transmission TOYOTA CAMRY 1999 Service Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: TOYOTA, Model Year: 1999, Model line: CAMRY, Model: TOYOTA CAMRY 1999Pages: 4592, PDF Size: 55.16 MB
Page 3954 of 4592
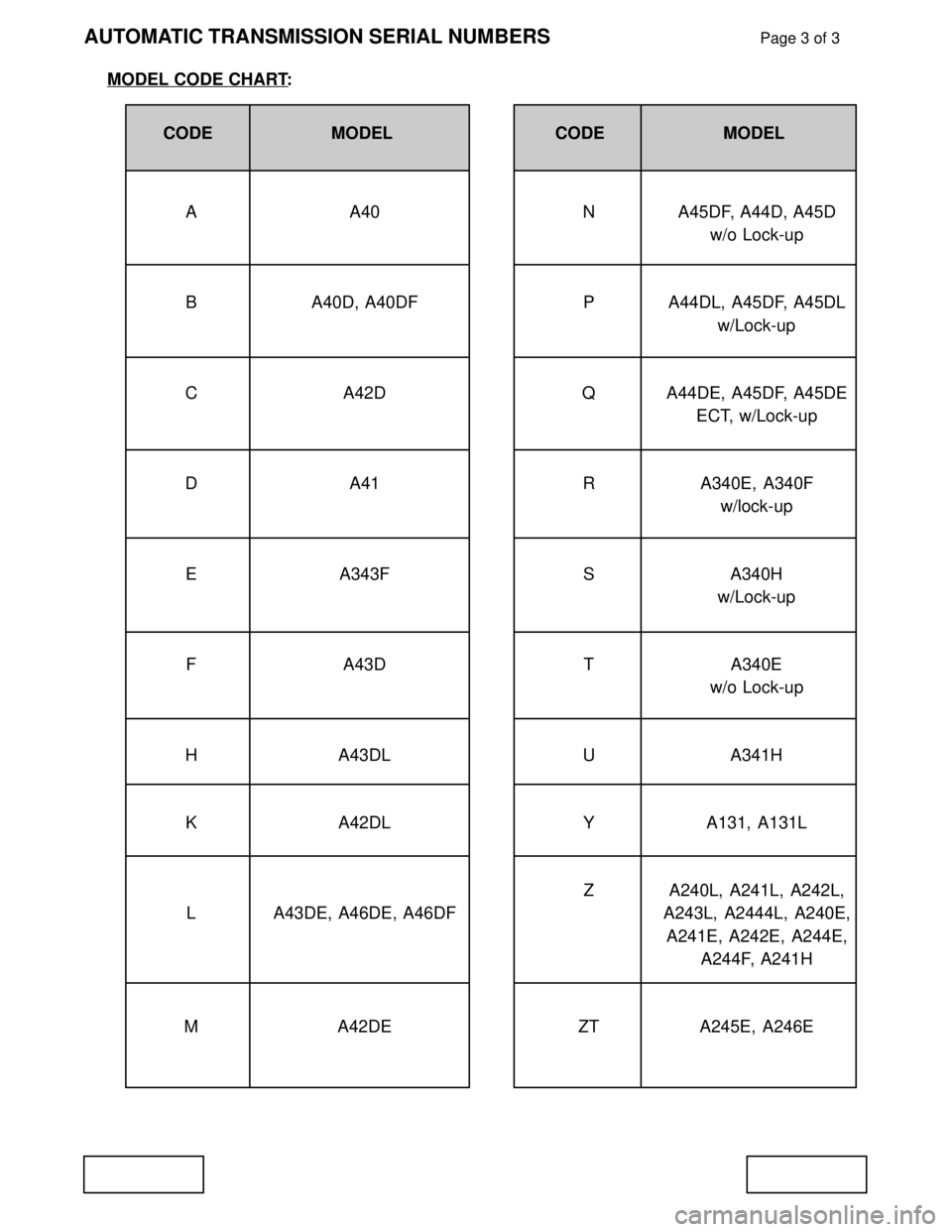
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION SERIAL NUMBERSPage 3 of 3
MODEL CODE CHART:
CODE MODEL CODE MODEL
A A40 N A45DF, A44D, A45D
w/o Lock-up
B A40D, A40DF P A44DL, A45DF, A45DL
w/Lock-up
C A42D Q A44DE, A45DF, A45DE
ECT, w/Lock-up
D A41 R A340E, A340F
w/lock-up
E A343F S A340H
w/Lock-up
F A43D T A340E
w/o Lock-up
H A43DL U A341H
K A42DL Y A131, A131L
Z A240L, A241L, A242L,
L A43DE, A46DE, A46DF A243L, A2444L, A240E,
A241E, A242E, A244E,
A244F, A241H
M A42DE ZT A245E, A246E
Page 3955 of 4592

TC008±89 TECHNICAL ASSURANCE DEPARTMENT
TOYOTA
SERVICE BULLETIN
TOYOTA MOTOR SALES, U.S.A., INC.VOLUME
10
REFERENCE
NUMBER
DATE
MODEL
TRANSMISSION &
CLUTCH
008 (REVISED)
03±22±02
Page 1 of 2
A/TM NUMBER AND LOCATION INFORMATION
The purpose of this Service Bulletin is to provide information regarding the location of the A/TM
numbers.
NOTE:
The transmission numbers must be included on the AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION CORE
INFORMATION/CREDIT REQUEST FORM when using the automatic transmission reman.
program.
AE, ST, SV, VV
(A131L) BR12E or BR18E
(A140E) BG, EG, CG, FG, DG
(A540e) ZF, GF19C
Page 4018 of 4592
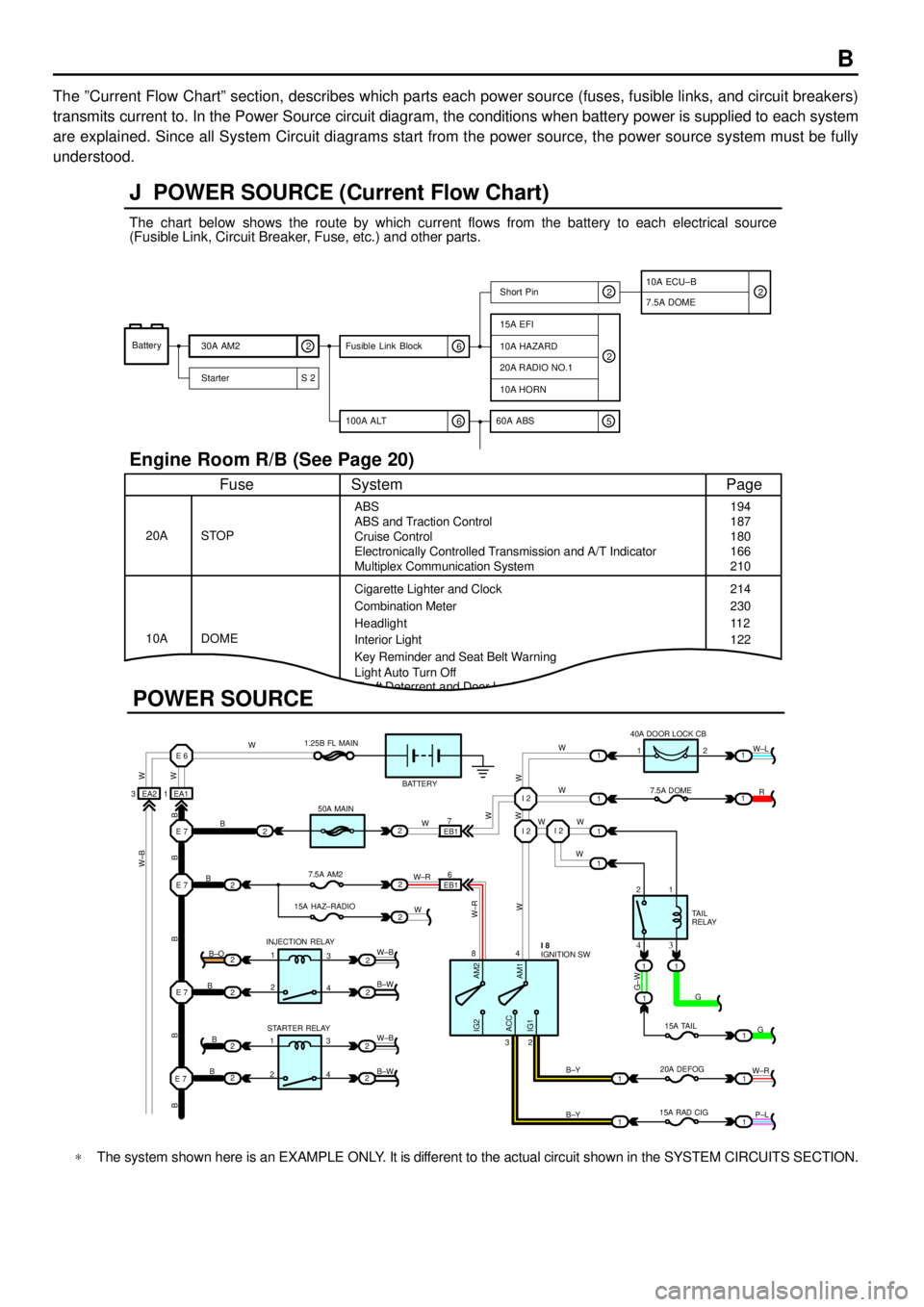
B
The ºCurrent Flow Chartº section, describes which parts each power source (fuses, fusible links, and circuit breakers)
transmits current to. In the Power Source circuit diagram, the conditions when battery power is supplied to each system
are explained. Since all System Circuit diagrams start from the power source, the power source system must be fully
understood.
Theft Deterrent and Door Lock Control
J POWER SOURCE (Current Flow Chart)
11
1
EA1 1EA2 3
7
EB16
E 6
E 7I 2I 2
I 2
E 7
E 7
E 7
2
1
1
2
2
2
2
2
B
B
W W
B B B B BW±B
B
B
B B±O
B±W
W±B
B±W STARTER RELAY INJECTION RELAY15A HAZ±RADIO7.5A AM250A MAIN 1.25B FL MAIN
BATTERY
WWW
W W W
R W±L
W
W
G±W
G
15A TAIL
20A DEFOG
15A RAD CIGTA I L
RELAY 7.5A DOME 40A DOOR LOCK CB
2 1
1 2
4 8
2 3
3 4
G
W±R
P±L B±Y
B±Y
W±R
AM2 IG2
ACC
IG1AM1W W
W±R
W W
W±B
21
1
1
1
1
2
2
2
2
3
4
3
4 1
2
1
22
1
11
1
IGNITION SW I 8
Battery
30A AM2
2
Starter S 220A RADIO NO.1
10A HORN
15A EFI
7.5A DOMEShort Pin
10A HAZARD
The chart below shows the route by which current flows from the battery to each electrical source
(Fusible Link, Circuit Breaker, Fuse, etc.) and other parts.
Engine Room R/B (See Page 20)
ABS
ABS and Traction Control
Cruise Control
Electronically Controlled Transmission and A/T Indicator
Multiplex Communication System
Cigarette Lighter and Clock
Key Reminder and Seat Belt Warning STOP
Fuse Page
194
214
11 2
System
DOME 20A
10ACombination Meter
Headlight
Interior Light
2
2
6 100A ALT
EB1
POWER SOURCE
Light Auto Turn Off187
180
166
210
230
122
10A ECU±B
5 60A ABS
2
6 Fusible Link Block2
*The system shown here is an EXAMPLE ONLY. It is different to the actual circuit shown in the SYSTEM CIRCUITS SECTION.
Page 4037 of 4592
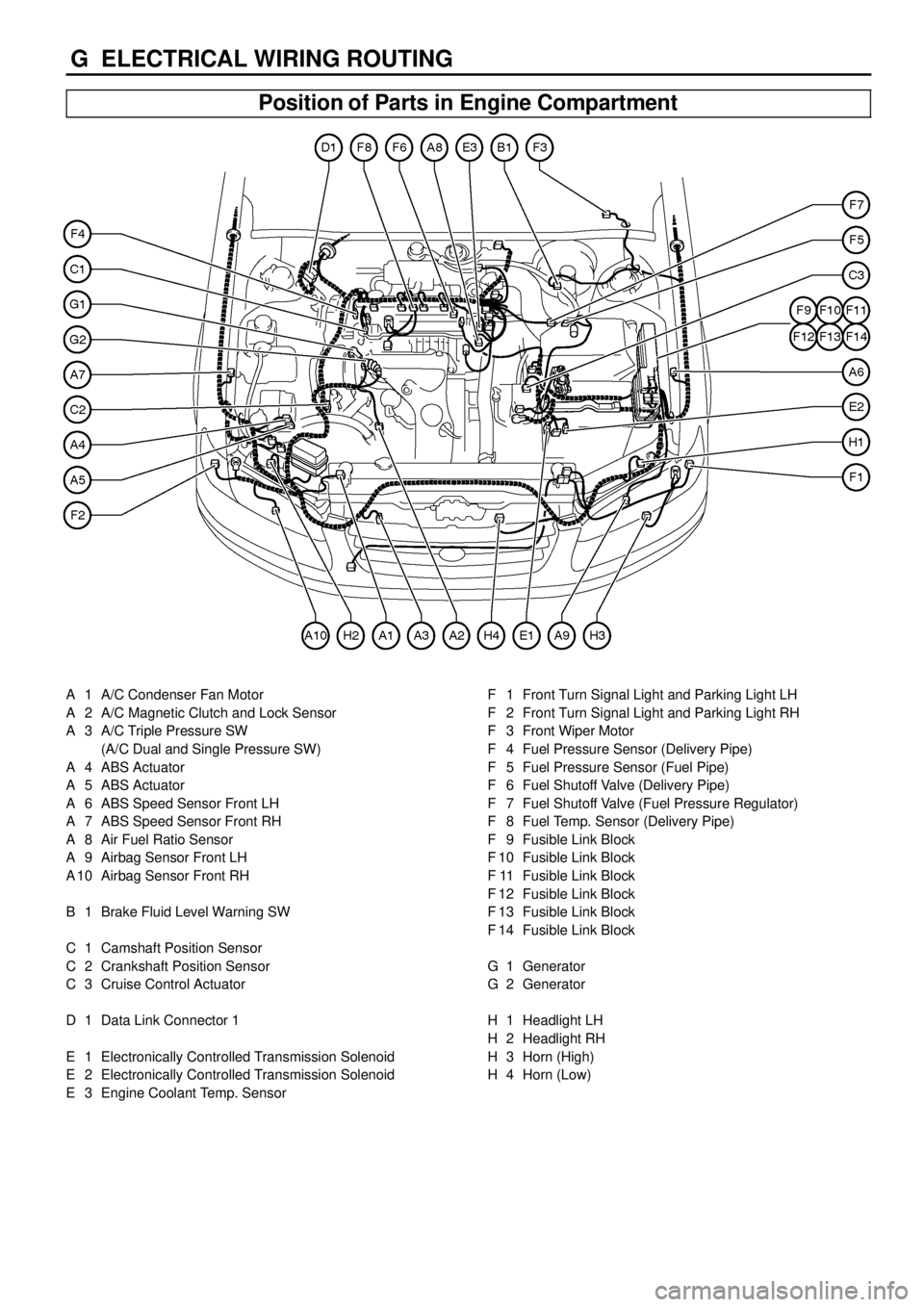
G ELECTRICAL WIRING ROUTING
Position of Parts in Engine Compartment
A 1 A/C Condenser Fan Motor
A 2 A/C Magnetic Clutch and Lock Sensor
A 3 A/C Triple Pressure SW
(A/C Dual and Single Pressure SW)
A 4 ABS Actuator
A 5 ABS Actuator
A 6 ABS Speed Sensor Front LH
A 7 ABS Speed Sensor Front RH
A 8 Air Fuel Ratio Sensor
A 9 Airbag Sensor Front LH
A 10 Airbag Sensor Front RH
B 1 Brake Fluid Level Warning SW
C 1 Camshaft Position Sensor
C 2 Crankshaft Position Sensor
C 3 Cruise Control Actuator
D 1 Data Link Connector 1
E 1 Electronically Controlled Transmission Solenoid
E 2 Electronically Controlled Transmission Solenoid
E 3 Engine Coolant Temp. SensorF 1 Front Turn Signal Light and Parking Light LH
F 2 Front Turn Signal Light and Parking Light RH
F 3 Front Wiper Motor
F 4 Fuel Pressure Sensor (Delivery Pipe)
F 5 Fuel Pressure Sensor (Fuel Pipe)
F 6 Fuel Shutoff Valve (Delivery Pipe)
F 7 Fuel Shutoff Valve (Fuel Pressure Regulator)
F 8 Fuel Temp. Sensor (Delivery Pipe)
F 9 Fusible Link Block
F 10 Fusible Link Block
F 11 Fusible Link Block
F 12 Fusible Link Block
F 13 Fusible Link Block
F 14 Fusible Link Block
G 1 Generator
G 2 Generator
H 1 Headlight LH
H 2 Headlight RH
H 3 Horn (High)
H 4 Horn (Low)
Page 4068 of 4592

This system utilizes an engine control module and maintains overall control of the engine, transmission and so on. An outline
of the engine control is explained here.
1. INPUT SIGNALS
(1) Engine coolant temp. signal circuit
The engine coolant temp. sensor detects the engine coolant temp. and has a built±in thermistor with a resistance which
varies according to the engine coolant temp. thus the engine coolant temp. is input in the form of a control signal into
TERMINAL THW of the engine control module.
(2) Intake air temp. signal circuit
The intake air temp. sensor detects the intake air temp. , which is input as a control signal into TERMINAL THA of the
engine control module.
(3) Oxygen sensor signal circuit
The oxygen density in the exhaust gases is detected and input as a control signal into TERMINAL OX2 of the engine
control module.
(4) RPM signal circuit
Camshaft position and crankshaft position are detected by the camshaft position sensor and crankshaft position sensor.
Camshaft position is input as a control signal to TERMINAL G of the engine control module, and engine RPM is input
into TERMINAL NE.
(5) Throttle signal circuit
The throttle position sensor detects the throttle valve opening angle, which is input as a control signal into TERMINAL
VTA of the engine control module.
(6) Vehicle speed signal circuit
The vehicle speed sensor, installed inside the transmission, detects the vehicle speed and inputs a control signal into
TERMINAL SPD of the engine control module.
(7) Park/Neutral position SW signal circuit
The Park/Neutral position SW detects whether the shift position are in neutral, parking or not, and inputs a control signal
into TERMINAL STA of the engine control module.
(8) A/C SW signal circuit
The A/C amplifier is built in the engine control module. The signal from the A/C SW is input into TERMINAL A/CS of the
engine control module.
(9) Battery signal circuit
Voltage is constantly applied to TERMINAL BATT of the engine control module. When the ignition SW is turned on, the
voltage for engine control module start±up power supply is applied to TERMINAL +B of engine control module via EFI
relay.
(10) Intake air volume signal circuit
Intake air volume is detected by the manifold absolute pressure sensor (for manifold pressure) and is input as a control
signal into TERMINAL PIM of the engine control module.
(11) Starter signal circuit
To confirm whether the engine is cranking, the voltage applied to the starter motor during cranking is detected and the
signal is input into TERMINAL NSW of the engine control module as a control signal.
(12) Electrical load signal circuit
The signal when systems such as the rear window defogger, headlights, etc. Which cause a high electrical burden are
on is input to TERMINAL ELS as a control signal.
(13) Air fuel ratio signal circuit
The air fuel ratio is detected and input as a control signal into TERMINAL AF+ of the engine control module.
SYSTEM OUTLINE
Page 4109 of 4592
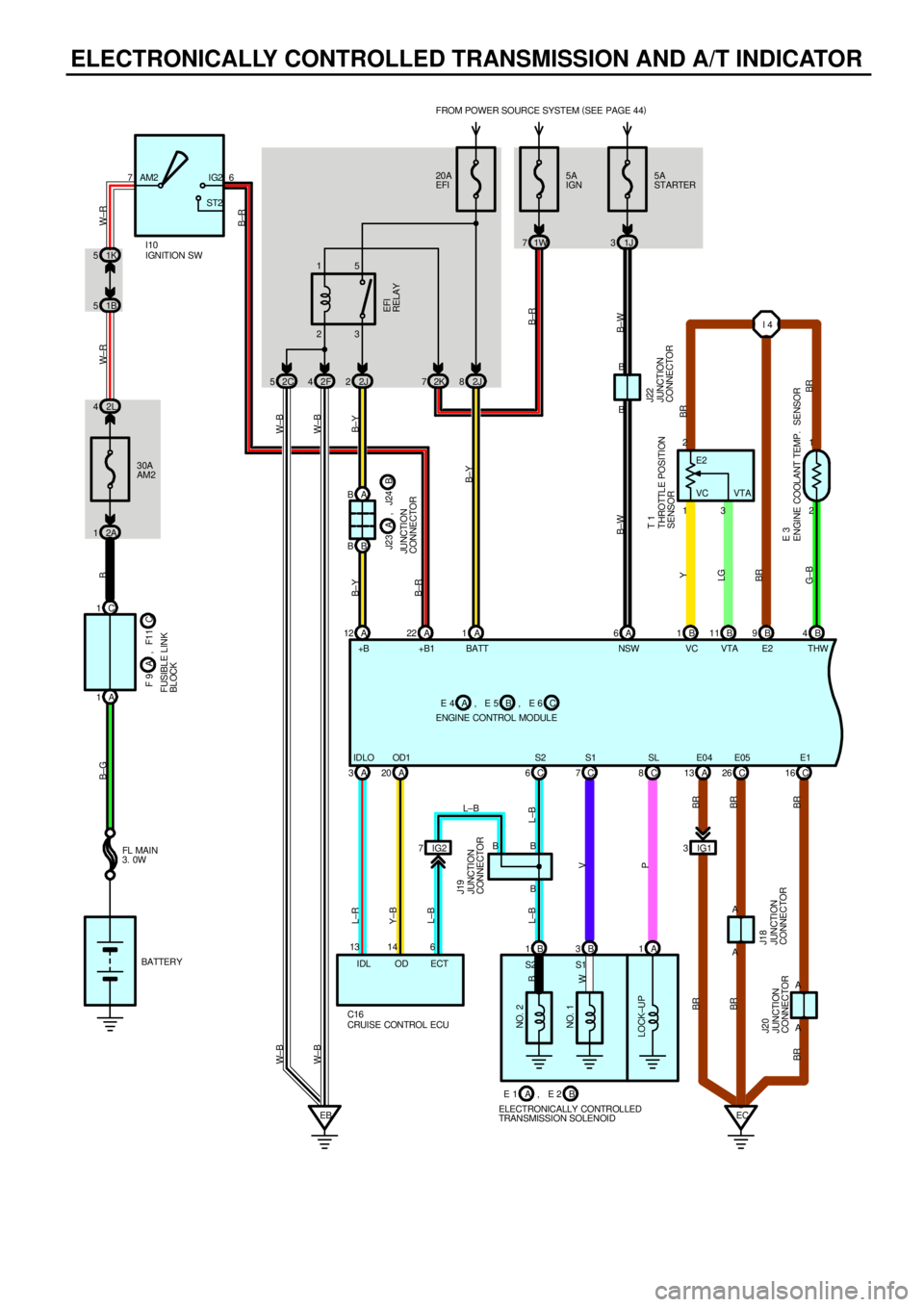
ELECTRONICALLY CONTROLLED TRANSMISSION AND A/T INDICATOR
72K
NO. 2
LOCK±UPNO. 1
B E 1
ELECTRONICALLY CONTROLLED
TRANSMISSION SOLENOIDAB 20A
EFI FROM POWER SOURCE SYSTEM (
SEE PAGE 44)
2J 8 3 15
2F 42J2
1 2
2 1
A 1B1B11 B4 B 9
C 6C7C8C16 A B
B B
EBEC B
A B3
A
B±YB±Y W±B W± B
BR
BR G±BLGY
BR L±B L±B
V
P
BR BREFI
RELAY
E 2
THROTTLE POSITION
SENSOR
ENGINE COOLANT TEMP. SENSORT 1
E 3 B
W
S2 S1 IG2 7 A 3A20
CRUISE CONTROL ECU C166 13 14
L±B L±R
Y±B
ECT IDL ODB ENGINE CONTROL MODULEB AC A 12
B±Y
B±R
JUNCTION
CONNECTOR J20JUNCTION
CONNECTOR J19
L±B5A
IGN
1W 7
1A 3B 1B
, E 4 , E 5 , E 6
J23
JUNCTION
CONNECTORB A, J24
A 65A
STARTER
1J 3
B±W B±W
JUNCTION
CONNECTOR J22
C 26
BR
B 2C 5
W±B
VC E2
VTA
+B BATT NSW VC VTA E2 THW
IDLO OD1 S2 S1 SL E05 E1
A 13
IG1 3
A A
JUNCTION
CONNECTOR J18 BRBR BR
2L 4
2A 1
B±G B
IGNITION SW
30A
AM2
BATTERY FL MAIN
3. 0WI10 7AM2 IG2
ST2
1B 51K 5
W± R W±R
C 1
A 1
F 9
FUSIBLE LINK
BLOCKC A, F11
A 22
B±R
6
W± B
2
B±R
+B1
E04I 4
Page 4111 of 4592
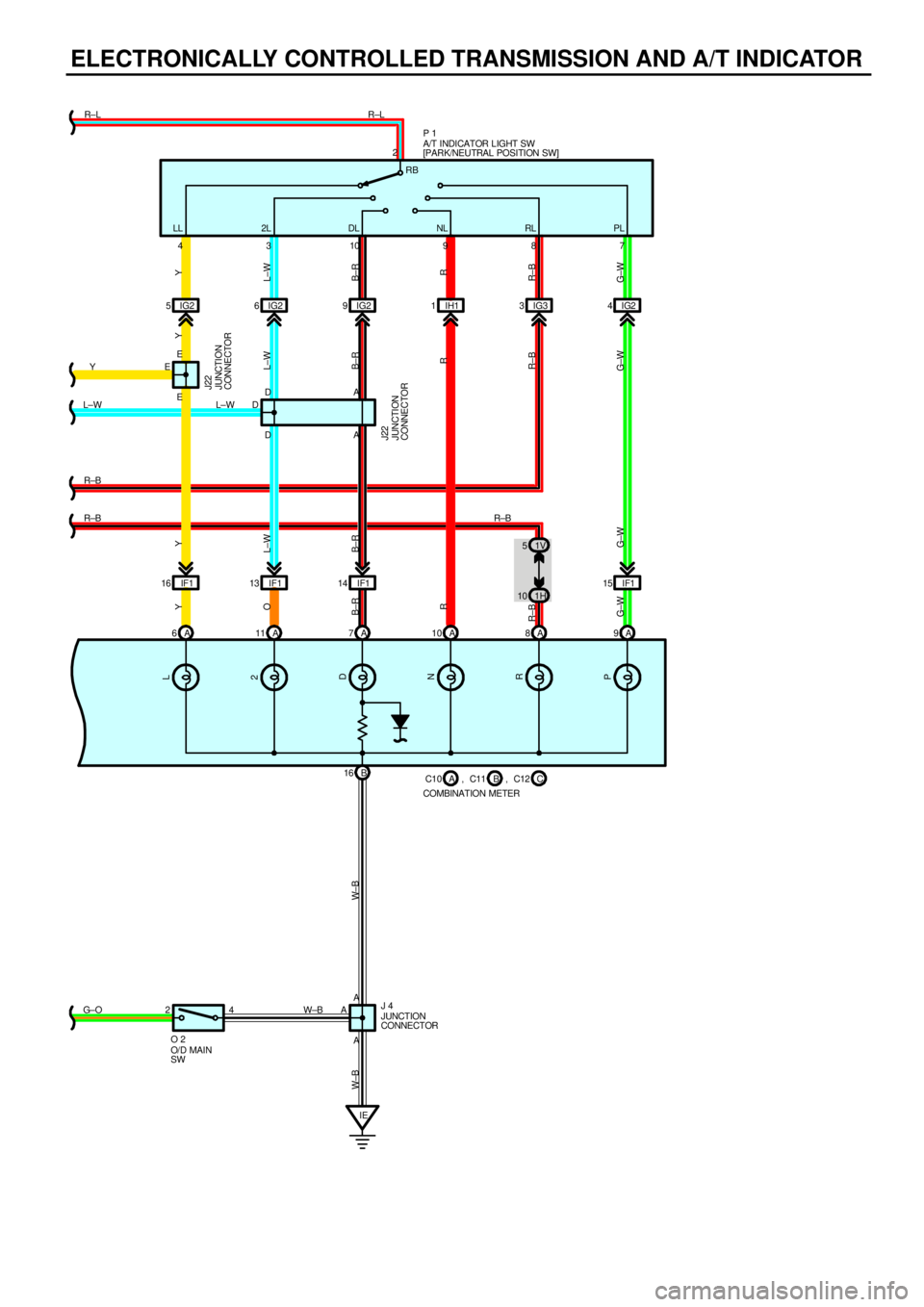
ELECTRONICALLY CONTROLLED TRANSMISSION AND A/T INDICATOR
A 6A11 A7A10 A8A9
B 16
IE IG2 5IG26IG29IH11IG33IG24
IF1 16 IF113 IF114 IF115 LL 2L DL NL RL PL
43109872
1V 5
1H 10 EE
DDA
AA E
DA
A L±WR±L
W±B
Y
O
B±R
R
R±B
G±WY
L±W
B±RY
L±W
B±R
R
R±B
G±W W± B W±B
COMBINATION METERB C10 C11ACC12
JUNCTION
CONNECTOR J 4A/T INDICATOR LIGHT SW
[PARK/NEUTRAL POSITION SW] P 1
JUNCTION
CONNECTOR J22JUNCTION
CONNECTOR J22 L
2
D
N
R
PY
L±W
B±R
R
R±B
G±W
G± OR±B R±B L±WY R±L
G±W
4 2
O/ D MAI N
SW O 2, , R±B RB
Page 4112 of 4592

The electronically controlled transmission, however, electrically controls the line pressure and lock±up pressure etc., through
the solenoid valve. Engine control module controls of the solenoid valve based on the input signals from each sensor which
makes smooth driving possible by shift selection for each gear which is most appropriate to the driving conditions at that
time.
1. GEAR SHIFT OPERATION
During driving, the engine control module selects the shift for each gear which is most appropriate to the driving conditions,
based on input signals from the engine coolant temp. sensor to TERMINAL THW of the engine control module, and also the
input signals to TERMINAL SPD of the engine control module from the vehicle speed sensor devoted to the electronically
controlled transmission. Current is then output to the electronically controlled transmission solenoid. When shifting to 1st
gear, current flows from TERMINAL S1 of the engine control module to TERMINAL (B) 3 of the solenoid to GROUND, and
continuity to the No.1 solenoid causes the shift.
For 2nd gear, current flows from TERMINAL S1 of the engine control module to TERMINAL (B) 3 of the solenoid to
GROUND, and from TERMINAL S2 of the engine control module to TERMINAL (B) 1 of the solenoid to GROUND, and
continuity to solenoids No.1 and No.2 causes the shift.
For 3rd gear, there is no continuity to No.1 solenoid, only to No.2, causing the shift.
Shifting into 4th gear (Overdrive) takes place when there is no continuity to either No.1 or No.2 solenoid.
2. LOCK±UP OPERATION
When the engine control module judges from each signal that lock±up operation conditions have been met, current flows
from TERMINAL SL of the engine control module to TERMINAL (A) 1 of the electronically controlled transmission solenoid to
GROUND, causing continuity to the lock±up solenoid and causing lock±up operation.
3. STOP LIGHT SW CIRCUIT
If the brake pedal is depressed (Stop light SW on) when driving in lock±up condition, a signal is input to TERMINAL STP of
the engine control module, the engine control module operates and continuity to the lock±up solenoid is cut.
4. OVERDRIVE CIRCUIT
*O/D main SW on
When the O/D main SW is turned on (O/D off indicator light turns off), a signal is input into TERMINAL OD2 of the engine
control module and engine control module operation causes gear shift when the conditions for overdrive are met.
*O/D main SW off
When the O/D main SW is turned to off, the current through the O/D off indicator light flows through the O/D main SW to
GROUND, causing the indicator light to light up. At the same time, a signal is input into TERMINAL OD2 of the engine
control module and engine control module operation prevents shift into overdrive.
E4 (A), E5 (B), E6 (C) ENGINE CONTROL MODULE
S1, S2±E1 :9.0±14.0 volts with the solenoid on
0±1.5 volts with the solenoid off
L±E1 :7.5±14.0 volts with the shift lever at L position
2±E1 :7.5±14.0 volts with the shift lever at 2 position
R±E1 :7.5±14.0 volts with the shift lever at R position
STP±E1 :9.0±14.0 volts with the brake pedal depressed
THW±E2 :0.2±1.0 volts with the ignition SW on and coolant temp. 80°C (176°F)
VTA±E2 :0.3±0.8 volts with the throttle valve fully closed
3.2±4.9 volts with the throttle valve fully opened
VC±E2 :4.5±5.5 volts
OD2±E1 :9.0±14.0 volts with the O/D main SW turned on
0±3.0 volts with the O/D main SW turned off
+B±E1 :9.0±14.0 volts
O2 O/D MAIN SW
2±4 : Closed with the O/D main SW off, open with the O/D main SW on
SYSTEM OUTLINE
SERVICE HINTS
Page 4113 of 4592
ELECTRONICALLY CONTROLLED TRANSMISSION AND A/T INDICATOR
: PARTS LOCATION
CodeSee PageCodeSee PageCodeSee Page
C10A30F9A28J2231
C11B30F11C28J23A31
C12C30I1030J24B31
C1630J331O231
E1A28J431P129
E2B28J531S431
E328J1531T129
E4A30J1831V129
E5B30J1931
E6C30J2031
������ ���: JUNCTION BLOCK AND WIRE HARNESS CONNECTOR
CodeSee PageJunction Block and Wire Harness (Connector Location)
1B22Cowl Wire and Instrument Panel J/B (Lower Finish Panel)1C22Cowl Wire and Instrument Panel J/B (Lower Finish Panel)
1D22Instrument Panel Wire and Instrument Panel J/B (Lower Finish Panel)1H22Instrument Panel Wire and Instrument Panel J/B (Lower Finish Panel)
1J
1K
1R22Cowl Wire and Instrument Panel J/B (Lower Finish Panel)
1V
()
1W
2A
2C24Engine Room Main Wire and Engine Room J/B No.2 (Engine Compartment Left)
2F
gg(g)
2J
2K24Cowl Wire and Engine Room J/B No.2 (Engine Compartment Left)
2L
g(g )
: CONNECTOR JOINING WIRE HARNESS AND WIRE HARNESS
CodeSee PageJoining Wire Harness and Wire Harness (Connector Location)
IF136Instrument Panel Wire and Cowl Wire (Under the Blower Motor)
IG1
IG238Engine Wire and Cowl Wire (Under the Blower Motor)
IG3
g()
IH138Engine Wire and Instrument Panel Wire (Under the Blower Motor)
: GROUND POINTS
CodeSee PageGround Points Location
EB34Left Radiator Side Support
EC34Intake Manifold
IE36Left Kick Panel
IG36Instrument Panel Brace RH
: SPLICE POINTS
CodeSee PageWire Harness with Splice PointsCodeSee PageWire Harness with Splice Points
I438Engine Wire
Page 4116 of 4592
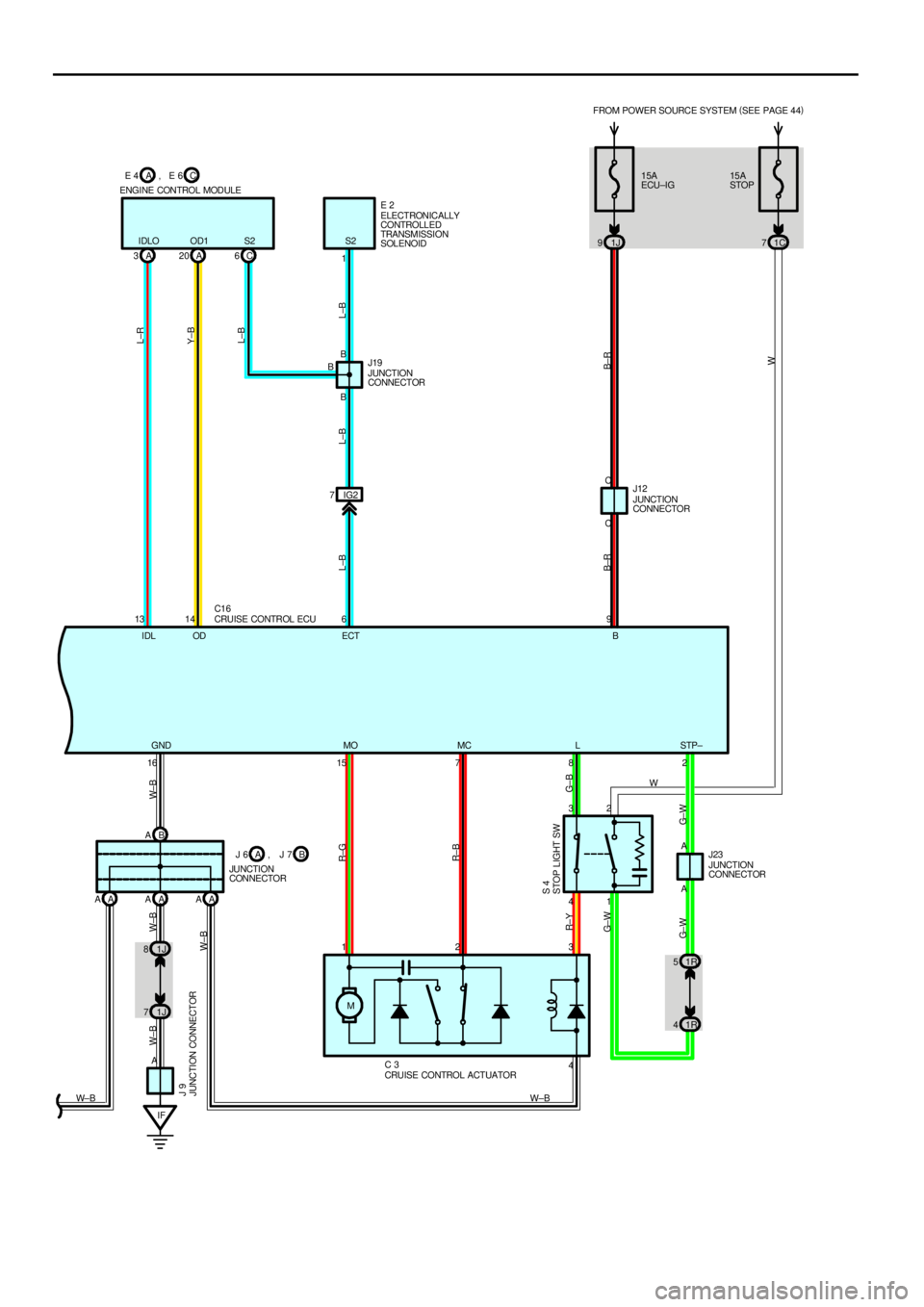
15A
ECU±IG
1J 9
C 6 A 20 A 315A
STOP FROM POWER SOURCE SYSTEM (
SEE PAGE 44)
1C 7
A AAAAA B A
IF1R 5
1R 4 16 15 8 2
41
4 B
C
12332
ABB
C
W± BGND IDLO OD1 S2
7 13 14 6 9
L±B L±B Y±BL±R
L±B
B±RL±B
B±R
W W± B
R±G
R±B
G±B R±Y W±B
G± W
W
W±B JUNCTION
CONNECTOR J19
JUNCTION
CONNECTOR J12
STOP LIGHT SW S 4
ENGINE CONTROL MODULE
JUNCTION
CONNECTOR
CRUISE CONTROL ACTUATOR C 3
G± W G± W
CRUISE CONTROL ECU
C16
1J 8
1J 7
W±B W±B
M
JUNCTION CONNECTOR J 9
IG2 7S2
B J 6 A , J 7 E 4 CA, E 6
1
IDL OD ECT B
MO MC L STP±
A A
JUNCTION
CONNECTOR J23 ELECTRONICALLY
CONTROLLED
TRANSMISSION
SOLENOID E 2