Front seal BMW 3 SERIES 1985 E30 Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: BMW, Model Year: 1985, Model line: 3 SERIES, Model: BMW 3 SERIES 1985 E30Pages: 228, PDF Size: 7.04 MB
Page 76 of 228

positions (don’t mix them up) with the arrows
pointing towards the front of the engine. Don’t
disturb the Plastigage.
13Starting with the centre main bearing and
working out toward the ends, progressively
tighten the main bearing cap bolts to the
torque listed in this Chapter’s Specifications.
On M10, M20 and M30 engines, tighten the
bolts in three stages. On the M40 engine,
tighten all the bolts initially to the Stage 1
torque, then angle-tighten them by the angle
given in the Specifications. Carry out the
angle-tightening on each bolt in one
controlled movement. Don’t rotate the
crankshaft at any time during the tightening
operation.
14Remove the bolts and carefully lift off the
main bearing caps. Keep them in order. Don’t
disturb the Plastigage or rotate the
crankshaft. If any of the main bearing caps are
difficult to remove, tap them gently from side-
to-side with a soft-face hammer to loosen
them.
15Compare the width of the crushed
Plastigage on each journal to the scale printed
on the Plastigage envelope to obtain the main
bearing oil clearance (see illustration). Check
the Specifications to make sure it’s correct.
16If the clearance is not as specified, thebearing shells may be the wrong size (which
means different ones will be required). Before
deciding that different shells are needed,
make sure that no dirt or oil was between the
bearing shells and the caps or block when the
clearance was measured. If the Plastigage
was wider at one end than the other, the
journal may be tapered (see Section 19).
17Carefully scrape all traces of the
Plastigage material off the main bearing
journals and/or the bearing faces. Use your
fingernail or the edge of a credit card - don’t
nick or scratch the bearing faces.
Final crankshaft refitting
18Carefully lift the crankshaft out of the
engine.
19Clean the bearing faces in the block, then
apply a thin, uniform layer of molybdenum
disulphide (“moly”) grease or engine oil to
each of the bearing surfaces. Be sure to coat
the thrust faces as well as the journal face of
the thrust bearing.
20Make sure the crankshaft journals are
clean, then lay the crankshaft back in place in
the block.
21Clean the faces of the bearings in the
caps, then apply engine oil to them.
22Refit the caps in their respective
positions, with the arrows pointing towards
the front of the engine.
23Refit the bolts finger-tight.
24Lightly tap the ends of the crankshaft
forward and backward with a lead or brass
hammer, to line up the main bearing and
crankshaft thrust surfaces.
25Tighten the bearing cap bolts to the
specified torque, working from the centre
outwards. On M10, M20 and M30 engines,
tighten the bolts in three stages to the final
torque, leaving out the thrust bearing cap
bolts at this stage. On M40 engines, tighten all
of the bolts in the two stages given in the
Specifications.
26On M10, M20 and M30 engines, tighten
the thrust bearing cap bolts to the torque
listed in this Chapter’s Specifications.
27On manual transmission models, fit a new
pilot bearing in the end of the crankshaft (see
Chapter 8).28Rotate the crankshaft a number of times
by hand to check for any obvious binding.
29The final step is to check the crankshaft
endfloat with a feeler gauge or a dial indicator
as described in Section 13. The endfloat
should be correct, providing the crankshaft
thrust faces aren’t worn or damaged, and new
bearings have been fitted.
30Fit the new seal, then bolt the housing to
the block (see Section 25).
25 Crankshaft rear oil seal-
refitting
3
1The crankshaft must be fitted first, and the
main bearing caps bolted in place. The new
seal should then be fitted in the retainer, and
the retainer bolted to the block.
2Before refitting the crankshaft, check the
seal contact surface very carefully for
scratches and nicks that could damage the
new seal lip and cause oil leaks. If the
crankshaft is damaged, the only alternative is
a new or different crankshaft, unless a
machine shop can suggest a means of repair.
3The old seal can be removed from the
housing with a hammer and punch by driving
it out from the back side (see illustration). Be
sure to note how far it’s recessed into the
housing bore before removing it; the new seal
will have to be recessed an equal amount. Be
very careful not to scratch or otherwise
damage the bore in the housing, or oil leaks
could develop.
4Make sure the retainer is clean, then apply
a thin coat of engine oil to the outer edge of
the new seal. The seal must be pressed
squarely into the housing bore, so hammering
it into place is not recommended. At the very
least, use a block of wood as shown, or a
section of large-diameter pipe (see
illustration). If you don’t have access to a
press, sandwich the housing and seal
between two smooth pieces of wood, and
press the seal into place with the jaws of a
large vice. The pieces of wood must be thick
enough to distribute the force evenly around
the entire circumference of the seal. Work
2B•20 General engine overhaul procedures
25.5 Lubricate the lip of the seal, and bolt
the retainer to the rear of the engine block25.4 Drive the new seal into the retainer
with a wooden block or a section of pipe, if
you have one large enough - make sure
the seal enters the retainer bore squarely25.3 After removing the retainer from the
block, support it on two wooden blocks,
and drive out the old seal with a punch and
hammer
24.15 Compare the width of the crushed
Plastigage to the scale on the envelope to
determine the main bearing oil clearance
(always take the measurement at the
widest point of the Plastigage); be sure to
use the correct scale - standard and
metric ones are included
Page 77 of 228
slowly, and make sure the seal enters the bore
squarely.
5The seal lips must be lubricated with multi-
purpose grease or clean engine oil before the
seal/retainer is slipped over the crankshaft
and bolted to the block (see illustration). Use
a new gasket - no sealant is required - and
make sure the dowel pins are in place before
refitting the retainer.
6Tighten the retainer nuts/screws a little at a
time until they’re all snug, then tighten them to
the torque listed in the Specifications in
Chapter 2A.
26 Pistons/connecting rods-
refitting and big-end bearing
oil clearance check
4
1Before refitting the piston/connecting rod
assemblies, the cylinder walls must be
perfectly clean, the top edge of each cylinder
must be chamfered, and the crankshaft must
be in place.
2Remove the cap from the end of No 1
connecting rod (refer to the marks made
during removal). Remove the original bearing
shells, and wipe the bearing surfaces of the
connecting rod and cap with a clean, lint-free
cloth. They must be kept spotlessly-clean.
Connecting rod big-end bearing
oil clearance check
3Clean the back side of the new upper
bearing shell, then lay it in place in the
connecting rod. Make sure the tab on the
bearing fits into the recess in the rod. Don’t
hammer the bearing shell into place, and be
very careful not to nick or gouge the bearing
face. Don’t lubricate the bearing at this time.
4Clean the back side of the other bearing
shell, and refit it in the rod cap. Again, make
sure the tab on the bearing fits into the recess
in the cap, and don’t apply any lubricant. It’s
critically important that the mating surfaces of
the bearing and connecting rod are perfectlyclean and oil-free when they’re assembled for
this check.
5Position the piston ring gaps so they’re
staggered 120° from each other.
6Where applicable, slip a section of plastic
or rubber hose over each connecting rod cap
bolt.
7Lubricate the piston and rings with clean
engine oil, and attach a piston ring
compressor to the piston. Leave the skirt
protruding about 6 or 7 mm to guide the
piston into the cylinder. The rings must be
compressed until they’re flush with the piston.
8Rotate the crankshaft until the No 1
connecting rod journal is at BDC (bottom
dead centre). Apply a coat of engine oil to the
cylinder walls.
9With the mark or notch on top of the piston
facing the front of the engine, gently insert the
piston/connecting rod assembly into the No 1
cylinder bore, and rest the bottom edge of the
ring compressor on the engine block.
10Tap the top edge of the ring compressor
to make sure it’s contacting the block around
its entire circumference.
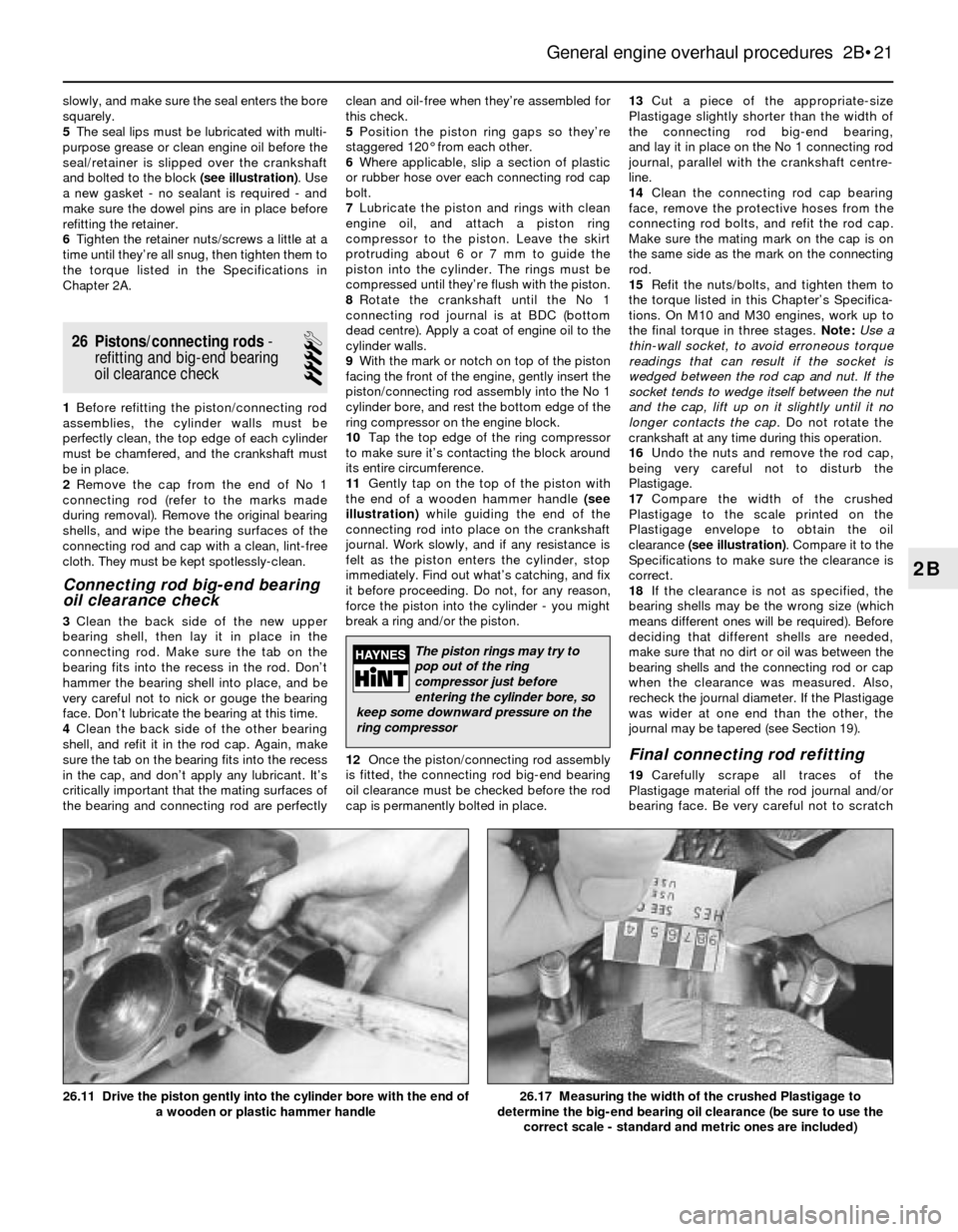
11Gently tap on the top of the piston with
the end of a wooden hammer handle (see
illustration)while guiding the end of the
connecting rod into place on the crankshaft
journal. Work slowly, and if any resistance is
felt as the piston enters the cylinder, stop
immediately. Find out what’s catching, and fix
it before proceeding. Do not, for any reason,
force the piston into the cylinder - you might
break a ring and/or the piston.
12Once the piston/connecting rod assembly
is fitted, the connecting rod big-end bearing
oil clearance must be checked before the rod
cap is permanently bolted in place.13Cut a piece of the appropriate-size
Plastigage slightly shorter than the width of
the connecting rod big-end bearing,
and lay it in place on the No 1 connecting rod
journal, parallel with the crankshaft centre-
line.
14Clean the connecting rod cap bearing
face, remove the protective hoses from the
connecting rod bolts, and refit the rod cap.
Make sure the mating mark on the cap is on
the same side as the mark on the connecting
rod.
15Refit the nuts/bolts, and tighten them to
the torque listed in this Chapter’s Specifica-
tions. On M10 and M30 engines, work up to
the final torque in three stages. Note:Use a
thin-wall socket, to avoid erroneous torque
readings that can result if the socket is
wedged between the rod cap and nut. If the
socket tends to wedge itself between the nut
and the cap, lift up on it slightly until it no
longer contacts the cap. Do not rotate the
crankshaft at any time during this operation.
16Undo the nuts and remove the rod cap,
being very careful not to disturb the
Plastigage.
17Compare the width of the crushed
Plastigage to the scale printed on the
Plastigage envelope to obtain the oil
clearance (see illustration). Compare it to the
Specifications to make sure the clearance is
correct.
18If the clearance is not as specified, the
bearing shells may be the wrong size (which
means different ones will be required). Before
deciding that different shells are needed,
make sure that no dirt or oil was between the
bearing shells and the connecting rod or cap
when the clearance was measured. Also,
recheck the journal diameter. If the Plastigage
was wider at one end than the other, the
journal may be tapered (see Section 19).
Final connecting rod refitting
19Carefully scrape all traces of the
Plastigage material off the rod journal and/or
bearing face. Be very careful not to scratch
General engine overhaul procedures 2B•21
26.17 Measuring the width of the crushed Plastigage to
determine the big-end bearing oil clearance (be sure to use the
correct scale - standard and metric ones are included)26.11 Drive the piston gently into the cylinder bore with the end of
a wooden or plastic hammer handle
2B
The piston rings may try to
pop out of the ring
compressor just before
entering the cylinder bore, so
keep some downward pressure on the
ring compressor
Page 79 of 228

3General
Coolant capacity . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 1
Thermostat rating
Opening temperature . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 80°C (176°F)
Fully open at . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 100°C (212°F)
Cooling fan thermo-switch - switching temperatures
Low-speed . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 91°C (196°F)
High-speed . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 99°C (210°F)
Torque wrench settingsNm
Mechanical cooling fan clutch-to-water pump securing
nut (left-hand thread) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
Mechanical cooling fan-to-clutch bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Water pump bolts
Small bolts (M6) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Large bolts (M8) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Thermostat housing bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Chapter 3
Cooling, heating and air conditioning systems
Air conditioner receiver-drier - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Air conditioning blower motor (E28/”old-shape” 5-series
models) - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Air conditioning compressor - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Air conditioning condenser - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Air conditioning system - precautions and maintenance . . . . . . . . . 12
Antifreeze - general information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Coolant level check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 1
Coolant temperature sender unit - check and renewal . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Cooling system check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 1
Cooling system servicing (draining, flushing and refilling)See Chapter 1Engine cooling fan(s) and clutch - check, removal and refitting . . . . 5
Evaporator matrix - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
General information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
Heater and air conditioner control assembly - removal and refitting 10
Heater and air conditioning blower motor - removal,testing and
refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Heater matrix - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Radiator - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
Thermostat - check and renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Water pump - check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Water pump - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
3•1
Easy,suitable for
novice with little
experienceFairly easy,suitable
for beginner with
some experienceFairly difficult,
suitable for competent
DIY mechanic
Difficult,suitable for
experienced DIY
mechanicVery difficult,
suitable for expert
DIY or professional
Degrees of difficulty
Specifications Contents
1 General information
Engine cooling system
All vehicles covered by this manual employ
a pressurised engine cooling system, with
thermostatically-controlled coolant circulation.
An impeller-type water pump mounted on
the front of the block pumps coolant through
the engine. The coolant flows around each
cylinder, and towards the rear of the engine.
Cast-in coolant passages direct coolantaround the intake and exhaust ports, near the
spark plug areas, and in close proximity to the
exhaust valve guides.
A wax-pellet-type thermostat is located in-
line in the bottom hose on M10 engines, in a
housing near the front of the engine on M20
and M30 engines, or behind an elbow under
the timing belt upper cover (on the front of the
cylinder head) on M40 engines. During warm-
up, the closed thermostat prevents coolant
from circulating through the radiator. As the
engine nears normal operating temperature,
the thermostat opens and allows hot coolant
to travel through the radiator, where it’s
cooled before returning to the engine.The pressure in the system raises the
boiling point of the coolant, and increases the
cooling efficiency of the radiator. The cooling
system is sealed by a pressure-type cap. If
the system pressure exceeds the cap
pressure relief value, the excess pressure in
the system forces the spring-loaded valve
inside the cap off its seat, and allows the
coolant to escape through the overflow tube.
The pressure cap on four-cylinder models is
on the top of the radiator; on six-cylinder models,
it’s on top of a translucent plastic expansion
tank. The cap pressure rating is moulded into the
top of the cap. The pressure rating is either
1.0 bar (14 psi) or 1.2 bars (17 psi).
Page 81 of 228
12If the outer surface of the fitting that
mates with the hose is deteriorated (corroded,
pitted, etc.), it may be damaged further by
hose removal. If it is, a new thermostat
housing cover will be required.
13Remove the bolts and detach the housing
cover. If the cover is stuck, tap it with a soft-
faced hammer to jar it loose. Be prepared for
some coolant to spill as the gasket seal is
broken.
14Note how it’s fitted, then remove the
thermostat.
15Stuff a rag into the engine opening, then
remove all traces of old gasket material (if the
gasket is paper type). Otherwise, remove the
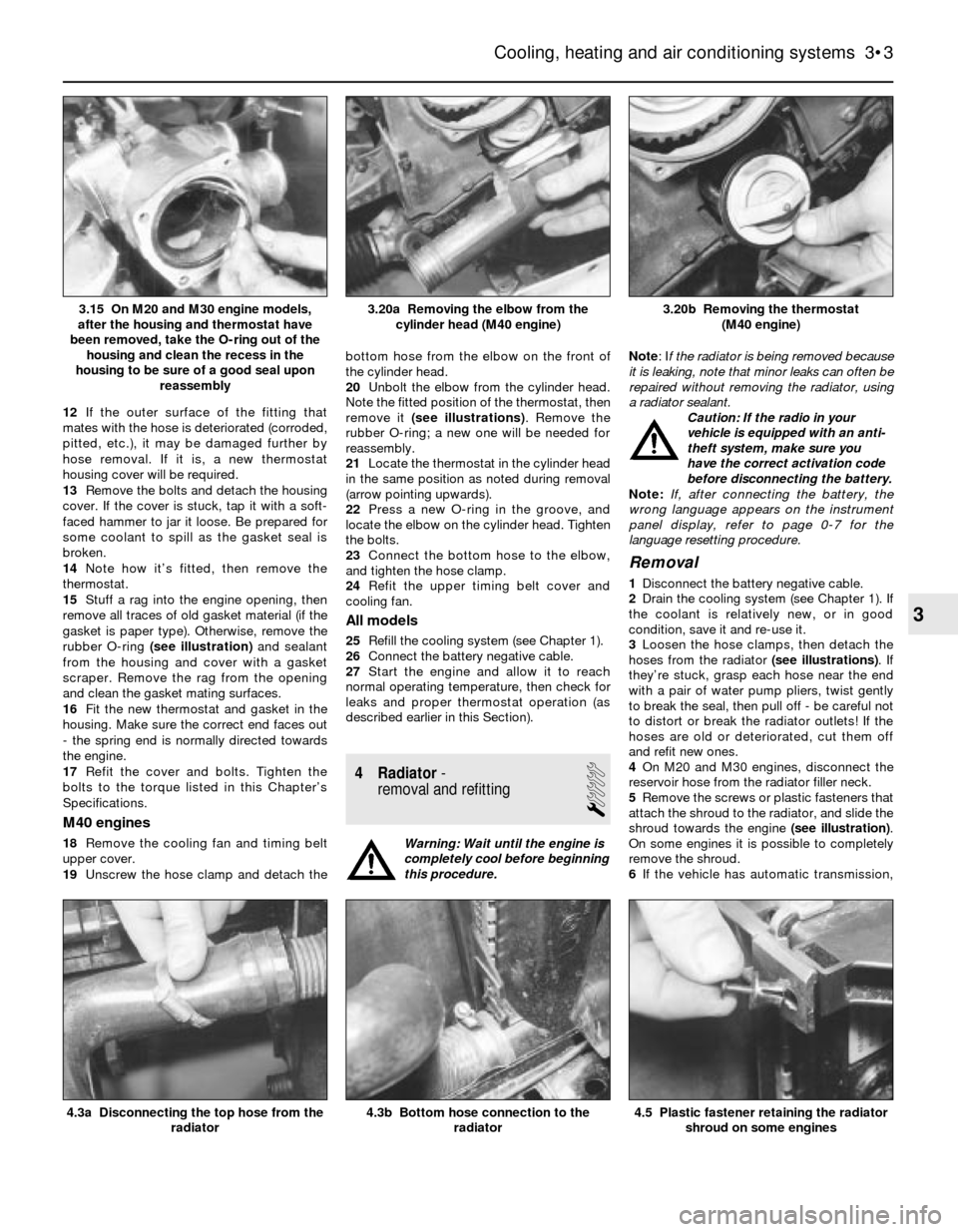
rubber O-ring (see illustration)and sealant
from the housing and cover with a gasket
scraper. Remove the rag from the opening
and clean the gasket mating surfaces.
16Fit the new thermostat and gasket in the
housing. Make sure the correct end faces out
- the spring end is normally directed towards
the engine.
17Refit the cover and bolts. Tighten the
bolts to the torque listed in this Chapter’s
Specifications.
M40 engines
18Remove the cooling fan and timing belt
upper cover.
19Unscrew the hose clamp and detach thebottom hose from the elbow on the front of
the cylinder head.
20Unbolt the elbow from the cylinder head.
Note the fitted position of the thermostat, then
remove it (see illustrations). Remove the
rubber O-ring; a new one will be needed for
reassembly.
21Locate the thermostat in the cylinder head
in the same position as noted during removal
(arrow pointing upwards).
22Press a new O-ring in the groove, and
locate the elbow on the cylinder head. Tighten
the bolts.
23Connect the bottom hose to the elbow,
and tighten the hose clamp.
24Refit the upper timing belt cover and
cooling fan.
All models
25Refill the cooling system (see Chapter 1).
26Connect the battery negative cable.
27Start the engine and allow it to reach
normal operating temperature, then check for
leaks and proper thermostat operation (as
described earlier in this Section).
4 Radiator-
removal and refitting
1
Warning: Wait until the engine is
completely cool before beginning
this procedure.Note: If the radiator is being removed because
it is leaking, note that minor leaks can often be
repaired without removing the radiator, using
a radiator sealant.
Caution: If the radio in your
vehicle is equipped with an anti-
theft system, make sure you
have the correct activation code
before disconnecting the battery.
Note: If, after connecting the battery, the
wrong language appears on the instrument
panel display, refer to page 0-7 for the
language resetting procedure.
Removal
1Disconnect the battery negative cable.
2Drain the cooling system (see Chapter 1). If
the coolant is relatively new, or in good
condition, save it and re-use it.
3Loosen the hose clamps, then detach the
hoses from the radiator (see illustrations). If
they’re stuck, grasp each hose near the end
with a pair of water pump pliers, twist gently
to break the seal, then pull off - be careful not
to distort or break the radiator outlets! If the
hoses are old or deteriorated, cut them off
and refit new ones.
4On M20 and M30 engines, disconnect the
reservoir hose from the radiator filler neck.
5Remove the screws or plastic fasteners that
attach the shroud to the radiator, and slide the
shroud towards the engine (see illustration).
On some engines it is possible to completely
remove the shroud.
6If the vehicle has automatic transmission,
Cooling, heating and air conditioning systems 3•3
3.20b Removing the thermostat
(M40 engine)3.20a Removing the elbow from the
cylinder head (M40 engine)3.15 On M20 and M30 engine models,
after the housing and thermostat have
been removed, take the O-ring out of the
housing and clean the recess in the
housing to be sure of a good seal upon
reassembly
4.5 Plastic fastener retaining the radiator
shroud on some engines4.3b Bottom hose connection to the
radiator4.3a Disconnecting the top hose from the
radiator
3
Page 83 of 228
3-Series models
14Remove the radiator grille assembly (see
Chapter 11).
15Unbolt and remove the fan bracket and
shroud assembly from the radiator (see
Section 5).
16Remove the radiator (see Section 4).
17Unbolt the air conditioning condenser
mounting bolts, where applicable. Do not
remove the condenser or disconnect any
refrigerant lines from the condenser.
18Carefully pull the condenser back towards
the engine, slightly, to gain access to lift the
auxiliary fan.
19Disconnect the fan motor electrical
connection and remove the auxiliary fan.
20Refitting is the reverse of removal.
5-Series models
21Remove the screws and trim panel in front
of the radiator.
22Unbolt the fan assembly from the
condenser mounting points.
23Disconnect the fan electrical connector.
24Remove the fan and housing from the car,
being careful not to damage the air
conditioning condenser (when applicable)
while removing the fan.
25Refitting is the reverse of removal.
Mechanical fan with viscous clutch
26Disconnect the battery negative cable.
Remove the fan shroud mounting screws or
plastic fasteners, and detach the shroud (see
Section 4).
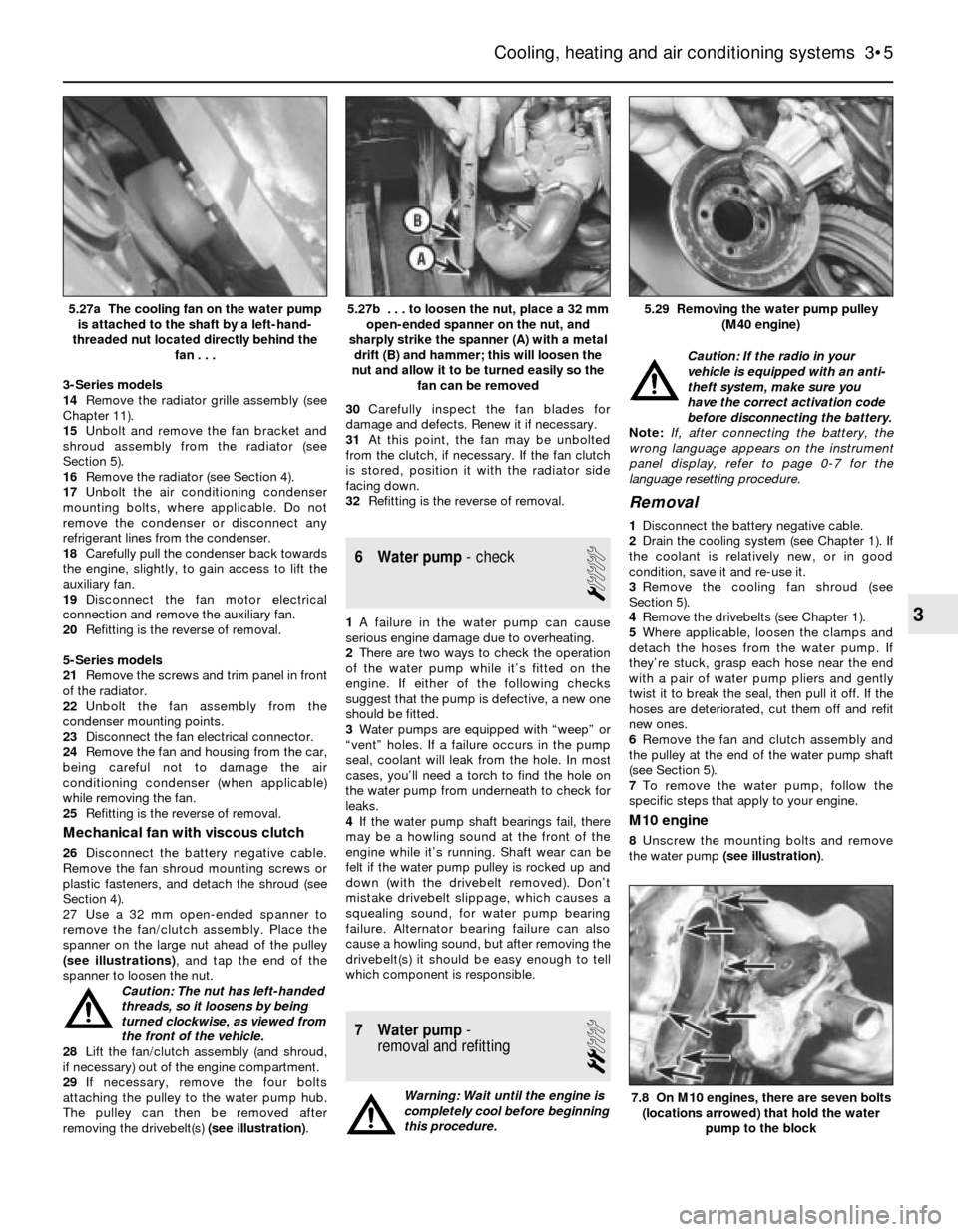
27 Use a 32 mm open-ended spanner to
remove the fan/clutch assembly. Place the
spanner on the large nut ahead of the pulley
(see illustrations), and tap the end of the
spanner to loosen the nut.
Caution: The nut has left-handed
threads, so it loosens by being
turned clockwise, as viewed from
the front of the vehicle.
28Lift the fan/clutch assembly (and shroud,
if necessary) out of the engine compartment.
29If necessary, remove the four bolts
attaching the pulley to the water pump hub.
The pulley can then be removed after
removing the drivebelt(s) (see illustration).30Carefully inspect the fan blades for
damage and defects. Renew it if necessary.
31At this point, the fan may be unbolted
from the clutch, if necessary. If the fan clutch
is stored, position it with the radiator side
facing down.
32Refitting is the reverse of removal.
6 Water pump- check
1
1A failure in the water pump can cause
serious engine damage due to overheating.
2There are two ways to check the operation
of the water pump while it’s fitted on the
engine. If either of the following checks
suggest that the pump is defective, a new one
should be fitted.
3Water pumps are equipped with “weep” or
“vent” holes. If a failure occurs in the pump
seal, coolant will leak from the hole. In most
cases, you’ll need a torch to find the hole on
the water pump from underneath to check for
leaks.
4If the water pump shaft bearings fail, there
may be a howling sound at the front of the
engine while it’s running. Shaft wear can be
felt if the water pump pulley is rocked up and
down (with the drivebelt removed). Don’t
mistake drivebelt slippage, which causes a
squealing sound, for water pump bearing
failure. Alternator bearing failure can also
cause a howling sound, but after removing the
drivebelt(s) it should be easy enough to tell
which component is responsible.
7 Water pump-
removal and refitting
2
Warning: Wait until the engine is
completely cool before beginning
this procedure.Caution: If the radio in your
vehicle is equipped with an anti-
theft system, make sure you
have the correct activation code
before disconnecting the battery.
Note: If, after connecting the battery, the
wrong language appears on the instrument
panel display, refer to page 0-7 for the
language resetting procedure.
Removal
1Disconnect the battery negative cable.
2Drain the cooling system (see Chapter 1). If
the coolant is relatively new, or in good
condition, save it and re-use it.
3Remove the cooling fan shroud (see
Section 5).
4Remove the drivebelts (see Chapter 1).
5Where applicable, loosen the clamps and
detach the hoses from the water pump. If
they’re stuck, grasp each hose near the end
with a pair of water pump pliers and gently
twist it to break the seal, then pull it off. If the
hoses are deteriorated, cut them off and refit
new ones.
6Remove the fan and clutch assembly and
the pulley at the end of the water pump shaft
(see Section 5).
7To remove the water pump, follow the
specific steps that apply to your engine.
M10 engine
8Unscrew the mounting bolts and remove
the water pump (see illustration).
Cooling, heating and air conditioning systems 3•5
5.29 Removing the water pump pulley
(M40 engine)5.27b . . . to loosen the nut, place a 32 mm
open-ended spanner on the nut, and
sharply strike the spanner (A) with a metal
drift (B) and hammer; this will loosen the
nut and allow it to be turned easily so the
fan can be removed5.27a The cooling fan on the water pump
is attached to the shaft by a left-hand-
threaded nut located directly behind the
fan . . .
7.8 On M10 engines, there are seven bolts
(locations arrowed) that hold the water
pump to the block
3
Page 85 of 228

4If a new sender unit is to be fitted, make
sure the engine is completely cool. There will
be some coolant loss when the unit is
unscrewed, so be prepared to catch it, or
have the new unit ready to fit immediately the
old one is removed. Disconnect the wiring,
then unscrew the old unit from the engine,
and fit the new one. Use sealant on the
threads. Reconnect the wiring, and check the
coolant level on completion.
9 Heater and air conditioning
blower motor- removal,
testing and refitting
1
Removal
Note: The 3-Series models covered by this
manual have always used a single blower
motor for ventilation, heating and air
conditioning. “Old-shape” (E28) 5-Series
models use two separate blower motors: one
for ventilation and heating, and another for air
conditioning. “New-shape” (E34) 5-Series
models have a single blower motor, like the 3-
Series. The removal and refitting of the single
blower motor, and the old-shape 5-Series
vent/heat motor, is described below. The
removal and refitting of the old-shape 5-Series
air conditioning blower motor is described in
Section 14 of this Chapter.
Caution: If the radio in your
vehicle is equipped with an anti-
theft system, make sure you have
the correct activation code
before disconnecting the battery.
Note: If, after connecting the battery, the
wrong language appears on the instrument
panel display, refer to page 0-7 for the
language resetting procedure.
1Disconnect the battery negative cable.
2The blower motor is located behind the
bulkhead, under an access panel. Remove the
panel securing screws (see illustrations).
3Disconnect or cut the plastic ties holding
the wiring harness to the panel, and move the
wiring out of the way.
4Remove the panel.
5Unclip the blower housing retaining clip,
and the clip securing the blower motor (see
illustrations).6Disconnect the wiring and remove the
blower motor (see illustration).
Testing
7You can test the blower motor by applying
battery voltage to the blower motor’s
terminals with fused jumper wires (be sure the
fan blades won’t hit anything when they
rotate). If the blower motor spins the fan
blades rapidly (this test simulates high-speed
operation), the blower motor is OK. If the
blower motor does not operate, or operates
slowly or noisily, renew it.
Note: If the fan blade assemblies need to be
removed, mark their relationship to the shaft.
The assemblies are balanced during
production, and excessive noise or shortened
bearing life could result if they are not refitted
in exactly the same position in relation to the
shaft.
Refitting
8Refitting is the reverse of removal. Note:
The blower motor may have to be rotated to
allow the retaining clip to line up correctly.
10 Heater and air conditioner
control assembly- removal
and refitting
1
Removal
1Disconnect the battery negative cable. Caution: If the radio in your
vehicle is equipped with an anti-
theft system, make sure you
have the correct activation code
before disconnecting the battery.
Note: If, after connecting the battery, the
wrong language appears on the instrument
panel display, refer to page 0-7 for the
language resetting procedure.
3-Series models
2Remove the centre console and side trim
pieces.
3Remove the radio (see Chapter 12), then
pull the knobs off the heater/air conditioning
control levers.
4Remove the heater trim panel to gain
access to the control cables.
5Disconnect the cables, marking them for
accurate refitting.
6Disconnect the electrical connector.
7Remove the lever assembly.
8Each lever assembly can be removed
separately.
5-Series models
9Remove the centre console (see Chap-
ter 11).
10Remove the radio (see Chapter 12), then
pull the knobs off the heater/air conditioning
control levers.
11Remove the trim bezel, and pull the
control unit from the dash. This will allow you
to disconnect the control cables from the
lever assembly.
Cooling, heating and air conditioning systems 3•7
9.5a Unclip the retaining strap to remove
the blower housing . . .
9.2b . . . a fastener from the top secure the
panel9.2a To get to the heater blower motor,
the access panel must be removed - a
fastener from the front and . . .
9.6 Lift out the assembly, and disconnect
the electrical connection from the blower
motor9.5b . . . and unclip the centre strap that
secures the blower motor assembly
3
Page 86 of 228
12Disconnect the cables from the clips
securing them to the lever assembly, marking
them for accurate refitting.
13Disconnect the electrical connection from
the control assembly.
14Remove the screws attaching the bezel to
the control assembly, and remove the control
assembly.
Refitting
15Refitting is the reverse of the removal
procedure.
11 Heater matrix-
removal and refitting
1
Caution: If the radio in your
vehicle is equipped with an anti-
theft system, make sure you
have the correct activation code
before disconnecting the battery.
Note: If, after connecting the battery, the
wrong language appears on the instrument
panel display, refer to page 0-7 for the
language resetting procedure.
1Disconnect the battery negative cable.
2Drain the cooling system (see Chapter 1).
3Remove the centre console (see Chap-
ter 11). Spread an old blanket over the front
carpeting; this will prevent stains if any
residual coolant spills.
Removal
3-Series models
4Remove the left-hand side heater ducting,
and set it aside.
5Remove the heater valve clamp.
6Remove the screws and detach the flange
where the two coolant lines enter the heater
matrix case. Be careful; some coolant may
spill.
7Remove the two screws holding the heater
matrix case to the heater main assembly.
8Slide the heater matrix out of the mounting.
Be careful not to spill any of the remaining
coolant in the heater matrix when removing it.
5-Series models
9Disconnect the temperature sensor
electrical connectors.
10Disconnect the straps holding the wiring
to the case, and set the wiring out of the way.
11Unfasten the cover fasteners.
12Remove the screws holding the cover in
place, then remove the cover.
13Disconnect all heater pipe connections
attached to the heater matrix. Be careful;
some coolant may spill.
14Lifting on the right side of the heater
matrix first, remove the heater matrix.
Refitting
Note: Always use new O-rings when attaching
the coolant lines to the heater matrix.15Refitting is the reverse of removal. Refill
the cooling system (see Chapter 1), then run
the engine with the heater on, and check for
correct operation and leaks.
12 Air conditioning system-
precautions and maintenance
1
Precautions
Warning: The air conditioning
system is under high pressure.
DO NOT loosen any hose or line
fittings, or remove any
components, until after the system has
been discharged. Air conditioning
refrigerant should be properly discharged
by a qualified refrigeration engineer. The
refrigerant used in the system must not be
allowed into contact with your skin or
eyes, or there is a risk of frostbite. Should
the refrigerant come into contact with a
naked flame, a poisonous gas will be
produced. Smoking in the presence of
refrigerant is therefore highly dangerous,
particularly if refrigerant vapour is inhaled
through a lighted cigarette. The refrigerant
is heavier than air, and it may cause
suffocation if discharged in an enclosed
space such as a domestic garage.
Finally, uncontrolled release of the
refrigerant causes environmental damage,
by contributing to the “greenhouse
effect”.
Maintenance
1The following maintenance checks should
be performed on a regular basis to ensure the
air conditioner continues to operate at peak
efficiency:
a) Check the drivebelt. If it’s worn or
deteriorated, renew it (see Chapter 1).
b) Check the system hoses. Look for cracks,
bubbles, hard spots and deterioration.
Inspect the hoses and all fittings for oil
bubbles and seepage. If there’s any
evidence of wear, damage or leaks, have
new hose(s) fitted.
c) Inspect the condenser fins for leaves, flies
and other debris. Use a “fin comb” or
compressed air to clean the condenser.
d) Make sure the system has the correct
refrigerant charge, as described below.
2It’s a good idea to operate the system for
about 10 minutes at least once a month,
particularly during the winter. Long-term non-
use can cause hardening, and subsequent
failure, of the seals.
3Because of the complexity of the air
conditioning system and the special
equipment necessary to service it, in-depth
fault diagnosis and repair procedures are not
included in this manual. However, simple
checks and component renewal procedures
are provided in this Chapter.
4The most common cause of poor cooling issimply a low system refrigerant charge. If a
noticeable loss of cool air output occurs, the
following quick check may help you determine
if the refrigerant level is low.
5Warm the engine up to normal operating
temperature.
6Set the air conditioning temperature
selector at the coldest setting, and put the
blower at the highest setting. Open the doors
(to make sure the air conditioning system
doesn’t switch off as soon as it cools the
passenger compartment).
7With the compressor engaged - the
compressor clutch will make an audible click,
and the centre of the clutch will rotate - feel
the tube located adjacent to the right front
frame rail, near the radiator.
8If a significant temperature drop is noticed,
the refrigerant level is probably OK.
9If the inlet line has frost accumulation, or
feels cooler than the receiver-drier surface,
the refrigerant charge is low. Recharging the
system should be carried out by a qualified
refrigeration engineer.
13 Air conditioning compressor
- removal and refitting
5
Warning: Due to the potential
dangers associated with the
system, you are strongly advised
to have any work on the air
conditioning system carried out by a BMW
dealer or air conditioning specialist. At the
very least, DO NOT dismantle any part of
the system (hoses, compressor, line
fittings, etc.) until after the system has
been discharged by a qualified engineer.
Refer to the precautions given at the start
of Section 12.
Note: If a new compressor is fitted, the
receiver-drier (see Section 16) should also be
renewed.
Removal
1Have the air conditioning system
discharged (see Warning above).
2Disconnect the battery negative cable.
Caution: If the radio in your
vehicle is equipped with an anti-
theft system, make sure you
have the correct activation code
before disconnecting the battery.
Note: If, after connecting the battery, the
wrong language appears on the instrument
panel display, refer to page 0-7 for the
language resetting procedure.
3Disconnect the compressor clutch wiring
harness.
4Remove the drivebelt (see Chapter 1).
5Disconnect the refrigerant lines from the
rear of the compressor. Plug the open fittings
to prevent entry of dirt and moisture.
6Unbolt the compressor from the mounting
3•8 Cooling, heating and air conditioning systems
Page 93 of 228
19Depressurise the fuel system (see Sec-
tion 2).
20Detach the battery negative cable.
Caution: If the radio in your
vehicle is equipped with an anti-
theft system, make sure you
have the correct activation code
before disconnecting the battery. Refer to
the information on page 0-7 at the front of
this manual before detaching the cable.
Note: If, after connecting the battery, the
wrong language appears on the instrument
panel display, refer to page 0-7 for the
language resetting procedure.
21Detach the fuel feed hose from the fuel
rail, and attach a fuel pressure gauge directly
to the hose. Note:If the tee fitting is still
connected to the gauge, be sure to plug the
open end.
22Reconnect the battery.
23Using a jumper wire, bridge the terminals
of the fuel pump relay.
24Turn the ignition switch on to operate the
fuel pump.
25Note the pressure reading on the gauge,
and compare the reading to the fuel pump
pressure listed in this Chapter’s Specifica-
tions.
26If the indicated pressure is less than
specified, inspect the fuel line for leaks
between the pump and gauge. If no leaks are
found, renew the fuel pump.
27Turn the ignition off and wait five minutes.
Note the reading on the gauge, and compare
it to the fuel pump hold pressure listed in this
Chapter’s Specifications. If the hold pressure
is less than specified, check the fuel lines
between the pump and gauge for leaks. If no
leaks are found, renew the fuel pump.
28Remove the jumper wire. Relieve the fuel
pressure by opening the bleed valve on the
gauge and directing the fuel into a suitable
container. Remove the gauge and reconnect
the fuel line.
Transfer pump pressure check
29Depressurise the fuel system (see Sec-
tion 2).
30Detach the battery negative cable.
Caution: If the radio in your
vehicle is equipped with an anti-
theft system, make sure you
have the correct activation code
before disconnecting the battery. Refer to
the information on page 0-7 at the front of
this manual before detaching the cable.
Note: If, after connecting the battery, the
wrong language appears on the instrument
panel display, refer to page 0-7 for the
language resetting procedure.
31Remove the transfer pump access plate
(on some models, it’s located under the rear
seat cushion - on others, it’s located under
the carpet in the luggage compartment).
Disconnect the output hose from the transfer
pump, and connect a fuel pressure gauge to
the outlet pipe.
32Reconnect the battery.33Using a jumper wire, bridge the terminals
of the fuel pump relay.
34Turn the ignition switch on to operate the
fuel pump.
35Note the pressure reading on the gauge,
and compare to the value listed in this
Chapter’s Specifications.
36If the indicated pressure is less than
specified, renew the transfer pump.
Fuel pump relay check
37Switch on the ignition.
38Using a voltmeter, probe the following
terminals from the back of the relay electrical
connector. Check for battery voltage at
terminal 30 (M20 and M30 engines) or
terminal 15 (M10 and M40 engines). Note:If
there is no voltage on models with luggage
compartment-mounted batteries, check for a
faulty fusible link. The 50-amp link is about
6 inches from the battery, in a black wire.
39Turn the ignition off, and disconnect the
relay from the electrical connector. Using a
voltmeter, probe the connector terminals that
correspond to fuel pump relay pins 85 (-) and
86(+) on M20 and M30 engines, or terminal 50
and earth on M10 and M40 engines. Have an
assistant turn the engine over on the starter,
and observe the voltage reading. Battery
voltage should be indicated.
40If there is no voltage, check the fuse(s)
and the wiring circuit for the fuel pump relay. If
the voltage readings are correct, and the fuel
pump only runs with the jumper wire in place,
then renew the relay.
41If the fuel pump still does not run, check
for the proper voltage at the fuel pump
terminals (see Section 4). If necessary, renew
the fuel pump.
4 Fuel pump, transfer pump
and fuel level sender unit-
removal and refitting
2
Warning: Fuel is extremely
flammable, so take extra
precautions when you work on
any part of the fuel system. Don’t
smoke, or allow open flames or bare light
bulbs, near the work area. Also, don’t work
in a garage where a natural gas-type
appliance with a pilot light is present.
Fuel pump (carburettor engines)
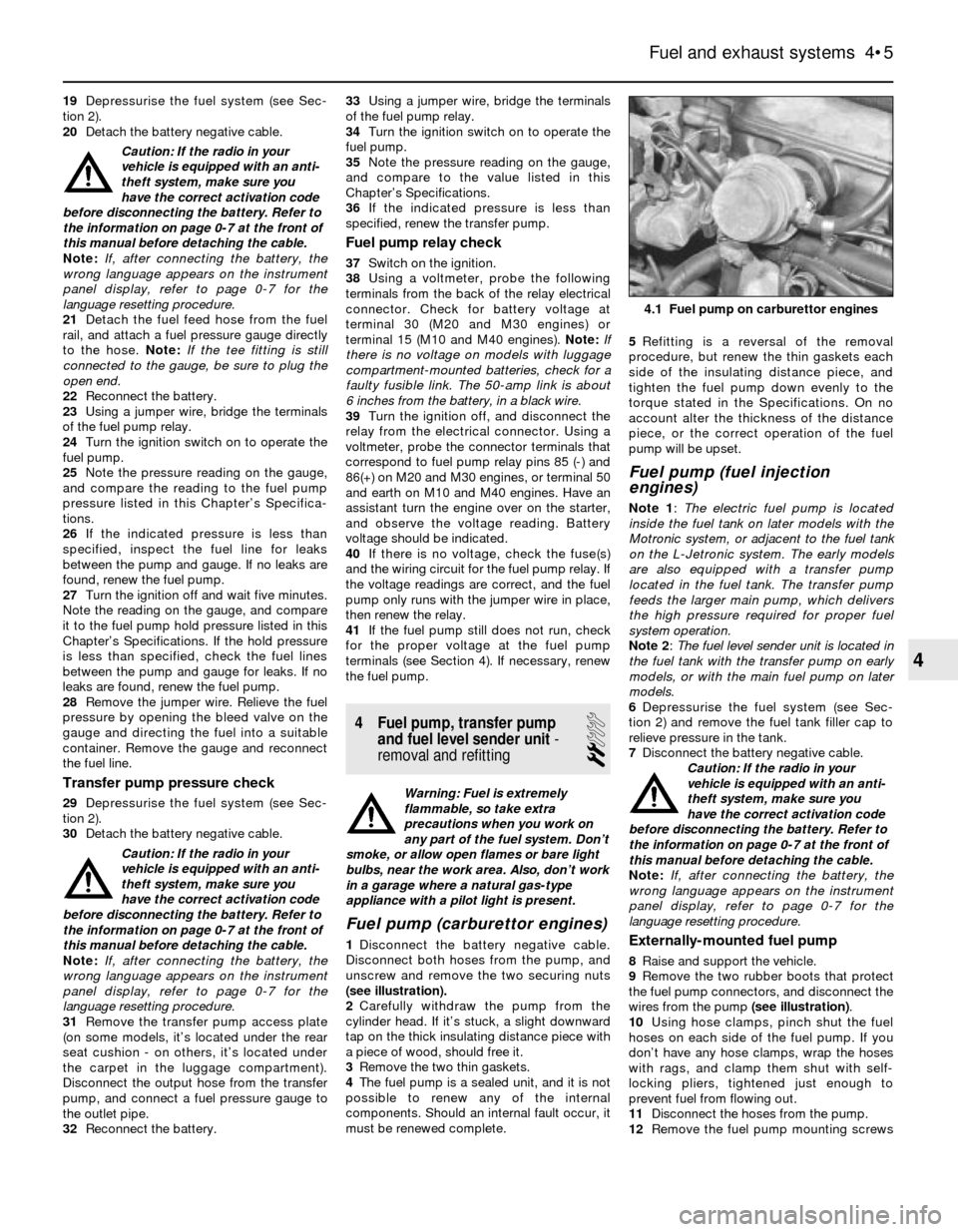
1Disconnect the battery negative cable.
Disconnect both hoses from the pump, and
unscrew and remove the two securing nuts
(see illustration).
2Carefully withdraw the pump from the
cylinder head. If it’s stuck, a slight downward
tap on the thick insulating distance piece with
a piece of wood, should free it.
3Remove the two thin gaskets.
4The fuel pump is a sealed unit, and it is not
possible to renew any of the internal
components. Should an internal fault occur, it
must be renewed complete.5Refitting is a reversal of the removal
procedure, but renew the thin gaskets each
side of the insulating distance piece, and
tighten the fuel pump down evenly to the
torque stated in the Specifications. On no
account alter the thickness of the distance
piece, or the correct operation of the fuel
pump will be upset.
Fuel pump (fuel injection
engines)
Note 1: The electric fuel pump is located
inside the fuel tank on later models with the
Motronic system, or adjacent to the fuel tank
on the L-Jetronic system. The early models
are also equipped with a transfer pump
located in the fuel tank. The transfer pump
feeds the larger main pump, which delivers
the high pressure required for proper fuel
system operation.
Note 2: The fuel level sender unit is located in
the fuel tank with the transfer pump on early
models, or with the main fuel pump on later
models.
6Depressurise the fuel system (see Sec-
tion 2) and remove the fuel tank filler cap to
relieve pressure in the tank.
7Disconnect the battery negative cable.
Caution: If the radio in your
vehicle is equipped with an anti-
theft system, make sure you
have the correct activation code
before disconnecting the battery. Refer to
the information on page 0-7 at the front of
this manual before detaching the cable.
Note: If, after connecting the battery, the
wrong language appears on the instrument
panel display, refer to page 0-7 for the
language resetting procedure.
Externally-mounted fuel pump
8Raise and support the vehicle.
9Remove the two rubber boots that protect
the fuel pump connectors, and disconnect the
wires from the pump (see illustration).
10Using hose clamps, pinch shut the fuel
hoses on each side of the fuel pump. If you
don’t have any hose clamps, wrap the hoses
with rags, and clamp them shut with self-
locking pliers, tightened just enough to
prevent fuel from flowing out.
11Disconnect the hoses from the pump.
12Remove the fuel pump mounting screws
Fuel and exhaust systems 4•5
4.1 Fuel pump on carburettor engines
4
Page 97 of 228

6Unscrew the four nuts retaining the air
cleaner to the carburettor, and remove the
metal ring (see illustrations).
7Unscrew the nut from the mounting bracket
(see illustration).
8Lift the air cleaner from the carburettor, and
disconnect the crankcase ventilation hose
(see illustration). If necessary, prise the
sealing ring from the bottom of the air cleaner.
9Refitting is a reversal of removal, but align
the arrow on the cover with the arrow on the
inlet tube (see illustration).
Fuel injection engines
10Detach the air intake duct from the front
side of the air cleaner.11Detach the duct between the air cleaner
and the throttle body.
12Remove the air filter (see Chapter 1).
13Unplug the electrical connector from the
airflow meter (see Section 12).
14Remove the air cleaner mounting bolts
(see illustration)and lift the air cleaner
assembly from the engine compartment.
15Refitting is the reverse of removal. Ensure
that all ducts are securely refitted, or air leaks
will result.
9 Accelerator cable- check,
adjustment and renewal
1
Check
1Separate the air intake duct from the
throttle body (fuel injection models) or remove
the air cleaner (carburettor models).
2Have an assistant depress the accelerator
pedal to the floor while you watch the throttle
valve. It should move to the fully-open
position.
3Release the accelerator pedal, and make
sure the throttle valve returns smoothly to the
fully-closed position. The throttle valve should
not contact the body at any time during its
movement; if it does, the unit must be renewed.
Adjustment
4Warm the engine to normal operating
temperature, then switch it off. Depress theaccelerator pedal to the floor twice, then
check the cable free play at the
carburettor/throttle body. Compare it to the
value listed in this Chapter’s Specifications.
5If the free play isn’t as specified, adjust it by
turning the adjustment nut (see illustration).
6Have an assistant help you verify the
throttle valve is fully open when the
accelerator pedal is depressed to the floor.
Renewal
Note:The following paragraphs describe the
procedure for fuel injection engines - the
procedure is similar on carburettor engines
7Disconnect the battery negative cable.
Fuel and exhaust systems 4•9
8.6b . . . and remove the metal ring8.6a Unscrew the four air cleaner-to-
carburettor nuts . . .8.4 Air cleaner inlet duct (1) and warm-air
hose (2)
9.5 To adjust the accelerator cable free
play, hold nut B stationary and turn nut A
(fuel injection engine shown)8.14 Remove the two nuts (arrowed) from
the air cleaner assembly (Motronic system
shown), and lift it off its mountings
8.8 Disconnecting the crankcase
ventilation hose from the air cleaner8.7 Air cleaner mounting bracket nut
(arrowed)8.9 Align the air cleaner cover arrows
when refitting
4
Page 120 of 228
the alternator complete, or take it to an
automotive electrician, who may be able to
overhaul it. Note:On models up to 1986, a
blown ignition/no-charge warning light bulb
will prevent the alternator from charging. After
1987, a resistor is wired in parallel with the
warning light, in order to allow current to
bypass the light in the event of a broken circuit
(blown warning light).
15 Alternator-
removal and refitting
1
Caution: If the radio in your
vehicle is equipped with an anti-
theft system, make sure you
have the correct activation code
before disconnecting the battery. Refer to
the information on page 0-7 at the front of
this manual before detaching the cable.
Note: If, after connecting the battery, the
wrong language appears on the instrument
panel display, refer to page 0-7 for the
language resetting procedure.
Removal
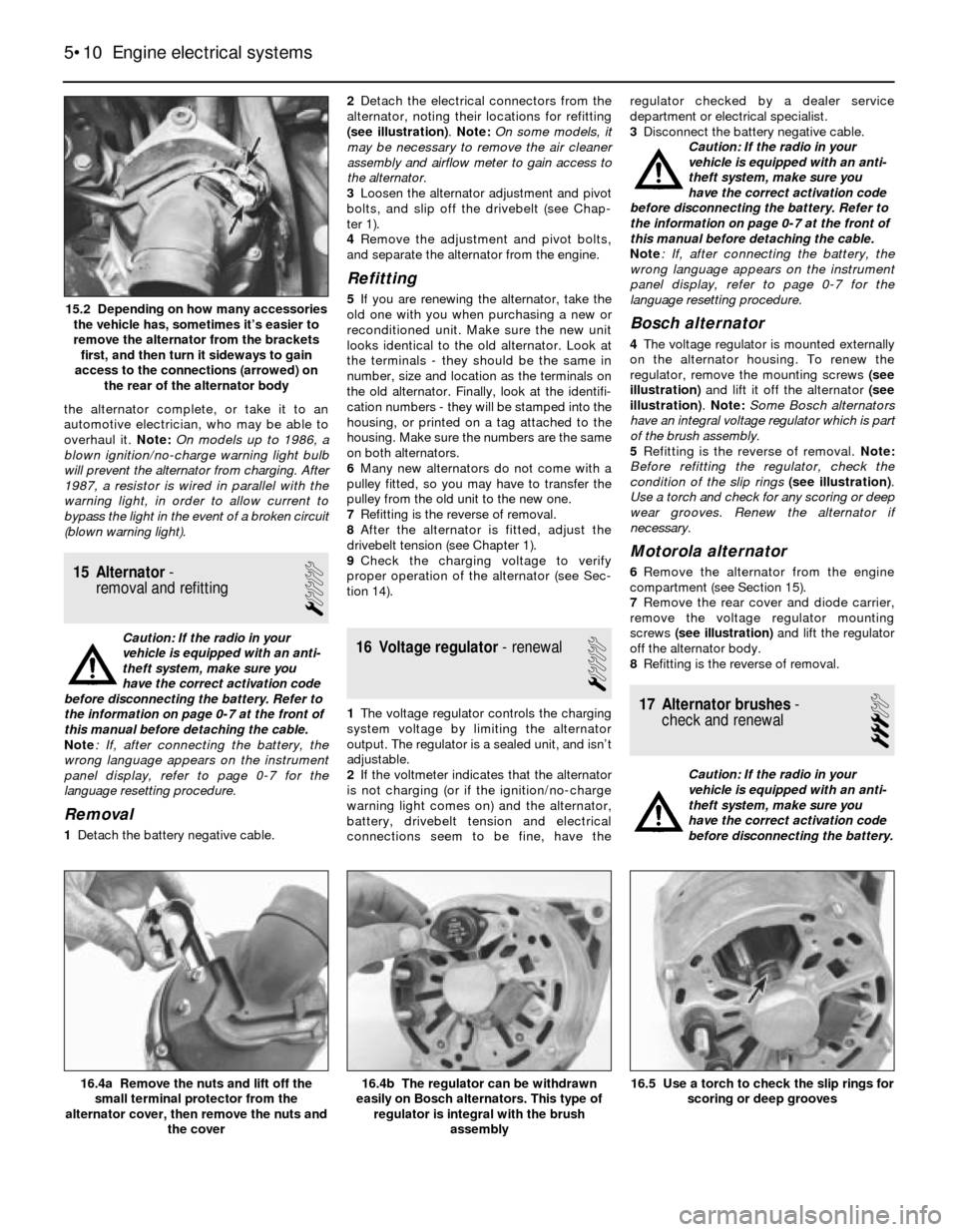
1Detach the battery negative cable.2Detach the electrical connectors from the
alternator, noting their locations for refitting
(see illustration). Note: On some models, it
may be necessary to remove the air cleaner
assembly and airflow meter to gain access to
the alternator.
3Loosen the alternator adjustment and pivot
bolts, and slip off the drivebelt (see Chap-
ter 1).
4Remove the adjustment and pivot bolts,
and separate the alternator from the engine.
Refitting
5If you are renewing the alternator, take the
old one with you when purchasing a new or
reconditioned unit. Make sure the new unit
looks identical to the old alternator. Look at
the terminals - they should be the same in
number, size and location as the terminals on
the old alternator. Finally, look at the identifi-
cation numbers - they will be stamped into the
housing, or printed on a tag attached to the
housing. Make sure the numbers are the same
on both alternators.
6Many new alternators do not come with a
pulley fitted, so you may have to transfer the
pulley from the old unit to the new one.
7Refitting is the reverse of removal.
8After the alternator is fitted, adjust the
drivebelt tension (see Chapter 1).
9Check the charging voltage to verify
proper operation of the alternator (see Sec-
tion 14).
16 Voltage regulator- renewal
1
1The voltage regulator controls the charging
system voltage by limiting the alternator
output. The regulator is a sealed unit, and isn’t
adjustable.
2If the voltmeter indicates that the alternator
is not charging (or if the ignition/no-charge
warning light comes on) and the alternator,
battery, drivebelt tension and electrical
connections seem to be fine, have theregulator checked by a dealer service
department or electrical specialist.
3Disconnect the battery negative cable.
Caution: If the radio in your
vehicle is equipped with an anti-
theft system, make sure you
have the correct activation code
before disconnecting the battery. Refer to
the information on page 0-7 at the front of
this manual before detaching the cable.
Note: If, after connecting the battery, the
wrong language appears on the instrument
panel display, refer to page 0-7 for the
language resetting procedure.
Bosch alternator
4The voltage regulator is mounted externally
on the alternator housing. To renew the
regulator, remove the mounting screws (see
illustration)and lift it off the alternator (see
illustration). Note: Some Bosch alternators
have an integral voltage regulator which is part
of the brush assembly.
5Refitting is the reverse of removal. Note:
Before refitting the regulator, check the
condition of the slip rings(see illustration).
Use a torch and check for any scoring or deep
wear grooves. Renew the alternator if
necessary.
Motorola alternator
6Remove the alternator from the engine
compartment (see Section 15).
7Remove the rear cover and diode carrier,
remove the voltage regulator mounting
screws (see illustration)and lift the regulator
off the alternator body.
8Refitting is the reverse of removal.
17 Alternator brushes-
check and renewal
3
Caution: If the radio in your
vehicle is equipped with an anti-
theft system, make sure you
have the correct activation code
before disconnecting the battery.
5•10 Engine electrical systems
16.5 Use a torch to check the slip rings for
scoring or deep grooves16.4b The regulator can be withdrawn
easily on Bosch alternators. This type of
regulator is integral with the brush
assembly16.4a Remove the nuts and lift off the
small terminal protector from the
alternator cover, then remove the nuts and
the cover
15.2 Depending on how many accessories
the vehicle has, sometimes it’s easier to
remove the alternator from the brackets
first, and then turn it sideways to gain
access to the connections (arrowed) on
the rear of the alternator body