ECU BMW 3 SERIES 1987 E30 Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: BMW, Model Year: 1987, Model line: 3 SERIES, Model: BMW 3 SERIES 1987 E30Pages: 228, PDF Size: 7.04 MB
Page 56 of 228
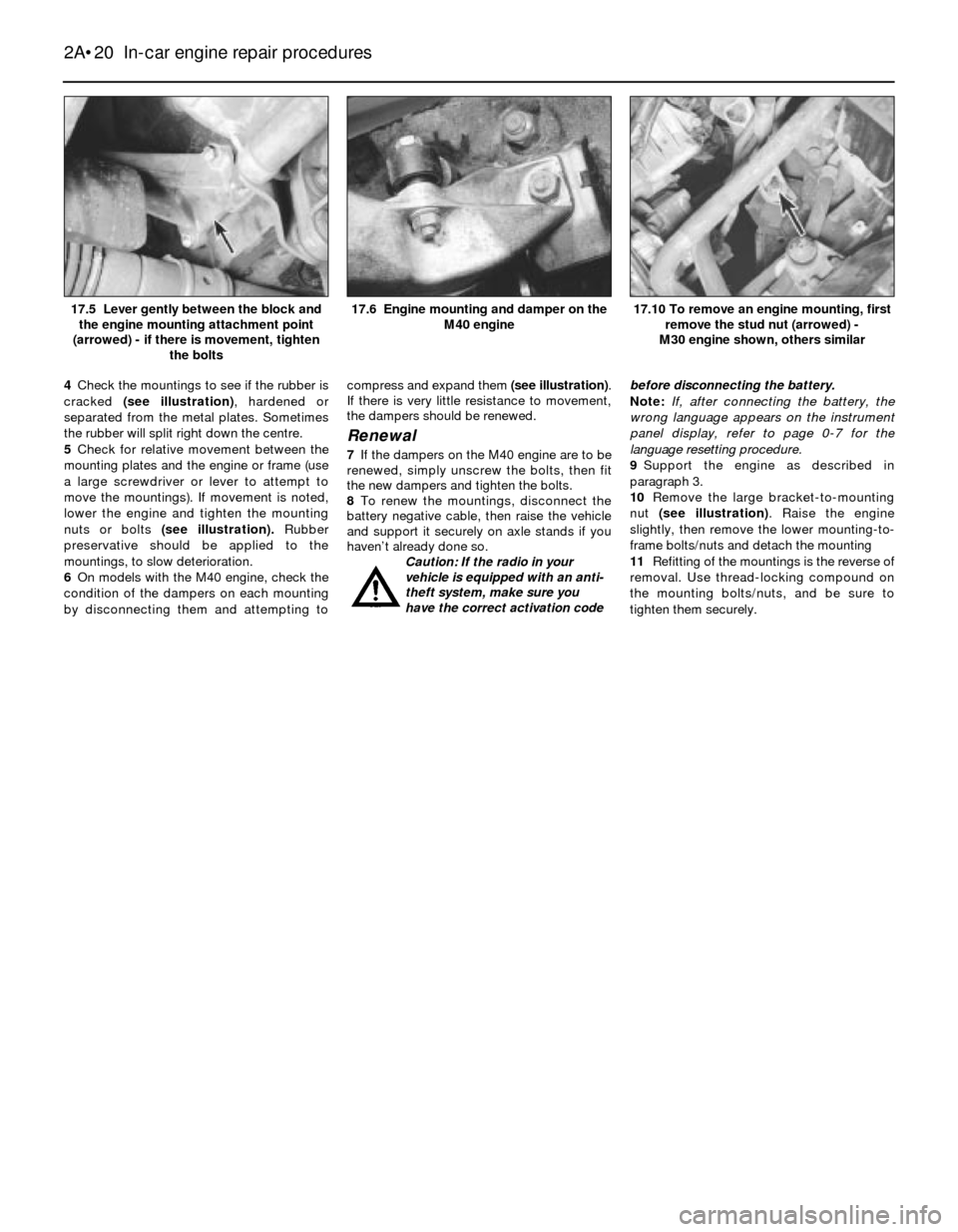
4Check the mountings to see if the rubber is
cracked (see illustration), hardened or
separated from the metal plates. Sometimes
the rubber will split right down the centre.
5Check for relative movement between the
mounting plates and the engine or frame (use
a large screwdriver or lever to attempt to
move the mountings). If movement is noted,
lower the engine and tighten the mounting
nuts or bolts (see illustration). Rubber
preservative should be applied to the
mountings, to slow deterioration.
6On models with the M40 engine, check the
condition of the dampers on each mounting
by disconnecting them and attempting tocompress and expand them (see illustration).
If there is very little resistance to movement,
the dampers should be renewed.
Renewal
7If the dampers on the M40 engine are to be
renewed, simply unscrew the bolts, then fit
the new dampers and tighten the bolts.
8To renew the mountings, disconnect the
battery negative cable, then raise the vehicle
and support it securely on axle stands if you
haven’t already done so.
Caution: If the radio in your
vehicle is equipped with an anti-
theft system, make sure you
have the correct activation codebefore disconnecting the battery.
Note: If, after connecting the battery, the
wrong language appears on the instrument
panel display, refer to page 0-7 for the
language resetting procedure.
9Support the engine as described in
paragraph 3.
10Remove the large bracket-to-mounting
nut (see illustration). Raise the engine
slightly, then remove the lower mounting-to-
frame bolts/nuts and detach the mounting
11Refitting of the mountings is the reverse of
removal. Use thread-locking compound on
the mounting bolts/nuts, and be sure to
tighten them securely.
2A•20 In-car engine repair procedures
17.10 To remove an engine mounting, first
remove the stud nut (arrowed) -
M30 engine shown, others similar17.6 Engine mounting and damper on the
M40 engine17.5 Lever gently between the block and
the engine mounting attachment point
(arrowed) - if there is movement, tighten
the bolts
Page 62 of 228
detach them. Pieces of masking tape with
numbers or letters written on them work well
(see illustration).
6Label and detach all coolant hoses from the
engine (see Chapter 3).
7Remove the cooling fan, shroud and
radiator (see Chapter 3). Note:On the M40
engine, it is only necessary to remove the
cooling fan and shroud; however, prevent
damage to the radiator by covering it with a
piece of wood or cardboard.
8Remove the drivebelts (see Chapter 1).
9Disconnect the fuel lines from the fuel rail
(see Chapter 4).
Warning: Fuel is extremely
flammable, so take extra
precautions when you work on
any part of the fuel system. Don’t
smoke, or allow open flames or bare light
bulbs, near the work area, and don’t work
in a garage where a natural gas-type
appliance (such as a water heater or
clothes dryer) with a pilot light is present.
If you spill any fuel on your skin, rinse it off
immediately with soap and water. When
you perform any kind of work on the fuel
system, wear safety glasses, and have a
fire extinguisher on hand.
10Disconnect the accelerator cable (see
Chapter 4) and kickdown linkage/speed
control cable (see Chapter 7B), if applicable,
from the engine.
11Where fitted, unbolt the power steering
pump (see Chapter 10). Leave the lines/hoses
attached, and make sure the pump is kept in
an upright position in the engine compartment
(use wire or rope to restrain it out of the way).
12On air-conditioned models, unbolt the
compressor (see Chapter 3) and set it aside,
or tie it up out of the way. Do not disconnect
the hoses.
13Drain the engine oil (see Chapter 1) and
remove the filter. Remove the engine splash
guard from under the engine.
14Remove the starter motor (see Chapter 5).15Remove the alternator (see Chapter 5).
This is not essential on all models, but it is a
good idea in any case to avoid accidental
damage.
16Unbolt the exhaust system from the
engine (see Chapter 4).
17If you’re working on a vehicle with an
automatic transmission, remove the torque
converter-to-driveplate fasteners (see
Chapter 7B). On the M40 engine, unbolt the
automatic transmission fluid coolant pipes
from the sump.
18Support the transmission with a jack.
Position a block of wood between them, to
prevent damage to the transmission. Special
transmission jacks with safety chains are
available - use one if possible.
19Attach an engine sling or a length of chain
to the lifting brackets on the engine. If the
brackets have been removed, the chain can
be bolted directly to the intake manifold studs,
but place a flat washer between the chain and
the nut, and tighten the nut all the way up to
the chain, to avoid the possibility of the studs
bending.
20Roll the hoist into position and connect
the sling to it. Take up the slack in the sling or
chain, but don’t lift the engine.
Warning: DO NOT place any part
of your body under the engine
when it’s supported only by a
hoist or other lifting device.
21On M10, M20 and M30 engines, remove
the transmission rear crossmember, and
slightly lower the rear of the transmission.
22Remove the transmission-to-engine block
bolts using a Torx socket. Note:The bolts
holding the bellhousing to the engine block
will require a swivel at the socket, and a very
long extension going back towards the
transmission.
23Remove the engine mounting-to-frame
bracket nuts. On the M40 engine, unbolt the
dampers from the mountings.
24Recheck to be sure nothing is still
connecting the engine to the transmission or
vehicle. Disconnect anything still remaining.
25Raise the engine slightly. Carefully work it
forwards to separate it from the transmission.
If you’re working on a vehicle with an
automatic transmission, you may find the
torque converter comes forward with theengine. If it stays with the transmission, leave
it, but you may find it easier to let it come
forward until it can be grasped easier and be
pulled from the crankshaft. Note:When
refitting the torque converter to the
transmission before the engine is refitted, be
sure to renew the transmission front pump
seal, which will probably be damaged when
the converter comes out with the engine.
Either method is acceptable, but be prepared
for some fluid to leak from the torque
converter if it comes out of the transmission. If
you’re working on a vehicle with a manual
transmission, draw the engine forwards until
the input shaft is completely disengaged from
the clutch. Slowly raise the engine out of the
engine compartment. Check carefully to make
sure everything is disconnected.
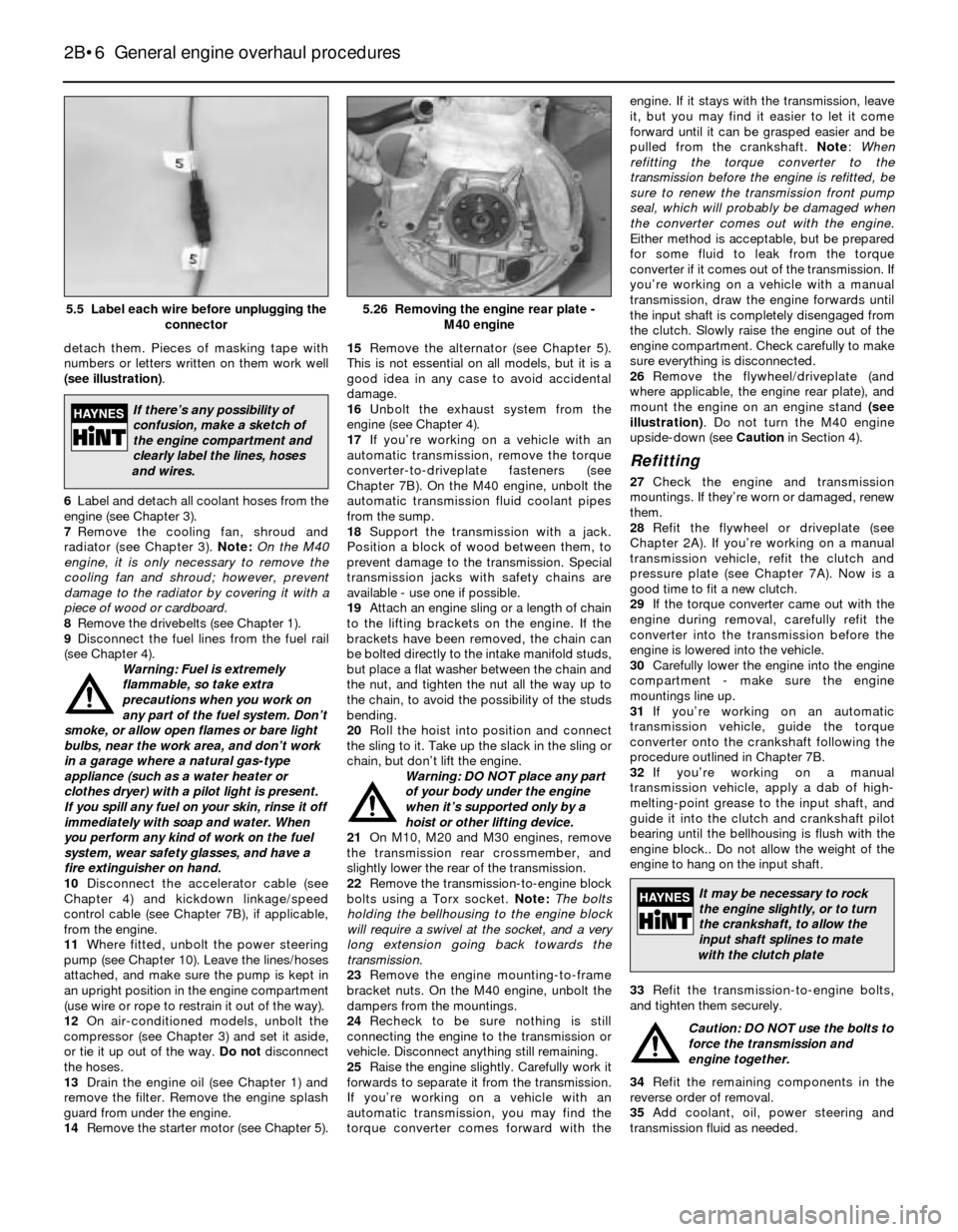
26Remove the flywheel/driveplate (and
where applicable, the engine rear plate), and
mount the engine on an engine stand (see
illustration). Do not turn the M40 engine
upside-down (see Cautionin Section 4).
Refitting
27Check the engine and transmission
mountings. If they’re worn or damaged, renew
them.
28Refit the flywheel or driveplate (see
Chapter 2A). If you’re working on a manual
transmission vehicle, refit the clutch and
pressure plate (see Chapter 7A). Now is a
good time to fit a new clutch.
29If the torque converter came out with the
engine during removal, carefully refit the
converter into the transmission before the
engine is lowered into the vehicle.
30Carefully lower the engine into the engine
compartment - make sure the engine
mountings line up.
31If you’re working on an automatic
transmission vehicle, guide the torque
converter onto the crankshaft following the
procedure outlined in Chapter 7B.
32If you’re working on a manual
transmission vehicle, apply a dab of high-
melting-point grease to the input shaft, and
guide it into the clutch and crankshaft pilot
bearing until the bellhousing is flush with the
engine block.. Do not allow the weight of the
engine to hang on the input shaft.
33Refit the transmission-to-engine bolts,
and tighten them securely.
Caution: DO NOT use the bolts to
force the transmission and
engine together.
34Refit the remaining components in the
reverse order of removal.
35Add coolant, oil, power steering and
transmission fluid as needed.
2B•6 General engine overhaul procedures
5.26 Removing the engine rear plate -
M40 engine5.5 Label each wire before unplugging the
connector
If there’s any possibility of
confusion, make a sketch of
the engine compartment and
clearly label the lines, hoses
and wires.
It may be necessary to rock
the engine slightly, or to turn
the crankshaft, to allow the
input shaft splines to mate
with the clutch plate
Page 64 of 228
M10, M20 and M30 engines
3Adjust all valves to their maximum clearance
by rotating the eccentric on the valve end of
the rocker arm towards the centre of the head
(see Chapter 1, if necessary).
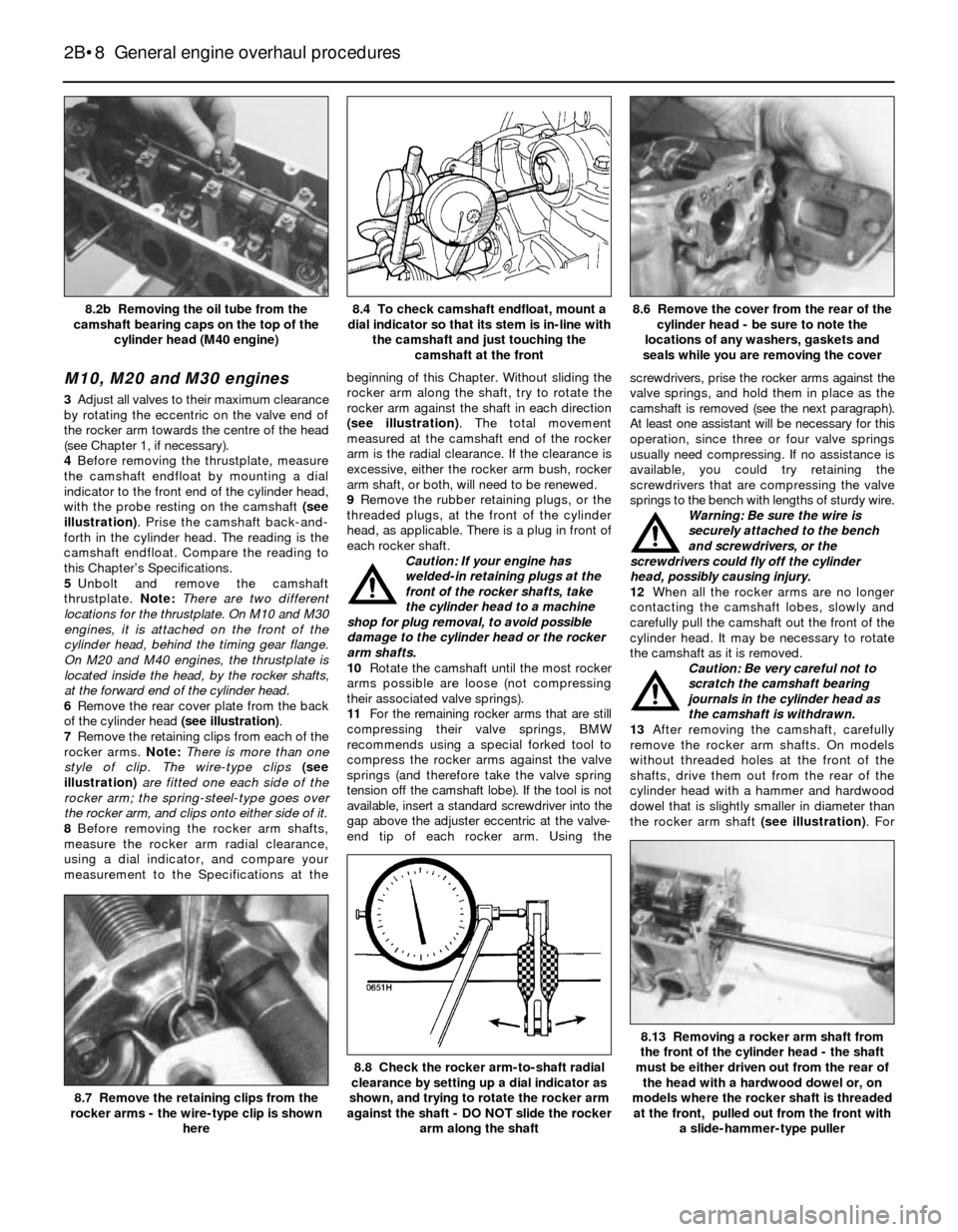
4Before removing the thrustplate, measure
the camshaft endfloat by mounting a dial
indicator to the front end of the cylinder head,
with the probe resting on the camshaft (see
illustration). Prise the camshaft back-and-
forth in the cylinder head. The reading is the
camshaft endfloat. Compare the reading to
this Chapter’s Specifications.
5Unbolt and remove the camshaft
thrustplate. Note:There are two different
locations for the thrustplate. On M10 and M30
engines, it is attached on the front of the
cylinder head, behind the timing gear flange.
On M20 and M40 engines, the thrustplate is
located inside the head, by the rocker shafts,
at the forward end of the cylinder head.
6Remove the rear cover plate from the back
of the cylinder head (see illustration).
7Remove the retaining clips from each of the
rocker arms. Note:There is more than one
style of clip. The wire-type clips (see
illustration)are fitted one each side of the
rocker arm; the spring-steel-type goes over
the rocker arm, and clips onto either side of it.
8Before removing the rocker arm shafts,
measure the rocker arm radial clearance,
using a dial indicator, and compare your
measurement to the Specifications at thebeginning of this Chapter. Without sliding the
rocker arm along the shaft, try to rotate the
rocker arm against the shaft in each direction
(see illustration). The total movement
measured at the camshaft end of the rocker
arm is the radial clearance. If the clearance is
excessive, either the rocker arm bush, rocker
arm shaft, or both, will need to be renewed.
9Remove the rubber retaining plugs, or the
threaded plugs, at the front of the cylinder
head, as applicable. There is a plug in front of
each rocker shaft.
Caution: If your engine has
welded-in retaining plugs at the
front of the rocker shafts, take
the cylinder head to a machine
shop for plug removal, to avoid possible
damage to the cylinder head or the rocker
arm shafts.
10Rotate the camshaft until the most rocker
arms possible are loose (not compressing
their associated valve springs).
11For the remaining rocker arms that are still
compressing their valve springs, BMW
recommends using a special forked tool to
compress the rocker arms against the valve
springs (and therefore take the valve spring
tension off the camshaft lobe). If the tool is not
available, insert a standard screwdriver into the
gap above the adjuster eccentric at the valve-
end tip of each rocker arm. Using thescrewdrivers, prise the rocker arms against the
valve springs, and hold them in place as the
camshaft is removed (see the next paragraph).
At least one assistant will be necessary for this
operation, since three or four valve springs
usually need compressing. If no assistance is
available, you could try retaining the
screwdrivers that are compressing the valve
springs to the bench with lengths of sturdy wire.
Warning: Be sure the wire is
securely attached to the bench
and screwdrivers, or the
screwdrivers could fly off the cylinder
head, possibly causing injury.
12When all the rocker arms are no longer
contacting the camshaft lobes, slowly and
carefully pull the camshaft out the front of the
cylinder head. It may be necessary to rotate
the camshaft as it is removed.
Caution: Be very careful not to
scratch the camshaft bearing
journals in the cylinder head as
the camshaft is withdrawn.
13After removing the camshaft, carefully
remove the rocker arm shafts. On models
without threaded holes at the front of the
shafts, drive them out from the rear of the
cylinder head with a hammer and hardwood
dowel that is slightly smaller in diameter than
the rocker arm shaft (see illustration). For
2B•8 General engine overhaul procedures
8.13 Removing a rocker arm shaft from
the front of the cylinder head - the shaft
must be either driven out from the rear of
the head with a hardwood dowel or, on
models where the rocker shaft is threaded
at the front, pulled out from the front with
a slide-hammer-type puller
8.8 Check the rocker arm-to-shaft radial
clearance by setting up a dial indicator as
shown, and trying to rotate the rocker arm
against the shaft - DO NOT slide the rocker
arm along the shaft
8.7 Remove the retaining clips from the
rocker arms - the wire-type clip is shown
here
8.6 Remove the cover from the rear of the
cylinder head - be sure to note the
locations of any washers, gaskets and
seals while you are removing the cover8.4 To check camshaft endfloat, mount a
dial indicator so that its stem is in-line with
the camshaft and just touching the
camshaft at the front8.2b Removing the oil tube from the
camshaft bearing caps on the top of the
cylinder head (M40 engine)
Page 69 of 228
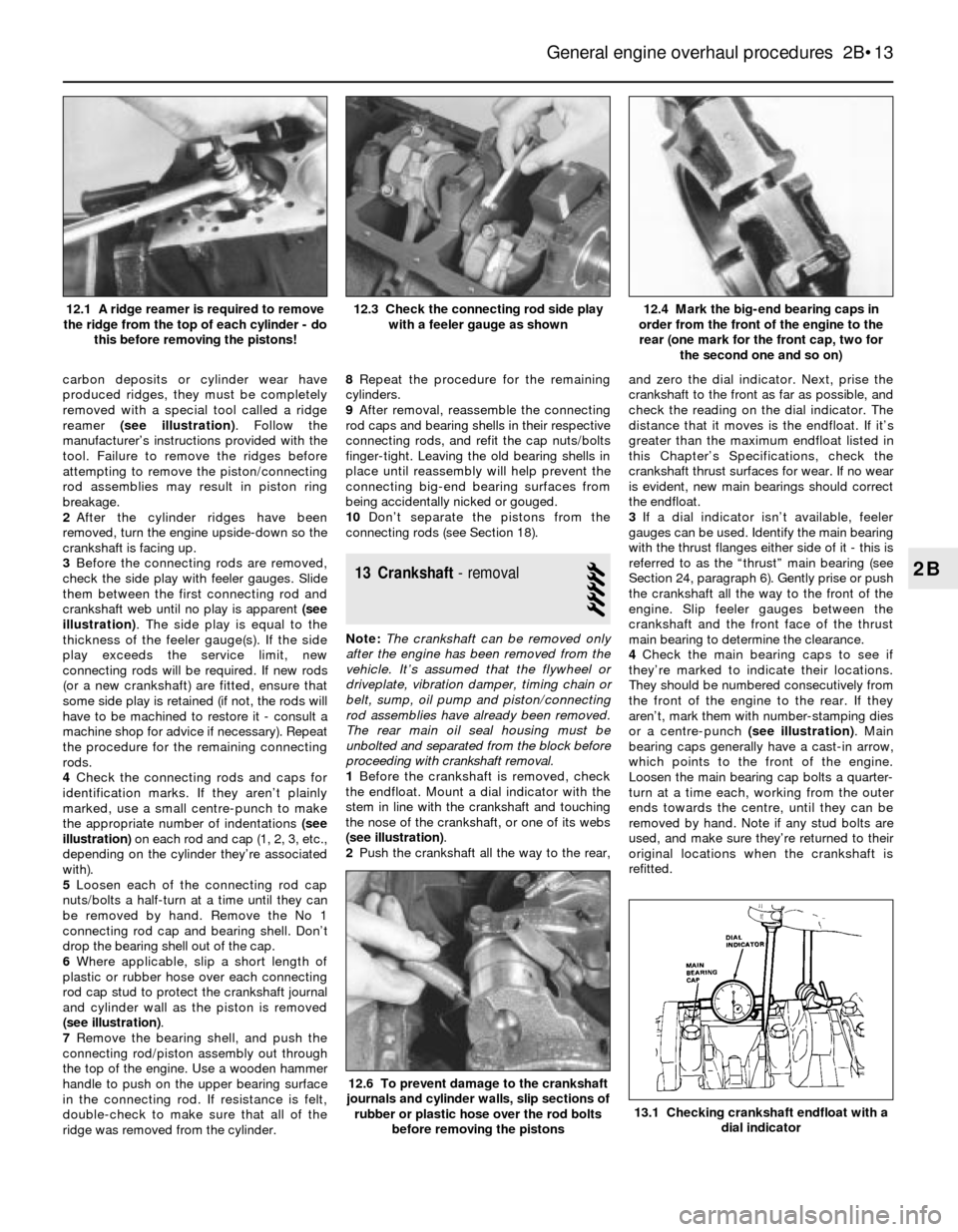
carbon deposits or cylinder wear have
produced ridges, they must be completely
removed with a special tool called a ridge
reamer (see illustration). Follow the
manufacturer’s instructions provided with the
tool. Failure to remove the ridges before
attempting to remove the piston/connecting
rod assemblies may result in piston ring
breakage.
2After the cylinder ridges have been
removed, turn the engine upside-down so the
crankshaft is facing up.
3Before the connecting rods are removed,
check the side play with feeler gauges. Slide
them between the first connecting rod and
crankshaft web until no play is apparent (see
illustration). The side play is equal to the
thickness of the feeler gauge(s). If the side
play exceeds the service limit, new
connecting rods will be required. If new rods
(or a new crankshaft) are fitted, ensure that
some side play is retained (if not, the rods will
have to be machined to restore it - consult a
machine shop for advice if necessary). Repeat
the procedure for the remaining connecting
rods.
4Check the connecting rods and caps for
identification marks. If they aren’t plainly
marked, use a small centre-punch to make
the appropriate number of indentations (see
illustration)on each rod and cap (1, 2, 3, etc.,
depending on the cylinder they’re associated
with).
5Loosen each of the connecting rod cap
nuts/bolts a half-turn at a time until they can
be removed by hand. Remove the No 1
connecting rod cap and bearing shell. Don’t
drop the bearing shell out of the cap.
6Where applicable, slip a short length of
plastic or rubber hose over each connecting
rod cap stud to protect the crankshaft journal
and cylinder wall as the piston is removed
(see illustration).
7Remove the bearing shell, and push the
connecting rod/piston assembly out through
the top of the engine. Use a wooden hammer
handle to push on the upper bearing surface
in the connecting rod. If resistance is felt,
double-check to make sure that all of the
ridge was removed from the cylinder.8Repeat the procedure for the remaining
cylinders.
9After removal, reassemble the connecting
rod caps and bearing shells in their respective
connecting rods, and refit the cap nuts/bolts
finger-tight. Leaving the old bearing shells in
place until reassembly will help prevent the
connecting big-end bearing surfaces from
being accidentally nicked or gouged.
10Don’t separate the pistons from the
connecting rods (see Section 18).
13 Crankshaft- removal
5
Note: The crankshaft can be removed only
after the engine has been removed from the
vehicle. It’s assumed that the flywheel or
driveplate, vibration damper, timing chain or
belt, sump, oil pump and piston/connecting
rod assemblies have already been removed.
The rear main oil seal housing must be
unbolted and separated from the block before
proceeding with crankshaft removal.
1Before the crankshaft is removed, check
the endfloat. Mount a dial indicator with the
stem in line with the crankshaft and touching
the nose of the crankshaft, or one of its webs
(see illustration).
2Push the crankshaft all the way to the rear,and zero the dial indicator. Next, prise the
crankshaft to the front as far as possible, and
check the reading on the dial indicator. The
distance that it moves is the endfloat. If it’s
greater than the maximum endfloat listed in
this Chapter’s Specifications, check the
crankshaft thrust surfaces for wear. If no wear
is evident, new main bearings should correct
the endfloat.
3If a dial indicator isn’t available, feeler
gauges can be used. Identify the main bearing
with the thrust flanges either side of it - this is
referred to as the “thrust” main bearing (see
Section 24, paragraph 6). Gently prise or push
the crankshaft all the way to the front of the
engine. Slip feeler gauges between the
crankshaft and the front face of the thrust
main bearing to determine the clearance.
4Check the main bearing caps to see if
they’re marked to indicate their locations.
They should be numbered consecutively from
the front of the engine to the rear. If they
aren’t, mark them with number-stamping dies
or a centre-punch (see illustration). Main
bearing caps generally have a cast-in arrow,
which points to the front of the engine.
Loosen the main bearing cap bolts a quarter-
turn at a time each, working from the outer
ends towards the centre, until they can be
removed by hand. Note if any stud bolts are
used, and make sure they’re returned to their
original locations when the crankshaft is
refitted.
General engine overhaul procedures 2B•13
12.4 Mark the big-end bearing caps in
order from the front of the engine to the
rear (one mark for the front cap, two for
the second one and so on)12.3 Check the connecting rod side play
with a feeler gauge as shown12.1 A ridge reamer is required to remove
the ridge from the top of each cylinder - do
this before removing the pistons!
13.1 Checking crankshaft endfloat with a
dial indicator
12.6 To prevent damage to the crankshaft
journals and cylinder walls, slip sections of
rubber or plastic hose over the rod bolts
before removing the pistons
2B
Page 70 of 228

5Gently tap the caps with a soft-faced
hammer, then separate them from the engine
block. If necessary, use the bolts as levers to
remove the caps. Try not to drop the bearing
shells if they come out with the caps.
6Carefully lift the crankshaft out of the
engine. It may be a good idea to have an
assistant available, since the crankshaft is
quite heavy (see illustration). With the
bearing shells in place in the engine block and
main bearing caps, return the caps to their
respective locations on the engine block, and
tighten the bolts finger-tight.
14 Intermediate shaft-
removal and inspection
5
Note:The intermediate shaft is used on the
M20 engine only. The shaft rotates in the
engine block parallel to the crankshaft. It is
driven by the timing belt, and its only purpose
is to drive the oil pump.
1Remove the timing belt (see Chapter 2A).
2With the belt removed, unbolt the gear from
the intermediate shaft and unbolt the front
cover.
3Remove the oil pump driveshaft (see
Chapter 2A).
4The shaft is held in the cylinder block by a
retaining plate with two bolts. Remove the
bolts, and pull the shaft forwards and out of
the block.
5Look for any signs of abnormal wear on the
bearing surfaces or the gear at the back end
of the shaft, which drives the oil pump shaft. If
the bearing surfaces in the engine block show
wear, they’ll have to be attended to by a
machine shop.
15 Engine block- cleaning
2
Caution: The core plugs may be
difficult or impossible to retrieve
if they’re driven into the block
coolant passages.
1Remove the core plugs from the engine
block. To do this, knock one side of each plug
into the block with a hammer and punch,
grasp the other side by its edge with large
pliers, and pull it out.
2Using a gasket scraper, remove all traces of
gasket material from the engine block. Be very
careful not to nick or gouge the gasket sealing
surfaces.
3Remove the main bearing caps, and
separate the bearing shells from the caps and
the engine block. Tag the bearings, indicating
which cylinder they were removed from and
whether they were in the cap or the block,
then set them aside.
4Remove all of the threaded oil gallery plugs
from the block. The plugs are usually very
tight - they may have to be drilled out and theholes retapped. Use new plugs when the
engine is reassembled.
5If the engine is extremely dirty, it should be
taken to a machine shop to be steam-
cleaned.
6After the block is returned, clean all oil
holes and oil galleries one more time. Brushes
specifically designed for this purpose are
available at most motor factors. Flush the
passages with warm water until the water runs
clear, dry the block thoroughly, and wipe all
machined surfaces with a light, rust-
preventive oil. If you have access to
compressed air, use it to speed the drying
process and to blow out all the oil holes and
galleries.
Warning: Wear eye protection
when using compressed air!
7If the block isn’t extremely dirty or sludged
up, you can do an adequate cleaning job with
hot soapy water and a stiff brush. Take plenty
of time, and do a thorough job. Regardless of
the cleaning method used, be sure to clean all
oil holes and galleries very thoroughly, dry the
block completely, and coat all machined
surfaces with light oil.
8The threaded holes in the block must be
clean to ensure accurate torque readingsduring reassembly. Run the proper-size tap
into each of the holes to remove rust,
corrosion, thread sealant or sludge, and to
restore damaged threads (see illustration). If
possible, use compressed air to clear the
holes of debris produced by this operation. Be
sure also that the holes are dry- any oil or
other fluid present could cause the block to
be cracked by hydraulic pressure when the
bolts are tightened. Now is a good time to
clean the threads on all bolts. Note that BMW
recommend that the cylinder head bolts and
main bearing bolts are renewed as a matter of
course.
9Refit the main bearing caps, and tighten the
bolts finger-tight.
10After coating the sealing surfaces of the
new core plugs with a suitable sealant, refit
them in the engine block (see illustration).
Make sure they’re driven in straight and
seated properly, or leakage could result.
Special tools are available for this purpose,
but a large socket, with an outside diameter
that will just slip into the core plug, a 1/2-inch
drive extension, and a hammer, will work just
as well.
11Apply non-hardening sealant to the new
oil gallery plugs, and thread them into the
holes in the block. Make sure they’re
tightened securely.
12If the engine isn’t going to be
reassembled right away, cover it with a large
plastic bag to keep it clean.
2B•14 General engine overhaul procedures
15.10 A large socket on an extension can
be used to drive the new core plugs into
the block
15.8 All bolt holes in the block -
particularly the main bearing cap and head
bolt holes - should be cleaned and
restored with a tap (be sure to remove
debris from the holes after this is done)
13.6 Remove the crankshaft by lifting
straight up. Be very careful when removing
the crankshaft - it is very heavy13.4 Use a centre-punch or number-
stamping dies to mark the main bearing
caps to ensure refitting in their original
locations on the block (make the punch
marks near one of the bolt heads)
Page 79 of 228

3General
Coolant capacity . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 1
Thermostat rating
Opening temperature . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 80°C (176°F)
Fully open at . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 100°C (212°F)
Cooling fan thermo-switch - switching temperatures
Low-speed . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 91°C (196°F)
High-speed . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 99°C (210°F)
Torque wrench settingsNm
Mechanical cooling fan clutch-to-water pump securing
nut (left-hand thread) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
Mechanical cooling fan-to-clutch bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Water pump bolts
Small bolts (M6) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Large bolts (M8) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Thermostat housing bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Chapter 3
Cooling, heating and air conditioning systems
Air conditioner receiver-drier - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Air conditioning blower motor (E28/”old-shape” 5-series
models) - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Air conditioning compressor - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Air conditioning condenser - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Air conditioning system - precautions and maintenance . . . . . . . . . 12
Antifreeze - general information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Coolant level check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 1
Coolant temperature sender unit - check and renewal . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Cooling system check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 1
Cooling system servicing (draining, flushing and refilling)See Chapter 1Engine cooling fan(s) and clutch - check, removal and refitting . . . . 5
Evaporator matrix - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
General information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
Heater and air conditioner control assembly - removal and refitting 10
Heater and air conditioning blower motor - removal,testing and
refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Heater matrix - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Radiator - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
Thermostat - check and renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Water pump - check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Water pump - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
3•1
Easy,suitable for
novice with little
experienceFairly easy,suitable
for beginner with
some experienceFairly difficult,
suitable for competent
DIY mechanic
Difficult,suitable for
experienced DIY
mechanicVery difficult,
suitable for expert
DIY or professional
Degrees of difficulty
Specifications Contents
1 General information
Engine cooling system
All vehicles covered by this manual employ
a pressurised engine cooling system, with
thermostatically-controlled coolant circulation.
An impeller-type water pump mounted on
the front of the block pumps coolant through
the engine. The coolant flows around each
cylinder, and towards the rear of the engine.
Cast-in coolant passages direct coolantaround the intake and exhaust ports, near the
spark plug areas, and in close proximity to the
exhaust valve guides.
A wax-pellet-type thermostat is located in-
line in the bottom hose on M10 engines, in a
housing near the front of the engine on M20
and M30 engines, or behind an elbow under
the timing belt upper cover (on the front of the
cylinder head) on M40 engines. During warm-
up, the closed thermostat prevents coolant
from circulating through the radiator. As the
engine nears normal operating temperature,
the thermostat opens and allows hot coolant
to travel through the radiator, where it’s
cooled before returning to the engine.The pressure in the system raises the
boiling point of the coolant, and increases the
cooling efficiency of the radiator. The cooling
system is sealed by a pressure-type cap. If
the system pressure exceeds the cap
pressure relief value, the excess pressure in
the system forces the spring-loaded valve
inside the cap off its seat, and allows the
coolant to escape through the overflow tube.
The pressure cap on four-cylinder models is
on the top of the radiator; on six-cylinder models,
it’s on top of a translucent plastic expansion
tank. The cap pressure rating is moulded into the
top of the cap. The pressure rating is either
1.0 bar (14 psi) or 1.2 bars (17 psi).
Page 84 of 228

M20 engine
9Remove the distributor cap and HT leads,
ignition rotor and dust shield (see Chapter 1).
10Where applicable, remove the timing
sensor (see Chapter 5).
11Remove the timing belt upper cover (see
Chapter 2A).
12Loosen all three water pump mounting
bolts. Remove the top and right-hand side
bolts, but DON’T remove the lower bolt (see
illustration).
13Rotate the pump downwards, and remove
the drivebelt tensioner spring and pin.
14 Remove the final water pump bolt, and
remove the pump.
Caution: Leave the tensioner bolt
tight. Be careful to not move the
camshaft gear, as damage can
occur if the valves are moved.
M30 engine
15Remove the engine lifting bracket.
16Remove the bolts that mount the water
pump to the engine block.
17Remove the water pump, and recover the
gasket.
M40 engine
18Unscrew the mounting bolts and remove
the water pump. If the pump is tight in the
cylinder head, insert two bolts in the special
lugs at the top and bottom of the pump, and
tighten them evenly to press the pump out of
the head (see illustrations).
Refitting
19Clean the bolt threads and the threaded
holes in the engine to remove corrosion and
sealant.
20Compare the new pump to the old one, to
make sure they’re identical.
21Remove all traces of old gasket material
from the engine with a gasket scraper.
22Clean the water pump mating surfaces.
23On the M40 engine, locate a new O-ring
on the pump (see illustration).
24Locate the gasket on the pump, and offer
the pump up to the engine (see illustration).
Slip a couple of bolts through the pump
mounting holes to hold the gasket in place.
25Carefully attach the pump and gasket to
the engine, threading the bolts into the holes
finger-tight.Note:On the M20 engine, refit the
lower bolt finger-tight, then rotate the water
pump into position with the drivebelt tensioner
spring and pin in position.
26Refit the remaining bolts (if they also hold
an accessory bracket in place, be sure to
reposition the bracket at this time). Tighten
them to the torque listed in this Chapter’s
Specifications, in quarter-turn increments.
Don’t overtighten them, or the pump may be
distorted.
27Refit all parts removed for access to the
pump.
28Refill the cooling system and check the
drivebelt tension (see Chapter 1). Run the
engine and check for leaks.8 Coolant temperature sender
unit- check and renewal
2
Warning: Wait until the engine is
completely cool before beginning
this procedure.
1The coolant temperature indicator system
is composed of a temperature gauge
mounted in the instrument panel, and a
coolant temperature sender unit that’s
normally mounted on the thermostat housing
(see illustration 3.11). Some vehicles have
more than one sender unit, but only one is
used for the temperature gauge. On the M40
engine, the sender unit is mounted on the left-
hand side of the cylinder head, towards the
rear.
2If the gauge reading is suspect, first check
the coolant level in the system. Make sure the
wiring between the gauge and the sending
unit is secure, and that all fuses are intact. (If
the fuel gauge reading is suspect as well, the
problem is almost certainly in the instrument
panel or its wiring.)
3Before testing the circuit, refer to the
relevant wiring diagrams (see Chapter 12).
Where the sender unit simply earths out the
circuit, test by earthing the wire connected to
the sending unit while the ignition is on (but
without the engine running, for safety). If the
gauge now deflects to the end of the scale,
renew the sender unit. If the gauge does not
respond satisfactorily, the gauge, or the wiring
to the gauge, is faulty. Where the sender unit
has two terminals, test the circuit by checking
the resistance of the unit. No figures were
available at the time of writing, but typically
readings of several hundred or several
thousand ohms (depending on temperature)
would be expected. A reading of zero (short-
circuit) or infinity (open-circuit) would indicate
a faulty sender unit.
Caution: Do not earth the wire
for more than a second or two, or
damage to the gauge could
occur.
3•6 Cooling, heating and air conditioning systems
7.24 New outer gasket on the M40 engine
water pump7.23 Fit a new O-ring on the M40 engine
water pump
7.18b . . . and remove the water pump
(M40 engine)7.18a With the water pump mounting bolts
removed, screw two bolts into the special
lugs (one top and one bottom) . . .7.12 Water pump bolt locations on the
M20 engine
Page 85 of 228

4If a new sender unit is to be fitted, make
sure the engine is completely cool. There will
be some coolant loss when the unit is
unscrewed, so be prepared to catch it, or
have the new unit ready to fit immediately the
old one is removed. Disconnect the wiring,
then unscrew the old unit from the engine,
and fit the new one. Use sealant on the
threads. Reconnect the wiring, and check the
coolant level on completion.
9 Heater and air conditioning
blower motor- removal,
testing and refitting
1
Removal
Note: The 3-Series models covered by this
manual have always used a single blower
motor for ventilation, heating and air
conditioning. “Old-shape” (E28) 5-Series
models use two separate blower motors: one
for ventilation and heating, and another for air
conditioning. “New-shape” (E34) 5-Series
models have a single blower motor, like the 3-
Series. The removal and refitting of the single
blower motor, and the old-shape 5-Series
vent/heat motor, is described below. The
removal and refitting of the old-shape 5-Series
air conditioning blower motor is described in
Section 14 of this Chapter.
Caution: If the radio in your
vehicle is equipped with an anti-
theft system, make sure you have
the correct activation code
before disconnecting the battery.
Note: If, after connecting the battery, the
wrong language appears on the instrument
panel display, refer to page 0-7 for the
language resetting procedure.
1Disconnect the battery negative cable.
2The blower motor is located behind the
bulkhead, under an access panel. Remove the
panel securing screws (see illustrations).
3Disconnect or cut the plastic ties holding
the wiring harness to the panel, and move the
wiring out of the way.
4Remove the panel.
5Unclip the blower housing retaining clip,
and the clip securing the blower motor (see
illustrations).6Disconnect the wiring and remove the
blower motor (see illustration).
Testing
7You can test the blower motor by applying
battery voltage to the blower motor’s
terminals with fused jumper wires (be sure the
fan blades won’t hit anything when they
rotate). If the blower motor spins the fan
blades rapidly (this test simulates high-speed
operation), the blower motor is OK. If the
blower motor does not operate, or operates
slowly or noisily, renew it.
Note: If the fan blade assemblies need to be
removed, mark their relationship to the shaft.
The assemblies are balanced during
production, and excessive noise or shortened
bearing life could result if they are not refitted
in exactly the same position in relation to the
shaft.
Refitting
8Refitting is the reverse of removal. Note:
The blower motor may have to be rotated to
allow the retaining clip to line up correctly.
10 Heater and air conditioner
control assembly- removal
and refitting
1
Removal
1Disconnect the battery negative cable. Caution: If the radio in your
vehicle is equipped with an anti-
theft system, make sure you
have the correct activation code
before disconnecting the battery.
Note: If, after connecting the battery, the
wrong language appears on the instrument
panel display, refer to page 0-7 for the
language resetting procedure.
3-Series models
2Remove the centre console and side trim
pieces.
3Remove the radio (see Chapter 12), then
pull the knobs off the heater/air conditioning
control levers.
4Remove the heater trim panel to gain
access to the control cables.
5Disconnect the cables, marking them for
accurate refitting.
6Disconnect the electrical connector.
7Remove the lever assembly.
8Each lever assembly can be removed
separately.
5-Series models
9Remove the centre console (see Chap-
ter 11).
10Remove the radio (see Chapter 12), then
pull the knobs off the heater/air conditioning
control levers.
11Remove the trim bezel, and pull the
control unit from the dash. This will allow you
to disconnect the control cables from the
lever assembly.
Cooling, heating and air conditioning systems 3•7
9.5a Unclip the retaining strap to remove
the blower housing . . .
9.2b . . . a fastener from the top secure the
panel9.2a To get to the heater blower motor,
the access panel must be removed - a
fastener from the front and . . .
9.6 Lift out the assembly, and disconnect
the electrical connection from the blower
motor9.5b . . . and unclip the centre strap that
secures the blower motor assembly
3
Page 86 of 228
12Disconnect the cables from the clips
securing them to the lever assembly, marking
them for accurate refitting.
13Disconnect the electrical connection from
the control assembly.
14Remove the screws attaching the bezel to
the control assembly, and remove the control
assembly.
Refitting
15Refitting is the reverse of the removal
procedure.
11 Heater matrix-
removal and refitting
1
Caution: If the radio in your
vehicle is equipped with an anti-
theft system, make sure you
have the correct activation code
before disconnecting the battery.
Note: If, after connecting the battery, the
wrong language appears on the instrument
panel display, refer to page 0-7 for the
language resetting procedure.
1Disconnect the battery negative cable.
2Drain the cooling system (see Chapter 1).
3Remove the centre console (see Chap-
ter 11). Spread an old blanket over the front
carpeting; this will prevent stains if any
residual coolant spills.
Removal
3-Series models
4Remove the left-hand side heater ducting,
and set it aside.
5Remove the heater valve clamp.
6Remove the screws and detach the flange
where the two coolant lines enter the heater
matrix case. Be careful; some coolant may
spill.
7Remove the two screws holding the heater
matrix case to the heater main assembly.
8Slide the heater matrix out of the mounting.
Be careful not to spill any of the remaining
coolant in the heater matrix when removing it.
5-Series models
9Disconnect the temperature sensor
electrical connectors.
10Disconnect the straps holding the wiring
to the case, and set the wiring out of the way.
11Unfasten the cover fasteners.
12Remove the screws holding the cover in
place, then remove the cover.
13Disconnect all heater pipe connections
attached to the heater matrix. Be careful;
some coolant may spill.
14Lifting on the right side of the heater
matrix first, remove the heater matrix.
Refitting
Note: Always use new O-rings when attaching
the coolant lines to the heater matrix.15Refitting is the reverse of removal. Refill
the cooling system (see Chapter 1), then run
the engine with the heater on, and check for
correct operation and leaks.
12 Air conditioning system-
precautions and maintenance
1
Precautions
Warning: The air conditioning
system is under high pressure.
DO NOT loosen any hose or line
fittings, or remove any
components, until after the system has
been discharged. Air conditioning
refrigerant should be properly discharged
by a qualified refrigeration engineer. The
refrigerant used in the system must not be
allowed into contact with your skin or
eyes, or there is a risk of frostbite. Should
the refrigerant come into contact with a
naked flame, a poisonous gas will be
produced. Smoking in the presence of
refrigerant is therefore highly dangerous,
particularly if refrigerant vapour is inhaled
through a lighted cigarette. The refrigerant
is heavier than air, and it may cause
suffocation if discharged in an enclosed
space such as a domestic garage.
Finally, uncontrolled release of the
refrigerant causes environmental damage,
by contributing to the “greenhouse
effect”.
Maintenance
1The following maintenance checks should
be performed on a regular basis to ensure the
air conditioner continues to operate at peak
efficiency:
a) Check the drivebelt. If it’s worn or
deteriorated, renew it (see Chapter 1).
b) Check the system hoses. Look for cracks,
bubbles, hard spots and deterioration.
Inspect the hoses and all fittings for oil
bubbles and seepage. If there’s any
evidence of wear, damage or leaks, have
new hose(s) fitted.
c) Inspect the condenser fins for leaves, flies
and other debris. Use a “fin comb” or
compressed air to clean the condenser.
d) Make sure the system has the correct
refrigerant charge, as described below.
2It’s a good idea to operate the system for
about 10 minutes at least once a month,
particularly during the winter. Long-term non-
use can cause hardening, and subsequent
failure, of the seals.
3Because of the complexity of the air
conditioning system and the special
equipment necessary to service it, in-depth
fault diagnosis and repair procedures are not
included in this manual. However, simple
checks and component renewal procedures
are provided in this Chapter.
4The most common cause of poor cooling issimply a low system refrigerant charge. If a
noticeable loss of cool air output occurs, the
following quick check may help you determine
if the refrigerant level is low.
5Warm the engine up to normal operating
temperature.
6Set the air conditioning temperature
selector at the coldest setting, and put the
blower at the highest setting. Open the doors
(to make sure the air conditioning system
doesn’t switch off as soon as it cools the
passenger compartment).
7With the compressor engaged - the
compressor clutch will make an audible click,
and the centre of the clutch will rotate - feel
the tube located adjacent to the right front
frame rail, near the radiator.
8If a significant temperature drop is noticed,
the refrigerant level is probably OK.
9If the inlet line has frost accumulation, or
feels cooler than the receiver-drier surface,
the refrigerant charge is low. Recharging the
system should be carried out by a qualified
refrigeration engineer.
13 Air conditioning compressor
- removal and refitting
5
Warning: Due to the potential
dangers associated with the
system, you are strongly advised
to have any work on the air
conditioning system carried out by a BMW
dealer or air conditioning specialist. At the
very least, DO NOT dismantle any part of
the system (hoses, compressor, line
fittings, etc.) until after the system has
been discharged by a qualified engineer.
Refer to the precautions given at the start
of Section 12.
Note: If a new compressor is fitted, the
receiver-drier (see Section 16) should also be
renewed.
Removal
1Have the air conditioning system
discharged (see Warning above).
2Disconnect the battery negative cable.
Caution: If the radio in your
vehicle is equipped with an anti-
theft system, make sure you
have the correct activation code
before disconnecting the battery.
Note: If, after connecting the battery, the
wrong language appears on the instrument
panel display, refer to page 0-7 for the
language resetting procedure.
3Disconnect the compressor clutch wiring
harness.
4Remove the drivebelt (see Chapter 1).
5Disconnect the refrigerant lines from the
rear of the compressor. Plug the open fittings
to prevent entry of dirt and moisture.
6Unbolt the compressor from the mounting
3•8 Cooling, heating and air conditioning systems
Page 90 of 228

Carburettor (Solex 2BE)
Main jet
Stage 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . X120
Stage 2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . X110
Air correction jet
Stage 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 140
Stage 2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
Venturi diameter
Stage 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24 mm
Stage 2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28 mm
Idle fuel jet
Stage 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47.5 mm
Idle air jet
Stage 2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 180
Float needle valve diameter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2.0 mm
Throttle positioner coil resistance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.97 to 1.63 ohms
Intake air temperature resistance
-10º C . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8200 to 10 500 ohms
20º C . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2200 to 2700 ohms
80º C . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 300 to 360 ohms
Float level
Stage 1 float chamber . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27.0 to 29.0 mm
Stage 2 float chamber . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29.0 to 31.0 mm
Fuel pressure checks (carburettor engines)
Fuel pump delivery pressure (engine idling) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.1 to 0.3 bars
Fuel pressure checks (fuel injection engines)
Fuel system pressure (relative to intake manifold pressure)
3-Series (E30)
316i with M40/B16 engine . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3.0 ± 0.06 bars
318i with M10/B18 engine . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2.5 to 3.0 bars
318i with M40/B18 engine . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3.0 ± 0.06 bars
320i with M20/B20 engine (L-Jetronic) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2.5 to 3.0 bars
320i with M20/B20 engine (Motronic) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2.5 ± 0.05 bars
325i with M20/B25 engine . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3.0 ± 0.05 bars
5-Series (E28/”old-shape”)
All models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2.5 to 3.0 bars
5-Series (E34/”new-shape”)
518i with M40/B18 engine . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3.0 ± 0.06 bars
All other models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2.5 to 3.0 bars
Fuel system hold pressure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2.1 bars
Fuel pump maximum pressure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6.3 to 6.9 bars
Fuel pump hold pressure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5.5 bars
Transfer pump pressure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.28 to 0.35 bars
Injectors
Injector resistance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14.5 to 17.5 ohms
Accelerator cable free play . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1.0 mm
Torque wrench settingsNm
Carburettor mountings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Fuel pump to cylinder head . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Throttle body nuts/bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19 to 26
4•2 Fuel and exhaust systems
1 General information
With the exception of early models (316 and
518 models) all engines are equipped with
electronic fuel injection.
Early 316 and 518 models are equipped
with Solex carburettors. The carburettor fitted
is either a Solex 2B4 (early models) or
2BE (later models). The mechanical fuel pumpis driven by an eccentric lobe on the
camshaft.
Fuel injection models are equipped with
either the L-Jetronic or the Motronic fuel
injection system. From 1988, fuel injection
models are equipped with an updated version
of the Motronic system - this system is easily
distinguished from the earlier system by the
absence of a cold start injector. The electric
fuel pump is located beneath the rear of the
vehicle, or inside the fuel tank. The fuel pump
relay on Motronic systems is activated from aearth signal from the Motronic control unit
(ECU). The fuel pump operates for a few
seconds when the ignition is first switched on,
and it continues to operate only when the
engine is actually running.Air intake system
The air intake system consists of the air
filter housing, the airflow meter and throttle
body (fuel injection models), and the intake
manifold. All components except the intake
manifold are covered in this Chapter; for