seat SUZUKI SX4 2006 1.G Service User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SUZUKI, Model Year: 2006, Model line: SX4, Model: SUZUKI SX4 2006 1.GPages: 1556, PDF Size: 37.31 MB
Page 76 of 1556

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1A-26 Engine General Information and Diagnosis:
• The MIL is turned on when the ECM and/or
TCM detect malfunction(s). Each ECM and
TCM stores diagnostic information as the
diagnostic trouble code (DTC) in its
memory and outputs the DTC to the scan
tool.
Therefore, check both of the ECM and TCM
for any DTC with the scan tool because the
DTC stored in ECM and TCM is not read
and displayed at a time. However, each of
the ECM and TCM needs not to be checked
with the generic scan tool because the
DTC stored in ECM and TCM is read and
displayed at a time.
1) Prepare CAN communication OBD generic scan tool
or SUZUKI scan tool.
Special tool
(A): SUZUKI scan tool (SUZUKI-SDT)
2) With ignition switch OFF, connect it to DLC (1)
located on underside of instrument panel at driver’s
seat side.
3) Turn ignition switch ON and confirm that MIL lights.
4) Read DTC and freeze frame data according to
instructions displayed on scan tool and print them or
write them down. Refer to scan tool operator’s
manual for details.
If communication between scan tool and ECM is not
possible, go to “Troubleshooting for Communication
Error with Scan Tool Using CAN”.
5) After completing the check, turn ignition switch off
and disconnect scan tool from DLC.
DTC ClearanceS6RW0D1104004
NOTE
There are two types of OBD system
depending on the vehicle specification.
For identification, refer to “Precaution on On-
Board Diagnostic (OBD) System”.
1) Connect SUZUKI scan tool or CAN communication
OBD generic scan tool to data link connector in the
same manner as when making this connection for
DTC check.2) Turn ignition switch OFF and then ON.
3) Erase DTC and pending DTC according to
instructions displayed on scan tool. Freeze frame
data is cleared with the DTC. Refer to scan tool
operator’s manual for further details.
If communication between scan tool and ECM is not
possible, go to “Troubleshooting for Communication
Error with Scan Tool Using CAN”.
4) After completing the clearance, turn ignition switch
OFF and disconnect scan tool from data link
connector.
NOTE
DTC and freeze frame data stored in ECM
memory are also cleared in the following
cases. Be careful not to clear them before
keeping their record.
• When power to ECM is cut off (by
disconnecting battery cable, removing
fuse or disconnecting ECM connectors).
• When the same malfunction (DTC) is not
detected again during 40 engine warm-up
cycles. (See “Warm-Up Cycle” of “On-
Board Diagnostic System Description”.)
Troubleshooting for Communication Error with
Scan Tool Using CAN
S6RW0D1104083
Perform this troubleshooting when it is not possible to
communicate between scan tool and ECM/TCM.
NOTE
• When performing this troubleshooting, be
sure to have full understanding of
“Precaution on CAN Troubleshooting” and
observe it.
• It may be possible that CAN system has
trouble because of fuse blown or low
battery voltage. Before troubleshooting,
check to make sure that fuse, battery
voltage and generator status are normal.
• When disconnecting each control module
connector in this troubleshooting, various
DTCs will be detected. Be sure to clear
DTCs in the following control modules
after completing this troubleshooting.
–ECM
–BCM
–TCM
– Keyless start control module
– 4WD control module
– HVAC control module (Auto A/C model)
– P/S control module
(A) 1I5RW0C110011-01
Page 95 of 1556
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine General Information and Diagnosis: 1A-45
Engine Symptom DiagnosisS6RW0D1104010
Perform troubleshooting referring to the followings when ECM has detected no DTC and no abnormality has been
found in “Visual Inspection” and “Engine Basic Inspection”.
Condition Possible cause Correction / Reference Item
Hard starting (Engine
cranks OK)Faulty spark plug“Spark Plug Inspection in Section 1H”
Leaky high-tension cord“High-Tension Cord Inspection in Section 1H”
Loose connection or disconnection of
high-tension cord(s) or lead wire(s)“High-Tension Cord Removal and Installation
in Section 1H”
Faulty ignition coil“Ignition Coil Assembly (Including Ignitor)
Inspection in Section 1H”
Dirty or clogged fuel hose or pipe“Fuel Pressure Check”
Malfunctioning fuel pump“Fuel Pressure Check”
Air drawn in through intake manifold
gasket or throttle body gasket
Faulty electric throttle body assembly“Electric Throttle Body Assembly On-Vehicle
Inspection in Section 1C”
Faulty APP sensor assembly“Accelerator Pedal Position (APP) Sensor
Assembly Inspection in Section 1C”
Faulty ECT sensor or MAF sensor“Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) Sensor
Inspection in Section 1C” or “Intake Air
Temperature (IAT) Sensor Inspection in
Section 1C”
Faulty ECM
Low compression“Compression Check in Section 1D”
Poor spark plug tightening or faulty
gasket“Spark Plug Removal and Installation in
Section 1H”
Compression leak from valve seat“Valves and Valve Guides Inspection in
Section 1D”
Sticky valve stem“Valves and Valve Guides Inspection in
Section 1D”
Weak or damaged valve springs“Valve Spring Inspection in Section 1D”
Compression leak at cylinder head
gasket“Cylinder Head Inspection in Section 1D”
Sticking or damaged piston ring“Cylinders, Pistons and Piston Rings
Inspection in Section 1D”
Worn piston, ring or cylinder“Cylinders, Pistons and Piston Rings
Inspection in Section 1D”
Malfunctioning PCV valve“PCV Valve Inspection in Section 1B”
Camshaft position control (VVT) system
out of order (for engine with VVT
system)“Oil Control Valve Inspection (For Engine with
VVT) in Section 1D”
Faulty EGR system“EGR System Inspection (If Equipped) in
Section 1B”
Low oil pressureImproper oil viscosity“Engine Oil and Filter Change in Section 0B”
Malfunctioning oil pressure switch“Oil Pressure Switch Inspection in Section 9C”
Clogged oil strainer“Oil Pan and Oil Pump Strainer Cleaning in
Section 1E”
Functional deterioration of oil pump“Oil Pump Inspection in Section 1E”
Worn oil pump relief valve“Oil Pump Inspection in Section 1E”
Excessive clearance in various sliding
parts
Page 97 of 1556
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine General Information and Diagnosis: 1A-47
Engine overheatingInoperative thermostat“Thermostat Inspection in Section 1F”
Poor water pump performance“Water Pump Inspection in Section 1F”
Clogged or leaky radiator“Radiator On-Vehicle Inspection and Cleaning
in Section 1F”
Improper engine oil grade“Engine Oil and Filter Change in Section 0B”
Clogged oil filter or oil strainer“Oil Pressure Check in Section 1E”
Poor oil pump performance“Oil Pressure Check in Section 1E”
Faulty radiator cooling fan control
system“Radiator Cooling Fan Control System Check”
Dragging brakesCondition “Dragging brakes” in “Brakes
Symptom Diagnosis in Section 4A”
Slipping clutch (for M/T model)Condition “Slipping clutch” in “Clutch System
Symptom Diagnosis in Section 5C” for M/T
model
Blown cylinder head gasket“Cylinder Head Inspection in Section 1D”
Air mixed in cooling system
Poor gasoline mileageLeaks or loose connection of high-
tension cord“High-Tension Cord Removal and Installation
in Section 1H”
Faulty spark plug (improper gap, heavy
deposits and burned electrodes, etc.)“Spark Plug Inspection in Section 1H”
Malfunctioning EGR valve“EGR Valve Inspection (If Equipped) in Section
1B”
High idle speedCondition “Improper engine idling or engine
fails to idle”
Poor performance of ECT sensor, MAF
sensor“Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) Sensor
Inspection in Section 1C”, or “Intake Air
Temperature (IAT) Sensor Inspection in
Section 1C”
Faulty electric throttle body assembly“Electric Throttle Body Assembly On-Vehicle
Inspection in Section 1C”
Faulty APP sensor assembly“Accelerator Pedal Position (APP) Sensor
Assembly Inspection in Section 1C”
Faulty fuel injector(s)“Fuel Injector Circuit Check”
Faulty ECM
Low compression“Compression Check in Section 1D”
Poor valve seating“Valves and Valve Guides Inspection in
Section 1D”
Dragging brakesCondition “Dragging brakes” in “Brakes
Symptom Diagnosis in Section 4A”
Slipping clutch (for M/T model)Condition “Slipping clutch” in “Clutch System
Symptom Diagnosis in Section 5C” for M/T
model
Thermostat out of order“Thermostat Inspection in Section 1F”
Improper tire pressure“Tires Description in Section 2D”
Camshaft position control (VVT) system
out of order (for engine with VVT
system)“Oil Control Valve Inspection (For Engine with
VVT) in Section 1D”
Excessive engine oil
consumption – Oil
leakageBlown cylinder head gasket“Cylinder Head Inspection in Section 1D”
Leaky camshaft oil seals“Camshaft, Tappet and Shim Inspection in
Section 1D” Condition Possible cause Correction / Reference Item
Page 267 of 1556
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Aux. Emission Control Devices: 1B-4
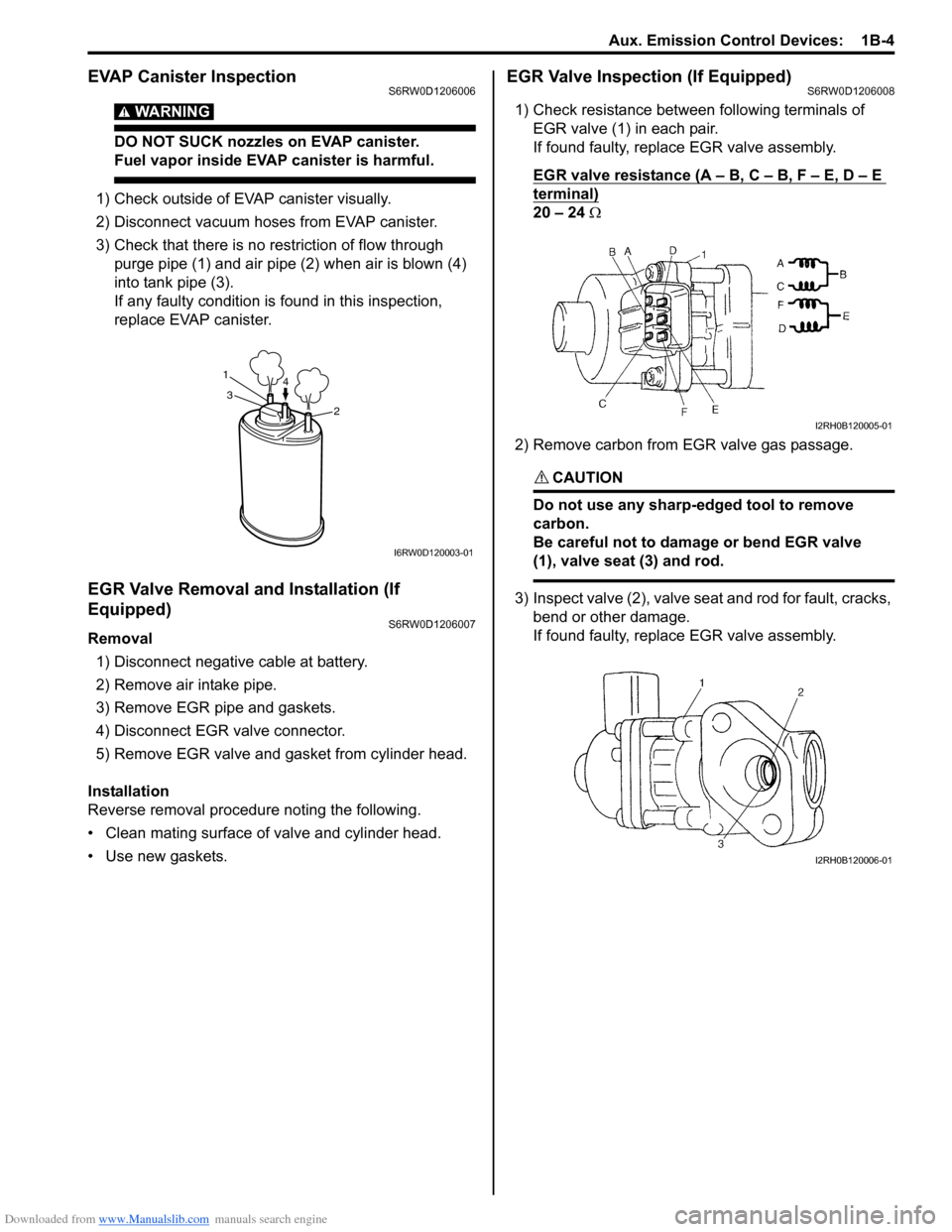
EVAP Canister InspectionS6RW0D1206006
WARNING!
DO NOT SUCK nozzles on EVAP canister.
Fuel vapor inside EVAP canister is harmful.
1) Check outside of EVAP canister visually.
2) Disconnect vacuum hoses from EVAP canister.
3) Check that there is no restriction of flow through
purge pipe (1) and air pipe (2) when air is blown (4)
into tank pipe (3).
If any faulty condition is found in this inspection,
replace EVAP canister.
EGR Valve Removal and Installation (If
Equipped)
S6RW0D1206007
Removal
1) Disconnect negative cable at battery.
2) Remove air intake pipe.
3) Remove EGR pipe and gaskets.
4) Disconnect EGR valve connector.
5) Remove EGR valve and gasket from cylinder head.
Installation
Reverse removal procedure noting the following.
• Clean mating surface of valve and cylinder head.
• Use new gaskets.
EGR Valve Inspection (If Equipped)S6RW0D1206008
1) Check resistance between following terminals of
EGR valve (1) in each pair.
If found faulty, replace EGR valve assembly.
EGR valve resistance (A – B, C – B, F – E, D – E
terminal)
20 – 24 Ω
2) Remove carbon from EGR valve gas passage.
CAUTION!
Do not use any sharp-edged tool to remove
carbon.
Be careful not to damage or bend EGR valve
(1), valve seat (3) and rod.
3) Inspect valve (2), valve seat and rod for fault, cracks,
bend or other damage.
If found faulty, replace EGR valve assembly.
4
3 1
2
I6RW0D120003-01
I2RH0B120005-01
I2RH0B120006-01
Page 321 of 1556
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine Mechanical: 1D-39
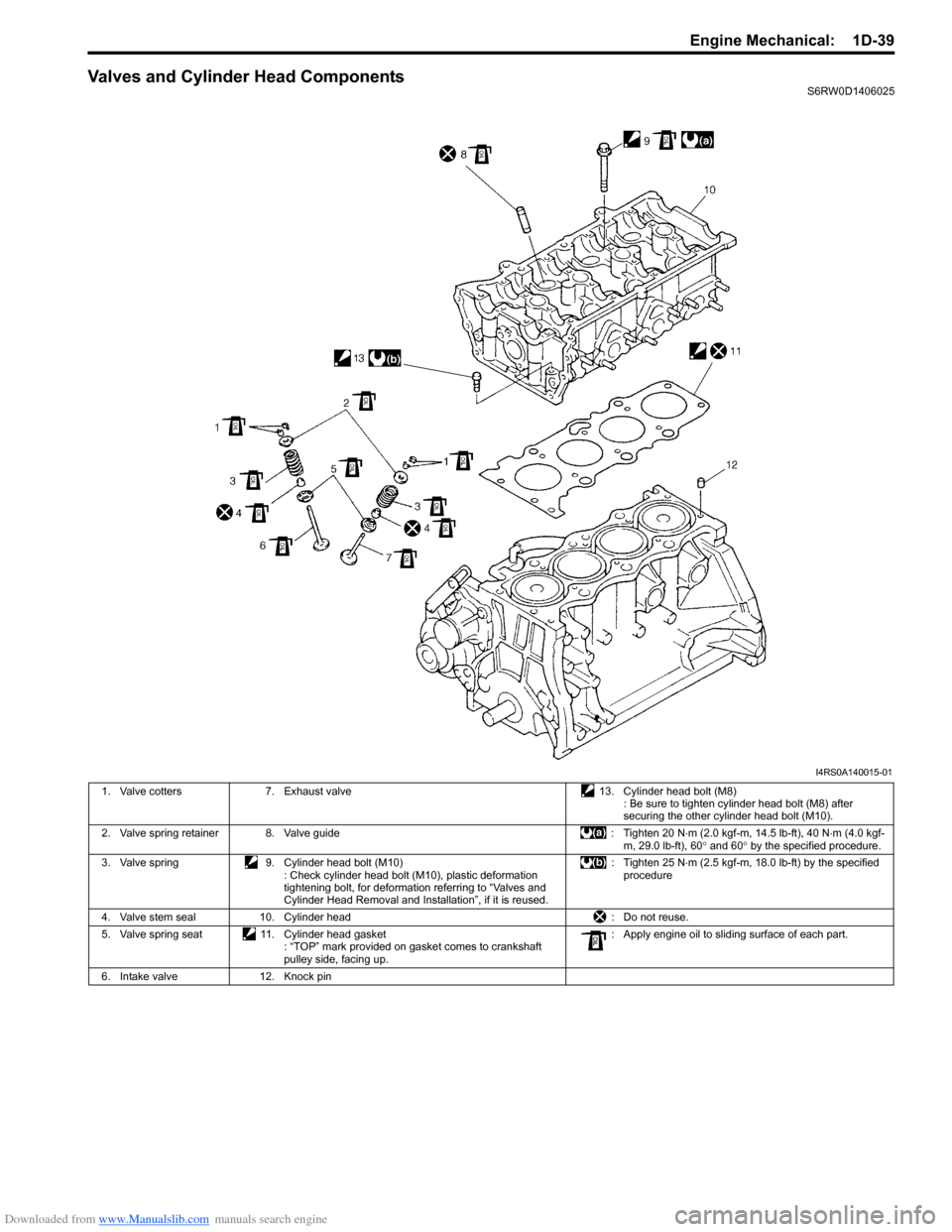
Valves and Cylinder Head ComponentsS6RW0D1406025
I4RS0A140015-01
1. Valve cotters 7. Exhaust valve 13. Cylinder head bolt (M8)
: Be sure to tighten cylinder head bolt (M8) after
securing the other cylinder head bolt (M10).
2. Valve spring retainer 8. Valve guide : Tighten 20 N⋅m (2.0 kgf-m, 14.5 lb-ft), 40 N⋅m (4.0 kgf-
m, 29.0 lb-ft), 60° and 60° by the specified procedure.
3. Valve spring 9. Cylinder head bolt (M10)
: Check cylinder head bolt (M10), plastic deformation
tightening bolt, for deformation referring to “Valves and
Cylinder Head Removal and Installation”, if it is reused.: Tighten 25 N⋅m (2.5 kgf-m, 18.0 lb-ft) by the specified
procedure
4. Valve stem seal 10. Cylinder head : Do not reuse.
5. Valve spring seat 11. Cylinder head gasket
: “TOP” mark provided on gasket comes to crankshaft
pulley side, facing up.: Apply engine oil to sliding surface of each part.
6. Intake valve 12. Knock pin
Page 323 of 1556
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine Mechanical: 1D-41
5) Install cylinder head to cylinder block.
Apply engine oil to new cylinder head bolts and
tighten them gradually as follows.
a) Tighten cylinder head bolts (“1” – “10”) to 20 N⋅m
(2.0 kgf-m, 14.5 lb-ft) according to numerical
order as shown by using a 12 corner socket
wrenches.
b) In the same manner as in Step a), tighten them
to 40 N⋅m (4.0 kgf-m, 29.0 lb-ft).
c) Turn all bolts 60° according to numerical order in
figure.
d) Repeat Step c).
e) Tighten cylinder head bolt (M8) (1) to specified
torque.
NOTE
Be sure to tighten M8 bolt (1) after securing
the other bolts.
Tightening torque
Cylinder head bolt for M8 (a): Tighten 25 N⋅m
(2.5 kgf-m, 18.0 lb-ft) by the specified
procedure
Cylinder head bolt for M10 (b): Tighten 20
N⋅m (2.0 kgf-m, 14.5 lb-ft), 40 N⋅m (4.0 kgf-m,
29.0 lb-ft), 60° and 60° by the specified
procedure
NOTE
• If cylinder head bolts (M10) are reused,
check thread diameters of cylinder head
bolt (1) for deformation according to the
follows and replace them with new ones if
thread diameter difference exceeds limit.
• Measure each thread diameter of cylinder
head bolt (1) at “A” on 83.5 mm (2.81 in.)
from seat side of flange bolt and “B” on
115 mm (4.53 in.) from seat side of flange
bolt by using a micrometer (2).
Then calculate difference in diameters (“A”
– “B”). If it exceeds limit, replace with new
one.
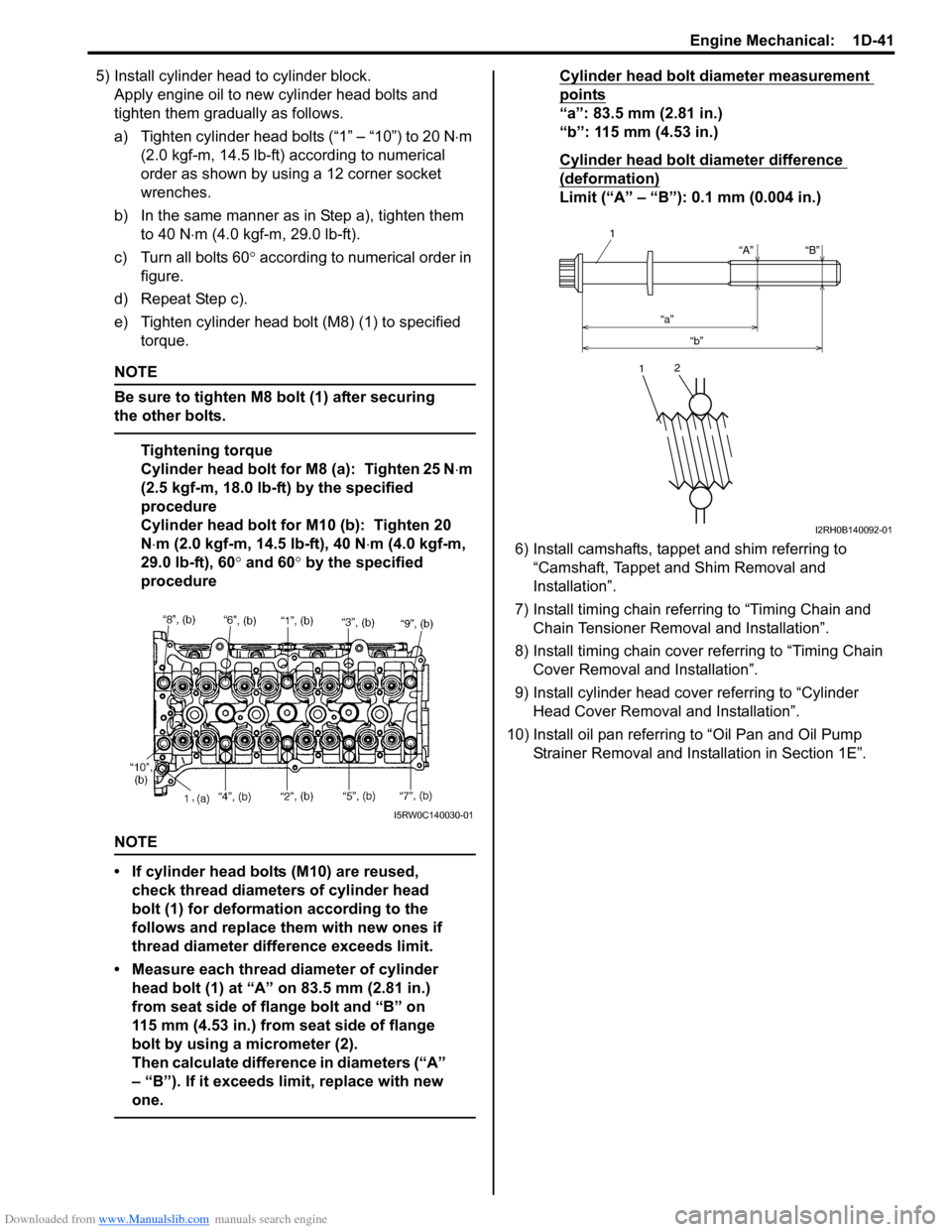
Cylinder head bolt diameter measurement
points
“a”: 83.5 mm (2.81 in.)
“b”: 115 mm (4.53 in.)
Cylinder head bolt diameter difference
(deformation)
Limit (“A” – “B”): 0.1 mm (0.004 in.)
6) Install camshafts, tappet and shim referring to
“Camshaft, Tappet and Shim Removal and
Installation”.
7) Install timing chain referring to “Timing Chain and
Chain Tensioner Removal and Installation”.
8) Install timing chain cover referring to “Timing Chain
Cover Removal and Installation”.
9) Install cylinder head cover referring to “Cylinder
Head Cover Removal and Installation”.
10) Install oil pan referring to “Oil Pan and Oil Pump
Strainer Removal and Installation in Section 1E”.
I5RW0C140030-01
“A”
“a”
“b”“B”
1
12
I2RH0B140092-01
Page 324 of 1556
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1D-42 Engine Mechanical:
Valves and Cylinder Head Disassembly and
Assembly
S6RW0D1406027
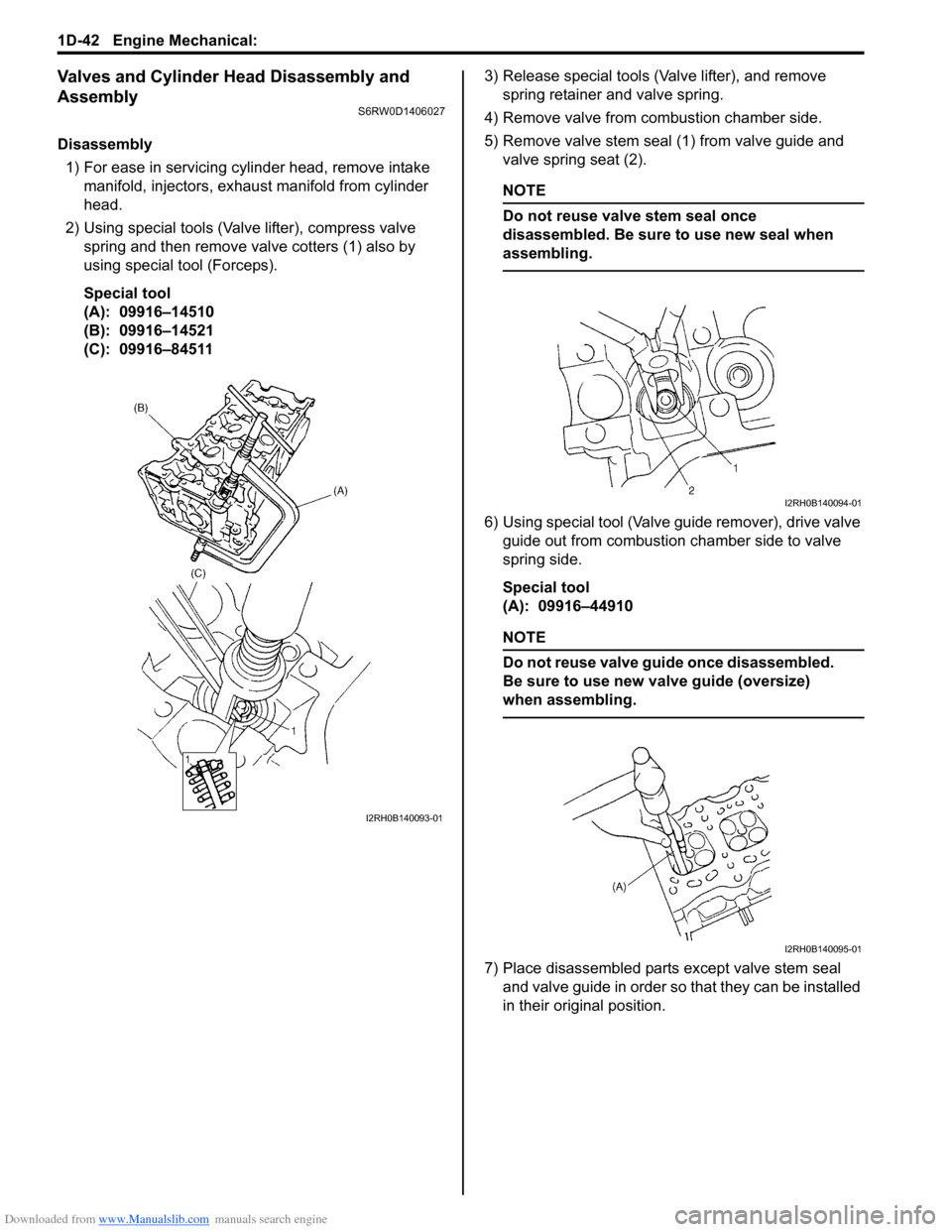
Disassembly
1) For ease in servicing cylinder head, remove intake
manifold, injectors, exhaust manifold from cylinder
head.
2) Using special tools (Valve lifter), compress valve
spring and then remove valve cotters (1) also by
using special tool (Forceps).
Special tool
(A): 09916–14510
(B): 09916–14521
(C): 09916–845113) Release special tools (Valve lifter), and remove
spring retainer and valve spring.
4) Remove valve from combustion chamber side.
5) Remove valve stem seal (1) from valve guide and
valve spring seat (2).
NOTE
Do not reuse valve stem seal once
disassembled. Be sure to use new seal when
assembling.
6) Using special tool (Valve guide remover), drive valve
guide out from combustion chamber side to valve
spring side.
Special tool
(A): 09916–44910
NOTE
Do not reuse valve guide once disassembled.
Be sure to use new valve guide (oversize)
when assembling.
7) Place disassembled parts except valve stem seal
and valve guide in order so that they can be installed
in their original position.
I2RH0B140093-01
I2RH0B140094-01
I2RH0B140095-01
Page 325 of 1556
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine Mechanical: 1D-43
Assembly
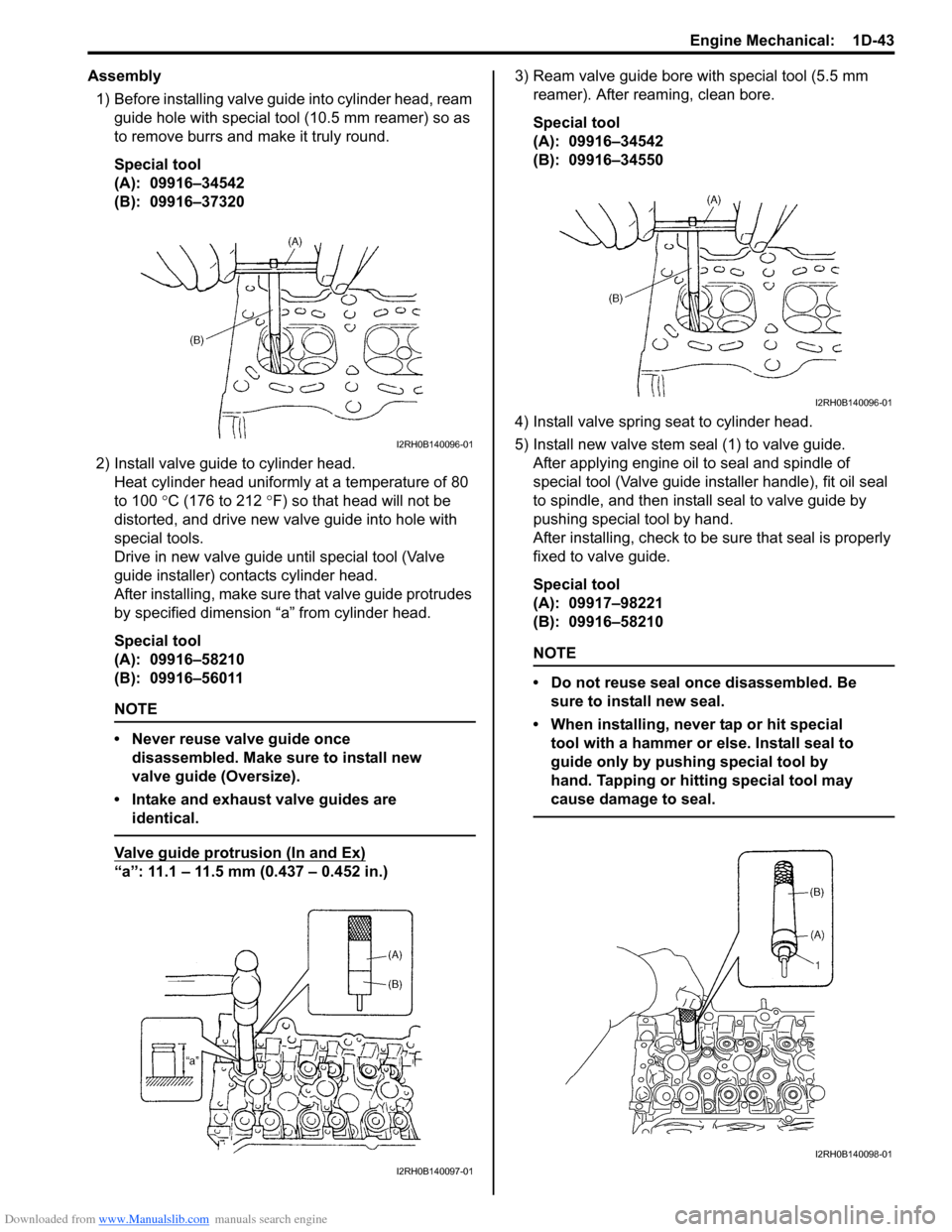
1) Before installing valve guide into cylinder head, ream
guide hole with special tool (10.5 mm reamer) so as
to remove burrs and make it truly round.
Special tool
(A): 09916–34542
(B): 09916–37320
2) Install valve guide to cylinder head.
Heat cylinder head uniformly at a temperature of 80
to 100 °C (176 to 212 °F) so that head will not be
distorted, and drive new valve guide into hole with
special tools.
Drive in new valve guide until special tool (Valve
guide installer) contacts cylinder head.
After installing, make sure that valve guide protrudes
by specified dimension “a” from cylinder head.
Special tool
(A): 09916–58210
(B): 09916–56011
NOTE
• Never reuse valve guide once
disassembled. Make sure to install new
valve guide (Oversize).
• Intake and exhaust valve guides are
identical.
Valve guide protrusion (In and Ex)
“a”: 11.1 – 11.5 mm (0.437 – 0.452 in.)3) Ream valve guide bore with special tool (5.5 mm
reamer). After reaming, clean bore.
Special tool
(A): 09916–34542
(B): 09916–34550
4) Install valve spring seat to cylinder head.
5) Install new valve stem seal (1) to valve guide.
After applying engine oil to seal and spindle of
special tool (Valve guide installer handle), fit oil seal
to spindle, and then install seal to valve guide by
pushing special tool by hand.
After installing, check to be sure that seal is properly
fixed to valve guide.
Special tool
(A): 09917–98221
(B): 09916–58210
NOTE
• Do not reuse seal once disassembled. Be
sure to install new seal.
• When installing, never tap or hit special
tool with a hammer or else. Install seal to
guide only by pushing special tool by
hand. Tapping or hitting special tool may
cause damage to seal.
I2RH0B140096-01
I2RH0B140097-01
I2RH0B140096-01
I2RH0B140098-01
Page 326 of 1556
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1D-44 Engine Mechanical:
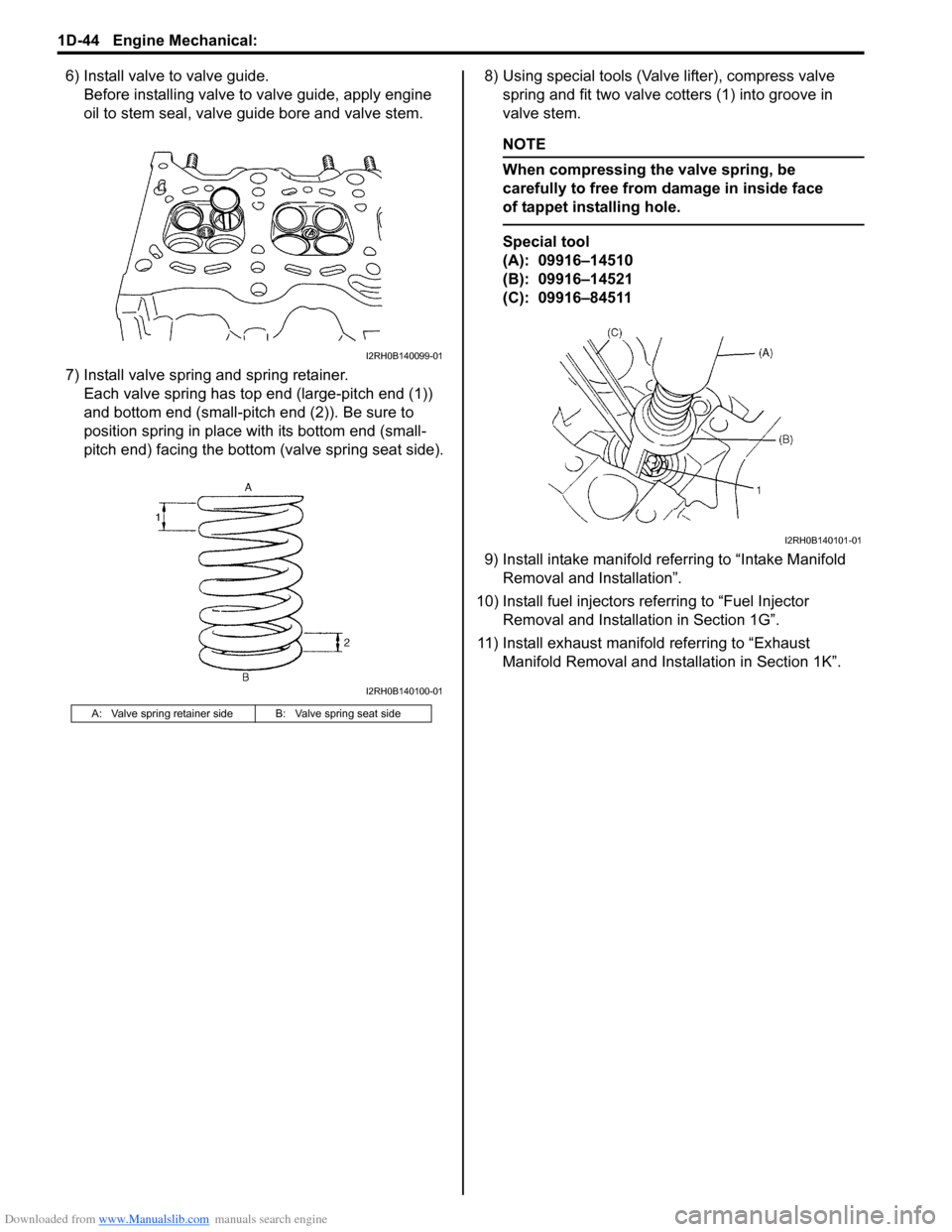
6) Install valve to valve guide.
Before installing valve to valve guide, apply engine
oil to stem seal, valve guide bore and valve stem.
7) Install valve spring and spring retainer.
Each valve spring has top end (large-pitch end (1))
and bottom end (small-pitch end (2)). Be sure to
position spring in place with its bottom end (small-
pitch end) facing the bottom (valve spring seat side).8) Using special tools (Valve lifter), compress valve
spring and fit two valve cotters (1) into groove in
valve stem.
NOTE
When compressing the valve spring, be
carefully to free from damage in inside face
of tappet installing hole.
Special tool
(A): 09916–14510
(B): 09916–14521
(C): 09916–84511
9) Install intake manifold referring to “Intake Manifold
Removal and Installation”.
10) Install fuel injectors referring to “Fuel Injector
Removal and Installation in Section 1G”.
11) Install exhaust manifold referring to “Exhaust
Manifold Removal and Installation in Section 1K”.
A: Valve spring retainer side B: Valve spring seat side
I2RH0B140099-01
I2RH0B140100-01
I2RH0B140101-01
Page 328 of 1556
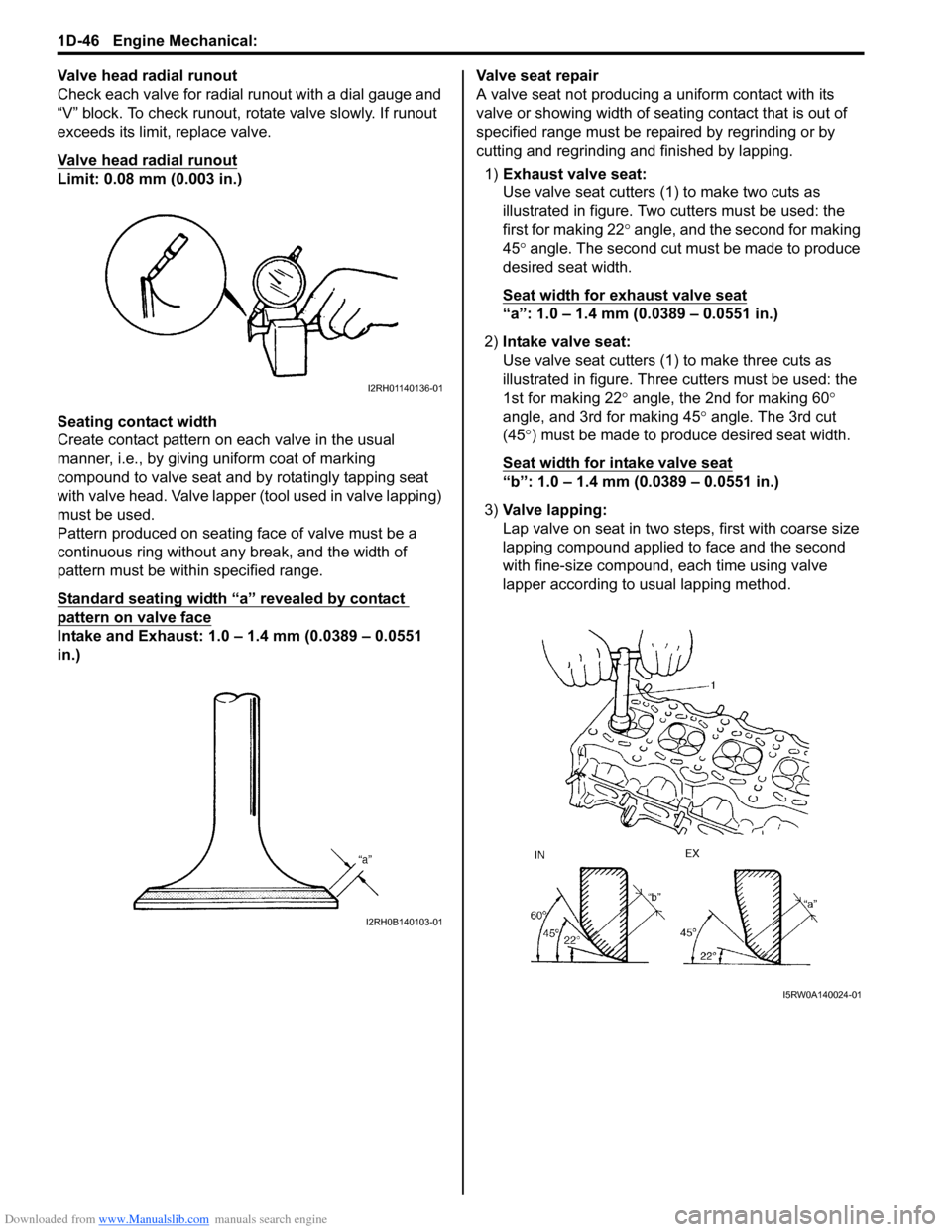
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1D-46 Engine Mechanical:
Valve head radial runout
Check each valve for radial runout with a dial gauge and
“V” block. To check runout, rotate valve slowly. If runout
exceeds its limit, replace valve.
Valve head radial runout
Limit: 0.08 mm (0.003 in.)
Seating contact width
Create contact pattern on each valve in the usual
manner, i.e., by giving uniform coat of marking
compound to valve seat and by rotatingly tapping seat
with valve head. Valve lapper (tool used in valve lapping)
must be used.
Pattern produced on seating face of valve must be a
continuous ring without any break, and the width of
pattern must be within specified range.
Standard seating width “a” revealed by contact
pattern on valve face
Intake and Exhaust: 1.0 – 1.4 mm (0.0389 – 0.0551
in.)Valve seat repair
A valve seat not producing a uniform contact with its
valve or showing width of seating contact that is out of
specified range must be repaired by regrinding or by
cutting and regrinding and finished by lapping.
1)Exhaust valve seat:
Use valve seat cutters (1) to make two cuts as
illustrated in figure. Two cutters must be used: the
first for making 22° angle, and the second for making
45° angle. The second cut must be made to produce
desired seat width.
Seat width for exhaust valve seat
“a”: 1.0 – 1.4 mm (0.0389 – 0.0551 in.)
2)Intake valve seat:
Use valve seat cutters (1) to make three cuts as
illustrated in figure. Three cutters must be used: the
1st for making 22° angle, the 2nd for making 60°
angle, and 3rd for making 45° angle. The 3rd cut
(45°) must be made to produce desired seat width.
Seat width for intake valve seat
“b”: 1.0 – 1.4 mm (0.0389 – 0.0551 in.)
3)Valve lapping:
Lap valve on seat in two steps, first with coarse size
lapping compound applied to face and the second
with fine-size compound, each time using valve
lapper according to usual lapping method.
I2RH01140136-01
I2RH0B140103-01
I5RW0A140024-01