fuel injection BMW 3 SERIES 1988 E30 User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: BMW, Model Year: 1988, Model line: 3 SERIES, Model: BMW 3 SERIES 1988 E30Pages: 228, PDF Size: 7.04 MB
Page 63 of 228
36Run the engine and check for leaks and
proper operation of all accessories, then refit
the bonnet and test drive the vehicle.
37Where necessary, have the air
conditioning system recharged and leak-
tested.
6 Engine overhaul- alternatives
The do-it-yourselfer is faced with a number
of options when performing an engine
overhaul. The decision to renew the engine
block, piston/connecting rod assemblies and
crankshaft depends on a number of factors,
with the number one consideration being the
condition of the block. Other considerations
are cost, access to machine shop facilities,
parts availability, time required to complete
the project, and the extent of prior mechanical
experience on the part of the do-it-yourselfer.
Some of the alternatives include:
Individual parts - If the inspection
procedures reveal that the engine block and
most engine components are in re-usable
condition, purchasing individual parts may be
the most economical alternative. The block,
crankshaft and piston/connecting rod
assemblies should all be inspected carefully.
Even if the block shows little wear, the
cylinder bores should be surface-honed.
Crankshaft kit- A crankshaft kit (where
available) consists of a reground crankshaft
with matched undersize new main and
connecting big-end bearings. Sometimes,
reconditioned connecting rods and new
pistons and rings are included with the kit
(such a kit is sometimes called an “engine
kit”). If the block is in good condition, but the
crankshaft journals are scored or worn, a
crankshaft kit and other individual parts may
be the most economical alternative.
Short block- A short block consists of an
engine block with a crankshaft and
piston/connecting rod assemblies already
fitted. New bearings are fitted, and all
clearances will be correct. The existing
camshaft, valve train components, cylinder
head and external parts can be bolted to the
short block with little or no machine shop
work necessary.
Full block - A “full” or “complete” block
consists of a short block plus an oil pump,
sump, cylinder head, valve cover, camshaft
and valve train components, timing sprockets
and chain (or belt) and timing cover. All
components are fitted with new bearings,
seals and gaskets used throughout. The
refitting of manifolds and external parts is all
that’s necessary.
Give careful thought to which alternative is
best for you, and discuss the situation with
local machine shops, parts dealers and
experienced rebuilders before ordering or
purchasing new parts.
7 Engine overhaul-
dismantling sequence
1It’s much easier to dismantle and work on
the engine if it’s mounted on a portable
engine stand. A stand can often be hired quite
cheaply from a tool hire shop. Before the
engine is mounted on a stand, the
flywheel/driveplate should be removed from
the engine.
2If a stand isn’t available, it’s possible to
dismantle the engine with it blocked up on the
floor. Be extra-careful not to tip or drop the
engine when working without a stand.
3If you’re going to obtain a rebuilt engine, all
the external components listed below must
come off first, to be transferred to the new
engine if applicable. This is also the case if
you’re doing a complete engine overhaul
yourself. Note:When removing the external
components from the engine, pay close
attention to details that may be helpful or
important during refitting. Note the fitted
position of gaskets, seals, spacers, pins,
brackets, washers, bolts and other small items.
Alternator and brackets
Emissions control components
Distributor, HT leads and spark plugs
Thermostat and housing cover
Water pump
Fuel injection/carburettor and fuel system
components
Intake and exhaust manifolds
Oil filter and oil pressure sending unit
Engine mounting brackets (see illustration)
Clutch and flywheel/driveplate
Engine rear plate (where applicable)
4If you’re obtaining a short block, which
consists of the engine block, crankshaft,
pistons and connecting rods all assembled,
then the cylinder head, sump and oil pump
will have to be removed as well. See Section 6
for additional information regarding the
different possibilities to be considered.
5If you’re planning a complete overhaul, the
engine must be dismantled and the internal
components removed in the following general
order:
Valve cover
Intake and exhaust manifolds
Timing belt or chain covers
Timing chain/belt
Water pump
Cylinder head
Sump
Oil pump
Piston/connecting rod assemblies
Crankshaft and main bearings
Camshaft
Rocker shafts and rocker arms (M10, M20
and M30 engines)
Cam followers and hydraulic tappets
(M40 engine)
Valve spring retainers and springs
Valves
6Before beginning the dismantling andoverhaul procedures, make sure the following
items are available. Also, refer to Section 21
for a list of tools and materials needed for
engine reassembly.
Common hand tools
Small cardboard boxes or plastic bags for
storing parts
Compartment-type metal box for storing
the hydraulic tappets (M40 engine)
Gasket scraper
Ridge reamer
Vibration damper puller
Micrometers
Telescoping gauges
Dial indicator set
Valve spring compressor
Cylinder surfacing hone
Piston ring groove cleaning tool
Electric drill motor
Tap and die set
Wire brushes
Oil gallery brushes
Cleaning solvent
8 Cylinder head- dismantling
4
1Remove the cylinder head (see Chapter 2A).
2Remove the oil supply tube from its
mounting on top of the cylinder head (see
illustrations). Note:It’s important to renew
the seals under the tube mounting bolts.
General engine overhaul procedures 2B•7
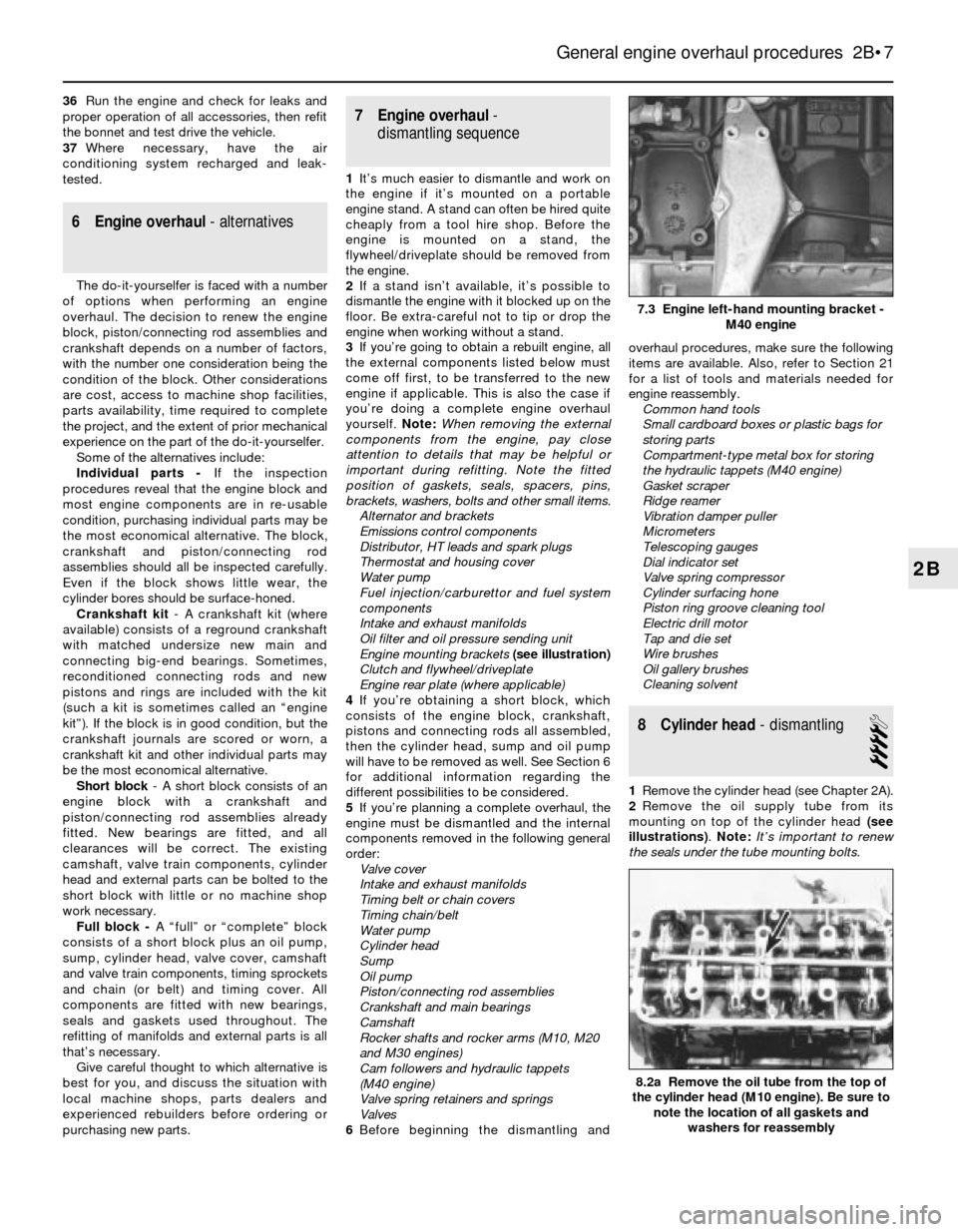
7.3 Engine left-hand mounting bracket -
M40 engine
8.2a Remove the oil tube from the top of
the cylinder head (M10 engine). Be sure to
note the location of all gaskets and
washers for reassembly
2B
Page 89 of 228

4
Carburettor (Solex 2B4)
Main jet
Stage 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . X120
Stage 2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . X90
Air correction jet
Stage 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 135
Stage 2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
Venturi diameter
Stage 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24 mm
Stage 2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28 mm
Idle/air jet
Stage 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50/120
Stage 2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40/125
Float needle valve diameter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2.0 mm
Choke gap (pulldown) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4.0 to 5.5 mm
Throttle positioner spring preload . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22.0 to 24.0 mm
Float level
Stage 1 float chamber . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27.0 to 29.0 mm
Stage 2 float chamber . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29.0 to 31.0 mm
Chapter 4 Fuel and exhaust systems
Accelerator cable - check, adjustment and renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Air cleaner assembly - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Air filter renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 1
Airflow meter - check, removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Carburettor - cleaning and adjustment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Carburettor - general information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Carburettor - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Cold start injector and thermotime switch -
checkand renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Engine idle speed check and adjustment . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 1
Exhaust system check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 1
Exhaust system servicing - general information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Fuel filter renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 1
Fuel injection system - check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Fuel injection system - depressurising . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2Fuel injection system - fault finding . . . . . . . . . . . . See end of Chapter
Fuel injection - general information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Fuel injection systems . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Fuel injectors - check and renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Fuel lines and fittings - repair and renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Fuel pressure regulator - check and renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Fuel pump, transfer pump and fuel level sender unit -
removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
Fuel pump/fuel pressure - check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Fuel system check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 1
Fuel tank - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Fuel tank cleaning and repair - general information . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
General information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
Idle air stabiliser valve - check, adjustment and renewal . . . . . . . . . 21
Throttle body - check, removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
4•1
Easy,suitable for
novice with little
experienceFairly easy,suitable
for beginner with
some experienceFairly difficult,
suitable for competent
DIY mechanic
Difficult,suitable for
experienced DIY
mechanicVery difficult,
suitable for expert
DIY or professional
Degrees of difficulty
Specifications Contents
Page 90 of 228

Carburettor (Solex 2BE)
Main jet
Stage 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . X120
Stage 2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . X110
Air correction jet
Stage 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 140
Stage 2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
Venturi diameter
Stage 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24 mm
Stage 2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28 mm
Idle fuel jet
Stage 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47.5 mm
Idle air jet
Stage 2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 180
Float needle valve diameter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2.0 mm
Throttle positioner coil resistance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.97 to 1.63 ohms
Intake air temperature resistance
-10º C . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8200 to 10 500 ohms
20º C . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2200 to 2700 ohms
80º C . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 300 to 360 ohms
Float level
Stage 1 float chamber . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27.0 to 29.0 mm
Stage 2 float chamber . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29.0 to 31.0 mm
Fuel pressure checks (carburettor engines)
Fuel pump delivery pressure (engine idling) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.1 to 0.3 bars
Fuel pressure checks (fuel injection engines)
Fuel system pressure (relative to intake manifold pressure)
3-Series (E30)
316i with M40/B16 engine . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3.0 ± 0.06 bars
318i with M10/B18 engine . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2.5 to 3.0 bars
318i with M40/B18 engine . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3.0 ± 0.06 bars
320i with M20/B20 engine (L-Jetronic) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2.5 to 3.0 bars
320i with M20/B20 engine (Motronic) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2.5 ± 0.05 bars
325i with M20/B25 engine . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3.0 ± 0.05 bars
5-Series (E28/”old-shape”)
All models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2.5 to 3.0 bars
5-Series (E34/”new-shape”)
518i with M40/B18 engine . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3.0 ± 0.06 bars
All other models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2.5 to 3.0 bars
Fuel system hold pressure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2.1 bars
Fuel pump maximum pressure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6.3 to 6.9 bars
Fuel pump hold pressure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5.5 bars
Transfer pump pressure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.28 to 0.35 bars
Injectors
Injector resistance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14.5 to 17.5 ohms
Accelerator cable free play . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1.0 mm
Torque wrench settingsNm
Carburettor mountings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Fuel pump to cylinder head . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Throttle body nuts/bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19 to 26
4•2 Fuel and exhaust systems
1 General information
With the exception of early models (316 and
518 models) all engines are equipped with
electronic fuel injection.
Early 316 and 518 models are equipped
with Solex carburettors. The carburettor fitted
is either a Solex 2B4 (early models) or
2BE (later models). The mechanical fuel pumpis driven by an eccentric lobe on the
camshaft.
Fuel injection models are equipped with
either the L-Jetronic or the Motronic fuel
injection system. From 1988, fuel injection
models are equipped with an updated version
of the Motronic system - this system is easily
distinguished from the earlier system by the
absence of a cold start injector. The electric
fuel pump is located beneath the rear of the
vehicle, or inside the fuel tank. The fuel pump
relay on Motronic systems is activated from aearth signal from the Motronic control unit
(ECU). The fuel pump operates for a few
seconds when the ignition is first switched on,
and it continues to operate only when the
engine is actually running.Air intake system
The air intake system consists of the air
filter housing, the airflow meter and throttle
body (fuel injection models), and the intake
manifold. All components except the intake
manifold are covered in this Chapter; for
Page 91 of 228

information on removing and refitting the
intake manifold, refer to Chapter 2A.
The throttle valve inside the throttle body or
carburettor is actuated by the accelerator
cable. When you depress the accelerator
pedal, the throttle plate opens and airflow
through the intake system increases.
On fuel injection systems, a flap inside the
airflow meter opens wider as the airflow
increases. A throttle position switch attached
to the pivot shaft of the flap detects the angle
of the flap (how much it’s open) and converts
this to a voltage signal, which it sends to the
computer.
Fuel system
On carburettor models, the fuel pump
supplies fuel under pressure to the
carburettor. A needle valve in the float
chamber maintains the fuel at a constant
level. A fuel return system channels excess
fuel back to the fuel tank.
On fuel injection models, an electric fuel
pump supplies fuel under constant pressure
to the fuel rail, which distributes fuel to the
injectors. The electric fuel pump is located
inside the fuel tank on later models, or beside
the fuel tank on early models. Early models
also have a transfer pump located in the fuel
tank. The transfer pump acts as an aid to the
larger main pump for delivering the necessary
pressure. A fuel pressure regulator controls
the pressure in the fuel system. The fuel
system also has a fuel pulsation damper
located near the fuel filter. The damper
reduces the pressure pulsations caused by
fuel pump operation, and the opening and
closing of the injectors. The amount of fuel
injected into the intake ports is precisely
controlled by an Electronic Control Unit (ECU
or computer). Some later 5-Series models
have a fuel cooler in the return line.
Electronic control system (fuel
injection system)
Besides altering the injector opening
duration as described above, the electronic
control unit performs a number of other tasks
related to fuel and emissions control. It
accomplishes these tasks by using data
relayed to it by a wide array of information
sensors located throughout the enginecompartment, comparing this information to
its stored map, and altering engine operation
by controlling a number of different actuators.
Since special equipment is required, most
fault diagnosis and repair of the electronic
control system is beyond the scope of the
home mechanic. Additional information and
testing procedures for the emissions system
components (oxygen sensor, coolant
temperature sensor, EVAP system, etc.) is
contained in Chapter 6.
2 Fuel injection system-
depressurising
1
Warning: Fuel is extremely
flammable, so take extra
precautions when you work on
any part of the fuel system. Don’t
smoke or allow open flames or bare light
bulbs near the work area. Also, don’t work
in a garage where a natural gas-type
appliance with a pilot light is present.
1Remove the fuel pump fuse from the main
fuse panel (see illustrations). Note:Consult
your owner’s handbook for the exact location
of the fuel pump fuse, if the information is not
stamped onto the fusebox cover.
2Start the engine, and wait for it to stall.
Switch off the ignition.
3Remove the fuel filler cap to relieve the fuel
tank pressure.
4The fuel system is now depressurised.
Note:Place a rag around fuel lines before
disconnecting, to prevent any residual fuel
from spilling onto the engine(see
illustration).
5Disconnect the battery negative cable
before working on any part of the system.
Caution: If the radio in your
vehicle is equipped with an anti-
theft system, make sure you
have the correct activation code
before disconnecting the battery. Refer to
the information on page 0-7 at the front of
this manual before detaching the cable.
Note: If, after connecting the battery, the
wrong language appears on the instrument
panel display, refer to page 0-7 for the
language resetting procedure.
3 Fuel pump/fuel pressure-
check
3
Warning: Fuel is extremely
flammable, so take extra
precautions when you work on
any part of the fuel system. Don’t
smoke, or allow open flames or bare light
bulbs, near the work area. Also, don’t work
in a garage where a natural gas-type
appliance with a pilot light is present.
Carburettor engines
1To test the fuel pump, it will be necessary to
connect a suitable pressure gauge between
the fuel pump outlet, and the carburettor
supply pipe. For this particular test, the fuel
return valve, which is normally connected in
the fuel line from the fuel pump to the
carburettor, mustbe bypassed.
2With the engine running at idle speed, the
pump pressure should be between 0.1 and
0.3 bars.
3Should a pressure gauge not be available, a
simpler (but less accurate) method of testing
the fuel pump is as follows.
4Disconnect the outlet hose from the fuel
pump.
5Disconnect the LT lead from the coil, to
prevent the engine firing, then turn the engine
over on the starter. Well-defined spurts of fuel
should be ejected from the outlet hose.
Fuel injection engines
Note 1:The electric fuel pump is located
inside the fuel tank on later models, or beside
the fuel tank on early models. Early models are
also equipped with a transfer pump located in
the fuel tank. The transfer pump feeds the
main pump, but can’t generate the high
pressure required by the system.
Note 2:The fuel pump relay on Motronic
systems is activated by an earth signal from
the Motronic control unit (ECU). The fuel
pump operates for a few seconds when the
ignition is first switched on, and then
continues to operate only when the engine is
actually running.
Fuel and exhaust systems 4•3
2.4 Be sure to place a rag under and
around any fuel line when disconnecting2.1b Removing the fuel pump fuse on
5-Series models2.1a Removing the fuel pump fuse on
3-Series models
4
Page 93 of 228
19Depressurise the fuel system (see Sec-
tion 2).
20Detach the battery negative cable.
Caution: If the radio in your
vehicle is equipped with an anti-
theft system, make sure you
have the correct activation code
before disconnecting the battery. Refer to
the information on page 0-7 at the front of
this manual before detaching the cable.
Note: If, after connecting the battery, the
wrong language appears on the instrument
panel display, refer to page 0-7 for the
language resetting procedure.
21Detach the fuel feed hose from the fuel
rail, and attach a fuel pressure gauge directly
to the hose. Note:If the tee fitting is still
connected to the gauge, be sure to plug the
open end.
22Reconnect the battery.
23Using a jumper wire, bridge the terminals
of the fuel pump relay.
24Turn the ignition switch on to operate the
fuel pump.
25Note the pressure reading on the gauge,
and compare the reading to the fuel pump
pressure listed in this Chapter’s Specifica-
tions.
26If the indicated pressure is less than
specified, inspect the fuel line for leaks
between the pump and gauge. If no leaks are
found, renew the fuel pump.
27Turn the ignition off and wait five minutes.
Note the reading on the gauge, and compare
it to the fuel pump hold pressure listed in this
Chapter’s Specifications. If the hold pressure
is less than specified, check the fuel lines
between the pump and gauge for leaks. If no
leaks are found, renew the fuel pump.
28Remove the jumper wire. Relieve the fuel
pressure by opening the bleed valve on the
gauge and directing the fuel into a suitable
container. Remove the gauge and reconnect
the fuel line.
Transfer pump pressure check
29Depressurise the fuel system (see Sec-
tion 2).
30Detach the battery negative cable.
Caution: If the radio in your
vehicle is equipped with an anti-
theft system, make sure you
have the correct activation code
before disconnecting the battery. Refer to
the information on page 0-7 at the front of
this manual before detaching the cable.
Note: If, after connecting the battery, the
wrong language appears on the instrument
panel display, refer to page 0-7 for the
language resetting procedure.
31Remove the transfer pump access plate
(on some models, it’s located under the rear
seat cushion - on others, it’s located under
the carpet in the luggage compartment).
Disconnect the output hose from the transfer
pump, and connect a fuel pressure gauge to
the outlet pipe.
32Reconnect the battery.33Using a jumper wire, bridge the terminals
of the fuel pump relay.
34Turn the ignition switch on to operate the
fuel pump.
35Note the pressure reading on the gauge,
and compare to the value listed in this
Chapter’s Specifications.
36If the indicated pressure is less than
specified, renew the transfer pump.
Fuel pump relay check
37Switch on the ignition.
38Using a voltmeter, probe the following
terminals from the back of the relay electrical
connector. Check for battery voltage at
terminal 30 (M20 and M30 engines) or
terminal 15 (M10 and M40 engines). Note:If
there is no voltage on models with luggage
compartment-mounted batteries, check for a
faulty fusible link. The 50-amp link is about
6 inches from the battery, in a black wire.
39Turn the ignition off, and disconnect the
relay from the electrical connector. Using a
voltmeter, probe the connector terminals that
correspond to fuel pump relay pins 85 (-) and
86(+) on M20 and M30 engines, or terminal 50
and earth on M10 and M40 engines. Have an
assistant turn the engine over on the starter,
and observe the voltage reading. Battery
voltage should be indicated.
40If there is no voltage, check the fuse(s)
and the wiring circuit for the fuel pump relay. If
the voltage readings are correct, and the fuel
pump only runs with the jumper wire in place,
then renew the relay.
41If the fuel pump still does not run, check
for the proper voltage at the fuel pump
terminals (see Section 4). If necessary, renew
the fuel pump.
4 Fuel pump, transfer pump
and fuel level sender unit-
removal and refitting
2
Warning: Fuel is extremely
flammable, so take extra
precautions when you work on
any part of the fuel system. Don’t
smoke, or allow open flames or bare light
bulbs, near the work area. Also, don’t work
in a garage where a natural gas-type
appliance with a pilot light is present.
Fuel pump (carburettor engines)
1Disconnect the battery negative cable.
Disconnect both hoses from the pump, and
unscrew and remove the two securing nuts
(see illustration).
2Carefully withdraw the pump from the
cylinder head. If it’s stuck, a slight downward
tap on the thick insulating distance piece with
a piece of wood, should free it.
3Remove the two thin gaskets.
4The fuel pump is a sealed unit, and it is not
possible to renew any of the internal
components. Should an internal fault occur, it
must be renewed complete.5Refitting is a reversal of the removal
procedure, but renew the thin gaskets each
side of the insulating distance piece, and
tighten the fuel pump down evenly to the
torque stated in the Specifications. On no
account alter the thickness of the distance
piece, or the correct operation of the fuel
pump will be upset.
Fuel pump (fuel injection
engines)
Note 1: The electric fuel pump is located
inside the fuel tank on later models with the
Motronic system, or adjacent to the fuel tank
on the L-Jetronic system. The early models
are also equipped with a transfer pump
located in the fuel tank. The transfer pump
feeds the larger main pump, which delivers
the high pressure required for proper fuel
system operation.
Note 2: The fuel level sender unit is located in
the fuel tank with the transfer pump on early
models, or with the main fuel pump on later
models.
6Depressurise the fuel system (see Sec-
tion 2) and remove the fuel tank filler cap to
relieve pressure in the tank.
7Disconnect the battery negative cable.
Caution: If the radio in your
vehicle is equipped with an anti-
theft system, make sure you
have the correct activation code
before disconnecting the battery. Refer to
the information on page 0-7 at the front of
this manual before detaching the cable.
Note: If, after connecting the battery, the
wrong language appears on the instrument
panel display, refer to page 0-7 for the
language resetting procedure.
Externally-mounted fuel pump
8Raise and support the vehicle.
9Remove the two rubber boots that protect
the fuel pump connectors, and disconnect the
wires from the pump (see illustration).
10Using hose clamps, pinch shut the fuel
hoses on each side of the fuel pump. If you
don’t have any hose clamps, wrap the hoses
with rags, and clamp them shut with self-
locking pliers, tightened just enough to
prevent fuel from flowing out.
11Disconnect the hoses from the pump.
12Remove the fuel pump mounting screws
Fuel and exhaust systems 4•5
4.1 Fuel pump on carburettor engines
4
Page 95 of 228
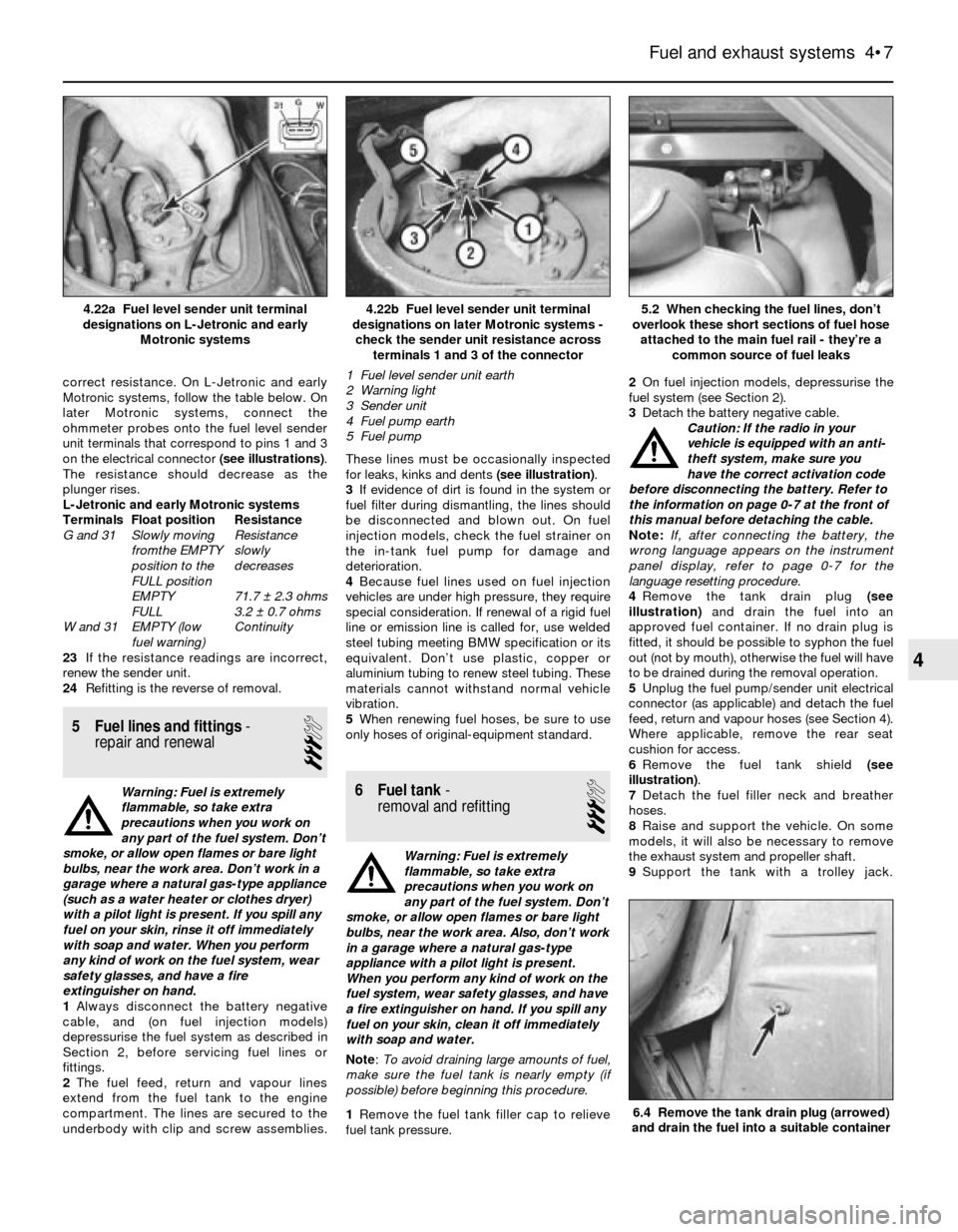
correct resistance. On L-Jetronic and early
Motronic systems, follow the table below. On
later Motronic systems, connect the
ohmmeter probes onto the fuel level sender
unit terminals that correspond to pins 1 and 3
on the electrical connector (see illustrations).
The resistance should decrease as the
plunger rises.
L-Jetronic and early Motronic systems
Terminals Float position Resistance
G and 31 Slowly moving Resistance
fromthe EMPTY slowly
position to the decreases
FULL position
EMPTY 71.7 ± 2.3 ohms
FULL 3.2 ± 0.7 ohms
W and 31 EMPTY (low Continuity
fuel warning)
23If the resistance readings are incorrect,
renew the sender unit.
24Refitting is the reverse of removal.
5 Fuel lines and fittings-
repair and renewal
3
Warning: Fuel is extremely
flammable, so take extra
precautions when you work on
any part of the fuel system. Don’t
smoke, or allow open flames or bare light
bulbs, near the work area. Don’t work in a
garage where a natural gas-type appliance
(such as a water heater or clothes dryer)
with a pilot light is present. If you spill any
fuel on your skin, rinse it off immediately
with soap and water. When you perform
any kind of work on the fuel system, wear
safety glasses, and have a fire
extinguisher on hand.
1Always disconnect the battery negative
cable, and (on fuel injection models)
depressurise the fuel system as described in
Section 2, before servicing fuel lines or
fittings.
2The fuel feed, return and vapour lines
extend from the fuel tank to the engine
compartment. The lines are secured to the
underbody with clip and screw assemblies.These lines must be occasionally inspected
for leaks, kinks and dents (see illustration).
3If evidence of dirt is found in the system or
fuel filter during dismantling, the lines should
be disconnected and blown out. On fuel
injection models, check the fuel strainer on
the in-tank fuel pump for damage and
deterioration.
4Because fuel lines used on fuel injection
vehicles are under high pressure, they require
special consideration. If renewal of a rigid fuel
line or emission line is called for, use welded
steel tubing meeting BMW specification or its
equivalent. Don’t use plastic, copper or
aluminium tubing to renew steel tubing. These
materials cannot withstand normal vehicle
vibration.
5When renewing fuel hoses, be sure to use
only hoses of original-equipment standard.6 Fuel tank-
removal and refitting
3
Warning: Fuel is extremely
flammable, so take extra
precautions when you work on
any part of the fuel system. Don’t
smoke, or allow open flames or bare light
bulbs, near the work area. Also, don’t work
in a garage where a natural gas-type
appliance with a pilot light is present.
When you perform any kind of work on the
fuel system, wear safety glasses, and have
a fire extinguisher on hand. If you spill any
fuel on your skin, clean it off immediately
with soap and water.
Note: To avoid draining large amounts of fuel,
make sure the fuel tank is nearly empty (if
possible) before beginning this procedure.
1Remove the fuel tank filler cap to relieve
fuel tank pressure.2On fuel injection models, depressurise the
fuel system (see Section 2).
3Detach the battery negative cable.
Caution: If the radio in your
vehicle is equipped with an anti-
theft system, make sure you
have the correct activation code
before disconnecting the battery. Refer to
the information on page 0-7 at the front of
this manual before detaching the cable.
Note: If, after connecting the battery, the
wrong language appears on the instrument
panel display, refer to page 0-7 for the
language resetting procedure.
4Remove the tank drain plug (see
illustration)and drain the fuel into an
approved fuel container. If no drain plug is
fitted, it should be possible to syphon the fuel
out (not by mouth), otherwise the fuel will have
to be drained during the removal operation.
5Unplug the fuel pump/sender unit electrical
connector (as applicable) and detach the fuel
feed, return and vapour hoses (see Section 4).
Where applicable, remove the rear seat
cushion for access.
6Remove the fuel tank shield (see
illustration).
7Detach the fuel filler neck and breather
hoses.
8Raise and support the vehicle. On some
models, it will also be necessary to remove
the exhaust system and propeller shaft.
9Support the tank with a trolley jack.
Fuel and exhaust systems 4•7
4.22b Fuel level sender unit terminal
designations on later Motronic systems -
check the sender unit resistance across
terminals 1 and 3 of the connector
1 Fuel level sender unit earth
2 Warning light
3 Sender unit
4 Fuel pump earth
5 Fuel pump4.22a Fuel level sender unit terminal
designations on L-Jetronic and early
Motronic systems
6.4 Remove the tank drain plug (arrowed)
and drain the fuel into a suitable container
5.2 When checking the fuel lines, don’t
overlook these short sections of fuel hose
attached to the main fuel rail - they’re a
common source of fuel leaks
4
Page 97 of 228

6Unscrew the four nuts retaining the air
cleaner to the carburettor, and remove the
metal ring (see illustrations).
7Unscrew the nut from the mounting bracket
(see illustration).
8Lift the air cleaner from the carburettor, and
disconnect the crankcase ventilation hose
(see illustration). If necessary, prise the
sealing ring from the bottom of the air cleaner.
9Refitting is a reversal of removal, but align
the arrow on the cover with the arrow on the
inlet tube (see illustration).
Fuel injection engines
10Detach the air intake duct from the front
side of the air cleaner.11Detach the duct between the air cleaner
and the throttle body.
12Remove the air filter (see Chapter 1).
13Unplug the electrical connector from the
airflow meter (see Section 12).
14Remove the air cleaner mounting bolts
(see illustration)and lift the air cleaner
assembly from the engine compartment.
15Refitting is the reverse of removal. Ensure
that all ducts are securely refitted, or air leaks
will result.
9 Accelerator cable- check,
adjustment and renewal
1
Check
1Separate the air intake duct from the
throttle body (fuel injection models) or remove
the air cleaner (carburettor models).
2Have an assistant depress the accelerator
pedal to the floor while you watch the throttle
valve. It should move to the fully-open
position.
3Release the accelerator pedal, and make
sure the throttle valve returns smoothly to the
fully-closed position. The throttle valve should
not contact the body at any time during its
movement; if it does, the unit must be renewed.
Adjustment
4Warm the engine to normal operating
temperature, then switch it off. Depress theaccelerator pedal to the floor twice, then
check the cable free play at the
carburettor/throttle body. Compare it to the
value listed in this Chapter’s Specifications.
5If the free play isn’t as specified, adjust it by
turning the adjustment nut (see illustration).
6Have an assistant help you verify the
throttle valve is fully open when the
accelerator pedal is depressed to the floor.
Renewal
Note:The following paragraphs describe the
procedure for fuel injection engines - the
procedure is similar on carburettor engines
7Disconnect the battery negative cable.
Fuel and exhaust systems 4•9
8.6b . . . and remove the metal ring8.6a Unscrew the four air cleaner-to-
carburettor nuts . . .8.4 Air cleaner inlet duct (1) and warm-air
hose (2)
9.5 To adjust the accelerator cable free
play, hold nut B stationary and turn nut A
(fuel injection engine shown)8.14 Remove the two nuts (arrowed) from
the air cleaner assembly (Motronic system
shown), and lift it off its mountings
8.8 Disconnecting the crankcase
ventilation hose from the air cleaner8.7 Air cleaner mounting bracket nut
(arrowed)8.9 Align the air cleaner cover arrows
when refitting
4
Page 102 of 228

Throttle positioner (2BE)
24Special tools are required to carry out a
comprehensive adjustment on the 2BE
carburettor. This work should therefore be left
to a BMW dealer.
13 Fuel injection -
general information
The fuel injection system is composed of
three basic sub-systems: fuel system, air
intake system and electronic control system.
Fuel system
An electric fuel pump, located inside the
fuel tank or beside the fuel tank, supplies fuel
under constant pressure to the fuel rail, which
distributes fuel evenly to all injectors. From
the fuel rail, fuel is injected into the intake
ports, just above the intake valves, by the fuel
injectors. The amount of fuel supplied by the
injectors is precisely controlled by an
Electronic Control Unit (ECU). An additional
injector, known as the cold start injector (L-
Jetronic and early Motronic systems only),
supplies extra fuel into the intake manifold for
starting. A pressure regulator controls system
pressure in relation to intake manifold
vacuum. A fuel filter between the fuel pump
and the fuel rail filters the fuel, to protect the
components of the system.
Air intake system
The air intake system consists of an air filter
housing, an airflow meter, a throttle body, the
intake manifold, and the associated ducting.
The airflow meter is an information-gathering
device for the ECU. These models are
equipped with the vane-type airflow meter. A
potentiometer measures intake airflow, and a
temperature sensor measures intake air
temperature. This information helps the ECU
determine the amount of fuel to be injected by
the injectors (injection duration). The throttle
plate inside the throttle body is controlled by
the driver. As the throttle plate opens, the
amount of air that can pass through the
system increases, so the potentiometer opens
further and the ECU signals the injectors to
increase the amount of fuel delivered to the
intake ports.
Electronic control system
The computer control system controls the
fuel system and other systems by means of
an Electronic Control Unit (ECU). The ECU
receives signals from a number of information
sensors which monitor such variables as
intake air volume, intake air temperature,
coolant temperature, engine rpm,
acceleration/deceleration, and exhaust
oxygen content. These signals help the ECU
determine the injection duration necessary for
the optimum air/fuel ratio. These sensors and
their corresponding ECU-controlled outputactuators are located throughout the engine
compartment. For further information
regarding the ECU and its relationship to the
engine electrical systems and ignition system,
refer to Chapters 5 and 6.
Either an L-Jetronic system or a Motronic
system is fitted. Later models have an
updated version of the original Motronic
system.
14 Fuel injection systems
L-Jetronic fuel injection system
The Bosch L-Jetronic fuel injection system
is used on most 3-Series models up to 1987,
and on most E28 (“old-shape”) 5-Series
models. It is an electronically-controlled fuel
injection system that utilises one solenoid-
operated fuel injector per cylinder. The system
is governed by an Electronic Control Unit
(ECU) which processes information sent by
various sensors, and in turn precisely
meters the fuel to the cylinders by
adjusting the amount of time that the injectors
are open.
An electric fuel pump delivers fuel under
high pressure to the injectors, through the fuel
feed line and an in-line filter. A pressure
regulator keeps fuel available at an optimum
pressure, allowing pressure to rise or fall
depending on engine speed and load. Any
excess fuel is returned to the fuel tank by a
separate line.
A sensor in the air intake duct constantly
measures the mass of the incoming air, and
the ECU adjusts the fuel mixture to provide an
optimum air/fuel ratio.
Other components incorporated in the
system are the throttle valve (which controls
airflow to the engine), the coolant temperature
sensor, the throttle position switch, idle
stabiliser valve (which bypasses air around
the throttle plate to control idle speed) and
associated relays and fuses.
Motronic fuel injection system
The Motronic system combines the fuel
control of the L-Jetronic fuel injection system
with the control of ignition timing, idle speed
and emissions into one control unit.
The fuel injection and idle speed control
functions are similar to those used on the L-
Jetronic system described above. For more
information on the Motronic system, see
Chapter 6.
An oxygen sensor is mounted in the
exhaust system on later models with a
catalytic converter. This sensor continually
reads the oxygen content of the exhaust gas.
The information is used by the ECU to adjust
the duration of injection, making it possible to
adjust the fuel mixture for optimum converter
efficiency and minimum emissions.
15 Fuel injection system-
check
2
Warning: Fuel is extremely
flammable, so take extra
precautions when you work on
any part of the fuel system. Don’t
smoke, or allow open flames or bare light
bulbs, near the work area. Don’t work in a
garage where a natural gas-type appliance
(such as a water heater or clothes dryer)
with a pilot light is present. If you spill any
fuel on your skin, rinse it off immediately
with soap and water. When you perform
any kind of work on the fuel system, wear
safety glasses, and have a fire
extinguisher on hand.
1Check the earth wire connections. Check
all wiring harness connectors that are related
to the system. Loose connectors and poor
earths can cause many problems that
resemble more serious malfunctions.
2Make sure the battery is fully charged, as
the control unit and sensors depend on an
accurate supply voltage in order to properly
meter the fuel.
3Check the air filter element - a dirty or
partially-blocked filter will severely impede
performance and economy (see Chapter 1).
4If a blown fuse is found, renew it and see if
it blows again. If it does, search for an earthed
wire in the harness related to the system.
5Check the air intake duct from the airflow
meter to the intake manifold for leaks. Intake
air leaks can cause a variety of problems. Also
check the condition of the vacuum hoses
connected to the intake manifold.
6Remove the air intake duct from the throttle
body, and check for dirt, carbon and other
residue build-up. If it’s dirty, clean it with
carburettor cleaner and a toothbrush.
7With the engine running, place a
screwdriver or a stethoscope against each
injector, one at a time, and listen for a clicking
sound, indicating operation (see illustration).
4•14 Fuel and exhaust systems
15.7 Use a stethoscope or screwdriver to
determine if the injectors are working
properly - they should make a steady
clicking sound that rises and falls with
engine speed changes
Page 106 of 228

6If the voltage is correct, unplug the
electrical connector and, using an ohmmeter,
check for continuity between the terminals of
the thermotime switch (see illustration).
Continuity should exist.
7Reconnect the coil lead, start the engine
and warm it up above 41ºC. When the engine
is warm, there should be no continuity
between the terminals. If there is, the switch is
faulty and must be renewed. Note: On 5-
Series models, there are several types of
thermotime switch. Each one is stamped with
an opening temperature and maximum
duration.
Renewal
Cold start injector
8Depressurise the fuel system (see Sec-
tion 2).
9Disconnect the electrical connector from
the cold start injector.
10Where applicable, using a ring spanner or
deep socket, remove the fuel line fitting
connected to the cold start injector. On other
models, simply loosen the hose clamp and
detach the hose from the injector.
11Remove the cold start injector securing
bolts, and remove the injector.
12Refitting is the reverse of removal. Clean
the mating surfaces, and use a new gasket.
Thermotime switch
Warning: Wait until the engine is
completely cool before beginning
this procedure. Also, remove the
cap from the expansion tank or
radiator to relieve any residual pressure in
the cooling system.
13Prepare the new thermotime switch for
fitting by applying a light coat of thread
sealant to the threads.
14Disconnect the electrical connector from
the old thermotime switch.
15Using a deep socket, or a ring spanner,
unscrew the switch. Once the switch is
removed coolant will start to leak out, so
insert the new switch as quickly as possible.
Tighten the switch securely, and plug in the
electrical connector.
20 Fuel injectors-
check and renewal
2
Warning: Fuel is extremely
flammable, so take extra
precautions when you work on
any part of the fuel system. Don’t
smoke, or allow open flames or bare light
bulbs, near the work area. Don’t work in a
garage where a natural gas-type appliance
(such as a water heater or clothes dryer)
with a pilot light is present. If you spill any
fuel on your skin, rinse it off immediately
with soap and water. When you perform
any kind of work on the fuel system, wear
safety glasses, and have a fire
extinguisher on hand.
Check
In-vehicle check
1Using a mechanic’s stethoscope (available
at most car accessory shops), check for a
clicking sound at each of the injectors while
the engine is idling (see illustration 15.7).
2The injectors should make a steady clicking
sound if they are operating properly.
3Increase the engine speed above 3500 rpm.
The frequency of the clicking sound should
rise with engine speed.
4If an injector isn’t functioning (not clicking),
purchase a special injector test light (a car
accessory shop or fuel injection specialist
may be able to help) and connect it to the
injector electrical connector. Start the engine
and make sure the light flashes. If it does, the
injector is receiving the proper voltage, so the
injector itself must be faulty.
5Unplug each injector connector, and checkthe resistance of the injector (see
illustration). Check your readings with the
values listed in this Chapter’s Specifications.
Renew any that do not give the correct
resistance reading.
Volume test
6Because a special injection checker is
required to test injector volume, this
procedure is beyond the scope of the home
mechanic. Have the injector volume test
performed by a BMW dealer or other
specialist.
Renewal
7Unplug the main electrical connector for the
fuel injector wiring harness. Remove the
intake manifold (see Chapter 2A).
8Detach the fuel hoses from the fuel rail, and
remove the fuel rail mounting bolts (see
illustration).
9Lift the fuel rail/injector assembly from the
intake manifold.
10Unplug the electrical connectors from the
fuel injectors. Detach the injectors from the
fuel rail.
11Refitting is the reverse of removal. Be sure
to renew all O-rings. Coat the O-rings with a
light film of engine oil to prevent damage
during refitting. Pressurise the fuel system
(refit the fuel pump fuse and switch on the
ignition) and check for leaks before starting
the engine.
21 Idle air stabiliser valve-
check, adjustment and
renewal
4
1The idle air stabiliser system works to
maintain engine idle speed within a 200 rpm
range, regardless of varying engine loads at
idle. An electrically-operated valve allows a
small amount of air to bypass the throttle
plate, to raise the idle speed whenever the idle
speed drops below approximately 750 rpm. If
the idle speed rises above approximately
950 rpm, the idle air stabiliser valve closes
and stops extra air from bypassing the throttle
plate, reducing the idle speed.
4•18 Fuel and exhaust systems
20.8 Remove the bolts (arrowed) and
separate the fuel rail and injectors from
the intake manifold20.5 Check the resistance of each of the
fuel injectors19.6 Check the resistance of the
thermotime switch with the engine coolant
temperature below 30º C. There should be
continuity
If you don’t have a
mechanic’s stethoscope, a
screwdriver can be used to
check for a clicking sound at
the injectors. Place the tip of the
screwdriver against the injector, and
press your ear against the handle.
Page 109 of 228

Fuel injection system - fault finding
L-Jetronic fuel injection system
Engine difficult to start, or fails to start (when cold)
Probable cause Corrective action
Cold start injector or thermotime switch faulty Test cold start injector and thermotime switch. Renew faulty components (see Section 19)
Fuel pump inoperative Check fuel pump fuse and fuel pump relay (see Sections 3 and 4)
Airflow meter flap (door) binding or stuck
in open position Inspect the airflow meter for damage (see Section 16)
Fuel pressure incorrect Test system pressure (see Section 3). Test fuel pressure regulator (Section 18)
Intake air leaks Inspect all vacuum lines, air ducts, and oil filler and dipstick seals
Fuel injectors clogged or not operating Check fuel injectors (see Section 20) and wiring harness
Coolant temperature sensor faulty or
wiring problem Test coolant temperature sensor (see Chapter 6, Section 4)
Throttle position sensor (TPS) incorrectly adjusted Check TPS adjustment (see Chapter 6, Section 4)
Incorrect ignition timing Check ignition timing (see Chapter 5). Check vacuum advance system
Dirt or other contaminants in fuel Check the fuel and drain the tank if necessary
Faulty ECU Have the ECU tested at a dealer service department or other specialist
Engine difficult to start, or fails to start (when warm)
Probable cause Corrective action
Cold start injector leaking or operating continuously Test cold start injector and thermotime switch (see Section 19)
Fuel pressure incorrect Test fuel pump(s). Renew if necessary (see Section 3)
Insufficient residual fuel pressure Test residual fuel pressure. Renew fuel pump or fuel accumulator as necessary
(see Section 18)
Fuel leak(s) Inspect fuel lines and fuel injectors for leaks. Correct leaks as required (see Chapter 4)
Coolant temperature sensor faulty or
wiring problem Test coolant temperature sensor (see Chapter 6, Section 4)
Vapour lock (warm weather) Check fuel pressure (see Section 3)
EVAP system faulty (where applicable) Check EVAP system (see Chapter 6, Section 6)
Incorrect ignition timing Check ignition timing (see Chapter 5). Check vacuum advance system
Faulty ECU Have the ECU tested at a dealer service department or other specialist
Idle speed control system faulty Test the idle air stabiliser valve (see Section 21)
Engine misses and hesitates under load
Probable cause Corrective action
Fuel injector clogged or faulty Test fuel injectors. Check for clogged injector lines. Renew faulty injectors (see Section 20)
Fuel pressure incorrect Test fuel system pressure (see Section 3). Test fuel pressure regulator (see Section 18)
Fuel leak(s) Inspect fuel lines and fuel injectors for leaks (see Chapter 4)
Engine maintenance Tune-up engine (see Chapter 1). Check the distributor cap, rotor, HT leads and spark
plugs, and renew any faulty components
Airflow meter flap (door) binding, or
stuck in open position Inspect the airflow meter for damage (see Section 16)
Intake air leaks Inspect all vacuum lines, air ducts and oil filler and dipstick seals
Engine has erratic idle speed
Probable cause Corrective action
Idle air stabiliser valve faulty Check the idle air stabiliser valve (see Section 21)
No power to the idle air stabiliser valve Check the idle air stabiliser relay and wiring circuit (see Chapter 12)
Vacuum advance system faulty Check vacuum advance system and electronic vacuum advance relay
Idle speed control unit faulty Have the idle speed control unit checked by a dealer
Motronic fuel injection system
Note:With this system, when faults occur, the ECU stores a fault code in its memory. These codes can only be read by a BMW dealer, as
specialised equipment is required. It may save time to have at least the initial fault diagnosis carried out by a dealer.
Lack of power
Probable cause Corrective action
Coolant temperature sensor faulty, Test coolant temperature sensor and wiring. Repair wiring or renew sensor if
or wire to sensor broken faulty (see Chapter 6)
Fuel pressure incorrect Check fuel pressure from main pump and transfer pump, as applicable (see Section 3)
Throttle plate not opening fully Check accelerator cable adjustment to make sure throttle is opening fully. Adjust cable if
necessary (see Section 9)
Fuel and exhaust systems 4•21
4