relay BMW 3 SERIES 1983 E30 User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: BMW, Model Year: 1983, Model line: 3 SERIES, Model: BMW 3 SERIES 1983 E30Pages: 228, PDF Size: 7.04 MB
Page 110 of 228

Engine difficult to start, or fails to start (when cold)
Probable cause Corrective action
Cold start injector or thermotime switch
faulty (early Motronic system only) Test cold start injector and thermotime switch. Renew faulty components (see Section 19)
Fuel pump not running Check fuel pump fuse and fuel pump relay (see Sections 2 and 3)
Airflow meter flap (door) binding, or
stuck in open position Inspect the airflow meter for damage (see Section 16)
Fuel pressure incorrect Test system pressure (see Section 3)
Intake air leaks Inspect all vacuum lines, air ducts and oil filler and dipstick seals
Fuel injectors clogged or not operating Check fuel injectors (see Section 20) and wiring harness
Coolant temperature sensor faulty or Test coolant temperature sensor (see Chapter 6, Section 4)
wiring problem
TPS (throttle position sensor) incorrectly adjusted Check TPS adjustment (see Chapter 6, Section 4)
Dirt or other contaminants in fuel Check the fuel and drain the tank if necessary
Faulty ECU Have the ECU tested at a dealer service department or other specialist
Crankshaft position signal missing Faulty position sensor or flywheel, or reference pin missing (see Chapter 5)
Engine difficult to start, or fails to start (when warm)
Probable cause Corrective action
Cold start injector leaking or operating
continuously (early Motronic system only) Test cold start injector and thermotime switch (see Section 19)
Fuel pressure incorrect Test fuel pressure (see Section 3)
Insufficient residual fuel pressure Test fuel system hold pressure (see Section 3)
Fuel leak(s) Inspect fuel lines and fuel injectors for leaks. Correct leaks as necessary
Coolant temperature sensor faulty
or wiring problem Test coolant temperature sensor (see Chapter 6, Section 4)
Vapour lock (in warm weather) Check fuel pressure (see Section 3)
EVAP system faulty Check EVAP system (see Chapter 6, Section 6)
Faulty ECU Have the ECU tested at a dealer service department or other specialist
Idle speed control system faulty Test the idle air stabiliser valve (see Section 21)
Oxygen sensor faulty (where applicable) Check the oxygen sensor (see Chapter 6, Section 4)
Engine misses and hesitates under load
Probable cause Corrective action
Fuel injector clogged Test fuel injectors. Check for clogged injector lines. Renew faulty injectors (see Section 20)
Fuel pressure incorrect Test fuel system pressure (see Section 3). Test fuel pressure regulator (see Section 18)
Fuel leak(s) Inspect fuel lines and fuel injectors for leaks (see Chapter 4)
Engine maintenance Tune-up engine (see Chapter 1). Check the distributor cap, rotor, HT leads and spark
plugs, and renew any faulty components
Airflow meter flap (door) binding, or Inspect the airflow meter for damage (see Section 16)
stuck in open position
Intake air leaks Inspect all vacuum lines, air ducts, and oil filler and dipstick seals
Throttle position sensor (TPS) incorrectly adjusted Check TPS adjustment (see Chapter 6)
Engine idles too fast
Probable cause Corrective action
Accelerator pedal, cable or throttle valve binding Check for worn or broken components, kinked cable, or other damage. Renew faulty
components
Air leaking past throttle valve Inspect throttle valve, and adjust or renew as required
Engine has erratic idle speed
Probable cause Corrective action
Idle air stabiliser valve faulty Check the idle air stabiliser valve (see Section 21)
No power to the idle air stabiliser valve Check the idle air stabiliser relay and wiring circuit (see Chapter 12)
Idle speed control unit faulty Have the idle speed control unit checked by a dealer
Poor fuel economy
Probable cause Corrective action
Cold start injector leaking
(early Motronic system only) Test and, if necessary, renew cold start injector (see Section 19)
Oxygen sensor faulty (where applicable) Test the oxygen sensor (see Chapter 6, Section 4))
Sticking handbrake/binding brakes Check the handbrake/braking system (see Chapter 9)
Tyre pressures low Check tyre pressures (Chapter 1)
4•22 Fuel and exhaust systems
Page 113 of 228

5 Ignition system- general
information and precautions
The ignition system includes the ignition
switch, the battery, the distributor, the primary
(low-voltage/low-tension or LT) and
secondary (high-voltage/high-tension or HT)
wiring circuits, the spark plugs and the spark
plug leads. Models fitted with a carburettor or
L-Jetronic fuel injection are equipped with a
Transistorised Coil Ignition (TCI) system.
Models fitted with the Motronic fuel injection
system have the ignition system incorporated
within the Motronic system (Digital Motor
Electronics or DME).
Transistorised Coil Ignition (TCI)
system
This system is has four major components;
the impulse generator, the ignition control
unit, the coil, and the spark plugs. The
impulse generator provides a timing signal for
the ignition system. Equivalent to cam-
actuated breaker points in a standard
distributor, the impulse generator creates an
A/C voltage signal every time the trigger
wheel tabs pass the impulse generator tabs.
When the ignition control unit (capacitive
discharge unit) receives the voltage signal, it
triggers a spark discharge from the coil by
interrupting the primary coil circuit. The
ignition dwell (coil charging time) is adjusted
by the ignition control unit for the most
intense spark. Note: The air gap (distance
between the impulse generator and trigger
wheel tabs) can be adjusted (see Section 11).
Ignition timing is mechanically adjusted
(see Section 7). A centrifugal advance unit
that consists of spring-loaded rotating
weights advances ignition timing as engine
speed increases. The vacuum advance
adjusts ignition timing to compensate for
changes in engine load.
Motronic ignition system
This system, also known as Digital Motor
Electronics (DME), incorporates all ignition
and fuel injection functions into one central
control unit or ECU (computer). The ignition
timing is based on inputs the ECU receives for
engine load, engine speed, coolant
temperature and intake air temperature. The
only function the distributor performs is the
distribution of the high voltage signal to the
individual spark plugs. The distributor is
attached directly to the cylinder head. There is
no mechanical spark advance system used on
these systems.
Ignition timing is electronically-controlled,
and is not adjustable on Motronic systems.
During starting, a crankshaft position sensor
(reference sensor) relays the crankshaft
position to the ECU, and an initial baseline
ignition point is determined. Once the engineis running, the ignition timing is continually
changing, based on the various input signals
to the ECU. Engine speed is signalled by a
speed sensor. Early Motronic systems have
the position reference sensor and the speed
sensor mounted on the bellhousing over the
flywheel on the left-hand side. Later Motronic
systems have a single sensor (pulse sensor)
mounted over the crankshaft pulley. This
sensor functions as a speed sensor as well as
a position reference sensor. Refer to Sec-
tion 12 for checking and renewing the ignition
sensors. Note: Some models are equipped
with a TDC sensor mounted on the front of the
engine. This sensor is strictly for the BMW
service test unit, and it is not part of the
Motronic ignition system.
Precautions
Certain precautions must be observed
when working on a transistorised ignition
system.
a) Do not disconnect the battery cables
when the engine is running
b) Make sure the ignition control unit (TCI
ignition system) is always well earthed
(see Section 10).
c) Keep water away from the distributor and
HT leads.
d) If a tachometer is to be connected to the
engine, always connect the tachometer
positive (+) lead to the ignition coil
negative terminal (-) and never to the
distributor.
e) Do not allow the coil terminals to be
earthed, as the impulse generator or coil
could be damaged.
f) Do not leave the ignition switch on for
more than ten minutes with the engine
off, or if the engine will not start.
6 Ignition system- check
2
Warning: Because of the high
voltage generated by the ignition
system, extreme care should be
taken whenever an operation is
performed involving ignition components.
This not only includes the impulse
generator (electronic ignition), coil,
distributor and spark plug HT leads, but
related components such as spark plug
connectors, tachometer and other test
equipment.
1If the engine turns over but will not start,
disconnect the spark plug HT lead from any
spark plug, and attach it to a calibrated spark
tester (available at most car accessory
shops).
Note:There are two different types of spark
testers. Be sure to specify electronic
(breakerless) ignition. Connect the clip on thetester to an earth point such as a metal
bracket (see illustration).
2If you are unable to obtain a calibrated
spark tester, remove the spark plug HT lead
from one of the spark plugs. Using an
insulated tool, hold the lead about a quarter-
inch from the engine block - make sure the
gap is not more than a quarter-inch, or
damage may be caused to the electronic
components.
3Crank the engine, and observe the tip of the
tester or spark plug HT lead to see if a spark
occurs. If bright-blue, well-defined sparks
occur, sufficient voltage is reaching the plugs
to fire the engine. However, the plugs
themselves may be fouled, so remove and
check them as described in Chapter 1.
4If there’s no spark, check another HT lead
in the same manner. A few sparks followed by
no spark is the same condition as no spark at
all.
5If no spark occurs, remove the distributor
cap, and check the cap and rotor as
described in Chapter 1. If moisture is present,
use a water-dispersant aerosol (or something
similar) to dry out the cap and rotor, then refit
the cap and repeat the spark test.
6If there’s still no spark, disconnect the coil
HT lead from the distributor cap, and
test this lead as described for the spark plug
leads.
7If no spark occurs, check the primary wire
connections at the coil to make sure they’re
clean and tight. Make any necessary repairs,
then repeat the check.
8If sparks do occur from the coil HT lead, the
distributor cap, rotor, plug HT lead(s) or spark
plug(s) may be defective. If there’s still no
spark, the coil-to-cap HT lead may be
defective. If a substitute lead doesn’t make
any difference, check the ignition coil (see
Section 9). Note:Refer to Sections 10 and 11
for more test procedures on the distributors
fitted with the TCI ignition system.
Engine electrical systems 5•3
6.1 To use a spark tester, simply
disconnect a spark plug HT lead, clip the
tester to a convenient earth (like a valve
cover bolt or nut) and operate the starter –
if there is enough power to fire the plug,
sparks will be visible between the
electrode tip and the tester body
5
Page 125 of 228
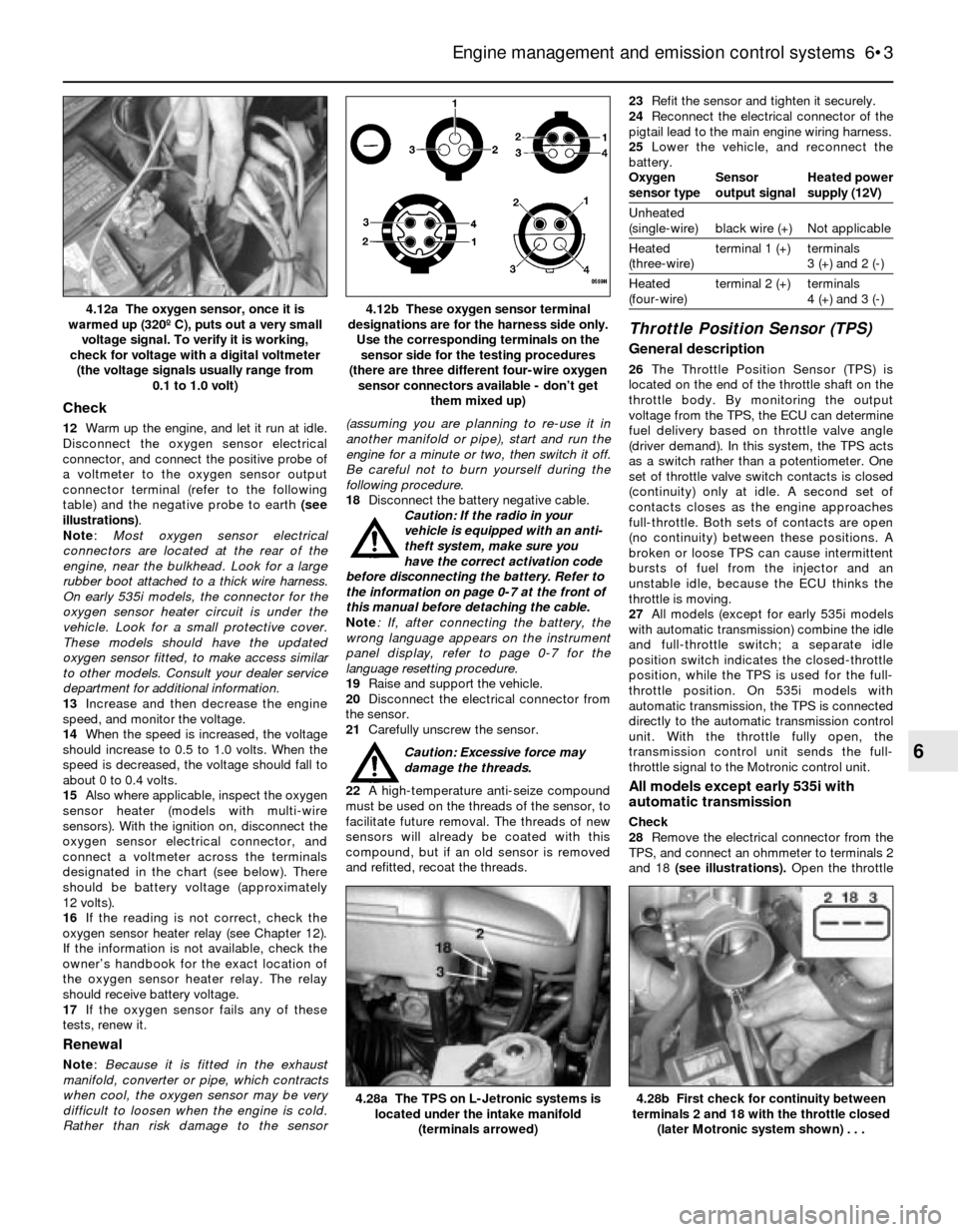
Check
12Warm up the engine, and let it run at idle.
Disconnect the oxygen sensor electrical
connector, and connect the positive probe of
a voltmeter to the oxygen sensor output
connector terminal (refer to the following
table) and the negative probe to earth (see
illustrations).
Note:Most oxygen sensor electrical
connectors are located at the rear of the
engine, near the bulkhead. Look for a large
rubber boot attached to a thick wire harness.
On early 535i models, the connector for the
oxygen sensor heater circuit is under the
vehicle. Look for a small protective cover.
These models should have the updated
oxygen sensor fitted, to make access similar
to other models. Consult your dealer service
department for additional information.
13Increase and then decrease the engine
speed, and monitor the voltage.
14When the speed is increased, the voltage
should increase to 0.5 to 1.0 volts. When the
speed is decreased, the voltage should fall to
about 0 to 0.4 volts.
15Also where applicable, inspect the oxygen
sensor heater (models with multi-wire
sensors). With the ignition on, disconnect the
oxygen sensor electrical connector, and
connect a voltmeter across the terminals
designated in the chart (see below). There
should be battery voltage (approximately
12 volts).
16If the reading is not correct, check the
oxygen sensor heater relay (see Chapter 12).
If the information is not available, check the
owner’s handbook for the exact location of
the oxygen sensor heater relay. The relay
should receive battery voltage.
17If the oxygen sensor fails any of these
tests, renew it.
Renewal
Note: Because it is fitted in the exhaust
manifold, converter or pipe, which contracts
when cool, the oxygen sensor may be very
difficult to loosen when the engine is cold.
Rather than risk damage to the sensor(assuming you are planning to re-use it in
another manifold or pipe), start and run the
engine for a minute or two, then switch it off.
Be careful not to burn yourself during the
following procedure.
18Disconnect the battery negative cable.
Caution: If the radio in your
vehicle is equipped with an anti-
theft system, make sure you
have the correct activation code
before disconnecting the battery. Refer to
the information on page 0-7 at the front of
this manual before detaching the cable.
Note: If, after connecting the battery, the
wrong language appears on the instrument
panel display, refer to page 0-7 for the
language resetting procedure.
19Raise and support the vehicle.
20Disconnect the electrical connector from
the sensor.
21Carefully unscrew the sensor.
Caution: Excessive force may
damage the threads.
22A high-temperature anti-seize compound
must be used on the threads of the sensor, to
facilitate future removal. The threads of new
sensors will already be coated with this
compound, but if an old sensor is removed
and refitted, recoat the threads.23Refit the sensor and tighten it securely.
24Reconnect the electrical connector of the
pigtail lead to the main engine wiring harness.
25Lower the vehicle, and reconnect the
battery.
Oxygen Sensor Heated power
sensor type output signal supply (12V)
Unheated
(single-wire) black wire (+) Not applicable
Heated terminal 1 (+) terminals
(three-wire) 3 (+) and 2 (-)
Heated terminal 2 (+) terminals
(four-wire) 4 (+) and 3 (-)
Throttle Position Sensor (TPS)
General description
26The Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) is
located on the end of the throttle shaft on the
throttle body. By monitoring the output
voltage from the TPS, the ECU can determine
fuel delivery based on throttle valve angle
(driver demand). In this system, the TPS acts
as a switch rather than a potentiometer. One
set of throttle valve switch contacts is closed
(continuity) only at idle. A second set of
contacts closes as the engine approaches
full-throttle. Both sets of contacts are open
(no continuity) between these positions. A
broken or loose TPS can cause intermittent
bursts of fuel from the injector and an
unstable idle, because the ECU thinks the
throttle is moving.
27All models (except for early 535i models
with automatic transmission) combine the idle
and full-throttle switch; a separate idle
position switch indicates the closed-throttle
position, while the TPS is used for the full-
throttle position. On 535i models with
automatic transmission, the TPS is connected
directly to the automatic transmission control
unit. With the throttle fully open, the
transmission control unit sends the full-
throttle signal to the Motronic control unit.
All models except early 535i with
automatic transmission
Check
28Remove the electrical connector from the
TPS, and connect an ohmmeter to terminals 2
and 18 (see illustrations). Open the throttle
Engine management and emission control systems 6•3
4.12b These oxygen sensor terminal
designations are for the harness side only.
Use the corresponding terminals on the
sensor side for the testing procedures
(there are three different four-wire oxygen
sensor connectors available - don’t get
them mixed up)4.12a The oxygen sensor, once it is
warmed up (320º C), puts out a very small
voltage signal. To verify it is working,
check for voltage with a digital voltmeter
(the voltage signals usually range from
0.1 to 1.0 volt)
4.28b First check for continuity between
terminals 2 and 18 with the throttle closed
(later Motronic system shown) . . .4.28a The TPS on L-Jetronic systems is
located under the intake manifold
(terminals arrowed)
6
Page 126 of 228
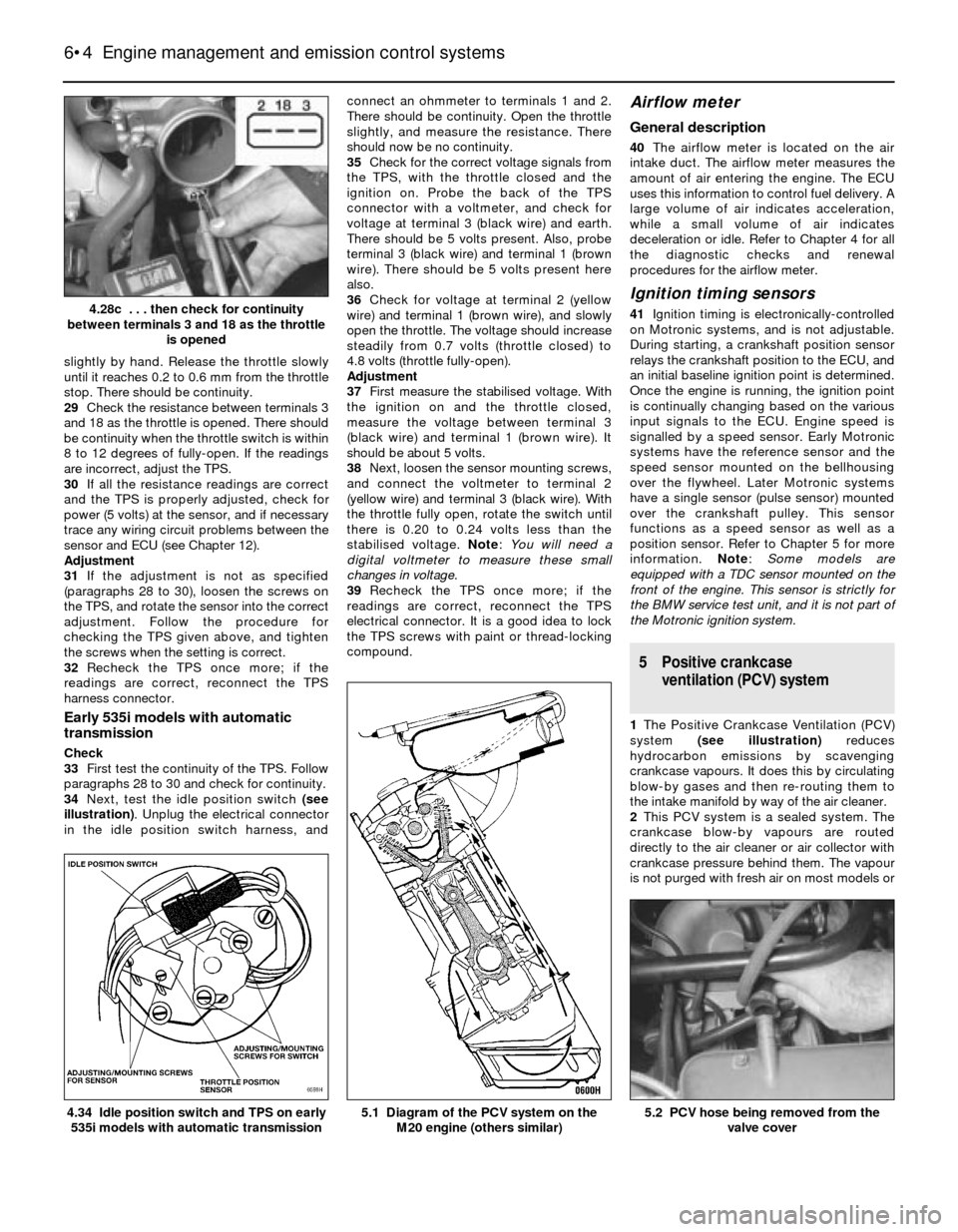
slightly by hand. Release the throttle slowly
until it reaches 0.2 to 0.6 mm from the throttle
stop. There should be continuity.
29Check the resistance between terminals 3
and 18 as the throttle is opened. There should
be continuity when the throttle switch is within
8 to 12 degrees of fully-open. If the readings
are incorrect, adjust the TPS.
30If all the resistance readings are correct
and the TPS is properly adjusted, check for
power (5 volts) at the sensor, and if necessary
trace any wiring circuit problems between the
sensor and ECU (see Chapter 12).
Adjustment
31If the adjustment is not as specified
(paragraphs 28 to 30), loosen the screws on
the TPS, and rotate the sensor into the correct
adjustment. Follow the procedure for
checking the TPS given above, and tighten
the screws when the setting is correct.
32Recheck the TPS once more; if the
readings are correct, reconnect the TPS
harness connector.
Early 535i models with automatic
transmission
Check
33First test the continuity of the TPS. Follow
paragraphs 28 to 30 and check for continuity.
34Next, test the idle position switch (see
illustration). Unplug the electrical connector
in the idle position switch harness, andconnect an ohmmeter to terminals 1 and 2.
There should be continuity. Open the throttle
slightly, and measure the resistance. There
should now be no continuity.
35Check for the correct voltage signals from
the TPS, with the throttle closed and the
ignition on. Probe the back of the TPS
connector with a voltmeter, and check for
voltage at terminal 3 (black wire) and earth.
There should be 5 volts present. Also, probe
terminal 3 (black wire) and terminal 1 (brown
wire). There should be 5 volts present here
also.
36Check for voltage at terminal 2 (yellow
wire) and terminal 1 (brown wire), and slowly
open the throttle. The voltage should increase
steadily from 0.7 volts (throttle closed) to
4.8 volts (throttle fully-open).
Adjustment
37First measure the stabilised voltage. With
the ignition on and the throttle closed,
measure the voltage between terminal 3
(black wire) and terminal 1 (brown wire). It
should be about 5 volts.
38Next, loosen the sensor mounting screws,
and connect the voltmeter to terminal 2
(yellow wire) and terminal 3 (black wire). With
the throttle fully open, rotate the switch until
there is 0.20 to 0.24 volts less than the
stabilised voltage. Note: You will need a
digital voltmeter to measure these small
changes in voltage.
39Recheck the TPS once more; if the
readings are correct, reconnect the TPS
electrical connector. It is a good idea to lock
the TPS screws with paint or thread-locking
compound.
Airflow meter
General description
40The airflow meter is located on the air
intake duct. The airflow meter measures the
amount of air entering the engine. The ECU
uses this information to control fuel delivery. A
large volume of air indicates acceleration,
while a small volume of air indicates
deceleration or idle. Refer to Chapter 4 for all
the diagnostic checks and renewal
procedures for the airflow meter.
Ignition timing sensors
41Ignition timing is electronically-controlled
on Motronic systems, and is not adjustable.
During starting, a crankshaft position sensor
relays the crankshaft position to the ECU, and
an initial baseline ignition point is determined.
Once the engine is running, the ignition point
is continually changing based on the various
input signals to the ECU. Engine speed is
signalled by a speed sensor. Early Motronic
systems have the reference sensor and the
speed sensor mounted on the bellhousing
over the flywheel. Later Motronic systems
have a single sensor (pulse sensor) mounted
over the crankshaft pulley. This sensor
functions as a speed sensor as well as a
position sensor. Refer to Chapter 5 for more
information. Note: Some models are
equipped with a TDC sensor mounted on the
front of the engine. This sensor is strictly for
the BMW service test unit, and it is not part of
the Motronic ignition system.
5 Positive crankcase
ventilation (PCV) system
1The Positive Crankcase Ventilation (PCV)
system (see illustration)reduces
hydrocarbon emissions by scavenging
crankcase vapours. It does this by circulating
blow-by gases and then re-routing them to
the intake manifold by way of the air cleaner.
2This PCV system is a sealed system. The
crankcase blow-by vapours are routed
directly to the air cleaner or air collector with
crankcase pressure behind them. The vapour
is not purged with fresh air on most models or
6•4 Engine management and emission control systems
5.2 PCV hose being removed from the
valve cover5.1 Diagram of the PCV system on the
M20 engine (others similar)4.34 Idle position switch and TPS on early
535i models with automatic transmission
4.28c . . . then check for continuity
between terminals 3 and 18 as the throttle
is opened
Page 169 of 228

12
Chapter 12 Body electrical systems
Bulb renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Central locking system - description and check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Cruise control system - description and check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Direction indicator/hazard warning flasher - check and renewal . . . 5
Electric windows - description and check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Electrical system fault finding - general information . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Fuses - general information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
General information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
Headlight housing - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Headlights - adjustment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Headlights - bulb renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12Heated rear window - check and repair . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Ignition switch - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Instrument cluster - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Radio - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Radio aerial - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Relays - general information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
Service Indicator (SI) board - general information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Steering column switches - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Supplemental Restraint System (SRS) - general information . . . . . . 18
Windscreen/tailgate wiper motor - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . 16
Wiring diagrams - general information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
12•1
Easy,suitable for
novice with little
experienceFairly easy,suitable
for beginner with
some experienceFairly difficult,
suitable for competent
DIY mechanic
Difficult,suitable for
experienced DIY
mechanicVery difficult,
suitable for expert
DIY or professional
Degrees of difficulty Contents
1 General information
The chassis electrical system of this vehicle
is of 12-volt, negative earth type. Power for
the lights and all electrical accessories is
supplied by a lead/acid-type battery, which is
charged by the alternator.
This Chapter covers repair and service
procedures for various chassis (non-engine
related) electrical components. For
information regarding the engine electrical
system components (battery, alternator,
distributor and starter motor), see Chapter 5.
Warning: To prevent electrical
short-circuits, fires and injury,
always disconnect the battery
negative terminal before
checking, repairing or renewing electrical
components.
Caution: If the radio in your
vehicle is equipped with an anti-
theft system, make sure you have
the correct activation code
before disconnecting the battery, Refer to
the information on page 0-7 at the front of
this manual before detaching the cable.
Note: If, after connecting the battery, the
wrong language appears on the instrument
panel display, refer to page 0-7 for the
language resetting procedure.
2 Electrical system fault
finding- general information
2
A typical electrical circuit consists of an
electrical component, any switches, relays,
motors, fuses, fusible links or circuit breakers,
etc related to that component, and the wiring
and connectors that link the components to
both the battery and the chassis. To help you
pinpoint an electrical circuit problem, wiring
diagrams are included at the end of this book.
Before tackling any troublesome electrical
circuit, first study the appropriate wiring
diagrams to get a complete understanding of
what makes up that individual circuit.
Troublespots, for instance, can often be
isolated by noting if other components related
to that circuit are routed through the same
fuse and earth connections.
Electrical problems usually stem from
simple causes such as loose or corroded
connectors, a blown fuse, a melted fusible
link, or a bad relay. Inspect all fuses, wires
and connectors in a problem circuit first.
The basic tools needed include a circuit
tester, a high-impedance digital voltmeter, a
continuity tester and a jumper wire with an in-
line circuit breaker for bypassing electrical
components. Before attempting to locate or
define a problem with electrical testinstruments, use the wiring diagrams to
decide where to make the necessary
connections.
Voltage checks
Perform a voltage check first when a circuit
is not functioning properly. Connect one lead
of a circuit tester to either the negative battery
terminal or a known good earth.
Connect the other lead to a connector in
the circuit being tested, preferably nearest to
the battery or fuse. If the bulb of the tester
lights up, voltage is present, which means that
the part of the circuit between the connector
and the battery is problem-free. Continue
checking the rest of the circuit in the same
fashion.
When you reach a point at which no voltage
is present, the problem lies between that point
and the last test point with voltage. Most of
the time, problems can be traced to a loose
connection.Note:Keep in mind that some
circuits receive voltage only when the ignition
key is turned to a certain position.
Electrical fault diagnosis is simple if you
keep in mind that all electrical circuits are
basically electricity running from the battery,
through the wires, switches, relays, fuses and
fusible links to each electrical component
(light bulb, motor, etc) and then to earth, from
where it is passed back to the battery. Any
electrical problem is an interruption in the flow
of electricity to and from the battery.
Page 170 of 228

Finding a short-circuit
One method of finding a short-circuit is to
remove the fuse and connect a test light or
voltmeter in its place. There should be no
voltage present in the circuit. Move the
electrical connectors from side-to-side while
watching the test light. If the bulb goes on,
there is a short to earth somewhere in that
area, probably where the insulation has been
rubbed through. The same test can be
performed on each component in a circuit,
even a switch.
Earth check
Perform a earth check to see whether a
component is properly earthed (passing
current back via the vehicle body). Disconnect
the battery, and connect one lead of a self-
powered test light (often known as a
continuity tester) to a known good earth.
Connect the other lead to the wire or earth
connection being tested. The bulb should
light, indicating a good earth connection. If
not, dismantle the connection, and clean all
relevant parts thoroughly. When re-making
the connection, use serrated (shakeproof)
washers if possible, and tighten all bolts, etc,
securely.
Caution: If the radio in your
vehicle is equipped with an anti-
theft system, make sure you have
the correct activation code
before disconnecting the battery, Refer to
the information on page 0-7 at the front of
this manual before detaching the cable.
Note: If, after connecting the battery, the
wrong language appears on the instrument
panel display, refer to page 0-7 for the
language resetting procedure.
Continuity check
A continuity check determines if there are
any breaks in a circuit - if it is conducting
electricity properly. With the circuit off (no
power in the circuit), a self-powered continuity
tester can be used to check the circuit.
Connect the test leads to both ends of the
circuit, and if the test light comes on, the
circuit is passing current properly. If the light
doesn’t come on, there is a break somewhere
in the circuit. The same procedure can be
used to test a switch, by connecting the
continuity tester to the power-in and power-
out sides of the switch. With the switch turned
on, the test light should come on.
Finding an open-circuit
When diagnosing for possible open-
circuits, it is often difficult to locate them by
sight, because oxidation or terminal
misalignment are hidden by the connectors.
Intermittent problems are often caused by
oxidised or loose connections. Merely
wiggling an electrical connector may correct
the open-circuit condition, albeit temporarily.
Dismantle the connector, and spray with a
water-dispersant aerosol. On simpler
connectors, it may be possible to carefullybend the connector pins inside, to improve
the metal-to-metal contact - don’t damage
the connector in the process, however.
3 Fuses- general information
1
The electrical circuits of the vehicle are
protected by a combination of fuses and
circuit breakers. The fusebox is located in the
left corner of the engine compartment (see
illustration). On some later models, it is
located under the rear seat cushion.
Each of the fuses is designed to protect a
specific circuit, and on some models, the
various circuits are identified on the fuse
panel itself.
Miniaturised fuses are employed in the
fuseboxes. These compact fuses, with blade
terminal design, allow fingertip removal and
renewal. If an electrical component fails,
always check the fuse first. A blown fuse is
easily identified through the clear plastic
body. Visually inspect the element for
evidence of damage. If a continuity check is
called for, the blade terminal tips are exposed
in the fuse body.
Be sure to renew blown fuses with the
correct type. Fuses of different ratings are
physically interchangeable, but only fuses of
the proper rating should be used. Replacing a
fuse with one of a higher or lower value than
specified is not recommended. Each electrical
circuit needs a specific amount of protection.
The amperage value of each fuse is moulded
into the fuse body.
If the new fuse immediately fails, don’t
renew it again until the cause of the problem
is isolated and corrected. In most cases, the
cause will be a short-circuit in the wiring
caused by a broken or deteriorated wire.
4 Relays- general information
1
Several electrical accessories in the vehicle
use relays to transmit the electrical signal to
the component. If the relay is defective, thatcomponent will not operate properly. Relays
are electrically-operated switches, which are
often used in circuits drawing high levels of
current, or where more complex switching
arrangements are required.
The various relays are grouped together for
convenience in several locations under the
dash and in the engine compartment (see
accompanying illustration and illus-
tration 3.1).
If a faulty relay is suspected, it can be
removed and tested by a dealer or qualified
automotive electrician. No overhaul is
possible. Like fuses, defective relays must be
replaced with the correct type; some relays
look identical, but perform very different
functions.
5 Direction indicator/hazard
warning flasher unit- check
and renewal
2
Warning: Some later models are
equipped with an airbag or
Supplemental Restraint System
(SRS). To avoid possible damage
to this system, the manufacturer
recommends that, on airbag-equipped
models, the following procedure should be
left to a dealer service department, or
other specialist, because of the special
tools and techniques required. There is a
risk of injury if the airbag is accidentally
triggered.
1The direction indicator/hazard flasher unit is
a small canister- or box-shaped unit located
in the wiring harness on or near the steering
column. Access is gained by removing the
steering column shrouds (see illustration).
2When the flasher unit is functioning
properly, a regular clicking noise can be heard
from it when the indicators or hazard flashers
are switched on. If the direction indicators fail
on one side or the other, and the flasher unit
does not make its characteristic clicking
sound, a faulty direction indicator bulb is
indicated.
3If both direction indicators fail to blink, the
problem may be due to a blown fuse, a faulty
flasher unit, a broken switch or a loose or open
connection. If a quick check of the fusebox
12•2 Body electrical systems
4.2 Engine compartment relays3.1 The fusebox is located in the engine
compartment under a cover - the box also
includes several relays
Page 176 of 228
12Refitting is a reversal of removal. When
fitting the motor, if necessary plug in the
connector and run the motor briefly until it is
in the “neutral” (wiper parked) position.
17 Heated rear window-
check and repair
2
1The heated rear window consists of a
number of horizontal elements on the glass
surface.
2Small breaks in the element can be repaired
without removing the rear window.
Check
3Switch on the ignition and the heated rear
window.
4Place the positive lead of a voltmeter to the
heater element nearest to the incoming power
source.
5Wrap a piece of aluminium foil around the
negative lead of the voltmeter on the positive
side of the suspected broken element, and
slide it slowly towards the negative side.
Watch the voltmeter needle - when it moves
from zero, you have located the break.
Repair
6Repair the break in the line using a repair kit
recommended specifically for this purpose,
such as BMW repair kit No. 81 22 9 (or
equivalent). Included in this kit is plastic
conductive epoxy. The following paragraphs
give general instructions for this type of repair;
follow the instructions supplied with the repair
kit if they are different.
7Prior to repairing a break, switch off the
circuit and allow it to cool down for a few
minutes.
8Lightly buff the element area with fine steel
wool, then clean it thoroughly.
9Use masking tape to mask off the area of
repair, leaving a slit to which the epoxy can be
applied.
10Mix the epoxy thoroughly, according to
the instructions on the package.
11Apply the epoxy material to the slit in the
masking tape, overlapping the undamaged
area about 20 mm on each end.12Allow the repair to cure for 24 hours
before removing the tape and using the
heated rear window.
18 Supplemental Restraint
System (SRS)- general
information
Later models are equipped with a
Supplemental Restraint System (SRS),
incorporating an airbag. This system is
designed to protect the driver from serious
injury in the event of a head-on or frontal
collision. It consists of an airbag module in the
centre of the steering wheel, two crash
sensors mounted on the front inner wing
panels, and a crash safety switch located
inside the passenger compartment.
The airbag module contains a housing
incorporating the airbag and the inflator units.
The inflator assembly is mounted on the back
of the housing over a hole through which gas
is expelled, inflating the bag almost instanta-
neously when an electrical signal is sent from
the system. This signal is carried by a wire
which is specially wound with several turns,
so the signal will be transmitted regardless of
the steering wheel position.
The SRS system has three sensors: two at
the front, mounted on the inner wing panels
(see illustration), and a safety switch located
inside the passenger compartment. The crash
sensors are basically pressure-sensitive
switches, which complete an electrical circuit
during an impact of sufficient force. The
electrical signal from the crash sensors is sent
to a third sensor, which then completes the
circuit and inflates the airbag.
The module containing the safety switch
monitors the system operation. It checks the
system every time the vehicle is started,
causing the AIRBAG warning light to come on,
then go out if the system is operating
correctly. If there is a fault in the system, the
light will stay on. If the AIRBAG warning light
does stay on, or if it comes on while driving,
take the vehicle to your dealer immediately.
19 Cruise control system-
description and check
1
The cruise control system maintains vehicle
speed using a vacuum-actuated servo motor
located in the engine compartment, which is
connected to the throttle linkage by a cable.
The system consists of the servo motor,
clutch switch, brake switch, control switches,
a relay, and associated vacuum hoses.
Because of the complexity of the cruise
control system, repair should be left to a
dealer service department. However, it is
possible for the home mechanic to make
simple checks of the wiring and vacuum
connections for minor faults which can be
easily repaired. These include:
a) Inspect the cruise control actuating switches
for broken wires and loose connections.
b) Check the cruise control fuse.
c) The cruise control system is operated by
vacuum, so it’s critical that all vacuum
switches, hoses and connections are
secure. Check the hoses in the engine
compartment for loose connections,
cracks, or obvious vacuum leaks.
20 Central locking system-
description and check
2
The central door locking system operates
the door lock actuators mounted in each
door. The system consists of the switches,
actuators and associated wiring. Diagnosis is
limited to simple checks of the wiring
connections and actuators for minor faults
which can be easily repaired. These include:
a) Check the system fuse and/or circuit
breaker (where applicable).
b) Check the switch wires for damage and
loose connections. Check the switches
for continuity.
c) Remove the door trim panel(s), and check
the actuator wiring connections to see if
they’re loose or damaged. Inspect the
actuator rods to make sure they aren’t
12•8 Body electrical systems
18.3 The SRS system crash sensors
(arrowed) are located in the engine
compartment - check the wiring regularly
for damage16.11b Tailgate wiper motor (5-Series)16.11c Wiper blade and pivot mechanism
on the rear window (5-Series)
Page 211 of 228

REF•10Fault Finding
Engine will not rotate when attempting to start
m mBattery terminal connections loose or corroded (Chapter 1).
m mBattery discharged or faulty (Chapter 1).
m mAutomatic transmission not completely engaged in Park (Chap-
ter 7B) or (on models with a clutch switch) clutch not completely
depressed (Chapter 8).
m mBroken, loose or disconnected wiring in the starting circuit
(Chapters 5 and 12).
m mStarter motor pinion jammed in flywheel ring gear (Chapter 5).
m mStarter solenoid faulty (Chapter 5).
m mStarter motor faulty (Chapter 5).
m mIgnition switch faulty (Chapter 12).
m mStarter pinion or flywheel teeth worn or broken (Chapter 5).
m mEngine internal problem (Chapter 2B).
Engine rotates, but will not start
m
mFuel tank empty.
m mBattery discharged (engine rotates slowly) (Chapter 5).
m mBattery terminal connections loose or corroded (Chapter 1).
m mLeaking fuel injector(s), faulty fuel pump, pressure regulator, etc
(Chapter 4).
m mFuel not reaching fuel injection system or carburettor (Chapter 4).
m mIgnition components damp or damaged (Chapter 5).
m mFuel injector stuck open (Chapter 4).
m mWorn, faulty or incorrectly-gapped spark plugs (Chapter 1).
m mBroken, loose or disconnected wiring in the starting circuit
(Chapter 5).
m mLoose distributor mounting bolts causing ignition timing to wander
(Chapters 1 and 5).
m mBroken, loose or disconnected wires at the ignition coil, or faulty
coil (Chapter 5).
Engine hard to start when cold
m mBattery discharged (Chapter 1).
m mFuel system malfunctioning (Chapter 4).
m mInjector(s) leaking or carburettor automatic choke faulty (Chap-
ter 4).
m mDistributor rotor carbon-tracked (Chapter 5).
Engine hard to start when hot
m
mAir filter element clogged (Chapter 1).
m mFuel not reaching the fuel injection system or carburettor (Chap-
ter 4).
m mCorroded battery connections, especially earth (negative)
connection (Chapter 1).
Starter motor noisy or excessively-rough in
engagement
m mPinion or flywheel gear teeth worn or broken (Chapter 5).
m mStarter motor mounting bolts loose or missing (Chapter 5).
Engine starts, but stops immediately
m
mLoose or faulty electrical connections at distributor, coil or
alternator (Chapter 5).
m mInsufficient fuel reaching the fuel injector(s) or carburettor
(Chapters 1 and 4).
m mDamaged fuel injection system speed sensors (Chapter 5).
m mFaulty fuel injection relays (Chapter 5).
Oil puddle under engine
m
mOil sump gasket and/or sump drain plug seal leaking (Chapter 2).
m mOil pressure sender unit leaking (Chapter 2).
m mValve cover gaskets leaking (Chapter 2).
m mEngine oil seals leaking (Chapter 2).
Engine idles erratically
m
mVacuum leakage (Chapter 4).
m mAir filter element clogged (Chapter 1).
m mFuel pump not delivering sufficient fuel to the fuel injection system
or carburettor (Chapter 4).
m mLeaking head gasket (Chapter 2).
m mTiming belt/chain and/or sprockets worn (Chapter 2).
m mCamshaft lobes worn (Chapter 2).
m mFaulty charcoal canister, where fitted (Chapter 6). This Section provides an easy-reference guide to the more
common problems which may occur during the operation of your
vehicle. These problems and their possible causes are grouped under
headings denoting various components or systems, such as Engine,
Cooling system, etc. They also refer you to the Chapter and/or
Section which deals with the problem.
Remember that successful fault diagnosis is not a mysterious
black art practised only by professional mechanics. It is simply the
result of the right knowledge combined with an intelligent, systematic
approach to the problem. Always work by a process of elimination,
starting with the simplest solution and working through to the mostcomplex - and never overlook the obvious. Anyone can run the fuel
tank dry or leave the lights on overnight, so don’t assume that you are
exempt from such oversights.
Finally, always establish a clear idea of why a problem has
occurred, and take steps to ensure that it doesn’t happen again. If the
electrical system fails because of a poor connection, check all other
connections in the system to make sure that they don’t fail as well. If a
particular fuse continues to blow, find out why - don’t just renew one
fuse after another. Remember, failure of a small component can often
be indicative of potential failure or incorrect functioning of a more
important component or system.
Engine
Page 227 of 228

REF•27
REF
Index
R
Radiator - 3•3, 11•4
Radio - 12•4
Receiver-drier - 3•9
Regulator (voltage) - 5•10
Regulator (window) - 11•8
Relays - 12•2
Repair procedures - REF•8
Respraying - 11•3
Reversing light switch - 7B•4
Rocker arms - 2B•11
Rotor - 1•18
Routine maintenance and servicing- 1•1
et seq
Routine maintenance - air conditioning
system - 3•8
Routine maintenance - bodywork and
underframe - 11•1
Routine maintenance - hinges and locks -
11•4
Routine maintenance - interior trim - 11•2
Routine maintenance - upholstery and
carpets - 11•2
Rust holes in bodywork - 11•2
S
Safety first! - 0•5
Scalding - 0•5
Scratches in bodywork - 11•2
Screw threads and fastenings - REF•8
Seat belt - 11•9, REF•2
Seats - 11•9, REF•2
Selector lever - 7B•3, 7B•5
Selector shaft - 7A•2
Service Indicator (SI) board - 12•4
Service indicator light - 1•26
Servo - 9•2, 9•10, 9•11
Shock absorber - 1•21, 10•7, 10•8, 10•9,
REF•2, REF•3
Shoes - 9•7
Short-circuit - 12•2Silencer - 4•20
Slave cylinder - 8•3
Spares - REF•19
Spark plug - 1•17, 1•18
Speed sensors - 5•8
Springs - 10•7, 10•9, REF•3
Starter inhibitor - 7B•4
Starter motor - 5•12
Starter motor fault - REF•10
Starting system - 5•11
Steering box - 10•15
Steering column - 11•9, 12•3, REF•1
Steering gear - 10•12, 10•13, REF•3
Steering linkage - 10•14
Steering wheel - 10•16, REF•1
Stop-light switch - 9•13
Struts - 1•21, 10•6, 10•7
Sump - 2A•15
Supplemental Restraint System (SRS) -
12•8
Suspension and steering systems- 1•21,
1•22, 10•1et seq, REF•2, REF•3
Suspension and steering fault finding -
REF•15
Switches - 7B•4, 9•13, 12•3
T
Tailgate - 11•6
Tappets - 2B•11
Thermostat - 3•2
Thermotime switch - 4•17, 4•18
Throttle body - 4•16
Throttle linkage - 1•20
Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) - 6•3
Throttle positioner - 4•13, 4•14
Thrust arm - 10•5
Timing - 5•4
Timing belt - 1•26, 2A•8, 2A•9
Timing chain - 2A•6, 2A•8
Timing sensors - 6•4
Tools - REF•5, REF•7, REF•8
Top Dead Centre (TDC) for No 1 piston -
2A•3Torque converter - 7B•5
Towing - 0•8
Track rod ends - 10•13
Trailing arms - 10•10
Transmission - SeeManual transmission or
Automatic transmission
Trim - 11•2, 11•6
Tyres - 1•9, 1•14, 10•16, REF•4, REF•15
U
Underframe - 11•1
Universal joints - 8•8
Upholstery - 11•2
V
Vacuum hoses - 1•14
Vacuum servo - 9•10
Valve clearances - 1•19
Valve cover - 2A•4
Valves - 2B•10, 2B•11
Vehicle identification - REF•2, REF•19
Voltage checks - 12•1
Voltage regulator - 5•10
W
Washer fluid - 1•9
Water pump - 3•5
Weekly checks- 1•7et seq
Wheel alignment - 10•17
Wheel bearings - 10•8, 10•11, REF•3
Wheel changing - 0•8
Wheels - 10•16, REF•4
Windows - 11•8, 12•9
Windscreen - REF•1
Wiper blades - 1•23
Wiper motor - 12•7
Wiring diagrams- 12•9et seq
Working faclities - REF•7