bolt pattern BMW 3 SERIES 1983 E30 Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: BMW, Model Year: 1983, Model line: 3 SERIES, Model: BMW 3 SERIES 1983 E30Pages: 228, PDF Size: 7.04 MB
Page 8 of 228

0•8Roadside Repairs
Jacking and wheel
changing
The jack supplied with the vehicle should
be used only for raising the vehicle when
changing a tyre or placing axle stands under
the frame.
Warning:Never crawl under the
vehicle or start the engine when
this jack is being used as the
only means of support.
When changing a wheel, the vehicle should
be on level ground, with the handbrake firmly
applied, and the wheels chocked. Select
reverse gear (manual transmission) or Park
(automatic transmission). Prise off the hub
cap (if equipped) using the tapered end of the
wheel brace. Loosen the wheel bolts half a
turn, leaving them in place until the wheel is
raised off the ground.
Position the head of the jack under the side
of the vehicle, making sure it engages with thepocket made for this purpose (just behind the
front wheel, or forward of the rear wheel).
Engage the wheel brace handle and turn it
clockwise until the wheel is raised off the
ground. Unscrew the bolts, remove the wheel
and fit the spare.
Refit the wheel bolts and tighten them
finger-tight. Lower the vehicle by turning the
wheel brace anti-clockwise. Remove the jack
and tighten the bolts in a diagonal pattern to
the torque listed in the Chapter 1
Specifications. If a torque wrench is not
available, have the torque checked by a BMW
dealer or tyre fitting specialist as soon as
possible. Refit the hubcap.
Towing
Vehicles with manual transmission can be
towed with all four wheels on the ground, if
necessary. Automatic transmission-equipped
vehicles can only be towed with all fourwheels on the ground providing that the
speed does not exceed 35 mph and the
distance is not over 50 miles, otherwise
transmission damage can result. For
preference, regardless of transmission type,
the vehicle should be towed with the driven
(rear) wheels off the ground.
Proper towing equipment, specifically
designed for the purpose, should be used,
and should be attached to the main structural
members of the vehicle, not to the bumpers or
bumper brackets. Sling-type towing
equipment must notbe used on these
vehicles.
Safety is a major consideration while
towing. The handbrake should be released,
and the transmission should be in neutral. The
steering must be unlocked (ignition switch
turned to position “1”). Remember that
power-assisted steering (where fitted) and the
brake servo will not work with the engine
switched off.
Jacking, towing and wheel changing
Page 23 of 228

Caution: Do not overfill the
reservoir. If too much fluid is
added, remove the excess with a
clean syringe. Refit the cap.
7If frequent topping-up is needed, check the
power steering hoses and connections for
leaks and wear (see Section 10).
8Check the condition and tension of the
drivebelt (see Section 11).
8 Automatic transmission fluid
level check
1
Caution: The use of transmission
fluid other than the type listed in
this Chapter’s Specifications
could result in transmission
malfunctions or failure.
1The automatic transmission fluid should be
carefully maintained. Low fluid level can lead
to slipping or loss of drive, while overfilling
can cause foaming and loss of fluid. Either
condition can cause transmission damage.
2Since transmission fluid expands as it heats
up, the fluid level should only be checked
when the transmission is warm (at normal
operating temperature). If the vehicle has just
been driven over 20 miles (32 km), the
transmission can be considered warm. You
can also check the fluid level when the
transmission is cold. If the vehicle has not
been driven for over five hours and the fluid is
about room temperature (20°C), the
transmission is cold. However, the fluid level
is normally checked with the transmission
warm, to ensure accurate results.
Caution: If the vehicle has just
been driven for a long time at
high speed or in city traffic, in hot
weather, or if it has been pulling
a trailer, an accurate fluid level reading
cannot be obtained. Allow the trans-
mission to cool down for about 30 minutes.
3Immediately after driving the vehicle, park it
on a level surface, apply the handbrake and
start the engine. While the engine is idling,
depress the brake pedal and move theselector lever through all the gear ranges,
beginning and ending in Park.
4The automatic transmission dipstick tube is
located in the left rear corner of the engine
compartment.
5With the engine still idling, pull the dipstick
out of the tube (see illustration), wipe it off
with a clean rag, push it all the way back into
the tube and withdraw it again, then note the
fluid level.
6The level should be between the two marks
(see illustration). If the level is low, add the
specified automatic transmission fluid through
the dipstick tube - use a clean funnel,
preferably equipped with a fine mesh filter, to
prevent spills.
Caution: Be careful not to
introduce dirt into the
transmission when topping up.
7Add just enough of the recommended fluid
to fill the transmission to the proper level. It
takes about half a litre to raise the level from
the low mark to the high mark when the fluid
is hot, so add the fluid a little at a time, and
keep checking the level until it’s correct.
8The condition of the fluid should also be
checked along with the level. If the fluid is
black or a dark reddish-brown colour, or if it
smells burned, it should be changed (see
Section 28). If you are in doubt about its
condition, purchase some new fluid, and
compare the two for colour and smell.
9 Tyre rotation
1
1The tyres can be rotated at the specified
intervals, or whenever uneven wear is noticed.
However, bear in mind that if rotation
succeeds in making all the tyres wear evenly,
you will eventually have to renew all four at
once. Since the vehicle will be raised and the
wheels removed anyway, check the brakes
also (see Section 26). Note: Even if you don’t
rotate the tyres, at least check the wheel bolt
tightness.
2It is recommended that the tyres be rotatedin a specific pattern (see illustration)so that
their direction of rotation remains the same.
3Refer to the information in “Jacking and
towing”at the front of this manual for the
proper procedure to follow when raising the
vehicle and changing a tyre.
4The vehicle must be raised on a hoist or
supported on axle stands to get all four tyres
off the ground. Make sure the vehicle is safely
supported!
5After the rotation procedure is finished,
check and adjust the tyre pressures as
necessary, and be sure to check the wheel
bolt tightness.
10 Underbonnet hose check
and renewal
3
Warning: Renewal of air
conditioning hoses must be left
to a dealer service department or
air conditioning specialist having
the equipment to depressurise the system
safely. Never disconnect air conditioning
hoses or components until the system has
been depressurised.
General
1High temperatures under the bonnet can
cause deterioration of the rubber and plastic
hoses used for various systems. Periodic
inspection should be made for cracks, loose
clamps, material hardening, and leaks.
2Information specific to the cooling system
can be found in Section 22, while the braking
system is covered in Section 26.
3Most (but not all) hoses are secured with
clamps. Where clamps are used, check to be
sure they haven’t lost their tension, allowing
the hose to leak. If clamps aren’t used, make
sure the hose has not expanded and/or
hardened where it slips over the fitting,
allowing it to leak.
Vacuum hoses
4It’s quite common for vacuum hoses,
especially those in the emissions system, to
be colour-coded or identified by coloured
1•13
9.2 The tyre rotation pattern for these
models8.6 With the fluid hot, the level should be
kept between the two dipstick notches,
preferably near the upper one8.5 The automatic transmission fluid
dipstick (arrowed) is located near the
bulkhead on the left side of the engine
compartment
1
Every 6000 miles
Page 33 of 228
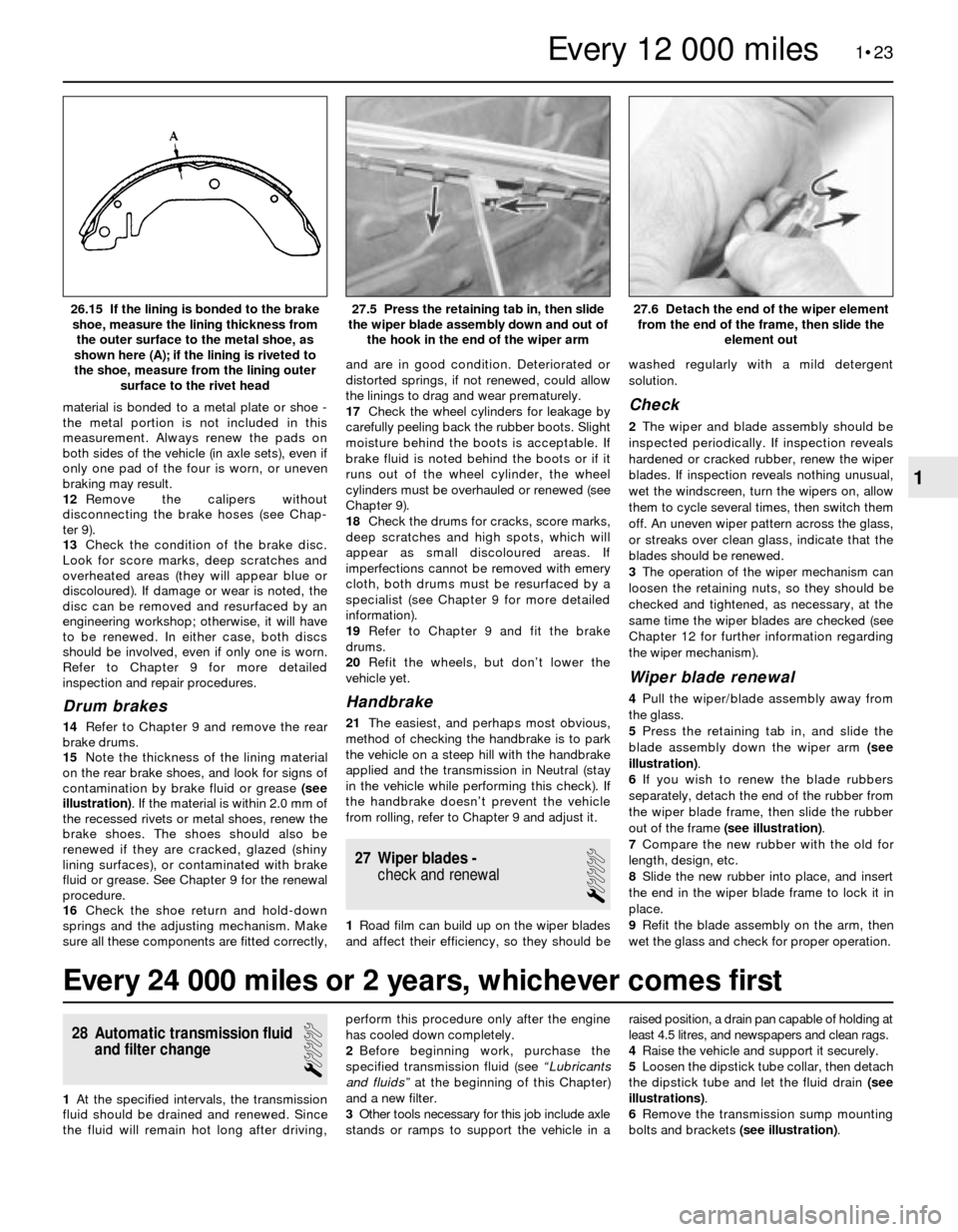
material is bonded to a metal plate or shoe -
the metal portion is not included in this
measurement. Always renew the pads on
both sides of the vehicle (in axle sets), even if
only one pad of the four is worn, or uneven
braking may result.
12Remove the calipers without
disconnecting the brake hoses (see Chap-
ter 9).
13Check the condition of the brake disc.
Look for score marks, deep scratches and
overheated areas (they will appear blue or
discoloured). If damage or wear is noted, the
disc can be removed and resurfaced by an
engineering workshop; otherwise, it will have
to be renewed. In either case, both discs
should be involved, even if only one is worn.
Refer to Chapter 9 for more detailed
inspection and repair procedures.
Drum brakes
14Refer to Chapter 9 and remove the rear
brake drums.
15Note the thickness of the lining material
on the rear brake shoes, and look for signs of
contamination by brake fluid or grease (see
illustration). If the material is within 2.0 mm of
the recessed rivets or metal shoes, renew the
brake shoes. The shoes should also be
renewed if they are cracked, glazed (shiny
lining surfaces), or contaminated with brake
fluid or grease. See Chapter 9 for the renewal
procedure.
16Check the shoe return and hold-down
springs and the adjusting mechanism. Make
sure all these components are fitted correctly,and are in good condition. Deteriorated or
distorted springs, if not renewed, could allow
the linings to drag and wear prematurely.
17Check the wheel cylinders for leakage by
carefully peeling back the rubber boots. Slight
moisture behind the boots is acceptable. If
brake fluid is noted behind the boots or if it
runs out of the wheel cylinder, the wheel
cylinders must be overhauled or renewed (see
Chapter 9).
18Check the drums for cracks, score marks,
deep scratches and high spots, which will
appear as small discoloured areas. If
imperfections cannot be removed with emery
cloth, both drums must be resurfaced by a
specialist (see Chapter 9 for more detailed
information).
19Refer to Chapter 9 and fit the brake
drums.
20Refit the wheels, but don’t lower the
vehicle yet.
Handbrake
21The easiest, and perhaps most obvious,
method of checking the handbrake is to park
the vehicle on a steep hill with the handbrake
applied and the transmission in Neutral (stay
in the vehicle while performing this check). If
the handbrake doesn’t prevent the vehicle
from rolling, refer to Chapter 9 and adjust it.
27 Wiper blades -
check and renewal
1
1Road film can build up on the wiper blades
and affect their efficiency, so they should bewashed regularly with a mild detergent
solution.
Check
2The wiper and blade assembly should be
inspected periodically. If inspection reveals
hardened or cracked rubber, renew the wiper
blades. If inspection reveals nothing unusual,
wet the windscreen, turn the wipers on, allow
them to cycle several times, then switch them
off. An uneven wiper pattern across the glass,
or streaks over clean glass, indicate that the
blades should be renewed.
3The operation of the wiper mechanism can
loosen the retaining nuts, so they should be
checked and tightened, as necessary, at the
same time the wiper blades are checked (see
Chapter 12 for further information regarding
the wiper mechanism).
Wiper blade renewal
4Pull the wiper/blade assembly away from
the glass.
5Press the retaining tab in, and slide the
blade assembly down the wiper arm (see
illustration).
6If you wish to renew the blade rubbers
separately, detach the end of the rubber from
the wiper blade frame, then slide the rubber
out of the frame (see illustration).
7Compare the new rubber with the old for
length, design, etc.
8Slide the new rubber into place, and insert
the end in the wiper blade frame to lock it in
place.
9Refit the blade assembly on the arm, then
wet the glass and check for proper operation.
1•23
27.6 Detach the end of the wiper element
from the end of the frame, then slide the
element out27.5 Press the retaining tab in, then slide
the wiper blade assembly down and out of
the hook in the end of the wiper arm26.15 If the lining is bonded to the brake
shoe, measure the lining thickness from
the outer surface to the metal shoe, as
shown here (A); if the lining is riveted to
the shoe, measure from the lining outer
surface to the rivet head
1
Every 12 000 miles
Every 24 000 miles or 2 years, whichever comes first
28 Automatic transmission fluid
and filter change
1
1At the specified intervals, the transmission
fluid should be drained and renewed. Since
the fluid will remain hot long after driving,perform this procedure only after the engine
has cooled down completely.
2Before beginning work, purchase the
specified transmission fluid (see “Lubricants
and fluids”at the beginning of this Chapter)
and a new filter.
3Other tools necessary for this job include axle
stands or ramps to support the vehicle in araised position, a drain pan capable of holding at
least 4.5 litres, and newspapers and clean rags.
4Raise the vehicle and support it securely.
5Loosen the dipstick tube collar, then detach
the dipstick tube and let the fluid drain (see
illustrations).
6Remove the transmission sump mounting
bolts and brackets (see illustration).
Page 43 of 228
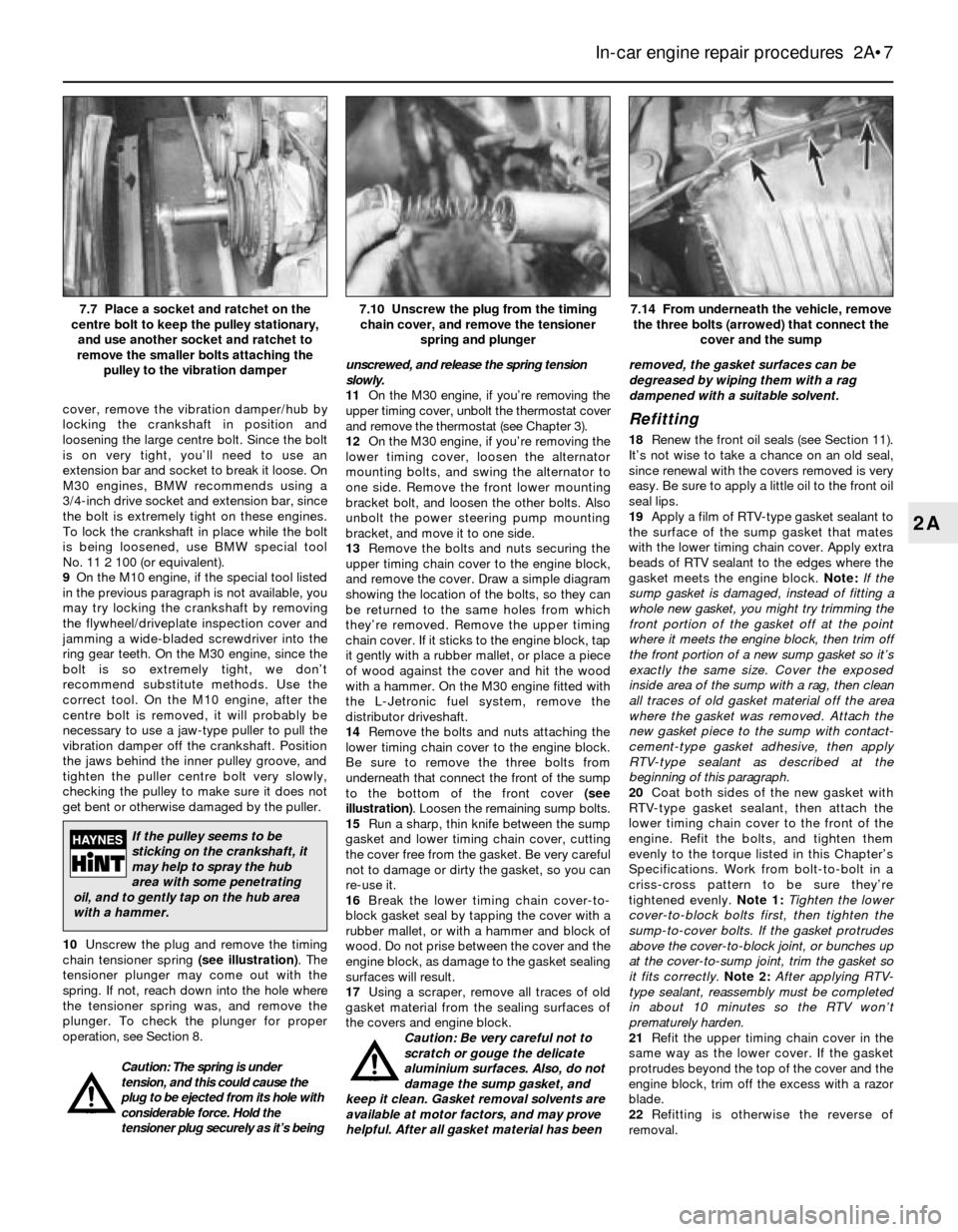
cover, remove the vibration damper/hub by
locking the crankshaft in position and
loosening the large centre bolt. Since the bolt
is on very tight, you’ll need to use an
extension bar and socket to break it loose. On
M30 engines, BMW recommends using a
3/4-inch drive socket and extension bar, since
the bolt is extremely tight on these engines.
To lock the crankshaft in place while the bolt
is being loosened, use BMW special tool
No. 11 2 100 (or equivalent).
9On the M10 engine, if the special tool listed
in the previous paragraph is not available, you
may try locking the crankshaft by removing
the flywheel/driveplate inspection cover and
jamming a wide-bladed screwdriver into the
ring gear teeth. On the M30 engine, since the
bolt is so extremely tight, we don’t
recommend substitute methods. Use the
correct tool. On the M10 engine, after the
centre bolt is removed, it will probably be
necessary to use a jaw-type puller to pull the
vibration damper off the crankshaft. Position
the jaws behind the inner pulley groove, and
tighten the puller centre bolt very slowly,
checking the pulley to make sure it does not
get bent or otherwise damaged by the puller.
10Unscrew the plug and remove the timing
chain tensioner spring (see illustration). The
tensioner plunger may come out with the
spring. If not, reach down into the hole where
the tensioner spring was, and remove the
plunger. To check the plunger for proper
operation, see Section 8.
Caution: The spring is under
tension, and this could cause the
plug to be ejected from its hole with
considerable force. Hold the
tensioner plug securely as it’s beingunscrewed, and release the spring tension
slowly.
11On the M30 engine, if you’re removing the
upper timing cover, unbolt the thermostat cover
and remove the thermostat (see Chapter 3).
12On the M30 engine, if you’re removing the
lower timing cover, loosen the alternator
mounting bolts, and swing the alternator to
one side. Remove the front lower mounting
bracket bolt, and loosen the other bolts. Also
unbolt the power steering pump mounting
bracket, and move it to one side.
13Remove the bolts and nuts securing the
upper timing chain cover to the engine block,
and remove the cover. Draw a simple diagram
showing the location of the bolts, so they can
be returned to the same holes from which
they’re removed. Remove the upper timing
chain cover. If it sticks to the engine block, tap
it gently with a rubber mallet, or place a piece
of wood against the cover and hit the wood
with a hammer. On the M30 engine fitted with
the L-Jetronic fuel system, remove the
distributor driveshaft.
14Remove the bolts and nuts attaching the
lower timing chain cover to the engine block.
Be sure to remove the three bolts from
underneath that connect the front of the sump
to the bottom of the front cover (see
illustration). Loosen the remaining sump bolts.
15Run a sharp, thin knife between the sump
gasket and lower timing chain cover, cutting
the cover free from the gasket. Be very careful
not to damage or dirty the gasket, so you can
re-use it.
16Break the lower timing chain cover-to-
block gasket seal by tapping the cover with a
rubber mallet, or with a hammer and block of
wood. Do not prise between the cover and the
engine block, as damage to the gasket sealing
surfaces will result.
17Using a scraper, remove all traces of old
gasket material from the sealing surfaces of
the covers and engine block.
Caution: Be very careful not to
scratch or gouge the delicate
aluminium surfaces. Also, do not
damage the sump gasket, and
keep it clean. Gasket removal solvents are
available at motor factors, and may prove
helpful. After all gasket material has beenremoved, the gasket surfaces can be
degreased by wiping them with a rag
dampened with a suitable solvent.Refitting
18Renew the front oil seals (see Section 11).
It’s not wise to take a chance on an old seal,
since renewal with the covers removed is very
easy. Be sure to apply a little oil to the front oil
seal lips.
19Apply a film of RTV-type gasket sealant to
the surface of the sump gasket that mates
with the lower timing chain cover. Apply extra
beads of RTV sealant to the edges where the
gasket meets the engine block. Note:If the
sump gasket is damaged, instead of fitting a
whole new gasket, you might try trimming the
front portion of the gasket off at the point
where it meets the engine block, then trim off
the front portion of a new sump gasket so it’s
exactly the same size. Cover the exposed
inside area of the sump with a rag, then clean
all traces of old gasket material off the area
where the gasket was removed. Attach the
new gasket piece to the sump with contact-
cement-type gasket adhesive, then apply
RTV-type sealant as described at the
beginning of this paragraph.
20Coat both sides of the new gasket with
RTV-type gasket sealant, then attach the
lower timing chain cover to the front of the
engine. Refit the bolts, and tighten them
evenly to the torque listed in this Chapter’s
Specifications. Work from bolt-to-bolt in a
criss-cross pattern to be sure they’re
tightened evenly.Note 1:Tighten the lower
cover-to-block bolts first, then tighten the
sump-to-cover bolts. If the gasket protrudes
above the cover-to-block joint, or bunches up
at the cover-to-sump joint, trim the gasket so
it fits correctly.Note 2:After applying RTV-
type sealant, reassembly must be completed
in about 10 minutes so the RTV won’t
prematurely harden.
21Refit the upper timing chain cover in the
same way as the lower cover. If the gasket
protrudes beyond the top of the cover and the
engine block, trim off the excess with a razor
blade.
22Refitting is otherwise the reverse of
removal.
In-car engine repair procedures 2A•7
7.14 From underneath the vehicle, remove
the three bolts (arrowed) that connect the
cover and the sump7.10 Unscrew the plug from the timing
chain cover, and remove the tensioner
spring and plunger7.7 Place a socket and ratchet on the
centre bolt to keep the pulley stationary,
and use another socket and ratchet to
remove the smaller bolts attaching the
pulley to the vibration damper
2A
If the pulley seems to be
sticking on the crankshaft, it
may help to spray the hub
area with some penetrating
oil, and to gently tap on the hub area
with a hammer.
Page 49 of 228

22Using a scraper, remove all traces of old
gasket material from the sealing surfaces of
the covers and engine block.
Caution: Be very careful not to
scratch or gouge the delicate
aluminium surfaces. Also, do not
damage the sump gasket, and
keep it clean. Gasket removal solvents are
available at motor factors, and may
prove helpful. After all gasket material has
been removed, the gasket surfaces
can be degreased by wiping them
with a rag dampened with a suitable
solvent.
23Support the cover on two blocks of wood,
and drive out the seals from behind with a
hammer and screwdriver. Be very careful not
to damage the seal bores in the process.
24Coat the outside diameters and lips of the
new seals with multi-purpose grease, and
drive the seals into the cover with a hammer
and a socket slightly smaller in diameter than
the outside diameter of the seal.
25Apply a film of RTV-type gasket sealant to
the surface of the sump gasket that mates
with the front cover. Apply extra beads of RTV
sealant to the edges where the gasket meets
the engine block. Note:If the sump gasket is
damaged, instead of fitting a whole new
gasket, you might try trimming the front
portion of the gasket off at the point where it
meets the engine block, then trim off the front
portion of a new sump gasket so it’s exactly
the same size. Cover the exposed inside area
of the sump with a rag, then clean all traces of
old gasket material off the area where the
gasket was removed. Attach the new gasket
piece to the sump with contact-cement-type
gasket adhesive, then apply RTV-type sealant
as described at the beginning of this
paragraph.
26Coat both sides of the new gasket with
RTV-type gasket sealant, then attach the front
cover to the front of the engine, carefully
working the seals over the crankshaft and
intermediate shaft. Refit the bolts and tighten
them evenly to the torque listed in this
Chapter’s Specifications. Work from bolt-to-
bolt in a criss-cross pattern, to be sure they’re
tightened evenly.Note 1:Tighten the front
cover-to-block bolts first, then tighten the
sump-to-cover bolts. Note 2:After applying
RTV-type sealant, reassembly must be
completed in about 10 minutes so the RTV
won’t prematurely harden.
27The remainder of refitting is the reverse of
removal.
Crankshaft front seal (M40 engines)
28Remove the timing belt and crankshaft
sprocket (see Section 10).
29Remove the Woodruff key from the
groove in the end of the crankshaft.
30Note the fitted position of the oil seal, then
prise it out from the front cover using a
screwdriver, but take care not to damage the
bore of the cover or the surface of thecrankshaft. If the seal is tight, drill two small
holes in the metal end of the seal, and use two
self-tapping screws to pull out the seal. Make
sure all remains of swarf are removed.
31Coat the outside diameter and lip of the
new seal with multi-purpose grease, then
drive it into the cover with a hammer and a
socket slightly smaller in diameter than the
outside diameter of the seal. Make sure the
seal enters squarely.
32The remainder of refitting is the reverse of
removal. Note that it is recommended that the
timing belt be renewed - see Section 10.
12 Cylinder head-
removal and refitting
5
Removal
1Relieve the fuel pressure on all fuel injection
engines (see Chapter 4).
2Disconnect the negative cable from the
battery. Where the battery is located in the
engine compartment, the battery may be
removed completely (see Chapter 5).
Caution: If the radio in your
vehicle is equipped with an anti-
theft system, make sure you
have the correct activation code
before disconnecting the battery.
Note: If, after connecting the battery, the
wrong language appears on the instrument
panel display, refer to page 0-7 for the
language resetting procedure.
3Remove the air cleaner assembly (see
Chapter 4).
4Disconnect the wiring from the distributor
(mark all wiring for position first, if necessary),
and the HT lead from the coil (see Chapter 5).
5Disconnect the lead from the coolant
temperature sender unit (see Chapter 3).
6Disconnect the fuel lines from the fuel rail or
carburettor as applicable (see Chapter 4).
7Drain the cooling system (see Chapter 3).
8Clearly label then disconnect all other
hoses from the throttle body, intake manifold,
carburettor and cylinder head, as applicable.
9Disconnect the throttle cable from the
throttle linkage or carburettor (see Chapter 4).
10Disconnect the exhaust manifold from the
cylinder head (see Section 6). Depending on
the engine type, It may not be necessary to
disconnect the manifold from the exhaust
pipe; however, on right-hand-drive models,
the steering column intermediate shaft may
not allow the manifold to clear the studs on
the cylinder head.
11Remove or disconnect any remaining
hoses or lines from the intake manifold,
including the ignition advance vacuum line(s),
and the coolant and heater hoses.
12On early carburettor models, disconnect
the wiring from the alternator and starter
motor.13Remove the intake manifold (see Sec-
tion 5). Do not dismantle or remove any fuel
injection system components unless it is
absolutely necessary.
14Remove the fan drivebelt and fan (see
Chapter 3).
15Remove the valve cover and gasket (see
Section 4). Remove the semi-circular rubber
seal from the front of the cylinder head, where
this is not incorporated in the valve cover
gasket.
16Set No 1 piston at Top Dead Centre on
the compression stroke (see Section 3).
17Remove the timing chain or belt (see
Section 8 or 10). Note:If you want to save
time by not removing and refitting the timing
belt or chain and re-timing the engine, you can
unfasten the camshaft sprocket and suspend
it out of the way - with the belt or chain still
attached - by a piece of rope. Be sure the
rope keeps firm tension on the belt or chain,
so it won’t become disengaged from any of
the sprockets.
18Loosen the cylinder head bolts a quarter-
turn at a time each, in the reverse of the
tightening sequence shown (see illustrations
12.30a, 12.30b, 12.30c or 12.30d). Do
notdismantle or remove the rocker arm
assembly at this time on M10, M20 and M30
engines.
19Remove the cylinder head by lifting it
straight up and off the engine block. Do not
prise between the cylinder head and the
engine block, as damage to the gasket sealing
surfaces may result. Instead, use a blunt bar
positioned in an intake port to gently prise the
head loose.
20Remove any remaining external
components from the head to allow for
thorough cleaning and inspection. See
Chapter 2B for cylinder head servicing
procedures. On the M40 engine, remove the
rubber O-ring from the groove in the top of the
oil pump/front end cover housing.
Refitting
21The mating surfaces of the cylinder head
and block must be perfectly clean when the
head is refitted.
22Use a gasket scraper to remove all traces
of carbon and old gasket material, then clean
the mating surfaces with a suitable solvent. If
there’s oil on the mating surfaces when the
head is refitted, the gasket may not seal
correctly, and leaks could develop. When
working on the block, stuff the cylinders with
clean rags to keep out debris. Use a vacuum
cleaner to remove material that falls into the
cylinders.
23Check the block and head mating
surfaces for nicks, deep scratches and other
damage. If the damage is slight, it can be
removed with a file; if it’s excessive,
machining may be the only alternative.
24Use a tap of the correct size to chase the
threads in the head bolt holes, then clean the
holes with compressed air - make sure that
In-car engine repair procedures 2A•13
2A
Page 51 of 228
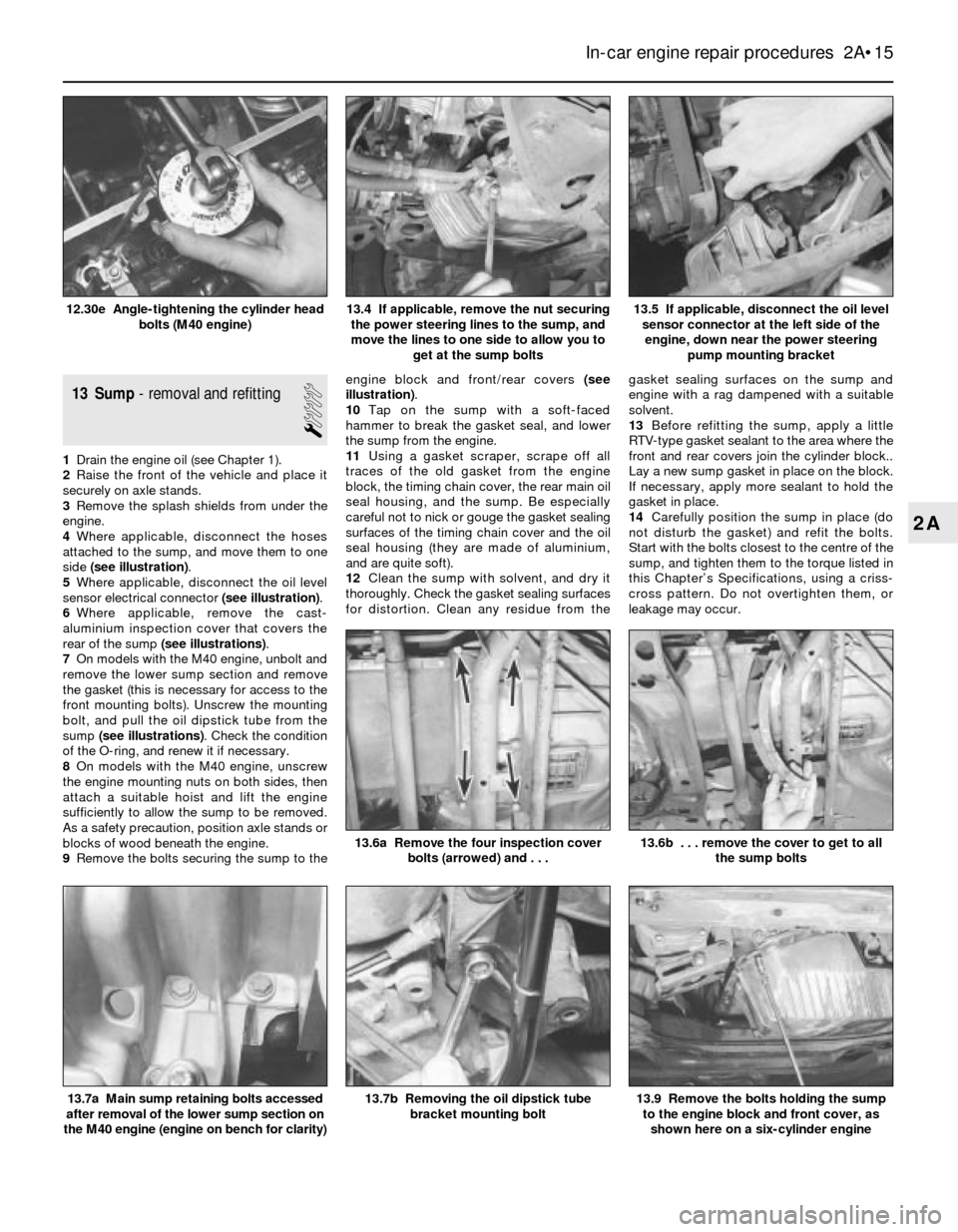
13 Sump- removal and refitting
1
1Drain the engine oil (see Chapter 1).
2Raise the front of the vehicle and place it
securely on axle stands.
3Remove the splash shields from under the
engine.
4Where applicable, disconnect the hoses
attached to the sump, and move them to one
side (see illustration).
5Where applicable, disconnect the oil level
sensor electrical connector (see illustration).
6Where applicable, remove the cast-
aluminium inspection cover that covers the
rear of the sump (see illustrations).
7On models with the M40 engine, unbolt and
remove the lower sump section and remove
the gasket (this is necessary for access to the
front mounting bolts). Unscrew the mounting
bolt, and pull the oil dipstick tube from the
sump (see illustrations). Check the condition
of the O-ring, and renew it if necessary.
8On models with the M40 engine, unscrew
the engine mounting nuts on both sides, then
attach a suitable hoist and lift the engine
sufficiently to allow the sump to be removed.
As a safety precaution, position axle stands or
blocks of wood beneath the engine.
9Remove the bolts securing the sump to theengine block and front/rear covers (see
illustration).
10Tap on the sump with a soft-faced
hammer to break the gasket seal, and lower
the sump from the engine.
11Using a gasket scraper, scrape off all
traces of the old gasket from the engine
block, the timing chain cover, the rear main oil
seal housing, and the sump. Be especially
careful not to nick or gouge the gasket sealing
surfaces of the timing chain cover and the oil
seal housing (they are made of aluminium,
and are quite soft).
12Clean the sump with solvent, and dry it
thoroughly. Check the gasket sealing surfaces
for distortion. Clean any residue from thegasket sealing surfaces on the sump and
engine with a rag dampened with a suitable
solvent.
13Before refitting the sump, apply a little
RTV-type gasket sealant to the area where the
front and rear covers join the cylinder block..
Lay a new sump gasket in place on the block.
If necessary, apply more sealant to hold the
gasket in place.
14Carefully position the sump in place (do
not disturb the gasket) and refit the bolts.
Start with the bolts closest to the centre of the
sump, and tighten them to the torque listed in
this Chapter’s Specifications, using a criss-
cross pattern. Do not overtighten them, or
leakage may occur.
In-car engine repair procedures 2A•15
13.5 If applicable, disconnect the oil level
sensor connector at the left side of the
engine, down near the power steering
pump mounting bracket13.4 If applicable, remove the nut securing
the power steering lines to the sump, and
move the lines to one side to allow you to
get at the sump bolts12.30e Angle-tightening the cylinder head
bolts (M40 engine)
13.9 Remove the bolts holding the sump
to the engine block and front cover, as
shown here on a six-cylinder engine13.7b Removing the oil dipstick tube
bracket mounting bolt
13.6b . . . remove the cover to get to all
the sump bolts13.6a Remove the four inspection cover
bolts (arrowed) and . . .
13.7a Main sump retaining bolts accessed
after removal of the lower sump section on
the M40 engine (engine on bench for clarity)
2A
Page 55 of 228
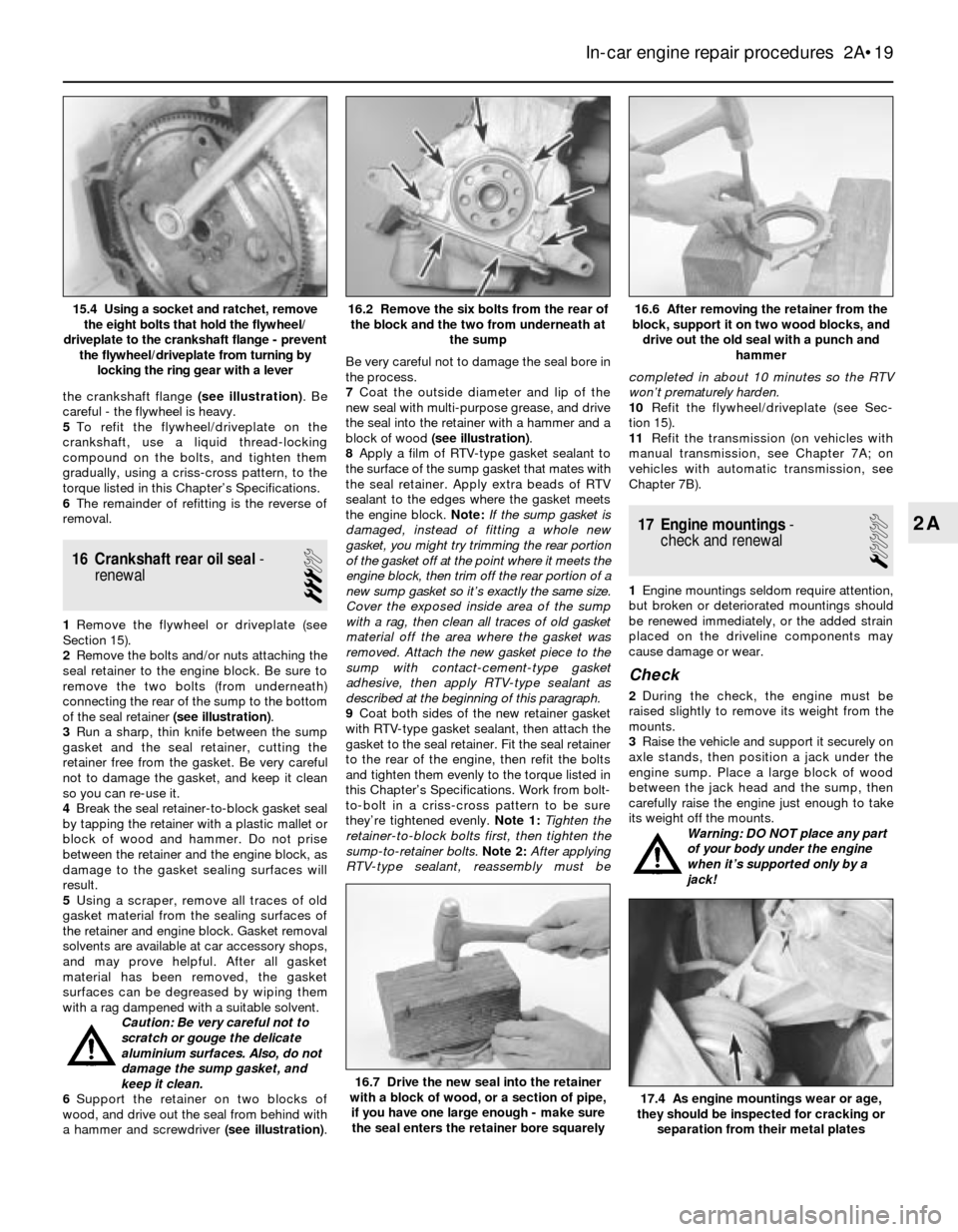
the crankshaft flange (see illustration). Be
careful - the flywheel is heavy.
5To refit the flywheel/driveplate on the
crankshaft, use a liquid thread-locking
compound on the bolts, and tighten them
gradually, using a criss-cross pattern, to the
torque listed in this Chapter’s Specifications.
6The remainder of refitting is the reverse of
removal.
16 Crankshaft rear oil seal-
renewal
3
1Remove the flywheel or driveplate (see
Section 15).
2Remove the bolts and/or nuts attaching the
seal retainer to the engine block. Be sure to
remove the two bolts (from underneath)
connecting the rear of the sump to the bottom
of the seal retainer (see illustration).
3Run a sharp, thin knife between the sump
gasket and the seal retainer, cutting the
retainer free from the gasket. Be very careful
not to damage the gasket, and keep it clean
so you can re-use it.
4Break the seal retainer-to-block gasket seal
by tapping the retainer with a plastic mallet or
block of wood and hammer. Do not prise
between the retainer and the engine block, as
damage to the gasket sealing surfaces will
result.
5Using a scraper, remove all traces of old
gasket material from the sealing surfaces of
the retainer and engine block. Gasket removal
solvents are available at car accessory shops,
and may prove helpful. After all gasket
material has been removed, the gasket
surfaces can be degreased by wiping them
with a rag dampened with a suitable solvent.
Caution: Be very careful not to
scratch or gouge the delicate
aluminium surfaces. Also, do not
damage the sump gasket, and
keep it clean.
6Support the retainer on two blocks of
wood, and drive out the seal from behind with
a hammer and screwdriver (see illustration).Be very careful not to damage the seal bore in
the process.
7Coat the outside diameter and lip of the
new seal with multi-purpose grease, and drive
the seal into the retainer with a hammer and a
block of wood (see illustration).
8Apply a film of RTV-type gasket sealant to
the surface of the sump gasket that mates with
the seal retainer. Apply extra beads of RTV
sealant to the edges where the gasket meets
the engine block. Note:If the sump gasket is
damaged, instead of fitting a whole new
gasket, you might try trimming the rear portion
of the gasket off at the point where it meets the
engine block, then trim off the rear portion of a
new sump gasket so it’s exactly the same size.
Cover the exposed inside area of the sump
with a rag, then clean all traces of old gasket
material off the area where the gasket was
removed. Attach the new gasket piece to the
sump with contact-cement-type gasket
adhesive, then apply RTV-type sealant as
described at the beginning of this paragraph.
9Coat both sides of the new retainer gasket
with RTV-type gasket sealant, then attach the
gasket to the seal retainer. Fit the seal retainer
to the rear of the engine, then refit the bolts
and tighten them evenly to the torque listed in
this Chapter’s Specifications. Work from bolt-
to-bolt in a criss-cross pattern to be sure
they’re tightened evenly.Note 1:Tighten the
retainer-to-block bolts first, then tighten the
sump-to-retainer bolts.Note 2:After applying
RTV-type sealant, reassembly must becompleted in about 10 minutes so the RTV
won’t prematurely harden.
10Refit the flywheel/driveplate (see Sec-
tion 15).
11Refit the transmission (on vehicles with
manual transmission, see Chapter 7A; on
vehicles with automatic transmission, see
Chapter 7B).
17 Engine mountings-
check and renewal
1
1Engine mountings seldom require attention,
but broken or deteriorated mountings should
be renewed immediately, or the added strain
placed on the driveline components may
cause damage or wear.
Check
2During the check, the engine must be
raised slightly to remove its weight from the
mounts.
3Raise the vehicle and support it securely on
axle stands, then position a jack under the
engine sump. Place a large block of wood
between the jack head and the sump, then
carefully raise the engine just enough to take
its weight off the mounts.
Warning: DO NOT place any part
of your body under the engine
when it’s supported only by a
jack!
In-car engine repair procedures 2A•19
16.6 After removing the retainer from the
block, support it on two wood blocks, and
drive out the old seal with a punch and
hammer16.2 Remove the six bolts from the rear of
the block and the two from underneath at
the sump15.4 Using a socket and ratchet, remove
the eight bolts that hold the flywheel/
driveplate to the crankshaft flange - prevent
the flywheel/driveplate from turning by
locking the ring gear with a lever
17.4 As engine mountings wear or age,
they should be inspected for cracking or
separation from their metal plates
16.7 Drive the new seal into the retainer
with a block of wood, or a section of pipe,
if you have one large enough - make sure
the seal enters the retainer bore squarely
2A
Page 71 of 228
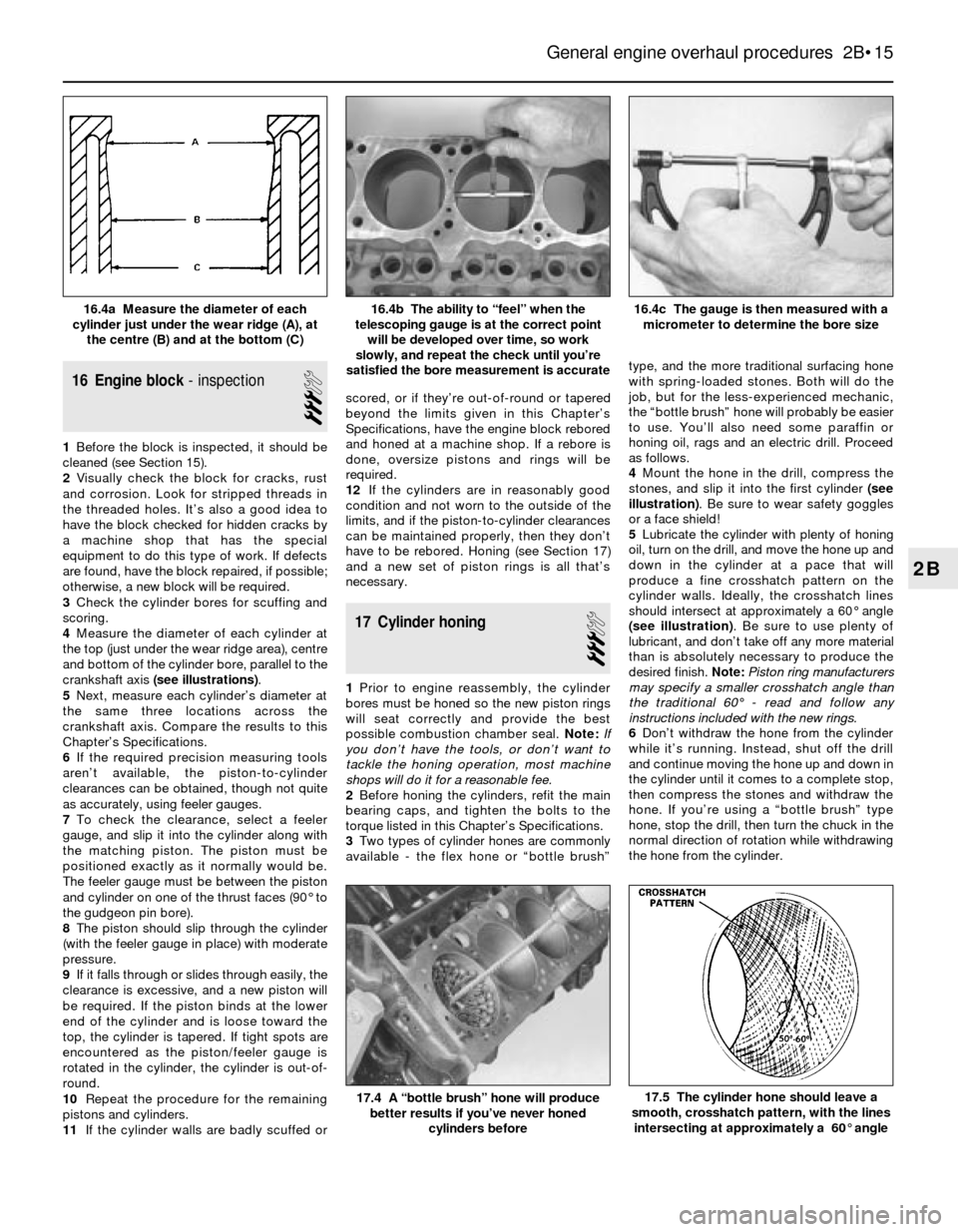
16 Engine block- inspection
3
1Before the block is inspected, it should be
cleaned (see Section 15).
2Visually check the block for cracks, rust
and corrosion. Look for stripped threads in
the threaded holes. It’s also a good idea to
have the block checked for hidden cracks by
a machine shop that has the special
equipment to do this type of work. If defects
are found, have the block repaired, if possible;
otherwise, a new block will be required.
3Check the cylinder bores for scuffing and
scoring.
4Measure the diameter of each cylinder at
the top (just under the wear ridge area), centre
and bottom of the cylinder bore, parallel to the
crankshaft axis (see illustrations).
5Next, measure each cylinder’s diameter at
the same three locations across the
crankshaft axis. Compare the results to this
Chapter’s Specifications.
6If the required precision measuring tools
aren’t available, the piston-to-cylinder
clearances can be obtained, though not quite
as accurately, using feeler gauges.
7To check the clearance, select a feeler
gauge, and slip it into the cylinder along with
the matching piston. The piston must be
positioned exactly as it normally would be.
The feeler gauge must be between the piston
and cylinder on one of the thrust faces (90° to
the gudgeon pin bore).
8The piston should slip through the cylinder
(with the feeler gauge in place) with moderate
pressure.
9If it falls through or slides through easily, the
clearance is excessive, and a new piston will
be required. If the piston binds at the lower
end of the cylinder and is loose toward the
top, the cylinder is tapered. If tight spots are
encountered as the piston/feeler gauge is
rotated in the cylinder, the cylinder is out-of-
round.
10Repeat the procedure for the remaining
pistons and cylinders.
11If the cylinder walls are badly scuffed orscored, or if they’re out-of-round or tapered
beyond the limits given in this Chapter’s
Specifications, have the engine block rebored
and honed at a machine shop. If a rebore is
done, oversize pistons and rings will be
required.
12If the cylinders are in reasonably good
condition and not worn to the outside of the
limits, and if the piston-to-cylinder clearances
can be maintained properly, then they don’t
have to be rebored. Honing (see Section 17)
and a new set of piston rings is all that’s
necessary.
17 Cylinder honing
3
1Prior to engine reassembly, the cylinder
bores must be honed so the new piston rings
will seat correctly and provide the best
possible combustion chamber seal. Note:If
you don’t have the tools, or don’t want to
tackle the honing operation, most machine
shops will do it for a reasonable fee.
2Before honing the cylinders, refit the main
bearing caps, and tighten the bolts to the
torque listed in this Chapter’s Specifications.
3Two types of cylinder hones are commonly
available - the flex hone or “bottle brush”type, and the more traditional surfacing hone
with spring-loaded stones. Both will do the
job, but for the less-experienced mechanic,
the “bottle brush” hone will probably be easier
to use. You’ll also need some paraffin or
honing oil, rags and an electric drill. Proceed
as follows.
4Mount the hone in the drill, compress the
stones, and slip it into the first cylinder (see
illustration). Be sure to wear safety goggles
or a face shield!
5Lubricate the cylinder with plenty of honing
oil, turn on the drill, and move the hone up and
down in the cylinder at a pace that will
produce a fine crosshatch pattern on the
cylinder walls. Ideally, the crosshatch lines
should intersect at approximately a 60° angle
(see illustration). Be sure to use plenty of
lubricant, and don’t take off any more material
than is absolutely necessary to produce the
desired finish. Note:Piston ring manufacturers
may specify a smaller crosshatch angle than
the traditional 60°- read and follow any
instructions included with the new rings.
6Don’t withdraw the hone from the cylinder
while it’s running. Instead, shut off the drill
and continue moving the hone up and down in
the cylinder until it comes to a complete stop,
then compress the stones and withdraw the
hone. If you’re using a “bottle brush” type
hone, stop the drill, then turn the chuck in the
normal direction of rotation while withdrawing
the hone from the cylinder.
General engine overhaul procedures 2B•15
16.4c The gauge is then measured with a
micrometer to determine the bore size16.4b The ability to “feel” when the
telescoping gauge is at the correct point
will be developed over time, so work
slowly, and repeat the check until you’re
satisfied the bore measurement is accurate16.4a Measure the diameter of each
cylinder just under the wear ridge (A), at
the centre (B) and at the bottom (C)
17.5 The cylinder hone should leave a
smooth, crosshatch pattern, with the lines
intersecting at approximately a 60° angle17.4 A “bottle brush” hone will produce
better results if you’ve never honed
cylinders before
2B
Page 105 of 228
gauge to the pressure regulator vacuum hose,
and check for vacuum (engine idling).
11If there is vacuum present, renew the fuel
pressure regulator.
12If there isn’t any reading on the gauge,
check the hose and its port for a leak or a
restriction.
Renewal
13Depressurise the fuel system (see Sec-
tion 2).
14Detach the battery negative cable.
Caution: If the radio in your
vehicle is equipped with an anti-
theft system, make sure you
have the correct activation code
before disconnecting the battery. Refer to
the information on page 0-7 at the front of
this manual before detaching the cable.
Note: If, after connecting the battery, the
wrong language appears on the instrument
panel display, refer to page 0-7 for the
language resetting procedure.
15Detach the vacuum hose and fuel return
hose from the pressure regulator, then
unscrew the mounting bolts (see illustration).
16Remove the pressure regulator.
17Refitting is the reverse of removal. Be sure
to use a new O-ring. Coat the O-ring with a
light film of engine oil prior to refitting.
18Check for fuel leaks after refitting the
pressure regulator.
19 Cold start injector and
thermotime switch- check
and renewal
2
Warning: Fuel is extremely
flammable, so take extra
precautions when you work on
any part of the fuel system. Don’t
smoke, or allow open flames or bare light
bulbs, near the work area. Don’t work in a
garage where a natural gas-type appliance
(such as a water heater or clothes dryer)
with a pilot light is present. If you spill any
fuel on your skin, rinse it off immediately
with soap and water. When you performany kind of work on the fuel system, wear
safety glasses, and have a fire
extinguisher on hand.
Check
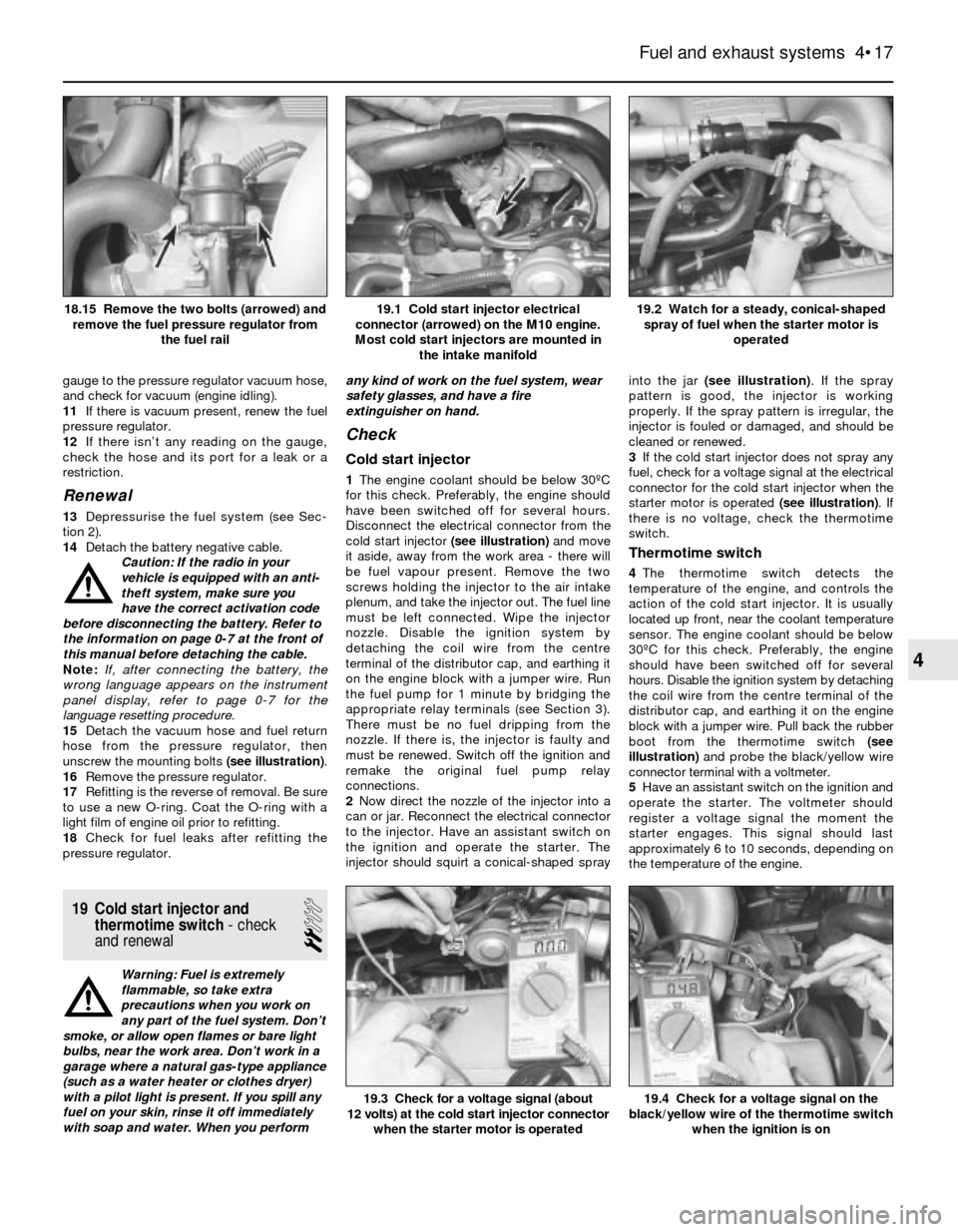
Cold start injector
1The engine coolant should be below 30ºC
for this check. Preferably, the engine should
have been switched off for several hours.
Disconnect the electrical connector from the
cold start injector (see illustration)and move
it aside, away from the work area - there will
be fuel vapour present. Remove the two
screws holding the injector to the air intake
plenum, and take the injector out. The fuel line
must be left connected. Wipe the injector
nozzle. Disable the ignition system by
detaching the coil wire from the centre
terminal of the distributor cap, and earthing it
on the engine block with a jumper wire. Run
the fuel pump for 1 minute by bridging the
appropriate relay terminals (see Section 3).
There must be no fuel dripping from the
nozzle. If there is, the injector is faulty and
must be renewed. Switch off the ignition and
remake the original fuel pump relay
connections.
2Now direct the nozzle of the injector into a
can or jar. Reconnect the electrical connector
to the injector. Have an assistant switch on
the ignition and operate the starter. The
injector should squirt a conical-shaped sprayinto the jar (see illustration). If the spray
pattern is good, the injector is working
properly. If the spray pattern is irregular, the
injector is fouled or damaged, and should be
cleaned or renewed.
3If the cold start injector does not spray any
fuel, check for a voltage signal at the electrical
connector for the cold start injector when the
starter motor is operated (see illustration). If
there is no voltage, check the thermotime
switch.
Thermotime switch
4The thermotime switch detects the
temperature of the engine, and controls the
action of the cold start injector. It is usually
located up front, near the coolant temperature
sensor. The engine coolant should be below
30ºC for this check. Preferably, the engine
should have been switched off for several
hours. Disable the ignition system by detaching
the coil wire from the centre terminal of the
distributor cap, and earthing it on the engine
block with a jumper wire. Pull back the rubber
boot from the thermotime switch (see
illustration)and probe the black/yellow wire
connector terminal with a voltmeter.
5Have an assistant switch on the ignition and
operate the starter. The voltmeter should
register a voltage signal the moment the
starter engages. This signal should last
approximately 6 to 10 seconds, depending on
the temperature of the engine.
Fuel and exhaust systems 4•17
19.2 Watch for a steady, conical-shaped
spray of fuel when the starter motor is
operated19.1 Cold start injector electrical
connector (arrowed) on the M10 engine.
Most cold start injectors are mounted in
the intake manifold18.15 Remove the two bolts (arrowed) and
remove the fuel pressure regulator from
the fuel rail
19.4 Check for a voltage signal on the
black/yellow wire of the thermotime switch
when the ignition is on19.3 Check for a voltage signal (about
12 volts) at the cold start injector connector
when the starter motor is operated
4