pin out JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE 2002 WJ / 2.G Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JEEP, Model Year: 2002, Model line: GRAND CHEROKEE, Model: JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE 2002 WJ / 2.GPages: 2199, PDF Size: 76.01 MB
Page 2093 of 2199

gap should be between 0.35 to 0.65 millimeter (0.014
to 0.026 inch). If the proper air gap is not obtained,
add or subtract shims as needed until the desired air
gap is obtained.
(9) Install the compressor shaft bolt. Tighten the
bolt to 13 N´m (115 in. lbs.).
NOTE: The shims may compress after tightening
the shaft bolt. Check the air gap in four or more
places to verify the air gap is still correct. Spin the
pulley before performing a final check of the air
gap.
(10) To complete the installation, (Refer to 24 -
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING/A/C
COMPRESSOR - INSTALLATION)
A/C COMPRESSOR CLUTCH
RELAY
DESCRIPTION
The compressor clutch relay is a International
Standards Organization (ISO) micro-relay. The termi-
nal designations and functions are the same as a con-
ventional ISO relay. However, the micro-relay
terminal orientation (footprint) is different, the cur-
rent capacity is lower, and the relay case dimensions
are smaller than those of the conventional ISO relay.
OPERATION
The compressor clutch relay is a electromechanical
device that switches battery current to the compres-
sor clutch coil when the Powertrain Control Module
(PCM) grounds the coil side of the relay. The PCM
responds to inputs from the a/c compressor switch on
the a/c heater control panel, the Automatic Zone Con-
trol (AZC) control module (if the vehicle is so
equipped), the a/c fin probe, and the a/c high pres-
sure transducer. (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR
CONDITIONING/CONTROLS/A/C COMPRESSOR
CLUTCH RELAY - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING)
The compressor clutch relay is located in the Power
Distribution Center (PDC) in the engine compart-
ment. Refer to the PDC label for relay identification
and location.
The compressor clutch relay cannot be repaired
and, if faulty or damaged, it must be replaced.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - A/C COMPRESSOR
CLUTCH RELAY
For circuit descriptions and diagrams, refer to the
appropriate wiring information.
The compressor clutch relay (Fig. 10) is located in
the Power Distribution Center (PDC). Refer to the
PDC label for relay identification and location.Remove the relay from the PDC to perform the fol-
lowing tests:
(1) A relay in the de-energized position should
have continuity between terminals 87A and 30, and
no continuity between terminals 87 and 30. If OK, go
to Step 2. If not OK, replace the faulty relay.
(2) Resistance between terminals 85 and 86 (elec-
tromagnet) should be 75 5 ohms. If OK, go to Step
3. If not OK, replace the faulty relay.
(3) Connect a battery to terminals 85 and 86.
There should now be continuity between terminals
30 and 87, and no continuity between terminals 87A
and 30. If OK, see the Relay Circuit Test procedure
in this group. If not OK, replace the faulty relay.
RELAY CIRCUIT TEST
For circuit descriptions and diagrams, refer to the
appropriate wiring information..
(1) The relay common feed terminal cavity (30) is
connected to fused battery feed. There should be bat-
tery voltage at the cavity for relay terminal 30 at all
times. If OK, go to Step 2. If not OK, repair the open
circuit to the fuse in the PDC as required.
(2) The relay normally closed terminal (87A) is not
used in this application. Go to Step 3.
(3) The relay normally open terminal cavity (87) is
connected to the compressor clutch coil. There should
be continuity between this cavity and the A/C com-
pressor clutch relay output circuit cavity of the com-
pressor clutch coil wire harness connector. If OK, go
to Step 4. If not OK, repair the open circuit as
required.
(4) The relay coil battery terminal (86) is con-
nected to the fused ignition switch output (run/start)
circuit. There should be battery voltage at the cavity
for relay terminal 86 with the ignition switch in the
On position. If OK, go to Step 5. If not OK, repair the
Fig. 10 A/C COMPRESSOR CLUTCH RELAY
30 - COMMON FEED
85 - COIL GROUND
86 - COIL BATTERY
87 - NORMALLY OPEN
87A - NORMALLY CLOSED
24 - 16 CONTROLSWJ
A/C COMPRESSOR CLUTCH (Continued)
Page 2114 of 2199

BLOWER MOTOR
DESCRIPTION
The blower motor and blower wheel are located in
the passenger side end of the HVAC housing, below
the glove box module. The blower motor controls the
velocity of the air flowing through the HVAC housing
by spinning a squirrel cage-type blower wheel within
the housing at the selected speed. The blower motor
and blower wheel can be serviced from the passenger
compartment side of the housing.
OPERATION
The blower motor will only operate when the igni-
tion switch is in the On position, and the a/c heater
mode control switch is in any position, except off. The
blower motor circuit is protected by a fuse in the
junction block. On models with the standard manual
temperature control system, the blower motor speed
is controlled by regulating the battery feed through
the blower motor switch and the blower motor resis-
tor. On models with the optional Automatic Zone
Control (AZC) system, the blower motor speed is con-
trolled by using Pulse Width Modulation (PWM). The
blower motor controller adjusts the battery feed volt-
age to the blower motor, based upon an input from
the blower motor switch, through the AZC control
module. Pulse width modulation of blower power
allows the blower to operate at any speed from sta-
tionary, to full speed.
The blower motor and blower motor wheel cannot
be repaired, and if faulty or damaged, they must be
replaced. The blower motor and blower wheel are
each serviced separately.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - BLOWER MOTOR
WARNING: ON VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH AIR-
BAGS, DISABLE THE AIRBAG SYSTEM BEFORE
ATTEMPTING ANY STEERING WHEEL, STEERING
COLUMN, OR INSTRUMENT PANEL COMPONENT
DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. DISCONNECT AND ISO-
LATE THE BATTERY NEGATIVE (GROUND) CABLE,
THEN WAIT TWO MINUTES FOR THE AIRBAG SYS-
TEM CAPACITOR TO DISCHARGE BEFORE PER-
FORMING FURTHER DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. THIS
IS THE ONLY SURE WAY TO DISABLE THE AIRBAG
SYSTEM. FAILURE TO TAKE THE PROPER PRE-
CAUTIONS COULD RESULT IN AN ACCIDENTAL
AIRBAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE PERSONAL
INJURY.
For circuit descriptions and diagrams, refer to the
appropriate wiring information. Possible causes of an
inoperative blower motor include:
²Faulty fuse²Faulty blower motor circuit wiring or wire har-
ness connections
²Faulty blower motor resistor (if the vehicle is so
equipped)
²Faulty blower motor controller (if the vehicle is
so equipped)
²Faulty blower motor switch
²Faulty a/c heater mode control switch
²Faulty blower motor.
Possible causes of the blower motor not operating
in all speeds include:
²Faulty fuse
²Faulty blower motor switch
²Faulty blower motor resistor (if the vehicle is so
equipped)
²Faulty blower motor controller (if the vehicle is
so equipped)
²Faulty AZC module (if the vehicle is so
equipped)
²Faulty blower motor circuit wiring or wire har-
ness connections.
VIBRATION
Possible causes of blower motor vibration include:
²Improper blower motor mounting
²Improper blower wheel mounting
²Blower wheel out of balance or bent
²Blower motor faulty.
NOISE
To verify that the blower is the source of the noise,
unplug the blower motor wire harness connector and
operate the HVAC system. If the noise goes away,
possible causes include:
²Foreign material in the HVAC housing
²Improper blower motor mounting
²Improper blower wheel mounting
²Blower motor faulty.
REMOVAL
WARNING: ON VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH AIR-
BAGS, DISABLE THE AIRBAG SYSTEM BEFORE
ATTEMPTING ANY STEERING WHEEL, STEERING
COLUMN, OR INSTRUMENT PANEL COMPONENT
DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. DISCONNECT AND ISO-
LATE THE BATTERY NEGATIVE (GROUND) CABLE,
THEN WAIT TWO MINUTES FOR THE AIRBAG SYS-
TEM CAPACITOR TO DISCHARGE BEFORE PER-
FORMING FURTHER DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. THIS
IS THE ONLY SURE WAY TO DISABLE THE AIRBAG
SYSTEM. FAILURE TO TAKE THE PROPER PRE-
CAUTIONS COULD RESULT IN AN ACCIDENTAL
AIRBAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE PERSONAL
INJURY.
WJDISTRIBUTION 24 - 37
Page 2122 of 2199

NOTE: The blend door sub-assembly is attached to
the housing with 2 screws, and may be removed for
service (Fig. 19).
ASSEMBLY
(1) Place the top half of the HVAC housing on the
bottom half. Be certain that each of the door pivot
pins align with the pivot holes in the HVAC housing.
(2) Install the 10 screws that secure the two hous-
ing halves to each other. Tighten the HVAC housing
screws to 2.2 N´m (20 in. lbs.).
(3) Attach the wire harness electrical connector(s)
to the mounts on the lower case at the blower motor
end of the unit.
(4) Install the 5 clips that secure the two housing
halves to each other. Check doors for binding after
replacement, and after assembly of housing.
(5) Install the screw with plastic washer holding
the lever assembly to the upper case section.
(6) Install the mode door actuator on the left side
of the housing.
INSTALLATION
WARNING: REVIEW THE WARNINGS AND CAU-
TIONS IN PLUMBING BEFORE PERFORMING THE
FOLLOWING OPERATION. (Refer to 24 - HEATING &
AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING - WARNING) (Refer
to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING -
CAUTION)Any kinks or sharp bends in the refrigerant plumb-
ing will reduce the capacity of the entire air condi-
tioning system. Kinks and sharp bends reduce the
flow of refrigerant in the system. A good rule for the
flexible hose refrigerant lines is to keep the radius of
all bends at least ten times the diameter of the hose.
In addition, the flexible hose refrigerant lines should
be routed so they are at least 80 millimeters (3
inches) from the exhaust manifold.
High pressures are produced in the refrigerant sys-
tem when the air conditioning compressor is operat-
ing. Extreme care must be exercised to make sure
that each of the refrigerant system connections is
pressure-tight and leak free. It is a good practice to
inspect all flexible hose refrigerant lines at least once
a year to make sure they are in good condition and
properly routed.
(1) Position the HVAC housing to the dash panel.
Be certain that the evaporator condensate drain tube
and the housing mounting studs are inserted into
their correct mounting holes.
(2) Install the HVAC housing mounting nuts to the
studs on the passenger compartment side of the dash
panel. Tighten the nuts to 4.5 N´m (40 in. lbs.).
(3) Connect the HVAC housing wire harness con-
nectors.
(4) Reinstall the rear floor heat ducts to the center
floor heat duct outlets.
(5) Install and tighten the nuts onto the HVAC
housing mounting studs on the engine compartment
side of the dash panel. Tighten the nuts to 7 N´m (60
in. lbs.).
(6) Reinstall the PCM to the passenger side dash
panel in the engine compartment. Refer to Electronic
Control Modules for the procedures.
(7) Reinstall the coolant reserve/overflow bottle to
the passenger side inner fender shield. Refer to Cool-
ing for the procedures.
(8) If the vehicle is equipped with the manual tem-
perature control system, connect the HVAC system
vacuum supply line connector to the tee fitting near
the heater core tubes.
(9) Unclamp/unplug the heater core hoses and
tubes. Connect the heater hoses to the heater core
tubes and fill the engine cooling system. Refer to
Cooling for the procedures.
(10) Unplug or remove the tape from the suction
line and the evaporator outlet tube fittings. Connect
the suction line to the evaporator outlet tube.
Tighten retaining nut to 28 N´m (250 in. lbs.).
(11) Unplug or remove the tape from the liquid
line and the evaporator inlet tube fittings. Connect
the liquid line to the evaporator inlet tube. Tighten
retaining nut to 28 N´m (250 in. lbs.).
(12) Evacuate the refrigerant system. (Refer to 24
- HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING -
Fig. 19 BLEND DOOR SUB-ASSEMBLY (AZC)
1 - PASSENGER SIDE BLEND DOOR
2 - BLEND DOOR SUB-ASSEMBLY
3 - DOOR PIVOT SHAFT BUSHING
4 - DOOR SHAFT LEVER
5 - DRIVER SIDE BLEND DOOR
WJDISTRIBUTION 24 - 45
HVAC HOUSING (Continued)
Page 2123 of 2199

STANDARD PROCEDURE - REFRIGERANT SYS-
TEM EVACUATE)
(13) Charge the refrigerant system. (Refer to 24 -
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE - REFRIGERANT SYS-
TEM CHARGE)
(14) Install the instrument panel in the vehicle(Re-
fer to 23 - BODY/INSTRUMENT PANEL - INSTAL-
LATION).
(15) Connect the battery negative cable.
(16) Start the engine and check for proper opera-
tion of the heating and air conditioning systems.
BLEND DOOR
REMOVAL
WARNING: ON VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH AIR-
BAGS, DISABLE THE AIRBAG SYSTEM BEFORE
ATTEMPTING ANY STEERING WHEEL, STEERING
COLUMN, OR INSTRUMENT PANEL COMPONENT
DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. DISCONNECT AND ISO-
LATE THE BATTERY NEGATIVE (GROUND) CABLE,
THEN WAIT TWO MINUTES FOR THE AIRBAG SYS-
TEM CAPACITOR TO DISCHARGE BEFORE PER-
FORMING FURTHER DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. THIS
IS THE ONLY SURE WAY TO DISABLE THE AIRBAG
SYSTEM. FAILURE TO TAKE THE PROPER PRE-
CAUTIONS COULD RESULT IN AN ACCIDENTAL
AIRBAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE PERSONAL
INJURY.
(1) Remove and disassemble the HVAC housing.
(Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/
DISTRIBUTION/HVAC HOUSING - REMOVAL)
(Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/
DISTRIBUTION/HVAC HOUSING - DISASSEMBLY)
(2) Remove evaporator from lower case to ease
access to plastic door shaft bushing.
(3) Pinch the retention tabs holding the blend door
pivot shaft to the case. The 3 plastic tabs, located on
the inside of the case, are part of the shaft retainer.
(4) Remove door(s).
INSTALLATION
(1) Install the blend door(s) by snapping the pivot
shaft into the HVAC case.
(2) Install the evaporator in the lower case.
(3) Reassemble the HVAC housing and install in
the vehicle. (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDI-
TIONING/DISTRIBUTION/HVAC HOUSING -
ASSEMBLY) (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CON-
DITIONING/DISTRIBUTION/HVAC HOUSING -
INSTALLATION)NOTE: The blend door sub-assembly is attached to
the housing with 2 screws, and may be removed for
service (Fig. 20).
MODE DOOR
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - PANEL OUTLET DOOR
WARNING: ON VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH AIR-
BAGS, DISABLE THE AIRBAG SYSTEM BEFORE
ATTEMPTING ANY STEERING WHEEL, STEERING
COLUMN, OR INSTRUMENT PANEL COMPONENT
DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. DISCONNECT AND ISO-
LATE THE BATTERY NEGATIVE (GROUND) CABLE,
THEN WAIT TWO MINUTES FOR THE AIRBAG SYS-
TEM CAPACITOR TO DISCHARGE BEFORE PER-
FORMING FURTHER DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. THIS
IS THE ONLY SURE WAY TO DISABLE THE AIRBAG
SYSTEM. FAILURE TO TAKE THE PROPER PRE-
CAUTIONS COULD RESULT IN AN ACCIDENTAL
AIRBAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE PERSONAL
INJURY.
(1) Remove and disassemble the HVAC housing.
(Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/
DISTRIBUTION/HVAC HOUSING - REMOVAL)
(Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/
DISTRIBUTION/HVAC HOUSING - DISASSEMBLY)
Fig. 20 BLEND DOOR SUB-ASSEMBLY
1 - PASSENGER SIDE BLEND DOOR
2 - BLEND DOOR SUB-ASSEMBLY
3 - DOOR PIVOT SHAFT BUSHING
4 - DOOR SHAFT LEVER
5 - DRIVER SIDE BLEND DOOR
24 - 46 DISTRIBUTIONWJ
HVAC HOUSING (Continued)
Page 2124 of 2199

(2) Pinch the retention tabs holding the panel out-
let door pivot shaft to the case. The 3 plastic tabs,
located on the inside of the case, are part of the shaft
retainer (Fig. 21).
(3) Using a trim stick or another suitable wide
flat-bladed tool, gently pry the panel outlet door pivot
shaft retainer from the pivot shaft.
(4) Remove the panel outlet door from the HVAC
housing.
REMOVAL - HEAT/DEFROST DOOR
WARNING: ON VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH AIR-
BAGS, DISABLE THE AIRBAG SYSTEM BEFORE
ATTEMPTING ANY STEERING WHEEL, STEERING
COLUMN, OR INSTRUMENT PANEL COMPONENT
DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. DISCONNECT AND ISO-
LATE THE BATTERY NEGATIVE (GROUND) CABLE,
THEN WAIT TWO MINUTES FOR THE AIRBAG SYS-
TEM CAPACITOR TO DISCHARGE BEFORE PER-
FORMING FURTHER DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. THIS
IS THE ONLY SURE WAY TO DISABLE THE AIRBAG
SYSTEM. FAILURE TO TAKE THE PROPER PRE-
CAUTIONS COULD RESULT IN AN ACCIDENTAL
AIRBAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE PERSONAL
INJURY.(1) Remove and disassemble the HVAC housing.
(Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/
DISTRIBUTION/HVAC HOUSING - REMOVAL)
(Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/
DISTRIBUTION/HVAC HOUSING - DISASSEMBLY)
(2) Remove the evaporator, and styrofoam tray
from the lower case.
(3) Place the HVAC housing upside down on a
work bench.
(4) Unscrew and remove the 2 floor heat ducts.
(5) Unsnap and remove the duct adapter from the
bottom of the heat/defrost door sub-assembly (Fig.
22).
(6) Gently pry the metal linkage from the heat/de-
frost door lever.
(7) Remove the heat/defrost door sub-assembly,
which is attached to the housing with 4 screws (Fig.
23).
(8) Pinch the retention tabs holding the heat/de-
frost door pivot shaft lever to the case. The 3 plastic
tabs, located on the inside of the case, are part of the
shaft retainer.
(9) Remove the heat/defrost door (Fig. 24).
Fig. 21 PANEL OUTLET DOOR
1 - PANEL/OUTLET DOOR
2 - DOOR SHAFT
3 - FOAM SEAL
(SPLIT)
4 - LOWER HOUSING
5 - PANEL OUTLET DOOR LEVER
6 - LEVER
Fig. 22 HEAT/DEFROST DOOR DUCTS, AND
ADAPTER
1 - FLOOR DUCT ADAPTER
2 - HEAT/DEFROST DOOR SUB-ASSEMBLY
3 - DOOR LEVERS
4 - LOWER HOUSING
5 - FLOOR DUCTS
6 - LINKAGE
7 - RETAINING TABS
WJDISTRIBUTION 24 - 47
MODE DOOR (Continued)
Page 2126 of 2199

INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - PANEL OUTLET DOOR
(1) Snap the panel outlet door pivot shaft retainer
on the pivot shaft.
(2) Attach the panel outlet door pivot shaft to the
HVAC case.
(3) Reassemble the HVAC housing and install in
the vehicle. (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDI-
TIONING/DISTRIBUTION/HVAC HOUSING -
ASSEMBLY) (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CON-
DITIONING/DISTRIBUTION/HVAC HOUSING -
INSTALLATION)
INSTALLATION - HEAT/DEFROST DOOR
(1) Install the heat/defrost door by snapping the
heat/defrost door pivot shaft into the HVAC case.
(2) Install the heat/defrost door sub-assembly and
tighten the mounting screws to 2.2 N´m (20 in. lbs.).
(3) Attach the metal linkage to the heat/defrost
door lever.
(4) Snap the duct adapter to the bottom of the
heat/defrost door sub-assembly.
(5) Install the 2 floor heat ducts and tighten the
mounting screws to 2.2 N´m (20 in. lbs.)..
(6) Install the evaporator, and styrofoam tray in
the lower case.
(7) Reassemble the HVAC housing and install in
the vehicle. (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDI-
TIONING/DISTRIBUTION/HVAC HOUSING -
ASSEMBLY) (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CON-
DITIONING/DISTRIBUTION/HVAC HOUSING -
INSTALLATION)
INSTALLATION - PANEL/DEFROST DOOR
(1) Snap the panel/defrost door pivot shaft retainer
on the pivot shaft.
(2) Attach the panel/defrost door pivot shaft to the
HVAC case.
(3) Reassemble the HVAC housing and install in
the vehicle. (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDI-
TIONING/DISTRIBUTION/HVAC HOUSING -
ASSEMBLY) (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CON-
DITIONING/DISTRIBUTION/HVAC HOUSING -
INSTALLATION)
RECIRCULATION DOOR
REMOVAL
WARNING: ON VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH AIR-
BAGS, DISABLE THE AIRBAG SYSTEM BEFORE
ATTEMPTING ANY STEERING WHEEL, STEERING
COLUMN, OR INSTRUMENT PANEL COMPONENT
DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. DISCONNECT AND ISO-
LATE THE BATTERY NEGATIVE (GROUND) CABLE,
THEN WAIT TWO MINUTES FOR THE AIRBAG SYS-
TEM CAPACITOR TO DISCHARGE BEFORE PER-
FORMING FURTHER DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. THIS
IS THE ONLY SURE WAY TO DISABLE THE AIRBAG
SYSTEM. FAILURE TO TAKE THE PROPER PRE-
CAUTIONS COULD RESULT IN AN ACCIDENTAL
AIRBAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE PERSONAL
INJURY.
(1) Remove the HVAC housing from the vehicle.
(Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/
DISTRIBUTION/HVAC HOUSING - REMOVAL)
(2) Place the HVAC housing right side up on the
work bench.
(3) Unplug the wire/vacuum connector from the
recirculation door actuator.
(4) Remove the 2 screws fastening the recircula-
tion door sub-assembly to the main housing (Fig. 26).
Fig. 26 RECIRCULATION DOOR HOUSING
1 - RECIRCULATION DOOR HOUSING
2 - ATTACHING SCREWS
WJDISTRIBUTION 24 - 49
MODE DOOR (Continued)
Page 2149 of 2199
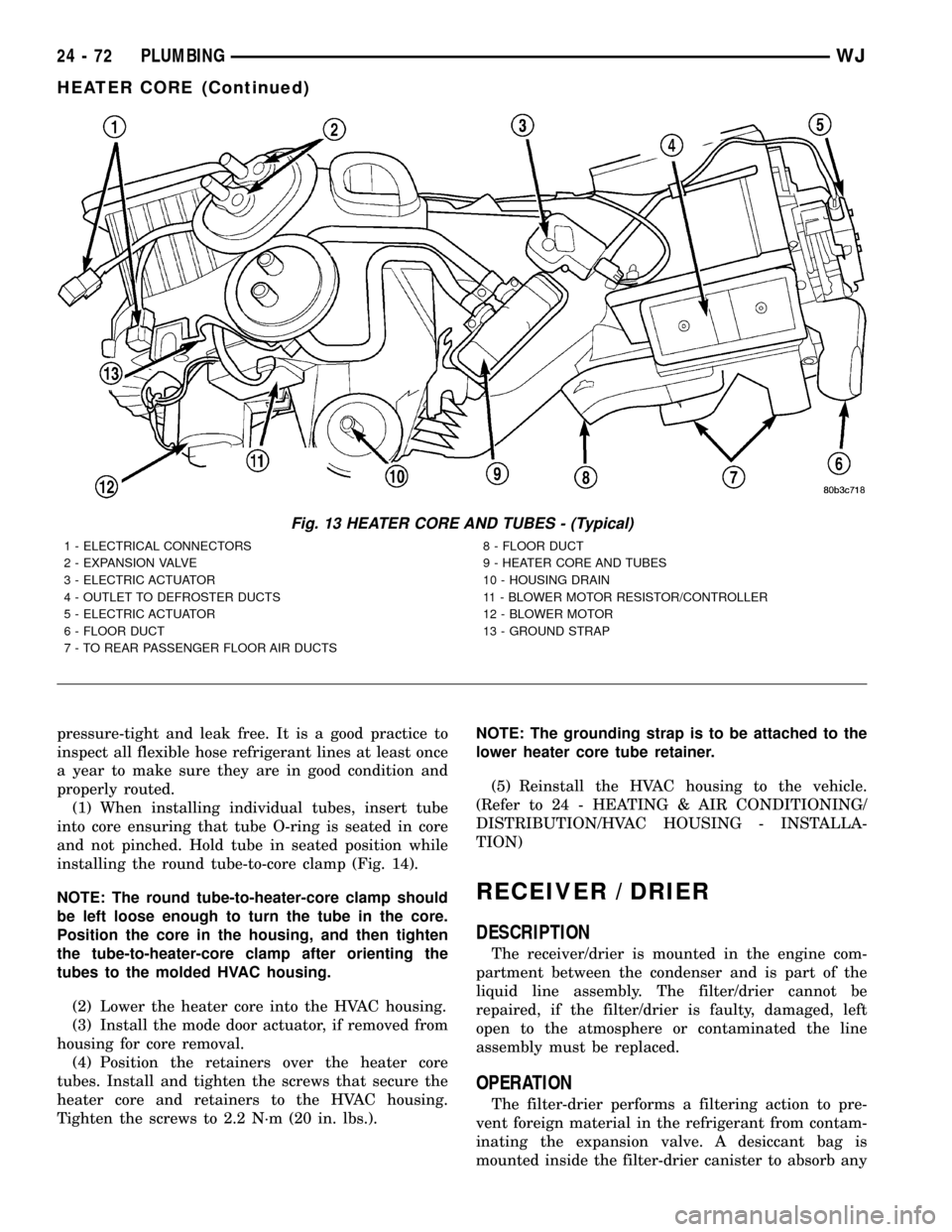

pressure-tight and leak free. It is a good practice to
inspect all flexible hose refrigerant lines at least once
a year to make sure they are in good condition and
properly routed.
(1) When installing individual tubes, insert tube
into core ensuring that tube O-ring is seated in core
and not pinched. Hold tube in seated position while
installing the round tube-to-core clamp (Fig. 14).
NOTE: The round tube-to-heater-core clamp should
be left loose enough to turn the tube in the core.
Position the core in the housing, and then tighten
the tube-to-heater-core clamp after orienting the
tubes to the molded HVAC housing.
(2) Lower the heater core into the HVAC housing.
(3) Install the mode door actuator, if removed from
housing for core removal.
(4) Position the retainers over the heater core
tubes. Install and tighten the screws that secure the
heater core and retainers to the HVAC housing.
Tighten the screws to 2.2 N´m (20 in. lbs.).NOTE: The grounding strap is to be attached to the
lower heater core tube retainer.
(5) Reinstall the HVAC housing to the vehicle.
(Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/
DISTRIBUTION/HVAC HOUSING - INSTALLA-
TION)
RECEIVER / DRIER
DESCRIPTION
The receiver/drier is mounted in the engine com-
partment between the condenser and is part of the
liquid line assembly. The filter/drier cannot be
repaired, if the filter/drier is faulty, damaged, left
open to the atmosphere or contaminated the line
assembly must be replaced.
OPERATION
The filter-drier performs a filtering action to pre-
vent foreign material in the refrigerant from contam-
inating the expansion valve. A desiccant bag is
mounted inside the filter-drier canister to absorb any
Fig. 13 HEATER CORE AND TUBES - (Typical)
1 - ELECTRICAL CONNECTORS
2 - EXPANSION VALVE
3 - ELECTRIC ACTUATOR
4 - OUTLET TO DEFROSTER DUCTS
5 - ELECTRIC ACTUATOR
6 - FLOOR DUCT
7 - TO REAR PASSENGER FLOOR AIR DUCTS8 - FLOOR DUCT
9 - HEATER CORE AND TUBES
10 - HOUSING DRAIN
11 - BLOWER MOTOR RESISTOR/CONTROLLER
12 - BLOWER MOTOR
13 - GROUND STRAP
24 - 72 PLUMBINGWJ
HEATER CORE (Continued)
Page 2168 of 2199
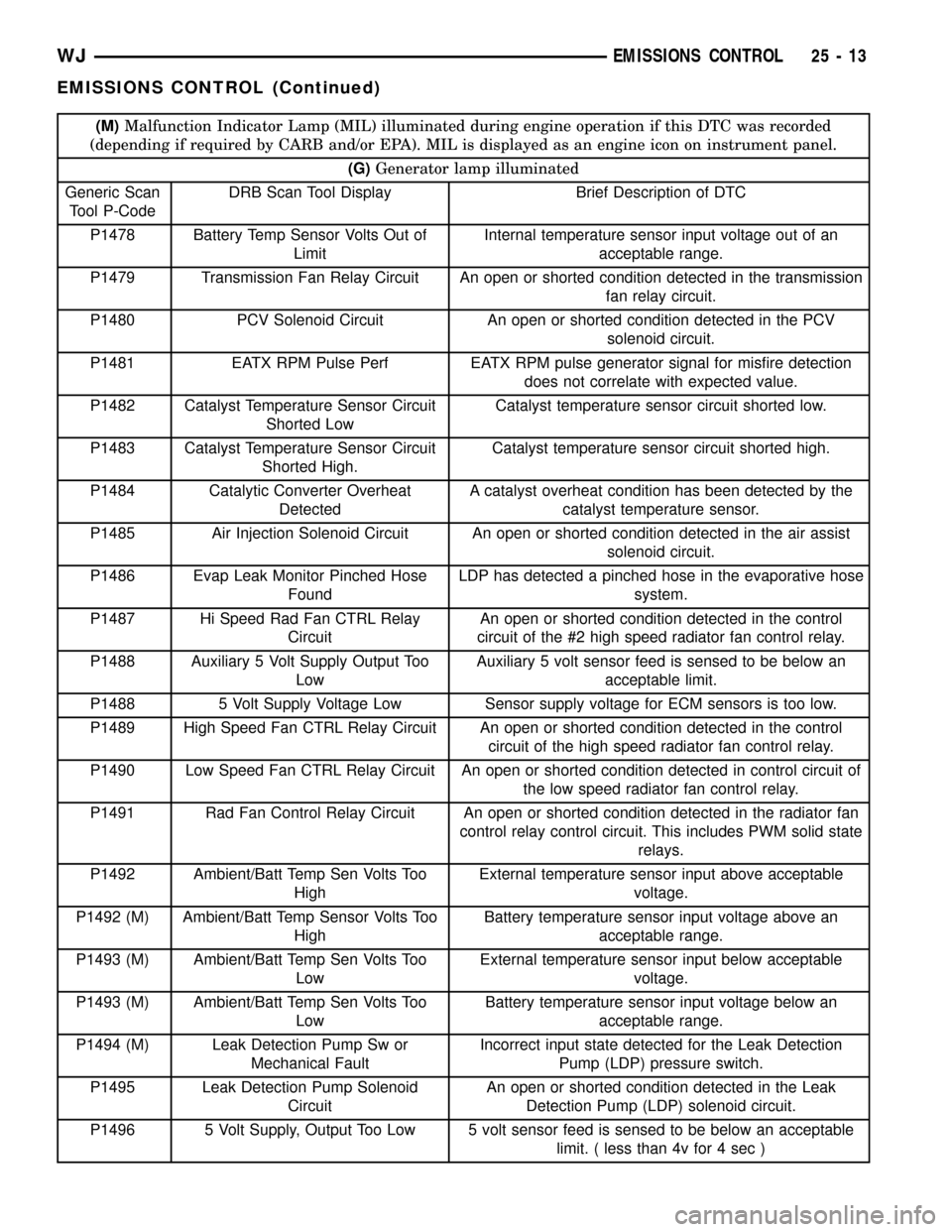
(M)Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) illuminated during engine operation if this DTC was recorded
(depending if required by CARB and/or EPA). MIL is displayed as an engine icon on instrument panel.
(G)Generator lamp illuminated
Generic Scan
Tool P-CodeDRB Scan Tool Display Brief Description of DTC
P1478 Battery Temp Sensor Volts Out of
LimitInternal temperature sensor input voltage out of an
acceptable range.
P1479 Transmission Fan Relay Circuit An open or shorted condition detected in the transmission
fan relay circuit.
P1480 PCV Solenoid Circuit An open or shorted condition detected in the PCV
solenoid circuit.
P1481 EATX RPM Pulse Perf EATX RPM pulse generator signal for misfire detection
does not correlate with expected value.
P1482 Catalyst Temperature Sensor Circuit
Shorted LowCatalyst temperature sensor circuit shorted low.
P1483 Catalyst Temperature Sensor Circuit
Shorted High.Catalyst temperature sensor circuit shorted high.
P1484 Catalytic Converter Overheat
DetectedA catalyst overheat condition has been detected by the
catalyst temperature sensor.
P1485 Air Injection Solenoid Circuit An open or shorted condition detected in the air assist
solenoid circuit.
P1486 Evap Leak Monitor Pinched Hose
FoundLDP has detected a pinched hose in the evaporative hose
system.
P1487 Hi Speed Rad Fan CTRL Relay
CircuitAn open or shorted condition detected in the control
circuit of the #2 high speed radiator fan control relay.
P1488 Auxiliary 5 Volt Supply Output Too
LowAuxiliary 5 volt sensor feed is sensed to be below an
acceptable limit.
P1488 5 Volt Supply Voltage Low Sensor supply voltage for ECM sensors is too low.
P1489 High Speed Fan CTRL Relay Circuit An open or shorted condition detected in the control
circuit of the high speed radiator fan control relay.
P1490 Low Speed Fan CTRL Relay Circuit An open or shorted condition detected in control circuit of
the low speed radiator fan control relay.
P1491 Rad Fan Control Relay Circuit An open or shorted condition detected in the radiator fan
control relay control circuit. This includes PWM solid state
relays.
P1492 Ambient/Batt Temp Sen Volts Too
HighExternal temperature sensor input above acceptable
voltage.
P1492 (M) Ambient/Batt Temp Sensor Volts Too
HighBattery temperature sensor input voltage above an
acceptable range.
P1493 (M) Ambient/Batt Temp Sen Volts Too
LowExternal temperature sensor input below acceptable
voltage.
P1493 (M) Ambient/Batt Temp Sen Volts Too
LowBattery temperature sensor input voltage below an
acceptable range.
P1494 (M) Leak Detection Pump Sw or
Mechanical FaultIncorrect input state detected for the Leak Detection
Pump (LDP) pressure switch.
P1495 Leak Detection Pump Solenoid
CircuitAn open or shorted condition detected in the Leak
Detection Pump (LDP) solenoid circuit.
P1496 5 Volt Supply, Output Too Low 5 volt sensor feed is sensed to be below an acceptable
limit. ( less than 4v for 4 sec )
WJEMISSIONS CONTROL 25 - 13
EMISSIONS CONTROL (Continued)
Page 2173 of 2199

tive system and seal the evaporative system so the
leak detection test can be run.
The primary components within the assembly are:
A three port solenoid that activates both of the func-
tions listed above; a pump which contains a switch,
two check valves and a spring/diaphragm, a canister
vent valve (CVV) seal which contains a spring loaded
vent seal valve.
Immediately after a cold start, between predeter-
mined temperature thresholds limits, the three port
solenoid is briefly energized. This initializes the
pump by drawing air into the pump cavity and also
closes the vent seal. During non test conditions the
vent seal is held open by the pump diaphragm
assembly which pushes it open at the full travel posi-
tion. The vent seal will remain closed while the
pump is cycling due to the reed switch triggering of
the three port solenoid that prevents the diaphragm
assembly from reaching full travel. After the brief
initialization period, the solenoid is de-energized
allowing atmospheric pressure to enter the pump
cavity, thus permitting the spring to drive the dia-
phragm which forces air out of the pump cavity and
into the vent system. When the solenoid is energized
and de energized, the cycle is repeated creating flow
in typical diaphragm pump fashion. The pump is con-
trolled in 2 modes:
Pump Mode:The pump is cycled at a fixed rate to
achieve a rapid pressure build in order to shorten the
overall test length.
Test Mode:The solenoid is energized with a fixed
duration pulse. Subsequent fixed pulses occur when
the diaphragm reaches the Switch closure point.
The spring in the pump is set so that the system
will achieve an equalized pressure of about 7.5º
water. The cycle rate of pump strokes is quite rapid
as the system begins to pump up to this pressure. As
the pressure increases, the cycle rate starts to drop
off. If there is no leak in the system, the pump would
eventually stop pumping at the equalized pressure. If
there is a leak, it will continue to pump at a rate rep-
resentative of the flow characteristic of the size of the
leak. From this information we can determine if the
leak is larger than the required detection limit (cur-
rently set at .040º orifice by CARB). If a leak is
revealed during the leak test portion of the test, the
test is terminated at the end of the test mode and no
further system checks will be performed.
After passing the leak detection phase of the test,
system pressure is maintained by turning on the
LDP's solenoid until the purge system is activated.
Purge activation in effect creates a leak. The cycle
rate is again interrogated and when it increases due
to the flow through the purge system, the leak check
portion of the diagnostic is complete.The canister vent valve will unseal the system
after completion of the test sequence as the pump
diaphragm assembly moves to the full travel position.
Evaporative system functionality will be verified by
using the stricter evap purge flow monitor. At an
appropriate warm idle the LDP will be energized to
seal the canister vent. The purge flow will be clocked
up from some small value in an attempt to see a
shift in the 02 control system. If fuel vapor, indicated
by a shift in the 02 control, is present the test is
passed. If not, it is assumed that the purge system is
not functioning in some respect. The LDP is again
turned off and the test is ended.
MISFIRE MONITOR
Excessive engine misfire results in increased cata-
lyst temperature and causes an increase in HC emis-
sions. Severe misfires could cause catalyst damage.
To prevent catalytic convertor damage, the PCM
monitors engine misfire.
The Powertrain Control Module (PCM) monitors
for misfire during most engine operating conditions
(positive torque) by looking at changes in the crank-
shaft speed. If a misfire occurs the speed of the
crankshaft will vary more than normal.
FUEL SYSTEM MONITOR
To comply with clean air regulations, vehicles are
equipped with catalytic converters. These converters
reduce the emission of hydrocarbons, oxides of nitro-
gen and carbon monoxide. The catalyst works best
when the Air Fuel (A/F) ratio is at or near the opti-
mum of 14.7 to 1.
The PCM is programmed to maintain the optimum
air/fuel ratio of 14.7 to 1. This is done by making
short term corrections in the fuel injector pulse width
based on the O2S sensor output. The programmed
memory acts as a self calibration tool that the engine
controller uses to compensate for variations in engine
specifications, sensor tolerances and engine fatigue
over the life span of the engine. By monitoring the
actual fuel-air ratio with the O2S sensor (short term)
and multiplying that with the program long-term
(adaptive) memory and comparing that to the limit,
it can be determined whether it will pass an emis-
sions test. If a malfunction occurs such that the PCM
cannot maintain the optimum A/F ratio, then the
MIL will be illuminated.
CATALYST MONITOR
To comply with clean air regulations, vehicles are
equipped with catalytic converters. These converters
reduce the emission of hydrocarbons, oxides of nitro-
gen and carbon monoxide.
Normal vehicle miles or engine misfire can cause a
catalyst to decay. This can increase vehicle emissions
25 - 18 EMISSIONS CONTROLWJ
EMISSIONS CONTROL (Continued)
Page 2185 of 2199

CAUTION: Remove the fuel tank filler tube cap to
relieve fuel tank pressure. The cap must be
removed prior to disconnecting any fuel system
component or before draining the fuel tank.
LEAK DETECTION PUMP
DESCRIPTION
The evaporative emission system is designed to
prevent the escape of fuel vapors from the fuel sys-
tem (Fig. 11). Leaks in the system, even small ones,
can allow fuel vapors to escape into the atmosphere.
Government regulations require onboard testing to
make sure that the evaporative (EVAP) system is
functioning properly. The leak detection system tests
for EVAP system leaks and blockage. It also performs
self-diagnostics. During self-diagnostics, the Power-
train Control Module (PCM) first checks the Leak
Detection Pump (LDP) for electrical and mechanical
faults. If the first checks pass, the PCM then uses
the LDP to seal the vent valve and pump air into the
system to pressurize it. If a leak is present, the PCM
will continue pumping the LDP to replace the air
that leaks out. The PCM determines the size of the
leak based on how fast/long it must pump the LDP
as it tries to maintain pressure in the system.
EVAP LEAK DETECTION SYSTEM COMPONENTS
Service Port: Used with special tools like the Miller
Evaporative Emissions Leak Detector (EELD) to test
for leaks in the system.
EVAP Purge Solenoid: The PCM uses the EVAP
purge solenoid to control purging of excess fuel
vapors stored in the EVAP canister. It remains closed
during leak testing to prevent loss of pressure.
EVAP Canister: The EVAP canister stores fuel
vapors from the fuel tank for purging.
EVAP Purge Orifice: Limits purge volume.
EVAP System Air Filter: Provides air to the LDP
for pressurizing the system. It filters out dirt while
allowing a vent to atmosphere for the EVAP system.
Fig. 11 TYPICAL SYSTEM COMPONENTS
1 - Throttle Body
2 - Service Vacuum Supply Tee (SVST)
3 - LDP Solenoid
4 - EVAP System Air Filter
5 - LDP Vent Valve
6 - EVAP Purge Orifice
7 - EVAP Purge Solenoid
8 - Service Port
9 - To Fuel Tank
10 - EVAP Canister
11 - LDP
12 - Intake Air Plenum
25 - 30 EVAPORATIVE EMISSIONSWJ
FUEL FILLER CAP (Continued)