Ignition switch BMW 3 SERIES 1985 E30 Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: BMW, Model Year: 1985, Model line: 3 SERIES, Model: BMW 3 SERIES 1985 E30Pages: 228, PDF Size: 7.04 MB
Page 114 of 228
7 Ignition timing (TCI system)-
check and adjustment
4
Warning: Keep hands, equipment
and wires well clear of the
viscous cooling fan during
adjustment of the ignition timing.
Note:This Section describes the procedure
for checking and adjusting the ignition timing
on engines fitted with the TCI system. On
engines fitted with the Motronic engine
management system, the ignition timing is
controlled by the electronic control unit, and
no adjustment is possible. The timing can be
checked using the following procedure, but no
ignition timing values were available at the
time of writing. If the timing is thought to be
incorrect, refer to a BMW dealer.
1Some special tools are required for this
procedure (see illustration). The engine must
be at normal operating temperature, and the
air conditioning (where fitted) must be
switched off. Make sure the idle speed is
correct.
2Apply the handbrake, and chock the wheels
to prevent movement of the vehicle. The
transmission must be in neutral (manual) or
Park (automatic).
3The timing marks are located on the engine
flywheel (viewed through the timing checkhole in the bellhousing) and/or on the vibration
damper on the front of the engine.
4Where applicable, disconnect the vacuum
hose from the distributor vacuum advance
unit.
5Connect a tachometer and timing light
according to the equipment manufacturer’s
instructions (an inductive pick-up timing light
is preferred). Generally, the power leads for
the timing light are attached to the battery
terminals, and the pick-up lead is attached to
the No 1 spark plug HT lead. The No 1 spark
plug is the one at the front of the engine.
Caution: If an inductive pick-up
timing light isn’t available, don’t
puncture the spark plug HT lead
to attach the timing light pick-up
lead. Instead, use an adapter between the
spark plug and HT lead. If the insulation on
the HT lead is damaged, the secondary
voltage will jump to earth at the damaged
point, and the engine will misfire.
Note:On some models, a TDC transmitter is
fitted for checking the ignition system.
However, a special BMW tester must be
connected to the diagnostic socket to use it,
so unless the special tester is available, a
conventional timing light should be used. The
ignition timing mark may be on the vibration
damper, but if not, normally the TDC mark will
be. If the timing light is of the adjustable delay
type, then the ignition timing may be
determined by zeroing the adjustment, then
turning the adjustment until the TDC marks are
aligned, and then reading off the amount of
advance from the timing light. If a standard
timing light is being used, make a mark on the
vibration damper in accordance with the
specified advance, using the following formula
to calculate the distance from the TDC mark
to the timing mark:
Distance = 2Pr x advance
360
where P = 3.142
r = radius of vibration damper
advance = specified advance
BTDC in degrees
6With the ignition off, loosen the distributor
clamp nut just enough to allow the distributor
to pivot without any slipping.7Make sure the timing light wires are routed
away from the drivebelts and fan, then start
the engine.
8Raise the engine rpm to the specified
speed, and then point the flashing timing light
at the timing marks - be very careful of moving
engine components.
9The mark on the flywheel or vibration
damper will appear stationary. If it’s aligned
with the specified point on the bellhousing or
engine front cover, the ignition timing is
correct (see illustrations).
10If the marks aren’t aligned, adjustment is
required. Turn the distributor very slowly until
the marks are aligned, taking care not to
touch the HT leads.
11Tighten the nut on the distributor clamp,
and recheck the timing.
12Switch off the engine, and remove the
timing light and tachometer. Reconnect the
vacuum hose where applicable.
8 Distributor-
removal and refitting
4
TCI system
Removal
1After carefully marking them for position,
remove the coil HT lead and spark plug HT
leads from the distributor cap (see Chapter 1).
2Remove No 1 spark plug (the one nearest
you when you are standing in front of the
engine).
3Manually rotate the engine to Top Dead
Centre (TDC) on the compression stroke for
No 1 piston (see Chapter 2A)
4Carefully mark the vacuum hoses, if more
than one is present on your distributor.
5Disconnect the vacuum hose(s).
6Disconnect the primary circuit wires from
the distributor.
7Mark the relationship of the rotor tip to the
distributor housing (see illustration). Also
mark the relationship of the distributor
housing to the engine.
5•4 Engine electrical systems
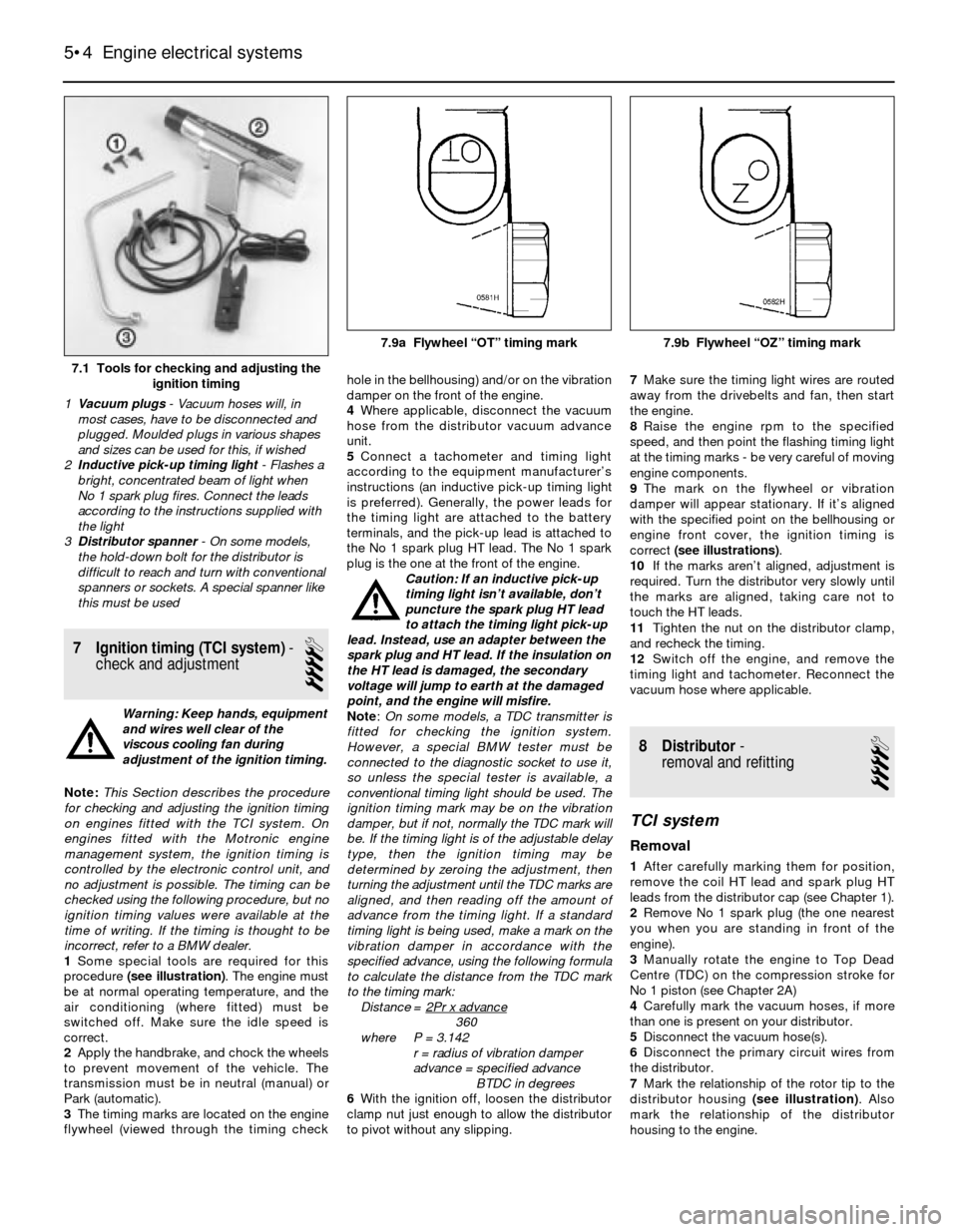
7.1 Tools for checking and adjusting the
ignition timing
1Vacuum plugs- Vacuum hoses will, in
most cases, have to be disconnected and
plugged. Moulded plugs in various shapes
and sizes can be used for this, if wished
2Inductive pick-up timing light- Flashes a
bright, concentrated beam of light when
No 1 spark plug fires. Connect the leads
according to the instructions supplied with
the light
3Distributor spanner - On some models,
the hold-down bolt for the distributor is
difficult to reach and turn with conventional
spanners or sockets. A special spanner like
this must be used
7.9a Flywheel “OT” timing mark 7.9b Flywheel “OZ” timing mark
Page 117 of 228
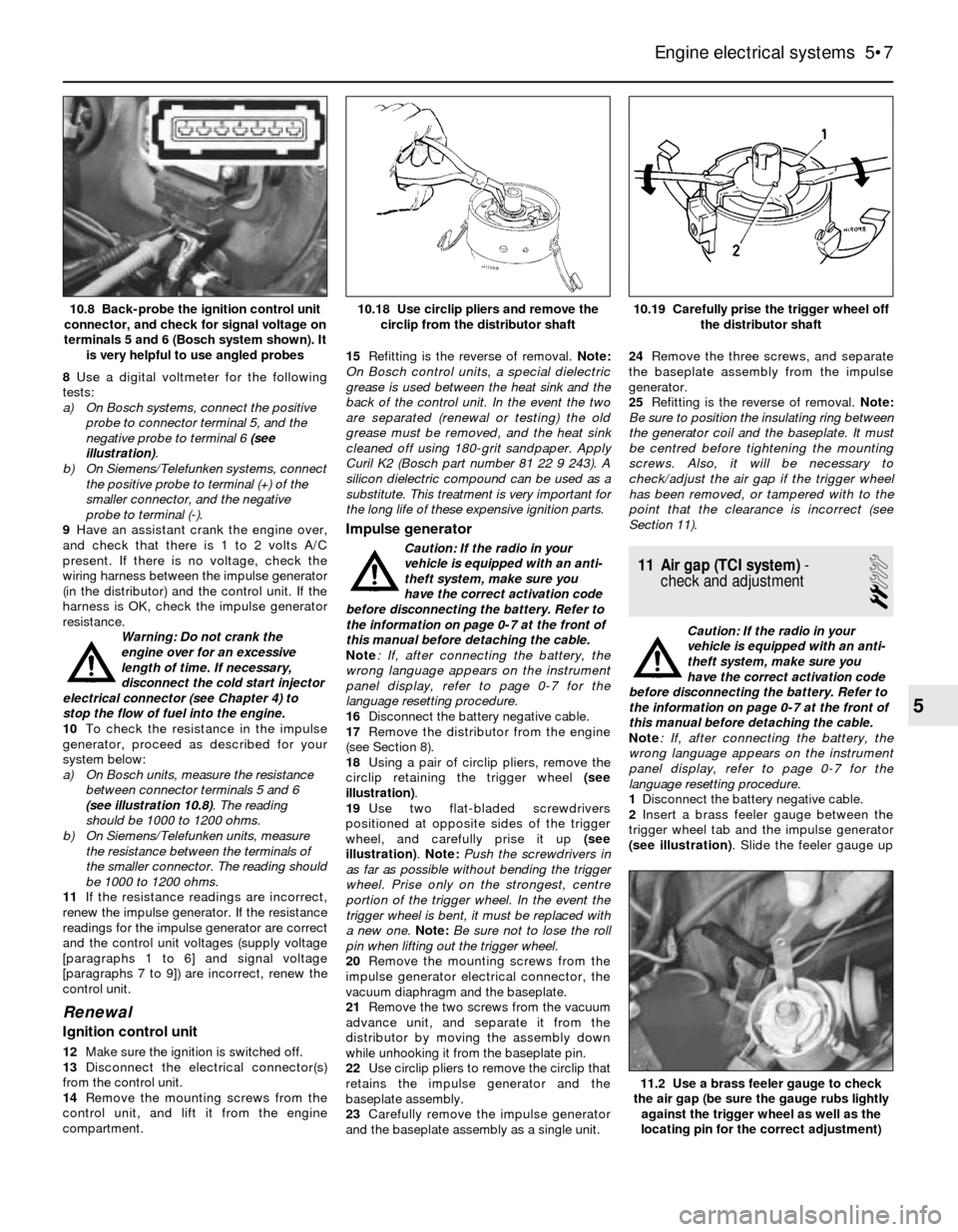
8Use a digital voltmeter for the following
tests:
a) On Bosch systems, connect the positive
probe to connector terminal 5, and the
negative probe to terminal 6 (see
illustration).
b) On Siemens/Telefunken systems, connect
the positive probe to terminal (+) of the
smaller connector, and the negative
probe to terminal (-).
9Have an assistant crank the engine over,
and check that there is 1 to 2 volts A/C
present. If there is no voltage, check the
wiring harness between the impulse generator
(in the distributor) and the control unit. If the
harness is OK, check the impulse generator
resistance.
Warning: Do not crank the
engine over for an excessive
length of time. If necessary,
disconnect the cold start injector
electrical connector (see Chapter 4) to
stop the flow of fuel into the engine.
10To check the resistance in the impulse
generator, proceed as described for your
system below:
a) On Bosch units, measure the resistance
between connector terminals 5 and 6
(see illustration 10.8). The reading
should be 1000 to 1200 ohms.
b) On Siemens/Telefunken units, measure
the resistance between the terminals of
the smaller connector. The reading should
be 1000 to 1200 ohms.
11If the resistance readings are incorrect,
renew the impulse generator. If the resistance
readings for the impulse generator are correct
and the control unit voltages (supply voltage
[paragraphs 1 to 6] and signal voltage
[paragraphs 7 to 9]) are incorrect, renew the
control unit.
Renewal
Ignition control unit
12Make sure the ignition is switched off.
13Disconnect the electrical connector(s)
from the control unit.
14Remove the mounting screws from the
control unit, and lift it from the engine
compartment.15Refitting is the reverse of removal. Note:
On Bosch control units, a special dielectric
grease is used between the heat sink and the
back of the control unit. In the event the two
are separated (renewal or testing) the old
grease must be removed, and the heat sink
cleaned off using 180-grit sandpaper. Apply
Curil K2 (Bosch part number 81 22 9 243). A
silicon dielectric compound can be used as a
substitute. This treatment is very important for
the long life of these expensive ignition parts.
Impulse generator
Caution: If the radio in your
vehicle is equipped with an anti-
theft system, make sure you
have the correct activation code
before disconnecting the battery. Refer to
the information on page 0-7 at the front of
this manual before detaching the cable.
Note: If, after connecting the battery, the
wrong language appears on the instrument
panel display, refer to page 0-7 for the
language resetting procedure.
16Disconnect the battery negative cable.
17Remove the distributor from the engine
(see Section 8).
18Using a pair of circlip pliers, remove the
circlip retaining the trigger wheel (see
illustration).
19Use two flat-bladed screwdrivers
positioned at opposite sides of the trigger
wheel, and carefully prise it up (see
illustration). Note: Push the screwdrivers in
as far as possible without bending the trigger
wheel. Prise only on the strongest, centre
portion of the trigger wheel. In the event the
trigger wheel is bent, it must be replaced with
a new one. Note:Be sure not to lose the roll
pin when lifting out the trigger wheel.
20Remove the mounting screws from the
impulse generator electrical connector, the
vacuum diaphragm and the baseplate.
21Remove the two screws from the vacuum
advance unit, and separate it from the
distributor by moving the assembly down
while unhooking it from the baseplate pin.
22Use circlip pliers to remove the circlip that
retains the impulse generator and the
baseplate assembly.
23Carefully remove the impulse generator
and the baseplate assembly as a single unit.24Remove the three screws, and separate
the baseplate assembly from the impulse
generator.
25Refitting is the reverse of removal. Note:
Be sure to position the insulating ring between
the generator coil and the baseplate. It must
be centred before tightening the mounting
screws. Also, it will be necessary to
check/adjust the air gap if the trigger wheel
has been removed, or tampered with to the
point that the clearance is incorrect (see
Section 11).
11 Air gap (TCI system)-
check and adjustment
2
Caution: If the radio in your
vehicle is equipped with an anti-
theft system, make sure you
have the correct activation code
before disconnecting the battery. Refer to
the information on page 0-7 at the front of
this manual before detaching the cable.
Note: If, after connecting the battery, the
wrong language appears on the instrument
panel display, refer to page 0-7 for the
language resetting procedure.
1Disconnect the battery negative cable.
2Insert a brass feeler gauge between the
trigger wheel tab and the impulse generator
(see illustration). Slide the feeler gauge up
Engine electrical systems 5•7
10.19 Carefully prise the trigger wheel off
the distributor shaft10.18 Use circlip pliers and remove the
circlip from the distributor shaft10.8 Back-probe the ignition control unit
connector, and check for signal voltage on
terminals 5 and 6 (Bosch system shown). It
is very helpful to use angled probes
11.2 Use a brass feeler gauge to check
the air gap (be sure the gauge rubs lightly
against the trigger wheel as well as the
locating pin for the correct adjustment)
5
Page 121 of 228
Refer to the information on page 0-7 at the
front of this manual before detaching the
cable.
Note: If, after connecting the battery, the
wrong language appears on the instrument
panel display, refer to page 0-7 for the
language resetting procedure.
1Disconnect the battery negative cable.
Bosch alternator
2Remove the voltage regulator from the back
of the alternator (see Section 16).
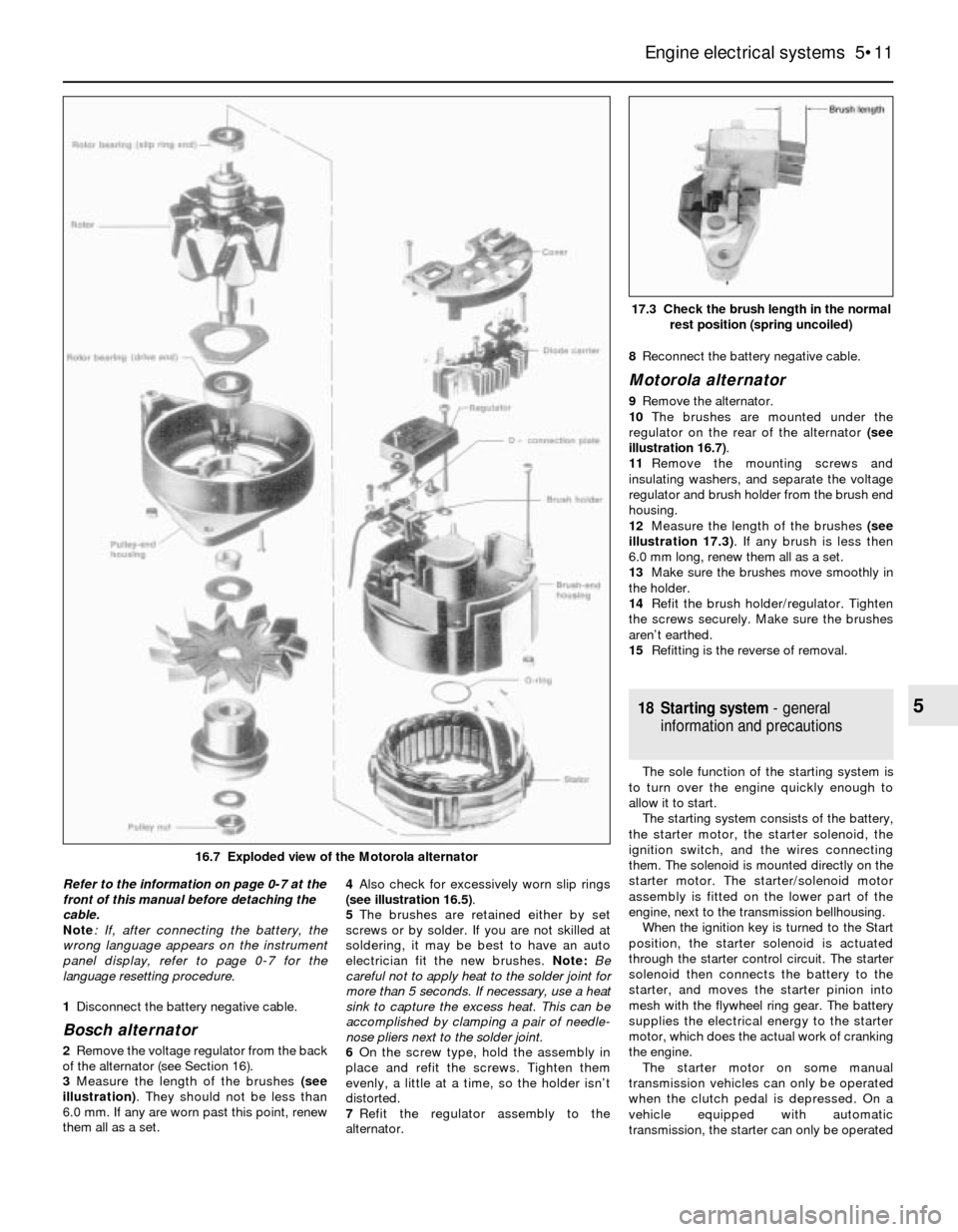
3Measure the length of the brushes (see
illustration). They should not be less than
6.0 mm. If any are worn past this point, renew
them all as a set. 4Also check for excessively worn slip rings
(see illustration 16.5).
5The brushes are retained either by set
screws or by solder. If you are not skilled at
soldering, it may be best to have an auto
electrician fit the new brushes. Note: Be
careful not to apply heat to the solder joint for
more than 5 seconds. If necessary, use a heat
sink to capture the excess heat. This can be
accomplished by clamping a pair of needle-
nose pliers next to the solder joint.
6On the screw type, hold the assembly in
place and refit the screws. Tighten them
evenly, a little at a time, so the holder isn’t
distorted.
7Refit the regulator assembly to the
alternator.8Reconnect the battery negative cable.
Motorola alternator
9Remove the alternator.
10The brushes are mounted under the
regulator on the rear of the alternator (see
illustration 16.7).
11Remove the mounting screws and
insulating washers, and separate the voltage
regulator and brush holder from the brush end
housing.
12Measure the length of the brushes (see
illustration 17.3). If any brush is less then
6.0 mm long, renew them all as a set.
13Make sure the brushes move smoothly in
the holder.
14Refit the brush holder/regulator. Tighten
the screws securely. Make sure the brushes
aren’t earthed.
15Refitting is the reverse of removal.
18 Starting system- general
information and precautions
The sole function of the starting system is
to turn over the engine quickly enough to
allow it to start.
The starting system consists of the battery,
the starter motor, the starter solenoid, the
ignition switch, and the wires connecting
them. The solenoid is mounted directly on the
starter motor. The starter/solenoid motor
assembly is fitted on the lower part of the
engine, next to the transmission bellhousing.
When the ignition key is turned to the Start
position, the starter solenoid is actuated
through the starter control circuit. The starter
solenoid then connects the battery to the
starter, and moves the starter pinion into
mesh with the flywheel ring gear. The battery
supplies the electrical energy to the starter
motor, which does the actual work of cranking
the engine.
The starter motor on some manual
transmission vehicles can only be operated
when the clutch pedal is depressed. On a
vehicle equipped with automatic
transmission, the starter can only be operated
Engine electrical systems 5•11
17.3 Check the brush length in the normal
rest position (spring uncoiled)
5
16.7 Exploded view of the Motorola alternator
Page 122 of 228

when the transmission selector lever is in Park
or Neutral.
Always detach the battery negative cable
before working on the starting system.
19 Starter motor-
in-vehicle check
2
Note:Before diagnosing starter problems,
make sure the battery is fully charged.
1If the starter motor does not turn at all when
the switch is operated, make sure that the
gear lever is in Neutral or Park (automatic
transmission) or, where applicable, that the
clutch pedal is depressed (manual
transmission).
2Make sure that the battery is charged, and
that all cables, both at the battery and starter
solenoid terminals, are clean and secure.
3If the starter motor spins but the engine is
not cranking, the overrun clutch in the starter
motor is slipping, and the starter motor must
be renewed.
4If, when the switch is actuated, the starter
motor does not operate at all but the solenoid
clicks, then the problem lies either in the
battery, the main solenoid contacts, or the
starter motor itself (or the engine is seized).
5If the solenoid plunger cannot be heard
when the switch is actuated, the battery is
faulty, the switch is defective, the fusible link
is burned-out (the circuit is open), or the
solenoid itself is defective.
6To check the solenoid, connect a jumper
lead between the battery (+) and the ignition
switch wire terminal (the small terminal) on the
solenoid. If the starter motor now operates,
the solenoid is OK and the problem is in the
ignition switch, starter inhibitor switch
(automatic transmission models), clutch
switch (some manual transmission models), or
the wiring.
7If the starter motor still does not operate,
remove the starter/solenoid assembly for
dismantling, testing and repair.
8If the starter motor cranks the engine at an
abnormally-slow speed, first make sure that
the battery is charged, and that all terminal
connections are tight. If the engine is partially-
seized, or has the wrong viscosity oil in it, it
will crank slowly.
9Run the engine until normal operating
temperature is reached, then disconnect the
coil HT lead from the distributor cap and earth
it on the engine.
10Connect a voltmeter positive lead to the
battery positive post, and connect the
negative lead to the negative post.11Crank the engine, and take the voltmeter
readings as soon as a steady figure is
indicated. Do not allow the starter motor to
turn for more than 10 seconds at a time. A
reading of 9 volts or more, with the starter
motor turning at normal cranking speed, is
normal. If the reading is 9 volts or more but
the cranking speed is slow, the solenoid
contacts are burned, there is a bad
connection, or the starter motor itself is faulty.
If the reading is less than 9 volts and the
cranking speed is slow, the starter motor is
faulty or the battery is responsible (defective
or discharged).
20 Starter motor-
removal and refitting
1
Note:If the starter motor is defective, it should
be renewed, or taken to an auto electrical
specialist for repair. Overhaul of the starter
motor is unlikely to be a practical proposition
for the home mechanic, even if spare parts are
available. However, the solenoid can be
renewed separately (see Section 21).
Removal
Caution: If the radio in your
vehicle is equipped with an anti-
theft system, make sure you
have the correct activation code
before disconnecting the battery. Refer to
the information on page 0-7 at the front of
this manual before detaching the cable.
Note: If, after connecting the battery, the
wrong language appears on the instrument
panel display, refer to page 0-7 for the
language resetting procedure.
1Detach the battery negative cable.
2Raise the vehicle and support it securely on
axle stands.
3Clearly label the wires from the terminals onthe starter motor and solenoid, then
disconnect them. Note: On some models, it
may be necessary to remove the air cleaner
(see Chapter 4), coolant expansion tank (see
Chapter 3) and the heater hoses to gain
access to the top of the starter. Carefully label
any hoses or components that need to be
removed from the engine compartment, to
avoid confusion when reassembling.
4Unscrew the mounting bolts and detach the
starter (see illustrations).
Refitting
5Refitting is the reverse of removal.
21 Starter solenoid-
removal and refitting
1
Removal
Caution: If the radio in your
vehicle is equipped with an anti-
theft system, make sure you
have the correct activation code
before disconnecting the battery. Refer to
the information on page 0-7 at the front of
this manual before detaching the cable.
Note: If, after connecting the battery, the
wrong language appears on the instrument
panel display, refer to page 0-7 for the
language resetting procedure.
1Disconnect the battery negative cable.
2Remove the starter motor (see Section 20).
3Disconnect the cable from the solenoid to
the starter motor terminal.
4Remove the screws which secure the
solenoid to the starter motor.
5Detach the solenoid from the starter body.
6Remove the plunger and plunger spring.
Refitting
7Refitting is the reverse of removal.
5•12 Engine electrical systems
20.4b Withdrawing the starter motor from
the M40 engine20.4a Working under the vehicle, remove
the starter lower mounting bolt and nut
(arrowed)
Page 125 of 228
Check
12Warm up the engine, and let it run at idle.
Disconnect the oxygen sensor electrical
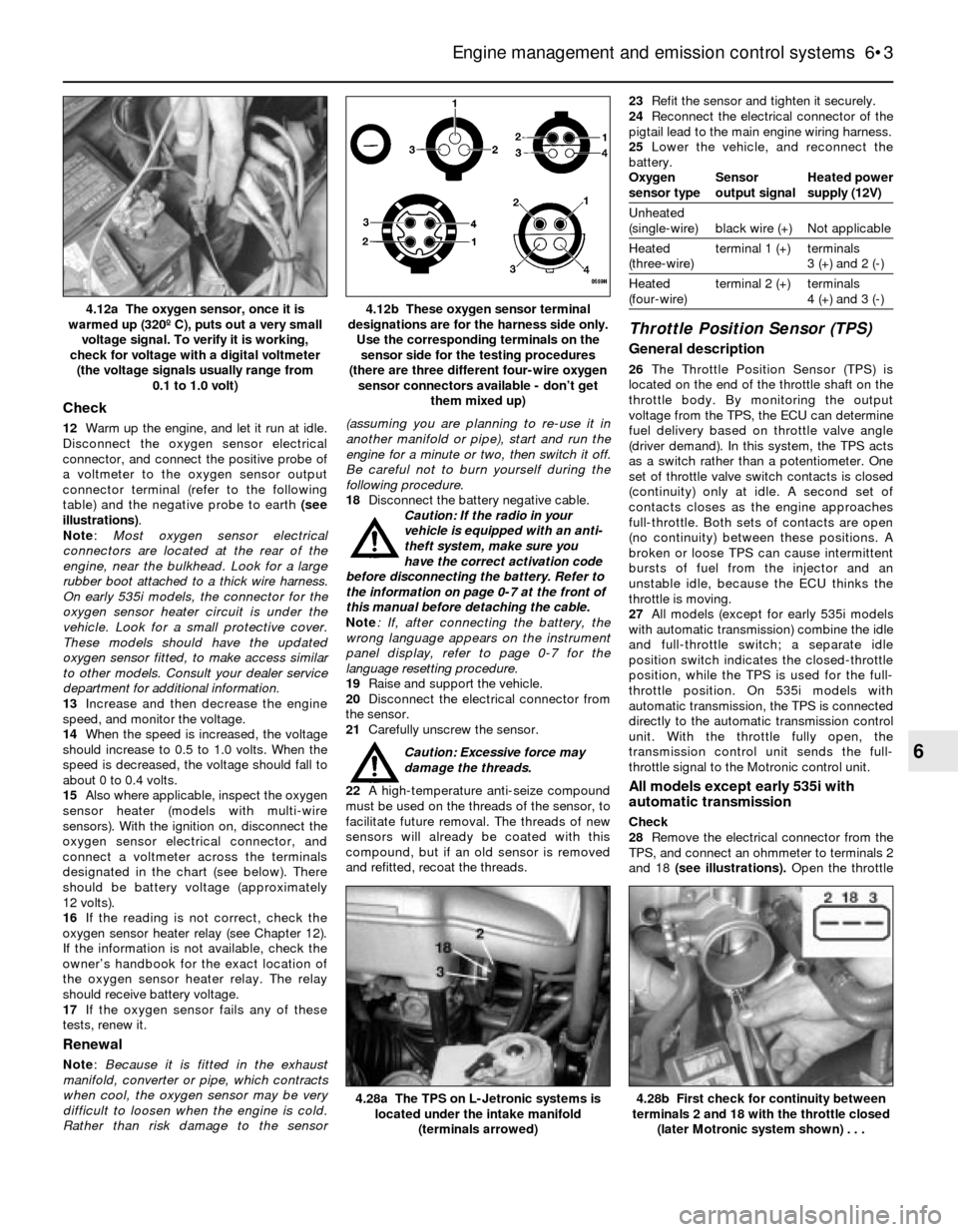
connector, and connect the positive probe of
a voltmeter to the oxygen sensor output
connector terminal (refer to the following
table) and the negative probe to earth (see
illustrations).
Note:Most oxygen sensor electrical
connectors are located at the rear of the
engine, near the bulkhead. Look for a large
rubber boot attached to a thick wire harness.
On early 535i models, the connector for the
oxygen sensor heater circuit is under the
vehicle. Look for a small protective cover.
These models should have the updated
oxygen sensor fitted, to make access similar
to other models. Consult your dealer service
department for additional information.
13Increase and then decrease the engine
speed, and monitor the voltage.
14When the speed is increased, the voltage
should increase to 0.5 to 1.0 volts. When the
speed is decreased, the voltage should fall to
about 0 to 0.4 volts.
15Also where applicable, inspect the oxygen
sensor heater (models with multi-wire
sensors). With the ignition on, disconnect the
oxygen sensor electrical connector, and
connect a voltmeter across the terminals
designated in the chart (see below). There
should be battery voltage (approximately
12 volts).
16If the reading is not correct, check the
oxygen sensor heater relay (see Chapter 12).
If the information is not available, check the
owner’s handbook for the exact location of
the oxygen sensor heater relay. The relay
should receive battery voltage.
17If the oxygen sensor fails any of these
tests, renew it.
Renewal
Note: Because it is fitted in the exhaust
manifold, converter or pipe, which contracts
when cool, the oxygen sensor may be very
difficult to loosen when the engine is cold.
Rather than risk damage to the sensor(assuming you are planning to re-use it in
another manifold or pipe), start and run the
engine for a minute or two, then switch it off.
Be careful not to burn yourself during the
following procedure.
18Disconnect the battery negative cable.
Caution: If the radio in your
vehicle is equipped with an anti-
theft system, make sure you
have the correct activation code
before disconnecting the battery. Refer to
the information on page 0-7 at the front of
this manual before detaching the cable.
Note: If, after connecting the battery, the
wrong language appears on the instrument
panel display, refer to page 0-7 for the
language resetting procedure.
19Raise and support the vehicle.
20Disconnect the electrical connector from
the sensor.
21Carefully unscrew the sensor.
Caution: Excessive force may
damage the threads.
22A high-temperature anti-seize compound
must be used on the threads of the sensor, to
facilitate future removal. The threads of new
sensors will already be coated with this
compound, but if an old sensor is removed
and refitted, recoat the threads.23Refit the sensor and tighten it securely.
24Reconnect the electrical connector of the
pigtail lead to the main engine wiring harness.
25Lower the vehicle, and reconnect the
battery.
Oxygen Sensor Heated power
sensor type output signal supply (12V)
Unheated
(single-wire) black wire (+) Not applicable
Heated terminal 1 (+) terminals
(three-wire) 3 (+) and 2 (-)
Heated terminal 2 (+) terminals
(four-wire) 4 (+) and 3 (-)
Throttle Position Sensor (TPS)
General description
26The Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) is
located on the end of the throttle shaft on the
throttle body. By monitoring the output
voltage from the TPS, the ECU can determine
fuel delivery based on throttle valve angle
(driver demand). In this system, the TPS acts
as a switch rather than a potentiometer. One
set of throttle valve switch contacts is closed
(continuity) only at idle. A second set of
contacts closes as the engine approaches
full-throttle. Both sets of contacts are open
(no continuity) between these positions. A
broken or loose TPS can cause intermittent
bursts of fuel from the injector and an
unstable idle, because the ECU thinks the
throttle is moving.
27All models (except for early 535i models
with automatic transmission) combine the idle
and full-throttle switch; a separate idle
position switch indicates the closed-throttle
position, while the TPS is used for the full-
throttle position. On 535i models with
automatic transmission, the TPS is connected
directly to the automatic transmission control
unit. With the throttle fully open, the
transmission control unit sends the full-
throttle signal to the Motronic control unit.
All models except early 535i with
automatic transmission
Check
28Remove the electrical connector from the
TPS, and connect an ohmmeter to terminals 2
and 18 (see illustrations). Open the throttle
Engine management and emission control systems 6•3
4.12b These oxygen sensor terminal
designations are for the harness side only.
Use the corresponding terminals on the
sensor side for the testing procedures
(there are three different four-wire oxygen
sensor connectors available - don’t get
them mixed up)4.12a The oxygen sensor, once it is
warmed up (320º C), puts out a very small
voltage signal. To verify it is working,
check for voltage with a digital voltmeter
(the voltage signals usually range from
0.1 to 1.0 volt)
4.28b First check for continuity between
terminals 2 and 18 with the throttle closed
(later Motronic system shown) . . .4.28a The TPS on L-Jetronic systems is
located under the intake manifold
(terminals arrowed)
6
Page 126 of 228
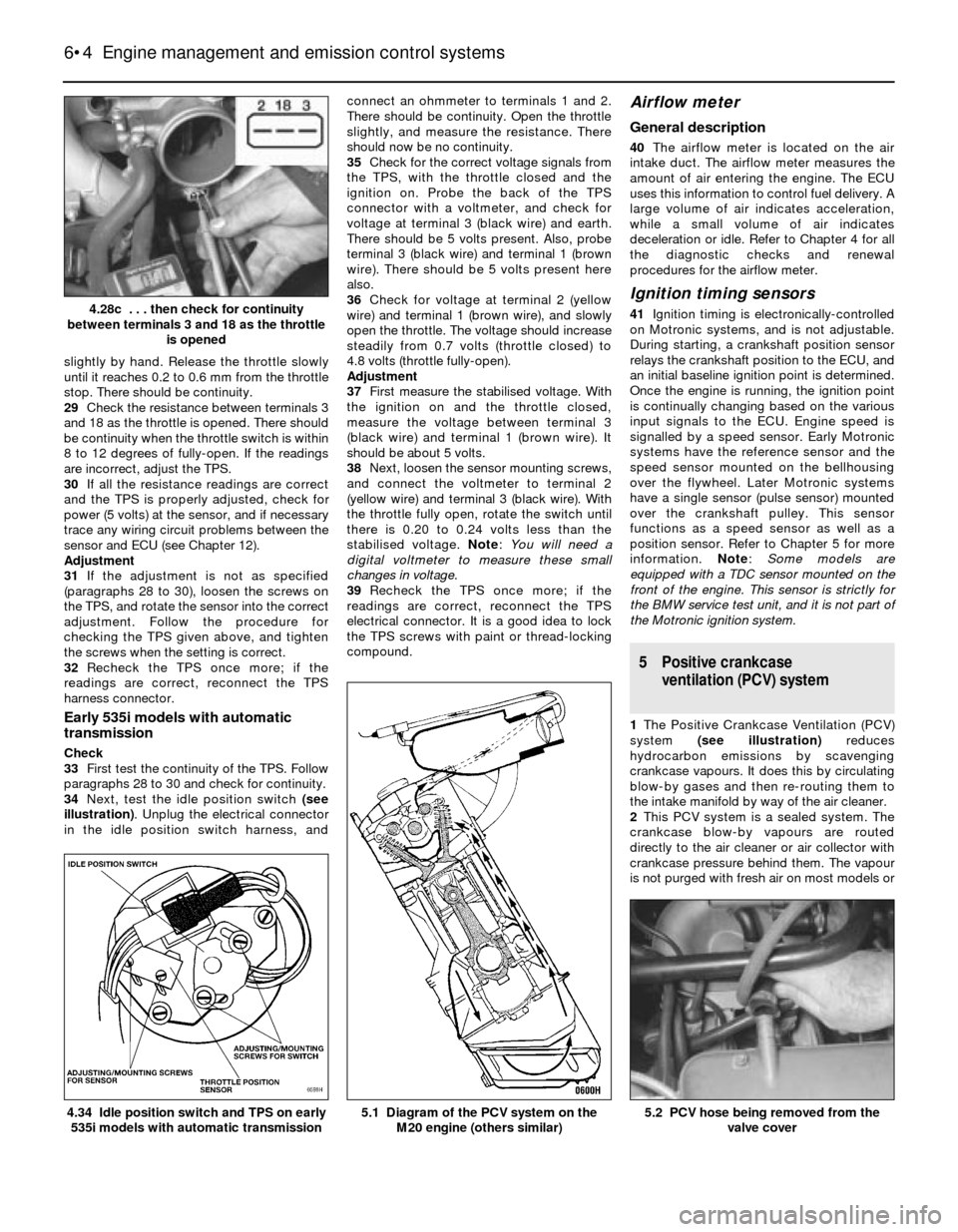
slightly by hand. Release the throttle slowly
until it reaches 0.2 to 0.6 mm from the throttle
stop. There should be continuity.
29Check the resistance between terminals 3
and 18 as the throttle is opened. There should
be continuity when the throttle switch is within
8 to 12 degrees of fully-open. If the readings
are incorrect, adjust the TPS.
30If all the resistance readings are correct
and the TPS is properly adjusted, check for
power (5 volts) at the sensor, and if necessary
trace any wiring circuit problems between the
sensor and ECU (see Chapter 12).
Adjustment
31If the adjustment is not as specified
(paragraphs 28 to 30), loosen the screws on
the TPS, and rotate the sensor into the correct
adjustment. Follow the procedure for
checking the TPS given above, and tighten
the screws when the setting is correct.
32Recheck the TPS once more; if the
readings are correct, reconnect the TPS
harness connector.
Early 535i models with automatic
transmission
Check
33First test the continuity of the TPS. Follow
paragraphs 28 to 30 and check for continuity.
34Next, test the idle position switch (see
illustration). Unplug the electrical connector
in the idle position switch harness, andconnect an ohmmeter to terminals 1 and 2.
There should be continuity. Open the throttle
slightly, and measure the resistance. There
should now be no continuity.
35Check for the correct voltage signals from
the TPS, with the throttle closed and the
ignition on. Probe the back of the TPS
connector with a voltmeter, and check for
voltage at terminal 3 (black wire) and earth.
There should be 5 volts present. Also, probe
terminal 3 (black wire) and terminal 1 (brown
wire). There should be 5 volts present here
also.
36Check for voltage at terminal 2 (yellow
wire) and terminal 1 (brown wire), and slowly
open the throttle. The voltage should increase
steadily from 0.7 volts (throttle closed) to
4.8 volts (throttle fully-open).
Adjustment
37First measure the stabilised voltage. With
the ignition on and the throttle closed,
measure the voltage between terminal 3
(black wire) and terminal 1 (brown wire). It
should be about 5 volts.
38Next, loosen the sensor mounting screws,
and connect the voltmeter to terminal 2
(yellow wire) and terminal 3 (black wire). With
the throttle fully open, rotate the switch until
there is 0.20 to 0.24 volts less than the
stabilised voltage. Note: You will need a
digital voltmeter to measure these small
changes in voltage.
39Recheck the TPS once more; if the
readings are correct, reconnect the TPS
electrical connector. It is a good idea to lock
the TPS screws with paint or thread-locking
compound.
Airflow meter
General description
40The airflow meter is located on the air
intake duct. The airflow meter measures the
amount of air entering the engine. The ECU
uses this information to control fuel delivery. A
large volume of air indicates acceleration,
while a small volume of air indicates
deceleration or idle. Refer to Chapter 4 for all
the diagnostic checks and renewal
procedures for the airflow meter.
Ignition timing sensors
41Ignition timing is electronically-controlled
on Motronic systems, and is not adjustable.
During starting, a crankshaft position sensor
relays the crankshaft position to the ECU, and
an initial baseline ignition point is determined.
Once the engine is running, the ignition point
is continually changing based on the various
input signals to the ECU. Engine speed is
signalled by a speed sensor. Early Motronic
systems have the reference sensor and the
speed sensor mounted on the bellhousing
over the flywheel. Later Motronic systems
have a single sensor (pulse sensor) mounted
over the crankshaft pulley. This sensor
functions as a speed sensor as well as a
position sensor. Refer to Chapter 5 for more
information. Note: Some models are
equipped with a TDC sensor mounted on the
front of the engine. This sensor is strictly for
the BMW service test unit, and it is not part of
the Motronic ignition system.
5 Positive crankcase
ventilation (PCV) system
1The Positive Crankcase Ventilation (PCV)
system (see illustration)reduces
hydrocarbon emissions by scavenging
crankcase vapours. It does this by circulating
blow-by gases and then re-routing them to
the intake manifold by way of the air cleaner.
2This PCV system is a sealed system. The
crankcase blow-by vapours are routed
directly to the air cleaner or air collector with
crankcase pressure behind them. The vapour
is not purged with fresh air on most models or
6•4 Engine management and emission control systems
5.2 PCV hose being removed from the
valve cover5.1 Diagram of the PCV system on the
M20 engine (others similar)4.34 Idle position switch and TPS on early
535i models with automatic transmission
4.28c . . . then check for continuity
between terminals 3 and 18 as the throttle
is opened
Page 127 of 228
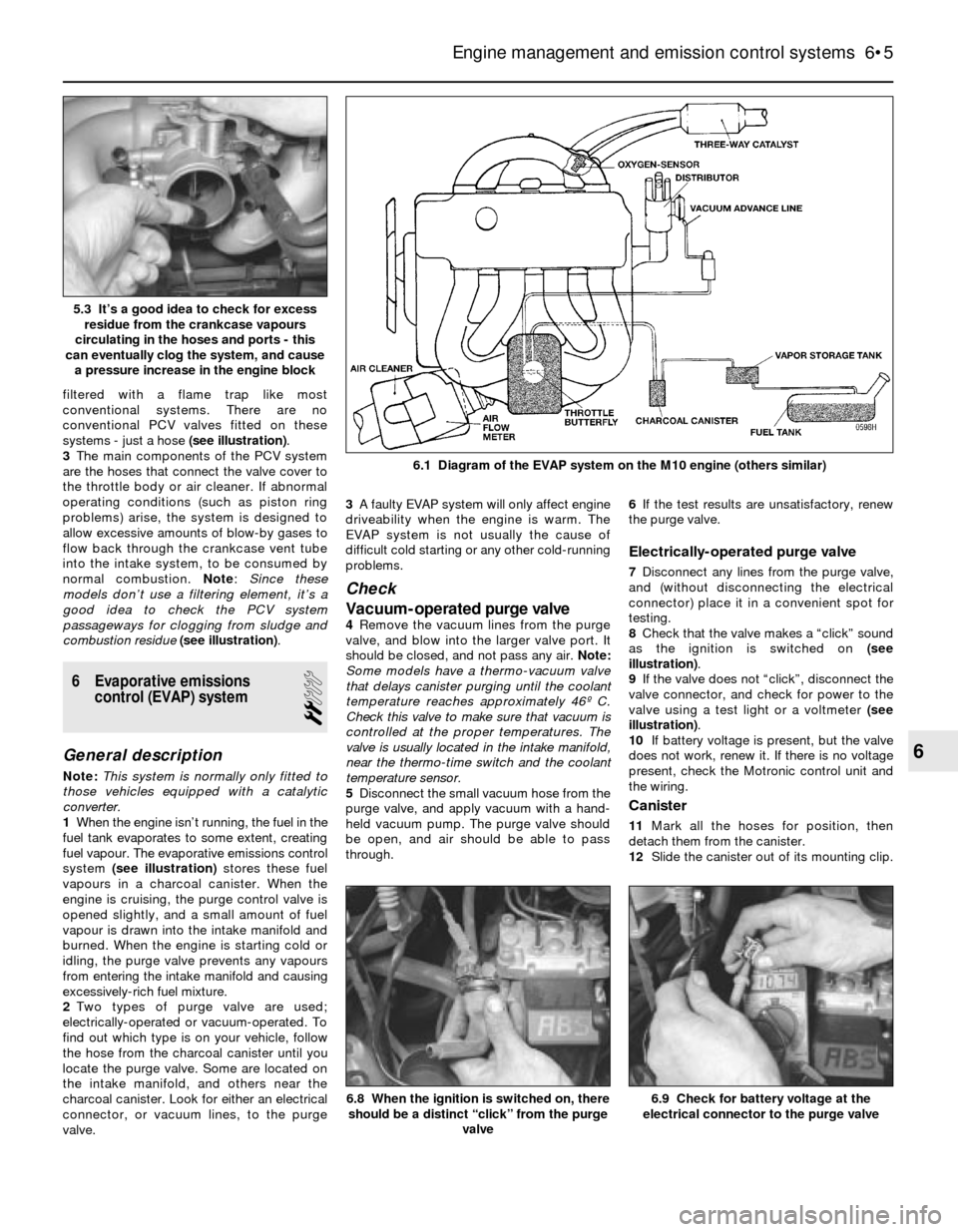
filtered with a flame trap like most
conventional systems. There are no
conventional PCV valves fitted on these
systems - just a hose (see illustration).
3The main components of the PCV system
are the hoses that connect the valve cover to
the throttle body or air cleaner. If abnormal
operating conditions (such as piston ring
problems) arise, the system is designed to
allow excessive amounts of blow-by gases to
flow back through the crankcase vent tube
into the intake system, to be consumed by
normal combustion. Note: Since these
models don’t use a filtering element, it’s a
good idea to check the PCV system
passageways for clogging from sludge and
combustion residue(see illustration).
6 Evaporative emissions
control (EVAP) system
2
General description
Note:This system is normally only fitted to
those vehicles equipped with a catalytic
converter.
1When the engine isn’t running, the fuel in the
fuel tank evaporates to some extent, creating
fuel vapour. The evaporative emissions control
system (see illustration)stores these fuel
vapours in a charcoal canister. When the
engine is cruising, the purge control valve is
opened slightly, and a small amount of fuel
vapour is drawn into the intake manifold and
burned. When the engine is starting cold or
idling, the purge valve prevents any vapours
from entering the intake manifold and causing
excessively-rich fuel mixture.
2Two types of purge valve are used;
electrically-operated or vacuum-operated. To
find out which type is on your vehicle, follow
the hose from the charcoal canister until you
locate the purge valve. Some are located on
the intake manifold, and others near the
charcoal canister. Look for either an electrical
connector, or vacuum lines, to the purge
valve.3A faulty EVAP system will only affect engine
driveability when the engine is warm. The
EVAP system is not usually the cause of
difficult cold starting or any other cold-running
problems.
Check
Vacuum-operated purge valve
4Remove the vacuum lines from the purge
valve, and blow into the larger valve port. It
should be closed, and not pass any air. Note:
Some models have a thermo-vacuum valve
that delays canister purging until the coolant
temperature reaches approximately 46º C.
Check this valve to make sure that vacuum is
controlled at the proper temperatures. The
valve is usually located in the intake manifold,
near the thermo-time switch and the coolant
temperature sensor.
5Disconnect the small vacuum hose from the
purge valve, and apply vacuum with a hand-
held vacuum pump. The purge valve should
be open, and air should be able to pass
through.6If the test results are unsatisfactory, renew
the purge valve.
Electrically-operated purge valve
7Disconnect any lines from the purge valve,
and (without disconnecting the electrical
connector) place it in a convenient spot for
testing.
8Check that the valve makes a “click” sound
as the ignition is switched on (see
illustration).
9If the valve does not “click”, disconnect the
valve connector, and check for power to the
valve using a test light or a voltmeter (see
illustration).
10If battery voltage is present, but the valve
does not work, renew it. If there is no voltage
present, check the Motronic control unit and
the wiring.
Canister
11Mark all the hoses for position, then
detach them from the canister.
12Slide the canister out of its mounting clip.
Engine management and emission control systems 6•5
6.1 Diagram of the EVAP system on the M10 engine (others similar)
6.9 Check for battery voltage at the
electrical connector to the purge valve6.8 When the ignition is switched on, there
should be a distinct “click” from the purge
valve
6
5.3 It’s a good idea to check for excess
residue from the crankcase vapours
circulating in the hoses and ports - this
can eventually clog the system, and cause
a pressure increase in the engine block
Page 128 of 228
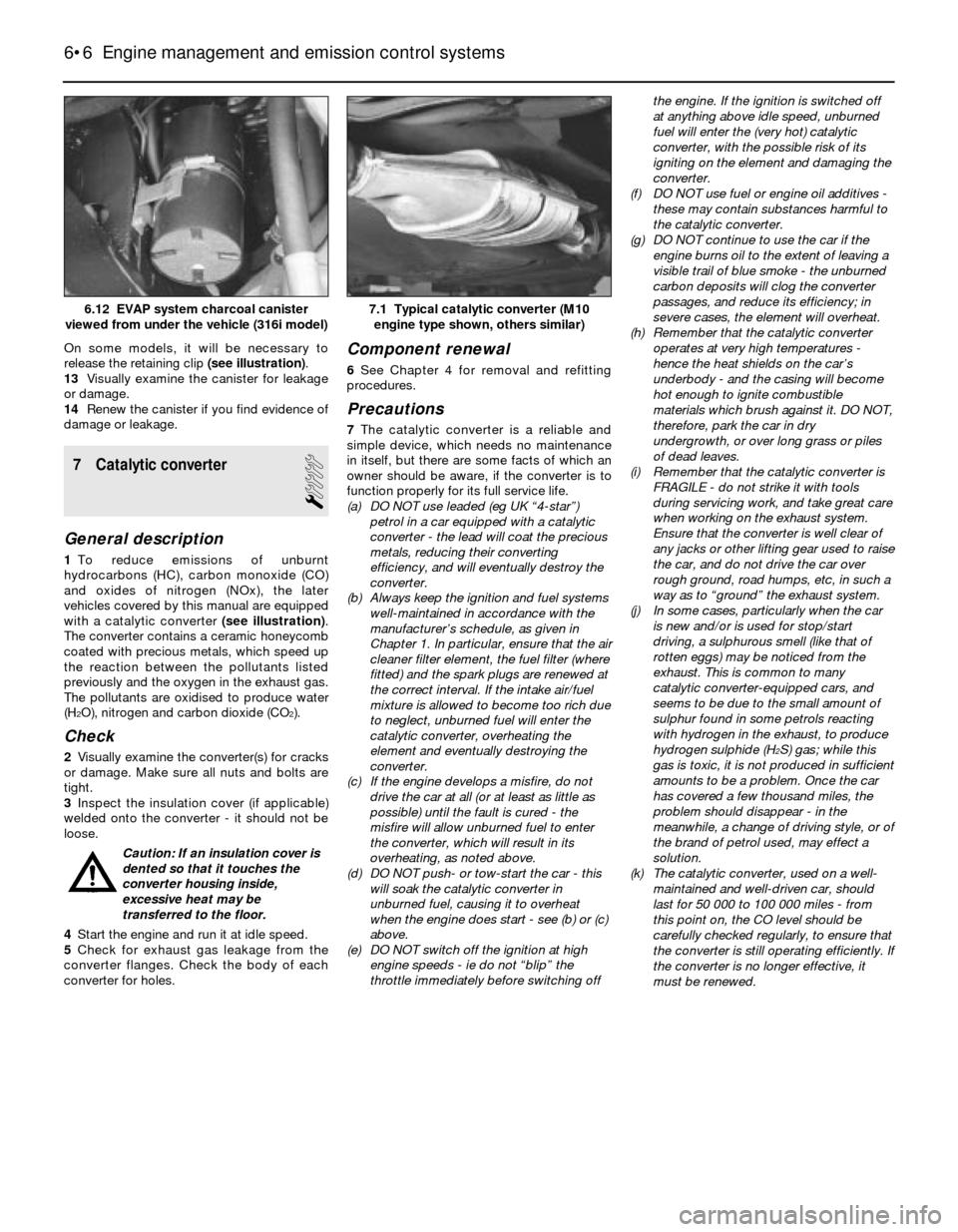
On some models, it will be necessary to
release the retaining clip (see illustration).
13Visually examine the canister for leakage
or damage.
14Renew the canister if you find evidence of
damage or leakage.
7 Catalytic converter
1
General description
1To reduce emissions of unburnt
hydrocarbons (HC), carbon monoxide (CO)
and oxides of nitrogen (NOx), the later
vehicles covered by this manual are equipped
with a catalytic converter (see illustration).
The converter contains a ceramic honeycomb
coated with precious metals, which speed up
the reaction between the pollutants listed
previously and the oxygen in the exhaust gas.
The pollutants are oxidised to produce water
(H
2O), nitrogen and carbon dioxide (CO2).
Check
2Visually examine the converter(s) for cracks
or damage. Make sure all nuts and bolts are
tight.
3Inspect the insulation cover (if applicable)
welded onto the converter - it should not be
loose.
Caution: If an insulation cover is
dented so that it touches the
converter housing inside,
excessive heat may be
transferred to the floor.
4Start the engine and run it at idle speed.
5Check for exhaust gas leakage from the
converter flanges. Check the body of each
converter for holes.
Component renewal
6See Chapter 4 for removal and refitting
procedures.
Precautions
7The catalytic converter is a reliable and
simple device, which needs no maintenance
in itself, but there are some facts of which an
owner should be aware, if the converter is to
function properly for its full service life.
(a) DO NOT use leaded (eg UK “4-star”)
petrol in a car equipped with a catalytic
converter - the lead will coat the precious
metals, reducing their converting
efficiency, and will eventually destroy the
converter.
(b) Always keep the ignition and fuel systems
well-maintained in accordance with the
manufacturer’s schedule, as given in
Chapter 1. In particular, ensure that the air
cleaner filter element, the fuel filter (where
fitted) and the spark plugs are renewed at
the correct interval. If the intake air/fuel
mixture is allowed to become too rich due
to neglect, unburned fuel will enter the
catalytic converter, overheating the
element and eventually destroying the
converter.
(c) If the engine develops a misfire, do not
drive the car at all (or at least as little as
possible) until the fault is cured - the
misfire will allow unburned fuel to enter
the converter, which will result in its
overheating, as noted above.
(d) DO NOT push- or tow-start the car - this
will soak the catalytic converter in
unburned fuel, causing it to overheat
when the engine does start - see (b) or (c)
above.
(e) DO NOT switch off the ignition at high
engine speeds - ie do not “blip” the
throttle immediately before switching offthe engine. If the ignition is switched off
at anything above idle speed, unburned
fuel will enter the (very hot) catalytic
converter, with the possible risk of its
igniting on the element and damaging the
converter.
(f) DO NOT use fuel or engine oil additives -
these may contain substances harmful to
the catalytic converter.
(g) DO NOT continue to use the car if the
engine burns oil to the extent of leaving a
visible trail of blue smoke - the unburned
carbon deposits will clog the converter
passages, and reduce its efficiency; in
severe cases, the element will overheat.
(h) Remember that the catalytic converter
operates at very high temperatures -
hence the heat shields on the car’s
underbody - and the casing will become
hot enough to ignite combustible
materials which brush against it. DO NOT,
therefore, park the car in dry
undergrowth, or over long grass or piles
of dead leaves.
(i) Remember that the catalytic converter is
FRAGILE - do not strike it with tools
during servicing work, and take great care
when working on the exhaust system.
Ensure that the converter is well clear of
any jacks or other lifting gear used to raise
the car, and do not drive the car over
rough ground, road humps, etc, in such a
way as to “ground” the exhaust system.
(j) In some cases, particularly when the car
is new and/or is used for stop/start
driving, a sulphurous smell (like that of
rotten eggs) may be noticed from the
exhaust. This is common to many
catalytic converter-equipped cars, and
seems to be due to the small amount of
sulphur found in some petrols reacting
with hydrogen in the exhaust, to produce
hydrogen sulphide (H
2S) gas; while this
gas is toxic, it is not produced in sufficient
amounts to be a problem. Once the car
has covered a few thousand miles, the
problem should disappear - in the
meanwhile, a change of driving style, or of
the brand of petrol used, may effect a
solution.
(k) The catalytic converter, used on a well-
maintained and well-driven car, should
last for 50 000 to 100 000 miles - from
this point on, the CO level should be
carefully checked regularly, to ensure that
the converter is still operating efficiently. If
the converter is no longer effective, it
must be renewed.
6•6 Engine management and emission control systems
7.1 Typical catalytic converter (M10
engine type shown, others similar)6.12 EVAP system charcoal canister
viewed from under the vehicle (316i model)
Page 169 of 228

12
Chapter 12 Body electrical systems
Bulb renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Central locking system - description and check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Cruise control system - description and check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Direction indicator/hazard warning flasher - check and renewal . . . 5
Electric windows - description and check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Electrical system fault finding - general information . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Fuses - general information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
General information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
Headlight housing - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Headlights - adjustment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Headlights - bulb renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12Heated rear window - check and repair . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Ignition switch - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Instrument cluster - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Radio - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Radio aerial - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Relays - general information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
Service Indicator (SI) board - general information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Steering column switches - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Supplemental Restraint System (SRS) - general information . . . . . . 18
Windscreen/tailgate wiper motor - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . 16
Wiring diagrams - general information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
12•1
Easy,suitable for
novice with little
experienceFairly easy,suitable
for beginner with
some experienceFairly difficult,
suitable for competent
DIY mechanic
Difficult,suitable for
experienced DIY
mechanicVery difficult,
suitable for expert
DIY or professional
Degrees of difficulty Contents
1 General information
The chassis electrical system of this vehicle
is of 12-volt, negative earth type. Power for
the lights and all electrical accessories is
supplied by a lead/acid-type battery, which is
charged by the alternator.
This Chapter covers repair and service
procedures for various chassis (non-engine
related) electrical components. For
information regarding the engine electrical
system components (battery, alternator,
distributor and starter motor), see Chapter 5.
Warning: To prevent electrical
short-circuits, fires and injury,
always disconnect the battery
negative terminal before
checking, repairing or renewing electrical
components.
Caution: If the radio in your
vehicle is equipped with an anti-
theft system, make sure you have
the correct activation code
before disconnecting the battery, Refer to
the information on page 0-7 at the front of
this manual before detaching the cable.
Note: If, after connecting the battery, the
wrong language appears on the instrument
panel display, refer to page 0-7 for the
language resetting procedure.
2 Electrical system fault
finding- general information
2
A typical electrical circuit consists of an
electrical component, any switches, relays,
motors, fuses, fusible links or circuit breakers,
etc related to that component, and the wiring
and connectors that link the components to
both the battery and the chassis. To help you
pinpoint an electrical circuit problem, wiring
diagrams are included at the end of this book.
Before tackling any troublesome electrical
circuit, first study the appropriate wiring
diagrams to get a complete understanding of
what makes up that individual circuit.
Troublespots, for instance, can often be
isolated by noting if other components related
to that circuit are routed through the same
fuse and earth connections.
Electrical problems usually stem from
simple causes such as loose or corroded
connectors, a blown fuse, a melted fusible
link, or a bad relay. Inspect all fuses, wires
and connectors in a problem circuit first.
The basic tools needed include a circuit
tester, a high-impedance digital voltmeter, a
continuity tester and a jumper wire with an in-
line circuit breaker for bypassing electrical
components. Before attempting to locate or
define a problem with electrical testinstruments, use the wiring diagrams to
decide where to make the necessary
connections.
Voltage checks
Perform a voltage check first when a circuit
is not functioning properly. Connect one lead
of a circuit tester to either the negative battery
terminal or a known good earth.
Connect the other lead to a connector in
the circuit being tested, preferably nearest to
the battery or fuse. If the bulb of the tester
lights up, voltage is present, which means that
the part of the circuit between the connector
and the battery is problem-free. Continue
checking the rest of the circuit in the same
fashion.
When you reach a point at which no voltage
is present, the problem lies between that point
and the last test point with voltage. Most of
the time, problems can be traced to a loose
connection.Note:Keep in mind that some
circuits receive voltage only when the ignition
key is turned to a certain position.
Electrical fault diagnosis is simple if you
keep in mind that all electrical circuits are
basically electricity running from the battery,
through the wires, switches, relays, fuses and
fusible links to each electrical component
(light bulb, motor, etc) and then to earth, from
where it is passed back to the battery. Any
electrical problem is an interruption in the flow
of electricity to and from the battery.
Page 171 of 228

indicates that the direction indicator and/or
hazard fuse has blown, check the wiring for a
short-circuit before fitting a new fuse.
4Make sure that the new unit is identical to
the original. Compare the old one to the new
one before fitting it.
5Refitting is the reverse of removal.
6 Steering column switches-
removal and refitting
1
Warning: Some later models are
equipped with an airbag or
Supplemental Restraint System
(SRS). To avoid possible damage
to this system, the manufacturer
recommends that, on airbag-equipped
models, the following procedure should be
left to a dealer service department, or
other specialist, because of the special
tools and techniques required. There is a
risk of injury if the airbag is accidentally
triggered.
Caution: If the radio in your
vehicle is equipped with an anti-
theft system, make sure you have
the correct activation code
before disconnecting the battery, Refer to
the information on page 0-7 at the front of
this manual before detaching the cable.
Note: If, after connecting the battery, the
wrong language appears on the instrument
panel display, refer to page 0-7 for the
language resetting procedure.
1Disconnect the battery negative cable,
remove the steering wheel (see Chapter 10)
and steering column shrouds (see Chapter 11).
Direction indicator/headlight
switch
2Where necessary, remove the switch
mounting screws. Depress the tabs and pull
the switch out of the steering column
mounting (see illustration).
3Trace the switch wires down the steering
column to the electrical connector, and
unplug them (see illustration).
4Refitting is the reverse of removal.
Wiper/washer switch
5Where necessary, remove the switch
mounting screws.
6Depress the release clip, and detach the
switch from the steering column mounting
(see illustration). Trace the switch wiring
down the steering column to the electrical
connector, and unplug it.
7Refitting is the reverse of removal.
Cruise control switch
8Remove the wiper/washer switch.
9Where necessary, remove the switch
mounting screw. Squeeze the release tabs,
and withdraw the switch from the mounting
(see illustration).
10Disconnect the switch electrical
connector from the harness at the base of the
steering column.
11Refitting is the reverse of removal.
7 Ignition switch-
removal and refitting
1
Warning: Some later models are
equipped with an airbag or
Supplemental Restraint System
(SRS). To avoid possible damage
to this system, the manufacturer
recommends that, on airbag-equipped
models, the following procedure should be
left to a dealer service department, or
other specialist, because of the specialtools and techniques required. There is a
risk of injury if the airbag is accidentally
triggered.
Caution: If the radio in your
vehicle is equipped with an anti-
theft system, make sure you have
the correct activation code
before disconnecting the battery, Refer to
the information on page 0-7 at the front of
this manual before detaching the cable.
Note: If, after connecting the battery, the
wrong language appears on the instrument
panel display, refer to page 0-7 for the
language resetting procedure.
Removal
1Disconnect the battery negative cable.
2Remove the steering wheel (see Chap-
ter 10).
3Remove the steering column shrouds (see
Chapter 11).
4Where necessary, remove the direction
indicator/headlight control switch (see Sec-
tion 6).
5Detach the clips by inserting a small
screwdriver into the openings on the sides
while pulling out on the switch (see
illustration).
6Unplug the electrical connector from the
harness at the base of the steering column,
and remove the switch.
Refitting
7Refitting is the reverse of removal.
Body electrical systems 12•3
6.3 Follow the wiring down the steering
column to the connector6.2 Squeeze the tabs to release the switch
from the mounting
6.9 Cruise control switch removal6.6 Squeeze the wiper/washer switch tabs
and pull it directly out of the mounting
12
5.1 The direction indicator/hazard warning
flasher unit is located on the steering
column on most models - squeeze the
tabs to detach it