roller SUZUKI SWIFT 2006 2.G Service User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SUZUKI, Model Year: 2006, Model line: SWIFT, Model: SUZUKI SWIFT 2006 2.GPages: 1496, PDF Size: 34.44 MB
Page 579 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Electronic Stability Program: 4F-5
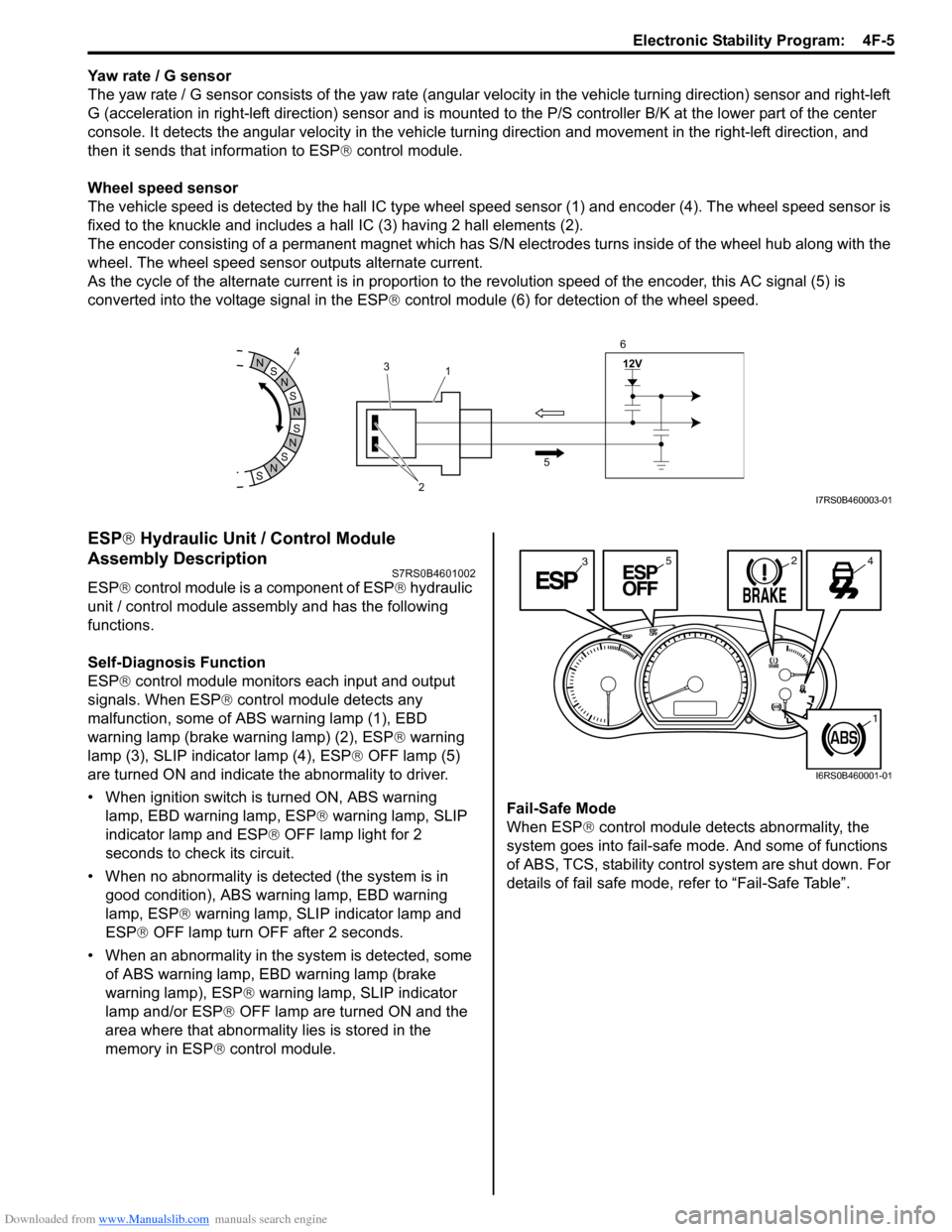
Yaw rate / G sensor
The yaw rate / G sensor consists of the yaw rate (angular velocity in the vehicle turning direction) sensor and right-left
G (acceleration in right-left direction) sensor and is mounted to the P/S controller B/K at the lower part of the center
console. It detects the angular velocity in the vehicle turn ing direction and movement in the right-left direction, and
then it sends that information to ESP ® control module.
Wheel speed sensor
The vehicle speed is detected by the hall IC type wheel speed sensor (1) and encoder (4). The wheel speed sensor is
fixed to the knuckle and includes a hall IC (3) having 2 hall elements (2).
The encoder consisting of a permanent ma gnet which has S/N electrodes turns inside of the wheel hub along with the
wheel. The wheel speed sensor outputs alternate current.
As the cycle of the alternate current is in proportion to the revolution speed of the encoder, this AC signal (5) is
converted into the voltage signal in the ESP ® control module (6) for detection of the wheel speed.
ESP ® Hydraulic Unit / Control Module
Assembly Description
S7RS0B4601002
ESP ® control module is a component of ESP ® hydraulic
unit / control module assembly and has the following
functions.
Self-Diagnosis Function
ESP ® control module monitors each input and output
signals. When ESP ® control module detects any
malfunction, some of ABS warning lamp (1), EBD
warning lamp (brake warning lamp) (2), ESP ® warning
lamp (3), SLIP indicator lamp (4), ESP ® OFF lamp (5)
are turned ON and indicate the abnormality to driver.
• When ignition switch is turned ON, ABS warning lamp, EBD warning lamp, ESP ® warning lamp, SLIP
indicator lamp and ESP ® OFF lamp light for 2
seconds to check its circuit.
• When no abnormality is detected (the system is in good condition), ABS warning lamp, EBD warning
lamp, ESP ® warning lamp, SLIP indicator lamp and
ESP ® OFF lamp turn OFF after 2 seconds.
• When an abnormality in the system is detected, some of ABS warning lamp, EBD warning lamp (brake
warning lamp), ESP ® warning lamp, SLIP indicator
lamp and/or ESP ® OFF lamp are turned ON and the
area where that abnormality lies is stored in the
memory in ESP ® control module. Fail-Safe Mode
When ESP
® control module detects abnormality, the
system goes into fail-safe mode. And some of functions
of ABS, TCS, stability control system are shut down. For
details of fail safe mode, re fer to “Fail-Safe Table”.
S
N
S
N
S
N
N
S
N
S
12V
2
3
1
5
4
6I7RS0B460003-01
3245
1
I6RS0B460001-01
Page 601 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Electronic Stability Program: 4F-27
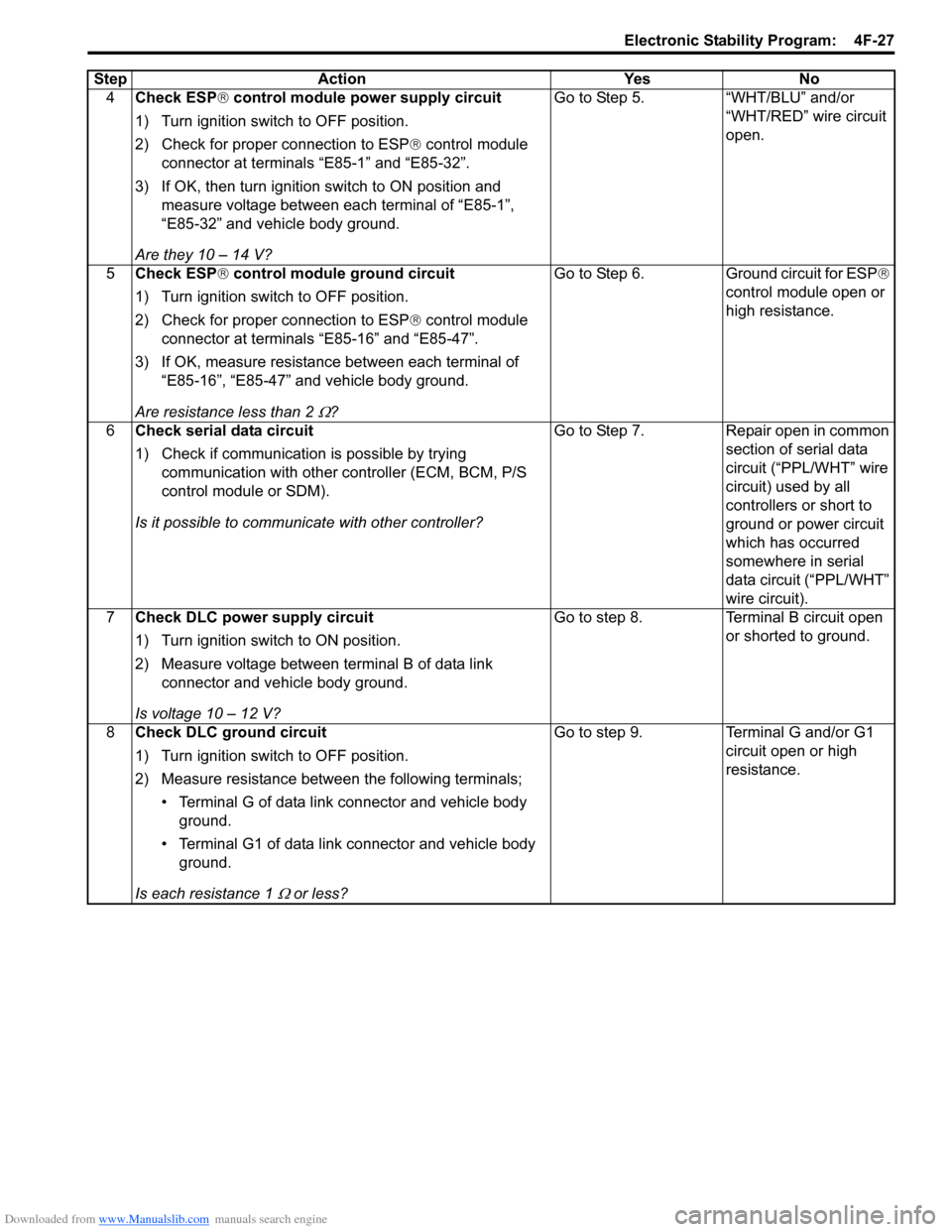
4Check ESP ® control module power supply circuit
1) Turn ignition switch to OFF position.
2) Check for proper connection to ESP ® control module
connector at terminals “E85-1” and “E85-32”.
3) If OK, then turn ignition switch to ON position and measure voltage between each terminal of “E85-1”,
“E85-32” and vehicle body ground.
Are they 10 – 14 V? Go to Step 5. “WHT/BLU” and/or
“WHT/RED” wire circuit
open.
5 Check ESP ® control module ground circuit
1) Turn ignition switch to OFF position.
2) Check for proper connection to ESP ® control module
connector at terminals “E85-16” and “E85-47”.
3) If OK, measure resistance between each terminal of “E85-16”, “E85-47” and vehicle body ground.
Are resistance less than 2
Ω? Go to Step 6. Ground circuit for ESP
®
control module open or
high resistance.
6 Check serial data circuit
1) Check if communication is possible by trying
communication with other c ontroller (ECM, BCM, P/S
control module or SDM).
Is it possible to commun icate with other controller? Go to Step 7. Repair open in common
section of serial data
circuit (“PPL/WHT” wire
circuit) used by all
controllers or short to
ground or power circuit
which has occurred
somewhere in serial
data circuit (“PPL/WHT”
wire circuit).
7 Check DLC power supply circuit
1) Turn ignition switch to ON position.
2) Measure voltage between terminal B of data link
connector and vehicle body ground.
Is voltage 10 – 12 V? Go to step 8. Terminal B circuit open
or shorted to ground.
8 Check DLC ground circuit
1) Turn ignition switch to OFF position.
2) Measure resistance between the following terminals;
• Terminal G of data link connector and vehicle body ground.
• Terminal G1 of data link connector and vehicle body ground.
Is each resistance 1
Ω or less? Go to step 9. Terminal G and/or G1
circuit open or high
resistance.
Step Action Yes No
Page 645 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Automatic Transmission/Transaxle: 5A-1
Transmission / Transaxle
Automatic Transmission/Transaxle
Precautions
Precautions in Diagnosing TroubleS7RS0B5100001
• Do not disconnect couplers from TCM, battery cable from battery, TCM ground wire harness from engine or
main fuse before checking the diagnostic information
(DTC, freeze frame data, etc.) stored in TCM memory.
Such disconnection will clea r memorized information
in TCM memory.
• Diagnostic information stored in TCM memory can be cleared as well as checked by using SUZUKI scan
tool or generic scan tool. Before using scan tool, read
its Operator’s (Instruction) Manual carefully to have
good understanding as to what functions are available
and how to use it.
It is indistinguishable wh ich module turns on MIL
because not only ECM but also TCM turns on MIL.
Therefore, check both ECM and TCM for DTC when
MIL lights on.
When checking TCM for DTC, keep in mind that DTC
is displayed on the scan tool as follows depending on
the scan tool used.
– SUZUKI scan tool displays DTC detected by TCM.
– Generic scan tool displays DTC detected by each of ECM and TCM simultaneously.
• Using SUZUKI scan tool the diagnostic information stored in TCM memory can be checked and cleared
as well. Before its use, be sure to read Operator’s
Manual supplied with it carefully to have good
understanding of its functions and usage.
• Be sure to read “Precautions for Electrical Circuit Service in Section 00” befo re inspection and observe
what is written there.
• TCM replacement
– When substituting a known-good TCM, check that all relays and actuators have resistance of
specified value.
Neglecting this check may result in damage to good
TCM.
• Communication of ECUs , ECM, TCM, ABS control
module, keyless start control module and BCM is
established by CAN (Controller Area Network).
Therefore, handle CAN communication line with care
referring to “Precaution for CAN Communication
System in Section 00”.
Precautions for Disassembly and ReassemblyS7RS0B5100002
When repairing automatic transaxle, it is necessary to
conduct the on-vehicle test to investigate where the
cause of the trouble lies first.
Then whether overhaul should be done or not is
determined. If the transaxle is disassembled without
such preliminary procedure, not only the cause of the
trouble would be unknown, but also a secondary trouble
may occur and often time would be wasted.
As the automatic transaxle consists of high precision
component, the following cautions should be strictly
observed when handling its parts in disassembly and
reassembly.
• Disassembling valve body assembly is prohibited
essentially. However, a few parts can be
disassembled. When disassembling valve body
component parts, confirm whether their parts are
allowed to disassemble or not referring to “Valve Body
Assembly Disassembly and Reassembly”.
• When component part of forward clutch, direct clutch, 2nd brake and/or O/D and 2nd coast brake, namely
clutch disc, brake disc, retaining plate and/or
separator plate, have been replaced, all learned
contents, which have been stored in TCM memory by
executing learning control, should be initialized
referring to “Learning Control Initialization”.
• Make sure to wash dirt off from the transaxle so that no such dirt will enter the transaxle during
dismounting and remounting.
• Select a clean place free from dust and dirt for overhauling.
• Place a rubber mat on the work bench to protect parts from damage.
• Work gloves or shop cloth should not be used. (Use a nylon cloth or a paper towel.)
• When separating the case joint, do not pry with a screwdriver or such but tap with a plastic hammer
lightly.
• Make sure to wash dirt off from the transaxle so that no such dirt will enter the transaxle during
disassembly and reassembly.
• Wash the disassembled parts in ATF (Automatic Transaxle Fluid) or kerosene (using care not to allow
ATF or kerosene to get on your face, etc.) and confirm
that each fluid passage is not clogged by blowing air
into it. But use kerosene to wash the discs, resin
washers and rubber parts.
• Replace each gasket, oil seal and O-ring with a new one.
• Apply ATF to sliding or rotating parts before
reassembly.
Page 815 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Manual Transmission/Transaxle: 5B-1
Transmission / Transaxle
Manual Transmission/Transaxle
General Description
Manual Transaxle Construction and ServicingS7RS0B5201001
The transaxle provides five forward speeds and one reverse speed by means of three synchromeshs and three shafts
(input shaft, countershaft and reverse gear shaft). All forward gears are in constant mesh, and reverse uses a sliding
idler gear arrangement.
The low speed synchronizer sleeve & hub is mounted on countershaft and engaged with countershaft 1st gear or 2nd
gear, while the high speed synchronizer sleeve & hub is don e on input shaft and engaged with input shaft 3rd gear or
4th gear. The 5th speed synchronizer sleev e & hub on input shaft is engaged with input shaft fifth gear mounted on the
input shaft.
To prevent the cracking noise from the reverse gear when shifting transaxle gear into the reverse gear, the reverse
shift braking device is used.
The device utilizes the 5th synchromesh, which is the lever synchro type, to appl y the brake on the input shaft rotation.
The double cone synchronizing mechanism is provided to 2nd gear synchromesh device for high performance of
shifting to 2nd gear.
The countershaft turns the final gear and differential assembly, thereby turning the front drive shafts which are
attached to the front wheels.
For servicing, it is ne cessary to use genuine sealant or its equivalent on mating surfaces of transaxle case which is
made of aluminum. The case fastening bolts must be tight ened to specified torque by means of torque wrench. It is
also important that all parts are thoroughly cleaned with cleaning fluid and air dried before reassembling.
Further, care must be taken to adjust preload of count ershaft taper roller bearings. New synchronizer rings are
prohibited from being lapped with respective gear cones by using lapping compound before they are assembled.
Page 896 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 6C-14 Power Assisted Steering System:
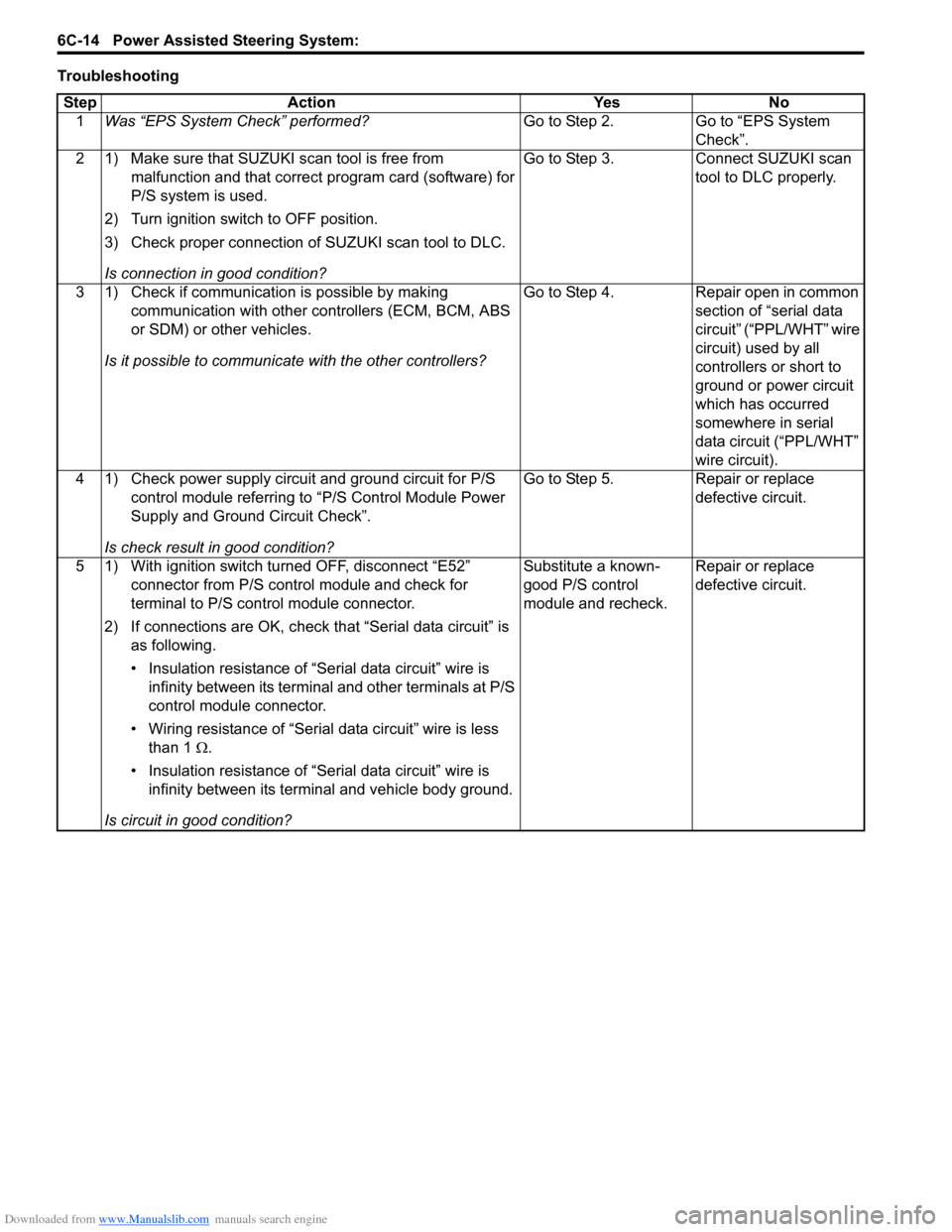
TroubleshootingStep Action Yes No 1 Was “EPS System Check” performed? Go to Step 2. Go to “EPS System
Check”.
2 1) Make sure that SUZUKI scan tool is free from malfunction and that correct program card (software) for
P/S system is used.
2) Turn ignition switch to OFF position.
3) Check proper connection of SUZUKI scan tool to DLC.
Is connection in good condition? Go to Step 3. Connect SUZUKI scan
tool to DLC properly.
3 1) Check if communication is possible by making communication with other controllers (ECM, BCM, ABS
or SDM) or other vehicles.
Is it possible to communic ate with the other controllers? Go to Step 4. Repair open in common
section of “serial data
circuit” (“PPL/WHT” wire
circuit) used by all
controllers or short to
ground or power circuit
which has occurred
somewhere in serial
data circuit (“PPL/WHT”
wire circuit).
4 1) Check power supply circuit and ground circuit for P/S control module referring to “P/S Control Module Power
Supply and Ground Circuit Check”.
Is check result in good condition? Go to Step 5. Repair or replace
defective circuit.
5 1) With ignition switch turned OFF, disconnect “E52” connector from P/S control module and check for
terminal to P/S control module connector.
2) If connections are OK, check t hat “Serial data circuit” is
as following.
• Insulation resistance of “Serial data circuit” wire is infinity between its terminal and other terminals at P/S
control module connector.
• Wiring resistance of “Seria l data circuit” wire is less
than 1 Ω.
• Insulation resistance of “Serial data circuit” wire is infinity between its terminal and vehicle body ground.
Is circuit in good condition? Substitute a known-
good P/S control
module and recheck.
Repair or replace
defective circuit.
Page 934 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 7-ii Table of Contents
Recommended Service Material ....................... 7B-33
Special Tool ...................................................... 7B-33
Automatic Type .................... .................................7B-34
Precautions.........................................................7B-34 A/C System Caution .......................................... 7B-34
Precautions in Diagnosing Trouble ................... 7B-34
Precautions on Servicing A/C System .............. 7B-34
General Description .......... .................................7B-34
Auto A/C System Descript ion ............................ 7B-34
HVAC Control Module Operation Description ... 7B-36
Refrigerant Type Identifica tion .......................... 7B-36
Sub-Cool A/C System Description .................... 7B-36
A/C Operation Description ................................ 7B-36
On-Board Diagnostic System Description ......... 7B-37
Schematic and Routing Diagram ......................7B-37 Major Components of A/C System .................... 7B-37
A/C System Wiring Diagra m ............................. 7B-38
Diagnostic Information and Procedures ..........7B-39 A/C System Symptom Diagnosis ...................... 7B-39
Abnormal Noise Sympto m Diagnosis of A/C
System ............................................................ 7B-42
DTC Check........................................................ 7B-42
DTC Clearance ................................................. 7B-43
DTC Table ......................................................... 7B-44
Fail-Safe Table ................. ................................. 7B-45
Scan Tool Data ................................................. 7B-46
Air Conditioning System Check......................... 7B-47
Visual Inspection ............................................... 7B-49
DTC B1502: Inside Air Temperature Sensor and/or Its Circuit Malfunction .......................... 7B-49
DTC B1503: A/C Evaporator Air Temperature Sensor and/or Its Circuit Malfunction .............. 7B-50
DTC B1504: Sunload Sensor and/or Its Circuit Malfunction ......... ................................. 7B-52
DTC B1511: Temperature Control Actuator (Position Sensor) and/or Its Circuit
Malfunction ...................................................... 7B-53
DTC B1512: Air flow Control Actuator (Position Sensor) and/or Its Circuit
Malfunction ...................................................... 7B-55
DTC B1513: Temperature Control Actuator and/or Its Circuit Malfunction .......................... 7B-57
DTC B1514: Air Flow Co ntrol Actuator and/or
Its Circuit Malfunction ...................................... 7B-60
DTC B1541: HVAC Control Module Back-Up Power Supply Malfunction .............................. 7B-62
DTC B1546: A/C Refrigerant Pressure Malfunction ...................................................... 7B-63
DTC B1551: Serial Communication Circuit Malfunction ...................................................... 7B-63
DTC B1552: Serial Communication Signal Malfunction ...................................................... 7B-64
DTC B1553: CAN Communication Signal Malfunction ...................................................... 7B-65
DTC B1557: Vehicle Speed Sensor Signal Malfunction ...................................................... 7B-65
DTC B1561: Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor Signal Malfunctio n .............................. 7B-66 DTC B1562: Outside Air Temperature Sensor
Signal Malfunction ........................................... 7B-66
DTC B1563: A/C Refr igerant Pressure
Sensor Signal Malfunction .............................. 7B-66
Inspection of HVAC Control Module and Its Circuit .............................................................. 7B-67
A/C System Performance Inspection ................ 7B-70
A/C System Inspection at ECM ......................... 7B-70
Repair Instructions ............ ................................7B-71
Operation Procedure for Refrigerant Charge .... 7B-71
HVAC Unit Components ................................... 7B-72
HVAC Unit Removal and In stallation ................ 7B-73
Temperature Control Actuator Removal and Installation ....................................................... 7B-73
Temperature Control Actuat or Inspection ......... 7B-73
Air Flow Control Actuator Removal and Installation ....................................................... 7B-74
Air Flow Control Actuator Inspection ................. 7B-74
Air Intake Control Actuator Removal and Installation ....................................................... 7B-75
Air Intake Control Actuator Inspection............... 7B-75
Actuator Linkage Inspection .............................. 7B-76
Blower Motor Controller Removal and Installation ....................................................... 7B-76
Blower Motor Controller Inspection ................... 7B-76
HVAC Control Module Removal and Installation ....................................................... 7B-77
Sunload Sensor Removal and Installation ........ 7B-77
Sunload Sensor Inspection ............................... 7B-77
Outside Air Temperature Sensor Removal and Installation ................................................ 7B-77
Outside Air Temperature Sensor Inspection ..... 7B-77
Inside Air Temperature Sensor Removal and Installation ....................................................... 7B-78
Inside Air Temperature Sens or Inspection ........ 7B-78
Condenser Assembly On-Vehicle Inspection .... 7B-78
Condenser Assembly Removal and Installation ....................................................... 7B-78
Receiver/Dryer Removal and Installation .......... 7B-78
Evaporator Inspection ....................................... 7B-78
Evaporator Temperature Sensor Removal and Installation ................................................ 7B-78
Evaporator Temperature Se nsor Inspection ..... 7B-78
Expansion Valve Removal an d Installation ....... 7B-78
Expansion Valve Inspection .............................. 7B-78
A/C Refrigerant Pressure Sensor and Its Circuit Inspection............................................. 7B-78
A/C Refrigerant Pressu re Sensor Removal
and Installation ................................................ 7B-78
Compressor Relay Inspection .
.......................... 7B-78
Compressor Drive Belt Inspection and Adjustment ...................................................... 7B-78
Compressor Drive Belt Removal and Installation ....................................................... 7B-79
Compressor Assembly Removal and Installation ....................................................... 7B-79
Compressor Assembly Components................. 7B-79
Magnet Clutch Removal and Installation........... 7B-79
Magnet Clutch Inspection.................................. 7B-79
Relief Valve Inspection...................................... 7B-79
Page 983 of 1496
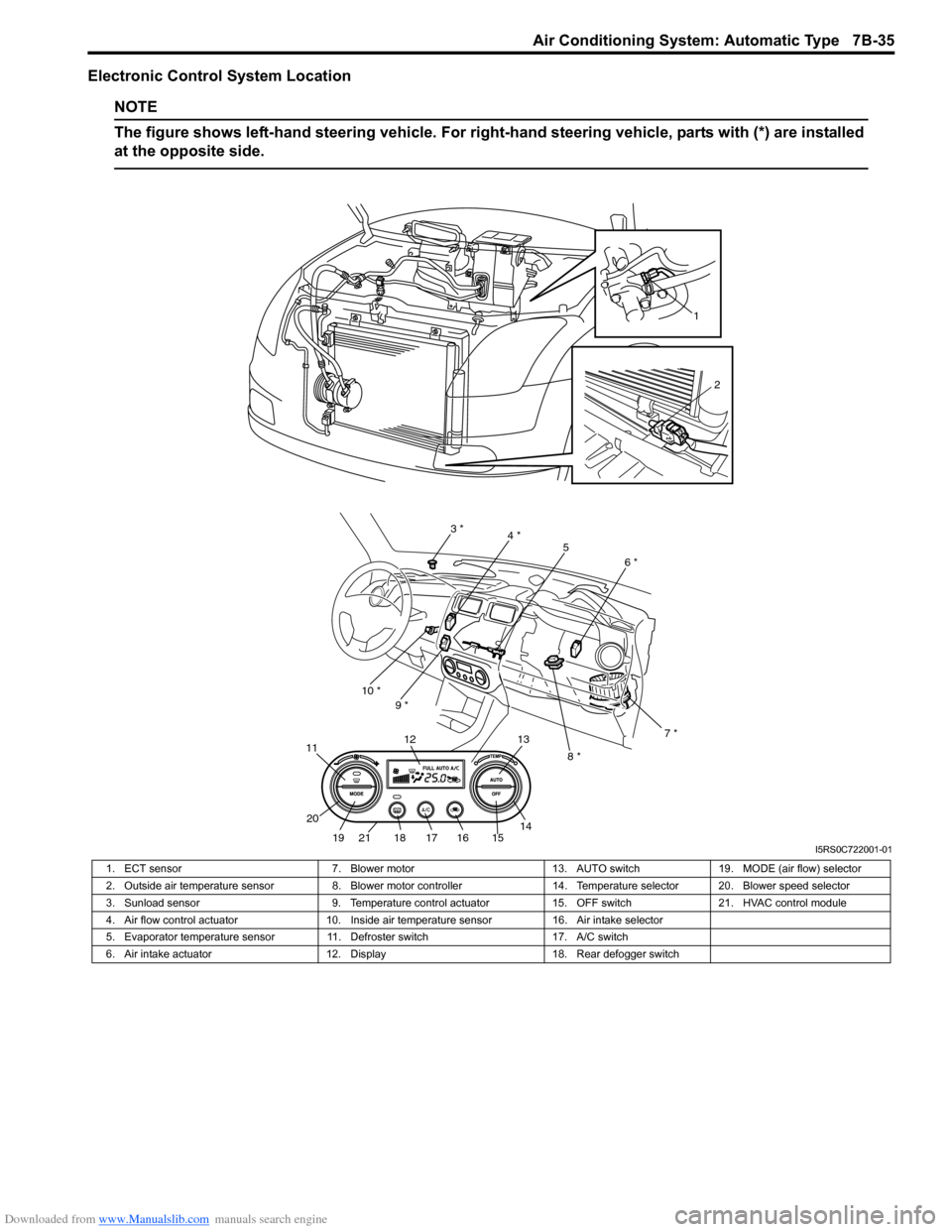
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Air Conditioning System: Automatic Type 7B-35
Electronic Control System Location
NOTE
The figure shows left-hand steering vehicle. For right-hand steering vehicle, parts with (*) are installed
at the opposite side.
1
2
3 * 4 *
5
6 *
7 *
8 *
9 *
10 *
21
11
12 13
14
15161718
19
20
I5RS0C722001-01
1. ECT sensor
7. Blower motor13. AUTO switch19. MODE (air flow) selector
2. Outside air temperature sensor 8. Blower motor controller 14. Temperature selector 20. Blower speed selector
3. Sunload sensor 9. Temperature control actuator15. OFF switch21. HVAC control module
4. Air flow control actuator 10. Inside air temperature sensor 16. Air intake selector
5. Evaporator temperature sensor 11. Defroster switch 17. A/C switch
6. Air intake actuator 12. Display 18. Rear defogger switch
Page 984 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 7B-36 Air Conditioning System: Automatic Type
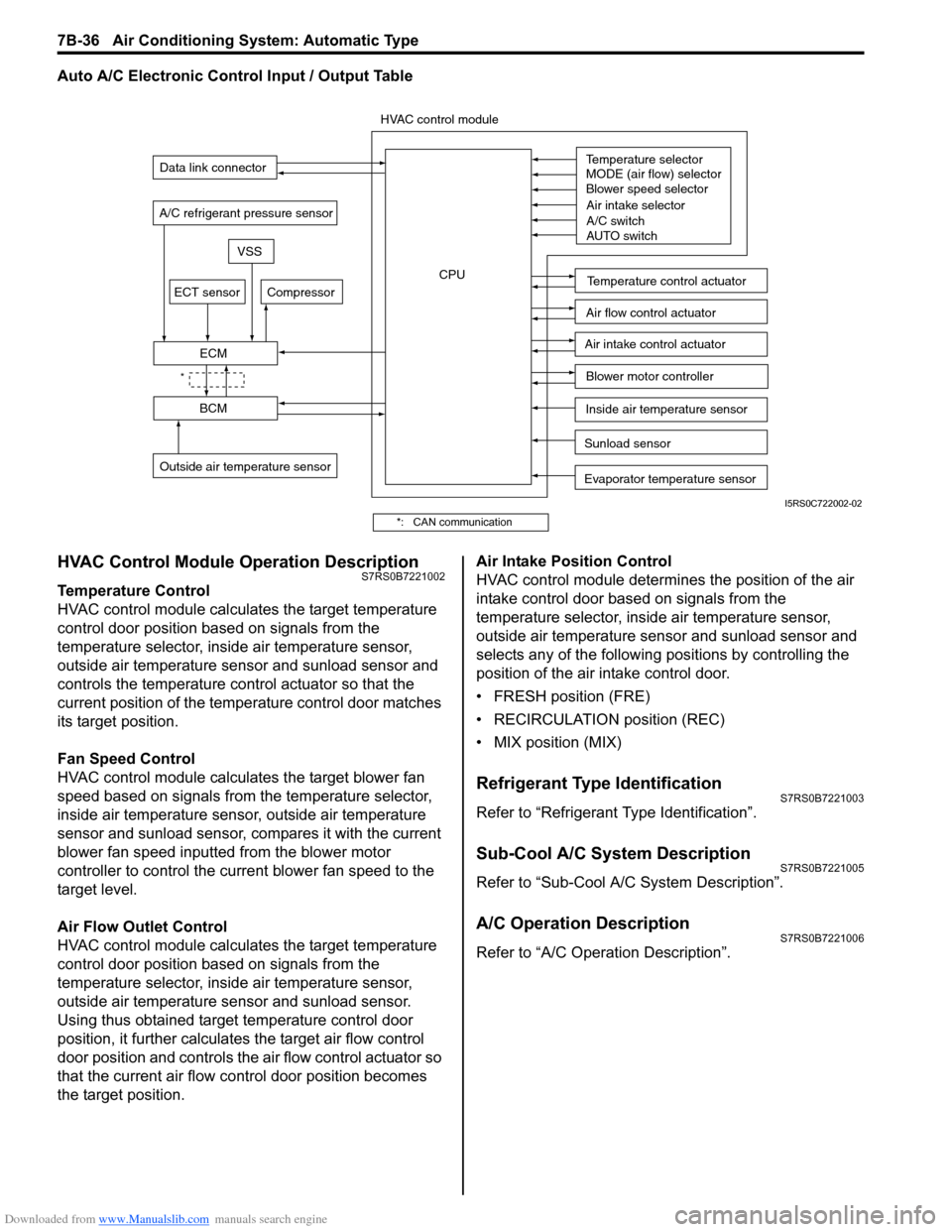
Auto A/C Electronic Control Input / Output Table
HVAC Control Module Operation DescriptionS7RS0B7221002
Temperature Control
HVAC control module calculates the target temperature
control door position based on signals from the
temperature selector, inside air temperature sensor,
outside air temperature sensor and sunload sensor and
controls the temperature control actuator so that the
current position of the temperature control door matches
its target position.
Fan Speed Control
HVAC control module calculates the target blower fan
speed based on signals from the temperature selector,
inside air temperature sensor, outside air temperature
sensor and sunload sensor, compares it with the current
blower fan speed inputted from the blower motor
controller to control the current blower fan speed to the
target level.
Air Flow Outlet Control
HVAC control module calculates the target temperature
control door position based on signals from the
temperature selector, inside air temperature sensor,
outside air temperature sensor and sunload sensor.
Using thus obtained target temperature control door
position, it further calculates the target air flow control
door position and controls the ai r flow control actuator so
that the current air flow c ontrol door position becomes
the target position. Air Intake Position Control
HVAC control module determines the position of the air
intake control door based on signals from the
temperature selector, inside air temperature sensor,
outside air temperature sensor and sunload sensor and
selects any of the following positions by controlling the
position of the air intake control door.
• FRESH position (FRE)
• RECIRCULATION position (REC)
• MIX position (MIX)
Refrigerant Type IdentificationS7RS0B7221003
Refer to “Refrigerant Type Identification”.
Sub-Cool A/C System DescriptionS7RS0B7221005
Refer to “Sub-Cool A/C System Description”.
A/C Operation DescriptionS7RS0B7221006
Refer to “A/C Operation Description”.
Sunload sensor
Outside air temperature sensor Evaporator temperature sensor
A/C refrigerant pressure sensor
Temperature selector
MODE (air flow) selector
Blower speed selector
Air intake selector
AUTO switch
A/C switch
Compressor
Blower motor controller
Temperature control actuator
Air flow control actuator
Air intake control actuator
BCM
ECM
Data link connector
HVAC control module
CPU
ECT sensor
Inside air temperature sensor
VSS
*
I5RS0C722002-02
*: CAN communication
Page 987 of 1496
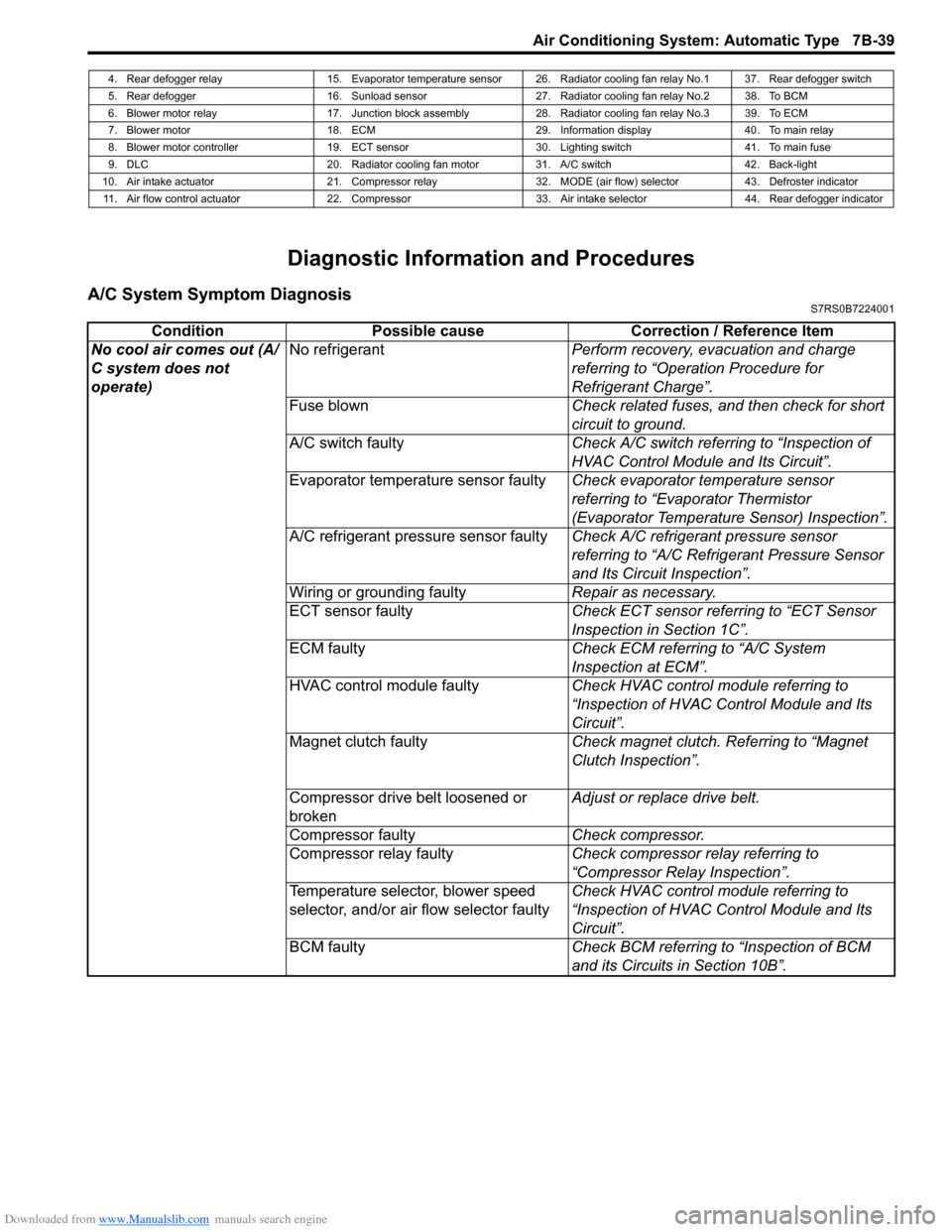
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Air Conditioning System: Automatic Type 7B-39
Diagnostic Information and Procedures
A/C System Symptom DiagnosisS7RS0B7224001
4. Rear defogger relay 15. Evaporator temperature sensor 26. Radiator cooling fan relay No.1 37. Rear defogger switch
5. Rear defogger 16. Sunload sensor 27. Radiator cooling fan relay No.2 38. To BCM
6. Blower motor relay 17. Junction block assembly 28. Radiator cooling fan relay No.3 39. To ECM
7. Blower motor 18. ECM 29. Information display 40. To main relay
8. Blower motor controller 19. ECT sensor 30. Lighting switch 41. To main fuse
9. DLC 20. Radiator cooling fan motor 31. A/C switch 42. Back-light
10. Air intake actuator 21. Compressor relay 32. MODE (air flow) selector 43. Defroster indicator 11. Air flow control actuator 22. Compressor 33. Air intake selector 44. Rear defogger indicator
Condition Possible cause Correction / Reference Item
No cool air comes out (A/
C system does not
operate) No refrigerant
Perform recovery, evacuation and charge
referring to “Operation Procedure for
Refrigerant Charge”.
Fuse blown Check related fuses, and then check for short
circuit to ground.
A/C switch faulty Check A/C switch referring to “Inspection of
HVAC Control Module and Its Circuit”.
Evaporator temperature sensor faulty Check evaporator temperature sensor
referring to “Evaporator Thermistor
(Evaporator Temperature Sensor) Inspection”.
A/C refrigerant pressure sensor faulty Check A/C refrigerant pressure sensor
referring to “A/C Refrigerant Pressure Sensor
and Its Circuit Inspection”.
Wiring or grounding faulty Repair as necessary.
ECT sensor faulty Check ECT sensor referring to “ECT Sensor
Inspection in Section 1C”.
ECM faulty Check ECM referring to “A/C System
Inspection at ECM”.
HVAC control module faulty Check HVAC control module referring to
“Inspection of HVAC Control Module and Its
Circuit”.
Magnet clutch faulty Check magnet clutch. Referring to “Magnet
Clutch Inspection”.
Compressor drive belt loosened or
broken Adjust or replace drive belt.
Compressor faulty Check compressor.
Compressor relay faulty Check compressor relay referring to
“Compressor Relay Inspection”.
Temperature selector, blower speed
selector, and/or air flow selector faulty Check HVAC control module referring to
“Inspection of HVAC Control Module and Its
Circuit”.
BCM faulty Check BCM referring to “Inspection of BCM
and its Circuits in Section 10B”.
Page 988 of 1496
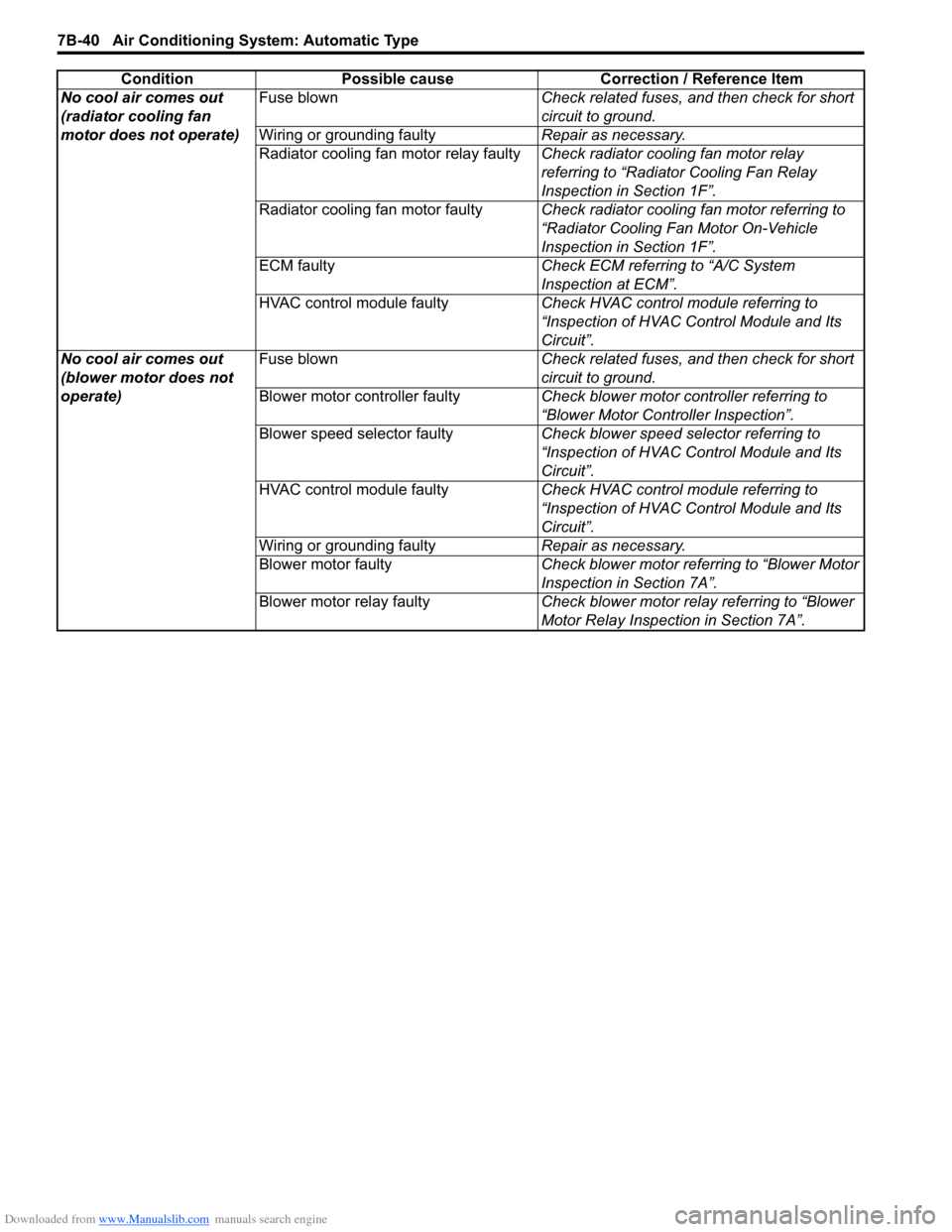
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 7B-40 Air Conditioning System: Automatic Type
No cool air comes out
(radiator cooling fan
motor does not operate)Fuse blown
Check related fuses, and then check for short
circuit to ground.
Wiring or grounding faulty Repair as necessary.
Radiator cooling fan motor relay faulty Check radiator cooling fan motor relay
referring to “Radiator Cooling Fan Relay
Inspection in Section 1F”.
Radiator cooling fan motor faulty Check radiator cooling fan motor referring to
“Radiator Cooling Fan Motor On-Vehicle
Inspection in Section 1F”.
ECM faulty Check ECM referring to “A/C System
Inspection at ECM”.
HVAC control module faulty Check HVAC control module referring to
“Inspection of HVAC Control Module and Its
Circuit”.
No cool air comes out
(blower motor does not
operate) Fuse blown
Check related fuses, and then check for short
circuit to ground.
Blower motor controller faulty Check blower motor controller referring to
“Blower Motor Controller Inspection”.
Blower speed selector faulty Check blower speed selector referring to
“Inspection of HVAC Control Module and Its
Circuit”.
HVAC control module faulty Check HVAC control module referring to
“Inspection of HVAC Control Module and Its
Circuit”.
Wiring or grounding faulty Repair as necessary.
Blower motor faulty Check blower motor referring to “Blower Motor
Inspection in Section 7A”.
Blower motor relay faulty Check blower motor relay referring to “Blower
Motor Relay Inspection in Section 7A”.
Condition Possible cause Correction / Reference Item