct.
• Inspect for a restriction or deposit in the intake throttle bore.
• Inspect for a restriction or leak in the intake manifold.
• Inspect for a restriction or damage at mass air flow (MAF) sensor.
Additional Checks •
Inspect the generator output voltage. Repair if less than 9 volts or more than 16
volts.
• Electromagnetic interference (EMI) on the reference circuit can cause an engine
miss condition. The scan tool can usually detect EMI by monitoring the engine
speed. A sudden increase in speed with little change in actual engine speed change
indicates that EMI is present. If a problem exists, check routing of high voltage
components, such as fuel injection solenoid wiring, near the sensor circuits.
Surges/Chuggles
Checks Action
DIFINITION:The engine has a power variation under a steady throttle or cruise. The vehicle seems to speed up and slow down
with no change in the accelerator pedal.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1371 of 6020
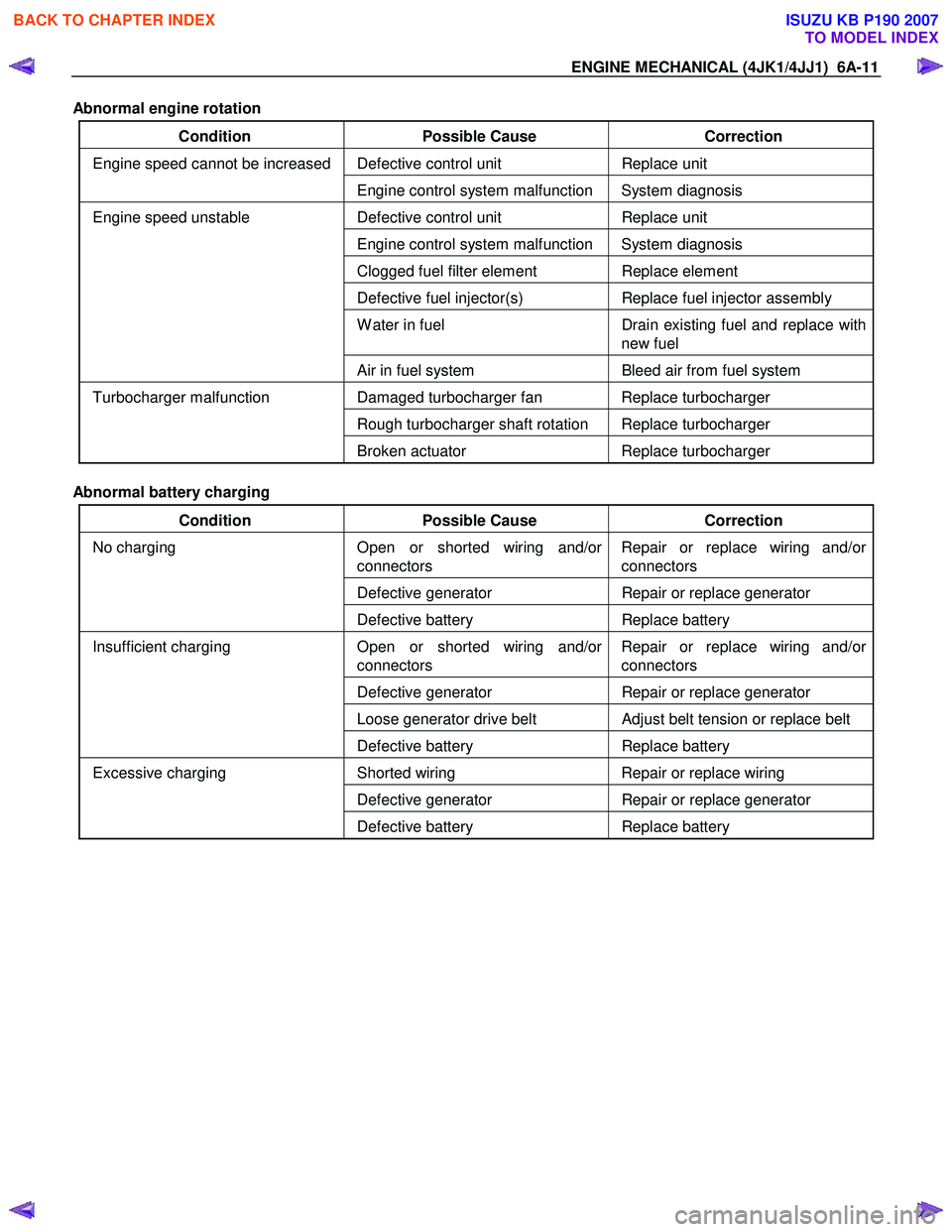
ENGINE MECHANICAL (4JK1/4JJ1) 6A-11
Abnormal engine rotation
Condition Possible Cause Correction
Defective control unit Replace unit Engine speed cannot be increased
Engine control system malfunction System diagnosis
Defective control unit Replace unit
Engine control system malfunction System diagnosis
Clogged fuel filter element Replace element
Defective fuel injector(s) Replace fuel injector assembly
W ater in fuel Drain existing fuel and replace with
new fuel
Engine speed unstable
Air in fuel system Bleed air from fuel system
Damaged turbocharger fan Replace turbocharger
Rough turbocharger shaft rotation Replace turbocharger
Turbocharger malfunction
Broken actuator Replace turbocharger
Abnormal battery charging
Condition Possible Cause Correction
Open or shorted wiring and/or
connectors Repair or replace wiring and/or
connectors
Defective generator Repair or replace generator
No charging
Defective battery Replace battery
Open or shorted wiring and/or
connectors Repair or replace wiring and/or
connectors
Defective generator Repair or replace generator
Loose generator drive belt Adjust belt tension or replace belt
Insufficient charging
Defective battery Replace battery
Shorted wiring Repair or replace wiring
Defective generator Repair or replace generator
Excessive charging
Defective battery Replace battery
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007