low oil pressure TOYOTA RAV4 2006 Service Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: TOYOTA, Model Year: 2006, Model line: RAV4, Model: TOYOTA RAV4 2006Pages: 2000, PDF Size: 45.84 MB
Page 1244 of 2000

AX–20U241E AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE – AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE SYSTEM
AX
(g) Depress the accelerator pedal as much as possible
with your right foot. Quickly read the highest line
pressure reading when the engine speed reaches
stall speed.
(h) Perform the measure line pressure test again with
the shift lever on R.
Specified line pressure:
Evaluation:
Condition Shift Lever on D Shift Lever on R
Idling 372 to 412 kPa
(3.8 to 4.2 kgf/cm
2, 54 to 60 psi)672 to 742 kPa
(6.9 to 7.6 kgf/cm2, 97 to 108 psi)
Stall 931 to 1,031 kPa
(9.5 to 10.5 kgf/cm
2, 135 to 150 psi)1,768 to 1,968 kPa
(18.0 to 20.0 kgf/cm2, 256 to 285 psi)
Problem Possible Cause
Measured values at all positions are higher than specified • Shift solenoid valve SLT defective
• Regulator valve defective
Measured values at all positions are lower than specified • Shift solenoid valve SLT defective
• Regulator valve defective
• Oil pump defective
• U/D (underdrive) direct clutch defective
Pressure is low when shift lever is on D only • D position circuit fluid leak
• Forward clutch defective
Pressure is low when shift lever is on R only • R position circuit fluid leak
• Direct clutch defective
• 1st and reverse brake defective
Page 1950 of 2000

ES–622AZ-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM – SFI SYSTEM
ES
P0300 Random / Multiple
Cylinder Misfire
Detected- Open or short in
engine wire harness
- Connector
connection
- Vacuum hose
connection
- Ignition system
- Injector
- Fuel pressure
- MAF meter
- ECT sensor
- Compression
pressure
- Valve clearance
- Valve timing
- PCV valve and hose
- PCV hose
connections
- Air induction system
- ECMComes on/Blinks* DTC storedES-156
P0301 Cylinder 1 Misfire
Detected- Same as DTC
P0300Comes on/Blinks* DTC storedES-156
P0302 Cylinder 2 Misfire
Detected- Same as DTC
P0300Comes on/Blinks* DTC storedES-156
P0303 Cylinder 3 Misfire
Detected- Same as DTC
P0300Comes on/Blinks* DTC storedES-156
P0304 Cylinder 4 Misfire
Detected- Same as DTC
P0300Comes on/Blinks* DTC storedES-156
P0327 Knock Sensor 1
Circuit Low Input
(Bank 1 or Single
Sensor)- Short in knock
sensor circuit
- Knock sensor
- ECMComes on DTC storedES-168
P0328 Knock Sensor 1
Circuit High Input
(Bank 1 or Single
Sensor)- Open in knock
sensor circuit
- Knock sensor
- ECMComes on DTC storedES-168
P0335 Crankshaft Position
Sensor "A" Circuit- Open or short in
Crankshaft Position
(CKP) sensor circuit
- CKP sensor
- CKP sensor plate
- ECMComes on DTC storedES-172
P0339 Crankshaft Position
Sensor "A" Circuit
Intermittent- Same as DTC
P0335- DTC storedES-172
P0340 Camshaft Position
Sensor "A" Circuit
(Bank 1 or Single
Sensor)- Open or short in
Camshaft Position
(CMP) sensor circuit
- CMP sensor
- Camshaft
- Jumped tooth of
timing chain
- ECMComes on DTC storedES-178
P0351 Ignition Coil "A"
Primary / Secondary
Circuit- Ignition system
- Open or short in
IGF1 or IGT circuit (1
to 4) between ignition
coil with igniter and
ECM
- No. 1 to No. 4
ignition coils with
igniters
- ECMComes on DTC storedES-183 DTC No. Detection Item Trouble Areas MIL Memory See page
Page 1951 of 2000
2AZ-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM – SFI SYSTEMES–63
ES
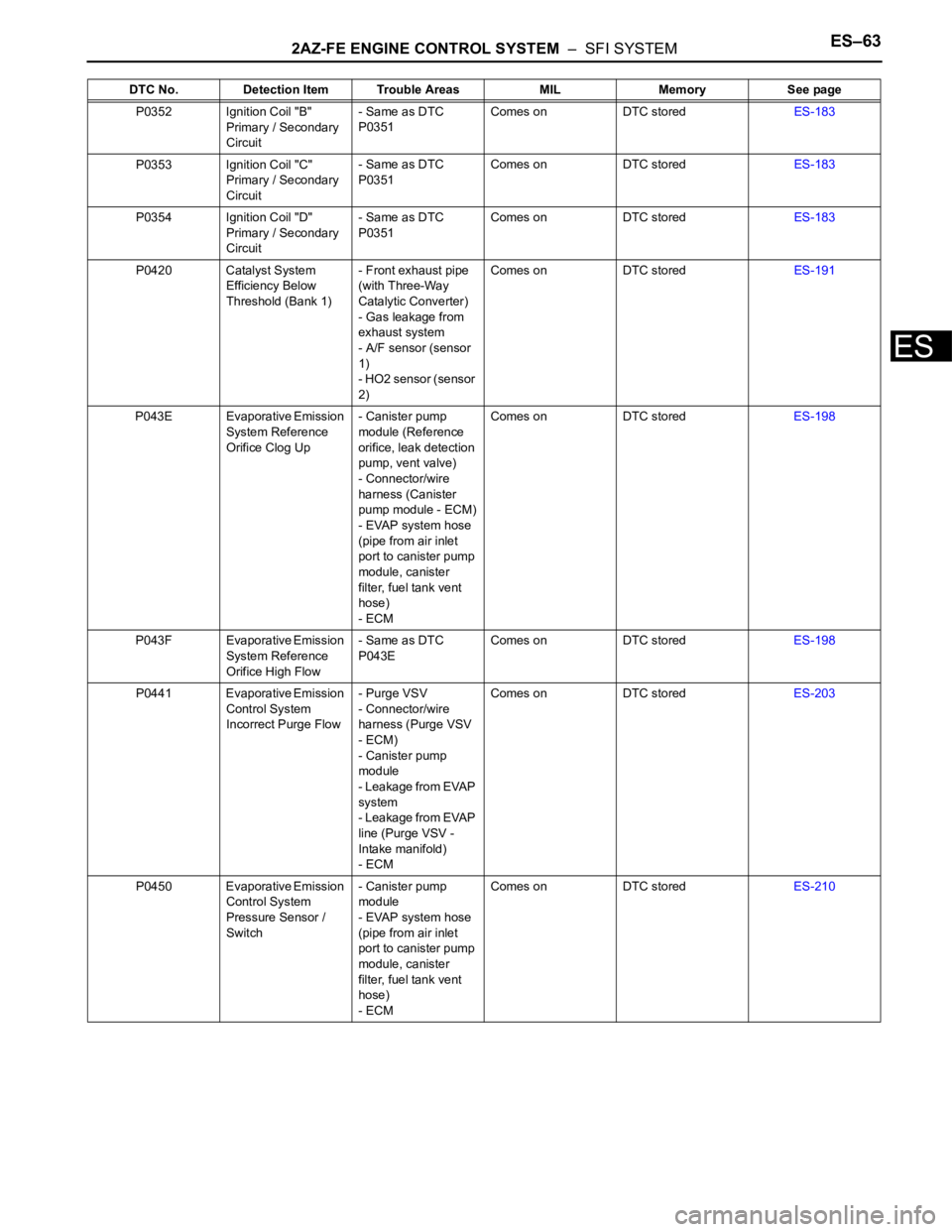
P0352 Ignition Coil "B"
Primary / Secondary
Circuit- Same as DTC
P0351Comes on DTC storedES-183
P0353 Ignition Coil "C"
Primary / Secondary
Circuit- Same as DTC
P0351Comes on DTC storedES-183
P0354 Ignition Coil "D"
Primary / Secondary
Circuit- Same as DTC
P0351Comes on DTC storedES-183
P0420 Catalyst System
Efficiency Below
Threshold (Bank 1)- Front exhaust pipe
(with Three-Way
Catalytic Converter)
- Gas leakage from
exhaust system
- A/F sensor (sensor
1)
- HO2 sensor (sensor
2)Comes on DTC storedES-191
P043E Evaporative Emission
System Reference
Orifice Clog Up- Canister pump
module (Reference
orifice, leak detection
pump, vent valve)
- Connector/wire
harness (Canister
pump module - ECM)
- EVAP system hose
(pipe from air inlet
port to canister pump
module, canister
filter, fuel tank vent
hose)
- ECMComes on DTC storedES-198
P043F Evaporative Emission
System Reference
Orifice High Flow- Same as DTC
P043EComes on DTC storedES-198
P0441 Evaporative Emission
Control System
Incorrect Purge Flow- Purge VSV
- Connector/wire
harness (Purge VSV
- ECM)
- Canister pump
module
- Leakage from EVAP
system
- Leakage from EVAP
line (Purge VSV -
Intake manifold)
- ECMComes on DTC storedES-203
P0450 Evaporative Emission
Control System
Pressure Sensor /
Switch- Canister pump
module
- EVAP system hose
(pipe from air inlet
port to canister pump
module, canister
filter, fuel tank vent
hose)
- ECMComes on DTC storedES-210 DTC No. Detection Item Trouble Areas MIL Memory See page
Page 1958 of 2000

E S –702AZ-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM – SFI SYSTEM
ES
MONITOR DESCRIPTION
The ECM optimizes the valve timing using the VVT system to control the intake camshaft. The VVT
system includes the ECM, the OCV and the VVT controller. The ECM sends a target duty-cycle control
signal to the OCV. This control signal regulates the oil pressure supplied to the VVT controller. The VVT
controller can advance or retard the intake camshaft.
After the ECM sends the target duty-cycle control signal to the OCV, the ECM monitors the OCV current
to establish an actual duty-cycle. The ECM determines the existence of a malfunction and sets the DTC
when the actual duty-cycle ratio varies from the target duty-cycle ratio.
MONITOR STRATEGY
TYPICAL ENABLING CONDITIONS
TYPICAL MALFUNCTION THRESHOLDS
COMPONENT OPERATING RANGE
Related DTCs P0010: VVT OCV range check
Required Sensors/Components (Main) VVT OCV
Required Sensors/Components (Related) -
Frequency of Operation Continuous
Duration 1 second
MIL Operation Immediate
Sequence of Operation None
Monitor runs whenever following DTCs not present None
All of following conditions met -
Starter OFF
Ignition switch ON
Time after ignition switch OFF to ON 0.5 seconds or more
One of following conditions met -
A. All of following conditions met -
Battery voltage 11 to 13 V
Target duty ratio Less than 70 %
Output signal duty ratio 100 %
B. All of following conditions met -
Battery voltage 13 V or more
Target duty ratio Less than 80 %
Output signal duty ratio 100 %
C. Both of following conditions met -
Current cut status Not cut
Output signal duty ratio 3 % or less
VVT OCV duty ratio 3 to 100 %
Page 1962 of 2000

ES–742AZ-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM – SFI SYSTEM
ES
MONITOR DESCRIPTION
The ECM optimizes the intake valve timing using the VVT (Variable Valve Timing) system to control the
intake camshaft. The VVT system includes the ECM, the Oil Control Valve (OCV) and the VVT controller.
The ECM sends a target duty-cycle control signal to the OCV. This control signal regulates the oil
pressure supplied to the VVT controller. The VVT controller can advance or retard the intake camshaft.
If the difference between the target and actual intake valve timings is large, and changes in the actual
intake valve timing are small, the ECM interprets this as the VVT controller stuck malfunction and sets a
DTC.
Example:
A DTC is set when the following conditions 1, 2 and 3 are met:
1. The difference between the target and actual intake valve timing is more than 5
CA (Crankshaft
Angle) and the condition continues for more than 4.5 seconds.
2. It takes 5 seconds or more to change the valve timing by 5
CA.
3. After above conditions 1 and 2 are met, the OCV is forcibly activated 63 times or more.
DTC P0011 (Advanced Cam Timing) is subject to 1 trip detection logic.
DTC P0012 (Retarded Cam Timing) is subject to 2 trip detection logic.
These DTCs indicate that the VVT controller cannot operate properly due to OCV malfunctions or the
presence of foreign objects in the OCV.
The monitor will run if all of the following conditions are met:
– The engine is warm (the engine coolant temperature is 75
C [167F] or more).
– The vehicle has been driven at more than 64 km/h (40 mph) for 3 minutes.
– The engine has idled for 3 minutes.
MONITOR STRATEGY
DTC No. DTC Detection Conditions Trouble Areas
P0011Advanced camshaft timing:
With warm engine and engine speed of between 550 rpm and
4,000 rpm, all conditions (1), (2) and (3) met (1 trip detection
logic):
1. Difference between target and actual intake valve timings
more than 5
CA (Crankshaft Angle) for 4.5 seconds
2. Current intake valve timing fixed (timing changes less than
5
CA in 5 seconds)
3. Variations in VVT controller timing more than 19
CA of
maximum delayed timing (malfunction in advance timing)• Valve timing
•OCV
• OCV filter
• Camshaft timing gear assembly
•ECM
P0012Retarded camshaft timing:
With warm engine and engine speed of between 550 rpm and
4,000 rpm, all conditions (1), (2) and (3) met (2 trip detection
logic):
1. Difference between target and actual intake valve timings
more than 5
CA (Crankshaft Angle) for 4.5 seconds
2. Current intake valve timing fixed (timing changes less than
5
CA in 5 seconds)
3. Variations in VVT controller timing 19CA or less of
maximum delayed timing (malfunction in retarded timing)• Valve timing
•OCV
• OCV filter
• Camshaft timing gear assembly
•ECM
Related DTCsP0011: Advanced camshaft timing
P0012: Retarded camshaft timing
Required Sensors/Components (Main) VVT OCV and VVT Actuator
Required Sensors/Components (Related)Crankshaft position sensor, camshaft position sensor and Engine
coolant temperature sensor
Frequency of Operation Once per driving cycle
Duration Within 10 seconds
MIL OperationAdvanced camshaft timing: Immediate
Retarded camshaft timing: 2 driving cycles
Sequence of Operation None
Page 1967 of 2000

2AZ-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM – SFI SYSTEMES–79
ES
DESCRIPTION
In the VVT (Variable Valve Timing) system, the appropriate intake valve open and close timing is
controlled by the ECM. The ECM performs intake valve control by performing the following: 1) controlling
the camshaft and camshaft timing oil control valve, and operating the camshaft timing gear; and 2)
changing the relative positions of the gaps between the camshaft and crankshaft.
MONITOR DESCRIPTION
The ECM optimizes the valve timing by using the VVT (Variable Valve Timing) system to control the intake
camshaft. The VVT system includes the ECM, the Oil Control Valve (OCV) and the VVT controller.
The ECM sends a target duty-cycle control signal to the OCV. This control signal regulates the oil
pressure supplied to the VVT controller. The VVT controller can advance or retard the intake camshaft.
The ECM calibrates the intake valve timing by setting the intake camshaft to the most retarded angle while
the engine is idling. The ECM closes the OCV to retard the cam. The ECM stores this value as the VVT
learning value. When the difference between the target and actual intake valve timings is 5
CA
(Crankshaft Angle) or less, the ECM stores it.
If the VVT learning value matches the following conditions, the ECM determines the existence of a
malfunction in the VVT system, and sets the DTC.
• VVT learning value: Less than 25
CA, or more than 51CA.
• Above condition continues for 18 seconds or more.
This DTC indicates that the angle between the intake camshaft and the crankshaft is incorrect due to
factors such as the timing chain having jumped a tooth.
This monitor begins to run after the engine has idled for 5 minutes.
MONITOR STRATEGY
TYPICAL ENABLING CONDITIONS
TYPICAL MALFUNCTION THRESHOLDS
DTC P0016Crankshaft Position - Camshaft Position Corre-
lation (Bank 1 Sensor A)
DTC No. DTC Detection Conditions Trouble Areas
P0016Deviation in crankshaft and camshaft position sensor signals
(2 trip detection logic)• Mechanical system (Timing chain has jumped tooth or
chain stretched)
•ECM
Related DTCs P0016: Camshaft timing misalignment at idling
Required Sensors/Components VVT actuator
Required Sensors/Components Camshaft position sensor, Crankshaft position sensor
Frequency of Operation Once per driving cycle
Duration Within 1 minute
MIL Operation 2 driving cycles
Sequence of Operation None
Monitor runs whenever following DTCs not presentP0011 (VVT system 1 - advance)
P0012 (VVT system 1 - retarded)
P0115 - P0118 (ECT sensor)
Engine RPM 550 to 1,000 rpm
One of following conditions met -
VVT learning value when camshaft maximum retarded Less than 27.8
CA
VVT learning value when camshaft maximum retarded More than 48
CA