oil JEEP CHEROKEE 1995 Service Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JEEP, Model Year: 1995, Model line: CHEROKEE, Model: JEEP CHEROKEE 1995Pages: 2198, PDF Size: 82.83 MB
Page 98 of 2198

MODEL 35 AXLE
INDEX
page page
Axle Shaft............................... 16
Axle Shaft Seal and Bearing................. 17
Backlash and Contact Pattern Analysis......... 27
Cleaning/Inspection........................ 20
Differential Assembly....................... 21
Differential Disassembly.................... 18
Differential Measurement and Installation........ 25
Differential Removal....................... 18
Drive Axle Assembly ReplacementÐXJ Vehicles . . 14Drive Axle Assembly ReplacementÐYJ Vehicles . . 14
Final Assembly........................... 29
General Information....................... 13
Lubricant Change......................... 13
Lubricant Specifications..................... 13
Pinion Gear Depth Information............... 21
Pinion Measurement and Assembly............ 22
Pinion Removal/Disassembly................. 19
Pinion Shaft Seal Replacement............... 15
GENERAL INFORMATION
The Model 35 housing has an iron center casting
(differential housing) with axle shaft tubes extending
from either side. The tubes are pressed into and
welded to the differential housing to form a one-piece
axle housing.
The integral type housing, hypoid gear design has
the centerline of the pinion set below the centerline
of the ring gear.
The axle has a vent hose to relieve internal pres-
sure caused by lubricant vaporization and internal
expansion.
The axles are equipped with semi-floating axle
shafts, meaning that loads are supported by the axle
shaft and bearings. The axle shafts are retained by
C-clips in the differential side gears.
The cover provides a means for servicing the differ-
ential without removing the axle.
Axles may be equipped with drum or disc brakes.
The axles that are equipped with ABS brake have a
tone ring pressed on the axle shaft. Use care when
removing axle shafts as NOT to damage the tone
wheel or the sensor.
The Model 35 axle has the assembly part number
and gear ratio listed on a tag. The tag is attached to
the housing cover. Build date identification codes are
stamped on the axle shaft tube cover side.
The differential case is a one-piece design. The dif-
ferential pinion mate shaft is retained with a
threaded roll pin. Differential bearing preload and
ring gear backlash is adjusted by the use of spacer
shims. Pinion bearing preload is set and maintained
by the use of a collapsible spacer.
For complete drive axle assembly removal
and installation refer to Drive Axle Assembly
Replacement in this Group.
LUBRICANT SPECIFICATIONS
Multi-purpose, hypoid gear lubricant should be
used for Model 35 axle. The lubricant should haveMIL-L-2105C and API GL 5 quality specifications.
MOPAR Hypoid Gear Lubricant conforms to both of
these specifications.
²Lubricant for Model 35 axle is a thermally stable
SAE 80W-90 gear lubricant.
²Lubricant for Model 35 axle with Trailer Tow is
SAE 75W-140 SYNTHETIC gear lubricant.
²Trac-Lok differentials add 4 oz. of friction modifier.
²Lubricant quantity is 1.66 L (3.50 pts.).
Refer to Group 0, Lubrication and Maintenance for
additional information.
CAUTION: If axle is submerged in water, lubricant
must be replaced immediately to avoid possible
premature axle failure.
LUBRICANT CHANGE
The gear lubricant will drain quicker if the vehicle
has been recently driven.
(1) Raise and support the vehicle.
(2) Remove the lubricant fill hole plug from the dif-
ferential housing cover.
(3) Remove the differential housing cover and
drain the lubricant from the housing.
(4) Clean the housing cavity with a flushing oil,
light engine oil or lint free cloth.Do not use water,
steam, kerosene or gasoline for cleaning.
(5) Remove the sealant from the housing and cover
surfaces.
(6) Apply a bead of MOPARtSilicone Rubber Seal-
ant to the housing cover (Fig. 1).Allow the sealant
to cure for a few minutes.
Install the housing cover within 5 minutes af-
ter applying the sealant. If not installed the
sealant must be removed and another bead ap-
plied.
(7) Install the cover and any identification tag.
Tighten the cover bolts to 41 Nzm (30 ft. lbs.) torque.
(8) Refill differential with Mopar Hypoid Gear Lu-
bricant to bottom of the fill plug hole.
JREAR SUSPENSION AND AXLES 3 - 13
Page 104 of 2198
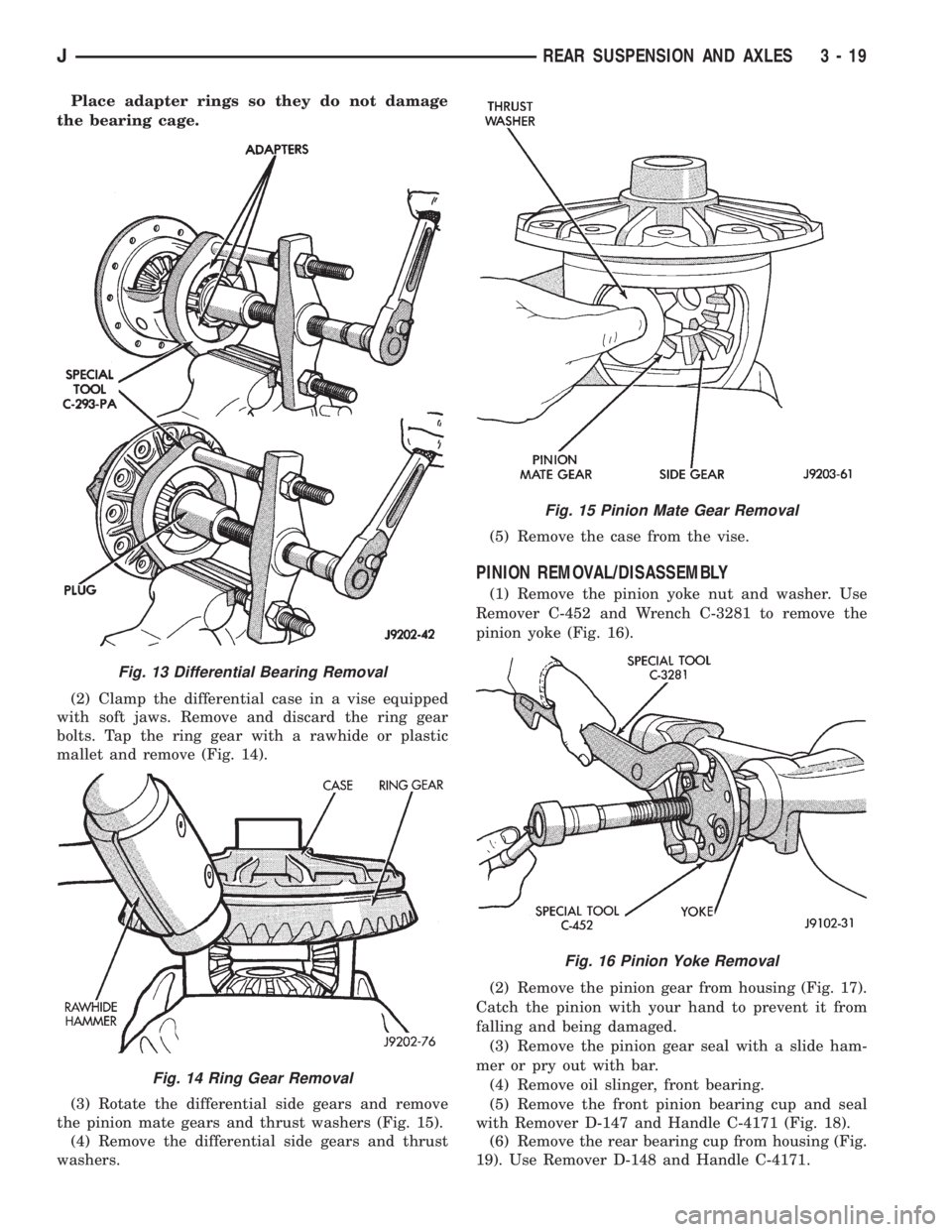
Place adapter rings so they do not damage
the bearing cage.
(2) Clamp the differential case in a vise equipped
with soft jaws. Remove and discard the ring gear
bolts. Tap the ring gear with a rawhide or plastic
mallet and remove (Fig. 14).
(3) Rotate the differential side gears and remove
the pinion mate gears and thrust washers (Fig. 15).
(4) Remove the differential side gears and thrust
washers.(5) Remove the case from the vise.
PINION REMOVAL/DISASSEMBLY
(1) Remove the pinion yoke nut and washer. Use
Remover C-452 and Wrench C-3281 to remove the
pinion yoke (Fig. 16).
(2) Remove the pinion gear from housing (Fig. 17).
Catch the pinion with your hand to prevent it from
falling and being damaged.
(3) Remove the pinion gear seal with a slide ham-
mer or pry out with bar.
(4) Remove oil slinger, front bearing.
(5) Remove the front pinion bearing cup and seal
with Remover D-147 and Handle C-4171 (Fig. 18).
(6) Remove the rear bearing cup from housing (Fig.
19). Use Remover D-148 and Handle C-4171.
Fig. 13 Differential Bearing Removal
Fig. 14 Ring Gear Removal
Fig. 15 Pinion Mate Gear Removal
Fig. 16 Pinion Yoke Removal
JREAR SUSPENSION AND AXLES 3 - 19
Page 105 of 2198
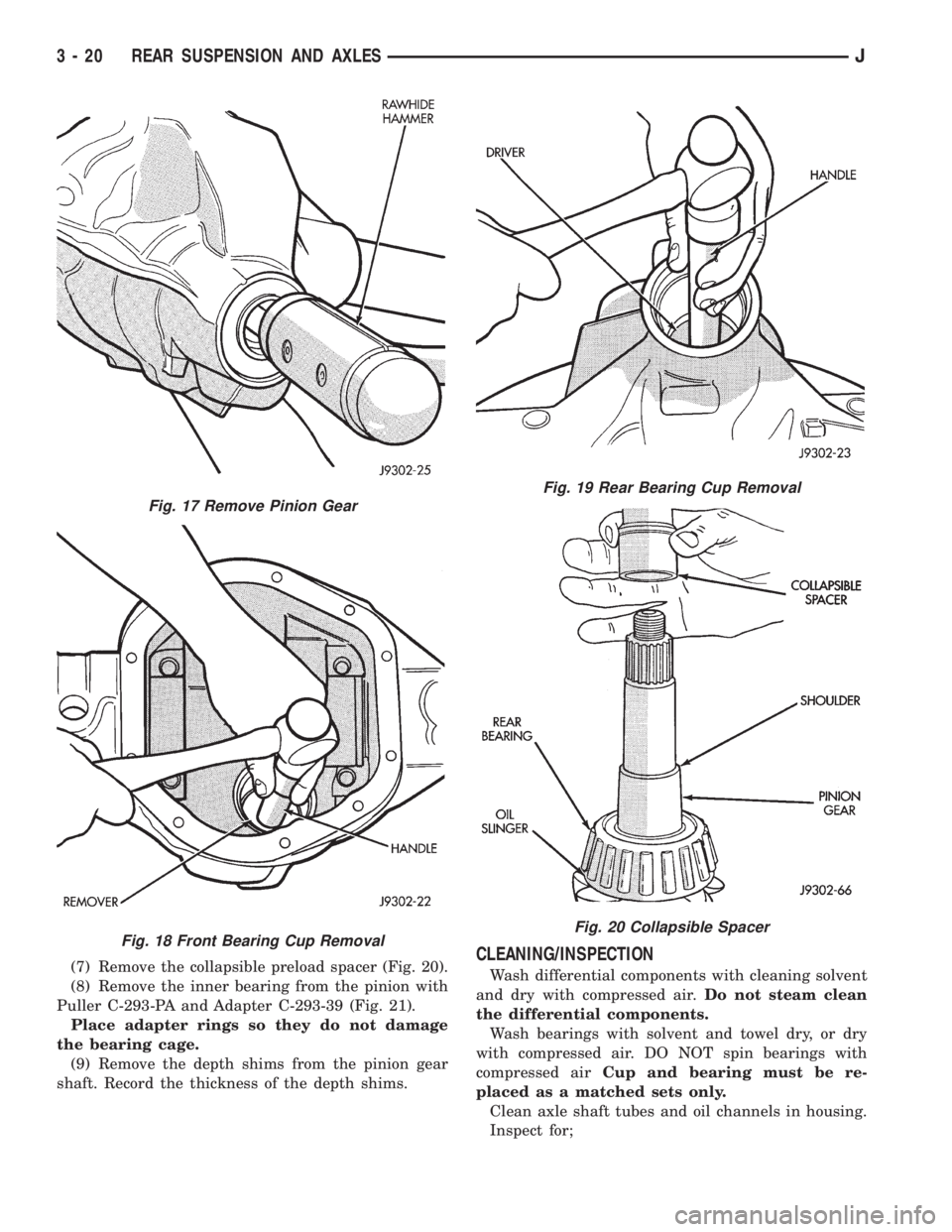
(7) Remove the collapsible preload spacer (Fig. 20).
(8) Remove the inner bearing from the pinion with
Puller C-293-PA and Adapter C-293-39 (Fig. 21).
Place adapter rings so they do not damage
the bearing cage.
(9) Remove the depth shims from the pinion gear
shaft. Record the thickness of the depth shims.CLEANING/INSPECTION
Wash differential components with cleaning solvent
and dry with compressed air.Do not steam clean
the differential components.
Wash bearings with solvent and towel dry, or dry
with compressed air. DO NOT spin bearings with
compressed airCup and bearing must be re-
placed as a matched sets only.
Clean axle shaft tubes and oil channels in housing.
Inspect for;
Fig. 17 Remove Pinion Gear
Fig. 18 Front Bearing Cup Removal
Fig. 19 Rear Bearing Cup Removal
Fig. 20 Collapsible Spacer
3 - 20 REAR SUSPENSION AND AXLESJ
Page 108 of 2198
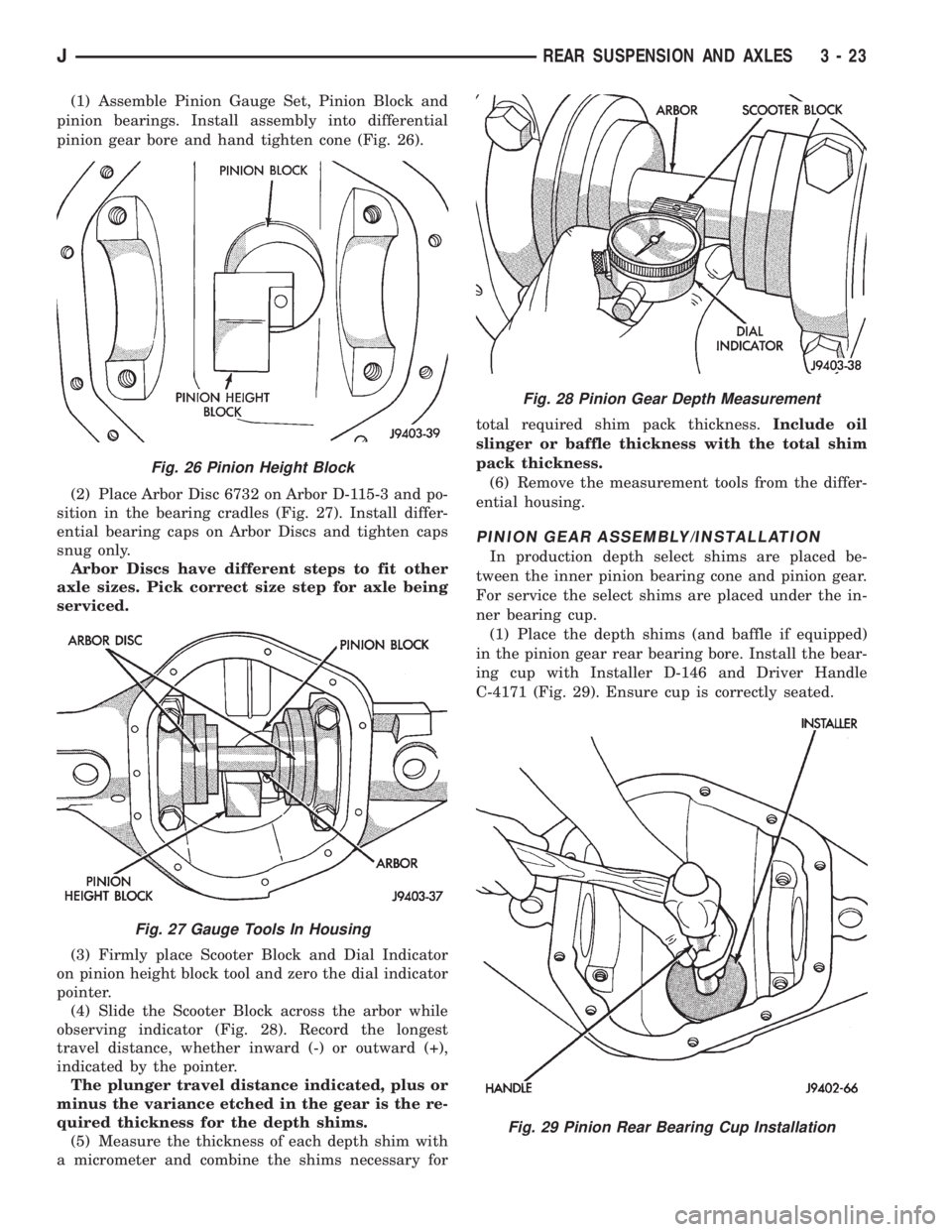
(1) Assemble Pinion Gauge Set, Pinion Block and
pinion bearings. Install assembly into differential
pinion gear bore and hand tighten cone (Fig. 26).
(2) Place Arbor Disc 6732 on Arbor D-115-3 and po-
sition in the bearing cradles (Fig. 27). Install differ-
ential bearing caps on Arbor Discs and tighten caps
snug only.
Arbor Discs have different steps to fit other
axle sizes. Pick correct size step for axle being
serviced.
(3) Firmly place Scooter Block and Dial Indicator
on pinion height block tool and zero the dial indicator
pointer.
(4) Slide the Scooter Block across the arbor while
observing indicator (Fig. 28). Record the longest
travel distance, whether inward (-) or outward (+),
indicated by the pointer.
The plunger travel distance indicated, plus or
minus the variance etched in the gear is the re-
quired thickness for the depth shims.
(5) Measure the thickness of each depth shim with
a micrometer and combine the shims necessary fortotal required shim pack thickness.Include oil
slinger or baffle thickness with the total shim
pack thickness.
(6) Remove the measurement tools from the differ-
ential housing.
PINION GEAR ASSEMBLY/INSTALLATION
In production depth select shims are placed be-
tween the inner pinion bearing cone and pinion gear.
For service the select shims are placed under the in-
ner bearing cup.
(1) Place the depth shims (and baffle if equipped)
in the pinion gear rear bearing bore. Install the bear-
ing cup with Installer D-146 and Driver Handle
C-4171 (Fig. 29). Ensure cup is correctly seated.
Fig. 26 Pinion Height Block
Fig. 27 Gauge Tools In Housing
Fig. 28 Pinion Gear Depth Measurement
Fig. 29 Pinion Rear Bearing Cup Installation
JREAR SUSPENSION AND AXLES 3 - 23
Page 109 of 2198
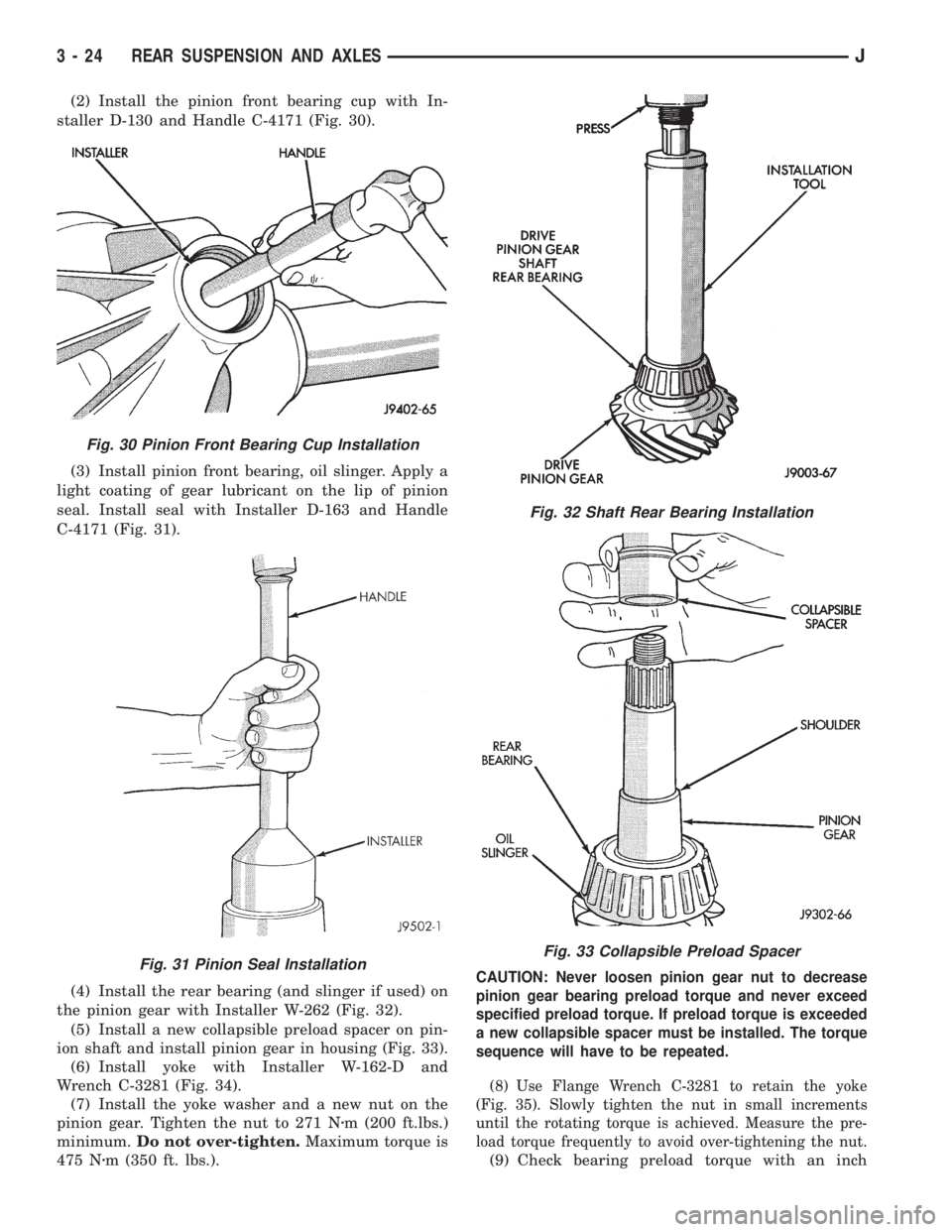
(2) Install the pinion front bearing cup with In-
staller D-130 and Handle C-4171 (Fig. 30).
(3) Install pinion front bearing, oil slinger. Apply a
light coating of gear lubricant on the lip of pinion
seal. Install seal with Installer D-163 and Handle
C-4171 (Fig. 31).
(4) Install the rear bearing (and slinger if used) on
the pinion gear with Installer W-262 (Fig. 32).
(5) Install a new collapsible preload spacer on pin-
ion shaft and install pinion gear in housing (Fig. 33).
(6) Install yoke with Installer W-162-D and
Wrench C-3281 (Fig. 34).
(7) Install the yoke washer and a new nut on the
pinion gear. Tighten the nut to 271 Nzm (200 ft.lbs.)
minimum.Do not over-tighten.Maximum torque is
475 Nzm (350 ft. lbs.).
CAUTION: Never loosen pinion gear nut to decrease
pinion gear bearing preload torque and never exceed
specified preload torque. If preload torque is exceeded
a new collapsible spacer must be installed. The torque
sequence will have to be repeated.
(8) Use Flange Wrench C-3281 to retain the yoke
(Fig. 35). Slowly tighten the nut in small increments
until the rotating torque is achieved. Measure the pre-
load torque frequently to avoid over-tightening the nut.
(9) Check bearing preload torque with an inch
Fig. 30 Pinion Front Bearing Cup Installation
Fig. 31 Pinion Seal Installation
Fig. 32 Shaft Rear Bearing Installation
Fig. 33 Collapsible Preload Spacer
3 - 24 REAR SUSPENSION AND AXLESJ
Page 116 of 2198

LUBRICANT SPECIFICATIONS
Multi-purpose, hypoid gear lubricant should be
used in the 8 1/4 inch axle. The lubricant should
have MIL-L-2105C and API GL 5 quality specifica-
tions. MOPARtHypoid Gear Lubricant conforms to
both of these specifications.
²The factory installed lubricant for the 8 1/4 inch
rear axle is SAE 80W 90 gear lubricant.
²The factory installed lubricant quantity is 6762
fluid oz.
CAUTION: Overfilling the differential can result in
lubricant foaming and overheating.
Refer to Group 0, Lubrication and Maintenance for
additional information.
CAUTION: If axle is submerged in water, lubricant
must be replaced immediately to avoid possible
premature axle failure.
DRIVE AXLE ASSEMBLY REPLACEMENTÐXJ
VEHICLES
REMOVAL
(1) Raise the vehicle. Position support stands un-
der the frame rails slightly in front the springs.
(2) Remove the rear wheels.
(3) Mark the drive shaft yoke and axle pinion yoke
for alignment reference. Disconnect the drive shaft
from the axle.
(4) Disconnect the axle vent hose.
(5) Disconnect the parking brake cables at the
equalizer or backing plate.
(6) Disconnect the shock absorbers from the axle
brackets.
(7) Disconnect the brake hose at the axle junction
block.Do not disconnect the wheel cylinder tub-
ing fittings.
(8) If equipped, disconnect ABS wiring connections
at the axle.
(9) Support the axle with a hydraulic jack under
the differential.
(10) Remove the spring U-bolts from the plate
brackets.
(11) Lower the jack enough to remove the axle.
INSTALLATION
CAUTION: Suspension components with rubber
bushings should be tightened with the vehicle at
normal height. It is important to have the springs
supporting the weight of the vehicle when the fas-
teners are torqued. If springs are not at their normal
ride position, vehicle ride comfort could be affected
and premature bushing wear may occur. Rubber
bushings must never be lubricated.(1) Support the axle on a hydraulic jack under the
differential. Position the axle under the vehicle.
(2) Raise the axle and align the spring center bolts
with the locating holes in the axle pads and plate
brackets.
(3) Install the spring U-bolts through the plate
brackets and tighten to 70 Nzm (52 ft. lbs.) torque.
(4) Install ABS wiring connections (if equipped) at
the axle.
(5) Connect the brake hose at the axle junction
block.
(6) Install the shock absorbers to the axle brackets
and tighten to 62 Nzm (46 ft. lbs.) torque.
(7) Connect the parking brake cables at the equal-
izer or backing plate.
(8) Connect the vent hose to the tube fitting.
(9) Align the reference marks and connect the
drive shaft to the axle yoke. Tighten the U-joint
clamp bolts to 19 Nzm (14 ft. lbs.) torque.
(10) Check differential lubricant and add if neces-
sary.
(11) Install the wheel and tire.
(12) Bleed the brakes.
(13) Remove the supports and lower the vehicle.
LUBRICANT CHANGE
The gear lubricant will drain quicker if the vehicle
has been recently driven.
(1) Raise and support the vehicle.
(2) Remove the lubricant fill hole plug from the dif-
ferential housing cover.
(3) Remove the differential housing cover and
drain the lubricant from the housing.
(4) Clean the housing cavity with a flushing oil,
light engine oil or lint free cloth.Do not use water,
steam, kerosene or gasoline for cleaning.
(5) Remove the sealant from the housing and cover
surfaces. Use solvent to clean the mating surfaces.
(6) Apply a bead of MOPARtSilicone Rubber Seal-
ant to the housing cover (Fig. 2). Allow the sealant to
cure for a few minutes.
Install the housing cover within 5 minutes after
applying the sealant. If not installed the sealant
must be removed and another bead applied.
(7) Install the cover and any identification tag.
Tighten the cover bolts in a criss-cross pattern to 47
Nzm (35 ft. lbs.) torque.
(8) Refill the differential with Mopar Hypoid Gear
Lubricant 13 mm (1/2 in.) below the fill plug hole.
With Trac-Lok differentials, add a container of Mopar
Hypoid Gear Lubricant Additive.
CAUTION: Overfilling the differential can result in
lubricant foaming and overheating.
(9) Install the fill hole plug and lower the vehicle.
JREAR SUSPENSION AND AXLES 3 - 31
Page 139 of 2198

ABS SYSTEM CHANGES
A different master cylinder, power brake booster,
and HCU are used in the 1995 Jeep ABS system.
The master cylinder reservoir has a single filler cap
and is no longer interconnected with the HCU. The
new HCU has built-in accumulators. The pedal travel
sensor has been eliminated and a new dual dia-
phragm power brake booster is used.
BRAKE FLUID/LUBRICANTS/CLEANING SOLVENTS
Recommended fluid for all Jeep vehicles is Mopar
DOT 3 brake fluid, or an equivalent meeting SAE
J1703 and DOT 3 standards.
Use Mopar Multi Mileage grease to lubricate drum
brake pivot pins and rear brakeshoe contact points
on the support plates. Use GE 661, or Dow 111 sili-
cone grease on caliper bushings and mounting bolts.
Use fresh brake fluid or Mopar brake cleaner to
clean or flush brake system components. These are
the only cleaning materials recommended.
CAUTION: Never use gasoline, kerosene, methyl or
isopropyl alcohol, paint thinner, or any fluid con-
taining mineral oil to clean brake parts. These fluids
damage rubber cups and seals. If system contami-
nation is suspected, check the fluid for dirt, discol-
oration, or separation into distinct layers. Drain and
flush the system with new brake fluid if contamina-
tion is suspected.
JEEP BODY CODE LETTERS
The body/model identification code letters for Jeep
vehicles are as follows:²Code letters XJ: Cherokee
²Code letters YJ: Wrangler/YJ
The code letters are used throughout this group to
simplify model identification and component applica-
tion.
BRAKE SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
WARNING: ALTHOUGH FACTORY INSTALLED
BRAKELINING ON JEEP VEHICLES IS MADE FROM
ASBESTOS FREE MATERIALS, SOME AFTER MAR-
KET BRAKELINING MAY CONTAIN ASBESTOS. THIS
SHOULD BE TAKEN INTO ACCOUNT WHEN RE-
PAIRING A VEHICLE WITH PRIOR BRAKE SERVICE.
WEAR A RESPIRATOR WHEN CLEANING BRAKE
COMPONENTS AS ASBESTOS FIBERS CAN BE A
HEALTH HAZARD. NEVER CLEAN WHEEL BRAKE
COMPONENTS WITH COMPRESSED AIR. USE A
VACUUM CLEANER SPECIFICALLY DESIGNED FOR
REMOVING BRAKE DUST. IF A VACUUM CLEANER
IS NOT AVAILABLE, CLEAN THE PARTS WITH WA-
TER DAMPENED SHOP RAGS. DO NOT CREATE
DUST BY SANDING BRAKELINING. DISPOSE OF
ALL DUST AND DIRT SUSPECTED OF CONTAINING
ASBESTOS FIBERS IN SEALED BAGS OR CON-
TAINERS. FOLLOW ALL SAFETY PRACTICES REC-
OMMENDED BY THE OCCUPATIONAL SAFETY AND
HEALTH ADMINISTRATION (OSHA) AND THE ENVI-
RONMENTAL PROTECTION AGENCY (EPA), FOR
HANDLING AND DISPOSAL OF ASBESTOS.
5 - 2 BRAKESJ
Page 141 of 2198

SERVICE BRAKE DIAGNOSIS
INDEX
page page
Brake Drag............................... 6
Brake Fade.............................. 6
Brake Fluid Contamination................... 7
Brake Noise.............................. 7
Brake Pull............................... 6
Brake Warning Light Operation................ 5
Brakes Do Not Hold After Driving Through Deep
Water Puddles........................... 7
Component Inspection...................... 5
Contaminated Brakelining.................... 7
Diagnosing Parking Brake Malfunctions.......... 8
Diagnosis Procedures....................... 4
General Information........................ 4Hard Pedal or High Pedal Effort............... 6
Low Pedal............................... 5
Master Cylinder/Power Booster Test............ 8
Pedal Falls Away.......................... 5
Pedal Pulsation (Non-ABS Brakes Only)......... 6
Power Booster Check Valve Test............... 9
Power Booster Vacuum Test.................. 9
Preliminary Brake Check..................... 4
Rear Brake Grab.......................... 7
Road Testing............................. 5
Spongy Pedal............................. 5
Wheel and Tire Problems.................... 7
GENERAL INFORMATION
The diagnosis information in this section covers
service brake components which include:
²disc brake calipers
²disc brakeshoes
²drum brake wheel cylinders
²drum brakeshoes and brake drums
²drum brake support plates
²parking brake mechanism
²master cylinder/combination valve
²vacuum power brake booster
²brake pedal and brakelight switch
²brake warning light
DIAGNOSIS PROCEDURES
Service brake diagnosis involves determining if a
problem is related to a mechanical, hydraulic or vac-
uum operated component. A preliminary brake check,
followed by road testing and component inspection
are needed to determine a problem cause.
Road testing will either verify proper brake opera-
tion or confirm the existence of a problem. Compo-
nent inspection will, in most cases, identify the
actual part responsible for a problem.
The first diagnosis step is the preliminary brake
check. This involves inspecting fluid level, parking
brake action, wheel and tire condition, checking for
obvious leaks or component damage and testing
brake pedal response. A road test will confirm or
deny the existence of a problem. The final diagnosis
procedure involves road test analysis and a visual in-
spection of brake components.
PRELIMINARY BRAKE CHECK
(1) If amber ABS light is illuminated, refer to ABS
Brake System Diagnosis. If red warning light is illu-
minated, or if neither warning light is illuminated,
continue with brake check.(2) Inspect condition of tires and wheels. Damaged
wheels and worn, damaged, or underinflated tires
can cause pull, shudder, tramp and a condition simi-
lar to grab.
(3) If complaint was based on noise when braking,
check suspension components. Jounce front and rear
of vehicle and listen for noise that might be caused
by loose, worn, or damaged suspension or steering
components.
(4) Inspect brake fluid level:
(a) If vehicle has one-piece master cylinder, fluid
level should be within 6 mm (1/4 in.) of reservoir
rim.
(b) If vehicle has nylon reservoir with single
filler cap, correct level is to FULL mark on side of
reservoir. Acceptable level is between FULL and
ADD marks.
(c) Remember that fluid level in the reservoir
compartments will decrease in proportion to nor-
mal lining wear. However, if fluid level is abnor-
mally low, look for leaks at calipers, wheel
cylinders, brakelines and master cylinder.
(5) Inspect brake fluid condition:
(a) Fluid should be free of foreign material.Note
that brake fluid tends to darken over time.
This is normal and should not be mistaken for
contamination. If fluid is clear of foreign ma-
terial, it is OK.
(b) If fluid is highly discolored, or appears to con-
tain foreign material, drain out a sample with a
clean suction gun. Pour sample in a glass container
and note condition described in step (c).
(c) If fluid separates into layers, obviously con-
tains oil, or a substance other than brake fluid,
system seals and cups will have to be replaced and
hydraulic system flushed.
(6) Check parking brake operation. Verify free
movement and full release of cables and foot pedal or
5 - 4 SERVICE BRAKE DIAGNOSISJ
Page 144 of 2198

fied. This causes pull to switch direction in favor of
the brake unit that is functioning normally.
When diagnosing a change in pull condition, re-
member that pull will return to the original direction
if the dragging brake unit is allowed to cool down
(and is not seriously damaged).
REAR BRAKE GRAB
Rear grab (or pull) is usually caused by contami-
nated lining, bent or binding shoes and support
plates, or improperly assembled components. This is
particularly true when only one rear wheel is in-
volved. However, when both rear wheels are affected,
the master cylinder could be at fault.
BRAKES DO NOT HOLD AFTER DRIVING THROUGH
DEEP WATER PUDDLES
This condition is caused by water soaked lining. If
the lining is only wet, it can be dried by driving with
the brakes lightly applied for a mile or two. However,
if the lining is both wet and dirty, disassembly and
cleaning will be necessary.
CONTAMINATED BRAKELINING
Brakelining contaminated by water is salvageable.
The lining can either be air dried or dried using heat.
In cases where brakelining is contaminated by oil,
grease, or brake fluid, the lining should be replaced.
Replacement is especially necessary when fluids/lu-
bricants have actually soaked into the lining mate-
rial. However, grease or dirt that gets onto the lining
surface (from handling) during brake repairs, can be
cleaned off. Spray the lining surface clean with Mo-
par brake cleaner.
BRAKE FLUID CONTAMINATION
There are two basic causes of brake fluid contami-
nation. The first involves allowing dirt, debris, or
other materials to enter the cylinder reservoirs when
the cover is off. The second involves adding non-rec-
ommended fluids to the cylinder reservoirs.
Brake fluid contaminated with only dirt, or debris
usually retains a normal appearance. In some cases,
the foreign material will remain suspended in the
fluid and be visible. The fluid and foreign material
can be removed from the reservoir with a suction gun
but only if the brakes have not been applied. If the
brakes are applied after contamination, system flush-
ing will be required. The master cylinder may also
have to be disassembled, cleaned and the piston seals
replaced. Foreign material lodged in the reservoir
compensator/return ports can cause brake drag by re-
stricting fluid return after brake application.
Brake fluid contaminated by a non-recommended
fluid may appear discolored, milky, oily looking, or
foamy. However, remember that brake fluid will
darken in time and occasionally be cloudy in appear-ance. These are normal conditions and should not be
mistaken for contamination.
If some type of oil has been added to the system,
the fluid will separate into distinct layers. To verify
this, drain off a sample with a clean suction gun.
Then pour the sample into a glass container and ob-
serve fluid action. If the fluid separates into distinct
layers, it is definitely contaminated.
The only real correction for contamination by non-
recommended fluid is to flush the entire hydraulic
system and replace all the seals.
BRAKE NOISE
Squeak/Squeal
Factory installed brakelining is made from as-
bestos free materials. These materials have dif-
ferent operating characteristics than previous
lining material. Under certain conditions, as-
bestos free lining may generate some squeak,
groan or chirp noise. This noise is considered
normal and does not indicate a problem. The
only time inspection is necessary, is when noise
becomes constant or when grinding, scraping
noises occur.
Constant brake squeak or squeal may be due to lin-
ings that are wet or contaminated with brake fluid,
grease, or oil. Glazed linings, rotors/drums with hard
spots, and dirt/foreign material embedded in the
brake lining also cause squeak. Loud squeak, squeal,
scraping, or grinding sounds are a sign of severely
worn brake lining. If the lining has worn completely
through in spots, metal-to-metal contact occurs.
Thump/Clunk
Thumping or clunk noises during braking are fre-
quentlynotcaused by brake components. In many
cases, such noises are caused by loose or damaged
steering, suspension, or engine components. However,
calipers that bind on the slide surfaces can generate
a thump or clunk noise. In addition, worn out, im-
properly adjusted, or improperly assembled rear
brakeshoes can also produce a thump noise.
Chatter/Shudder
Brake chatter, or shudder is usually caused by
loose or worn components, or glazed/burnt lining. Ro-
tors with hard spots can also contribute to chatter.
Additional causes of chatter are out of tolerance ro-
tors, brake lining not securely attached to the shoes,
loose wheel bearings and contaminated brake lining.
WHEEL AND TIRE PROBLEMS
Some conditions attributed to brake components
may actually be caused by a wheel or tire problem.
A damaged wheel can cause shudder, vibration and
pull. A worn or damaged tire can also cause pull.
Severely worn tires with very little tread left can
JSERVICE BRAKE DIAGNOSIS 5 - 7
Page 147 of 2198

BRAKE FLUIDÐBRAKE BLEEDINGÐBRAKELINES AND HOSES
INDEX
page page
Brake Bleeding (With ABS Brakes)............ 11
Brake Bleeding (With Standard Brakes)......... 11
Brake Bleeding Recommendations............ 10
Brake Fluid Contamination.................. 10Brake Fluid Level......................... 10
Brakeline Charts.......................... 12
Brakelines and Hoses...................... 12
Recommended Brake Fluid.................. 10
RECOMMENDED BRAKE FLUID
Recommended brake fluid for Jeep vehicles is Mo-
par brake fluid, or an equivalent fluid meeting SAE
J1703 and DOT 3 standards. The recommendation
applies to models with standard or ABS brakes.
Use new brake fluid to top off the master cyl-
inder or refill the system. Never use reclaimed
fluid, fluid not meeting the SAE/DOT standards
or fluid from an unsealed container. Do not use
fluid from any container that has been left
open for any length of time. Fluid in open con-
tainers can absorb moisture.
BRAKE FLUID LEVEL
Always clean the master cylinder reservoir and
cover or cap before adding fluid. This avoids having
dirt from the cap or reservoir exterior fall into the
fluid.
If the vehicle has a one piece master cylinder, cor-
rect fluid level is to within 6 mm (1/4 in.) of the res-
ervoir rim (Fig. 1).
If the vehicle has a plastic reservoir with a single
cap, preferred fluid level is to the FULL mark (Fig.
2).
CAUTION: Do not allow brake fluid to contact
painted surfaces. Fluid spills must be cleaned up
immediately as brake fluid can loosen and lift paint.
BRAKE FLUID CONTAMINATION
Oil in the fluid will cause brake system rubber
seals to soften and swell. The seals may also become
porous and begin to deteriorate.If fluid contamination is suspected, drain off a sam-
ple from the master cylinder. A suction gun or similar
device can be used for this purpose.
Empty the drained fluid into a glass container.
Contaminants in the fluid will cause the fluid to sep-
arate into distinct layers. If contamination has oc-
curred, the system rubber seals, hoses and cups must
be replaced and the system thoroughly flushed with
clean brake fluid.
BRAKE BLEEDING RECOMMENDATIONS
²Use Mopar DOT 3 brake fluid, or an equivalent
meeting SAE/DOT standards J1703-F and DOT 3, to
fill and bleed the system.
²Bleeding can be performed manually, or with vac-
uum or pressure equipment. Vacuum and pressure
bleeding equipment are both available. Both types
are effective but should be used only as described in
the manufacturers instructions.
²Do not allow the master cylinder to run out of
fluid when bleeding the brakes. An empty cylinder
will allow additional air to be drawn into the system.
Check fluid level frequently during bleed operations.
²Do not pump the brake pedal at any time while
bleeding. Air in system will be compressed into small
Fig. 1 Correct Fluid Level (4-Cylinder Models)
Fig. 2 Correct Fluid Level (All Except 4-Cylinder
Models)
5 - 10 BRAKE FLUIDÐBRAKE BLEEDINGÐBRAKELINES AND HOSESJ