inspection BMW 3 SERIES 1985 E30 Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: BMW, Model Year: 1985, Model line: 3 SERIES, Model: BMW 3 SERIES 1985 E30Pages: 228, PDF Size: 7.04 MB
Page 66 of 228
24Repeat the procedure for the remaining
valves. Remember to keep all the parts for
each valve together, so they can be refitted in
the same locations.
25Once the valves and related components
have been removed and stored in an
organised manner, the head should be
thoroughly cleaned and inspected. If a
complete engine overhaul is being done,
finish the engine dismantling procedures
before beginning the cylinder head cleaning
and inspection process.
9 Cylinder head and
components-
cleaning and inspection
4
1Thorough cleaning of the cylinder head(s)
and related valve train components, followed
by a detailed inspection, will enable you to
decide how much valve service work must be
done during the engine overhaul. Note: If the
engine was severely overheated, the cylinder
head is probably warped (see paragraph 10).
Cleaning
2Scrape all traces of old gasket material and
sealing compound off the cylinder head,
intake manifold and exhaust manifold sealing
surfaces. Be very careful not to gouge the
cylinder head. Special gasket removal
solvents are available at motor factors.
3Remove all built-up scale from the coolant
passages.
4Run a stiff brush through the various holes
to remove deposits that may have formed in
them.
5Run an appropriate-size tap into each of the
threaded holes, to remove corrosion and
thread sealant that may be present. If
compressed air is available, use it to clear the
holes of debris produced by this operation.
Warning: Wear eye protection
when using compressed air!
6Clean the cylinder head with solvent, and
dry it thoroughly. Compressed air will speed
the drying process, and ensure that all holesand recessed areas are clean. Note:
Decarbonising chemicals are available, and
may prove very useful when cleaning cylinder
heads and valve train components. They are
very caustic, however, and should be used
with caution. Be sure to follow the instructions
on the container.
7Clean all the rocker shafts/arms/followers,
springs, valve springs, spring seats, keepers
and retainers with solvent, and dry them
thoroughly. Clean the components from one
valve at a time, to avoid mixing up the parts.
Caution: DO NOT clean the
hydraulic tappets of the M40
engine; leave them completely
immersed in oil.
8Scrape off any heavy deposits that may
have formed on the valves, then use a
motorised wire brush to remove deposits from
the valve heads and stems. Again, make sure
the valves don’t get mixed up.
Inspection
Note: Be sure to perform all of the following
inspection procedures before concluding that
machine shop work is required. Make a list of
the items that need attention.
Cylinder head
9Inspect the head very carefully for cracks,
evidence of coolant leakage, and other
damage. If cracks are found, check with an
machine shop concerning repair. If repair isn’t
possible, a new cylinder head should be
obtained.
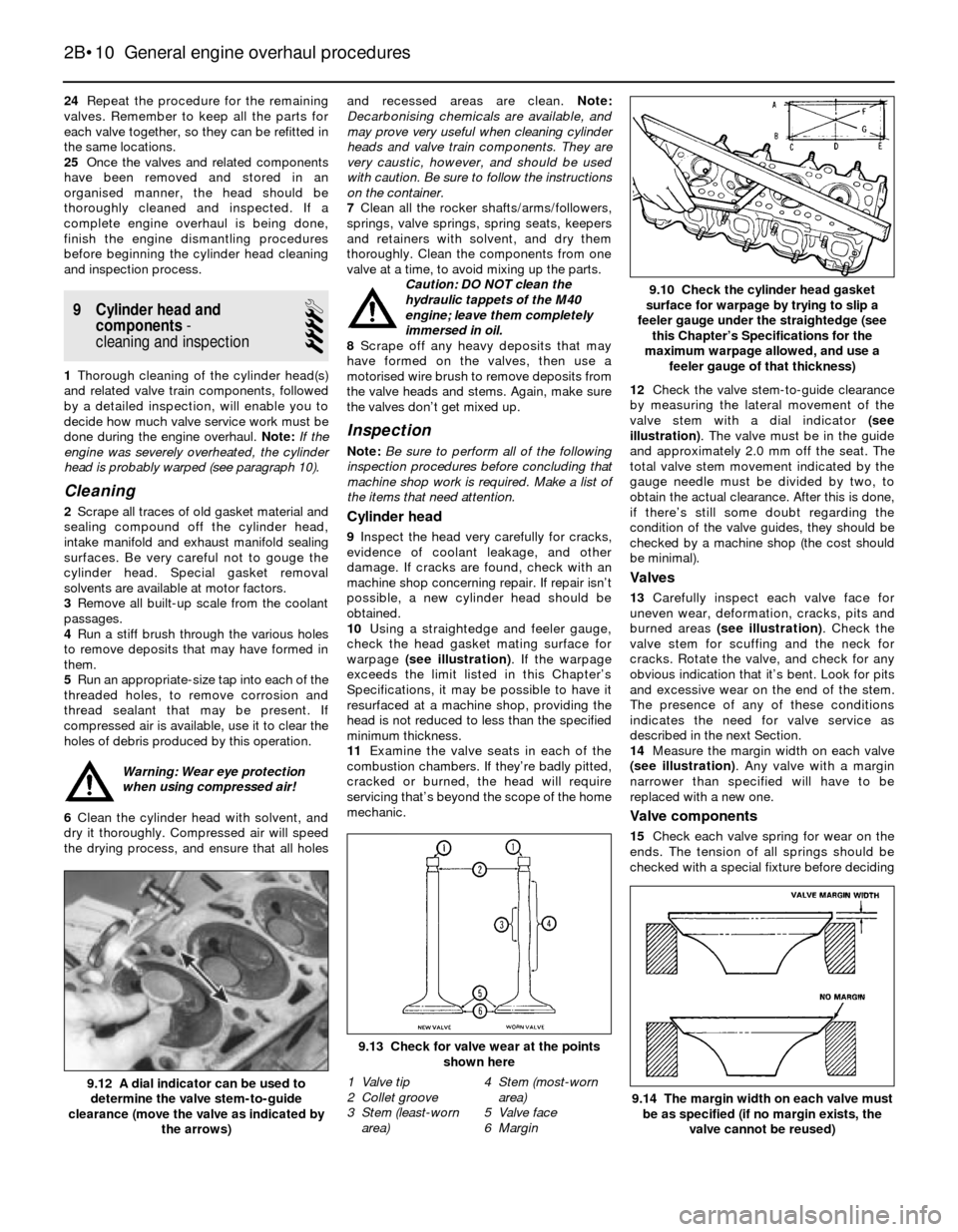
10Using a straightedge and feeler gauge,
check the head gasket mating surface for
warpage (see illustration). If the warpage
exceeds the limit listed in this Chapter’s
Specifications, it may be possible to have it
resurfaced at a machine shop, providing the
head is not reduced to less than the specified
minimum thickness.
11Examine the valve seats in each of the
combustion chambers. If they’re badly pitted,
cracked or burned, the head will require
servicing that’s beyond the scope of the home
mechanic.12Check the valve stem-to-guide clearance
by measuring the lateral movement of the
valve stem with a dial indicator (see
illustration). The valve must be in the guide
and approximately 2.0 mm off the seat. The
total valve stem movement indicated by the
gauge needle must be divided by two, to
obtain the actual clearance. After this is done,
if there’s still some doubt regarding the
condition of the valve guides, they should be
checked by a machine shop (the cost should
be minimal).
Valves
13Carefully inspect each valve face for
uneven wear, deformation, cracks, pits and
burned areas (see illustration). Check the
valve stem for scuffing and the neck for
cracks. Rotate the valve, and check for any
obvious indication that it’s bent. Look for pits
and excessive wear on the end of the stem.
The presence of any of these conditions
indicates the need for valve service as
described in the next Section.
14Measure the margin width on each valve
(see illustration). Any valve with a margin
narrower than specified will have to be
replaced with a new one.
Valve components
15Check each valve spring for wear on the
ends. The tension of all springs should be
checked with a special fixture before deciding
2B•10 General engine overhaul procedures
9.14 The margin width on each valve must
be as specified (if no margin exists, the
valve cannot be reused)
9.13 Check for valve wear at the points
shown here
9.12 A dial indicator can be used to
determine the valve stem-to-guide
clearance (move the valve as indicated by
the arrows)
9.10 Check the cylinder head gasket
surface for warpage by trying to slip a
feeler gauge under the straightedge (see
this Chapter’s Specifications for the
maximum warpage allowed, and use a
feeler gauge of that thickness)
1 Valve tip
2 Collet groove
3 Stem (least-worn
area)4 Stem (most-worn
area)
5 Valve face
6 Margin
Page 70 of 228

5Gently tap the caps with a soft-faced
hammer, then separate them from the engine
block. If necessary, use the bolts as levers to
remove the caps. Try not to drop the bearing
shells if they come out with the caps.
6Carefully lift the crankshaft out of the
engine. It may be a good idea to have an
assistant available, since the crankshaft is
quite heavy (see illustration). With the
bearing shells in place in the engine block and
main bearing caps, return the caps to their
respective locations on the engine block, and
tighten the bolts finger-tight.
14 Intermediate shaft-
removal and inspection
5
Note:The intermediate shaft is used on the
M20 engine only. The shaft rotates in the
engine block parallel to the crankshaft. It is
driven by the timing belt, and its only purpose
is to drive the oil pump.
1Remove the timing belt (see Chapter 2A).
2With the belt removed, unbolt the gear from
the intermediate shaft and unbolt the front
cover.
3Remove the oil pump driveshaft (see
Chapter 2A).
4The shaft is held in the cylinder block by a
retaining plate with two bolts. Remove the
bolts, and pull the shaft forwards and out of
the block.
5Look for any signs of abnormal wear on the
bearing surfaces or the gear at the back end
of the shaft, which drives the oil pump shaft. If
the bearing surfaces in the engine block show
wear, they’ll have to be attended to by a
machine shop.
15 Engine block- cleaning
2
Caution: The core plugs may be
difficult or impossible to retrieve
if they’re driven into the block
coolant passages.
1Remove the core plugs from the engine
block. To do this, knock one side of each plug
into the block with a hammer and punch,
grasp the other side by its edge with large
pliers, and pull it out.
2Using a gasket scraper, remove all traces of
gasket material from the engine block. Be very
careful not to nick or gouge the gasket sealing
surfaces.
3Remove the main bearing caps, and
separate the bearing shells from the caps and
the engine block. Tag the bearings, indicating
which cylinder they were removed from and
whether they were in the cap or the block,
then set them aside.
4Remove all of the threaded oil gallery plugs
from the block. The plugs are usually very
tight - they may have to be drilled out and theholes retapped. Use new plugs when the
engine is reassembled.
5If the engine is extremely dirty, it should be
taken to a machine shop to be steam-
cleaned.
6After the block is returned, clean all oil
holes and oil galleries one more time. Brushes
specifically designed for this purpose are
available at most motor factors. Flush the
passages with warm water until the water runs
clear, dry the block thoroughly, and wipe all
machined surfaces with a light, rust-
preventive oil. If you have access to
compressed air, use it to speed the drying
process and to blow out all the oil holes and
galleries.
Warning: Wear eye protection
when using compressed air!
7If the block isn’t extremely dirty or sludged
up, you can do an adequate cleaning job with
hot soapy water and a stiff brush. Take plenty
of time, and do a thorough job. Regardless of
the cleaning method used, be sure to clean all
oil holes and galleries very thoroughly, dry the
block completely, and coat all machined
surfaces with light oil.
8The threaded holes in the block must be
clean to ensure accurate torque readingsduring reassembly. Run the proper-size tap
into each of the holes to remove rust,
corrosion, thread sealant or sludge, and to
restore damaged threads (see illustration). If
possible, use compressed air to clear the
holes of debris produced by this operation. Be
sure also that the holes are dry- any oil or
other fluid present could cause the block to
be cracked by hydraulic pressure when the
bolts are tightened. Now is a good time to
clean the threads on all bolts. Note that BMW
recommend that the cylinder head bolts and
main bearing bolts are renewed as a matter of
course.
9Refit the main bearing caps, and tighten the
bolts finger-tight.
10After coating the sealing surfaces of the
new core plugs with a suitable sealant, refit
them in the engine block (see illustration).
Make sure they’re driven in straight and
seated properly, or leakage could result.
Special tools are available for this purpose,
but a large socket, with an outside diameter
that will just slip into the core plug, a 1/2-inch
drive extension, and a hammer, will work just
as well.
11Apply non-hardening sealant to the new
oil gallery plugs, and thread them into the
holes in the block. Make sure they’re
tightened securely.
12If the engine isn’t going to be
reassembled right away, cover it with a large
plastic bag to keep it clean.
2B•14 General engine overhaul procedures
15.10 A large socket on an extension can
be used to drive the new core plugs into
the block
15.8 All bolt holes in the block -
particularly the main bearing cap and head
bolt holes - should be cleaned and
restored with a tap (be sure to remove
debris from the holes after this is done)
13.6 Remove the crankshaft by lifting
straight up. Be very careful when removing
the crankshaft - it is very heavy13.4 Use a centre-punch or number-
stamping dies to mark the main bearing
caps to ensure refitting in their original
locations on the block (make the punch
marks near one of the bolt heads)
Page 71 of 228
16 Engine block- inspection
3
1Before the block is inspected, it should be
cleaned (see Section 15).
2Visually check the block for cracks, rust
and corrosion. Look for stripped threads in
the threaded holes. It’s also a good idea to
have the block checked for hidden cracks by
a machine shop that has the special
equipment to do this type of work. If defects
are found, have the block repaired, if possible;
otherwise, a new block will be required.
3Check the cylinder bores for scuffing and
scoring.
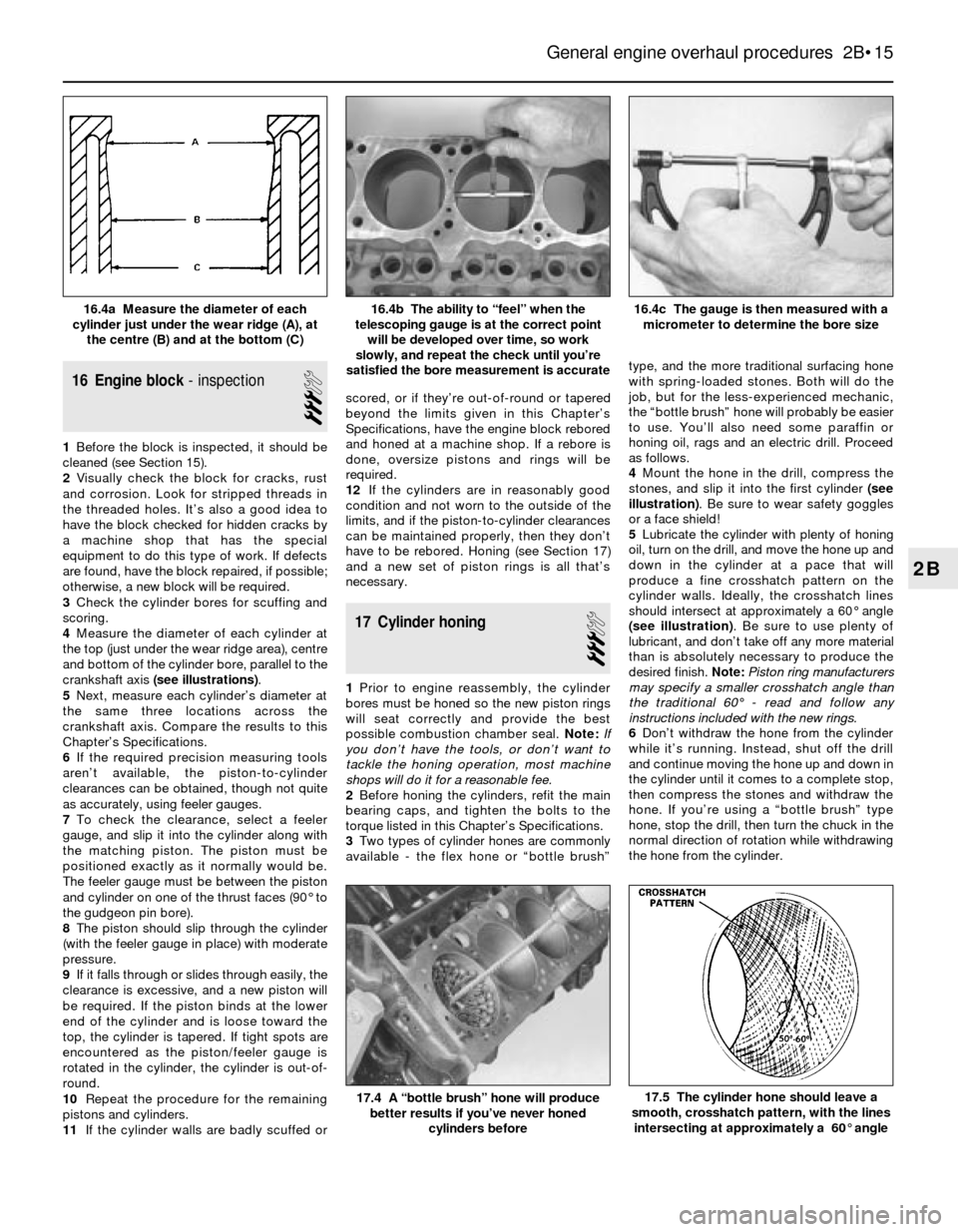
4Measure the diameter of each cylinder at
the top (just under the wear ridge area), centre
and bottom of the cylinder bore, parallel to the
crankshaft axis (see illustrations).
5Next, measure each cylinder’s diameter at
the same three locations across the
crankshaft axis. Compare the results to this
Chapter’s Specifications.
6If the required precision measuring tools
aren’t available, the piston-to-cylinder
clearances can be obtained, though not quite
as accurately, using feeler gauges.
7To check the clearance, select a feeler
gauge, and slip it into the cylinder along with
the matching piston. The piston must be
positioned exactly as it normally would be.
The feeler gauge must be between the piston
and cylinder on one of the thrust faces (90° to
the gudgeon pin bore).
8The piston should slip through the cylinder
(with the feeler gauge in place) with moderate
pressure.
9If it falls through or slides through easily, the
clearance is excessive, and a new piston will
be required. If the piston binds at the lower
end of the cylinder and is loose toward the
top, the cylinder is tapered. If tight spots are
encountered as the piston/feeler gauge is
rotated in the cylinder, the cylinder is out-of-
round.
10Repeat the procedure for the remaining
pistons and cylinders.
11If the cylinder walls are badly scuffed orscored, or if they’re out-of-round or tapered
beyond the limits given in this Chapter’s
Specifications, have the engine block rebored
and honed at a machine shop. If a rebore is
done, oversize pistons and rings will be
required.
12If the cylinders are in reasonably good
condition and not worn to the outside of the
limits, and if the piston-to-cylinder clearances
can be maintained properly, then they don’t
have to be rebored. Honing (see Section 17)
and a new set of piston rings is all that’s
necessary.
17 Cylinder honing
3
1Prior to engine reassembly, the cylinder
bores must be honed so the new piston rings
will seat correctly and provide the best
possible combustion chamber seal. Note:If
you don’t have the tools, or don’t want to
tackle the honing operation, most machine
shops will do it for a reasonable fee.
2Before honing the cylinders, refit the main
bearing caps, and tighten the bolts to the
torque listed in this Chapter’s Specifications.
3Two types of cylinder hones are commonly
available - the flex hone or “bottle brush”type, and the more traditional surfacing hone
with spring-loaded stones. Both will do the
job, but for the less-experienced mechanic,
the “bottle brush” hone will probably be easier
to use. You’ll also need some paraffin or
honing oil, rags and an electric drill. Proceed
as follows.
4Mount the hone in the drill, compress the
stones, and slip it into the first cylinder (see
illustration). Be sure to wear safety goggles
or a face shield!
5Lubricate the cylinder with plenty of honing
oil, turn on the drill, and move the hone up and
down in the cylinder at a pace that will
produce a fine crosshatch pattern on the
cylinder walls. Ideally, the crosshatch lines
should intersect at approximately a 60° angle
(see illustration). Be sure to use plenty of
lubricant, and don’t take off any more material
than is absolutely necessary to produce the
desired finish. Note:Piston ring manufacturers
may specify a smaller crosshatch angle than
the traditional 60°- read and follow any
instructions included with the new rings.
6Don’t withdraw the hone from the cylinder
while it’s running. Instead, shut off the drill
and continue moving the hone up and down in
the cylinder until it comes to a complete stop,
then compress the stones and withdraw the
hone. If you’re using a “bottle brush” type
hone, stop the drill, then turn the chuck in the
normal direction of rotation while withdrawing
the hone from the cylinder.
General engine overhaul procedures 2B•15
16.4c The gauge is then measured with a
micrometer to determine the bore size16.4b The ability to “feel” when the
telescoping gauge is at the correct point
will be developed over time, so work
slowly, and repeat the check until you’re
satisfied the bore measurement is accurate16.4a Measure the diameter of each
cylinder just under the wear ridge (A), at
the centre (B) and at the bottom (C)
17.5 The cylinder hone should leave a
smooth, crosshatch pattern, with the lines
intersecting at approximately a 60° angle17.4 A “bottle brush” hone will produce
better results if you’ve never honed
cylinders before
2B
Page 72 of 228

7Wipe the oil out of the cylinder, and repeat
the procedure for the remaining cylinders.
8After the honing job is complete, chamfer
the top edges of the cylinder bores with a
small file, so the rings won’t catch when the
pistons are refitted. Be very careful not to nick
the cylinder walls with the end of the file.
9The entire engine block must be washed
again very thoroughly with warm, soapy
water, to remove all traces of the abrasive grit
produced during the honing operation. Note:
The bores can be considered clean when a
lint-free white cloth - dampened with clean
engine oil - used to wipe them out doesn’t
pick up any more honing residue, which will
show up as grey areas on the cloth.Be sure to
run a brush through all oil holes and galleries,
and flush them with running water.
10After rinsing, dry the block, and apply a
coat of light rust-preventive oil to all machined
surfaces. Wrap the block in a plastic bag to
keep it clean, and set it aside until
reassembly.
18 Pistons/connecting rods-
inspection
3
1Before the inspection process can be
carried out, the piston/connecting rod
assemblies must be cleaned and the original
piston rings removed from the pistons.Note:
Always use new piston rings when the engine
is reassembled.
2Using a piston ring refitting tool, carefully
remove the rings from the pistons. Be careful
not to nick or gouge the pistons in the
process (see illustration).
3Scrape all traces of carbon from the top of
the piston. A hand-held wire brush or a piece
of fine emery cloth can be used once the
majority of the deposits have been scraped
away. Do not, under any circumstances, use a
wire brush mounted in a drill motor to remove
deposits from the pistons. The piston material
is soft, and may be damaged by the wire
brush.
4Use a piston ring groove cleaning tool to
remove carbon deposits from the ring
grooves. Be very careful to remove only thecarbon deposits - don’t remove any metal,
and do not nick or scratch the sides of the
ring grooves (see illustration).
5Once the deposits have been removed,
clean the piston/rod assemblies with solvent,
and dry them with compressed air (if
available). Make sure the oil return holes in the
back sides of the ring grooves are clear.
6If the pistons and cylinder walls aren’t
damaged or worn excessively, and if the
engine block is not rebored, new pistons
won’t be necessary. Normal piston wear
appears as even vertical wear on the piston
thrust surfaces (90° to the gudgeon pin bore),
and slight looseness of the top ring in its
groove. New piston rings, however, should
always be used when an engine is rebuilt.
7Carefully inspect each piston for cracks
around the skirt, at the pin bosses, and at the
ring lands.
8Look for scoring and scuffing on the thrust
faces of the skirt, holes in the piston crown,
and burned areas at the edge of the crown. If
the skirt is scored or scuffed, the engine may
have been suffering from overheating and/or
abnormal combustion, which caused
excessively high operating temperatures. The
cooling and lubrication systems should be
checked thoroughly. A hole in the piston crown
is an indication that abnormal combustion (pre-
ignition) was occurring. Burned areas at the
edge of the piston crown are usually evidence
of spark knock (detonation). If any of the aboveproblems exist, the causes must be corrected,
or the damage will occur again. The causes
may include intake air leaks, incorrect fuel/air
mixture, or incorrect ignition timing. On later
vehicles with high levels of exhaust emission
control, including catalytic converters, the
problem may be with the EGR (exhaust gas
recirculation) system, where applicable.
9Corrosion of the piston, in the form of small
pits, indicates that coolant is leaking into the
combustion chamber and/or the crankcase.
Again, the cause must be corrected or the
problem may persist in the rebuilt engine.
10Measure the piston ring side clearance by
laying a new piston ring in each ring groove
and slipping a feeler gauge in beside it(see
illustration). Check the clearance at three or
four locations around each groove. Be sure to
use the correct ring for each groove - they are
different. If the side clearance is greater than
the figure listed in this Chapter’s Specifi-
cations, new pistons will have to be used.
11Check the piston-to-bore clearance by
measuring the bore (see Section 16) and the
piston diameter. Make sure the pistons and
bores are correctly matched. Measure the
piston across the skirt, at 90° to, and in line
with, the gudgeon pin (see illustration). (Any
difference between these two measurements
indicates that the piston is no longer perfectly
round.) Subtract the piston diameter from the
bore diameter to obtain the clearance. If it’s
greater than specified, the block will have to
be rebored, and new pistons and rings fitted.
2B•16 General engine overhaul procedures
18.11 Measure the piston diameter at a
90-degree angle to the gudgeon pin, at the
same height as the gudgeon pin
18.10 Check the ring side clearance with a
feeler gauge at several points around the
groove18.4 The piston ring grooves can be
cleaned with a special tool, as shown
here18.2 Removing the compression rings with
a ring expander - note the mark (arrowed)
facing up
If a groove cleaning tool isn’t available,
a piece broken off the old ring will do
the job, but protect your hands - piston
rings can be sharp
Page 73 of 228
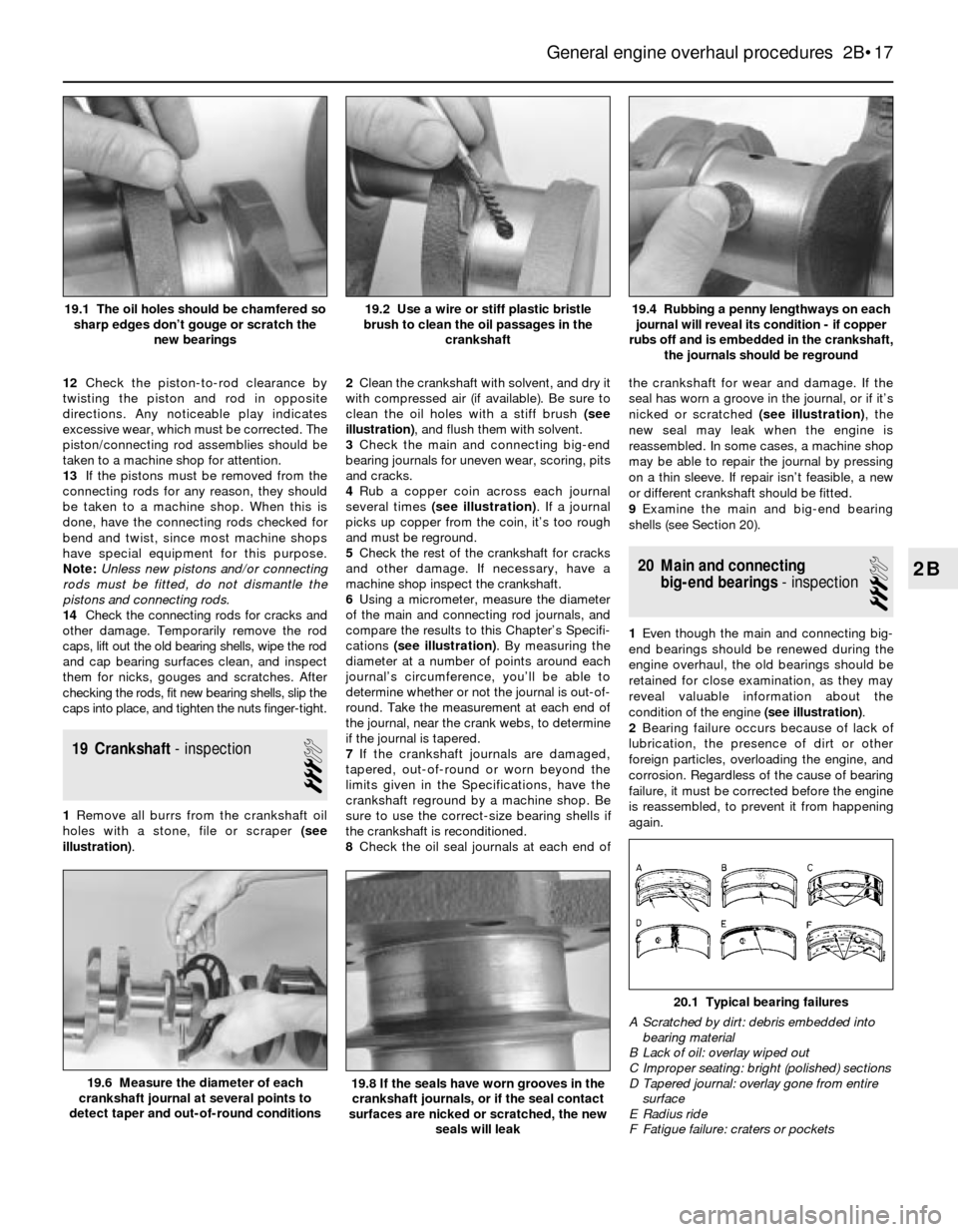

12Check the piston-to-rod clearance by
twisting the piston and rod in opposite
directions. Any noticeable play indicates
excessive wear, which must be corrected. The
piston/connecting rod assemblies should be
taken to a machine shop for attention.
13If the pistons must be removed from the
connecting rods for any reason, they should
be taken to a machine shop. When this is
done, have the connecting rods checked for
bend and twist, since most machine shops
have special equipment for this purpose.
Note:Unless new pistons and/or connecting
rods must be fitted, do not dismantle the
pistons and connecting rods.
14Check the connecting rods for cracks and
other damage. Temporarily remove the rod
caps, lift out the old bearing shells, wipe the rod
and cap bearing surfaces clean, and inspect
them for nicks, gouges and scratches. After
checking the rods, fit new bearing shells, slip the
caps into place, and tighten the nuts finger-tight.
19 Crankshaft- inspection
3
1Remove all burrs from the crankshaft oil
holes with a stone, file or scraper (see
illustration).2Clean the crankshaft with solvent, and dry it
with compressed air (if available). Be sure to
clean the oil holes with a stiff brush (see
illustration), and flush them with solvent.
3Check the main and connecting big-end
bearing journals for uneven wear, scoring, pits
and cracks.
4Rub a copper coin across each journal
several times (see illustration). If a journal
picks up copper from the coin, it’s too rough
and must be reground.
5Check the rest of the crankshaft for cracks
and other damage. If necessary, have a
machine shop inspect the crankshaft.
6Using a micrometer, measure the diameter
of the main and connecting rod journals, and
compare the results to this Chapter’s Specifi-
cations (see illustration). By measuring the
diameter at a number of points around each
journal’s circumference, you’ll be able to
determine whether or not the journal is out-of-
round. Take the measurement at each end of
the journal, near the crank webs, to determine
if the journal is tapered.
7If the crankshaft journals are damaged,
tapered, out-of-round or worn beyond the
limits given in the Specifications, have the
crankshaft reground by a machine shop. Be
sure to use the correct-size bearing shells if
the crankshaft is reconditioned.
8Check the oil seal journals at each end ofthe crankshaft for wear and damage. If the
seal has worn a groove in the journal, or if it’s
nicked or scratched (see illustration), the
new seal may leak when the engine is
reassembled. In some cases, a machine shop
may be able to repair the journal by pressing
on a thin sleeve. If repair isn’t feasible, a new
or different crankshaft should be fitted.
9Examine the main and big-end bearing
shells (see Section 20).
20 Main and connecting
big-end bearings- inspection
3
1Even though the main and connecting big-
end bearings should be renewed during the
engine overhaul, the old bearings should be
retained for close examination, as they may
reveal valuable information about the
condition of the engine (see illustration).
2Bearing failure occurs because of lack of
lubrication, the presence of dirt or other
foreign particles, overloading the engine, and
corrosion. Regardless of the cause of bearing
failure, it must be corrected before the engine
is reassembled, to prevent it from happening
again.
General engine overhaul procedures 2B•17
19.4 Rubbing a penny lengthways on each
journal will reveal its condition - if copper
rubs off and is embedded in the crankshaft,
the journals should be reground19.2 Use a wire or stiff plastic bristle
brush to clean the oil passages in the
crankshaft19.1 The oil holes should be chamfered so
sharp edges don’t gouge or scratch the
new bearings
20.1 Typical bearing failures
A Scratched by dirt: debris embedded into
bearing material
B Lack of oil: overlay wiped out
C Improper seating: bright (polished) sections
D Tapered journal: overlay gone from entire
surface
E Radius ride
F Fatigue failure: craters or pockets
19.8 If the seals have worn grooves in the
crankshaft journals, or if the seal contact
surfaces are nicked or scratched, the new
seals will leak19.6 Measure the diameter of each
crankshaft journal at several points to
detect taper and out-of-round conditions
2B
Page 123 of 228
6
Chapter 6
Engine management and emission control systems
Catalytic converter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Electronic Control Unit (ECU) - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Evaporative emissions control (EVAP) system . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Evaporative emissions control system inspection . . . See Chapter 1
General information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1Information sensors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
Motronic engine management system self-diagnosis -
general information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Positive crankcase ventilation (PCV) system . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
6•1
Easy,suitable for
novice with little
experienceFairly easy,suitable
for beginner with
some experienceFairly difficult,
suitable for competent
DIY mechanic
Difficult,suitable for
experienced DIY
mechanicVery difficult,
suitable for expert
DIY or professional
Degrees of difficulty Contents
1 General information
To prevent pollution of the atmosphere
from incomplete combustion or evaporation
of the fuel, and to maintain good driveability
and fuel economy, a number of emission
control systems are used on these vehicles.
Not all of these systems are fitted to all
models, but they include the following:
Catalytic converter
Evaporative emission control (EVAP) system
Positive crankcase ventilation (PCV) system
Electronic engine management
The Sections in this Chapter include
general descriptions and checking
procedures within the scope of the home
mechanic, as well as component renewal
procedures (when possible) for each of the
systems listed above.
Before assuming that an emissions control
system is malfunctioning, check the fuel and
ignition systems carefully. The diagnosis of
some emission control devices requires
specialised tools, equipment and training. If
checking and servicing become too difficult,
or if a procedure is beyond your ability,
consult a dealer service department or other
specialist.This doesn’t mean, however, that emission
control systems are particularly difficult to
maintain and repair. You can quickly and
easily perform many checks, and do most of
the regular maintenance at home with
common tune-up and hand tools.
Pay close attention to any special
precautions outlined in this Chapter. It should
be noted that the illustrations of the various
systems may not exactly match the system
fitted on your vehicle because of
changes made by the manufacturer during
production.
2 Motronic engine management
system self-diagnosis-
general information
The Motronic engine management system
control unit (computer) has a built-in self-
diagnosis system, which detects malfunctions
in the system sensors and stores them as
fault codes in its memory. It is not possible
without dedicated test equipment to extract
these fault codes from the control unit.
However, the procedures given in Chapters 4
and 5 may be used to check individual
components and sensors of the Motronic
system. If this fails to pinpoint a fault, then the
vehicle should be taken to a BMW dealer, who
will have the necessary diagnostic
equipment to call up the fault codes from the
control unit. You will then have the
option to repair the fault yourself, or
alternatively have the fault repaired by the
BMW dealer.
3 Electronic control unit (ECU)
- removal and refitting
2
Removal
1The Electronic Control Unit (ECU) is located
either inside the passenger compartment
under the right-hand side of the facia panel on
3-Series models, or in the engine
compartment on the right-hand side on 5-
Series models (see Chapter 4).
2Disconnect the battery negative cable.
Caution: If the radio in your
vehicle is equipped with an anti-
theft system, make sure you
have the correct activation code
before disconnecting the battery. Refer to
the information on page 0-7 at the front of
this manual before detaching the cable.
Note: If, after connecting the battery, the
wrong language appears on the instrument
panel display, refer to page 0-7 for the
language resetting procedure.
3First remove the access cover on models
with the ECU on the right-hand side of the
engine compartment (see Chapter 4).
4If the ECU is located inside the vehicle,
remove the access cover on the right-hand side.
5Unplug the electrical connectors from the
ECU.
6Remove the retaining bolts from the ECU
bracket.
7Carefully remove the ECU. Note: Avoid static
electricity damage to the ECU by wearing rubber
gloves, and do not touch the connector pins.
Refitting
8Refitting is a reversal of removal.
The most frequent cause of
emission system problems is
simply a leaking vacuum hose
or loose wire, so always
check the hose and wiring connections
first.
Page 129 of 228

9
General
Brake fluid type . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 1
Disc brakes
Minimum brake pad thickness . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 1
Brake disc minimum permissible thickness (wear limit)*
Front
3-Series
Solid discs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10.7 mm
Ventilated discs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20.0 mm
5-Series
Solid discs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10.0 mm
Ventilated discs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20.0 mm
Rear . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8.0 mm
Brake disc minimum thickness after machining
Front
3-Series
Solid discs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11.1 mm
Ventilated discs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20.4 mm
5-Series
Solid discs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10.4 mm
Ventilated discs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20.4 mm
Rear . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8.4 mm
Parallelism (difference between any two measurements) . . . . . . . . . . . 0.02 mm
Maximum disc run-out . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.2 mm
*Refer to marks cast into the disc (they supersede information printed here)
Brake pedal adjustments
Brake pedal/servo pushrod adjustment (A) (3-Series) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 125 mm
Brake pedal height (pedal-to-bulkhead distance)
3-Series
Left-hand-drive . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 235 mm
Right-hand-drive . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 273 mm
5-Series . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 245 mm
Stop-light switch adjustment (dimension A - see text) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5.0 mm to 6.0 mm
Handbrake
Handbrake shoe lining minimum thickness . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1.5 mm
Handbrake lever travel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5 to 8 clicks
Chapter 9 Braking system
Anti-lock brake system (ABS) - general information . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Brake check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 1
Brake disc - inspection, removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Brake fluid level check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 1
Brake hoses and lines - inspection and renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Brake hydraulic system - bleeding . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Brake pedal - adjustment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Brake vacuum servo - check, removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Disc brake caliper - removal, overhaul and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4Disc brake pads - renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Drum brake shoes - renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
General information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
Handbrake assembly - check, removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Handbrake - adjustment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Handbrake cable(s) - renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Hydraulic brake servo - description, removal and refitting . . . . . . . . 9
Master cylinder - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Stop-light switch - check and adjustment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
9•1
Easy,suitable for
novice with little
experienceFairly easy,suitable
for beginner with
some experienceFairly difficult,
suitable for competent
DIY mechanic
Difficult,suitable for
experienced DIY
mechanicVery difficult,
suitable for expert
DIY or professional
Degrees of difficulty
Specifications Contents
Page 130 of 228

Torque wrench settingsNm
Front disc brake caliper
Caliper guide (mounting) bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30 to 35
Caliper bracket-to-strut housing bolts
3-Series, E30 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 123
5-Series, E28 (“old-shape”) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 123
5-Series, E34 (“new-shape”) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 110
Rear disc brake caliper
Caliper guide (mounting) bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30 to 35
Carrier-to-trailing arm bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67
Brake hose-to-caliper fitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14 to 17
Master cylinder-to-brake servo nuts
3-Series . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
5-Series . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25 to 29
Brake servo mounting nuts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22 to 24
Hydraulic line-to-hydraulic brake servo threaded
fittings - 5-Series, E28 (“old-shape”) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Wheel bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 1
9•2 Braking system
1 General information
All 3-Series models, and 5-Series E28 (“old-
shape”) models, are equipped with front disc
brakes and either rear drum or rear disc
brakes. 5-Series E34 (“new-shape”) models
have disc brakes front and rear. Front and
rear brakes are self-adjusting on all models.
Some later models are equipped with an Anti-
lock Braking System (ABS); this is described
in Section 2.
Hydraulic system
The hydraulic system consists of two
separate circuits. The master cylinder has
separate reservoirs for the two circuits; in the
event of a leak or failure in one hydraulic
circuit, the other circuit will remain operative.
Brake servo
The vacuum brake servo, utilising engine
manifold vacuum and atmospheric pressure
to provide assistance to the hydraulically
operated brakes, is mounted on the bulkhead
in the engine compartment.
A hydraulic brake servo system is used on
5-Series E28 models. This system uses
hydraulic pressure from the power steering
pump to assist braking.
Handbrake
The handbrake operates the rear brakes,
and is cable-operated via a lever mounted in
the centre console. The handbrake assembly
on rear drum brake models is part of the rear
drum brake assembly, and is self-adjusting.
On rear disc brake models, the handbrake
uses a pair of brake shoes located inside the
centre portion of the rear brake disc, and is
manually-adjusted.
Brake pad wear warning system
The brake pad wear warning system is
linked to a red warning light in the instrumentcluster, which comes on when the brake pads
have worn down to the point at which they
require renewal. DO NOT ignore this reminder.
If you don’t renew the pads shortly after the
brake pad wear warning light comes on, the
brake discs will be damaged.
On some models, the brake pad wear
warning system also includes an early
warning light that comes on only when the
brake pedal is depressed, letting you know in
advance that the pads need to be renewed.
The wear sensor is attached to the brake
pads. The sensor is located at the left front
wheel; on some models, there is another
sensor at the right rear wheel. The wear
sensor is part of a closed circuit. Once the
pads wear down to the point at which they’re
flush with the sensor, the disc grinds away the
side of the sensor facing the disc. Thus, the
wire inside the sensor is broken, and the red
light on the instrument panel comes on.
Always check the sensor(s) when renewing
the pads. If you change the pads before the
warning light comes on, the sensor(s) may still
be good; once the light has come on, renew
the sensor.
Service
After completing any operation involving
dismantling of any part of the brake system,
always test drive the vehicle to check for
proper braking performance before resuming
normal driving. When testing the brakes, try to
select a clean, dry, road with no camber (ie as
flat as possible) and with no other traffic.
Conditions other than these can lead to
inaccurate test results.
Test the brakes at various speeds with both
light and heavy pedal pressure. The vehicle
should stop evenly, without pulling to one side
or the other. Avoid locking the brakes,
because this slides the tyres and diminishes
braking efficiency and control of the vehicle.
Tyres, vehicle load and wheel alignment are
factors which also affect braking
performance.
2 Anti-lock Braking system
(ABS)- general information
The Anti-lock Braking System is designed
to maintain vehicle control, directional stability
and optimum deceleration under severe
braking conditions on most road surfaces. It
does so by monitoring the rotational speed of
each wheel and controlling the brake line
pressure to each wheel during braking. This
prevents the wheels from locking up.
The ABS system has three main
components - the wheel speed sensors, the
electronic control unit, and the hydraulic
control unit. The sensors - one at each wheel
since 1985, but at both front wheels and one
at the rear differential on earlier models - send
a variable voltage signal to the control unit,
which monitors these signals, compares them
to its program information, and determines
whether a wheel is about to lock up. When a
wheel is about to lock up, the control unit
signals the hydraulic unit to reduce hydraulic
pressure (or not increase it further) at that
wheel’s brake caliper. Pressure modulation is
handled by electrically-operated solenoid
valves.
If a problem develops within the system, an
“ABS” warning light will glow on the
dashboard. Sometimes, a visual inspection of
the ABS system can help you locate the
problem. Carefully inspect the ABS wiring
harness. Pay particularly close attention to the
harness and connections near each wheel.
Look for signs of chafing and other damage
caused by incorrectly-routed wires. If a wheel
sensor harness is damaged, the sensor
should be renewed (the harness and sensor
are integral).
Warning: DO NOT try to repair an
ABS wiring harness. The ABS
system is sensitive to even the
smallest changes in resistance. Repairing
the harness could alter resistance values
Page 133 of 228
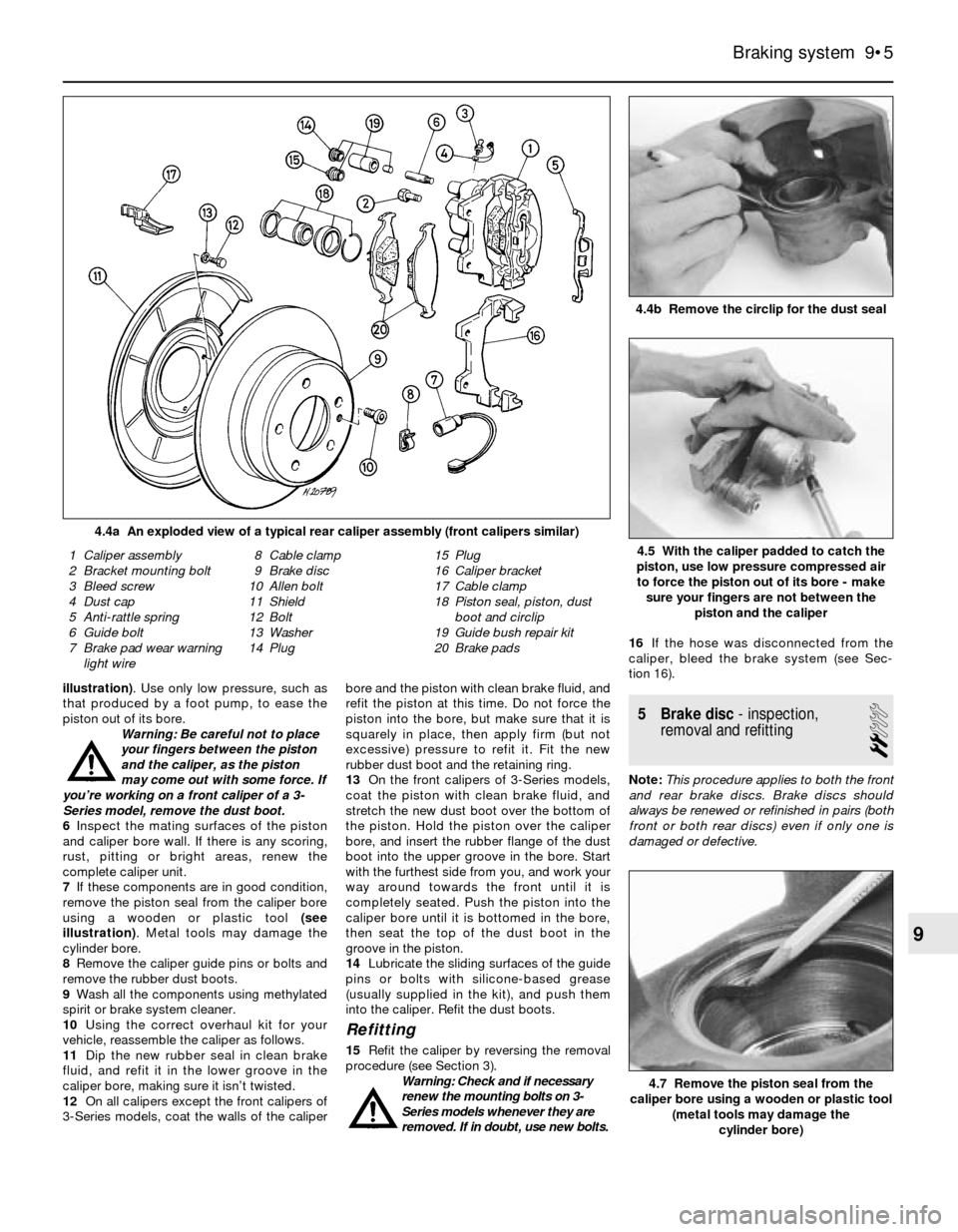
illustration). Use only low pressure, such as
that produced by a foot pump, to ease the
piston out of its bore.
Warning: Be careful not to place
your fingers between the piston
and the caliper, as the piston
may come out with some force. If
you’re working on a front caliper of a 3-
Series model, remove the dust boot.
6Inspect the mating surfaces of the piston
and caliper bore wall. If there is any scoring,
rust, pitting or bright areas, renew the
complete caliper unit.
7If these components are in good condition,
remove the piston seal from the caliper bore
using a wooden or plastic tool (see
illustration). Metal tools may damage the
cylinder bore.
8Remove the caliper guide pins or bolts and
remove the rubber dust boots.
9Wash all the components using methylated
spirit or brake system cleaner.
10Using the correct overhaul kit for your
vehicle, reassemble the caliper as follows.
11Dip the new rubber seal in clean brake
fluid, and refit it in the lower groove in the
caliper bore, making sure it isn’t twisted.
12On all calipers except the front calipers of
3-Series models, coat the walls of the caliperbore and the piston with clean brake fluid, and
refit the piston at this time. Do not force the
piston into the bore, but make sure that it is
squarely in place, then apply firm (but not
excessive) pressure to refit it. Fit the new
rubber dust boot and the retaining ring.
13On the front calipers of 3-Series models,
coat the piston with clean brake fluid, and
stretch the new dust boot over the bottom of
the piston. Hold the piston over the caliper
bore, and insert the rubber flange of the dust
boot into the upper groove in the bore. Start
with the furthest side from you, and work your
way around towards the front until it is
completely seated. Push the piston into the
caliper bore until it is bottomed in the bore,
then seat the top of the dust boot in the
groove in the piston.
14Lubricate the sliding surfaces of the guide
pins or bolts with silicone-based grease
(usually supplied in the kit), and push them
into the caliper. Refit the dust boots.
Refitting
15Refit the caliper by reversing the removal
procedure (see Section 3).
Warning: Check and if necessary
renew the mounting bolts on 3-
Series models whenever they are
removed. If in doubt, use new bolts.16If the hose was disconnected from the
caliper, bleed the brake system (see Sec-
tion 16).
5 Brake disc- inspection,
removal and refitting
2
Note:This procedure applies to both the front
and rear brake discs. Brake discs should
always be renewed or refinished in pairs (both
front or both rear discs) even if only one is
damaged or defective.
Braking system 9•5
4.4b Remove the circlip for the dust seal
4.4a An exploded view of a typical rear caliper assembly (front calipers similar)
4.7 Remove the piston seal from the
caliper bore using a wooden or plastic tool
(metal tools may damage the
cylinder bore)
1 Caliper assembly
2 Bracket mounting bolt
3 Bleed screw
4 Dust cap
5 Anti-rattle spring
6 Guide bolt
7 Brake pad wear warning
light wire8 Cable clamp
9 Brake disc
10 Allen bolt
11 Shield
12 Bolt
13 Washer
14 Plug15 Plug
16 Caliper bracket
17 Cable clamp
18 Piston seal, piston, dust
boot and circlip
19 Guide bush repair kit
20 Brake pads4.5 With the caliper padded to catch the
piston, use low pressure compressed air
to force the piston out of its bore - make
sure your fingers are not between the
piston and the caliper
9
Page 134 of 228
Inspection
1Loosen the wheel bolts, raise the vehicle
and support it securely on axle stands.
Remove the wheel, and refit three bolts to
hold the disc in place. If the rear brake disc is
being worked on, release the handbrake.
2Remove the brake caliper as outlined in
Section 4. It is not necessary to disconnect
the brake hose. After removing the caliper,
suspend it out of the way with a piece of wire.
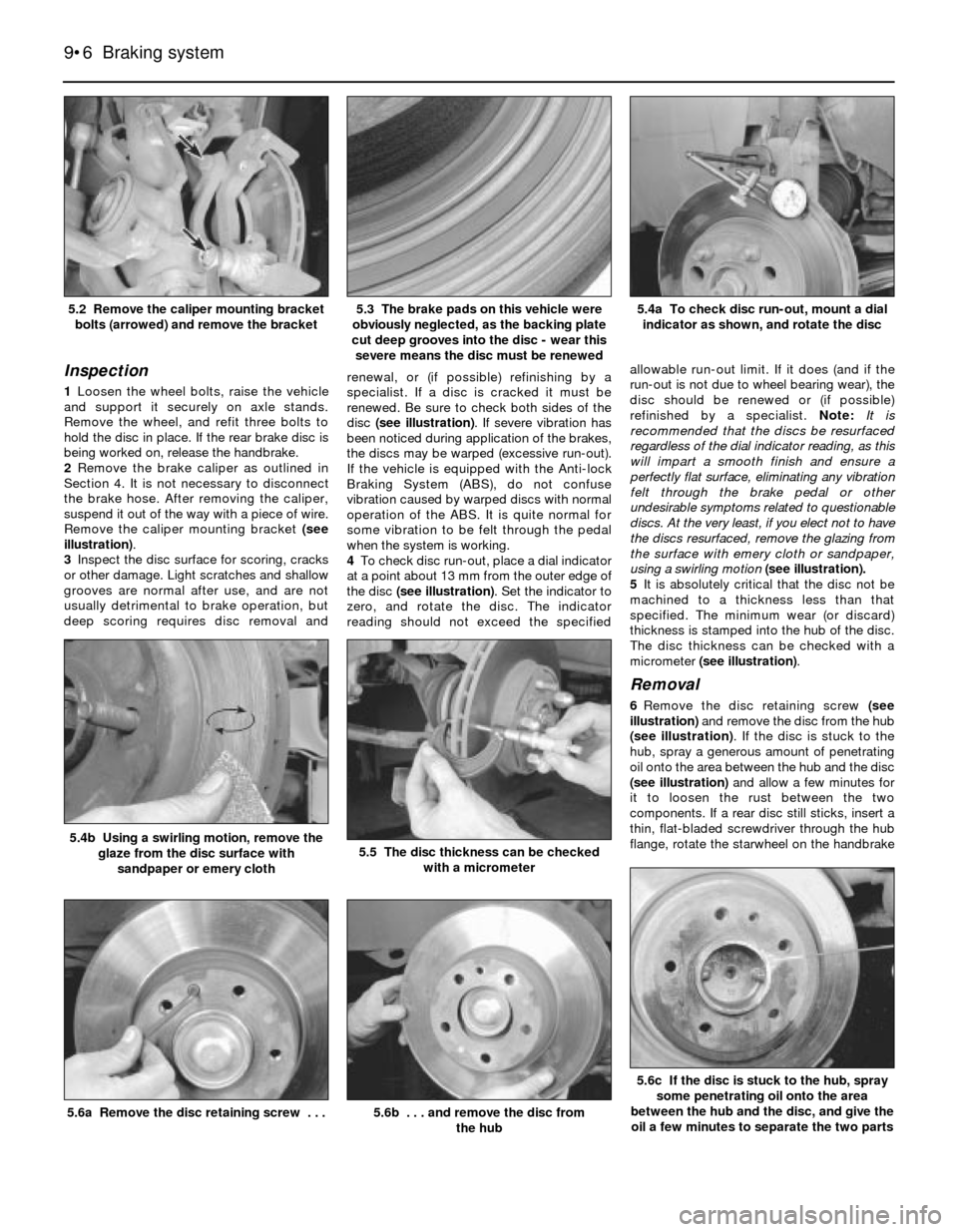
Remove the caliper mounting bracket (see
illustration).
3Inspect the disc surface for scoring, cracks
or other damage. Light scratches and shallow
grooves are normal after use, and are not
usually detrimental to brake operation, but
deep scoring requires disc removal andrenewal, or (if possible) refinishing by a
specialist. If a disc is cracked it must be
renewed. Be sure to check both sides of the
disc (see illustration). If severe vibration has
been noticed during application of the brakes,
the discs may be warped (excessive run-out).
If the vehicle is equipped with the Anti-lock
Braking System (ABS), do not confuse
vibration caused by warped discs with normal
operation of the ABS. It is quite normal for
some vibration to be felt through the pedal
when the system is working.
4To check disc run-out, place a dial indicator
at a point about 13 mm from the outer edge of
the disc (see illustration). Set the indicator to
zero, and rotate the disc. The indicator
reading should not exceed the specifiedallowable run-out limit. If it does (and if the
run-out is not due to wheel bearing wear), the
disc should be renewed or (if possible)
refinished by a specialist. Note:It is
recommended that the discs be resurfaced
regardless of the dial indicator reading, as this
will impart a smooth finish and ensure a
perfectly flat surface, eliminating any vibration
felt through the brake pedal or other
undesirable symptoms related to questionable
discs. At the very least, if you elect not to have
the discs resurfaced, remove the glazing from
the surface with emery cloth or sandpaper,
using a swirling motion (see illustration).
5It is absolutely critical that the disc not be
machined to a thickness less than that
specified. The minimum wear (or discard)
thickness is stamped into the hub of the disc.
The disc thickness can be checked with a
micrometer (see illustration).
Removal
6Remove the disc retaining screw (see
illustration) and remove the disc from the hub
(see illustration). If the disc is stuck to the
hub, spray a generous amount of penetrating
oil onto the area between the hub and the disc
(see illustration)and allow a few minutes for
it to loosen the rust between the two
components. If a rear disc still sticks, insert a
thin, flat-bladed screwdriver through the hub
flange, rotate the starwheel on the handbrake
9•6 Braking system
5.6c If the disc is stuck to the hub, spray
some penetrating oil onto the area
between the hub and the disc, and give the
oil a few minutes to separate the two parts
5.6b . . . and remove the disc from
the hub5.6a Remove the disc retaining screw . . .
5.5 The disc thickness can be checked
with a micrometer5.4b Using a swirling motion, remove the
glaze from the disc surface with
sandpaper or emery cloth
5.4a To check disc run-out, mount a dial
indicator as shown, and rotate the disc5.3 The brake pads on this vehicle were
obviously neglected, as the backing plate
cut deep grooves into the disc - wear this
severe means the disc must be renewed5.2 Remove the caliper mounting bracket
bolts (arrowed) and remove the bracket