bolt pattern JEEP YJ 1995 Service And Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JEEP, Model Year: 1995, Model line: YJ, Model: JEEP YJ 1995Pages: 2158, PDF Size: 81.9 MB
Page 74 of 2158

MODEL 30 AXLE AND TUBE AXLE (2WD)
INDEX
page page
Axle Bushing Replacement.................. 34
Axle ShaftÐCardan U-Joint.................. 26
Backlash and Contact Pattern Analysis......... 45
Cleaning/Inspection........................ 37
Differential and Pinion Measurement........... 40
Differential Assembly....................... 38
Differential Disassembly.................... 35
Differential Installation...................... 44
Differential Removal....................... 34
Differential Shim Pack Measurement and
Adjustment............................ 43
Drive Axle Assembly ReplacementÐXJ Vehicles . . 23
Drive Axle Assembly ReplacementÐYJ Vehicles . . 24Final Assembly........................... 46
Hub Bearing and Axle Shaft................. 25
Information.............................. 22
Inner Axle Shaft Oil Seal Replacement......... 35
Lubricant Change......................... 23
Lubricant Specifications..................... 22
Pinion Gear Assembly/Installation............. 42
Pinion Gear Depth Information............... 39
Pinion Removal/Disassembly................. 36
Pinion Seal Replacement................... 25
Steering Knuckle and Ball Studs.............. 32
Vacuum Disconnect AxleÐYJ Vehicles......... 27
INFORMATION
The Model 30 front axles consists of a cast iron dif-
ferential housing with axle shaft tubes extending
from either side. The tubes are pressed into the dif-
ferential housing and welded.
The integral type housing, hypoid gear design has
the centerline of the pinion set above the centerline
of the ring gear.
The axle has a fitting for a vent hose used to re-
lieve internal pressure caused by lubricant vaporiza-
tion and internal expansion.
The axles are equipped with semi-floating axle
shafts, meaning that loads are supported by the hub
bearings. The axle shafts are retained by nuts at the
hub bearings. The hub bearings are bolted to the
steering knuckle at the outboard end of the axle tube
yoke. The hub bearings are serviced as an assembly.
The axles are equipped with ABS brake sensors.
The sensors are attached to the knuckle assemblies
and tone rings are pressed on the axle shaft.Use
care when removing axle shafts as NOT to dam-
age the tone wheel or the sensor.
The stamped steel cover provides a means for in-
spection and servicing the differential.
The Model 30 axle has the assembly part number
and gear ratio listed on a tag. The tag is attached to
the housing cover. Build date identification codes are
stamped on the axle shaft tube cover side.
The differential case is a one-piece design. The dif-
ferential pinion mate shaft is retained with a roll
pin. Differential bearing preload and ring gear back-
lash is adjusted by the use of shims (select thick-
ness). The shims are located between the differential
bearing cones and case. Pinion bearing preload is set
and maintained by the use of collapsible spacer.
COMMAND-TRACÐYJ VEHICLES
The Command-Trac system is a vacuum disconnect
axle. The system has a two-piece axle shaft coupled
together by a shift collar. For two-wheel drive opera-
tion, the vacuum motor and shift fork disengages the
axle shaft splines. For four-wheel drive operation, the
vacuum motor and shift fork engages the axle
splines.
SELEC-TRACÐXJ VEHICLES
The Selec-Trac system is a non-disconnect axle.
Shifting from two-wheel to four-wheel drive is done
at the transfer case.
For XJ vehicles equipped withSelec-Tracand
ABS brake system, refer to Group 5ÐBrakes for ad-
ditional service information.
LUBRICANT SPECIFICATIONS
Multi-purpose, hypoid gear lubricant should be
used for Model 30 axles. The lubricant should have
MIL-L-2105C and API GL 5 quality specifications.
MOPARtHypoid Gear Lubricant conforms to both of
these specifications.
²The factory fill for the Model 30 axle is SAE Ther-
mally Stable 80W-90 gear lubricant.Do not use
heavier weight lubricant, this will cause axle
engagement difficulties.
²The factory installed lubricant quantity for the
NON-DISCONNECT TYPE AXLE is 1.48 L (3.13
pts.).
²The factory installed lubricant quantity for the
VACUUM-DISCONNECT TYPE AXLE is 1.65 L (3.76
pts.).
Refer to Group 0, Lubrication and Maintenance for
additional information regarding temperature range,
viscosity and fluid level.
2 - 22 FRONT SUSPENSION AND AXLEJ
Page 75 of 2158

CAUTION: If axle is submerged in water, lubricant
must be replaced immediately to avoid possible
premature axle failure.
LUBRICANT CHANGE
The gear lubricant will drain quicker if the vehicle
has been recently driven.
(1) Raise and support the vehicle.
(2) Remove the lubricant fill hole plug from the dif-
ferential housing cover.
(3) Remove the differential housing cover and
drain the lubricant from the housing.
(4) Clean the housing cavity with a flushing oil,
light engine oil or lint free cloth.Do not use water,
steam, kerosene or gasoline for cleaning.
(5) Remove the sealant from the housing and cover
surfaces. Use solvent to clean the mating surfaces.
(6) Apply a bead of MOPARtSilicone Rubber Seal-
ant to the housing cover (Fig. 1).Allow the sealant
to cure for a few minutes.
Install the housing cover within 5 minutes af-
ter applying the sealant. If not installed the
sealant must be removed and another bead ap-
plied.
(7) Install the cover and any identification tag.
Tighten the cover bolts in a criss-cross pattern to 41
Nzm (30 ft. lbs.) torque.
(8) Refill the differential with MOPARtHypoid
Gear Lubricant to bottom of the fill plug hole.
(9) Install the fill hole plug and lower the vehicle.
DRIVE AXLE ASSEMBLY REPLACEMENTÐXJ
VEHICLES
REMOVAL
(1) Raise the vehicle and position support stands
under the frame rails behind the lower suspension
arm frame brackets.
(2) Remove the front wheels.
(3) Remove the brake components and ABS brake
sensor (if equipped). Refer to Group 5ÐBrakes.
(4) On 4WD vehicles, disconnect the axle vent
hose.
(5) On 4WD vehicles, mark the drive shaft yoke
and axle pinion yoke for alignment reference. Discon-
nect the drive shaft from the axle.
(6) Disconnect the stabilizer bar link at the axle
bracket.
(7) Disconnect the shock absorbers from axle
bracket.
(8) Disconnect the track bar from the axle bracket.
(9) Disconnect the tie rod and drag link from the
steering knuckle. Disconnect the steering damper
from the axle bracket.
(10) Support the axle with a hydraulic jack under
the differential.
(11) Disconnect the upper and lower suspension
arms from the axle bracket.
(12) Lower the jack enough to remove the axle.
The coil springs will drop with the axle.
(13) Remove the coil springs from the axle bracket.
INSTALLATION
CAUTION: Suspension components with rubber
bushings should be tightened with the vehicle at
normal height. It is important to have the springs
supporting the weight of the vehicle when the fas-
teners are torqued. If springs are not at their normal
ride position, vehicle ride comfort could be affected
and premature bushing wear may occur. Rubber
bushings must never be lubricated.
(1) Install the springs and retainer clip. Tighten
the retainer bolts to 21 Nzm (16 ft. lbs.) torque.
(2) Support the axle on a hydraulic jack under the
differential. Position the axle under the vehicle.
(3) Raise the axle with a floor jack and align it
with the spring pads.
(4) Position the upper and lower suspension arm at
the axle bracket. Install bolts and nuts finger
tighten.
(5) Connect the track bar to the axle bracket and
install the bolt.Do not tighten at this time.
It is important that the springs support the
weight of the vehicle when the track bar is con-
nected. If springs are not at their usual posi-
tion, vehicle ride comfort could be affected.
Fig. 1 Typical Housing Cover With Sealant
JFRONT SUSPENSION AND AXLE 2 - 23
Page 91 of 2158
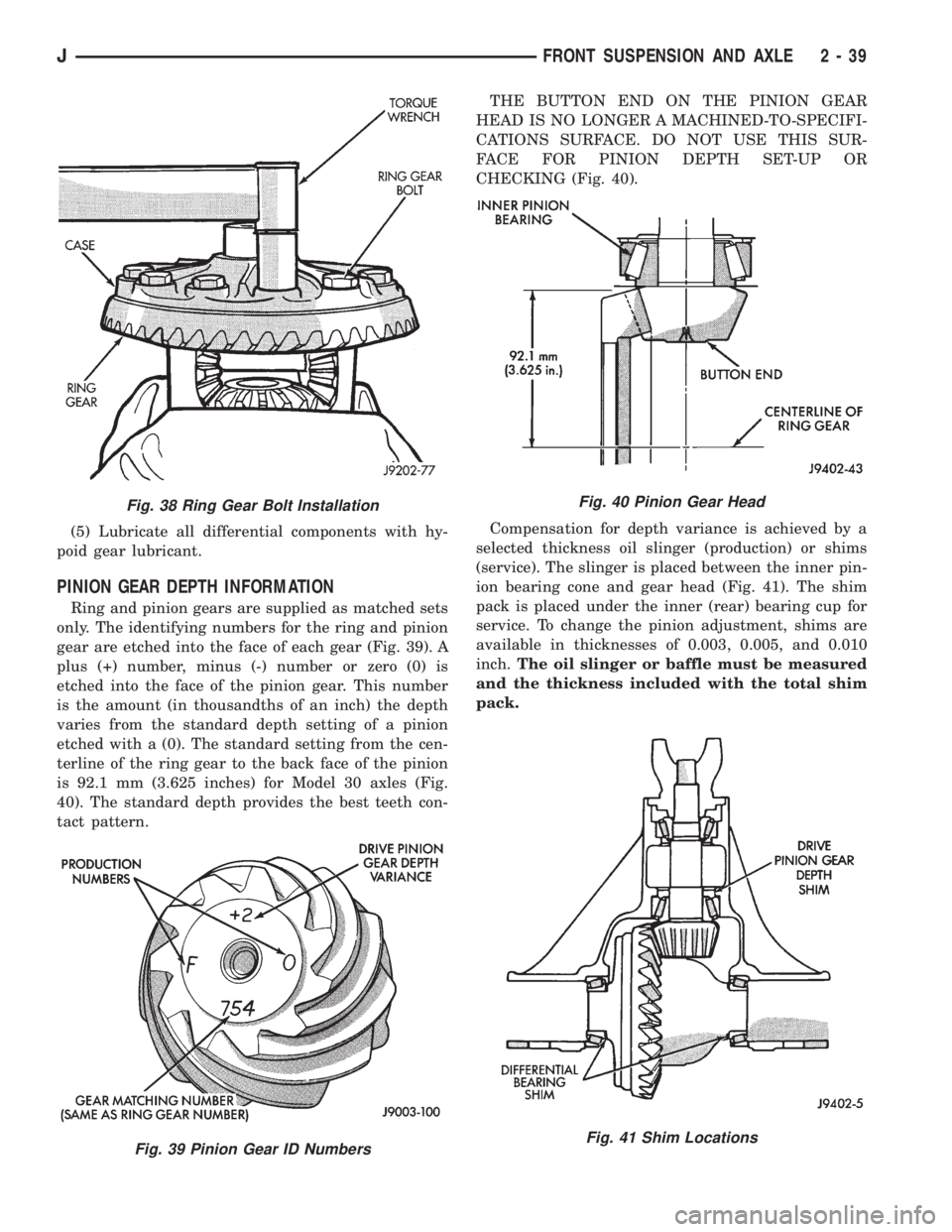
(5) Lubricate all differential components with hy-
poid gear lubricant.
PINION GEAR DEPTH INFORMATION
Ring and pinion gears are supplied as matched sets
only. The identifying numbers for the ring and pinion
gear are etched into the face of each gear (Fig. 39). A
plus (+) number, minus (-) number or zero (0) is
etched into the face of the pinion gear. This number
is the amount (in thousandths of an inch) the depth
varies from the standard depth setting of a pinion
etched with a (0). The standard setting from the cen-
terline of the ring gear to the back face of the pinion
is 92.1 mm (3.625 inches) for Model 30 axles (Fig.
40). The standard depth provides the best teeth con-
tact pattern.THE BUTTON END ON THE PINION GEAR
HEAD IS NO LONGER A MACHINED-TO-SPECIFI-
CATIONS SURFACE. DO NOT USE THIS SUR-
FACE FOR PINION DEPTH SET-UP OR
CHECKING (Fig. 40).
Compensation for depth variance is achieved by a
selected thickness oil slinger (production) or shims
(service). The slinger is placed between the inner pin-
ion bearing cone and gear head (Fig. 41). The shim
pack is placed under the inner (rear) bearing cup for
service. To change the pinion adjustment, shims are
available in thicknesses of 0.003, 0.005, and 0.010
inch.The oil slinger or baffle must be measured
and the thickness included with the total shim
pack.
Fig. 38 Ring Gear Bolt Installation
Fig. 39 Pinion Gear ID Numbers
Fig. 40 Pinion Gear Head
Fig. 41 Shim Locations
JFRONT SUSPENSION AND AXLE 2 - 39
Page 97 of 2158
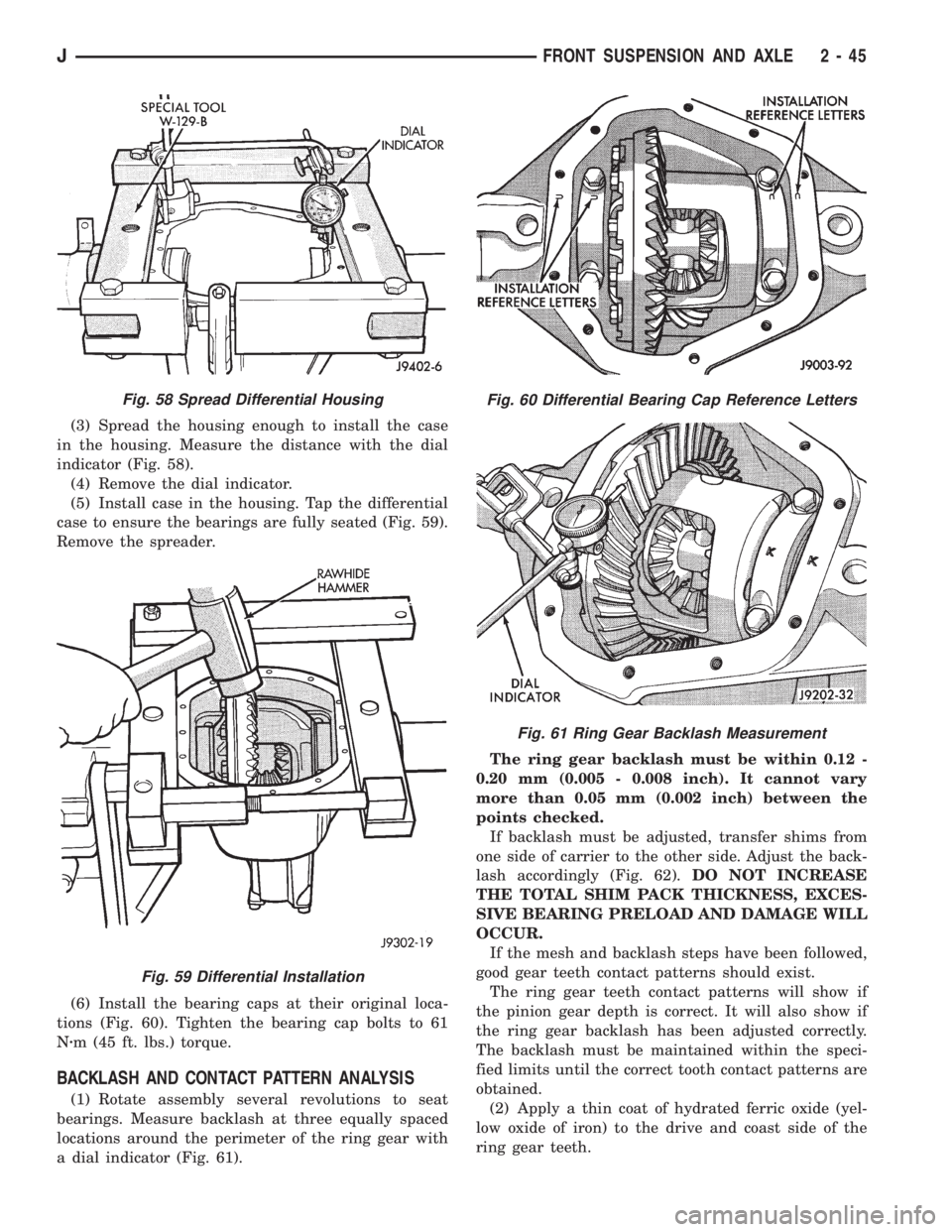
(3) Spread the housing enough to install the case
in the housing. Measure the distance with the dial
indicator (Fig. 58).
(4) Remove the dial indicator.
(5) Install case in the housing. Tap the differential
case to ensure the bearings are fully seated (Fig. 59).
Remove the spreader.
(6) Install the bearing caps at their original loca-
tions (Fig. 60). Tighten the bearing cap bolts to 61
Nzm (45 ft. lbs.) torque.
BACKLASH AND CONTACT PATTERN ANALYSIS
(1) Rotate assembly several revolutions to seat
bearings. Measure backlash at three equally spaced
locations around the perimeter of the ring gear with
a dial indicator (Fig. 61).The ring gear backlash must be within 0.12 -
0.20 mm (0.005 - 0.008 inch). It cannot vary
more than 0.05 mm (0.002 inch) between the
points checked.
If backlash must be adjusted, transfer shims from
one side of carrier to the other side. Adjust the back-
lash accordingly (Fig. 62).DO NOT INCREASE
THE TOTAL SHIM PACK THICKNESS, EXCES-
SIVE BEARING PRELOAD AND DAMAGE WILL
OCCUR.
If the mesh and backlash steps have been followed,
good gear teeth contact patterns should exist.
The ring gear teeth contact patterns will show if
the pinion gear depth is correct. It will also show if
the ring gear backlash has been adjusted correctly.
The backlash must be maintained within the speci-
fied limits until the correct tooth contact patterns are
obtained.
(2) Apply a thin coat of hydrated ferric oxide (yel-
low oxide of iron) to the drive and coast side of the
ring gear teeth.
Fig. 58 Spread Differential Housing
Fig. 59 Differential Installation
Fig. 60 Differential Bearing Cap Reference Letters
Fig. 61 Ring Gear Backlash Measurement
JFRONT SUSPENSION AND AXLE 2 - 45
Page 98 of 2158

(3) Rotate the ring gear one complete revolution in
both directions while a load is being applied. Insert a
pry bar between the differential housing and the case
flange to load gears. This will produce a distinct con-
tact patterns on both the drive side and coast side of
the ring gear teeth.(4) Note patterns in compound. Refer to (Fig. 63)
for interpretation of contact patterns and adjust ac-
cordingly.
FINAL ASSEMBLY
(1) Install the axle shafts. Refer to Axle Shaft In-
stallation in this Group.
(2) Scrape the residual sealant from the housing
and cover mating surfaces. Clean the mating surfaces
with mineral spirits. Apply a bead of MOPARtSili-
cone Rubber Sealant on the housing cover (Fig. 64).
Allow the sealant to cure for a few minutes.
Install the housing cover within 5 minutes af-
ter applying the sealant. If not installed the
sealant must be removed and another bead ap-
plied.
(3) Install the cover on the differential with the at-
taching bolts. Install the identification tag. Tighten
the cover bolts with 41 Nzm (30 ft. lbs.) torque.
CAUTION: Overfilling the differential can result in
lubricant foaming and overheating.
(4) Refill the differential housing with the specified
quantity of MOPARtHypoid Gear Lubricant.
(5) Install the fill hole plug and tighten to 34 Nzm
(25 ft. lbs.) torque.
Fig. 62 Backlash Shim Adjustment
2 - 46 FRONT SUSPENSION AND AXLEJ
Page 114 of 2158

MODEL 35 AXLE
INDEX
page page
Axle Shaft............................... 16
Axle Shaft Seal and Bearing................. 17
Backlash and Contact Pattern Analysis......... 27
Cleaning/Inspection........................ 20
Differential Assembly....................... 21
Differential Disassembly.................... 18
Differential Measurement and Installation........ 25
Differential Removal....................... 18
Drive Axle Assembly ReplacementÐXJ Vehicles . . 14Drive Axle Assembly ReplacementÐYJ Vehicles . . 14
Final Assembly........................... 29
General Information....................... 13
Lubricant Change......................... 13
Lubricant Specifications..................... 13
Pinion Gear Depth Information............... 21
Pinion Measurement and Assembly............ 22
Pinion Removal/Disassembly................. 19
Pinion Shaft Seal Replacement............... 15
GENERAL INFORMATION
The Model 35 housing has an iron center casting
(differential housing) with axle shaft tubes extending
from either side. The tubes are pressed into and
welded to the differential housing to form a one-piece
axle housing.
The integral type housing, hypoid gear design has
the centerline of the pinion set below the centerline
of the ring gear.
The axle has a vent hose to relieve internal pres-
sure caused by lubricant vaporization and internal
expansion.
The axles are equipped with semi-floating axle
shafts, meaning that loads are supported by the axle
shaft and bearings. The axle shafts are retained by
C-clips in the differential side gears.
The cover provides a means for servicing the differ-
ential without removing the axle.
Axles may be equipped with drum or disc brakes.
The axles that are equipped with ABS brake have a
tone ring pressed on the axle shaft. Use care when
removing axle shafts as NOT to damage the tone
wheel or the sensor.
The Model 35 axle has the assembly part number
and gear ratio listed on a tag. The tag is attached to
the housing cover. Build date identification codes are
stamped on the axle shaft tube cover side.
The differential case is a one-piece design. The dif-
ferential pinion mate shaft is retained with a
threaded roll pin. Differential bearing preload and
ring gear backlash is adjusted by the use of spacer
shims. Pinion bearing preload is set and maintained
by the use of a collapsible spacer.
For complete drive axle assembly removal
and installation refer to Drive Axle Assembly
Replacement in this Group.
LUBRICANT SPECIFICATIONS
Multi-purpose, hypoid gear lubricant should be
used for Model 35 axle. The lubricant should haveMIL-L-2105C and API GL 5 quality specifications.
MOPAR Hypoid Gear Lubricant conforms to both of
these specifications.
²Lubricant for Model 35 axle is a thermally stable
SAE 80W-90 gear lubricant.
²Lubricant for Model 35 axle with Trailer Tow is
SAE 75W-140 SYNTHETIC gear lubricant.
²Trac-Lok differentials add 4 oz. of friction modifier.
²Lubricant quantity is 1.66 L (3.50 pts.).
Refer to Group 0, Lubrication and Maintenance for
additional information.
CAUTION: If axle is submerged in water, lubricant
must be replaced immediately to avoid possible
premature axle failure.
LUBRICANT CHANGE
The gear lubricant will drain quicker if the vehicle
has been recently driven.
(1) Raise and support the vehicle.
(2) Remove the lubricant fill hole plug from the dif-
ferential housing cover.
(3) Remove the differential housing cover and
drain the lubricant from the housing.
(4) Clean the housing cavity with a flushing oil,
light engine oil or lint free cloth.Do not use water,
steam, kerosene or gasoline for cleaning.
(5) Remove the sealant from the housing and cover
surfaces.
(6) Apply a bead of MOPARtSilicone Rubber Seal-
ant to the housing cover (Fig. 1).Allow the sealant
to cure for a few minutes.
Install the housing cover within 5 minutes af-
ter applying the sealant. If not installed the
sealant must be removed and another bead ap-
plied.
(7) Install the cover and any identification tag.
Tighten the cover bolts to 41 Nzm (30 ft. lbs.) torque.
(8) Refill differential with Mopar Hypoid Gear Lu-
bricant to bottom of the fill plug hole.
JREAR SUSPENSION AND AXLES 3 - 13
Page 122 of 2158
²Smooth appearance with no broken/dented sur-
faces on the bearing rollers or the roller contact sur-
faces
²Bearing cups must not be distorted or cracked
²Machined surfaces should be smooth and without
any raised edges
²Raised metal on shoulders of cup bores should be
removed with a hand stone
²Wear and damage to pinion gear mate shaft, pin-
ion gears, side gears and thrust washers. Replace as
a matched set only.
²Ring and pinion gear for worn and chipped teeth
²Ring gear for damaged bolt threads. Replaced as a
matched set only.
²Pinion yoke for cracks, worn splines, pitted areas,
and a rough/corroded seal contact surface. Repair or
replace as necessary.
²Preload shims for damage and distortion. Install
new shims if necessary.
DIFFERENTIAL ASSEMBLY
(1) Install the following components in the differ-
ential case.
²Differential side gears and thrust washers
²Pinion gears and thrust washers
²Pinion gear mate shaft (align holes in shaft and
case)
(2) Lubricate all differential components with hy-
poid gear lubricant.
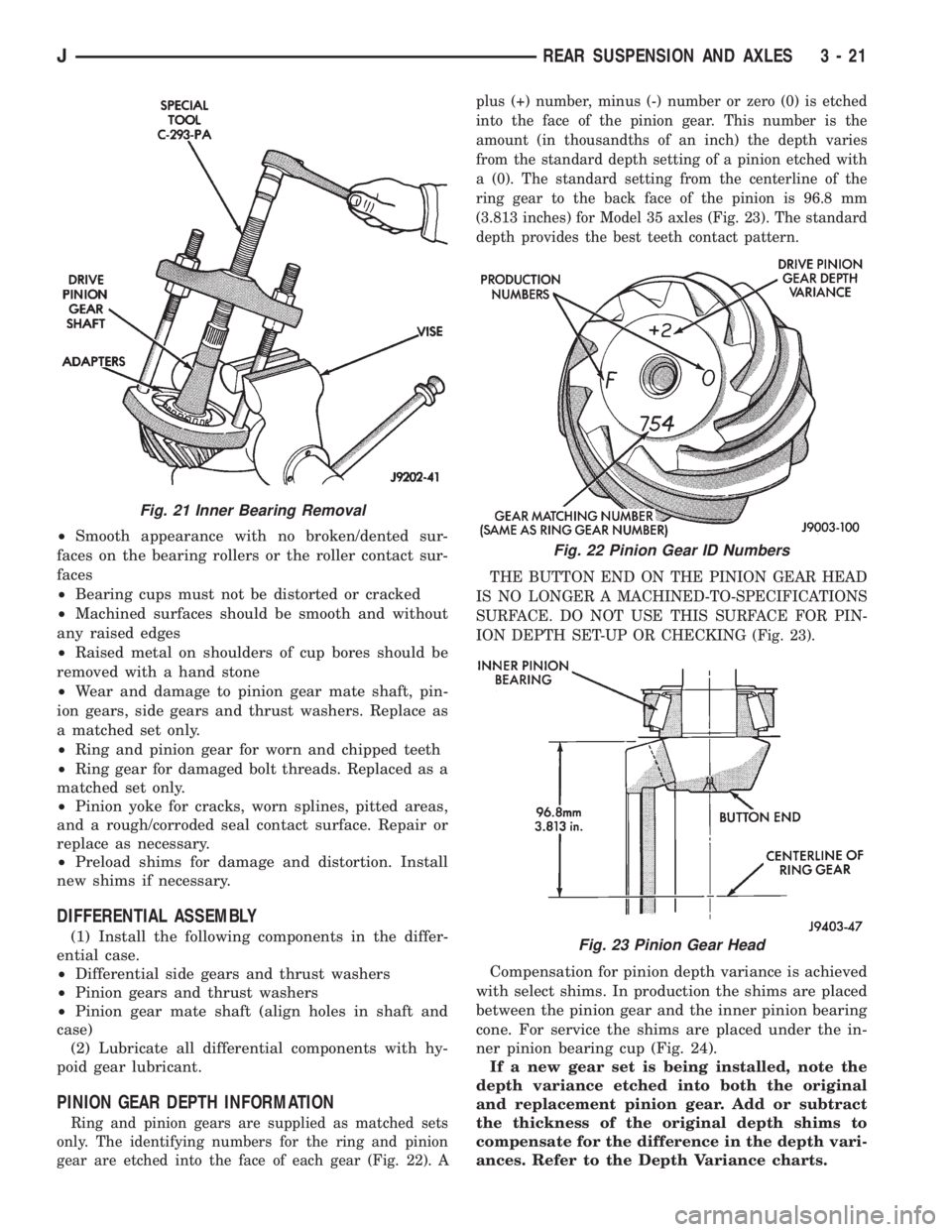
PINION GEAR DEPTH INFORMATION
Ring and pinion gears are supplied as matched sets
only. The identifying numbers for the ring and pinion
gear are etched into the face of each gear (Fig. 22). Aplus (+) number, minus (-) number or zero (0) is etched
into the face of the pinion gear. This number is the
amount (in thousandths of an inch) the depth varies
from the standard depth setting of a pinion etched with
a (0). The standard setting from the centerline of the
ring gear to the back face of the pinion is 96.8 mm
(3.813 inches) for Model 35 axles (Fig. 23). The standard
depth provides the best teeth contact pattern.
THE BUTTON END ON THE PINION GEAR HEAD
IS NO LONGER A MACHINED-TO-SPECIFICATIONS
SURFACE. DO NOT USE THIS SURFACE FOR PIN-
ION DEPTH SET-UP OR CHECKING (Fig. 23).
Compensation for pinion depth variance is achieved
with select shims. In production the shims are placed
between the pinion gear and the inner pinion bearing
cone. For service the shims are placed under the in-
ner pinion bearing cup (Fig. 24).
If a new gear set is being installed, note the
depth variance etched into both the original
and replacement pinion gear. Add or subtract
the thickness of the original depth shims to
compensate for the difference in the depth vari-
ances. Refer to the Depth Variance charts.
Fig. 21 Inner Bearing Removal
Fig. 22 Pinion Gear ID Numbers
Fig. 23 Pinion Gear Head
JREAR SUSPENSION AND AXLES 3 - 21
Page 132 of 2158

LUBRICANT SPECIFICATIONS
Multi-purpose, hypoid gear lubricant should be
used in the 8 1/4 inch axle. The lubricant should
have MIL-L-2105C and API GL 5 quality specifica-
tions. MOPARtHypoid Gear Lubricant conforms to
both of these specifications.
²The factory installed lubricant for the 8 1/4 inch
rear axle is SAE 80W 90 gear lubricant.
²The factory installed lubricant quantity is 6762
fluid oz.
CAUTION: Overfilling the differential can result in
lubricant foaming and overheating.
Refer to Group 0, Lubrication and Maintenance for
additional information.
CAUTION: If axle is submerged in water, lubricant
must be replaced immediately to avoid possible
premature axle failure.
DRIVE AXLE ASSEMBLY REPLACEMENTÐXJ
VEHICLES
REMOVAL
(1) Raise the vehicle. Position support stands un-
der the frame rails slightly in front the springs.
(2) Remove the rear wheels.
(3) Mark the drive shaft yoke and axle pinion yoke
for alignment reference. Disconnect the drive shaft
from the axle.
(4) Disconnect the axle vent hose.
(5) Disconnect the parking brake cables at the
equalizer or backing plate.
(6) Disconnect the shock absorbers from the axle
brackets.
(7) Disconnect the brake hose at the axle junction
block.Do not disconnect the wheel cylinder tub-
ing fittings.
(8) If equipped, disconnect ABS wiring connections
at the axle.
(9) Support the axle with a hydraulic jack under
the differential.
(10) Remove the spring U-bolts from the plate
brackets.
(11) Lower the jack enough to remove the axle.
INSTALLATION
CAUTION: Suspension components with rubber
bushings should be tightened with the vehicle at
normal height. It is important to have the springs
supporting the weight of the vehicle when the fas-
teners are torqued. If springs are not at their normal
ride position, vehicle ride comfort could be affected
and premature bushing wear may occur. Rubber
bushings must never be lubricated.(1) Support the axle on a hydraulic jack under the
differential. Position the axle under the vehicle.
(2) Raise the axle and align the spring center bolts
with the locating holes in the axle pads and plate
brackets.
(3) Install the spring U-bolts through the plate
brackets and tighten to 70 Nzm (52 ft. lbs.) torque.
(4) Install ABS wiring connections (if equipped) at
the axle.
(5) Connect the brake hose at the axle junction
block.
(6) Install the shock absorbers to the axle brackets
and tighten to 62 Nzm (46 ft. lbs.) torque.
(7) Connect the parking brake cables at the equal-
izer or backing plate.
(8) Connect the vent hose to the tube fitting.
(9) Align the reference marks and connect the
drive shaft to the axle yoke. Tighten the U-joint
clamp bolts to 19 Nzm (14 ft. lbs.) torque.
(10) Check differential lubricant and add if neces-
sary.
(11) Install the wheel and tire.
(12) Bleed the brakes.
(13) Remove the supports and lower the vehicle.
LUBRICANT CHANGE
The gear lubricant will drain quicker if the vehicle
has been recently driven.
(1) Raise and support the vehicle.
(2) Remove the lubricant fill hole plug from the dif-
ferential housing cover.
(3) Remove the differential housing cover and
drain the lubricant from the housing.
(4) Clean the housing cavity with a flushing oil,
light engine oil or lint free cloth.Do not use water,
steam, kerosene or gasoline for cleaning.
(5) Remove the sealant from the housing and cover
surfaces. Use solvent to clean the mating surfaces.
(6) Apply a bead of MOPARtSilicone Rubber Seal-
ant to the housing cover (Fig. 2). Allow the sealant to
cure for a few minutes.
Install the housing cover within 5 minutes after
applying the sealant. If not installed the sealant
must be removed and another bead applied.
(7) Install the cover and any identification tag.
Tighten the cover bolts in a criss-cross pattern to 47
Nzm (35 ft. lbs.) torque.
(8) Refill the differential with Mopar Hypoid Gear
Lubricant 13 mm (1/2 in.) below the fill plug hole.
With Trac-Lok differentials, add a container of Mopar
Hypoid Gear Lubricant Additive.
CAUTION: Overfilling the differential can result in
lubricant foaming and overheating.
(9) Install the fill hole plug and lower the vehicle.
JREAR SUSPENSION AND AXLES 3 - 31
Page 226 of 2158

when handling the cover and disc. Impact can distort
the cover, diaphragm spring, release fingers and the
hub of the clutch disc.
Use an alignment tool when positioning the disc on
the flywheel. The tool prevents accidental misalign-
ment which could result in cover distortion and disc
damage.
A frequent cause of clutch cover distortion (and
consequent misalignment) is improper bolt tighten-
ing. To avoid warping the cover, the bolts must tight-
ened alternately (diagonal pattern) and evenly (2-3
threads at a time) to specified torque.
CLUTCH HOUSING MISALIGNMENT
Clutch housing alignment is important to proper
clutch operation. The housing maintains alignment
between the crankshaft and transmission input
shaft. Misalignment can cause clutch noise, hard
shifting, incomplete release and chatter. It can also
result in premature wear of the pilot bearing, cover
release fingers and clutch disc. In severe cases, mis-
alignment can also cause premature wear of the
transmission input shaft and front bearing.
Housing misalignment is generally caused by incor-
rect seating on the engine or transmission, loose
housing bolts, missing alignment dowels, or housing
damage. Infrequently, misalignment may also be
caused by housing mounting surfaces that are not
completely parallel. Misalignment can be corrected
with shims.
INSTALLATION METHODS AND PARTS USAGE
Distortion of clutch components during installation
and the use of non-standard components are addi-
tional causes of clutch malfunction.Improper clutch cover bolt tightening can distort
the cover. The usual result is clutch grab, chatter
and rapid wear. Tighten the cover bolts as described
in Clutch Service section.
An improperly seated flywheel and/or clutch hous-
ing are additional causes of clutch failure. Improper
seating will produce misalignment and additional
clutch problems.
The use of non-standard or low quality parts will
also lead to problems and wear. Use recommended
factory quality parts to avoid comebacks.
A cocked pilot bearing is another cause of clutch
noise, drag, and hard shifting, and rapid bearing
wear. Always use an alignment tool to install a new
bearing. This practice helps avoid cocking the bear-
ing during installation.
INSPECTION AND DIAGNOSIS CHARTS
The clutch inspection chart (Fig. 1) outlines items
to be checked before and during clutch installation.
Use the chart as a check list to help avoid overlook-
ing potential problem sources during service opera-
tions.
The diagnosis charts describe common clutch prob-
lems, causes and correction. Fault conditions are
listed at the top of each chart. Conditions, causes and
corrective action are outlined in the indicated col-
umns.
The charts are provided as a convenient reference
when diagnosing faulty clutch operation.
6 - 4 CLUTCH DIAGNOSISJ
Page 1282 of 2158

CAUTION: DO NOT use engine or transmission oil,
mineral spirits or kerosene.
(3) Honing should be done by moving the hone up
and down fast enough to get a crosshatch pattern.
The hone marks should INTERSECT at 50É to 60É
for proper seating of rings (Fig. 1).
(4) A controlled hone motor speed between 200 and
300 RPM is necessary to obtain the proper cross-
hatch angle. The number of up and down strokes per
minute can be regulated to get the desired 50É to 60É
angle. Faster up and down strokes increase the cross-
hatch angle.
(5) After honing, it is necessary that the block be
cleaned to remove all traces of abrasive. Use a brush
to wash parts with a solution of hot water and deter-
gent. Dry parts thoroughly. Use a clean, white, lint-
free cloth to check that the bore is clean. Oil the
bores after cleaning to prevent rusting.
MEASURING WITH PLASTIGAGE
CRANKSHAFT MAIN BEARING CLEARANCE
Engine crankshaft bearing clearances can be deter-
mined by use of Plastigage, or equivalent. The follow-
ing is the recommended procedures for the use of
Plastigage:
(1) Remove oil film from surface to be checked.
Plastigage is soluble in oil.
(2) The total clearance of the main bearings can
only be determined by removing the weight of the
crankshaft. This can be accomplished by either of two
methods:
METHOD - 1 (PREFERRED)ÐShim the bear-
ings adjacent to the bearing to be checked. This will
remove the clearance between upper bearing shell
and the crankshaft. Place a minimum of 0.254 mm
(0.010 inch) shim between the bearing shell and the
adjacent bearing cap. Tighten the bolts to 18 Nzm (13
ft. lbs.) torque.²ALL ENGINESÐWhen checking No.1 main bear-
ing; shim No.2 main bearing.
²ALL ENGINESÐWhen checking No.2 main bear-
ing; shim No.1 and No.3 main bearing.
²ALL ENGINESÐWhen checking No.3 main bear-
ing; shim No.2 and No.4 main bearing.
²ALL ENGINESÐWhen checking No.4 main bear-
ing; shim No.3 and No.5 main bearing.
²2.5L ENGINEÐWhen checking No.5 main bear-
ing; shim No.4 main bearing.
²4.0L ENGINEÐWhen checking No.5 main bear-
ing; shim No.4 and No.6 main bearing.
²4.0L ENGINEÐWhen checking No.6 main bear-
ing; shim No.5 and No.7 main bearing.
²4.0L ENGINEÐWhen checking No.7 main bear-
ing; shim No.6 main bearing.
Remove all shims before assembling engine.
METHOD - 2 (ALTERNATIVE)ÐThe weight of
the crankshaft is supported by a jack under the coun-
terweight adjacent to the bearing being checked.
(3) Place a piece of Plastigage across the entire
width of the bearing cap shell (Fig. 2). Position the
Plastigage approximately 6.35 mm (1/4 inch) off cen-
ter and away from the oil holes. In addition, suspect
areas can be checked by placing the Plastigage in
that area. Tighten the bearing cap bolts of the bear-
ing being checked to 108 Nzm (80 ft. lbs.) torque.DO
NOT rotate the crankshaft or the Plastigage
may be smeared, giving inaccurate results.
(4) Remove the bearing cap and compare the width
of the flattened Plastigage with the scale provided on
the package (Fig. 3). Plastigage generally comes in 2
scales (one scale is in inches and the other is a met-
ric scale). Locate the band closest to the same width.
This band shows the amount of clearance. Differ-
ences in readings between the ends indicate the
amount of taper present. Record all readings taken
(refer to Engine Specifications).
(5) Plastigage is available in a variety of clearance
ranges. The 0.025-0.076 mm (0.001-0.003 inch) range
is usually the most appropriate for checking engine
bearing clearances.
Fig. 1 Cylinder Bore Crosshatch Pattern
Fig. 2 Placement of Plastigage in Bearing Shell
JENGINES 9 - 3