sensor OPEL VECTRA 1988 Service User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: OPEL, Model Year: 1988, Model line: VECTRA, Model: OPEL VECTRA 1988Pages: 525, PDF Size: 58.26 MB
Page 54 of 525

12•40Wiring diagrams
Key to wiring diagrams for 1991 models (continued)
NoDescriptionTrackNoDescriptionTrack
S1.2Key contact switch586
S2.1Lighting switch404 to 407
S2.2Courtesy lamp switch487
S2.3Instrument illumination lamp dimmer328
S3Heater blower switch853 to 860
S4Heated rear window and mirror switch554 to 556
S5.2Dipped beam switch438 to 439
S5.3Direction indicator switch480 to 482
S5.4Sidelamp switch401 to 402
S7Reversing lamp switch497
S8Brake lamp switch462
S9.2Windscreen wiper interval switch501 to 504
S9.5Rear window washer/wiper switch514 to 516
S10Automatic transmission starter inhibitor switch773 to 779
S11Brake fluid level warning sensor31
S13Handbrake-on warning switch315
S14Oil pressure switch310
S15Luggage compartment lamp switch485
S17Passenger door courtesy lamp switch490
S21Front fog lamp switch450 to 452
S22Rear foglamp switch455 to 457
S24Air conditioning blower motor switch804 to 811
S27Air conditioning compressor low-pressure switch821
S28Air conditioning compressor high-pressure switch821
S29Cooling fan switch113
S30Driver’s seat heater switch560 to 562
S31Rear door courtesy lamp switch - left491
S32Rear door courtesy lamp switch - right491
S37Driver’s door electric window switch assembly668 to 694
S37.1Electric window switch - front left668 to 670
S37.2Electric window switch - front right686 to 688
S37.3Electric window switch - rear left674 to 676
S37.4Electric window switch - rear right692 to 694
S37.5Electric window safety cut-out switch672 to 673
S37.6Electric window anti-jam switch690
S37.7Electric window automatic control677 to 682
S39Electric window switch - rear left door678 to 680
S40Electric window switch - rear right door696 to 698
S41Central locking switch - driver’s door601 to 603
S42Central locking switch - passenger door605
S44Throttle position sensor278 to 279
S47Driver’s door courtesy lamp switch493 to 494
S52Hazard warning flasher switch469 to 474
S55Passenger seat heater switch564 to 566
S57Sunroof switch864 to 869, 872 to 877
S63.1Trip computer function reset switch656
S63.2Trip computer clock hours adjustment switch657
S63.3Trip computer function select switch658
S63.5Trip computer clock minutes adjustment switch659
S64Horn switch592, 595
S68.1Door mirror adjustment switch538 to 540, 945 to 950
S68.3Door mirror left/right selector switch537 to 541, 946 to 950
S68.4Door mirror parking position switch952
S76Air conditioning compressor switch - high-pressure fan827
S82Washer pump switch347, 392
S88Cooling fan switch115 to 116, 935 to 936
S93Coolant level sensor348, 393
S95Oil level sensor349, 394
S98Headlamp aim adjustment switch758 to 760
S99Electric window switch - driver’s door685
S100Electric window switch - passenger door683
S101Air conditioning compressor switch822 to 824
S102Air conditioning circulation switch816 to 818
S104Automatic transmission kickdown switch794
S105Automatic transmission “Winter” mode button796 to 798
S106Automatic transmission “Economy/Sport” mode button793S109Air conditioning compressor switch818
S115Automatic transmission coolant temperature switch788 to 789
S116Brake lamp switch464 to 465
S117Four-wheel-drive hydraulic pressure switch729
S119Air conditioning refrigerant temperature switch829, 843
S120Anti-theft alarm bonnet switch635
S127Central locking switch - tailgate (Calibra models)630
S128Air conditioning refrigerant temperature cooling switch825 to 826
S131Air conditioning defroster lever limit switch815
U2Trip computer651 to 662
U4ABS hydraulic modulator assembly705 to 718, 738 to 751
U4.1ABS hydraulic pump relay706 to 709, 739 to 742
U4.2ABS solenoid valves relay715 to 718, 747 to 751
U4.3ABS hydraulic pump705, 738
U4.4ABS diode717
U4.5ABS solenoid valve - front left710, 743
U4.6ABS solenoid valve - front right711, 744
U4.7ABS solenoid valve - rear left712, 745
U4.8ABS solenoid valve - rear right713
U5Check control display347 to 355
U5.1Check control washer fluid level warning lamp352
U5.2Check control oil level warning lamp351
U5.3Check control coolant level warning lamp350
U5.4Check control tail lamp and dipped beam bulb
failure warning lamp349
U5.5Check control brake lamp bulb failure warning lamp348
U5.6Check control brake wear warning lamp347
U6LCD instruments
U6.1Check control washer fluid level warning lamp392
U6.2Check control oil level warning lamp394
U6.3Check control coolant level warning lamp393
U6.4Check control tail lamp and dipped beam bulb
failure warning lamp391
U6.5Check control brake lamp bulb failure warning lamp395
U6.6Check control brake pad wear warning lamp396
U12.1Temperature switch (Diesel models)898, 931
U12.2Fuel filter heater (Diesel models)899, 932
U13AF14/20automatic transmission782 to 786
U13.1Solenoid - 1/2 and 3/4 shift up782
U13.2Solenoid - 2/3 shift up783
U13.3Solenoid - converter lock-up control784
U13.4Solenoid - main fluid pressure control785
V1Brake fluid level warning lamp test diode312
V8Air conditioning compressor diode820
Y1Air conditioning compressor clutch821
Y4Headlamp washer solenoid valve520
Y5Fuel solenoid valve (Diesel models)893, 928
Y7Fuel injectors187 to 194, 280 to 287
Y10Distributor (Hall-effect)246 to 251
Y23Distributor (inductive discharge)123 to 127
Y24Distributor (inductive discharge)129 to 136
Y25Idle-up solenoid valve (automatic transmission)242
Y30Cold start valve (Diesel models)896
Y32Fuel injector140, 979
Y33Distributor170, 262, 972 to 974
Y34Fuel tank vent valve193, 292
Y35Air conditioning circulation solenoid valve816
Y44Four-wheel-drive solenoid valve731
Y47Parking brake lock lifting magnet (automatic transmission)769
X13Diagnostic equipment connector149, 170 to 171, 254 to 255,
269 to 270, 325, 339 to 340,
752 to 753, 774 to 775, 992 to 993
X15Octane coding plug160, 184 to 185, 248 to 249, 990 to 991
X54Ignition coding plug270 to 271
X1 onWiring connectorsVarious
Page 70 of 525

12•56Wiring diagrams
Key to wiring diagrams for 1992 and later models (continued)
NoDescriptionTrackNoDescriptionTrack
K95Traction control control unit1125 to 1140
K97Headlamps washer pump time delay relay630 to 632
K101Parking position mirror relay774 to 777
K102Park brake shift lock control unit 469 to 471
L1Ignition coil150, 172, 205, 273, 241, 302, 361
L2Ignition coil1000 to 1004, 1054 to 1059
M1Starter105, 106
M2Windshield wiper motor601 to 604
M3Heating blower motor127 to 129
M4Radiator blower motor118, 120, 140, 356, 431, 948, 954, 980
M6Left headlamp wiper motor622 to 624
M7Right headlamp wiper motor 626 to 628
M8Back window wiper motor611 to 613
M10Air conditioning blower motor905 to 908
M11Radiator blower motor136, 434, 962, 984
M13Vectra/Cavalier sun roof motor1172 to 1175
M13.1Sun roof motor1172, 1174
M13.2Timing box microswitch1172
M13.3Timing box microswitch1174
M18Driver door central locking motor807 to 810
M19Left rear door central locking motor821 to 823
M20Right rear door central locking motor825 to 827
M21Fuel pump232, 263, 297, 339, 399, 834, 1098, 1039
M23Alternator blower motor135, 974
M24Headlamps washer pump632
M26Automatic antenna motor798 to 799
M30Driver side outside mirror638 to 641
M31Passenger side outside mirror644 to 647
M32Passenger door central locking motor813 to 816
M33Idle speed actuator285, 286, 317, 318, 381,
382, 1019, 1020, 1075, 1076
M37Tail gate/boot lid central locking motor818 to 821
M39Left headlamp levelling motor 692 to 695
M40Right headlamp levelling motor696 to 699
M41Fuel filler door central locking motor823, 824
M47Driver door window lifter motor867 to 871
M48Passenger door window lifter motor885 to 889
M49Left rear window lifter motor873 to 877
M50Right rear window lifter motor891 to 895
M55Windshield and back window washer pump617
M57Coolant pump134, 970
M60Calibra tailgate central locking motor827, 828
M61Calibra sun roof motor1178 to 1186
M61.1Sun roof motor1179 to 1182
M61.2Relay 11178, 1179
M61.3Relay 21184 to 1186
M62Driver side outside mirror760 to 767
M63Passenger side outside mirror769 to 776
M65TC throttle valve actuator1130 to 1134
M66Idle air stepper motor215 to 218, 250 to 253
P1Fuel indicator704
P2Coolant temperature indicator706
P3Clock862
P4Fuel sensor704
P5Coolant temperature sensor706
P7Tachometer708
P11Airflow meter 285 to 289
P12Coolant temperature sensor282, 381
P13Outside temperature sensor856
P14Distance sensor412, 413
P17Left front revolution sensor1110, 1154
P18Right front revolution sensor1113, 1157
P19Left rear revolution sensor1116, 1160
P20Right rear revolution sensor1119, 1163P21Distance sensor731
P23Intake manifold absolute pressure sensor160, 161, 185, 186,
217 to 219, 250 to 252
P24Engine oil temperature sensor162, 187
P27Left front brake lining sensor740
P28Right front brake lining sensor740
P29Intake manifold temperature sensor382, 1016, 1072
P30Coolant temperature sensor215, 248, 313, 1017, 1073
P32Heated exhaust oxygen sensor294, 295, 331, 332, 391,
392, 1034, 1035, 1093, 1094
P33Exhaust oxygen sensor229, 257
P34Throttle valve potentiometer221 to 223, 280, 281, 253 to 255,
383 to 385, 478, 479, 1018, 1019, 1074, 1075
P35Crankshaft impulse sensor178 to 180, 289 to 291, 248 to 250,
318 to 320, 373 to 375, 1025 to 1027, 1084 to 1086
P38Transmission oil temperature sensor494
P39Trailer bulb test sensor752 to 754
P43Electronic speedometer733
P44Air mass meter393 to 397, 334 to 338,
1037, 1038, 1096, 1097
P45Transmission input revolution sensor490, 491
P46Knock control sensor322, 323, 377, 378,
1022, 1023, 1078, 1079
P47Cylinder identification hall sensor325 to 327, 385 to 387,
1028 to 1030, 1087, 1089
P48Automatic transmission distance sensor488, 489
P50Catalytic converter temperature sensor463, 464
P53Driver side anti-theft warning unit sensor839 to 847
P54Passenger side anti-theft warning unit sensor839 to 847
P55Engine coolant temperature sensor415
P56Knock control sensor II1080, 1081
P57Antenna797
R3Cigarette lighter675
R5Glow plugs418 to 420, 441 to 443
R13Left heated washer nozzle 626
R14Right heated washer nozzle628
R19Radiator blower preresistor120, 140, 945
R22Glow plugs pre-resistor423
R23Driver airbag squib1194
S1Starter switch103 to 106
S1.2Key contact switch783
S2Light switch assy
S2.1Light switch504 to 507
S2.2Passenger compartment lamp switch587
S2.3Instrument lights dimmer728
S3Heating blower switch123 to 130
S4Heated back window & mirror switch654 to 657
S5Turn signal switch assy
S5.2Low beam switch536, 537
S5.3Turn signal switch580 to 582
S5.4Parking lamp switch501, 502
S7Back up lamp switch597, 599
S8Stop lamp switch562
S9Wiper unit switch
S9.2Interval windshield wiper switch601 to 604
S9.5Back window and washer unit wiper switch614 to 616
S10Automatic transmission switch472 to 478
S11Brake fluid control switch712
S13Parking brake switch713
S14Oil pressure switch710
S15Boot lamp switch585
S17Passenger door contact switch590
S20Pressure switch
S20.1Low pressure compressor switch925
Page 71 of 525

Wiring diagrams 12•57
12
Key to wiring diagrams for 1992 and later models (continued)
NoDescriptionTrackNoDescriptionTrack
S20.2High pressure compressor switch925
S20.3High pressure blower compressor switch939
S21Fog lamps switch555 to 557
S22Rear fog lamp switch549 to 551
S24Air conditioning blower switch904 to 911
S29Coolant temperature switch118, 137, 357, 942, 957, 972
S30Left front heating mat switch660 to 662
S31Rear left door contact switch591
S32Rear right door contact switch592
S33Traction control switch1130, 1131
S37Window lifter switch868 to 894
S37.1Left window lifter switch868 to 870
S37.2Right window lifter switch886 to 888
S37.3Left rear window lifter switch874 to 876
S37.4Right rear window lifter switch892 to 894
S37.5Safety switch872, 873
S37.6Window anti-jam off switch890
S37.7Automatic window lifter control877 to 882
S39Left rear door window lifter switch878 to 880
S40Right rear door window lifter switch896 to 898
S41Driver door burglary locking switch800 to 802
S42Passenger door central locking switch805
S44Throttle valve switch316, 317
S47Driver door contact switch593, 594
S52Hazard warning switch569 to 573
S53First gear identification switch372
S55Right front heating mat switch664 to 666
S57Sun roof switch1170 to 1183
S63Computer switch
S63.1Function reset switch856
S63.2Clock hours adjustment switch857
S63.3Function select switch858
S63.4Clock minute adjustment switch859
S64Horn switch672
S68Outside mirror switch assy
S68.1Outside mirror adjustment switch638 to 640, 758 to 762
S68.3Left/right outside mirror switch637 to 641, 759 to 763
S68.4Parking position switch765
S82Washer fluid minimum capacity control switch736
S882 stage coolant temperature switch120, 121, 137, 138, 430, 431
S89Seat belt switch998
S93Coolant minimum capacity control switch737
S95Engine oil minuimum capacity control switch738
S98Headlamps levelling switch691 to 693
S99ZV driver door window lifter switch865
S100ZV passenger door window lifter switch883
S101Compressor switch926 to 928
S102Circulation switch918 to 920
S103Transmission temperature switch350
S104Kickdown switch493
S105Start-up assistance switch495 to 497
S106Economy power program switch492
S109Acceleration revolution pressure switch921
S115Coolant temperature switch487, 488
S116Stop lamp switch564, 565
S117Hydraulic pressure switch346
S120Engine compartment hood (anti-theft warning unit) switch835
S127Calibra tail gate central locking switch831
S128Coolant temperature switch936,937S131Defroster lever limit switch918
U2Computer851 to 862
U4ABS hydroaggregate1102 to 1122, 1146 to 1164
U4.1Pump motor relay1102, 1103, 1146, 1147
U4.2Solenoid valves relay1104, 1105, 1148, 1149
U4.3Pump motor1102,1146
U4.4Diode1105,1149
U4.5Left front solenoid valve1109,1153
U4.6Right front solenoid valve1111,1155
U4.7Rear axle solenoid valve1113,1157
U4.8ABS control unit1106 to 1122, 1150 to 1164
U4.9Solenoid valves plug1109 to 1113, 1153 to 1157
U5Check control display
U5.1Washer fluid minimum capacity telltale741
U5.2Oil minimum capacity telltale740
U5.3Coolant minimum capacity telltale739
U5.4Tail light & low beam telltale738
U5.5Stop light failure telltale737
U5.6Front brake lining telltale736
U12Filter heater
U12.1Temperature switch426, 452
U12.2Filter heater427, 453
U13Automatic transmission
U13.1Solenoid valve (shift 1)481
U13.2Solenoid valve (shift 2)482
U13.3Solenoid valve (lock up control)483
U13.4Solenoid valve (pressure control)484
U17Roof antenna amplifier795
V1Brake fluid test bulb diode712
V8Air conditioning compressor diode926
X1 onWiring connectorsVarious
X10Anti theft warning unit code837
X13Diagnostic link164, 165, 189, 190, 226, 270, 271, 258, 259,
309, 310, 370, 371, 343, 344, 473, 474, 573, 725, 836, 837, 860,
861, 1012, 1013, 1069, 1070, 1118, 1119, 1136, 1162, 1163
X15Octane number plug157, 158, 182, 183, 225, 226,
257, 258, 284, 285
X54Ignition coding plug310, 311, 1014, 1070, 1071
Y1Air conditioning compressor clutch925
Y4Headlamps washer solenoid valve620
Y5Fuel solenoid valve410, 445
Y7Fuel injection valves287 to 294,320 to 327,
384 to 391,1025 to 1032,1078 to 1089
Y10Hall sensor ignition distributor153 to 158
Y11Hot start solenoid valve375, 376
Y12Charging pressure control changeover valve377, 378
Y18Exhaust gas recirculation valve1093
Y23Inductive sensor distributor201 to 208
Y24Distributor (inductive discharge)
Y25Acceleration revolution solenoid valve155, 177
Y30Cold start acceleration solenoid valve 448
Y32Fuel injection valve212, 245
Y33Ignition distributor175 to 177, 268 to 270, 238 to 240,
301 to 303, 360 to 362
Y34Tank ventilation valve293, 331, 332, 379, 380,
1092, 1016, 1017,
Y35Circulation solenoid valve918
Y44Four wheel drive solenoid valve350
Y47Park brake shift lock lifting magnet469
Page 88 of 525
5
System type . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12 volt, negative earth
Battery capacity . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36, 44, 55 or 66 Ah
Alternator
Type . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Bosch or Delco-Remy
Output . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55 or 70 A, depending upon model
Minimum brush length:
Bosch type alternator . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5.0 mm protrusion
Delco-Remy type alternator . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11.0 mm overall length
Starter motor
Type . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Pre-engaged, Bosch or Delco-Remy
Minimum brush length:
Bosch DF type starter motor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11.5 mm
Bosch DM type starter motor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3.0 mm
Bosch DW type starter motor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4.5 mm
Delco-Remy type starter motor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4.0 mm
System type
14 NV . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . HEI (High Energy Ignition) system
16 SV and 18 SV . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . MSTS-i (Microprocessor Spark Timing System)
C16 NZ, C16 NZ2 and C18 NZ . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Multec, with MSTS-i
X16 SZ . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Multec, with DIS (Direct Ignition System)
20 NE, C20 NE and 20 SEH, (up to 1990) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Motronic M4.1
20 NE, C20 NE and 20 SEH, (from 1990) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Motronic M1.5
20 XEJ and C20 XE, (up to 1993) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Motronic M2.5
C20 XE (from 1993) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Motronic M2.8
X20 XEV . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Simtec 56.1
Coil
Output . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16.0 to 20.0 kilovolts
Primary winding resistance (DOHC models only) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.2 to 0.34 ohms
Secondary winding resistance (DOHC models only) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7.2 to 8.2 ohms
Chapter 5
Engine electrical systems
Alternator - description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7
Alternator - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .9
Alternator - testing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10
Alternator brushes - removal, inspection and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . .11
Alternator drivebelt - removal, refitting and adjusting . . . . . . . . . . . . .8
Battery - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6
Battery - testing and charging . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5
Camshaft phase sensor (C20 XE engine) - removal and refitting . . . .27
DIS module - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .26
Distributor - dismantling, inspection and reassembly . . . . . . . . . . . .20
Distributor (DOHC models) - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .19
Distributor (SOHC models) - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .18
Distributor cap and rotor arm - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . .17
Electrical system - general . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1Electrical system - precautions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3
Electronic modules - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .23
Ignition coil - removal, testing and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .16
Ignition system - general . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2
Ignition system testing - general . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4
Ignition timing - adjustment for use with unleaded petrol . . . . . . . . .22
Ignition timing - checking and adjustment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .21
Motronic system components - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . .25
MSTS-i components - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .24
Starter motor - general . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
Starter motor - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14
Starter motor - overhaul . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15
Starter motor - testing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13
5•1
Specifications Contents
Easy,suitable for
novice with little
experienceFairly easy,suitable
for beginner with
some experienceFairly difficult,
suitable for competent
DIY mechanic
Difficult,suitable for
experienced DIY
mechanicVery difficult,
suitable for expert DIY
or professional
Degrees of difficulty
54321
Page 89 of 525

Distributor
Direction of rotor arm rotation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Anti-clockwise (viewed from cap)
Firing order . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1-3-4-2 (No 1 cylinder at timing belt end of engine)
Dwell angle . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Automatically controlled by electronic module (not adjustable)
Ignition timing
14 NV . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5°BTDC
16 SV, X 16 SZ, C 16 NZ, C 16 NZ2 and C 18 NZ . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10°BTDC *
18 SV and 2.0 litres models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8 to 12°BTDC *
* Ignition timing electronically controlled no adjustment possible
Spark plugs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .See Chapter 1 Specifications
Torque wrench settingNmlbf ft
Alternator mounting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2518
Camshaft phase sensor disc . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .86
Camshaft phase sensor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1511
‘Compact’ series alternator lower mounting bolt . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3526
‘Compact’ series alternator upper mounting bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2015
DIS module . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .75
Inductive pulse pick-up to block . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .86
Spark plugs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2518
Starter motor mounting bracket-to-cylinder block . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2518
Starter motor mounting:
1.4 and 1.6 litre models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2518
1.8 and 2.0 litre models:
Engine side . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4533
Transmission side . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7555
1Electrical system - general
1The electrical system is of the 12 volt
negative earth type, and consists of a 12 volt
battery, alternator with integral voltage
regulator, starter motor, and related electrical
accessories, components and wiring.
2The battery is of the maintenance-free
“sealed for life” type, and is charged by an
alternator, which is belt-driven from the
crankshaft pulley. The starter motor is of the
pre-engaged type, incorporating an integral
solenoid. On starting, the solenoid moves the
drive pinion into engagement with the flywheel
ring gear before the starter motor is
energised. Once the engine has started, a
one-way clutch prevents the motor armature
being driven by the engine until the pinion
disengages from the flywheel.
3It is necessary to take extra care when
working on the electrical system, to avoid
damage to semi-conductor devices (diodes
and transistors), and to avoid the risk of
personal injury. Along with the precautions
given in the “Safety first!” Section at the
beginning of this manual, take note of the
following points when working on the system.4Always remove rings, watches, etc. before
working on the electrical system. Even with
the battery disconnected, discharge could
occur if a component live terminal is earthed
through a metal object. This could cause a
shock or nasty burn.
5Do not reverse the battery connections.
Components such as the alternator, or any
other component having semi-conductor
circuitry, could be irreparably damaged.
6If the engine is being started using jump
leads and a slave battery, connect the
batteries positive to positive and negative to
negative. This also applies when connecting a
battery charger.
7Never disconnect the battery terminals, or
alternator multi-plug connector, when the
engine is running.
8The battery leads and alternator wiring
must be disconnected before carrying out any
electric welding on the vehicle.
9Never use an ohmmeter of the type
incorporating a hand-cranked generator for
circuit or continuity testing.
2Ignition system - general
1The ignition system is responsible for
igniting the air/fuel mixture in each cylinder at
the correct moment, in relation to engine
speed and load. A number of different types
of ignition systems are fitted to models within
the range. Ranging from a basic breakerless
electronic system, to a fully integrated engine
management system controlling both ignition
and fuel injection systems. Each system isdescribed in further detail later in this Section.
2The ignition system is based on feeding low
tension voltage from the battery to the coil,
where it is converted to high tension voltage.
The high tension voltage is powerful enough
to jump the spark plug gap in the cylinders
many times a second under high compression
pressures, providing that the system is in
good condition. The low tension (or primary)
circuit consists of the battery, the lead to the
ignition switch. The lead from the ignition
switch to the low tension coil windings and
the supply terminal on the electronic module.
The lead from the low tension coil windings to
the control terminal on the electronic module.
The high tension (or secondary) circuit
consists of the high tension coil windings, the
HT (high tension) lead from the coil to the
distributor cap, the rotor arm, the HT leads to
the spark plugs, and the spark plugs.
3The system functions in the following
manner. Current flowing through the low
tension coil windings produces a magnetic
field around the high tension windings. As the
engine rotates, a sensor produces an
electrical impulse that is amplified in the
electronic module and used to switch off the
low tension circuit.
4The subsequent collapse of the magnetic
field over the high tension windings produces
a high tension voltage, which is then fed to the
relevant spark plug through the distributor
cap and rotor arm. The low tension circuit is
automatically switched on again by the
electronic module, to allow the magnetic field
to build up again before the firing of the next
spark plug. The ignition is advanced and
retarded automatically, to ensure that the
spark occurs at the correct instant with the
engine speed and load.
5•2Engine electrical systems
Caution: Before carrying out
any work on the vehicle
electrical system, read through
the precautions given in the
“Safety first!” Section at the beginning of
this manual, and in Section 3 of this
Chapter.
Page 90 of 525

HEI (High Energy Ignition)
system
5This comprises of a breakerless distributor
and an electronic switching/amplifier module
along with the coil and spark plugs.
6The electrical impulse that is required to
switch off the low tension circuit is generated
by a magnetic trigger coil in the distributor. A
trigger wheel rotates within a magnetic stator,
the magnetic field being provided by a
permanent magnet. The magnetic field across
the two poles (stator arm and trigger wheel) is
dependent on the air gap between the two
poles. When the air gap is at its minimum, the
trigger wheel arm is directly opposite the
stator arm, and this is the trigger point. As the
magnetic flux between the stator arm and
trigger wheel varies, a voltage is induced in the
trigger coil mounted below the trigger wheel.
This voltage is sensed and then amplified by
the electronic module, and used to switch off
the low tension circuit. There is one trigger arm
and one stator arm for each cylinder.
7The ignition advance is a function of the
distributor, and is controlled both
mechanically and by a vacuum-operated
system. The mechanical governor mechanism
consists of two weights that move out from
the distributor shaft due to centrifugal force as
the engine speed rises. As the weights move
outwards, they rotate the trigger wheel
relative to the distributor shaft and so
advance the spark. The weights are held in
position by two light springs, and it is the
tension of the springs that is largely
responsible for correct spark advancement.
8The vacuum control consists of a
diaphragm, one side of which is connected by
way of a small-bore hose to the carburettor,
and the other side to the distributor.
Depression in the inlet manifold and
carburettor, which varies with engine speed
and throttle position, causes the diaphragm to
move, so moving the baseplate and
advancing or retarding the spark. A fine
degree of control is achieved by a spring in
the diaphragm assembly.
MSTS-i (Microprocessor-
controlled Spark Timing System)
9This system comprises a “Hall-effect”
distributor (or a crankshaft speed/position
sensor on X 16 SZ models), a manifold pressure
sensor, an oil temperature sensor, and a
module, along with the coil and spark plugs.
10On 1.6 litre models, the electrical impulse
that is required to switch off the low tension
circuit is generated by a sensor in the
distributor. A trigger vane rotates in the gap
between a permanent magnet and the sensor.
The trigger vane has four cut-outs, one for
each cylinder. When one of the trigger vane
cut-outs is in line with the sensor, magnetic
flux can pass between the magnet and the
sensor. When a trigger vane segment is in line
with the sensor, the magnetic flux is diverted
through the trigger vane away from thesensor. The sensor senses the change in
magnetic flux, and sends an impulse to the
MSTS-i module, which switches off the low
tension circuit.
11On 1.8 litre models, the electrical impulse
that is required to switch off the low tension
circuit is generated by a crankshaft
speed/position sensor, which is activated by a
toothed wheel on the crankshaft. The toothed
wheel has 35 equally spaced teeth, with a gap
in the 36th position. The gap is used by the
sensor to determine the crankshaft position
relative to TDC (top dead centre) of No 1 piston.
12Engine load information is supplied to the
MSTS-i module by a pressure sensor, which
is connected to the carburettor by a vacuum
pipe. Additional information is supplied by an
oil temperature sensor. The module selects
the optimum ignition advance setting based
on the information received from the sensors.
The degree of advance can thus be constantly
varied to suit the prevailing engine conditions.
Multec, with MSTS-i
13The ignition system is fully electronic in
operation and incorporates the Electronic
Control Unit (ECU) mounted in the driver’s
footwell. A distributor (driven off the camshaft
left-hand end and incorporating the amplifier
module) as well as the octane coding plug,
the spark plugs, HT leads, ignition HT coil and
associated wiring.
14The ECU controls both the ignition system
and the fuel injection system, integrating the
two in a complete engine management
system. Refer to Chapters 4B and 4C for
further information that is not detailed here.
15For ignition the ECU receives information
in the form of electrical impulses or signals
from the distributor (giving it the engine speed
and crankshaft position), from the coolant
temperature sensor (giving it the engine
temperature) and from the manifold absolute
pressure sensor (giving it the load on the
engine). In addition, the ECU receives input
from the octane coding plug (to provide
ignition timing appropriate to the grade of fuel
used) and from, where fitted, the automatic
transmission control unit (to smooth gear
changing by retarding the ignition as changes
are made).
16All these signals are compared by the
ECU with set values pre-programmed
(mapped) into its memory. Considering this
information, the ECU selects the ignition
timing appropriate to those values and
controls the ignition HT coil by way of the
amplifier module accordingly.
17The system is so sensitive that, at idle
speed, the ignition timing may be constantly
changing; this should be remembered if trying
to check the ignition timing.
18The system fitted to C18 NZ models, is
similar to that described above, except that
the amplifier module is separate. The ECU
determines engine speed and crankshaft
position using a sensor mounted in the
right-hand front end of the engine’s cylinderblock; this registers with a 58-toothed disc
mounted on the crankshaft so that the gap left
by the missing two teeth provides a reference
point, so enabling the ECU to recognise TDC.
19Note that this simplifies the distributor’s
function, which is merely to distribute the HT
pulse to the appropriate spark plug; it has no
effect whatsoever on the ignition timing.
DIS (Direct Ignition System)
20On all X16 SZ engines, and on C20 XE
(DOHC) engines from 1993-on, a DIS (Direct
Ignition System) module is used in place of
the distributor and coil. On the X16 SZ engine
the DIS module is attached to the camshaft
housing in the position normally occupied by
the distributor. On the C20 XE engine, a
camshaft phase sensor is attached to the
cylinder head at the non-driven end of the
exhaust camshaft, in the position normally
occupied by the distributor. The DIS module
is attached, by a bracket, to the cylinder head
at the non-driven end of the inlet camshaft.
21The DIS module consists of two ignition
coils and an electronic control module housed
in a cast casing. Each ignition coil supplies
two spark plugs with HT voltage. One spark is
provided in a cylinder with its piston on the
compression stroke, and one spark is
provided to a cylinder with its piston on the
exhaust stroke. This means that a “wasted
spark” is supplied to one cylinder during each
ignition cycle, but this has no detrimental
effect. This system has the advantage that
there are no moving parts (therefore there is
no wear), and the system is largely
maintenance-free.
Motronic M4.1 and M1.5
22This system controls both the ignition and
the fuel injection systems.
23The Motronic module receives information
from a crankshaft speed/position sensor, an
engine coolant temperature sensor mounted
in the thermostat housing. A throttle position
sensor, an airflow meter, and on models fitted
with a catalytic converter, an oxygen sensor
mounted in the exhaust system (Chapter 4C).
24The module provides outputs to control
the fuel pump, fuel injectors, idle speed and
ignition circuit. Using the inputs from the
various sensors, the module computes the
optimum ignition advance, and fuel injector
pulse duration, to suit the prevailing engine
conditions. This system gives very accurate
control of the engine under all conditions,
improving fuel consumption and driveability,
and reducing exhaust gas emissions.
25Further details of the fuel injection system
components are given in Chapter 4B.
Motronic M2.5 and M2.8
26The system is similar to that described for
SOHC models, with the following differences.
27Along with the crankshaft speed/position
sensor, a “Hall-effect” distributor is used
(similar to that described in this Section, with
the MSTS-i system).
Engine electrical systems 5•3
5
Page 91 of 525

28The system also incorporates a separate
ignition amplifier module that transmits
amplified signals from the main system
module to trigger the HT pulse from the
ignition coil. The module is mounted on the
ignition coil’s bracket/baseplate.
29Additionally, the Motronic module
receives information from a cylinder
block-mounted knock sensor, which senses
“knocking” (or pre-ignition) just as it begins to
occur, enabling the module to retard the
ignition timing, thus preventing engine
damage.
Simtec 56.1
30This system uses increased amount of
electronic components instead of mechanical
parts as sensors and actuators with the
Simtec engine management system. This
provides more precise operating data as well
as greater problem free motoring.
31The control unit is equipped with
electronic ignition control. Called ‘Micropro-
cessor Spark Timing System, inductive
triggered’, (or MSTS-i), and means that the
mechanical high voltage distributor is no
longer needed. It is located behind the trim
panel, on the right-hand side footwell (door
pillar).
32The ignition coil is replaced by a dual
spark ignition coil, which is switched directly
by the output stages in the control unit.
33A camshaft sensor will maintain
emergency operation, should the crankshaft
inductive pulse pick-up, malfunction. These
sense TDC (‘Top Dead Centre’), crankshaft
angle and engine speed. The signals are used
by the control unit to calculate ignition point
and for fuel injection.
34The ‘hot film airflow meter’ determines the
mass of air taken in by the engine. The system
uses this information to calculate the correct
amount of fuel needed for injection in the
engine.
35The air inlet temperature sensor (NTC), is
fitted in the air inlet duct between the air
cleaner and the hot mass air flow meter.
36A controlled canister purge valve is
actuated by the system. The tank ventilation is
monitored closely with the Lambda control (or
oxygen sensor) and adaptation by the
computer within the control unit.
37A knock control system is also fitted. This
eliminates the need for octane number
adjustment, as it is performed automatically
through the control unit.
3Electrical system -
precautions
1It is necessary to take extra care when
working on the electrical system, to avoid
damage to semi-conductor devices (diodes
and transistors), and to avoid the risk of
personal injury. Along with the precautions
given in the “Safety first!” Section at the
beginning of this manual, take note of the
following points when working on the system.
2Always remove rings, watches, etc. before
working on the electrical system. Even with
the battery disconnected, discharge could
occur if a component live terminal is earthed
through a metal object. This could cause a
shock or nasty burn.
3Do not reverse the battery connections.
Components such as the alternator, or any
other component having semi-conductor
circuitry, could be irreparably damaged.
4If the engine is being started using jump
leads and a slave battery, connect the
batteries positive to positive and negative to
negative. This also applies when connecting a
battery charger.
5Never disconnect the battery terminals, or
alternator multi-plug connector, when the
engine is running.
6The battery leads and alternator wiring
must be disconnected before carrying out any
electric welding on the vehicle.
7Never use an ohmmeter of the type
incorporating a hand-cranked generator for
circuit or continuity testing.
8Engine management modules are very
sensitive components, and certain
precautions must be taken, to avoid damage
to the module when working on a vehicle
equipped with an engine management
system, as follows.
9When carrying out welding operations on
the vehicle using electric welding equipment,
the battery and alternator should be
disconnected.
10Although underbonnet-mounted modules
will tolerate normal underbonnet conditions,
they can be adversely affected by excess heat
or moisture. If using welding equipment or
pressure washing equipment near the
module, take care not to direct heat, or jets of
water or steam, at the module. If this cannot
be avoided, remove the module from the
vehicle, and protect its wiring plug with a
plastic bag.
11Before disconnecting any wiring, or
removing components, always ensure that the
ignition is switched off.
12Do not attempt to improvise fault
diagnosis procedures using a test lamp or
multimeter, as irreparable damage could be
caused to the module.13After working on ignition/engine
management system components, ensure
that all wiring is correctly reconnected before
reconnecting the battery or switching on the
ignition.
14Any ignition system that uses a
“Hall-effect” generator in the distributor,
cannot be tested. Test equipment that uses
its own power source (e.g. an ohmmeter),
when connected to the distributor or the
“Hall-effect” generator, will be damaged.
4Ignition system testing -
general
3
Note: Refer to Section 3 before proceeding.
Always switch off the ignition before
disconnecting or connecting any component
and when using a multi-meter to check
resistances. Any voltmeter or multi-meter
used to test ignition system components must
have an impedance of 10 meg ohms or
greater
1Electronic ignition system components are
normally very reliable. Most faults are far more
likely to be due to loose or dirty connections,
or to “tracking” of HT voltage due to dirt,
dampness or damaged insulation than to
component failure. Always check all wiring
thoroughly before condemning an electrical
component and work methodically to
eliminate all other possibilities before deciding
that a particular component is faulty.
2The old practice of checking for a spark by
holding the live end of a HT lead a short
distance away from the engine is not
recommended. Not only is there a high risk of
a powerful electric shock, but the ignition coil
or amplifier module will be damaged.
Similarly, never try to “diagnose” misfires by
pulling off one HT lead at a time. Note also
that the ECU is at risk if the system is
triggered with an open (i.e., not properly
earthed) HT circuit; ECU’s are very expensive
to replace, so take care!
3If you are in any doubt as to your skill and
ability to test an ignition system component or
if you do not have the required equipment,
take the vehicle to a suitably equipped
Vauxhall dealer. It is better to pay the labour
charges involved in having the vehicle
checked by an expert than to risk damage to
the system or to yourself.
4If the engine either will not turn over at all,
or only turns very slowly, check the battery
and starter motor. Connect a voltmeter across
the battery terminals (meter positive probe to
battery positive terminal) and disconnect the
ignition coil HT lead from the distributor cap
and earth. Note the voltage reading obtained
while turning over the engine on the starter for
(no more than) ten seconds. If the reading
obtained is less than approximately 9.5 volts,
check the battery, battery connections, starter
motor and charging system.
5•4Engine electrical systems
Warning: The HT voltage
generated by an electronic
ignition system is extremely
high and, in certain
circumstances, could prove fatal. Take
care to avoid receiving electric shocks
from the HT side of the ignition system.
Do not handle HT leads, or touch the
distributor or coil, when the engine is
running. If tracing faults in the HT circuit,
use well-insulated tools to manipulate live
leads
Page 92 of 525

5If the engine turns over at normal speed but
will not start, check the HT circuit by
connecting a timing light and turning the
engine over on the starter motor. If the light
flashes, voltage is reaching the spark plugs,
so these should be checked first. If the light
does not flash, check the HT leads
themselves followed by the distributor cap,
carbon brush and rotor arm.
6If there is a spark, check the fuel system for
faults as far as possible (Chapters 4A or 4B).
7If there is still no spark, check the voltage at
the ignition coil “+” or “15” terminal; it should
be the same as the battery voltage (i.e., at
least 11.7 volts). If the voltage at the coil is
more than 1 volt less than that at the battery,
check the connections back through the
ignition switch to the battery and its earth until
the fault is found. Note, however, that the
ECU controls the coil’s feed; do not attempt
to “test” the ECU with anything other than the
correct test equipment, which will be available
only to a Vauxhall dealer. If any of the wires
are to be checked which lead to the ECU,
always first unplug the relevant connector
from the ECU so that there is no risk of the
ECU being damaged by the application of
incorrect voltages from test equipment.
8If the feed to the ignition coil is sound,
check the coil’s primary and secondary
windings (refer to Section 16). Renew the coil
if faulty, but check the condition of the LT
connections themselves before doing so, to
ensure that the fault is not due to dirty or
poorly fastened connectors.
9If the ignition coil is in good condition, the
fault may be within the amplifier module or the
distributor on the C16 NZ and C16 NZ2
engines, or the amplifier or the crankshaft
speed/position sensor on the C18 NZ engine.
A quick check of these components can be
made by connecting a low-wattage bulb
across the ignition coil’s (disconnected) LT
terminals. If the bulb flickers or flashes when
the engine is turned over, the amplifier and
distributor (C16 NZ and C16 NZ2 engines), or
amplifier and crankshaft speed/position
sensor (C18 NZ engine), are sound.
10If this is the case, the entire LT circuit is in
good condition; the fault, if it lies in the
ignition system, must be in the HT circuit
components. These should be checked
carefully, as outlined above.
11If the indicator or bulb does not flash, the
fault is in either the amplifier or the distributor
(C16 NZ and C16 NZ2 engines), or the
amplifier or crankshaft speed/position sensor
(C18 NZ engine). Owners should note,
however, that by far the commonest cause of
“failure” of either of these is a poor
connection, either between the components
themselves or in the LT circuit wiring
connections. If such a fault is suspected, the
vehicle must be taken to a suitably equipped
Vauxhall dealer for testing; no information is
available to eliminate these components by
other means.12An irregular misfire suggests either a
loose connection or intermittent fault on the
primary circuit, or a HT fault on the coil side of
the rotor arm.
13With the ignition switched off, check
carefully through the system ensuring that all
connections are clean and securely fastened.
If the equipment is available, check the LT
circuit as described in paragraphs 7 to 11
above.
14Check that the HT coil, the distributor cap
and the HT leads are clean and dry. Check the
leads and the spark plugs (by substitution, if
necessary), then check the distributor cap,
carbon brush and rotor arm.
15Regular misfiring is almost certainly due to
a fault in the distributor cap, HT leads or spark
plugs. Use a timing light (paragraph 5, above)
to check whether HT voltage is present at all
leads.
16If HT voltage is not present on any
particular lead, the fault will be in that lead or
in the distributor cap. If HT is present on all
leads, the fault will be in the spark plugs;
check and renew them if there is any doubt
about their condition.
17If no HT voltage is present, check the
ignition coil; its secondary windings may be
breaking down under load.
18If all components have been checked for
signs of obvious faults but the system is still
thought to be faulty, take the vehicle to a
Vauxhall dealer for testing on special
equipment.
5Battery - testing and charging
2
Note: Refer to Section 3 before proceeding.
Testing
1Topping-up and testing of the electrolyte in
each cell is not possible. The condition of the
battery can therefore only be tested by
observing the battery condition indicator.
2The battery condition indicator is fitted in
the top of the battery casing, and indicates
the condition of the battery from its colour. If
the indicator shows green, then the battery is
in a good state of charge. If the indicator turns
darker, eventually to black, then the battery
requires charging, as described later in this
Section. If the indicator shows clear/yellow,
then the electrolyte level in the battery is too
low to allow further use, and the battery
should be renewed.
Charging
3Do not attempt to charge, load or jump start
a battery when the indicator shows
clear/yellow. If the battery is to be charged,
remove it from the vehicle and charge it as
follows.
4The maintenance-free type battery takes
considerably longer to fully recharge than the
standard type, the time taken being
dependent on the extent of discharge.5A constant-voltage type charger is required,
to be set, when connected, to 13.9 to 14.9
volts with a charger current below 25 amps.
6If the battery is to be charged from a fully
discharged state (less than 12.2 volts output),
have it recharged by a Vauxhall dealer or
battery specialist, as the charge rate will be
high and constant supervision during charging
is necessary.
6Battery - removal and refitting
2
Note: Refer to Section 3 before proceeding.
Removal
1The battery is located at the left-hand front
corner of the engine compartment.
2Disconnect the lead(s) at the negative
(earth) terminal by unscrewing the retaining
nut and removing the terminal clamp.
3Disconnect the positive terminal lead(s) in
the same way.
4Unscrew the clamp bolt sufficiently to
enable the battery to be lifted from its
location. Keep the battery in an upright
position, to avoid spilling electrolyte on the
bodywork.
Refitting
5Refitting is a reversal of removal, but smear
petroleum jelly on the terminals when
reconnecting the leads, and always connect
the positive lead first and the negative lead
last.
7Alternator - description
1A Delco-Remy or Bosch alternator may be
fitted, depending on model and engine
capacity. The maximum output of the
alternator varies accordingly.
2The alternator is belt-driven from the
crankshaft pulley. Cooling is provided by a
fan, mounted outside the casing on the end of
the rotor shaft. An integral voltage regulator is
incorporated, to control the output voltage.
3The alternator provides a charge to the
battery even at very low engine speed, and
consists of a coil-wound stator in which a
rotor rotates. The rotor shaft is supported in
ball-bearings, and slip rings are used to
conduct current to and from the field coils
through the carbon brushes.
4The alternator generates ac (alternating
current), which is rectified by an internal diode
circuit to dc (direct current) for supply to the
battery.
5Later models are fitted with a Delco-Remy,
‘compact’ series alternators (see illustration).
They use a ribbed V-belt type drivebelt with
automatic tensioner. They are rigidly mounted
to the engine.
Engine electrical systems 5•5
5
Page 99 of 525

been removed, check that No 1 cylinder is on
its firing stroke by removing No 1 cylinder
spark plug and placing a finger over the plug
hole. Turn the crankshaft until compression
can be felt, which indicates that No 1 piston is
rising on its compression stroke. Continue
turning the crankshaft until the relevant timing
marks are in alignment.
11Turn the rotor arm to the position noted in
paragraph 6c, and hold the rotor arm in this
position as the distributor is fitted. Note that
the distributor driveshaft will only engage with
the camshaft in one position. If the original
distributor is being refitted, align the marks
made on the distributor body and camshaft
housing before removal.
12Refit the clamp plate and nut, but do not
fully tighten the nut at this stage.
13On the Bosch distributor, remove the rotor
arm, then refit the plastic shield and the rotor
arm.
14On 14 NV models, reconnect the vacuum
pipe to the diaphragm unit.
15Reconnect the distributor wiring plug.
16Refit the distributor cap as described in
Section 17.
17Reconnect the battery negative lead.
18Check and if necessary adjust the ignition
timing, as described in Section 21.
19Distributor (DOHC models),
where applicable - removal
and refitting
3
Removal
1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
2Remove the distributor cap, as described in
Section 17.
3Disconnect the distributor wiring plug.
4Unscrew the two securing bolts, and
remove the distributor from the cylinder head.
5Examine the O-ring on the rear of the
distributor, and renew if necessary.
Refitting
6Refitting is a reversal of removal. However,
note that the distributor should be fitted so
that the wiring plug is positioned on the upper
left-hand side of the distributor body, when
viewed from the distributor cap end.
20Distributor - dismantling,
inspection and reassembly
3
Note: Before contemplating dismantling of a
distributor, check the cost and availability of
replacement parts. It may prove more
economical to renew the complete distributor
assembly
14 NV models
Dismantling
1With the distributor removed as described
in Section 18, continue as follows.
2Pull off the rotor arm, and remove the
plastic shield.
3The top bearing plate can be removed after
unscrewing the two securing screws, however
(other than the vacuum diaphragm unit), no
spares are available for the distributor and no
adjustments are required.
4If desired, the vacuum diaphragm unit can
be removed by extracting the two securing
screws and unhooking the operating arm from
the distributor baseplate. Note that the
screws are of differing lengths, the longer
screw also secures one of the distributor cap
clips.
Inspection
5The vacuum unit can be tested by applying
suction to the vacuum port, and checking that
the operating rod moves into the unit as
suction is applied. Remove the suction, and
check that the operating rod returns to its
original position. If the operating rod does not
move as described, renew the vacuum unit.
6Check the distributor cap for corrosion of
the segments, and for signs of tracking,
indicated by a thin black line between the
segments. Make sure that the carbon brush in
the centre of the cap moves freely and stands
proud of the surface of the cap. Renew the
cap if necessary.
7If the metal portion of the rotor arm is badly
burnt or loose, renew it. If slightly burnt or
corroded; it may be cleaned with a fine file.
8Examine the seal ring at the rear of the
distributor body, and renew if necessary.
Reassembly
9Reassembly is a reversal of dismantling,
ensuring that the vacuum unit operating arm
is correctly engaged with the peg on the
baseplate, several attempts may be required
to reconnect it.
10Refit the distributor as described in
Section 18, and then check and if necessary
adjust the ignition timing, as described in
Section 21.
16 SV models
Dismantling
11With the distributor removed as described
in Section 18, pull off the rotor arm and, on
the Bosch distributor, remove the plastic
shield.
12Using a pin punch, carefully drive out the
roll pin securing the plastic drive collar to the
rear of the distributor shaft (see illustration).
13Lift off the drive collar, and remove the
thrustwashers from the end of the shaft (see
illustration).
14Withdraw the shaft, complete with the
trigger vane, from the distributor body, and
recover the thrustwashers from the shaft (see
illustration).
15On the Lucas distributor, extract the
spring clip from inside the body, then
withdraw the terminal block. Pull the small
wiring plug from inside the terminal block (see
illustrations).
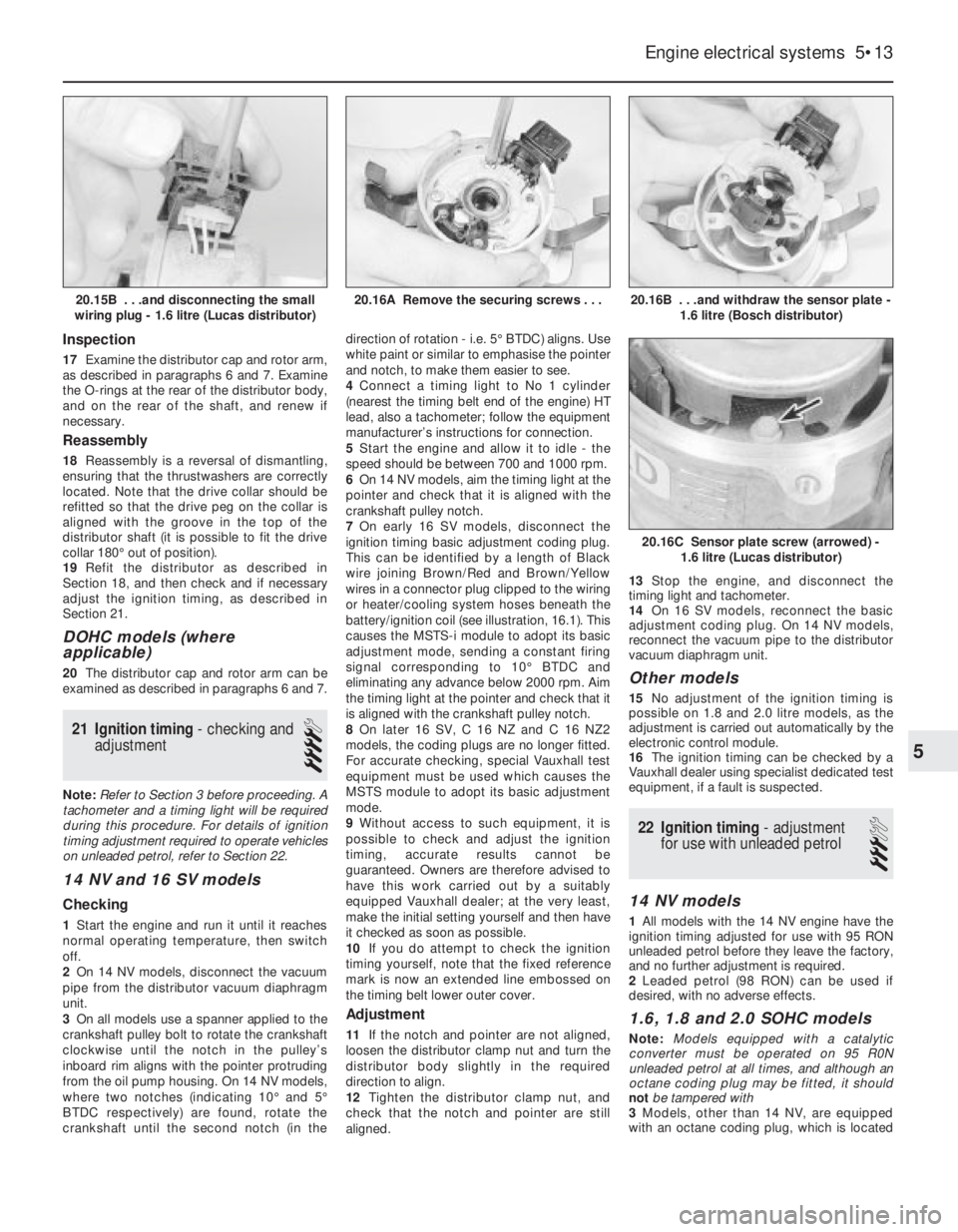
16Remove the screws, and lift the sensor
plate from the distributor body (see
illustrations).
5•12Engine electrical systems
20.15A Removing the spring clip . . .20.14 Recovering the thrustwashers from
the shaft - 1.6 litre (Bosch distributor)20.13 Removing the thrustwashers
20.12 Removing the drive collar roll pin -
1.6 litre models (Bosch distributor)
Page 100 of 525
Inspection
17Examine the distributor cap and rotor arm,
as described in paragraphs 6 and 7. Examine
the O-rings at the rear of the distributor body,
and on the rear of the shaft, and renew if
necessary.
Reassembly
18Reassembly is a reversal of dismantling,
ensuring that the thrustwashers are correctly
located. Note that the drive collar should be
refitted so that the drive peg on the collar is
aligned with the groove in the top of the
distributor shaft (it is possible to fit the drive
collar 180°out of position).
19Refit the distributor as described in
Section 18, and then check and if necessary
adjust the ignition timing, as described in
Section 21.
DOHC models (where
applicable)
20The distributor cap and rotor arm can be
examined as described in paragraphs 6 and 7.
21Ignition timing -checking and
adjustment
4
Note: Refer to Section 3 before proceeding. A
tachometer and a timing light will be required
during this procedure. For details of ignition
timing adjustment required to operate vehicles
on unleaded petrol, refer to Section 22.
14 NV and 16 SV models
Checking
1Start the engine and run it until it reaches
normal operating temperature, then switch
off.
2On 14 NV models, disconnect the vacuum
pipe from the distributor vacuum diaphragm
unit.
3On all models use a spanner applied to the
crankshaft pulley bolt to rotate the crankshaft
clockwise until the notch in the pulley’s
inboard rim aligns with the pointer protruding
from the oil pump housing. On 14 NV models,
where two notches (indicating 10°and 5°
BTDC respectively) are found, rotate the
crankshaft until the second notch (in thedirection of rotation -i.e. 5°BTDC) aligns. Use
white paint or similar to emphasise the pointer
and notch, to make them easier to see.
4Connect a timing light to No 1 cylinder
(nearest the timing belt end of the engine) HT
lead, also a tachometer; follow the equipment
manufacturer’s instructions for connection.
5Start the engine and allow it to idle -the
speed should be between 700 and 1000 rpm.
6On 14 NV models, aim the timing light at the
pointer and check that it is aligned with the
crankshaft pulley notch.
7On early 16 SV models, disconnect the
ignition timing basic adjustment coding plug.
This can be identified by a length of Black
wire joining Brown/Red and Brown/Yellow
wires in a connector plug clipped to the wiring
or heater/cooling system hoses beneath the
battery/ignition coil (see illustration, 16.1). This
causes the MSTS-i module to adopt its basic
adjustment mode, sending a constant firing
signal corresponding to 10°BTDC and
eliminating any advance below 2000 rpm. Aim
the timing light at the pointer and check that it
is aligned with the crankshaft pulley notch.
8On later 16 SV, C 16 NZ and C 16 NZ2
models, the coding plugs are no longer fitted.
For accurate checking, special Vauxhall test
equipment must be used which causes the
MSTS module to adopt its basic adjustment
mode.
9Without access to such equipment, it is
possible to check and adjust the ignition
timing, accurate results cannot be
guaranteed. Owners are therefore advised to
have this work carried out by a suitably
equipped Vauxhall dealer; at the very least,
make the initial setting yourself and then have
it checked as soon as possible.
10If you do attempt to check the ignition
timing yourself, note that the fixed reference
mark is now an extended line embossed on
the timing belt lower outer cover.
Adjustment
11If the notch and pointer are not aligned,
loosen the distributor clamp nut and turn the
distributor body slightly in the required
direction to align.
12Tighten the distributor clamp nut, and
check that the notch and pointer are still
aligned. 13Stop the engine, and disconnect the
timing light and tachometer.
14On 16 SV models, reconnect the basic
adjustment coding plug. On 14 NV models,
reconnect the vacuum pipe to the distributor
vacuum diaphragm unit.
Other models
15No adjustment of the ignition timing is
possible on 1.8 and 2.0 litre models, as the
adjustment is carried out automatically by the
electronic control module.
16The ignition timing can be checked by a
Vauxhall dealer using specialist dedicated test
equipment, if a fault is suspected.
22Ignition timing -adjustment
for use with unleaded petrol
3
14 NV models
1All models with the 14 NV engine have the
ignition timing adjusted for use with 95 RON
unleaded petrol before they leave the factory,
and no further adjustment is required.
2Leaded petrol (98 RON) can be used if
desired, with no adverse effects.
1.6, 1.8 and 2.0 SOHC models
Note: Models equipped with a catalytic
converter must be operated on 95 R0N
unleaded petrol at all times, and although an
octane coding plug may be fitted, it should
not be tampered with
3Models, other than 14 NV, are equipped
with an octane coding plug, which is located
Engine electrical systems 5•13
20.16B . . .and withdraw the sensor plate -
1.6 litre (Bosch distributor)
20.16C Sensor plate screw (arrowed) -
1.6 litre (Lucas distributor)
20.16A Remove the securing screws . . .20.15B . . .and disconnecting the small
wiring plug - 1.6 litre (Lucas distributor)
5