ABS AUDI A5 COUPE 2008 User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: AUDI, Model Year: 2008, Model line: A5 COUPE, Model: AUDI A5 COUPE 2008Pages: 313, PDF Size: 13.86 MB
Page 173 of 313

Seat belts171
Controls
Safety
Driving tips
General maintenance
Self-help
Technical data
Important safety instructions for using seat belts
There are a number of safety points concerning the seat
belts which you should remember. This will help to reduce
the risk of injury in an accident.
WARNING
•
The seat belts can only provi de maximum protection if the
seats are adjusted properly ⇒page 70, “Seats and storage”.
•
To ensure proper protection, it is important to wear the seat
belts in the co rrect position ⇒page 173, “How to wear seat belts
properly”. Ensure that the seat belts are worn exactly as recom-
mended in this chapter. Belts wh ich are not worn properly can
increase the risk of injury in accidents considerably.
•
Do not allow the seat belt to be come twisted or jammed, or to
rub on any sharp edges.
•
Never allow two passengers (even children) to share the same
seat belt. It is especially dangerou s to place a seat belt over a child
sitting on your lap.
•
Do not wear the belt over hard or fragile objects (such as
glasses or pens, etc. ) because this can cause injuries.
•
Loose, bulky clothing (such as an overcoat over a jacket)
impairs the proper fit an d function of the belts.
•
The belts must be kept clean, otherwise the retractors may not
work properly ⇒page 226, “Seat belts”.
•
The slot in the seat belt buckle must not be blocked with paper
or other objects, as this can prev ent the latch plate from engaging
properly.
•
The latch plate of the belt mu st always be engaged in the
correct buckle for that seat, ot herwise the belt will not be fully
effective.
•
Check the condition of the seat bel ts at regular intervals. If you
notice that the belt webbing, fi ttings, retractor mechanism or buckle of any of the belts is da
maged, the belt must be replaced
by a qualified workshop.
•
The seat belts must not be remov ed or modified in any way. Do
not attempt to repair a damaged belt yourself.
•
Seat belts which have been worn in an accident and stretched
must be replaced by a qualified workshop. The belt anchorages
should also be checked.
Forces acting in a collisionThe physical principles involved in a frontal impact
Very large forces are generat ed during a collision; these
forces have to be absorbed.
WARNING (continued)
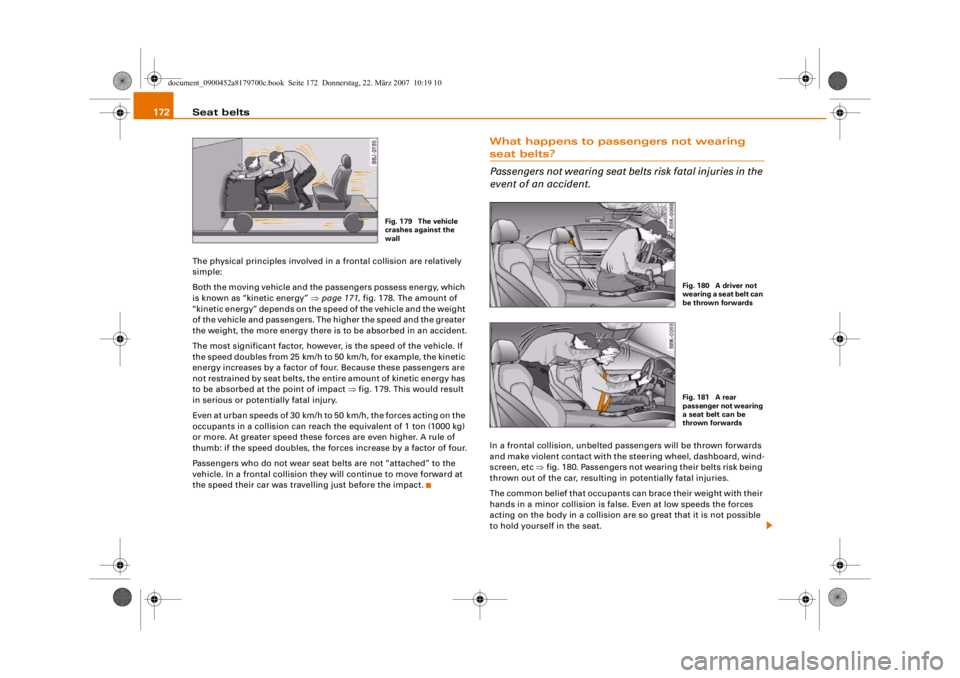
Fig. 178 Passengers of
a vehicle which is
headed for a brick wall.
They are not using seat
belts.
document_0900452a8179700c.book Seite 171 Donnerstag, 22. März 2007 10:19 10
--4 -
-T
•
-+ +-
Page 174 of 313
Seat belts
172The physical principles involved in a frontal collision are relatively
simple:
Both the moving vehicle and the passengers possess energy, which
is known as “kinetic energy” ⇒ page 171, fig. 178. The amount of
“kinetic energy” depends on the speed of the vehicle and the weight
of the vehicle and passengers. The higher the speed and the greater
the weight, the more energy there is to be absorbed in an accident.
The most significant factor, however, is the speed of the vehicle. If
the speed doubles from 25 km/h to 50 km/h, for example, the kinetic
energy increases by a factor of four. Because these passengers are
not restrained by seat belts, the entire amount of kinetic energy has
to be absorbed at the point of impact ⇒fig. 179. This would result
in serious or potentially fatal injury.
Even at urban speeds of 30 km/h to 50 km/h, the forces acting on the
occupants in a collision can reach the equivalent of 1 ton (1000 kg)
or more. At greater speed these forces are even higher. A rule of
thumb: if the speed doubles, the forces increase by a factor of four.
Passengers who do not wear seat belts are not “attached” to the
vehicle. In a frontal collision they will continue to move forward at
the speed their car was travelling just before the impact.
What happens to passengers not wearing seat belts?
Passengers not wearing seat belts risk fatal injuries in the
event of an accident.In a frontal collision, unbelted passengers will be thrown forwards
and make violent contact with the steering wheel, dashboard, wind-
screen, etc ⇒ fig. 180. Passengers not wearing their belts risk being
thrown out of the car, resulting in potentially fatal injuries.
The common belief that occupants can brace their weight with their
hands in a minor collision is false. Even at low speeds the forces
acting on the body in a collision are so great that it is not possible
to hold yourself in the seat.
Fig. 179 The vehicle
crashes against the
wall
Fig. 180 A driver not
wearing a seat belt can
be thrown forwardsFig. 181 A rear
passenger not wearing
a seat belt can be
thrown forwards
document_0900452a8179700c.book Seite 172 Donnerstag, 22. März 2007 10:19 10
--4 -
-T
-+ +-
•
Page 180 of 313
Airbag system
178Front airbagsDescription of front airbags
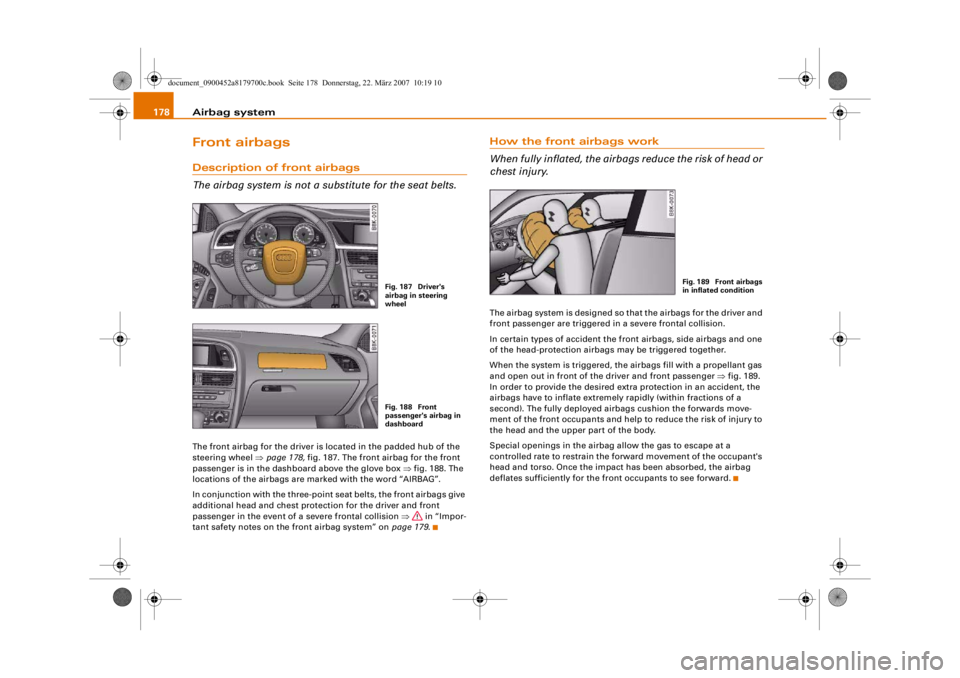
The airbag system is not a substitute for the seat belts.The front airbag for the driver is located in the padded hub of the
steering wheel ⇒page 178, fig. 187. The front airbag for the front
passenger is in the dashboard above the glove box ⇒fig. 188. The
locations of the airbags are ma rked with the word “AIRBAG”.
In conjunction with the three-point seat belts, the front airbags give
additional head and chest protection for the driver and front
passenger in the event of a severe frontal collision ⇒ in “Impor-
tant safety notes on th e front airbag system” on page 179.
How the front airbags work
When fully inflated, the airbags reduce the risk of head or
chest injury.The airbag system is designed so th at the airbags for the driver and
front passenger are triggered in a severe frontal collision.
In certain types of accident the front airbags, side airbags and one
of the head-protection airbags may be triggered together.
When the system is triggered, the airbags fill with a propellant gas
and open out in front of the driver and front passenger ⇒fig. 189.
In order to provide the desired extra protection in an accident, the
airbags have to inflate extremel y rapidly (within fractions of a
second). The fully deployed airbags cushion the forwards move-
ment of the front occupants and help to reduce the risk of injury to
the head and the upper part of the body.
Special openings in the airbag allow the gas to escape at a
controlled rate to restrain the forward movement of the occupant's
head and torso. Once the impact has been absorbed, the airbag
deflates sufficiently for the front occupants to see forward.
Fig. 187 Driver's
airbag in steering
wheelFig. 188 Front
passenger's airbag in
dashboard
Fig. 189 Front airbags
in inflated condition
document_0900452a8179700c.book Seite 178 Donnerstag, 22. März 2007 10:19 10
--4 -
-T
-+ +-
•
•
Page 198 of 313
Intelligent technology
196Intelligent technologyElectronic stabilisation program (ESP)General notes
The electronic stabilisation program increases the car's
stability on the road.The ESP is designed to enhance the control over the vehicle in crit-
ical handling situations, such as when accelerating and cornering.
It reduces the tendency to skid under all road conditions and
improves the stability and roadholding of the vehicle. The system
works at all speeds. The anti-lock brake system (ABS),
the electronic differential lock
(EDL) and the traction control system (ASR) are all integrated into
the electronic stabilisation program.
How the system works
The ESP control unit processes data from the three integrated
systems. It also processes addition al inputs provided by other high-
precision sensors. These register the vehicle's rotation about the
vertical axis (yaw rate), lateral acceleration, brake pressure and
steering wheel angle.
The system uses the steering wheel angle and road speed to calcu-
late the changes of direction intended by the driver, and constantly
compares them with the actual be haviour of the vehicle. If the
desired course is not being maintained (for instance, if the car is
starting to skid), then the ESP compensates automatically by
braking the appropriate wheel.
The forces acting on the braked wheel effectively bring the car back
to a stable condition. If the car is oversteering (rear wheels losing
grip first) the brake application is concentrated on the outside front
wheel; if the car is understeering (front wheels losing grip first), ESP
brakes the inside rear wheel. This automatic brake application is
accompanied by characteristic noises.
The ESP works in conj unction with the ABS ⇒page 197 . If a
malfunction should occur in the A BS, the ESP will also be out of
action.
Switching on
The ESP is switched on automatically when the engine is started
and performs a self-test routine. As soon as this routine is complete,
the system switches back to normal operating mode. You can press
the button ⇒fig. 203 or ⇒ fig. 204 to switch on the ESP or traction
control system (ASR) if they have been switched off. The message
ESP/ASR on will appear briefly in the display.
Fig. 203 Without MMI:
Centre console with
ESP switchFig. 204 Centre
console with ESP
switch
document_0900452a8179700c.book Seite 196 Donnerstag, 22. März 2007 10:19 10
ei-4---------4--
-
~
-+
-4
r
....
j
' ,.~
'
' I l
----t-
4-
---,- 1 -
Page 199 of 313
Intelligent technology197
Controls
Safety
Driving tips
General maintenance
Self-help
Technical data
Switching off
The ESP should normally be left switched on at all times. If required,
you can press the ESP OFF button to switch off the traction control
system (ASR) or the electronic stabilisation program (ESP).
•
Switching off the traction control system (ASR):
Press the ESP
button briefly. The traction control system (ASR) can be switched off
in special driving conditions, e.g. if you are driving with snow chains
⇒ page 198 . The message ASR off will appear in the display.
•
Switching off the ESP/traction control system (ASR): Press the
ESP button for longer than 3 seconds. The ESP/ASR warning lamp
lights up when the system is switched off, see ⇒page 16 . The
message ESP switched off will appear in the display.
WARNING
•
The ESP is not able to overcome th e physical limits of adhesion.
Even with ESP, you sh ould always adjust your speed to suit the
conditions. Please bear this in mind, especially on wet or slippery
road surfaces. Do not let the extr a safety provided tempt you into
taking any risks when drivin g – this can cause accidents.
•
Please note that, when the ESP or ESP/traction control system
(ASR) is switched off, the driven wheels may start to spin, causing
the vehicle to lose grip, in part icular on slippery or wet roads -
danger of skidding!
Anti-lock brake system (ABS)
ABS prevents the wheels from locking up under braking.The anti-lock brake system (ABS) is an important part of the car's
active safety system. However, the ABS will not necessarily guar-
antee shorter stopping distances in all conditions. For instance, on
loose gravel or fresh snow on top of an icy surface (conditions which
anyway require extreme care and reduced speed), the stopping
distance with ABS may even be slightly longer. How the ABS works
The system runs an automatic self-check when the car reaches a
road speed of about 6 km/h. This may be accompanied by a noise
from the ABS pump.
If one of the wheels is turning too slowly in relation to the road
speed, and is close to locking up, the system will reduce the pres-
sure in the brake line to this wheel. The driver is made aware of this
control process by a
pulsating of the brake pedal and accompa-
nying noise. This is a deliberate warning to the driver that one or
more of the wheels is tending to lock up and the ABS control func-
tion has intervened. In this situation it is important to keep the brake
pedal fully depressed so the ABS can regulate the brake application
- do not “pump” the brake pedal.
WARNING
The grip provided by ABS is still su bject to the physical limits of
adhesion. Always bear this in mind, especially on wet or slippery
roads. If you notice that the AB S is working (to counteract locked
wheels under braking), you should reduce speed immediately to
suit the road and traffic conditio ns. Do not let the extra safety
provided tempt you into taking an y risks when driving – this can
cause accidents.
Note
If a malfunction should occur in the ABS, this is indicated by a
warning lamp ⇒page 18 .Brake assist system
The brake assist system helps the driver to achieve
optimum braking effect.The brake assist system helps to increase braking power and thus to
achieve a shorter stopping distance . If the driver presses the brake
document_0900452a8179700c.book Seite 197 Donnerstag, 22. März 2007 10:19 10
--4 -
-T
-+
f------&
-----------j
&
+-
•
[I]
•
Page 200 of 313
Intelligent technology
198pedal very quickly, the brake assist system automatically boosts the
braking force to the maximum level, up to the point where the anti-
lock brake function (ABS) intervenes to stop the wheels from
locking. You should then keep the brake pedal pressed until the
vehicle has braked to the required speed. The brake assist system
switches itself off as soon as you release the brake pedal.
The brake assist system will not be operative if there is a malfunc-
tion in the ABS.
WARNING
Please remember that the accident risk always increases if you
drive too fast, especially in corners or on a slippery road, or if you
follow too close behind the vehicle in front of you. An increased
accident risk cannot be compensated even by the brake assist
system, so always be sure to maintain a safe speed.Traction control system (ASR)
The traction control system prevents the driven wheels
from spinning when the car is accelerating.General notes
The traction control system (ASR) is one of the functions incorpo-
rated in the electronic stabilisation program (ESP).
The traction control system (ASR) helps the car to start moving,
accelerate and climb a gradient in slippery conditions where this
may otherwise be difficult or even impossible.
How the system works
The ASR acts automatically i.e. without the driver's intervention.
With the aid of the ABS sensors ⇒page 197 , the ASR monitors the
speed of the driven wheels. If the wheels start to spin, the engine
power is reduced automatically to match the amount of grip avail-
able. The system works at all speeds. The ASR works in conjunction with the ABS. If a malfunction should
occur in the ABS, the ASR will also be out of action.
Switching on
The ESP is switched on automatically when the engine is started
and performs a self-test routine. As soon as this routine is complete,
the system switches back to normal operating mode. If the traction
control system (ASR) has been deactivated (for one of the reasons
noted below) you can switch it back on manually by pressing the
switch
⇒page 196, fig. 203. The message ESP/ASR on will appear
briefly in the display. If the traction control system (ASR) has been
deactivated, it will switch back on automatically at a speed of about
70 km/h on vehicles with front-wheel drive.
You can switch the traction control system (ASR) on again if neces-
sary by pressing the switch ⇒page 196, fig. 203.
Switching off
If required, the ASR can also be switched off manually by pressing
the switch briefly ⇒page 196, fig. 203 (for less than 3 seconds). The
ESP warning lamp lights up when the traction control system (ASR)
is switched off, see ⇒page 16 . The message ASR off will appear in
the display. For safety reasons, the system can only be switched off
at speeds below 50 km/h on vehicl es with front-wheel drive. The
ASR can be deactivated at any speed on vehicles with four-wheel
drive.
The traction control system should normally remain switched on at
all times. It should only be switched off manually in particular
circumstances where a certain amount of wheel slip may be desir-
able. For example:
•
when driving with snow chains
•
when driving in deep snow or on loose surfaces
•
when rocking the car backwards and forwards to free it.
The ASR should be switched on again afterwards as soon as
possible.
document_0900452a8179700c.book Seite 198 Donnerstag, 22. März 2007 10:19 10
--4 -
-T
-+
•
+-
Page 201 of 313
Intelligent technology199
Controls
Safety
Driving tips
General maintenance
Self-help
Technical data
Note
To ensure that the ASR works properly, all four wheels must be fitted
with identical tyres. Any differences in the rolling radius of the tyres
can cause the system to reduce engine power when this is not
desired. Also refer to ⇒page 245, “Replacing wheels and tyres”.Electronic differential lock (EDL)
The electronic differential lock monitors the speed of the
driven wheels.General notes
The electronic differential lock (EDL) helps the car to start moving,
accelerate and climb a gradient in slippery conditions where this
may otherwise be difficult or even impossible.
How the system works
The EDL acts automatically. With the aid of the ABS sensors
⇒page 197 , the system monitors the rotational speed of the driven
wheels on each axle. Whenever it detects a significant difference in
the speed of the driven wheels of one axle (for example, if the road is
slippery on one side ) the system applies the brake to slow down the
spinning wheel so that more of the power is directed to the other
wheel of this axle (or to the three other wheels on vehicles with four-
wheel drive). This function is active up to about 100 km/h. The brake
system will make noises while it is working.
Driving away from a standstill
Sometimes one wheel has less grip and starts spinning, for
example, if one of the driven wheels is on ice. In this case, keep
pressing the accelerator gradually until the car starts moving, even
though the wheel with less grip will still spin.
Overheating of the brakes
To prevent the disc brake of the braked wheel from overheating, the
EDL cuts out automatically if subjected to excessive loads. The car remains operational and will behave in the same way as a car
without EDL.
The EDL will switch on again automatically when the brake has
cooled down.
WARNING
•
When accelerating on a uniforml
y slippery surface (for instance
all four wheels on ice or snow), press the accelerator gradually and
carefully. The driven wheels may ot herwise start to spin (in spite
of the EDL), which would impair th e car's stability and could lead
to an accident.
•
Even with EDL, you should always adjust your speed to suit the
conditions. Do not let the extr a safety provided tempt you into
taking any risks when drivin g – this can cause accidents.Note
If the ABS warning lamp lights up, th is can also mean there is a fault
in the EDL. Please contact a qualified workshop as soon as
possible.BrakesNew brake pads
New brake pads do not give full br aking effect for the first 400 km,
they must first be “bedded in”. However, you can compensate for
the slightly reduced braking effect by applying more pressure on
the brake pedal. Avoid placing a heavy load on the brakes during the
running-in period.
We ar
The rate of wear on the brake pads depends a great deal on how you
drive and the conditions in which the vehicle is operated. Negative
document_0900452a8179700c.book Seite 199 Donnerstag, 22. März 2007 10:19 10
--4 -
-
(I]
T
• &
-+
(I]
•
+-
Page 225 of 313

Care of vehicle and cleaning223
Controls
Safety
Driving tips
General maintenance
Self-help
Technical data
After washing, the wheels should only be cleaned with an "acid-
free" cleaning agent for alloy wheels. This is available from Audi
dealers and specialist retailers. Never leave the cleaning agent on
the rims for any longer than specified in the instructions before
rinsing it off. If the wheel cleaner fluid contains acid it can attack the
surfaces of the wheel bolts.
Car polish or other abrasive agents should not be used. If the
protective paint coating is damaged by stone chips etc., the
damaged area should be touched up immediately.
WARNING
Please note when cleaning the wheel
s that water, ice and road salt
can impair the effectiveness of the brakes – this can cause an
accident.Care of interiorMMI display screen and control consoleThe MMI display screen can be cl eaned with a soft cloth and a
special “LCD cleaner” (available from retailers of electrical goods).
Moisten the cloth with a small amount of the cleaning fluid.
Clean the MMI control console with a fine brush first to prevent any
dirt from getting in between the control buttons and the housing.
We then recommend wiping the MMI control console using a cloth
moistened with washing-up liquid and water.
Caution
To avoid scratching the screen, do not wipe the MMI display with a
dry cloth.•
To avoid any possibility of damage, do not let any liquid get
inside the control console.
Plastic parts and leatherettePlastic parts and leatherette can be cleaned with a damp cloth. If
this is not sufficient, plastic parts and leatherette should only be
treated with a special solvent-free plastic cleaner .Textile covers and trim partsTextile covers and trim parts (e.g. seats, door trim) should be
cleaned regularly with a vacuum cleaner. This will remove surface
dirt which could otherwise be rubbed into the textile material
during use. Do not use steam cleaners, as the steam could carry the
dirt deeper into the textile material.
Normal cleaning
We recommend that you use a soft sponge or lint-free, micro-fibre
cloth for normal cleaning. Only use brushes on floor coverings and
mats, as other textile surfaces could become damaged.
In the case of normal surface dirt you can use a foam cleaner. Use a
sponge to spread the foam on the textile surface and to work it into
the material lightly. However, make sure that the textile material
does not become soaking wet. Then dab off the foam with a dry and
absorbent cloth (e.g. a micro-fibre cloth) and vacuum off any
residue once the surface is completely dry.
Removal of stains
To treat stains caused by spilled drinks (coffee, fruit juice or similar)
make up a solution with a mild detergent for sensitive fabrics and
apply it with a sponge. If the stains are difficult to remove, a
washing paste can be applied directly onto the stain and worked
into the fabric. The surface will then have to be wiped with clear
water to remove any residue left by the paste. To do so, use a damp
cloth or sponge and then dab th e stain with an absorbent cloth.
Treat chocolate or make-up stains with a washing paste and then
rinse off with water (using a damp sponge).
document_0900452a8179700c.book Seite 223 Donnerstag, 22. März 2007 10:19 10
--4 -
-T
•
-+ +-
CD
•
Page 226 of 313
Care of vehicle and cleaning
224A spirit-based cleaner can be used to remove grease, oil, lipstick or
ball point pen. Then dab the dissolved grease or colour particles off
with an absorbent cloth or similar. You may also have to treat the
stain once more using washing paste and water.
If the covers or textile trim panels are badly soiled we recommend
that you have them cleaned by a professional cleaning company.
Note
Please make sure you close any velcro fasteners on your clothing, as
these could otherwise damage the upholstery.Applies to vehicles: with leather upholsteryNatural leather
Audi does everything possible to preserve the special
qualities of leather as a natural product.General notes
We have a wide selection of leathers. The main type used is nappa
in various forms, that is leather with a smooth surface in a selection
of colours.
The amount of dye used determines the appearance and properties
of leather. If the leather is left in a more natural state, it retains its
typical natural appearance and is pleasant and comfortable for the
seat occupants. Fine veins, healed scars, insect bites, wrinkles and
a subtle variation in shading remain visible; these are the character-
istic features of genuine natural leather.
Natural napped leather does not ha ve a protective surface coating
of dye. It is therefore somewhat more prone to damage. You should
bear this in mind if children or pets often travel in the car, or if there
are other factors that could lead to damage.
Types of leather with a coloured surface coating are likely to be
more resistant to damage. This has a great advantage for day-to-day use. However, this means that the typical natural characteristics of
the surface are less apparent, though
this does not affect quality.
Cleaning and care
Because of the natural properties of the specially selected hides
employed, the finished leather has a certain sensitivity to grease
and dirt, etc. so a degree of care is required in everyday use and
when looking after the leather. Dark clothing (especially if damp or
incorrectly dyed) may stain leather upholstery. Dust and grit in the
pores and seams can have an abrasive effect and damage the
surface of the leather. Therefore leather should be cleaned at
regular intervals, depending on the actual amount of use. When
they have been in use for a certain time, your car seats will acquire
a typical and distinctive patina. This is characteristic for real leather
upholstery, and is a sign of genuine quality.
To maintain the value of natural leather you should note the
following points:
Caution
•
Avoid exposing leather to direct sunlight for long periods, other-
wise it may tend to lose some of its colour. If the car is left for a
prolonged period in the bright sun, it is best to cover the leather.
•
Sharp-edged objects on clothing, such as belts, zip fasteners,
rivets or similar, can also leave permanent scratches and rough
marks on the surface of the leather.Note
•
Use a suitable impregnating cream wi th ultra-violet protection at
regular intervals and after cleaning. This cream will nourish and
moisturise the leather, keep it supple and able to breathe. In addi-
tion, it will also help to protect the surface of the leather.
•
Clean the leather every 2 to 3 months and remove fresh dirt as
necessary.
document_0900452a8179700c.book Seite 224 Donnerstag, 22. März 2007 10:19 10
--4 -
-T
[I)
•
-+
CD
+-
[I)
Page 227 of 313
Care of vehicle and cleaning225
Controls
Safety
Driving tips
General maintenance
Self-help
Technical data
•
Remove stains from fresh ball-pen and other inks, lipstick, shoe
cream and similar stains as soon as possible.
•
Preserve the colour of the leather. A special coloured cream will
renew the colour of the leather when required and will eliminate
differences in colour.
Applies to vehicles: with leather upholsteryCleaning and care of leather upholstery
Natural leather requires an extra degree of attention and
care.Normal cleaning
– Moisten a cotton or woollen cloth with water and wipe over the leather surfaces.
More stubborn dirt
– More stubborn dirt can be removed using a mild soap solution (pure liquid soap: two tablespoons dissolved in
one litre of water).
– It is very important not to let the water soak through the leather or penetrate into the seams.
– Then wipe off with a soft, dry cloth.
Removal of stains
– Remove fresh water-based stains such as coffee, tea,
juices, blood etc. with an ab sorbent cloth or kitchen roll,
dried-on stains with the cleaning agent from the care set.
– Remove fresh fat-based stains on the surface such as
butter, mayonnaise, chocolate, etc. with an absorbent
cloth or kitchen roll or with the cleaning agent from the
care set. –Treat
fat-based, dried-in stains with grease-dissolving
spray.
–Treat less common stains such as ball-pen and other
inks, felt-tip pens, nail polish, dispersion paint, shoe
cream etc. with a special leather stain remover.
Leather care products
– The leather should be treated regularly (about twice a year) with a special leather-care product.
– Apply the cream very sparingly.
– Then wipe off with a soft, dry cloth.
Should you have any questions regarding the care and cleaning of
the leather upholstery in your vehicle, we recommend that you
contact your Audi dealer. The staff there will gladly provide you with
further information on cleaning and care of your upholstery and on
our complete range of leather care products:•
Cleaning and care set
•
Coloured leather-care cream
•
Stain remover for ball-pen inks, shoe cream etc.
•
Grease dissolving spray
•
New products and further developmentsCaution
On no account use solvents (such as petrol, turpentine), wax polish,
shoe cream or similar materials.
document_0900452a8179700c.book Seite 225 Donnerstag, 22. März 2007 10:19 10
--4 -
-T
•
-+ +-
0
•