Fuel tank BMW 3 SERIES 1985 E30 Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: BMW, Model Year: 1985, Model line: 3 SERIES, Model: BMW 3 SERIES 1985 E30Pages: 228, PDF Size: 7.04 MB
Page 6 of 228
0•6Safety First!
Working on your car can be dangerous.
This page shows just some of the potential
risks and hazards, with the aim of creating a
safety-conscious attitude.
General hazards
Scalding
• Don’t remove the radiator or expansion
tank cap while the engine is hot.
• Engine oil, automatic transmission fluid or
power steering fluid may also be dangerously
hot if the engine has recently been running.
Burning
• Beware of burns from the exhaust system
and from any part of the engine. Brake discs
and drums can also be extremely hot
immediately after use.
Crushing
• When working under or near
a raised vehicle,
always
supplement the
jack with axle
stands, or use
drive-on
ramps.
Never
venture
under a car which
is only supported by a jack.
• Take care if loosening or tightening high-
torque nuts when the vehicle is on stands.
Initial loosening and final tightening should
be done with the wheels on the ground.
Fire
• Fuel is highly flammable; fuel vapour is
explosive.
• Don’t let fuel spill onto a hot engine.
• Do not smoke or allow naked lights
(including pilot lights) anywhere near a
vehicle being worked on. Also beware of
creating sparks
(electrically or by use of tools).
• Fuel vapour is heavier than air, so don’t
work on the fuel system with the vehicle over
an inspection pit.
• Another cause of fire is an electrical
overload or short-circuit. Take care when
repairing or modifying the vehicle wiring.
• Keep a fire extinguisher handy, of a type
suitable for use on fuel and electrical fires.
Electric shock
• Ignition HT
voltage can be
dangerous,
especially to
people with heart
problems or a
pacemaker. Don’t
work on or near the
ignition system with
the engine running or
the ignition switched on.• Mains voltage is also dangerous. Make
sure that any mains-operated equipment is
correctly earthed. Mains power points should
be protected by a residual current device
(RCD) circuit breaker.
Fume or gas intoxication
• Exhaust fumes are
poisonous; they often
contain carbon
monoxide, which is
rapidly fatal if inhaled.
Never run the
engine in a
confined space
such as a garage
with the doors shut.
• Fuel vapour is also
poisonous, as are the vapours from some
cleaning solvents and paint thinners.
Poisonous or irritant substances
• Avoid skin contact with battery acid and
with any fuel, fluid or lubricant, especially
antifreeze, brake hydraulic fluid and Diesel
fuel. Don’t syphon them by mouth. If such a
substance is swallowed or gets into the eyes,
seek medical advice.
• Prolonged contact with used engine oil can
cause skin cancer. Wear gloves or use a
barrier cream if necessary. Change out of oil-
soaked clothes and do not keep oily rags in
your pocket.
• Air conditioning refrigerant forms a
poisonous gas if exposed to a naked flame
(including a cigarette). It can also cause skin
burns on contact.
Asbestos
• Asbestos dust can cause cancer if inhaled
or swallowed. Asbestos may be found in
gaskets and in brake and clutch linings.
When dealing with such components it is
safest to assume that they contain asbestos.
Special hazards
Hydrofluoric acid
• This extremely corrosive acid is formed
when certain types of synthetic rubber, found
in some O-rings, oil seals, fuel hoses etc, are
exposed to temperatures above 400
0C. The
rubber changes into a charred or sticky
substance containing the acid. Once formed,
the acid remains dangerous for years. If it
gets onto the skin, it may be necessary to
amputate the limb concerned.
• When dealing with a vehicle which has
suffered a fire, or with components salvaged
from such a vehicle, wear protective gloves
and discard them after use.
The battery
• Batteries contain sulphuric acid, which
attacks clothing, eyes and skin. Take care
when topping-up or carrying the battery.
• The hydrogen gas given off by the battery
is highly explosive. Never cause a spark or
allow a naked light nearby. Be careful when
connecting and disconnecting battery
chargers or jump leads.
Air bags
• Air bags can cause injury if they go off
accidentally. Take care when removing the
steering wheel and/or facia. Special storage
instructions may apply.
Diesel injection equipment
• Diesel injection pumps supply fuel at very
high pressure. Take care when working on
the fuel injectors and fuel pipes.
Warning: Never expose the hands,
face or any other part of the body
to injector spray; the fuel can
penetrate the skin with potentially fatal
results.
Remember...
DO
• Do use eye protection when using power
tools, and when working under the vehicle.
• Do wear gloves or use barrier cream to
protect your hands when necessary.
• Do get someone to check periodically
that all is well when working alone on the
vehicle.
• Do keep loose clothing and long hair well
out of the way of moving mechanical parts.
• Do remove rings, wristwatch etc, before
working on the vehicle – especially the
electrical system.
• Do ensure that any lifting or jacking
equipment has a safe working load rating
adequate for the job.
A few tips
DON’T
• Don’t attempt to lift a heavy component
which may be beyond your capability – get
assistance.
• Don’t rush to finish a job, or take
unverified short cuts.
• Don’t use ill-fitting tools which may slip
and cause injury.
• Don’t leave tools or parts lying around
where someone can trip over them. Mop
up oil and fuel spills at once.
• Don’t allow children or pets to play in or
near a vehicle being worked on.
Page 13 of 228

Tyre pressures (cold) - bars (psi)Front Rear
3-Series, E30
316 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1.9 (28) 2.1 (30)
316i
Saloon . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2.0 (29) 2.1 (30)
Estate . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2.0 (29) 2.2 (32)
318i . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1.8 (26) 1.9 (28)
320i . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1.9 (28) 2.0 (29)
325i . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2.2 (32) 2.3 (33)
5-Series, E28 (“old-shape”)
518 and 518i . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2.0 (29) 2.0 (29)
525i and 528i . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2.2 (32) 2.2 (32)
535i and M535i . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2.3 (33) 2.5 (36)
5-Series, E34 (“new-shape”)
518i . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2.0 (29) 2.0 (29)
520i . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2.2 (32) 2.1 (30)
525i, 530i and 535i . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2.0 (29) 2.3 (33)
Torque wrench settingsNm
Automatic transmission sump bolts
Three-speed . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8 to 9
Four-speed . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5 to 7
Spark plugs
M10 engines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20 to 30
Except M10 engines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30 to 33
Oxygen sensor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30 to 33
Wheel bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 100
Lubricants and fluids
Component or system Lubricant type/specification
Engine . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Multigrade engine oil, viscositySAE 10W/40 to 20W/50, to API SG
Cooling system . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Ethylene glycol-based antifreeze with corrosion inhibitors
Manual transmission* . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Gear oil, viscosity SAE 80 to API-GL4, or single-grade mineral-based
engine oil, viscosity SAE 20, 30 or 40 to API-SG
Automatic transmission . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Dexron ll type ATF
Final drive . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . BMW-approved hypoid gear oil, viscosity SAE 90**
Brake and clutch hydraulic systems . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Hydraulic brake fluid to SAE J 1703 or DOT 4
Power steering . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Dexron ll type ATF
* E34 520i & 525i with air conditioning, E34 530i & 535i - Dexron II type ATF)
** Only available in bulk; refer to your BMW dealer
Capacities*
1•3
1
Engine oil
M10 engines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4.0 litres
M20 engines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4.3 litres
M30 engines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5.8 litres
M40 engines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4.0 litres
Cooling system
M10 engines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7.0 litres
M20 engines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10.5 litres
M30 engines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12.0 litres
M40 engines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7.0 litres
Fuel tank
3-Series, E30
Saloon . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55 litres (early),
64 litres (later)
Estate . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63 litres (early),
70 litres (later)
5-Series
E28 (“old-shape”) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70 litres
E34 (“new-shape”) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81 litresManual transmission
ZF . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1.2 litres
Getrag . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1.0 to 1.5 litres
Automatic transmission (refill)
3-speed . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2.0 litres
4-speed . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3.0 litres
Final drive capacity (drain and refill)
3-Series, E30 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.9 litres
5-Series, E28 (“old-shape”) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.9 litres
5-Series, E34 (“new-shape”) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1.7 litres
*All capacities approximate
Servicing Specifications
Page 16 of 228
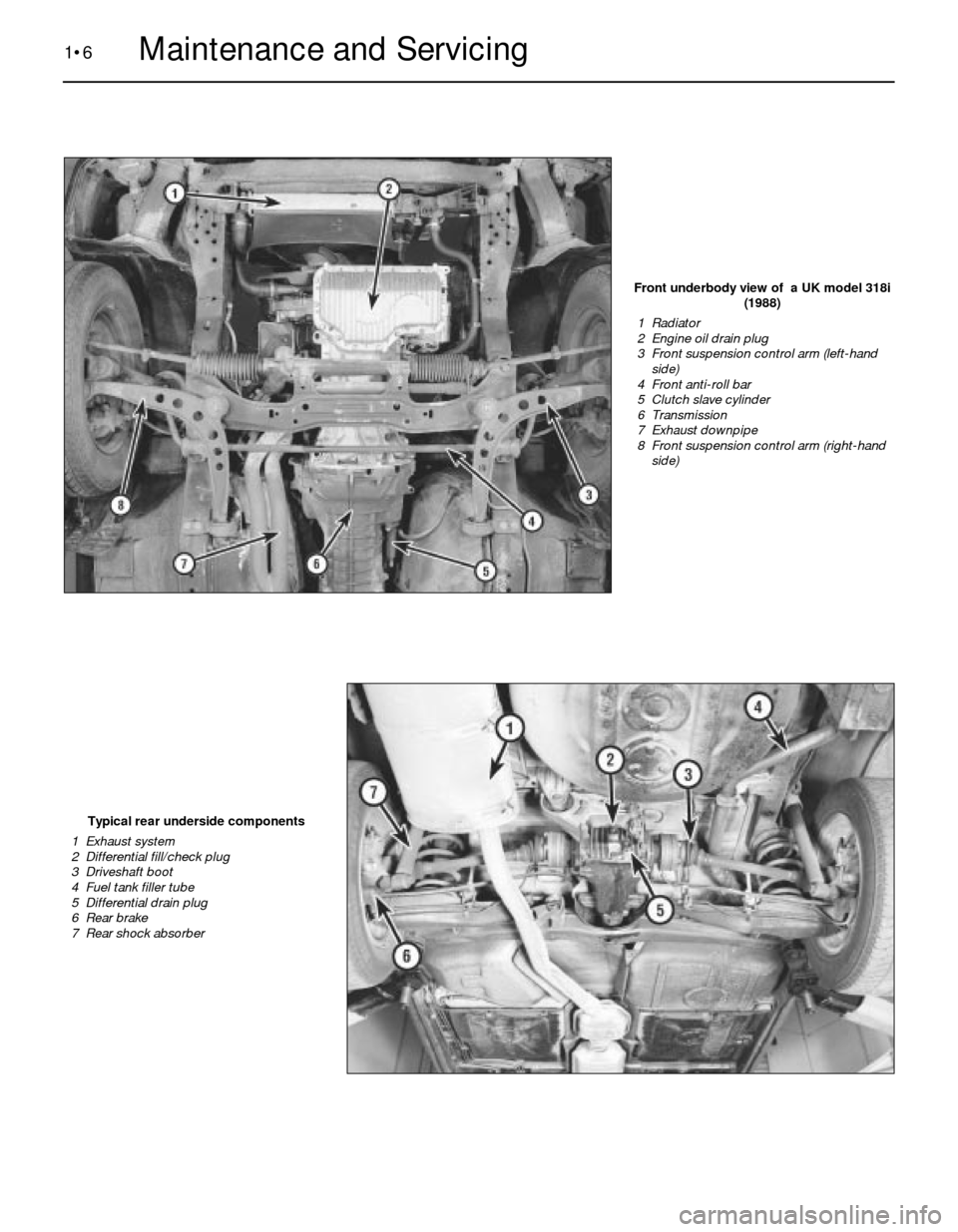
1•6Maintenance and Servicing
Front underbody view of a UK model 318i
(1988)
1 Radiator
2 Engine oil drain plug
3 Front suspension control arm (left-hand
side)
4 Front anti-roll bar
5 Clutch slave cylinder
6 Transmission
7 Exhaust downpipe
8 Front suspension control arm (right-hand
side)
Typical rear underside components
1 Exhaust system
2 Differential fill/check plug
3 Driveshaft boot
4 Fuel tank filler tube
5 Differential drain plug
6 Rear brake
7 Rear shock absorber
Page 31 of 228

4Since some components of the fuel system
- the fuel tank and some of the fuel feed and
return lines, for example - are underneath the
vehicle, they can be inspected more easily
with the vehicle raised on a hoist. If that’s not
possible, raise the vehicle and support it on
axle stands or ramps.
5With the vehicle raised and safely
supported, inspect the fuel tank and filler neck
for punctures, cracks or other damage. The
connection between the filler neck and the
tank is particularly critical. Sometimes a
rubber filler neck will leak because of loose
clamps or deteriorated rubber. Inspect all fuel
tank mounting brackets and straps, to be sure
the tank is securely attached to the vehicle.
Warning: Do not, under any
circumstances, try to repair a fuel
tank (except rubber
components). A welding torch or
any naked flame can easily cause fuel
vapours inside the tank to explode.
6Carefully check all flexible hoses and metal
lines leading away from the fuel tank. Check
for loose connections, deteriorated hoses,
crimped lines, and other damage. Repair or
renew damaged sections as necessary (see
Chapter 4).
22 Cooling system check
1
1Many major engine failures can be
attributed to cooling system problems. If the
vehicle has automatic transmission, the
engine cooling system also plays an importantrole in prolonging transmission life, because it
cools the transmission fluid.
2The engine should be cold for the cooling
system check, so perform the following
procedure before the vehicle is driven for the
day, or after it has been switched off for at
leastthree hours.
3Remove the radiator cap, doing so slowly
and taking adequate precautions against
scalding if the engine is at all warm. Clean the
cap thoroughly, inside and out, with clean
water. Also clean the filler neck on the
radiator. The presence of rust or corrosion in
the filler neck means the coolant should be
changed (see Section 29). The coolant inside
the radiator should be relatively clean and
clear. If it’s rust-coloured, drain the system
and refill with new coolant.
4Carefully check the radiator hoses and the
smaller-diameter heater hoses. Inspect each
coolant hose along its entire length, renewing
any hose which is cracked, swollen or
deteriorated (see illustration). Cracks will
show up better if the hose is squeezed. Pay
close attention to hose clamps that secure the
hoses to cooling system components. Hose
clamps can pinch and puncture hoses,
resulting in coolant leaks.
5Make sure all hose connections are tight. A
leak in the cooling system will usually show up
as white or rust-coloured deposits on the area
adjoining the leak. If wire-type clamps are
used on the hoses, it may be a good idea to
replace them with screw-type clamps.
6Clean the front of the radiator (and, where
applicable, the air conditioning condenser)
with compressed air if available, or a soft
brush. Remove all flies, leaves, etc,
embedded in the radiator fins. Be extremely
careful not to damage the cooling fins or to
cut your fingers on them.
7If the coolant level has been dropping
consistently and no leaks are detected, have
the radiator cap and cooling system pressure-
tested.
23 Exhaust system check
1
1The engine should be cold for this check,
so perform the following procedure before the
vehicle is driven for the day, or after it has
been switched off for at leastthree hours.
Check the complete exhaust system from the
engine to the end of the tailpipe. Ideally, the
inspection should be done with the vehicle on
a hoist, to give unrestricted access. If a hoist
isn’t available, raise the vehicle and support it
securely on axle stands or ramps.
2Check the exhaust pipes and connections
for evidence of leaks, severe corrosion, and
damage. Make sure that all brackets and
mountings are in good condition, and that
they are tight (see illustration).
3At the same time, inspect the underside of
the body for holes, corrosion, open seams,etc. which may allow exhaust gases to enter
the passenger compartment. Seal all body
openings with suitable sealant.
4Rattles and other noises can often be
traced to the exhaust system, especially the
mountings and heat shields. Try to move the
pipes, silencers (and, where applicable, the
catalytic converter). If the components can
come in contact with the body or suspension
parts, re-hang the exhaust system with new
mountings.
5The running condition of the engine may be
checked by inspecting inside the end of the
tailpipe. The exhaust deposits here are an
indication of the engine’s state of tune. If the
pipe is black and sooty, the engine may be
running too rich, indicating the need for a
thorough fuel system inspection.
24 Steering and suspension
check
1
Note: The steering linkage and suspension
components should be checked periodically.
Worn or damaged suspension and steering
linkage components can result in excessive
and abnormal tyre wear, poor ride quality and
vehicle handling, and reduced fuel economy.
For detailed illustrations of the steering and
suspension components, refer to Chapter 10.
Strut/shock absorber check
1Park the vehicle on level ground, turn the
engine off and apply the handbrake. Check
the tyre pressures.
2Push down at one corner of the vehicle,
then release it while noting the movement of
the body. It should stop moving and come to
rest in a level position with one or two
bounces.
3If the vehicle continues to move up and
down, or if it fails to return to its original
position, a worn or weak strut or shock
absorber is probably the reason.
4Repeat the above check at each of the
three remaining corners of the vehicle.
5Raise the vehicle and support it on axle
stands.
6Check the struts/shock absorbers for
evidence of fluid leakage. A light film of fluid is
1•21
22.4 Hoses, like drivebelts, have a habit of
failing at the worst possible time - to
prevent the inconvenience of a blown
radiator or heater hose, inspect them
carefully as shown here
23.2 Check the exhaust system rubber
mountings for cracks
1
Every 12 000 miles
Page 35 of 228

Flushing
7Once the system is completely drained,
flush the radiator with fresh water from a
garden hose until the water runs clear at the
drain or bottom hose. If the radiator is
severely corroded, damaged or leaking, it
should be removed (see Chapter 3) and taken
to a radiator repair specialist.
8Flushing in this way will remove sediments
from the radiator, but will not remove rust and
scale from the engine and cooling tube
surfaces. These deposits can be removed by
using a chemical cleaner. Follow the
procedure outlined in the cleaner
manufacturer’s instructions. Remove the
cylinder block drain plug before flushing the
engine.
9On models so equipped, remove the
overflow hose from the coolant recovery
reservoir. Drain the reservoir and flush it with
clean water, then reconnect the hose.
Refilling
10Tighten the radiator drain plug, or
reconnect the radiator bottom hose. Refit and
tighten the cylinder block drain plug.
Four-cylinder engines
11Slowly add new coolant (a 40%/60%
mixture of antifreeze to water) to the radiator
until it is full. Add coolant to the reservoir up
to the lower mark.
12Leave the radiator cap off, and run the
engine in a well-ventilated area until the
thermostat opens (coolant will begin flowing
through the radiator, and the upper radiator
hose will become hot).
13Turn the engine off, and let it cool. Add
more coolant mixture to bring the coolant
level back up to the lip on the radiator filler
neck. On the M40 engine, unscrew the bleed
screw from the top of the radiator, and add
coolant until it comes out of the bleed screw
hole. Refit and tighten the bleed screw.
14Squeeze the upper radiator hose to expel
air, then add more coolant mixture if
necessary. Refit the radiator cap.
15Start the engine, allow it to reach normal
operating temperature, and check for leaks.
Six-cylinder engines
16Loosen the bleed screw in the thermostat
housing (see illustration)
17Fill the radiator with a 40%/60% solution
of antifreeze and water until it comes out of
the bleed screw opening. Tighten the bleed
screw.
18Refit the radiator cap, and run the engine
until the thermostat opens (the upper radiator
hose will become hot). Slowly loosen the
bleed screw until no bubbles emerge, then
tighten the screw.
19Repeat the procedure until the air is bled
from the system.
30 Fuel filter renewal
1
Warning: Fuel is extremely
flammable, so take extra
precautions when you work on
any part of the fuel system. Don’t
smoke, or allow open flames or bare light
bulbs, near the work area. Don’t work in a
garage where a natural gas-type appliance
(such as a water heater or clothes dryer)
with a pilot light is present. If you spill any
fuel on your skin, rinse it off immediately
with soap and water. When you perform
any kind of work on the fuel system, wear
safety glasses, and have a fire
extinguisher on hand.
1On fuel injection engines, depressurise the
fuel system (see Chapter 4).
2The fuel filter is located in the engine
compartment on the bulkhead, or under the
vehicle adjacent to the fuel tank.
3Because on some models the filter is
located adjacent to the starter motor, fuel
could leak onto the electrical connections. For
safety reasons, therefore, disconnect the
battery negative cable before beginning work.
Caution: If the radio in your
vehicle is equipped with an anti-
theft system, make sure you have
the correct activation code
before disconnecting the battery.Note: If, after connecting the battery, the
wrong language appears on the instrument
panel display, refer to page 0-7 for the
language resetting procedure.
4Place a pan or rags under the fuel filter to
catch any spilled fuel. If suitable hose clamps
are available, clamp the inlet and outlet hoses.
5 Detach the hoses and remove the bracket
screws/nuts, then remove the filter and where
applicable the bracket assembly (see
illustration).
6Detach the filter from the bracket.
7Refitting is the reverse of removal. Be sure
the arrow on the filter points in the direction of
fuel flow.
31 Manual transmission
lubricant change
1
1Tools necessary for this job include axle
stands to support the vehicle in a raised
position, an Allen key to remove the drain
plug, a drain pan, newspapers and clean rags.
The correct amount of the specified lubricant
should also be available (see “Lubricants and
fluids”at the start of this Chapter).
2The lubricant should be drained when it is
hot (ie immediately after the vehicle has been
driven); this will remove any contaminants
better than if the lubricant were cold. Because
1•25
30.5 To renew the fuel filter, disconnect
the hoses (A), then unscrew the nut (B) and
detach the filter from the bracket (fuel
injection type shown)29.16 The bleed screw (arrowed) is
located on the thermostat housing (six-
cylinder models)29.4 Radiator drain plug location
(arrowed) - not fitted to all models
31.5 Use an Allen key to remove the drain
plug (arrowed) from the bottom of the
transmission
1
Every 24 000 miles
Page 36 of 228
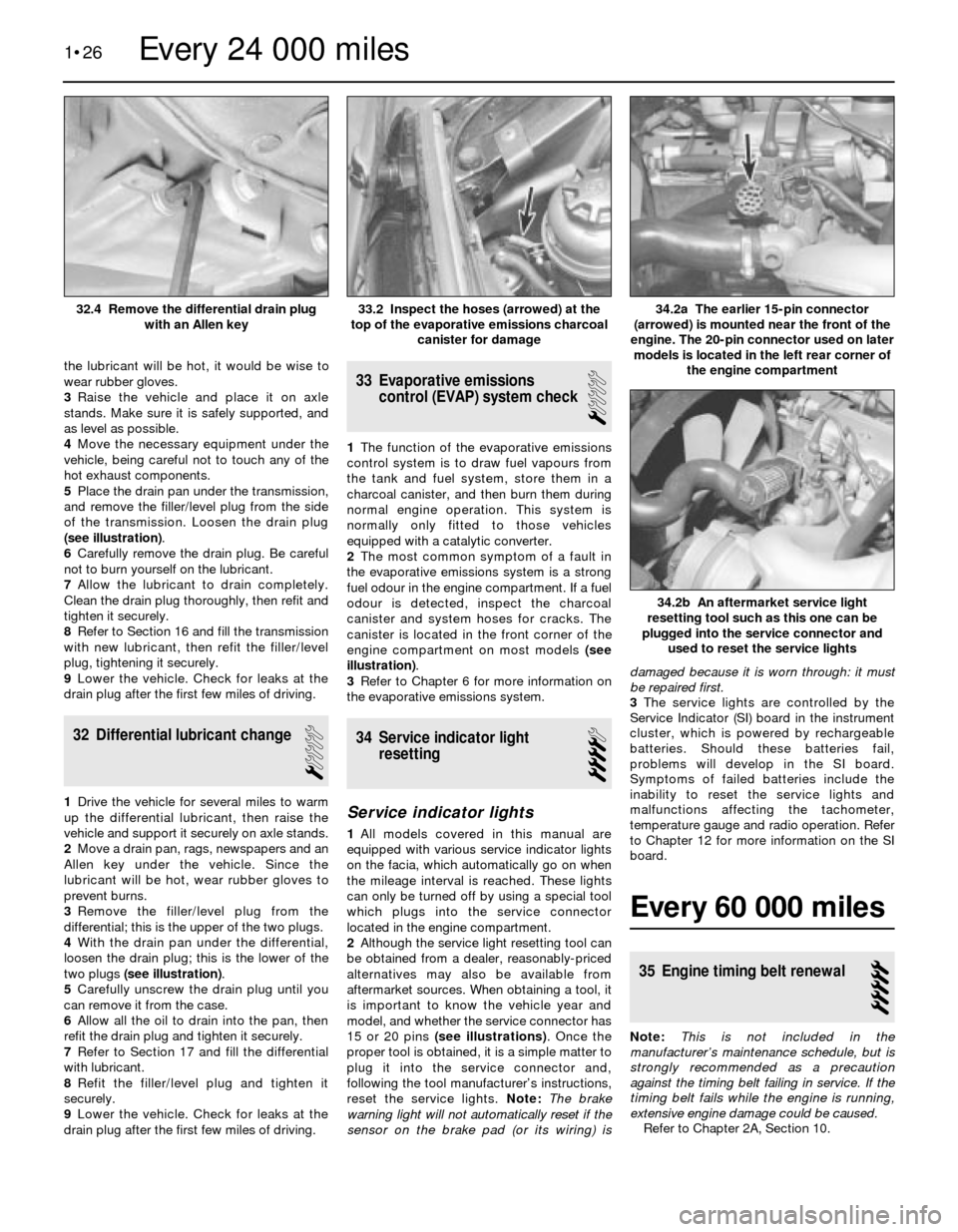
the lubricant will be hot, it would be wise to
wear rubber gloves.
3Raise the vehicle and place it on axle
stands. Make sure it is safely supported, and
as level as possible.
4Move the necessary equipment under the
vehicle, being careful not to touch any of the
hot exhaust components.
5Place the drain pan under the transmission,
and remove the filler/level plug from the side
of the transmission. Loosen the drain plug
(see illustration).
6Carefully remove the drain plug. Be careful
not to burn yourself on the lubricant.
7Allow the lubricant to drain completely.
Clean the drain plug thoroughly, then refit and
tighten it securely.
8Refer to Section 16 and fill the transmission
with new lubricant, then refit the filler/level
plug, tightening it securely.
9Lower the vehicle. Check for leaks at the
drain plug after the first few miles of driving.
32 Differential lubricant change
1
1Drive the vehicle for several miles to warm
up the differential lubricant, then raise the
vehicle and support it securely on axle stands.
2Move a drain pan, rags, newspapers and an
Allen key under the vehicle. Since the
lubricant will be hot, wear rubber gloves to
prevent burns.
3Remove the filler/level plug from the
differential; this is the upper of the two plugs.
4With the drain pan under the differential,
loosen the drain plug; this is the lower of the
two plugs (see illustration).
5Carefully unscrew the drain plug until you
can remove it from the case.
6Allow all the oil to drain into the pan, then
refit the drain plug and tighten it securely.
7Refer to Section 17 and fill the differential
with lubricant.
8Refit the filler/level plug and tighten it
securely.
9Lower the vehicle. Check for leaks at the
drain plug after the first few miles of driving.
33 Evaporative emissions
control (EVAP) system check
1
1The function of the evaporative emissions
control system is to draw fuel vapours from
the tank and fuel system, store them in a
charcoal canister, and then burn them during
normal engine operation. This system is
normally only fitted to those vehicles
equipped with a catalytic converter.
2The most common symptom of a fault in
the evaporative emissions system is a strong
fuel odour in the engine compartment. If a fuel
odour is detected, inspect the charcoal
canister and system hoses for cracks. The
canister is located in the front corner of the
engine compartment on most models (see
illustration).
3Refer to Chapter 6 for more information on
the evaporative emissions system.
34 Service indicator light
resetting
4
Service indicator lights
1All models covered in this manual are
equipped with various service indicator lights
on the facia, which automatically go on when
the mileage interval is reached. These lights
can only be turned off by using a special tool
which plugs into the service connector
located in the engine compartment.
2Although the service light resetting tool can
be obtained from a dealer, reasonably-priced
alternatives may also be available from
aftermarket sources. When obtaining a tool, it
is important to know the vehicle year and
model, and whether the service connector has
15 or 20 pins (see illustrations). Once the
proper tool is obtained, it is a simple matter to
plug it into the service connector and,
following the tool manufacturer’s instructions,
reset the service lights. Note: The brake
warning light will not automatically reset if the
sensor on the brake pad (or its wiring) isdamaged because it is worn through: it must
be repaired first.
3The service lights are controlled by the
Service Indicator (SI) board in the instrument
cluster, which is powered by rechargeable
batteries. Should these batteries fail,
problems will develop in the SI board.
Symptoms of failed batteries include the
inability to reset the service lights and
malfunctions affecting the tachometer,
temperature gauge and radio operation. Refer
to Chapter 12 for more information on the SI
board.
Every 60 000 miles
35 Engine timing belt renewal
5
Note:This is not included in the
manufacturer’s maintenance schedule, but is
strongly recommended as a precaution
against the timing belt failing in service. If the
timing belt fails while the engine is running,
extensive engine damage could be caused.
Refer to Chapter 2A, Section 10.
1•26
34.2b An aftermarket service light
resetting tool such as this one can be
plugged into the service connector and
used to reset the service lights
34.2a The earlier 15-pin connector
(arrowed) is mounted near the front of the
engine. The 20-pin connector used on later
models is located in the left rear corner of
the engine compartment33.2 Inspect the hoses (arrowed) at the
top of the evaporative emissions charcoal
canister for damage32.4 Remove the differential drain plug
with an Allen key
Every 24 000 miles
Page 80 of 228

Warning: Do not remove the
pressure cap from the radiator or
expansion tank until the engine
has cooled completely and
there’s no pressure remaining in the
cooling system. Removing the cap from a
hot engine risks personal injury by
scalding.
Heating system
The heating system consists of a blower fan
and heater matrix located in the heater box,
with hoses connecting the heater matrix to the
engine cooling system, and the heater/air
conditioning control head on the dashboard.
Hot engine coolant is circulated through the
heater matrix passages all the time the engine
is running. Switching the heater on opens a
flap door to direct air through the heater
matrix, and the warmed air enters the
passenger compartment. A fan switch on the
control head activates the blower motor,
which forces more air through the heater
matrix, giving additional heater output for
demisting, etc.
Air conditioning system
The air conditioning system consists of a
condenser mounted in front of the radiator, an
evaporator mounted adjacent to the heater
matrix, a compressor mounted on the engine,
a filter-drier (receiver-drier) which contains a
high-pressure relief valve, and the plumbing
connecting all of the above components.
A blower fan forces the warmer air of the
passenger compartment through the
evaporator matrix (a radiator-in-reverse),
transferring the heat from the air to the
refrigerant. The liquid refrigerant boils off into
low-pressure vapour, taking the heat with it
when it leaves the evaporator.
Note: Refer to the precautions at the start
of Section 12 concerning the potential
dangers associated with the air conditioning
system.
2 Antifreeze-
general information
Warning: Do not allow antifreeze
to come in contact with your skin
or painted surfaces of the
vehicle. Rinse off spills
immediately with plenty of water. If
consumed, antifreeze can be fatal;
children and pets are attracted by its
sweet taste, so wipe up garage floor and
drip pan coolant spills immediately. Keep
antifreeze containers covered, and repair
leaks in your cooling system as soon as
they are noticed.
The cooling system should be filled with a
60/40% water/ethylene-glycol-based anti-
freeze solution, which will prevent freezing
down to approximately -27°C (-17°F). The
antifreeze also raises the boiling point of thecoolant, and (if of good quality) provides
protection against corrosion.
The cooling system should be drained,
flushed and refilled at the specified intervals
(see Chapter 1). Old or contaminated
antifreeze solutions are likely to cause
damage, and encourage the formation of rust
and scale in the system. Use distilled water
with the antifreeze, if available, or clean
rainwater. Tap water will do, but not if the
water in your area is at all “hard”.
Before adding antifreeze, check all hose
connections, because antifreeze tends to
search out and leak through very minute
openings. Engines don’t normally consume
coolant, so if the level goes down, find the
cause and correct it.
The antifreeze mixture should be
maintained at its correct proportions; adding
too much antifreeze reduces the efficiency of
the cooling system. If necessary, consult the
mixture ratio chart on the antifreeze container
before adding coolant. Hydrometers are
available at most car accessory shops to test
the coolant. Use antifreeze which meets the
vehicle manufacturer’s specifications.
3 Thermostat-
check and renewal
1
Warning: Do not remove the
radiator cap, drain the coolant, or
renew the thermostat until the
engine has cooled completely.
Check
1Before assuming the thermostat is to blame
for a cooling system problem, check the
coolant level, drivebelt tension (see Chapter 1)
and temperature gauge (or warning light)
operation.
2If the engine seems to be taking a long time
to warm up (based on heater output or
temperature gauge operation), the thermostat
is probably stuck open. Renew the
thermostat.
3If the engine runs hot, use your hand to
check the temperature of the upper radiator
hose. If the hose isn’t hot, but the engine is,
the thermostat is probably stuck closed,preventing the coolant inside the engine from
circulating to the radiator. Renew the
thermostat.
Caution: Don’t drive the vehicle
without a thermostat. The engine
will be very slow to warm-up in
cold conditions, resulting in poor
fuel economy and driveability. A new
thermostat is normally an inexpensive
component anyway.
4If the upper radiator hose is hot, it means
that the coolant is flowing and the thermostat
is at least partly open. Consult the “Fault
finding” Section at the rear of this manual for
cooling system diagnosis.
Renewal
All models
5Disconnect the negative cable from the
battery.
Caution: If the radio in your
vehicle is equipped with an anti-
theft system, make sure you
have the correct activation code
before disconnecting the battery.
Note: If, after connecting the battery, the
wrong language appears on the instrument
panel display, refer to page 0-7 for the
language resetting procedure.
6Drain the cooling system (see Chapter 1). If
the coolant is relatively new or in good
condition, save it and re-use it.
M10 engines
7The thermostat is located in the bottom
hose. First remove the cooling fan.
8Note the fitted position of the thermostat,
then unscrew the hose clamps and withdraw
the thermostat from the hose connections
(see illustration).
9Refit the thermostat-to-hose connections,
and tighten the hose clamps.
10Refit the cooling fan.
M20 and M30 engines
11Loosen the hose clamp (see illustration),
then detach the hose(s) from the thermostat
cover.
3•2 Cooling, heating and air conditioning systems
3.11 On M20 and M30 engine models,
loosen the hose clamp (A) and disconnect
the hose from the thermostat housing
cover - note that the coolant temperature
sender unit (barely visible behind the fuel
pressure regulator) is located at the top of
the thermostat housing (B)
3.8 On the M10 (four-cylinder) engine, the
thermostat (arrowed) is connected in-line
in the radiator hose
Page 89 of 228

4
Carburettor (Solex 2B4)
Main jet
Stage 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . X120
Stage 2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . X90
Air correction jet
Stage 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 135
Stage 2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
Venturi diameter
Stage 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24 mm
Stage 2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28 mm
Idle/air jet
Stage 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50/120
Stage 2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40/125
Float needle valve diameter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2.0 mm
Choke gap (pulldown) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4.0 to 5.5 mm
Throttle positioner spring preload . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22.0 to 24.0 mm
Float level
Stage 1 float chamber . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27.0 to 29.0 mm
Stage 2 float chamber . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29.0 to 31.0 mm
Chapter 4 Fuel and exhaust systems
Accelerator cable - check, adjustment and renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Air cleaner assembly - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Air filter renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 1
Airflow meter - check, removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Carburettor - cleaning and adjustment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Carburettor - general information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Carburettor - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Cold start injector and thermotime switch -
checkand renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Engine idle speed check and adjustment . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 1
Exhaust system check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 1
Exhaust system servicing - general information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Fuel filter renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 1
Fuel injection system - check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Fuel injection system - depressurising . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2Fuel injection system - fault finding . . . . . . . . . . . . See end of Chapter
Fuel injection - general information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Fuel injection systems . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Fuel injectors - check and renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Fuel lines and fittings - repair and renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Fuel pressure regulator - check and renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Fuel pump, transfer pump and fuel level sender unit -
removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
Fuel pump/fuel pressure - check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Fuel system check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 1
Fuel tank - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Fuel tank cleaning and repair - general information . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
General information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
Idle air stabiliser valve - check, adjustment and renewal . . . . . . . . . 21
Throttle body - check, removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
4•1
Easy,suitable for
novice with little
experienceFairly easy,suitable
for beginner with
some experienceFairly difficult,
suitable for competent
DIY mechanic
Difficult,suitable for
experienced DIY
mechanicVery difficult,
suitable for expert
DIY or professional
Degrees of difficulty
Specifications Contents
Page 90 of 228

Carburettor (Solex 2BE)
Main jet
Stage 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . X120
Stage 2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . X110
Air correction jet
Stage 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 140
Stage 2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
Venturi diameter
Stage 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24 mm
Stage 2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28 mm
Idle fuel jet
Stage 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47.5 mm
Idle air jet
Stage 2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 180
Float needle valve diameter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2.0 mm
Throttle positioner coil resistance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.97 to 1.63 ohms
Intake air temperature resistance
-10º C . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8200 to 10 500 ohms
20º C . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2200 to 2700 ohms
80º C . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 300 to 360 ohms
Float level
Stage 1 float chamber . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27.0 to 29.0 mm
Stage 2 float chamber . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29.0 to 31.0 mm
Fuel pressure checks (carburettor engines)
Fuel pump delivery pressure (engine idling) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.1 to 0.3 bars
Fuel pressure checks (fuel injection engines)
Fuel system pressure (relative to intake manifold pressure)
3-Series (E30)
316i with M40/B16 engine . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3.0 ± 0.06 bars
318i with M10/B18 engine . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2.5 to 3.0 bars
318i with M40/B18 engine . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3.0 ± 0.06 bars
320i with M20/B20 engine (L-Jetronic) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2.5 to 3.0 bars
320i with M20/B20 engine (Motronic) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2.5 ± 0.05 bars
325i with M20/B25 engine . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3.0 ± 0.05 bars
5-Series (E28/”old-shape”)
All models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2.5 to 3.0 bars
5-Series (E34/”new-shape”)
518i with M40/B18 engine . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3.0 ± 0.06 bars
All other models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2.5 to 3.0 bars
Fuel system hold pressure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2.1 bars
Fuel pump maximum pressure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6.3 to 6.9 bars
Fuel pump hold pressure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5.5 bars
Transfer pump pressure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.28 to 0.35 bars
Injectors
Injector resistance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14.5 to 17.5 ohms
Accelerator cable free play . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1.0 mm
Torque wrench settingsNm
Carburettor mountings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Fuel pump to cylinder head . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Throttle body nuts/bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19 to 26
4•2 Fuel and exhaust systems
1 General information
With the exception of early models (316 and
518 models) all engines are equipped with
electronic fuel injection.
Early 316 and 518 models are equipped
with Solex carburettors. The carburettor fitted
is either a Solex 2B4 (early models) or
2BE (later models). The mechanical fuel pumpis driven by an eccentric lobe on the
camshaft.
Fuel injection models are equipped with
either the L-Jetronic or the Motronic fuel
injection system. From 1988, fuel injection
models are equipped with an updated version
of the Motronic system - this system is easily
distinguished from the earlier system by the
absence of a cold start injector. The electric
fuel pump is located beneath the rear of the
vehicle, or inside the fuel tank. The fuel pump
relay on Motronic systems is activated from aearth signal from the Motronic control unit
(ECU). The fuel pump operates for a few
seconds when the ignition is first switched on,
and it continues to operate only when the
engine is actually running.Air intake system
The air intake system consists of the air
filter housing, the airflow meter and throttle
body (fuel injection models), and the intake
manifold. All components except the intake
manifold are covered in this Chapter; for
Page 91 of 228

information on removing and refitting the
intake manifold, refer to Chapter 2A.
The throttle valve inside the throttle body or
carburettor is actuated by the accelerator
cable. When you depress the accelerator
pedal, the throttle plate opens and airflow
through the intake system increases.
On fuel injection systems, a flap inside the
airflow meter opens wider as the airflow
increases. A throttle position switch attached
to the pivot shaft of the flap detects the angle
of the flap (how much it’s open) and converts
this to a voltage signal, which it sends to the
computer.
Fuel system
On carburettor models, the fuel pump
supplies fuel under pressure to the
carburettor. A needle valve in the float
chamber maintains the fuel at a constant
level. A fuel return system channels excess
fuel back to the fuel tank.
On fuel injection models, an electric fuel
pump supplies fuel under constant pressure
to the fuel rail, which distributes fuel to the
injectors. The electric fuel pump is located
inside the fuel tank on later models, or beside
the fuel tank on early models. Early models
also have a transfer pump located in the fuel
tank. The transfer pump acts as an aid to the
larger main pump for delivering the necessary
pressure. A fuel pressure regulator controls
the pressure in the fuel system. The fuel
system also has a fuel pulsation damper
located near the fuel filter. The damper
reduces the pressure pulsations caused by
fuel pump operation, and the opening and
closing of the injectors. The amount of fuel
injected into the intake ports is precisely
controlled by an Electronic Control Unit (ECU
or computer). Some later 5-Series models
have a fuel cooler in the return line.
Electronic control system (fuel
injection system)
Besides altering the injector opening
duration as described above, the electronic
control unit performs a number of other tasks
related to fuel and emissions control. It
accomplishes these tasks by using data
relayed to it by a wide array of information
sensors located throughout the enginecompartment, comparing this information to
its stored map, and altering engine operation
by controlling a number of different actuators.
Since special equipment is required, most
fault diagnosis and repair of the electronic
control system is beyond the scope of the
home mechanic. Additional information and
testing procedures for the emissions system
components (oxygen sensor, coolant
temperature sensor, EVAP system, etc.) is
contained in Chapter 6.
2 Fuel injection system-
depressurising
1
Warning: Fuel is extremely
flammable, so take extra
precautions when you work on
any part of the fuel system. Don’t
smoke or allow open flames or bare light
bulbs near the work area. Also, don’t work
in a garage where a natural gas-type
appliance with a pilot light is present.
1Remove the fuel pump fuse from the main
fuse panel (see illustrations). Note:Consult
your owner’s handbook for the exact location
of the fuel pump fuse, if the information is not
stamped onto the fusebox cover.
2Start the engine, and wait for it to stall.
Switch off the ignition.
3Remove the fuel filler cap to relieve the fuel
tank pressure.
4The fuel system is now depressurised.
Note:Place a rag around fuel lines before
disconnecting, to prevent any residual fuel
from spilling onto the engine(see
illustration).
5Disconnect the battery negative cable
before working on any part of the system.
Caution: If the radio in your
vehicle is equipped with an anti-
theft system, make sure you
have the correct activation code
before disconnecting the battery. Refer to
the information on page 0-7 at the front of
this manual before detaching the cable.
Note: If, after connecting the battery, the
wrong language appears on the instrument
panel display, refer to page 0-7 for the
language resetting procedure.
3 Fuel pump/fuel pressure-
check
3
Warning: Fuel is extremely
flammable, so take extra
precautions when you work on
any part of the fuel system. Don’t
smoke, or allow open flames or bare light
bulbs, near the work area. Also, don’t work
in a garage where a natural gas-type
appliance with a pilot light is present.
Carburettor engines
1To test the fuel pump, it will be necessary to
connect a suitable pressure gauge between
the fuel pump outlet, and the carburettor
supply pipe. For this particular test, the fuel
return valve, which is normally connected in
the fuel line from the fuel pump to the
carburettor, mustbe bypassed.
2With the engine running at idle speed, the
pump pressure should be between 0.1 and
0.3 bars.
3Should a pressure gauge not be available, a
simpler (but less accurate) method of testing
the fuel pump is as follows.
4Disconnect the outlet hose from the fuel
pump.
5Disconnect the LT lead from the coil, to
prevent the engine firing, then turn the engine
over on the starter. Well-defined spurts of fuel
should be ejected from the outlet hose.
Fuel injection engines
Note 1:The electric fuel pump is located
inside the fuel tank on later models, or beside
the fuel tank on early models. Early models are
also equipped with a transfer pump located in
the fuel tank. The transfer pump feeds the
main pump, but can’t generate the high
pressure required by the system.
Note 2:The fuel pump relay on Motronic
systems is activated by an earth signal from
the Motronic control unit (ECU). The fuel
pump operates for a few seconds when the
ignition is first switched on, and then
continues to operate only when the engine is
actually running.
Fuel and exhaust systems 4•3
2.4 Be sure to place a rag under and
around any fuel line when disconnecting2.1b Removing the fuel pump fuse on
5-Series models2.1a Removing the fuel pump fuse on
3-Series models
4