engine MITSUBISHI DIAMANTE 1900 User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: MITSUBISHI, Model Year: 1900, Model line: DIAMANTE, Model: MITSUBISHI DIAMANTE 1900Pages: 408, PDF Size: 71.03 MB
Page 14 of 408
GENERALINFORMATIONAND MAINTENANCE l-15
10. install the air cleaner assembly and the re- *Wrap shop towels around the fitting that is
tainer bolts. being dtsconnected to absorb residual fuel in
11. Connect the air intake hose. the lines. 9. While holding the fuel filter nut with aback-
up wrench, tighten the banjo bolt to 22 ft. Ibs. (30
Nm). Tighten the flare nut to 25 ft. Ibs. (35 Nm), with
12. Attach the solenoid valve.
4. Cover the hose connection with shop towels to a back-up wrench on the nut.
13. Connect the boost hose.
14. Attach the air flow sensor connector. prevent any splash of fuel that could be caused by 10. Tighten the filter mounting bolts to 10 ft. Ibs.
residual pressure in the fuel pipe line. Hold the fuel (14 Nm).
15. Connect the negative battery cable. 11.
filter nut securely with a backup wrench, then remove Connect the negative battery cable. Turn the
REMOVAL &INSTALLATION the banjo bolt on the engine feed line. Disconnect the
high-pressure fuel line from the filter. Remove and
discard the gaskets.
5. While holding the fuel filter nut securely with a
back-up wrench, loosen the filter feed pipe flare nut key to the ON position to pressurize the fuel system
and check for leaks.
12. If repairs of a leak are required, remember to
release the fuel pressure before opening the fuel sys-
tern.
u See Figures 43 thru 48
On most vehicles covered by this manual, the fuel
filter is located in the engine compartment, mounted
to the firewall.
Do not use conventional fuel filters, hoses or
clamps when servicing fuel injection sys
terns. They are not compatible with the injec-
tion
system and could fail, causing personal
injury or damage to the vehicle. Use only
hoses and clamps specifically designed for
fuel injection systems.
1. Properly relieve the fuel system pressure as
outlined in Section 5 of this manual. on the bottom of the filter. Separate the flare nut con-
nection from the filter. If equipped, remove and dis-
card the gaskets.
6. Remove the mounting bolts and remove
. ,,,. ,.
.a r I,.,< I the
ruer rrrter. II necessary, remove me ruer rrrrer oracket.
To install:
7. Install the filter to its bracket only finger-tight.
Movement of the filter will ease attachment of the fuel
lines.
Ensure that the filter is installed with the flow
arrow in the proper direction. The flow arrow
typically points toward the engine side of the
filter. improper installation of the fuel filter
will cause the vehicle to run poorly.
2. If not already done, disconnect the negative REMOVAL&INSTALLATION
u See Figures 49, 50, and 51
1, Disconnect the negative battery cable.
2. If necessary for access, remove the air intake
hose and air cleaner assembly.
3. If necessary, unfasten the retaining clamp, then
disconnect the ventilation hose from the PCV valve.
4. Remove the PCV valve from the camshaft
(rocker) cover.
To install:
5. Install the PCV valve into the rocker cover. If
the valve is threaded, tighten the valve until snug.
battery cable.
3. On most models. the iob is made easier if the
air inlet hose and upper air cleaner housing is re-
moved from the vehicle. *Make sure new O-rings are installed prior
to installation.
8. Insert the filter feed pipe to the lower connec-
tion of the filter and manually screw in the main
pipe’s flare nut. 6. Reconnect the ventilation hose to the valve.
7. If removed, install the air intake hose and the
a .ir cleaner assembly.
8. Connect the negative battery cable.
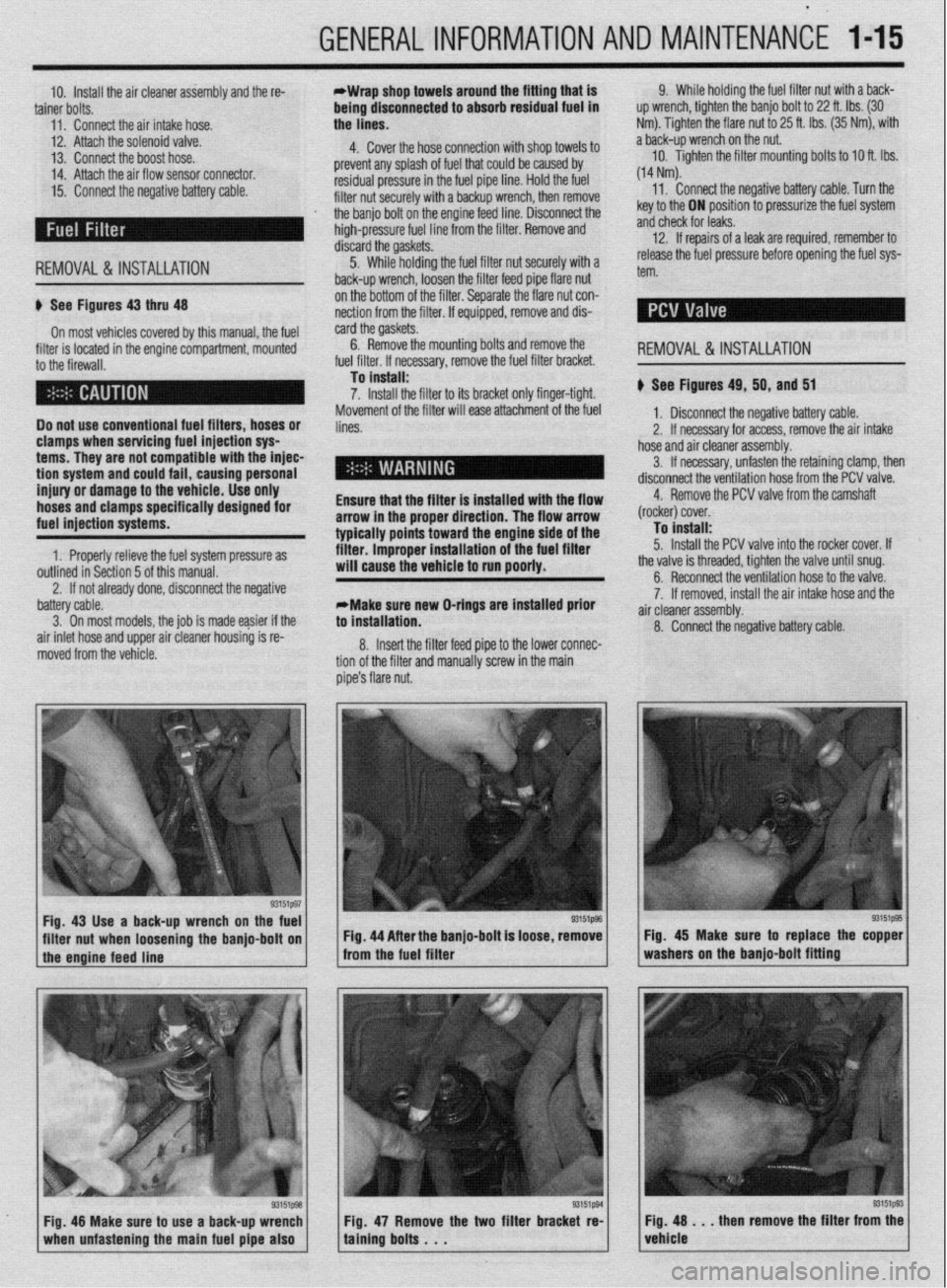
Fig. 43 Use a back-up wrench on the fuel
I I
93151@3
filter nut when loosening the banjo-bolt on Fig. 44 After the banjo-bolt is loose, remove
I
1 the engine feed line - from the fuel filter
93151p93 Fig. 48 Make sure to use a back-up wrench
1 when unfastening the main fuel pipe also 1 Fig. 47 Remove the two filter bracket re-
taining bolts . . . Fig. 45 Make sure to replace the copper
washers on the banjo-bolt fitting
Fig. 48 . . . then remove the filter from the
vehicle
Page 17 of 408

l
1-18 GENERALINFORMATIONAND MAINTENANCE
the clamps and remove the cables, negative cable
first. On batteries with posts on top, the use of a
puller specially made for this purpose is recom-
mended. These are inexoensive and available in most alternator or turn the adjusting bolt to adjust belt ten-
sion. Once the desired value is reached, secure the
bolt or locknut and recheck tension.
d”t” lJdlL> X”lt;>. 31°C LtXlllllldl lJdllt2)’ MLJIC, dlt’ X- cured with a small bolt. ST& I REMOVAL &INSTALLATION
Clean the cable clamps and the battery terminal I
with a wire brush, until all corrosion, grease, etc., is
removed and the metal is shinv. It is esneciallv imnnr-
tant to c
knife is useful nere), since a smart
material or oxidation there will pre Clean the cable clamps and the battery terminal
with a wire brush, until all corrosion, grease, etc., is
removed and the metal is shiny. It is especially impor-
tant to clean the inside of the clamp thoroughly (an old
knife is useful here), since a small deposit of foreign
material or oxidation there will prevent a sound electri-
cal connection and inhibit either starting or charging.
Special tools are available for cleaning these parts,
one type for conventional top post batteries and an-
other type for side terminal batteries. It is also a good
idea to apply some dielectric grease to the terminal, as
this will aid in the prevention of corrosion,
After the clamps and terminals are clean, reinstall
the cables, negative cable last; DO NOT hammer the
clamps onto battery posts. Tighten the clamps se-
curely, but do not distort them. Give the clamps and
terminals a thin external coating of grease after in-
stallation, to retard corrosion.
Check the cables at the same time that the terminals
are cleaned. If the cable insulation is cracked or bro-
ken, or if the ends are frayed, the cable should be re-
placed with a new cable of the same length and gauge.
CHARGING
the cables, negative cable last; DO NOT hammer the
curely, but do not distort them. Give the clamps and
terminals a thin external coating of grease after in-
stallation, to retard corrosion.
Check the cables at the same time that the terminals
are cleaned. If the cable insulation is cracked or bro-
ken, or if the ends are frayed, the cable should be re-
placed with a new cable of the same length and aauae.
CHARGING
Fig. 62 mere are typically 3 types of ac-
cessory drive belts found on vehicles today 1. Loosen the alternator support nut.
2. Loosen the adjuster lock bolt.
3. Rotate the adjuster bolt counter clockwise to
I .I , . . . * . .
I Tn i”et*ll* Fig. 62 There are typically 3 types of ac-
Fig. 64 Deep cracks in this belt will cause
flex, building up heat that will eventually 11, 1.8L, 2.OL and 2.4L Engines
cal connection and inhibit either starting or charging.
Special tools are available for cleaning these parts,
one type for conventional top post batteries and an-
other type for side terminal batterin, I+ if QI@* 3 nnnd
idea to apply some dielectric grr
this will aid in the prevention of ,,vIIuaIUII.
After the clamps and terminals are clean, reinstall 1.5L, 1.6
AL TERNA TOR BE1 T
e See Figures 67,68, and 69
1. Loosen the alternator support nut.
2. Loosen the adjuster lock bolt.
3. Rotate the adjuster bolt counter clockwise to
release the tension on the belt.
4. Remove the belt.
To install:
5. Install the belt on the pulleys.
6. Rotate the adjuster bolt clockwise until the
proper tension is reached.
7. Tighten the adjuster lock bolt and the alternator
support nut.
POWER STEERING BELT
8 See Figures 70 and 71
1. Remove the alternator belt as described above.
2. Loosen the power steering pump adjusting
bolts.
3. Remove the power steering oumo fixed bolt on
R Rntatn the cxiillrtm hnit A&+,& until the r -r- .- .- ._.. ._ .______
7. Tighten the adjuster lock bolt and the alternator
support nut.
POWER STEERING BELT
1 ..“‘.I ““..Y...Y up II”“. ..IU. ..m.*
1 lead to belt failure V.
I
I
The chemical reaction which takes place in - 1 the rear of the bracket.
4. Rotate the pump toward the engine and remove
the belt.
all batteries generates explosive hydrogen
gas. A spark can cause the battery to explode
and splash acid. To avoid serious personal
injury, be sure there is proper ventilation and
take appropriate fire safety precautions when
connecting, disconnecting, or charging a bat-
tery and when using jumper cables. To fnstall:
5. Install the belt on the pulleys.
A battery should be charged at a slow rate to keep
the plates inside from getting too hot. However, if
some maintenance-free batteries are allowed to dis-
charge until they are almost “dead,” they may have to
be charged at a high rate to bring them back to “life.”
Always follow the charger manufacturers instructions
on charging the battery. 85 The cover of this belt ex-
Fig. is worn,
REPLACEMENT
When it becomes necessary to reolace thn haeoN
‘” yyL’“‘J’ I or oreMer
select one with an amperage rating equal tc .
a ----
than the battery originally installed. Deterioration and
just plain aging of the battery cables, starter motor,
and associated wires makes the battery’s job harder
in successive years. The slow increase in electrical
resistance over time makes it prudent to install a new
battery with a greater capacity than the old. 1 Fig. 67 Loosen the adjuster lock bolt . . .
I ‘-
I -. -_ tm1217 Fig. 66 Installing too wide a belt can resylt
in serious belt wear and/or breakage
the belt and run outward. All worn or damaged drive
belts should be replaced immediately. It is best to re-
place all drive belts at one time, as a preventive
uring this service operation. maintenance measure, d
- ADJUSTMENT : *
INSPECTION Excessive belt tension will cause damage to the al-
e See Figures 62, 83, 64, 65, and 88
Inspect the belts for signs of glazing or cracking. A
glazed belt will be perfectly smooth from slippage,
while a good belt will have a slight texture of fabric
visible. Cracks will usually start at the inner edge of pulley bearings, while, on
It tension will
Droduce slin ternator and water pump
the other hand, loose be
r ------ r
and premature wear on the belt. Therefore, be sure to
adjust the belt tension to the proper level.
To
adjust the tension ’ ’ ’ ” ’ ‘* adjusting bolt or fixing b
alternator bracket or tens on a onve Den. loosen me I Fig. 68 . . . then
from the engine remove the alternator
bolt locknut on the alternator,
iion pulley. Then move the
Page 18 of 408

GENERAL INFORMATION AND MAlNTENANdE l-19
792UQ4 Fig. 69 Accessory V-belt routing-Mii
subishf 1.6L, 1.6L,-1.6L, 2.OL and 2.4L en
gines
33151PM Fig. 70 After the adjusting and fixed bolt!
are loosened, rotate the pump . . .
/ F$71t immtl$mm&a the power ::: 6. Rotate the pump until the proper tension is
reached.
7. Tighten the adjusting bolts on the pump.
8. Tighten the fixed bolt on the rear of the bracket.
9. Install the alternator belt.
A/r: COMPRESSOIl BEL f
1. Loosen the tension oullev and remove the belt.
2. The installation is the reverse of the removal.
.3.gL DGHC, 3.OL SOHC (Gaiant models
only) and 3.5L Engines 4. Remove the belt.
To install:
5. Install the belt on the crankshaft and alternator
pulleys.
6. Using the adjusting bolt on the tensioner,
tighten the belt to the desired tension.
7. Tighten the fixing nut to hold the adjustment.
8. Install the undercover and lower the vehicle to
_,
the tloor.
9. Connect the negative battery cable.
POWER SliEERlNG BEL f
6 See Figures 72 and 73 1. Disconnect the neaative batteN cah+P
-I
Wait at least 60 seconds after the negative
battery cable is disconnected to prevent poS-
sibie deployment of the air bag.
2. Raise and safely support the vehicle and re-
mob re the undercover.
3. Remove the alternator and NC compressor
belt.
4. Lower the vehicle and remove the cruise con-
trol oumn link iW%mblV. 79244Q.37
-- I-- r ---- - _I
Fig. 72 Serpentine belt routing-Mitsubishi 5. Place the power steering hose under the oil
reservoir.
3.OL engines (except 1696-00 Galant mod-
6.
Loosen the tension pulley fixing bolts and re-
els)
Generator pulP
1 move the power steering pump drive belt.
To install:
1 7. install the Dower steerina oumu r+r+v~ hp++
8. Insert an extension bar &eoufvaik;;t”f;;id‘he
opening at the end of the tension pulley bracket and
pivot the pulley to apply tension to the belt.
9. Tighten the fixing bolts.
10. Raise the vehicle and install the alternator and
compressor belt.
Il. Install the undercover and lower +hfi vph+r+p
.I,., .VII.“.Y.
12. Connect the negative battery cable.
I 3.OL SGHC (Diamante Models Onivl Enotne
I ,r ” 1. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
2.’ Loosen the lockbolt on the face nf the A/C _ __.- tensioner pulley.
3
Turn the adiustina bolt of the A/C +fincrnner
pulley to loosen the tension of the A/C belt.
4. Remove the A/C compressor belt.
5.
Loosen the locknut on the face of the power
to loosen the tc
7. Remov
Fig. 73 Accessory V-belt routing-Mitsubishi
3.5L and 1996-00 3.OL SOHC Galant en-
gines steering/alternator tensloner pulley.
6. Turn the adjusting bolt of the tensioner pulley
msion of the belt.
‘e the power steering/alternator belt.
To install:
8. Install the power steering/alternator belt first
.* .* . ,^
ssor drive belt. ana tnen tne A/ti compre:
9. Adjust the belts t+
ing the adjusting bolts anu
II~IIWII pueey tlxmg I the proper tension by turn-
A.:-L I-..-.. I,^, .’
nut/bolt.
10. Tighten the mounting nut of the power steer-
ing/alternator tensioner pulley to 36 ft. Ibs. (50 Nm).
Wait at least 60 seconds after the negative
battery cable is disconnected to prevent pos-
sible deployment of the air bag. -The manufacturer does not provide a
torque specification for the bolt that secures
A/C tensioner pulley.
2. Raise and safely support the vehicle and re- 11. Connect the negative battery cable.
move the front undercover.
3. Loosen the tension pulley fixing nut and relieve
the tension on the belt by turning the adjusting bolt.
Page 19 of 408

.
l-20 GENERALINFORMATIONAND MAINTENANCE
INSPECTION
# See Figures 74 thru 81
All engines covered by this manual utilize timing
belts to drive the camshaft from the crankshafts turn-
ing motion and to maintain proper valve timing.
Some manufacturers schedule periodic timing belt
replacement to assure optimum engine performance,
to make sure the motorist is never stranded should
the belt break (as the engine will stop instantly) and
for some (manufacturers with interference motors) to
prevent the possibility of severe internal engine dam-
age
St10Ula the Delt break. Although the 1.5L and 1.8L engines are not listed
as an interference motors (it is not listed by the man-
ufacturer as a motor whose valves might contact the
pistons if the camshaft was rotated separately from
the crankshaft) the first 2 reasons for periodic re-
placement still apply and the timing belt should be
replaced at 60,000 miles (96,000 km). The 1.6L,
2.01,2.4L, 3.OL, and 35L engines are listed as inter-
ference motors, so the timing belt MUST be replaced
at 60,000 miles (96,000 km) to avoid severe engine
damage if the belt should break.
But whether or not you decide to replace the tim-
ing belt in the manufacturers schedule, you would be
wise to check it periodically to make sure it has not
become damaged or worn. Generally speaking, a se-
verelv worn belt mav cause enaine oerformance to
drop~dramatically, but a damaged belt (which could
give out suddenly) may not give as much warning. In
general, any time the engine timing cover(s) is (are)
removed you should inspect the belt for premature
parting, severe cracks or missing teeth. Also, an ac-
cess plug is provided in the upper portion of the tim-
ing cover so that camshaft timing can be checked
without cover removal. If timing is found to be off,
cover removal and further belt inspection or replace-
ment is necessary.
tml245 Fig. 76 look for noticeable cracks or wear
on the belt face
_
For the timing belt removal and installation proce-
dure, please refer to Section 3 of this manual. Fig. 74 Check for premature parting of the
belt
INSPECTION
. 75 Check if the teeth are cracked or
fig. 77 You may only have damage on one
side of the belt; if so, the guide could be
the culprit
b See Figures 82,8S, 84, and 85 .
Upper and lower radiator hoses, along with the
heater hoses, should be checked for deterioration,
leaks and loose hose clamps at least every 30,000
miles (48,000 km). It is also wise to check the hoses
periodically in early spring and at the beginning of
the fall or winter when you are performing other
maintenance. A quick visual inspection could dis-
cover a weakened hose which might have left you
stranded if it had remained unrepaired.
Whenever you are checking the hoses, make sure
the engine and cooling system are cold. Visually in-
spect for cracking, rotting or collapsed hoses, and w-
place as necessary. Run your hand along the length
of the hose. If a weak or swollen spot is noted when
squeezing the hose wall, the hose should be re- Fig. 78 Foreign materials can get in be- Fig. 79 Inspect the timing belt for c
tween the teeth and cause damage fraying, glazing or damage of any kind
Fig. 80 Damage on only one side of the tim-
I I Fig. 81 ALWAYS replace the timing belt at
ing belt may indicate a faulty guide
the interval specified by the manufacturer
, L placed.
Page 20 of 408

GENERALINFORMATIONAND MAINTENANCE l-21
IWSIZXJ FM. 83 A hose clamn that is taa tiaht can
Fig. 82 The cracks developing along this
hose are a result of age-related hardening caise older hoses td separate and ‘iear on
either side of the clamp
lCCS1221 Fig. 84 A soft spongy hose (identifiable by
1 the swollen section) will eventually burst
and should be replaced
IEMOVAL &,INSTALLATION '
1. Remove the radiator pressure cap. her of the sorina tension tvoe (which reouire oliers
3 squeeze the 6bs and loosenj or of the’screw ten-
ion type (which require screw or hex drivers to
oosen). Pull the clamps back on the hose away from
he connection. Never remove the pressure cap while the en-
gine is running, or personal injury from
scalding hot coolant or steam may result. If
possible, wait until the engine has cooled to
remove the pressure cap. If this is not possi-
ble, wrap a thick cloth around the pressure
cap and turn it slowly to the stop. Step back
while the pressure is released from the cool-
ing system. When you are sure all the pres-
sure has been released, use the cloth to turn
and remove the cao.
2. Position a clean container under the radiator
and/or engine draincock or plug, then open the drain
and allow the cooling system to drain to an appropri-
ate level. For some upper hoses, only a little coolant
must be drained. To remove hoses positioned lower
on the engine, such as a lower radiator hose, the en-
tire cooling system must be emptied.
When draining coolant, keep in mind that
cats and dogs are attracted by ethylene gly-
col antifreeze, and are quite likely to drink
any that is left in an uncovered container or
in puddles on the ground. This will prove fa-
tal in sufficient quantity. Always drain
coolant into a sealable container. Coolant
may be reused unless it is contaminated or
several years old. 9. Close the radiator or engine drains and prop-
erly refill the cooling system with the clean drained
engine coolant or a suitable mixture of ethylene gly-
cot coolant and water.
10. If available, install a pressure tester and check
for leaks. If a pressure tester is not available, run the
engine until normal operating temperature is reached
(allowing the system to naturally pressurize), then
check for leaks.
If you are checking for leaks with the system
at normal operating temperature, BE EX-
TREMELY CAREFUL not to touch any moving
or hot engine parts. Once temperature has
been reached. shut the enaine OFF. and
Fig. 85 Hoses are likely to deteriorate from
the inside if the cooling system is not peri-
odically flushed check for leaks around the-hose fittings and
connections which were removed earlier.
INSPECTION
b See Figures 88 and 87
The CV (Constant Velocity) boots should be
checked for damage each time the oil is changed and
any other time the vehicle is raised for service. These
boots keep water, grime, dirt and other damaging
matter from entering the CV-joints. Any of these
could cause early CV-joint failure which can be ex-
pensive to repair. Heavy grease thrown around the in-
side of the front wheel(s) and on the brake
caliper/drum can be an indication of a torn boot.
Thorouahlv check the boots for missina clamos and 3. Loosen the hose clamps at each end of the
rose requiring replacement. Clamps are usually ei-
4. Twist, pull and slide the hose off the fitting,
sking care not to damage the neck of the component
rom which the hose is being removed.
*If the hose is stuck at the connection, do
lot try to insert a screwdriver or other sharp
ool under the hose end in an eff art to free it,
IS the connection and/or hose may become
lamaged. Heater connections especially
nay be easily damaged by such a procedure.
f the hose is to be replaced, use a single-
!dged razor blade to make a slice along the
lortion of the hose which is stuck on the con-
section, perpendicular to the end of the
lose. 00 not cut deep so as to prevent dam-
aging the connection. The hose can then be
keeled from the connection and discarded. Fig. 86 CV-boots must be inspected period-
5.. Clean both hose mounting connections. In-
,pect the condition of the hose clamps and replace
hem, if necessary.
To install:
6. Dip the ends of the new hose into clean en-
fine coolant to ease installation.
7. Slide the clamps over the replacement hose,
hen slide the hose ends over the connections into
rosition.
8. Position and secure the clamps at least l/d in.
6.35mm) from the ends of the hose. Make sure they
Ire located beyond the raised bead of the connector.
Page 21 of 408

l-22 GENERALINFORMATIONAND MAINTENANCE
tears. If the boot is damaged, it should be replaced
trode is to the block’s cooling passages) the cooler it
your driving is long distance, high speed travel, use a
immediately. Please refer to Section 7 for procedures.
will operate. A plug that absorbs little heat and re-
colder plug; if most of your driving is stop and go,
mains too cool will quickly accumulate deposits of
use a hotter plug. Original equipment plugs are gen-
oil and carbon since it is not hot enough to burn
erally a good compromise between the 2 styles and
them off. This leads to plug fouling and consequently
most people never have the need to change their
to misfiring. A plug that absorbs too much heat will
plugs from the factory-recommended heat range.
ti See Figure 88 have no deposits but, due to the excessive heat, the
,electrodes will burn away quickly and might possibly
REMOVAL &INSTALLATION
A typical spark plug consists of a metal shell sur- lead to preignition or other ignition problems. Preig-
rounding a ceramic insulator. A metal electrode ex- nition takes place when plug tips get so hot that they
ti See Figures 90 thru 95
tends downward through the center of the insulator glow sufficiently to ignite the air/fuel mixture before
and protrudes a small distance. Located at the end of the actual spark occurs. This early ignition will usu- A set of spark plugs usually requires replacement
the plug and attached to the side of the outer metal ally cause a pinging during low speeds and heavy after about 20,000-30,000 miles (32,000-48,000
shell is the side electrode. The side electrode bends loads. km), depending on your style of driving. In normal
in at a 90” angle so that its tip is just past and paral- The general rule of thumb for choosing the correct operation plug gap increases about 0.001 in.
lel to the tio of the center electrode. The distance be- heat range when picking a spark plug is: if most of (0.025mrn) for every 2,500 miles
(4,000 km). As the
tween these two electrodes (measured in thousandths
of an inch or hundredths of a millimeter) is called the
spark piug gap.
The spark plug does not produce a spark, but in-
steed provides a gap across which the current can
arc. The coil produces anywhere from 20,000 to
50,000 volts (depending on the type and application)
which travels through the wires to the spark plugs.
The current passes along the center electrode and
jumps the gap to the side electrode, and in doing so,
ignites the air/fuel mixture in the combustion charn-
ber.
SPARKPLUG HEATRANGE
ti See Figure 89
Spark plug heat range is the ability of the plug to
dissipate heat. The longer the insulator (or the farther
INSULATOR CRACKS
OFTEN OCCUR HERE
SIDE ELECTRODE ENTER ELECTRODE:
(SEND TO ADJUST GAP) FILE FLAT WHEN
ADJUSTING GAP;
DO NOT BEND
Fig. 88 Cross-section of a spark plug
it extends into the engine), the hotter the plug will
operate; the shorter the insulator (the closer the elec- Fig. 90 Carefully twist the boot end of the
I
spark plug wire and withdraw the spark plug
wire boot from the cylinder head
Fig. 92 A locking extension such as this is
extremely helpful when removing spark
plugs that are centrally located in the cyhn-
Fig. 94 . . .
then carefully withdraw the
spark plug from the engine Fig. 91 A special spark plug socket with a
rubber insert is required to remove the
spark plugs. Typically the spark plugs
re-
quire a Ya spark plug socket
Fig, 93 Using the appropriate sized spark
plug socket, necessary extensions and drive
tools, loosen the spark plug . . .
93151ptxl Fig. 95 After removing the plug from the en-
gine, inspect it using the spark plug condi-
tion chart in this section to determine the
running condition of your engine
Page 22 of 408

t
GENERALINFORMATIONAND MAINTENANCE l-23
gap increases, the plug’s voltage requirement also in-
creases. It requires a greater voltage to jump the the spark plug counterclockwise to loosen and re-
move the spark plug from the bore.
wider gap and about &o to three times as much volt-
age to fire the plug at high speeds than at idle. The
improved air/fuel ratio control of modern fuel injec-
tion combined with the higher voltage output of mod- Be sure not to use a flexible extension on the place. The click may be felt or heard, then gently pull
ern ignition systems will often allow an engine to run socket. Use of a flexible extension may allow back on the boot to assure proper contact.
.___. . _
significantly longer on a set of standard spark plugs, a shear force to be agptf’ ea to me plug.
A 12. On the 3.OL fSOHC and DOHC) and 3.5L en-
LL_ _I___ -u I_ IL-
but keep in mind that efficiency will drop as the gap shear force could break tne pug on III me
tion 3 for the installation procedure.
widens (along with fuel economy and power). cylinder head, leading to costly and frustrat-
13. If equipped, install the center cover.
When you’re removing spark plugs, work on one ing repairs.
at a time. Don’t start by removing the plug wires all at
once, because, unless you number them, they may To install:
INSPECTION & GAPPING
11. Apply a small amount of silicone dielectric
compound to the end of the spark plug lead or inside
the spark plug boot to prevent sticking, then install
the boot to the spark plug and push until it clicks into
gines, install the upper intake manifold. Refer to Sec-
,,Y” ..1111 uy”’ 1 the neaative bat&v cable and if become mixed up. Take a minute before you begin
and number the wrrpc with +sne
1. Disconnect. ~~.~
--..-., -..-.-, -..-
thevehicle has been run recently, allow the engine to
thoroughly cool.
2. If equipped, remove the center cover.
3. On the 3.OL (SOHC and DOHC) and 3.5L en-
gines, the upper intake manifold must be removed to
access the rear spark plugs. Refer to Section 3 for the
removal procedure.
4. Carefully twist the spark plug wire boot to
loosen it, then pull upward and remove the boot from
the plug. Be sure to pull on the boot and not on the
wire, otherwise the connector located inside the boot
may become separated.
5. Using compressed air, blow any water or de-
bris from the spark plug well to assure that no harm-
ful contaminants are allowed to enter the combustion
chamber when the spark plug is removed. If com-
pressed air is not available, use a raa or a brush to must be replaced.
Check the plugs for deposits and wear, If they are 7. Inspect the spark plug boot for tears or dam-
age. If.a damaged boot is found, the spark plug wire
8. Using a wire feelergauge, check and adjust
the spark plug gap. When using a gauge, the proper
size should pass between the electrodes with a slight
drag. The next larger size should not be able to pass
while the next smaller size should pass freely.
9. Carefully thread the plug into the bore by
hand. If resistance is felt before the plug is almost
completely threaded, back the plug out and begin
threading again. In small, hard to reach areas, an old
spark plug wire and boot could be used as a thread-
ing tool. The boot will hold the plug while you twist
the end of the wire and the wire is supple enough to
twist before it would allow the plug to crossthread.
Do not use the spark plug sock?
l -- K-rrA tha nhme Alwmm rarntdlv thw GL I” IlllGa”
the possibility of crossthreading and damag- lad the plug
. ..Y f..“YY. rn”Y,‘““mY*“.‘, .I**” by hand or using an old plug wire to prevent
ing the cylinder head bore.
10. Carefully tighten the spark plug. If the plug
you are installing is equipped with a crush washer,
seat the plug, then tighten about I/, turn to crush the
washer. If you are installing a tapered seat plug,
tighten the plug to specifications provided by the ve-
hicle or plug manufacturer. b See Figures 98, 97, 98, 99, and 100
not going to be replaced, clean the plugs thoroughly.
Remember that any kind of deposit will decrease the
efficiency of the plug. Plugs can be cleaned on a
spark plug cleaning machine, which can sometimes
be found in service stations, or you can do an accept-
able job of cleaning with a stiff brush. If the plugs are’
cleaned, the electrodes must be filed flat. Use an ig-
nition points file, not an emery board or the like,
which will leave deposits. The electrodes must be
filed perfectly flat with sharp edges; rounded edges
reduce the spark plug voltage by as much as 50%.
Check spark plug gap before installation. The
ground electrode (the L-shaped one connected to the
body of the plug) must be parallel to the center elec-
trode and the specified size wire gauge (please refer
to the Tune-Up Specifications chart for details) must
pass between the electrodes with a slight drag:
*,NEVER adjust the gap on a used platinum
. clean the area.
*Remove the spark plugs when the engine
is cold, if possible, to prevent damage to the
threads. If removal of the plugs is difficult,
apply a few drops of penetrating oil or sili-
cone spray to the area around the base of the
plug, and allow it a few minutes to work.
6. Using a spark plug socket that is equipped
with a rubber insert to properly hold the plug, turn type spark plug.
Always check the gap on new plugs as they are
not always set correctly at the factory. Do not use a
flat feeler gauge when measuring the gap on a used
plug, because the reading may be inaccurate. A
round-wire type gapping tool is the best way to check
the gap. The correct gauge should pass through the
electrode gap with a slight drag. If you’re in doubt, try
one size smaller and one laraer. The smaller aauqe
Page 23 of 408

l-24 GENERALINFORMATIONAND MAINTENANCE
b%slZl2 Fig. 97 A variety of tools and gauges are
needed for spark plug service tm2903 Fig. 98 Checking the spark plug @au with a tccs2904 feeler gauge. - Fig. 99 Adjusting the spark plug gap
ig. 100 If the standard plug Is in good con-
ftlon, the electrode may be filed flat- the two ends. Take the length and multiply it by 6,000
to achieve the maximum resistance allowable in each
wire, resistance should not exceed this value. If resis-
tance does exceed this value, replace the wire.
*Whenever the high tension wires are re- ’
moved from the plugs, coil, or distributor,
silicone grease must be applied to the boot
before reconnection. Coat the entire Interior
surface with a suitable silicone grease.
REMOVAL &INSTALLATION
# See Figures 90,103 and 104
1. Remove the air cleaner inlet tube.
2. If eouiooed, remove the center cover from the
WARNING: do not file platinum plugs
valve covei.
3. Label each spark plug wire and make a note of
should go through easily, while the larger one its routing.
I’ shouldn’t go through at all. Wire gapping tools usu-
ally have a bending tool attached. Use that to adjust
the side electrode until the proper distance is ob-
tained. Absolutely never attempt to bend the center
electrode. Also, be careful not to bend the side elec- *Don’t rely on wiring diagrams or sketches
for spark plug wire routing. Improper
arrangement of spark plug wires will induce
voltage between wires, causing misfiring
and surging. Be careful to arrange spark plug
wires properly.
4. Starting with the longest wire, disconnect the
spark plug wire from the spark plug and then from
the coil pack or distributor cap.
To install:
5. If replacing the spark plug wires, match the olc
wire with an appropriately sized wire in the new set.
6. Lubricate the boots and terminals with dielec-
tric grease and install the wire on the coil pack. Make
sure the wire snaps into place.
a 7. Route the wire in the exact path as the original
nd connect the wire to the spark plug.
8. Repeat the process for each remaining wire,
iorking from the longest wire to the shortest.
9. Install the air cleaner inlet tube.
trode too far or too often as it may weaken and break
off within the engine, requiring removal of the cylin-
der head to retrieve it.
TESTING
# See Figures 191 and 102
At every tune-up/inspection, visually check the
spark plug cables for burns cuts, or breaks in the in-
sulation. Check the boots and the nipples on the dis-
tributor cap and/or coil. Replace any damaged wiring.
Every 50,000 miles (80,000 km) or 60 months, the
resistance of the wires should be checked with an
ohmmeter. Wires with excessive resistance will cause
misfiring, and may make the engine difficult to start in
damp weather.
To check resistance, an ohmmeter should be used ’
on each wire to test resistance between the end con-
nectors. Remove and install/replace the wires in or- ’
der, one-by-one.
Resistance on these wires should be 4,000-6,000
ohms per foot. To properly measure this, remove the
wires from the plugs and the coil pack. Do not pierce
any ignition wire for any reason. Measure only from Fig. 103 Remove the spark plug wires from
tcG1009 Fig. 102 Checking individual plug wire re-
sistance with a digital ohmmeter
Fig. 104 Remove the plug wires from the
wire dividers
Page 25 of 408

.
1-26 GENERALINFORMATIONAND MAINTENANCE
TDC of the compression stroke. If this happens, the
piston WIII be at the beginning of the power stroke
just as the compressed and ignited air/fuel mixture
forces the piston down and turns the crankshaft. Be-
cause it takes a fraction of a second for the spark
plug to ignite the mixture in the cylinder, the spark
plug must fire a little before the piston reaches TDC.
Otherwise, the mixture will not be completely ignited
as the piston passes TDC and the full power of the
explosion will not be used by the engine.
The timing measurement is given in degrees of
crankshaft rotation before the piston reaches TDC
(BTDC). If the setting for the ignition timing is 10”
BTDC, each spark plug must fire 10 degrees before
each piston reaches TDC. This only holds true, how-
ever, when the engine is at idle speed. The combus-
tion process must be complete by 23”ATDC to main-
tain proper engine performance, fuel mileage, and
low emissions.
As the engine speed increases, the pistons go
faster. The spark plugs have to ignite the fuel even
sooner if it IS to be completely ignited when the pis-
ton reaches TDC. If the ignition is set too far ad-
vanced (BTDC), the ignition and expansion of the fuel
in the cylinder wtll occur too soon and tend to force
the piston down while it is still traveling up. Thus
causes pre ignition or “knockmg and pinging”. If the
ignition spark is set too far retarded, or after TDC
(ATDC), the piston will have already started on its
way down when the fuel is ignited. The piston will be
forced down for only a portion of its travel, resulting
in poor engine performance and lack of power.
Timing marks or scales can be found on the rim of
the crankshaft pulley and the timing cover. The marks
on the pulley correspond to the posrtion of the piston
in the No. 1 cylinder. A stroboscopic (dynamic) tim-
ing light is hooked onto the No. 1 cylinder spark plug
wrre. Every time the spark plug fires, the timing light
flashes. By aiming the light at the timing marks while
the engine is running, the exact position of the piston
within the cylinder can be easily read (the flash of
light makes the mark on the pulley appear to be
standing still). Proper timing is indicated when the
mark and scale are in specified alignment.
When checking timing with the engine run-
ning, take care not to get the timing light
wires tangled in the tan blades and/or drive
belts.
INSPECTION &ADJUSTMENT
1990-96 Models
e See Figures 113 thru 119
1. Set the parking brake, start and run the engine
until normal operating temperature is obtained. Keep
all lights and accessories OFF and the front wheels
straight-ahead. Place the transaxle in
P for automatic
transaxle or Neutral for manual transaxle.
2. If not at specification, set the idle speed to the
correct level.
3. Turn the engine
OFF. Remove the water-
proof cover from the igmtion timing adjusting con-
nector, and connect a jumper wire from this terminal
Fig. 113 Ignition timing adjustment con-
nector-1990-92 Mirage with 1.5L engine
93151QM Fig. 115 Ignition timing adjustment con-
nectar-Galant with 2.OL engines
93151QO1 Fig. 117 Ignition timing adjustment con.
nectar-1994-96 Galant
to a good ground. Refer to the corresponding illustra-
tions for the correct location of the timing adjustment
connector.
4. Connect a conventional power timing light to
the No. 1 cylinder spark plug wire. Start the engine
and run at idle.
5. Aim the timing light at the timing scale lo-
cated near the crankshaft pulley.
6. Loosen the distributor or crank angle sensor
hold-down nut just enough so the housing can be ro-
tated.
7. Turn the housing in the proper direction until
the specified timing is reached. Tighten the hold-
down nut and recheck the timing. Turn the engine
OFF. 8. Remove the jumper wire from the ignition
timing adjusting terminal and install the water-proof
cover.
9. Start the engine and check the actual timing
(the timing without the terminal grounded). This
reading should be approximately 5 degrees more
than the basic timing. Actual timing may increase ac-
cording to altitude. Also, actual timing may fluctuate
because of slight variation accomplished by the ECU.
Fig. 114 Ignition timing adjustment con-
nectar-Miracle with 1.6L enaine
CHECK CONNECTOR 93151QO! Fig. 116 Ignition timing adjustment con.
nectar-1992-96 Oiamante
93151gOB Fig. 116 Ignition timing adjustment con-
nector-1993-96 Mirage with 1.5L engine
Fig. 119 Ignition timing adjustment con-
nector-1993-96 Mirage with 1.6L engine
As long as the basic timing is correct, the engine is
timed correctly.
10. Turn the engine
OFF. 11. Disconnect the timing apparatus and
tachometer.
1997-00 Models
The ignition timing is controlled by the Engine
Control Module (ECM) and is not adjustable. How-
ever it can be inspected using a scan tool.
Page 26 of 408
GENERALINFORMATIONAND MAlNTENANdE I-27
ADJUSTMENT
u See Figures 120 and 121
The only engines that require periodic adjustment
of the valves are the 1.5L engine in the 1990-95 Mi-
rage and the 1.8L in the 1993-95 Mirage.
Incorrect valve clearance will cause noisy
and/or unsteady engine operation, reduced
engine output, and possible engine damage.
Check the valve clearances and adjust as re-
quired while the engine is hot.
1. Warm the engine to operating temperature.
Turn the engine OFF. Disconnect the negative battery
cable.
2. Remove all spark plugs so engine can be eas-
ily turned by hand
3. Remove the valve cover.
4. Turn the crankshaft clockwise until the notch
on the pulley is aligned with the
T mark on the timing
belt lower cover. This brings both No. 1 and 4 cylin-
der pistons to Top Dead Center (TDC).
5. Wiggle the rocker arms on No. 1 and 4 cylin-
ders up and down to determine which cylinder is at
TDC on the compression stroke. Both rocker arms
should move if the piston in that cylinder is at TDC
on the compression stroke.
6. Measure the valve clearance with a feeler
gauge. When the No. 1 piston is at TDC on the com-
pression stroke, check No. 1 intake and
exhaust; No.
2 intake and exhaust. Then turn the crankshaft clock-
wise 1 turn to bring No. 4 to TDC on its compression
stroke. With No. 4 on TDC, compression stroke,
check No. 2 exhaust and intake; and No. 4 intake and
exhaust. Clearance is as follows:
1990-92 1.5L engine:
No.1 No.2
No.3 No.4
when engine is on TDC of cylinder 1 and (B) when engine is on TDC of cylinder 4
No.1 No.2
No.3 No.4
AA AA BB BB
93151g10 Fig. 121 Adjusting the valve clearance
l Exhaust valve: 0.0098 in. (0.25mm) screw. When at specification, tighten the locknut. Be l Intake valve: 0.0059 in. (0.15mm)
1993-95 1.5L engine: sure to hold the screw securely in place when tight-
l Exhaust valve: 0.0098 in. (0.25mm) ening the locknut to prevent it from turning when
* Intake valve: 0.008 in. (0.20mm) tightening the locknut. Tightening torque of the lock-
nut is as follows:
1993-95 1.8L engine:
l Exhaust valve: 0.012 in. (0.30mm) l 1.5L engine: 9-11 ft. Ibs. (12-15 Nm)
l Intake valve: 0.008 in. (0.20mm) l 1.8L engine: 7 ft. Ibs. (9 Nm)
8. Recheck the clearance and readjust.
7. If the valve clearance is out of specification,
9. After adjusting the valves, install the valve
loosen the rocker arm locknut and adjust the clear-
ante using a feeler gauge while turning the adjusting cover and spark plugs, and connect the negative bat-
tery cable.
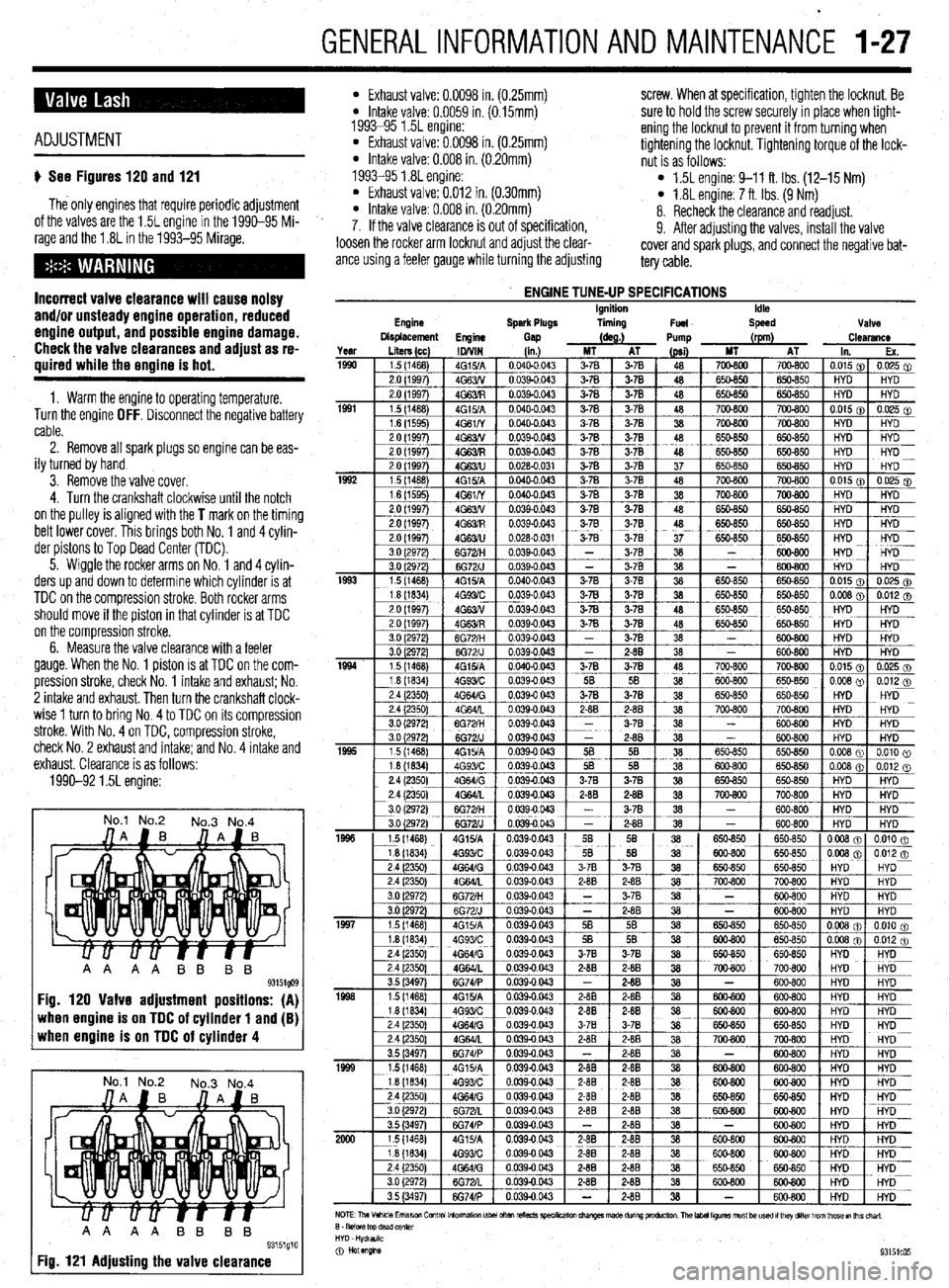
Engine
ENGINE TUNE-UP SPECIFICATIONS Ignition
Spark Plugs liming
Fuel Idle
Speed Valve
Displacement
Engine
Gap (as.) Pump (rpm)
Clearance