Tools BMW 3 SERIES 1988 E30 Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: BMW, Model Year: 1988, Model line: 3 SERIES, Model: BMW 3 SERIES 1988 E30Pages: 228, PDF Size: 7.04 MB
Page 128 of 228
On some models, it will be necessary to
release the retaining clip (see illustration).
13Visually examine the canister for leakage
or damage.
14Renew the canister if you find evidence of
damage or leakage.
7 Catalytic converter
1
General description
1To reduce emissions of unburnt
hydrocarbons (HC), carbon monoxide (CO)
and oxides of nitrogen (NOx), the later
vehicles covered by this manual are equipped
with a catalytic converter (see illustration).
The converter contains a ceramic honeycomb
coated with precious metals, which speed up
the reaction between the pollutants listed
previously and the oxygen in the exhaust gas.
The pollutants are oxidised to produce water
(H
2O), nitrogen and carbon dioxide (CO2).
Check
2Visually examine the converter(s) for cracks
or damage. Make sure all nuts and bolts are
tight.
3Inspect the insulation cover (if applicable)
welded onto the converter - it should not be
loose.
Caution: If an insulation cover is
dented so that it touches the
converter housing inside,
excessive heat may be
transferred to the floor.
4Start the engine and run it at idle speed.
5Check for exhaust gas leakage from the
converter flanges. Check the body of each
converter for holes.
Component renewal
6See Chapter 4 for removal and refitting
procedures.
Precautions
7The catalytic converter is a reliable and
simple device, which needs no maintenance
in itself, but there are some facts of which an
owner should be aware, if the converter is to
function properly for its full service life.
(a) DO NOT use leaded (eg UK “4-star”)
petrol in a car equipped with a catalytic
converter - the lead will coat the precious
metals, reducing their converting
efficiency, and will eventually destroy the
converter.
(b) Always keep the ignition and fuel systems
well-maintained in accordance with the
manufacturer’s schedule, as given in
Chapter 1. In particular, ensure that the air
cleaner filter element, the fuel filter (where
fitted) and the spark plugs are renewed at
the correct interval. If the intake air/fuel
mixture is allowed to become too rich due
to neglect, unburned fuel will enter the
catalytic converter, overheating the
element and eventually destroying the
converter.
(c) If the engine develops a misfire, do not
drive the car at all (or at least as little as
possible) until the fault is cured - the
misfire will allow unburned fuel to enter
the converter, which will result in its
overheating, as noted above.
(d) DO NOT push- or tow-start the car - this
will soak the catalytic converter in
unburned fuel, causing it to overheat
when the engine does start - see (b) or (c)
above.
(e) DO NOT switch off the ignition at high
engine speeds - ie do not “blip” the
throttle immediately before switching offthe engine. If the ignition is switched off
at anything above idle speed, unburned
fuel will enter the (very hot) catalytic
converter, with the possible risk of its
igniting on the element and damaging the
converter.
(f) DO NOT use fuel or engine oil additives -
these may contain substances harmful to
the catalytic converter.
(g) DO NOT continue to use the car if the
engine burns oil to the extent of leaving a
visible trail of blue smoke - the unburned
carbon deposits will clog the converter
passages, and reduce its efficiency; in
severe cases, the element will overheat.
(h) Remember that the catalytic converter
operates at very high temperatures -
hence the heat shields on the car’s
underbody - and the casing will become
hot enough to ignite combustible
materials which brush against it. DO NOT,
therefore, park the car in dry
undergrowth, or over long grass or piles
of dead leaves.
(i) Remember that the catalytic converter is
FRAGILE - do not strike it with tools
during servicing work, and take great care
when working on the exhaust system.
Ensure that the converter is well clear of
any jacks or other lifting gear used to raise
the car, and do not drive the car over
rough ground, road humps, etc, in such a
way as to “ground” the exhaust system.
(j) In some cases, particularly when the car
is new and/or is used for stop/start
driving, a sulphurous smell (like that of
rotten eggs) may be noticed from the
exhaust. This is common to many
catalytic converter-equipped cars, and
seems to be due to the small amount of
sulphur found in some petrols reacting
with hydrogen in the exhaust, to produce
hydrogen sulphide (H
2S) gas; while this
gas is toxic, it is not produced in sufficient
amounts to be a problem. Once the car
has covered a few thousand miles, the
problem should disappear - in the
meanwhile, a change of driving style, or of
the brand of petrol used, may effect a
solution.
(k) The catalytic converter, used on a well-
maintained and well-driven car, should
last for 50 000 to 100 000 miles - from
this point on, the CO level should be
carefully checked regularly, to ensure that
the converter is still operating efficiently. If
the converter is no longer effective, it
must be renewed.
6•6 Engine management and emission control systems
7.1 Typical catalytic converter (M10
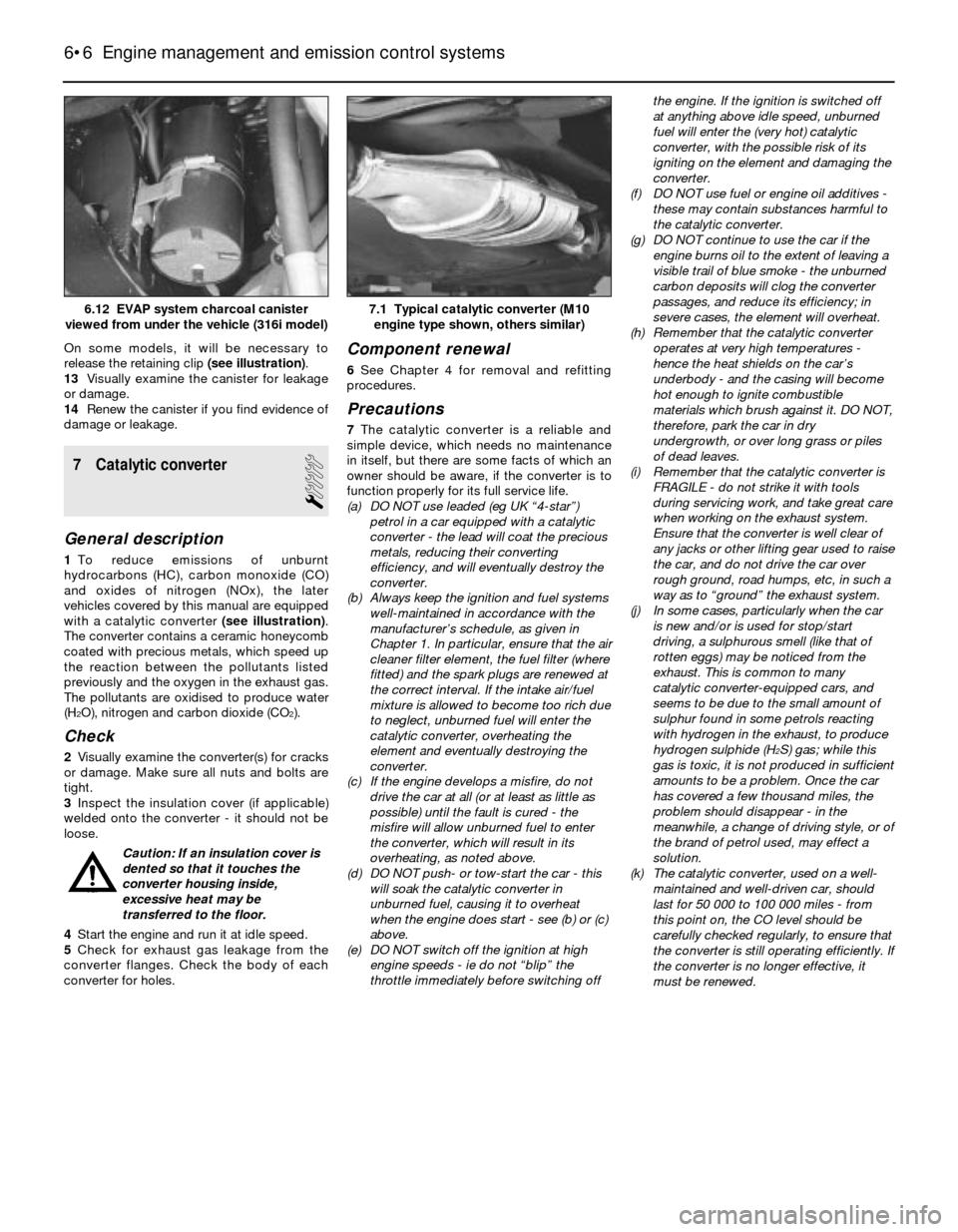
engine type shown, others similar)6.12 EVAP system charcoal canister
viewed from under the vehicle (316i model)
Page 131 of 228
and cause the system to malfunction. If
the ABS wiring harness is damaged in any
way, it must be renewed.
Caution: Make sure the ignition is
turned off before unplugging or
re-making any electrical
connections.
Diagnosis and repair
If the dashboard warning light comes on
and stays on while the vehicle is in operation,
the ABS system requires attention. Although
special electronic ABS diagnostic testing
tools are necessary to properly diagnose the
system, you can perform a few preliminary
checks before taking the vehicle to a dealer
service department.
a) Check the brake fluid level in the
reservoir.
b) Verify that the electronic control unit
connectors are securely connected.
c) Check the electrical connectors at the
hydraulic control unit.
d) Check the fuses.
e) Follow the wiring harness to each front
and rear wheel, and verify that all
connections are secure and that the
wiring is undamaged.
If the above preliminary checks do not
rectify the problem, the vehicle should bediagnosed by a dealer service department.
Due to the complex nature of this system, all
actual repair work must be done by a dealer
service department.
3 Disc brake pads- renewal
2
Warning: Disc brake pads must
be renewed on both front wheels
or both rear wheels at the same
time - NEVER renew the pads on
only one wheel. Also, the dust created by
the brake system may contain asbestos,
which is harmful to your health. Never
blow it out with compressed air, and don’t
inhale any of it. An approved filtering mask
should be worn when working on the
brakes. Do not, under any circumstances,
use petroleum-based solvents to clean
brake parts. Use brake system cleaner
only! When servicing the disc brakes, use
only original-equipment or high-quality
brand-name pads.
Warning: Brake fluid is
poisonous. It is also an effective
paint stripper. Refer to the
warning at the start of Section 16.
Note:This procedure applies to both the front
and rear disc brakes.
1Remove the cap(s) from the brake fluid
reservoir, and syphon off about two-thirds of
the fluid from the reservoir. Failing to do thiscould result in the reservoir overflowing when
the caliper pistons are pressed back into their
bores.
2Loosen the wheel bolts, raise the front or
rear of the vehicle and support it securely on
axle stands.
3Remove the front or rear wheels, as
applicable. Work on one brake assembly at a
time, using the assembled brake for reference
if necessary.
4Inspect the brake disc carefully as outlined
in Section 5. If machining is necessary, follow
the information in that Section to remove the
disc, at which time the pads can be removed
from the calipers as well.
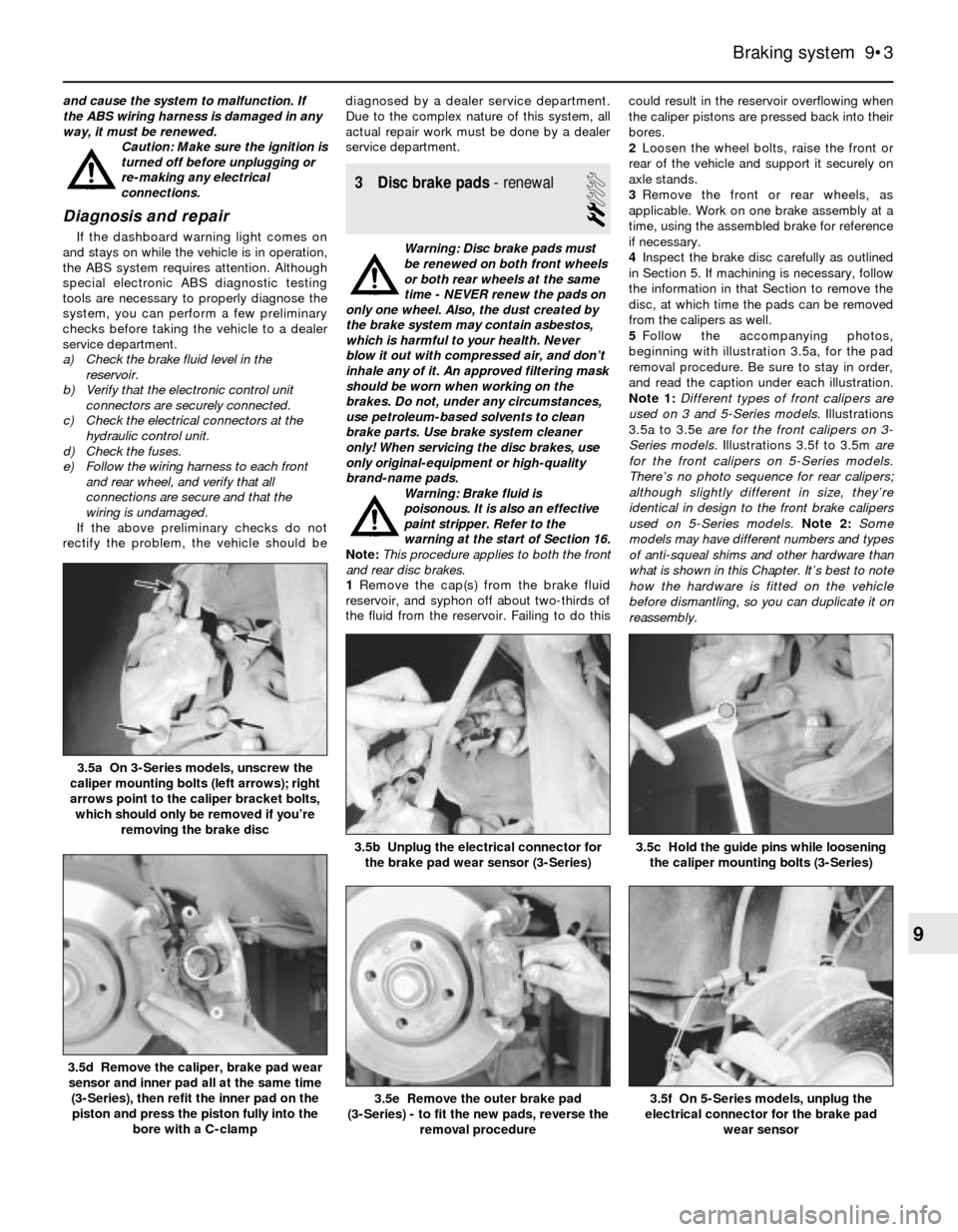
5Follow the accompanying photos,
beginning with illustration 3.5a, for the pad
removal procedure. Be sure to stay in order,
and read the caption under each illustration.
Note 1:Different types of front calipers are
used on 3 and 5-Series models. Illustrations
3.5a to 3.5e are for the front calipers on 3-
Series models.Illustrations 3.5f to 3.5m are
for the front calipers on 5-Series models.
There’s no photo sequence for rear calipers;
although slightly different in size, they’re
identical in design to the front brake calipers
used on 5-Series models.Note 2: Some
models may have different numbers and types
of anti-squeal shims and other hardware than
what is shown in this Chapter. It’s best to note
how the hardware is fitted on the vehicle
before dismantling, so you can duplicate it on
reassembly.
Braking system 9•3
3.5c Hold the guide pins while loosening
the caliper mounting bolts (3-Series)3.5b Unplug the electrical connector for
the brake pad wear sensor (3-Series)
3.5a On 3-Series models, unscrew the
caliper mounting bolts (left arrows); right
arrows point to the caliper bracket bolts,
which should only be removed if you’re
removing the brake disc
3.5f On 5-Series models, unplug the
electrical connector for the brake pad
wear sensor3.5e Remove the outer brake pad
(3-Series) - to fit the new pads, reverse the
removal procedure
3.5d Remove the caliper, brake pad wear
sensor and inner pad all at the same time
(3-Series), then refit the inner pad on the
piston and press the piston fully into the
bore with a C-clamp
9
Page 133 of 228
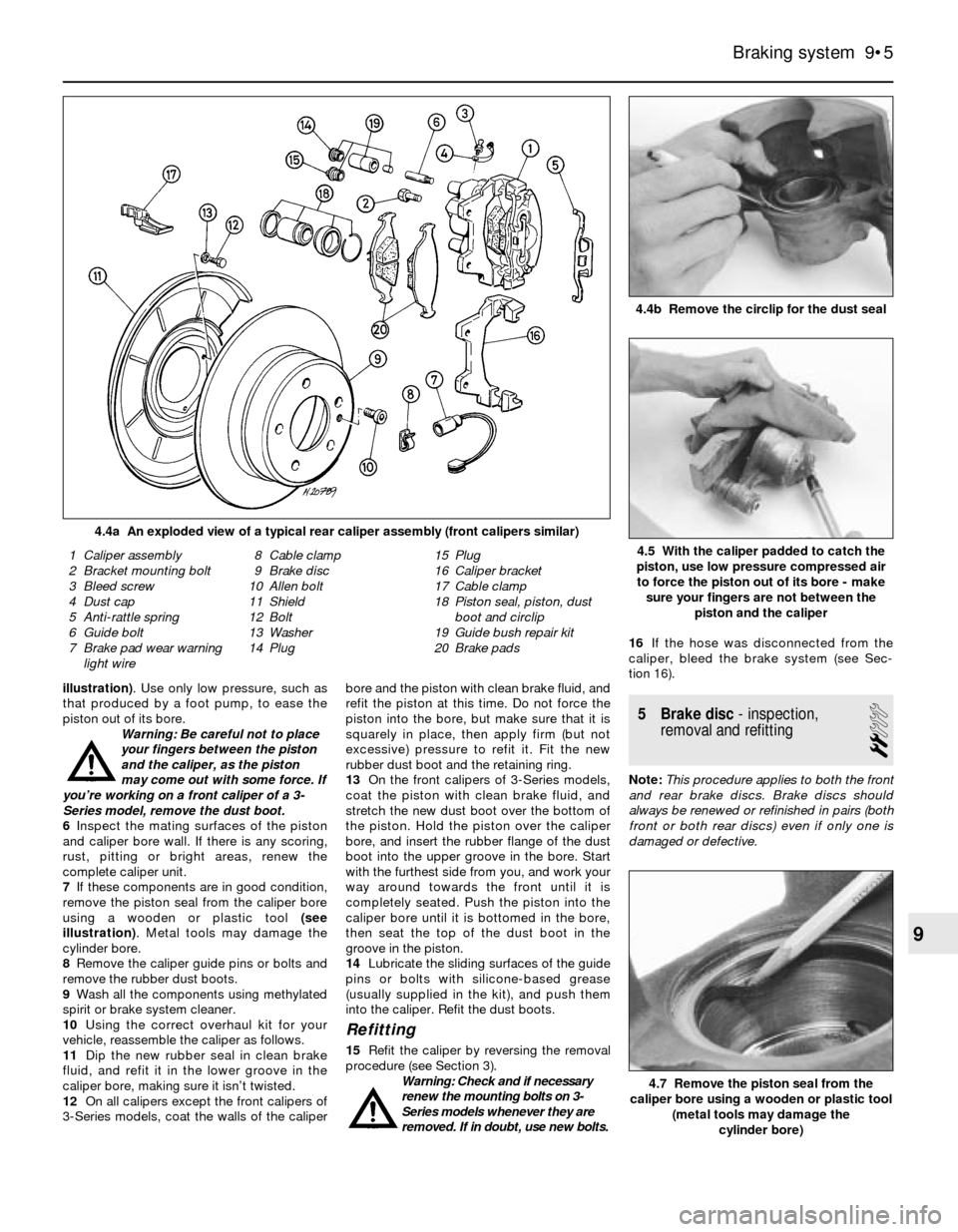
illustration). Use only low pressure, such as
that produced by a foot pump, to ease the
piston out of its bore.
Warning: Be careful not to place
your fingers between the piston
and the caliper, as the piston
may come out with some force. If
you’re working on a front caliper of a 3-
Series model, remove the dust boot.
6Inspect the mating surfaces of the piston
and caliper bore wall. If there is any scoring,
rust, pitting or bright areas, renew the
complete caliper unit.
7If these components are in good condition,
remove the piston seal from the caliper bore
using a wooden or plastic tool (see
illustration). Metal tools may damage the
cylinder bore.
8Remove the caliper guide pins or bolts and
remove the rubber dust boots.
9Wash all the components using methylated
spirit or brake system cleaner.
10Using the correct overhaul kit for your
vehicle, reassemble the caliper as follows.
11Dip the new rubber seal in clean brake
fluid, and refit it in the lower groove in the
caliper bore, making sure it isn’t twisted.
12On all calipers except the front calipers of
3-Series models, coat the walls of the caliperbore and the piston with clean brake fluid, and
refit the piston at this time. Do not force the
piston into the bore, but make sure that it is
squarely in place, then apply firm (but not
excessive) pressure to refit it. Fit the new
rubber dust boot and the retaining ring.
13On the front calipers of 3-Series models,
coat the piston with clean brake fluid, and
stretch the new dust boot over the bottom of
the piston. Hold the piston over the caliper
bore, and insert the rubber flange of the dust
boot into the upper groove in the bore. Start
with the furthest side from you, and work your
way around towards the front until it is
completely seated. Push the piston into the
caliper bore until it is bottomed in the bore,
then seat the top of the dust boot in the
groove in the piston.
14Lubricate the sliding surfaces of the guide
pins or bolts with silicone-based grease
(usually supplied in the kit), and push them
into the caliper. Refit the dust boots.
Refitting
15Refit the caliper by reversing the removal
procedure (see Section 3).
Warning: Check and if necessary
renew the mounting bolts on 3-
Series models whenever they are
removed. If in doubt, use new bolts.16If the hose was disconnected from the
caliper, bleed the brake system (see Sec-
tion 16).
5 Brake disc- inspection,
removal and refitting
2
Note:This procedure applies to both the front
and rear brake discs. Brake discs should
always be renewed or refinished in pairs (both
front or both rear discs) even if only one is
damaged or defective.
Braking system 9•5
4.4b Remove the circlip for the dust seal
4.4a An exploded view of a typical rear caliper assembly (front calipers similar)
4.7 Remove the piston seal from the
caliper bore using a wooden or plastic tool
(metal tools may damage the
cylinder bore)
1 Caliper assembly
2 Bracket mounting bolt
3 Bleed screw
4 Dust cap
5 Anti-rattle spring
6 Guide bolt
7 Brake pad wear warning
light wire8 Cable clamp
9 Brake disc
10 Allen bolt
11 Shield
12 Bolt
13 Washer
14 Plug15 Plug
16 Caliper bracket
17 Cable clamp
18 Piston seal, piston, dust
boot and circlip
19 Guide bush repair kit
20 Brake pads4.5 With the caliper padded to catch the
piston, use low pressure compressed air
to force the piston out of its bore - make
sure your fingers are not between the
piston and the caliper
9
Page 138 of 228
expel the air from the master cylinder. A large
Phillips screwdriver can be used to push on
the piston assembly.
11To prevent air from being drawn back into
the master cylinder, the plug must be refitted
and tightened down before releasing the
pressure on the piston assembly.
12Repeat the procedure until brake fluid free
of air bubbles is expelled from the brake line
outlet hole. Repeat the procedure with the
other outlet hole and plug. Be sure to keep the
master cylinder reservoir filled with brake
fluid, to prevent the introduction of air into the
system.
13High pressure is not involved in the bench
bleeding procedure, so the plugs described
above need not be refitted each time the
piston is released, if wished. Instead, before
releasing the piston, simply put your finger
tightly over the hole to keep air from being
drawn back into the master cylinder. Wait
several seconds for brake fluid to be drawn
from the reservoir into the piston bore, then
depress the piston again, removing your
finger as brake fluid is expelled. Be sure to put
your finger back over the hole each time
before releasing the piston, and when the
bleeding procedure is complete for that outlet,
refit the plug and tighten it up before going on
to the other port.
Refitting
14Refit the master cylinder (together with a
new O-ring) over the studs on the brake servo,
and tighten the mounting nuts only finger-tight
at this time.
15Thread the brake line fittings into the
master cylinder. Since the master cylinder is
still a bit loose, it can be moved slightly in
order for the fittings to thread in easily. Do not
strip the threads as the fittings are tightened.
16Tighten the brake fittings securely, and
the mounting nuts to the torque listed in this
Chapter’s Specifications.
17Fill the master cylinder reservoir with fluid,
then bleed the master cylinder (only if the
cylinder has not already been bled) and the
brake system as described in Section 16.
18To bleed the cylinder on the vehicle, have
an assistant pump the brake pedal severaltimes and then hold the pedal to the floor.
Loosen the fitting nut to allow air and fluid to
escape, then tighten the nut. Repeat this
procedure on both fittings until the fluid is
clear of air bubbles. Test the operation of the
brake system carefully before returning the
vehicle to normal service.
8 Brake vacuum servo-
check, removal and refitting
3
Operating check
1Depress the brake pedal several times with
the engine off, until there is no change in the
pedal travel.
2Depress and hold the pedal, then start the
engine. If the pedal goes down slightly,
operation is normal.
Airtightness check
3Start the engine, and turn it off after one or
two minutes. Depress the brake pedal several
times slowly. If the pedal goes down further
the first time but gradually rises after the
second or third depression, the servo is
airtight.
4Depress the brake pedal while the engine is
running, then stop the engine with the pedal
depressed. If there is no change in the pedal
travel after holding the pedal for 30 seconds,
the servo is airtight.
Removal and refitting
5Dismantling the vacuum servo requires
special tools, and cannot be performed by the
home mechanic. If a problem develops, it is
recommended that a new unit be fitted.
6Remove the master cylinder as described in
Section 7.
7Disconnect the vacuum hose from the
brake servo.
8Working in the passenger compartment,
remove the glovebox and lower left-hand trim
panels.
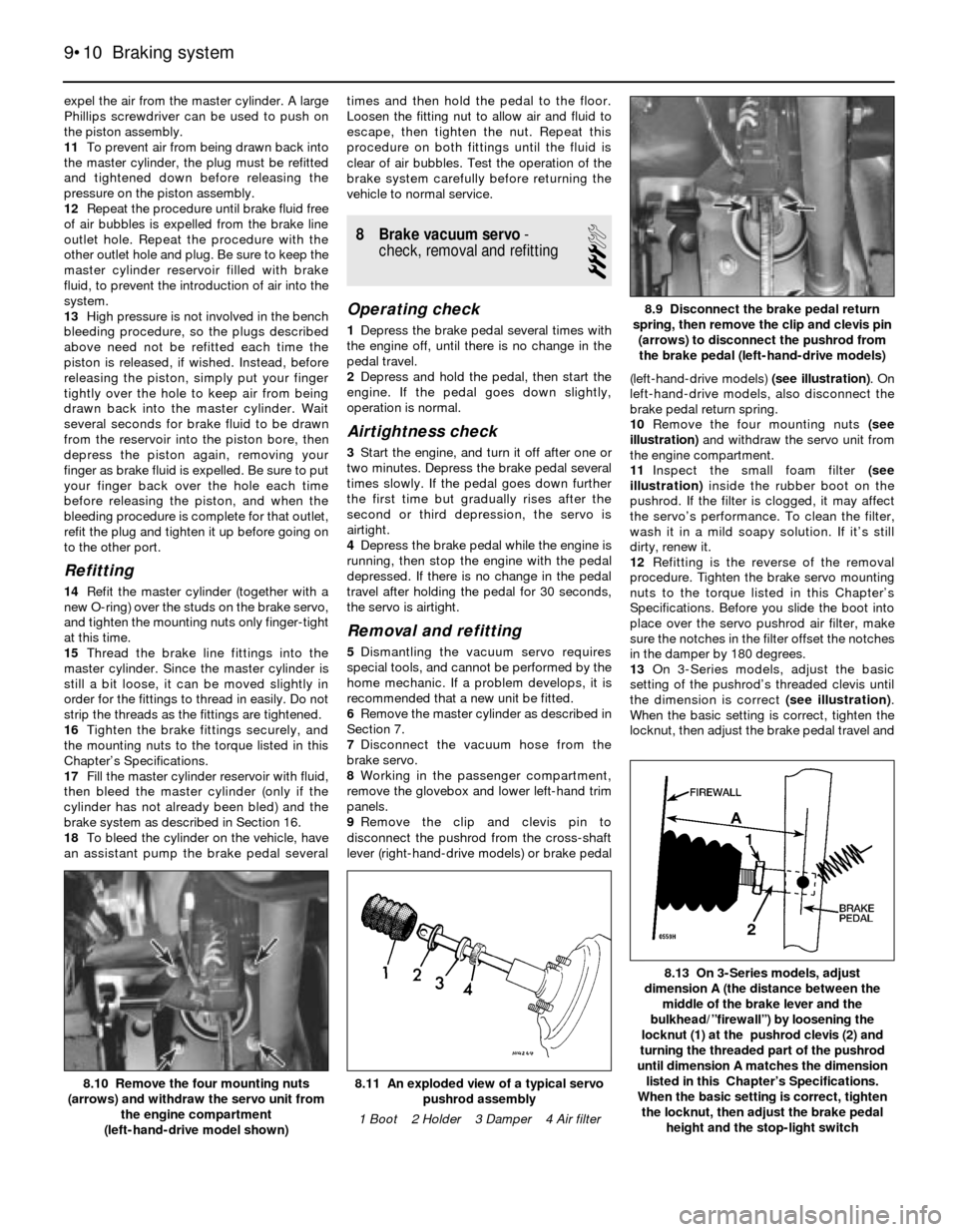
9Remove the clip and clevis pin to
disconnect the pushrod from the cross-shaft
lever (right-hand-drive models) or brake pedal(left-hand-drive models) (see illustration). On
left-hand-drive models, also disconnect the
brake pedal return spring.
10Remove the four mounting nuts (see
illustration)and withdraw the servo unit from
the engine compartment.
11Inspect the small foam filter (see
illustration)inside the rubber boot on the
pushrod. If the filter is clogged, it may affect
the servo’s performance. To clean the filter,
wash it in a mild soapy solution. If it’s still
dirty, renew it.
12Refitting is the reverse of the removal
procedure. Tighten the brake servo mounting
nuts to the torque listed in this Chapter’s
Specifications. Before you slide the boot into
place over the servo pushrod air filter, make
sure the notches in the filter offset the notches
in the damper by 180 degrees.
13On 3-Series models, adjust the basic
setting of the pushrod’s threaded clevis until
the dimension is correct (see illustration).
When the basic setting is correct, tighten the
locknut, then adjust the brake pedal travel and
9•10 Braking system
8.13 On 3-Series models, adjust
dimension A (the distance between the
middle of the brake lever and the
bulkhead/”firewall”) by loosening the
locknut (1) at the pushrod clevis (2) and
turning the threaded part of the pushrod
until dimension A matches the dimension
listed in this Chapter’s Specifications.
When the basic setting is correct, tighten
the locknut, then adjust the brake pedal
height and the stop-light switch
8.11 An exploded view of a typical servo
pushrod assembly
1 Boot 2 Holder 3 Damper 4 Air filter8.10 Remove the four mounting nuts
(arrows) and withdraw the servo unit from
the engine compartment
(left-hand-drive model shown)
8.9 Disconnect the brake pedal return
spring, then remove the clip and clevis pin
(arrows) to disconnect the pushrod from
the brake pedal (left-hand-drive models)
Page 139 of 228
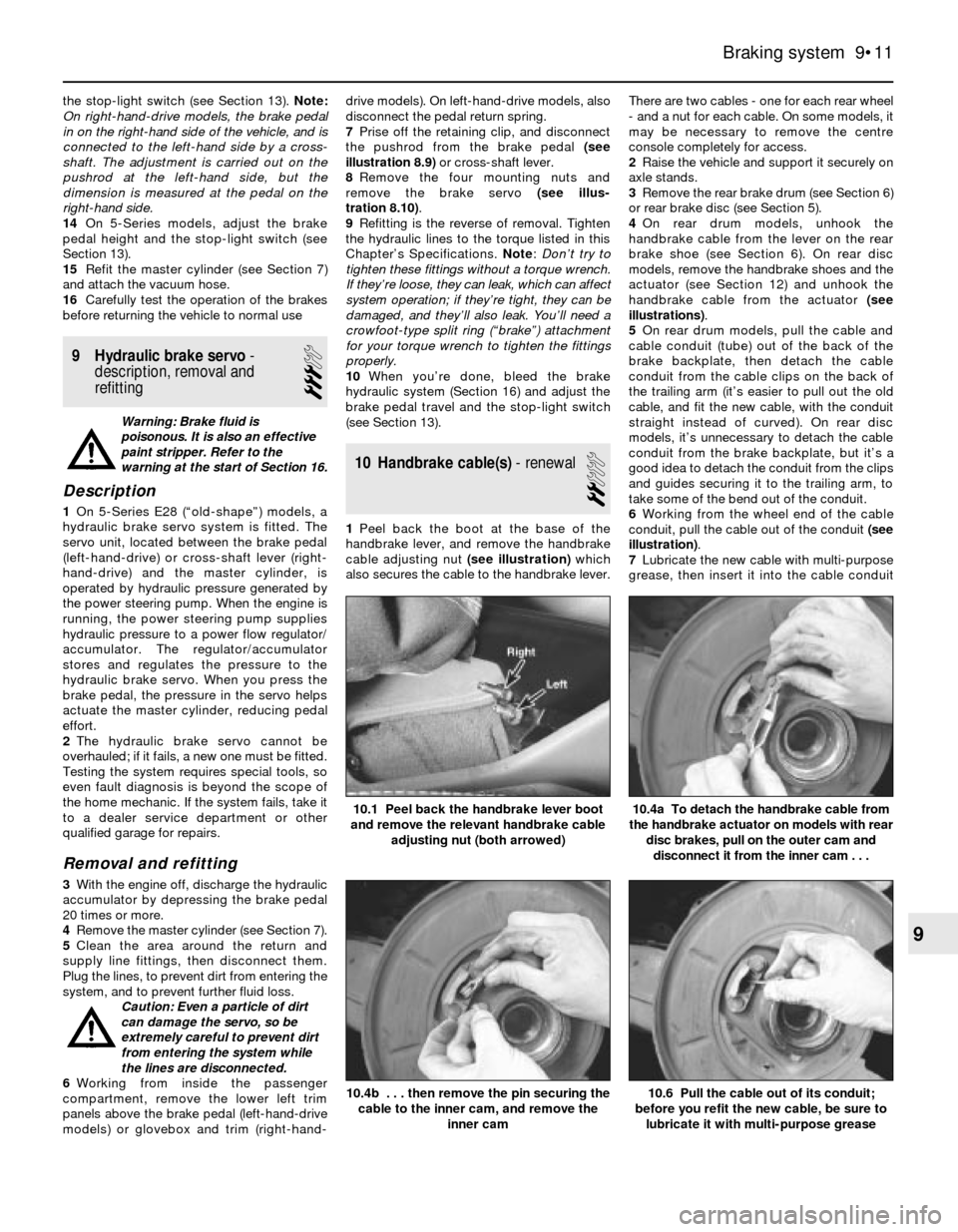
the stop-light switch (see Section 13). Note:
On right-hand-drive models, the brake pedal
in on the right-hand side of the vehicle, and is
connected to the left-hand side by a cross-
shaft. The adjustment is carried out on the
pushrod at the left-hand side, but the
dimension is measured at the pedal on the
right-hand side.
14On 5-Series models, adjust the brake
pedal height and the stop-light switch (see
Section 13).
15Refit the master cylinder (see Section 7)
and attach the vacuum hose.
16Carefully test the operation of the brakes
before returning the vehicle to normal use
9 Hydraulic brake servo-
description, removal and
refitting
3
Warning: Brake fluid is
poisonous. It is also an effective
paint stripper. Refer to the
warning at the start of Section 16.
Description
1On 5-Series E28 (“old-shape”) models, a
hydraulic brake servo system is fitted. The
servo unit, located between the brake pedal
(left-hand-drive) or cross-shaft lever (right-
hand-drive) and the master cylinder, is
operated by hydraulic pressure generated by
the power steering pump. When the engine is
running, the power steering pump supplies
hydraulic pressure to a power flow regulator/
accumulator. The regulator/accumulator
stores and regulates the pressure to the
hydraulic brake servo. When you press the
brake pedal, the pressure in the servo helps
actuate the master cylinder, reducing pedal
effort.
2The hydraulic brake servo cannot be
overhauled; if it fails, a new one must be fitted.
Testing the system requires special tools, so
even fault diagnosis is beyond the scope of
the home mechanic. If the system fails, take it
to a dealer service department or other
qualified garage for repairs.
Removal and refitting
3With the engine off, discharge the hydraulic
accumulator by depressing the brake pedal
20 times or more.
4Remove the master cylinder (see Section 7).
5Clean the area around the return and
supply line fittings, then disconnect them.
Plug the lines, to prevent dirt from entering the
system, and to prevent further fluid loss.
Caution: Even a particle of dirt
can damage the servo, so be
extremely careful to prevent dirt
from entering the system while
the lines are disconnected.
6Working from inside the passenger
compartment, remove the lower left trim
panels above the brake pedal (left-hand-drive
models) or glovebox and trim (right-hand-drive models). On left-hand-drive models, also
disconnect the pedal return spring.
7Prise off the retaining clip, and disconnect
the pushrod from the brake pedal (see
illustration 8.9) or cross-shaft lever.
8Remove the four mounting nuts and
remove the brake servo (see illus-
tration 8.10).
9Refitting is the reverse of removal. Tighten
the hydraulic lines to the torque listed in this
Chapter’s Specifications. Note:Don’t try to
tighten these fittings without a torque wrench.
If they’re loose, they can leak, which can affect
system operation; if they’re tight, they can be
damaged, and they’ll also leak. You’ll need a
crowfoot-type split ring (“brake”) attachment
for your torque wrench to tighten the fittings
properly.
10When you’re done, bleed the brake
hydraulic system (Section 16) and adjust the
brake pedal travel and the stop-light switch
(see Section 13).
10 Handbrake cable(s)- renewal
2
1Peel back the boot at the base of the
handbrake lever, and remove the handbrake
cable adjusting nut (see illustration)which
also secures the cable to the handbrake lever.There are two cables - one for each rear wheel
- and a nut for each cable. On some models, it
may be necessary to remove the centre
console completely for access.
2Raise the vehicle and support it securely on
axle stands.
3Remove the rear brake drum (see Section 6)
or rear brake disc (see Section 5).
4On rear drum models, unhook the
handbrake cable from the lever on the rear
brake shoe (see Section 6). On rear disc
models, remove the handbrake shoes and the
actuator (see Section 12) and unhook the
handbrake cable from the actuator (see
illustrations).
5On rear drum models, pull the cable and
cable conduit (tube) out of the back of the
brake backplate, then detach the cable
conduit from the cable clips on the back of
the trailing arm (it’s easier to pull out the old
cable, and fit the new cable, with the conduit
straight instead of curved). On rear disc
models, it’s unnecessary to detach the cable
conduit from the brake backplate, but it’s a
good idea to detach the conduit from the clips
and guides securing it to the trailing arm, to
take some of the bend out of the conduit.
6Working from the wheel end of the cable
conduit, pull the cable out of the conduit (see
illustration).
7Lubricate the new cable with multi-purpose
grease, then insert it into the cable conduit
Braking system 9•11
10.1 Peel back the handbrake lever boot
and remove the relevant handbrake cable
adjusting nut (both arrowed)
10.6 Pull the cable out of its conduit;
before you refit the new cable, be sure to
lubricate it with multi-purpose grease10.4b . . . then remove the pin securing the
cable to the inner cam, and remove the
inner cam
10.4a To detach the handbrake cable from
the handbrake actuator on models with rear
disc brakes, pull on the outer cam and
disconnect it from the inner cam . . .
9
Page 154 of 228
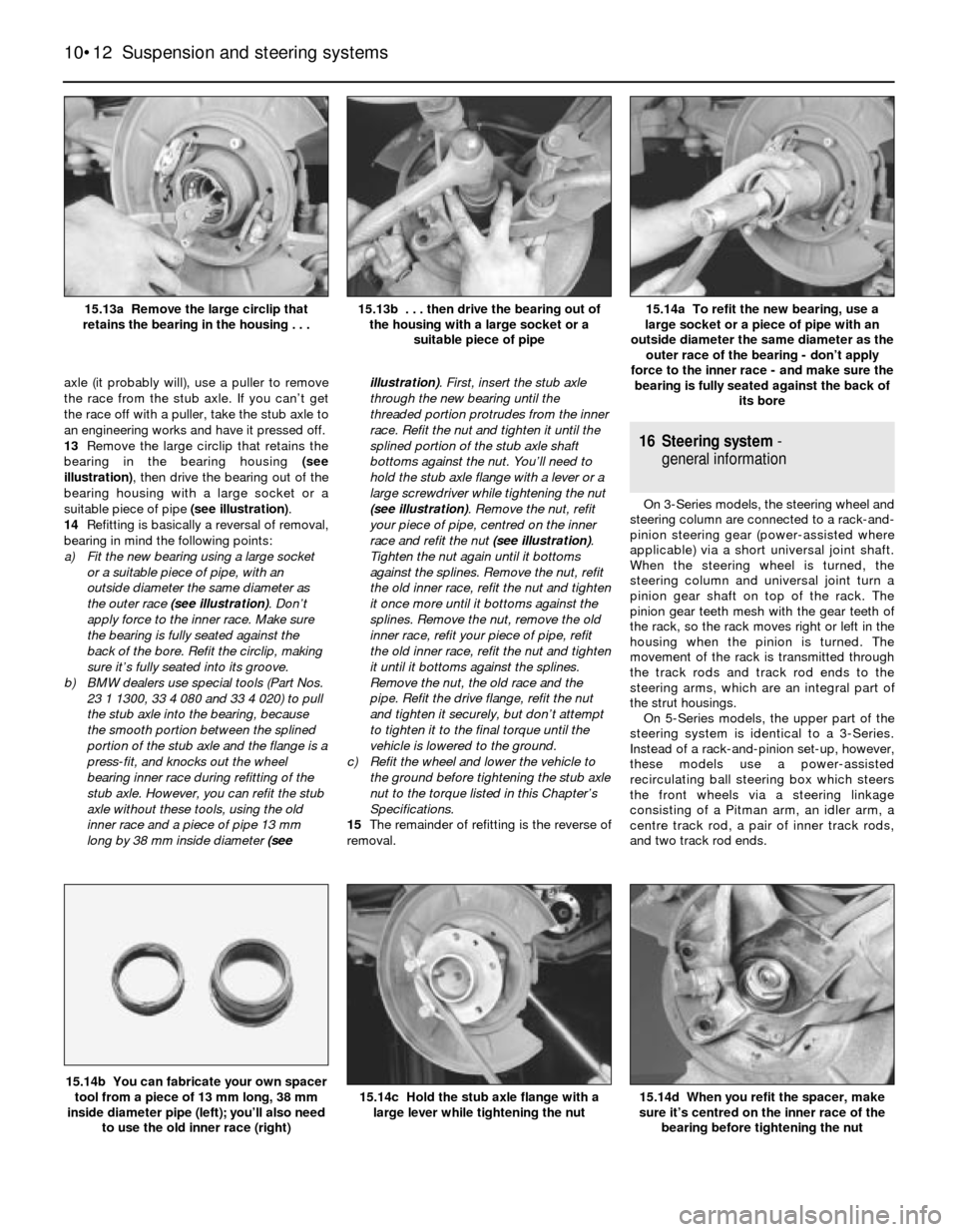
axle (it probably will), use a puller to remove
the race from the stub axle. If you can’t get
the race off with a puller, take the stub axle to
an engineering works and have it pressed off.
13Remove the large circlip that retains the
bearing in the bearing housing (see
illustration), then drive the bearing out of the
bearing housing with a large socket or a
suitable piece of pipe (see illustration).
14Refitting is basically a reversal of removal,
bearing in mind the following points:
a) Fit the new bearing using a large socket
or a suitable piece of pipe, with an
outside diameter the same diameter as
the outer race (see illustration). Don’t
apply force to the inner race. Make sure
the bearing is fully seated against the
back of the bore. Refit the circlip, making
sure it’s fully seated into its groove.
b) BMW dealers use special tools (Part Nos.
23 1 1300, 33 4 080 and 33 4 020) to pull
the stub axle into the bearing, because
the smooth portion between the splined
portion of the stub axle and the flange is a
press-fit, and knocks out the wheel
bearing inner race during refitting of the
stub axle. However, you can refit the stub
axle without these tools, using the old
inner race and a piece of pipe 13 mm
long by 38 mm inside diameter (seeillustration). First, insert the stub axle
through the new bearing until the
threaded portion protrudes from the inner
race. Refit the nut and tighten it until the
splined portion of the stub axle shaft
bottoms against the nut. You’ll need to
hold the stub axle flange with a lever or a
large screwdriver while tightening the nut
(see illustration). Remove the nut, refit
your piece of pipe, centred on the inner
race and refit the nut (see illustration).
Tighten the nut again until it bottoms
against the splines. Remove the nut, refit
the old inner race, refit the nut and tighten
it once more until it bottoms against the
splines. Remove the nut, remove the old
inner race, refit your piece of pipe, refit
the old inner race, refit the nut and tighten
it until it bottoms against the splines.
Remove the nut, the old race and the
pipe. Refit the drive flange, refit the nut
and tighten it securely, but don’t attempt
to tighten it to the final torque until the
vehicle is lowered to the ground.
c) Refit the wheel and lower the vehicle to
the ground before tightening the stub axle
nut to the torque listed in this Chapter’s
Specifications.
15The remainder of refitting is the reverse of
removal.
16 Steering system-
general information
On 3-Series models, the steering wheel and
steering column are connected to a rack-and-
pinion steering gear (power-assisted where
applicable) via a short universal joint shaft.
When the steering wheel is turned, the
steering column and universal joint turn a
pinion gear shaft on top of the rack. The
pinion gear teeth mesh with the gear teeth of
the rack, so the rack moves right or left in the
housing when the pinion is turned. The
movement of the rack is transmitted through
the track rods and track rod ends to the
steering arms, which are an integral part of
the strut housings.
On 5-Series models, the upper part of the
steering system is identical to a 3-Series.
Instead of a rack-and-pinion set-up, however,
these models use a power-assisted
recirculating ball steering box which steers
the front wheels via a steering linkage
consisting of a Pitman arm, an idler arm, a
centre track rod, a pair of inner track rods,
and two track rod ends.
10•12 Suspension and steering systems
15.14d When you refit the spacer, make
sure it’s centred on the inner race of the
bearing before tightening the nut15.14c Hold the stub axle flange with a
large lever while tightening the nut15.14b You can fabricate your own spacer
tool from a piece of 13 mm long, 38 mm
inside diameter pipe (left); you’ll also need
to use the old inner race (right)
15.14a To refit the new bearing, use a
large socket or a piece of pipe with an
outside diameter the same diameter as the
outer race of the bearing - don’t apply
force to the inner race - and make sure the
bearing is fully seated against the back of
its bore15.13b . . . then drive the bearing out of
the housing with a large socket or a
suitable piece of pipe15.13a Remove the large circlip that
retains the bearing in the housing . . .
Page 157 of 228
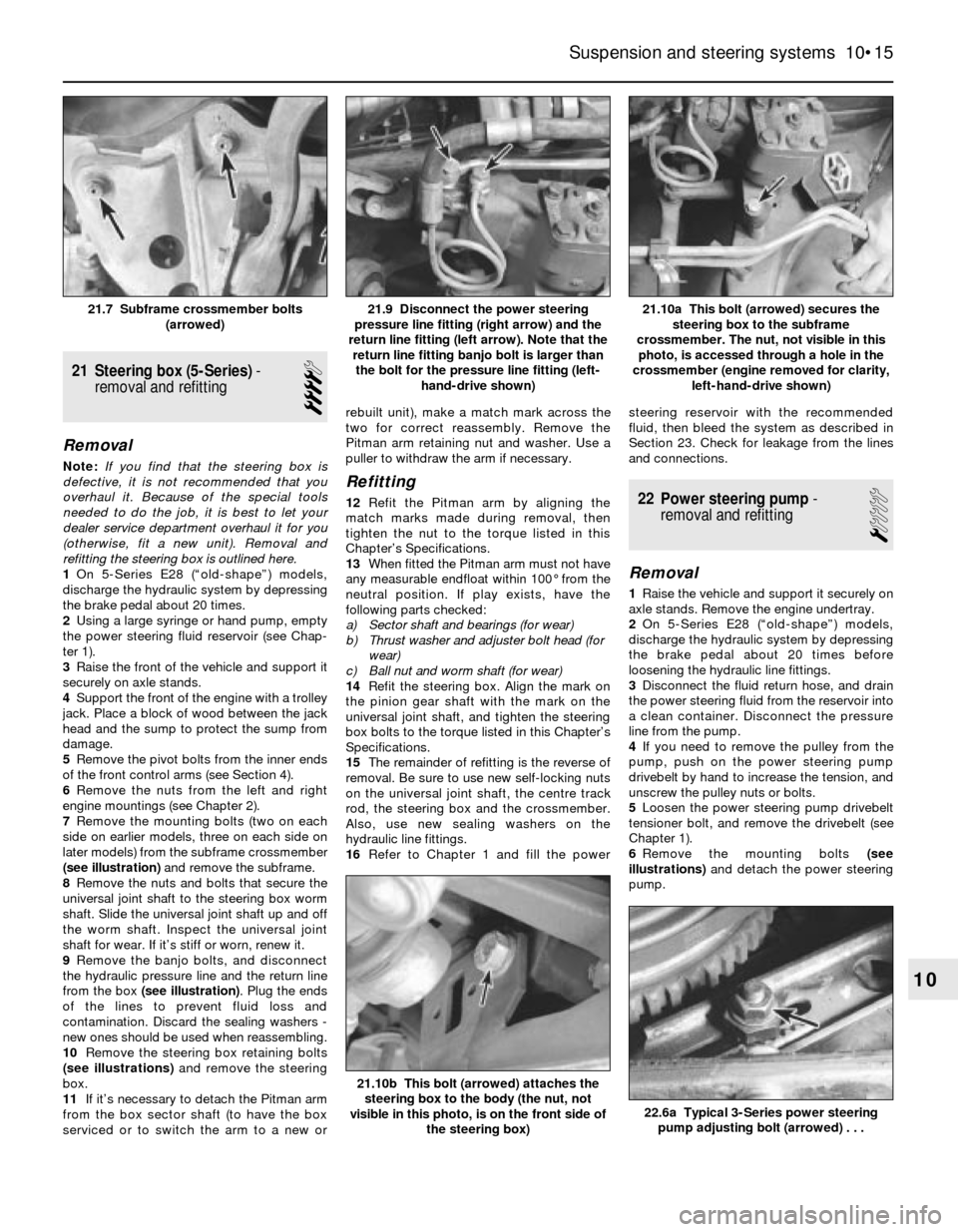
21 Steering box (5-Series)-
removal and refitting
4
Removal
Note:If you find that the steering box is
defective, it is not recommended that you
overhaul it. Because of the special tools
needed to do the job, it is best to let your
dealer service department overhaul it for you
(otherwise, fit a new unit). Removal and
refitting the steering box is outlined here.
1On 5-Series E28 (“old-shape”) models,
discharge the hydraulic system by depressing
the brake pedal about 20 times.
2Using a large syringe or hand pump, empty
the power steering fluid reservoir (see Chap-
ter 1).
3Raise the front of the vehicle and support it
securely on axle stands.
4Support the front of the engine with a trolley
jack. Place a block of wood between the jack
head and the sump to protect the sump from
damage.
5Remove the pivot bolts from the inner ends
of the front control arms (see Section 4).
6Remove the nuts from the left and right
engine mountings (see Chapter 2).
7Remove the mounting bolts (two on each
side on earlier models, three on each side on
later models) from the subframe crossmember
(see illustration)and remove the subframe.
8Remove the nuts and bolts that secure the
universal joint shaft to the steering box worm
shaft. Slide the universal joint shaft up and off
the worm shaft. Inspect the universal joint
shaft for wear. If it’s stiff or worn, renew it.
9Remove the banjo bolts, and disconnect
the hydraulic pressure line and the return line
from the box (see illustration). Plug the ends
of the lines to prevent fluid loss and
contamination. Discard the sealing washers -
new ones should be used when reassembling.
10Remove the steering box retaining bolts
(see illustrations)and remove the steering
box.
11If it’s necessary to detach the Pitman arm
from the box sector shaft (to have the box
serviced or to switch the arm to a new orrebuilt unit), make a match mark across the
two for correct reassembly. Remove the
Pitman arm retaining nut and washer. Use a
puller to withdraw the arm if necessary.
Refitting
12Refit the Pitman arm by aligning the
match marks made during removal, then
tighten the nut to the torque listed in this
Chapter’s Specifications.
13When fitted the Pitman arm must not have
any measurable endfloat within 100° from the
neutral position. If play exists, have the
following parts checked:
a) Sector shaft and bearings (for wear)
b) Thrust washer and adjuster bolt head (for
wear)
c) Ball nut and worm shaft (for wear)
14Refit the steering box. Align the mark on
the pinion gear shaft with the mark on the
universal joint shaft, and tighten the steering
box bolts to the torque listed in this Chapter’s
Specifications.
15The remainder of refitting is the reverse of
removal. Be sure to use new self-locking nuts
on the universal joint shaft, the centre track
rod, the steering box and the crossmember.
Also, use new sealing washers on the
hydraulic line fittings.
16Refer to Chapter 1 and fill the powersteering reservoir with the recommended
fluid, then bleed the system as described in
Section 23. Check for leakage from the lines
and connections.22 Power steering pump-
removal and refitting
1
Removal
1Raise the vehicle and support it securely on
axle stands. Remove the engine undertray.
2On 5-Series E28 (“old-shape”) models,
discharge the hydraulic system by depressing
the brake pedal about 20 times before
loosening the hydraulic line fittings.
3Disconnect the fluid return hose, and drain
the power steering fluid from the reservoir into
a clean container. Disconnect the pressure
line from the pump.
4If you need to remove the pulley from the
pump, push on the power steering pump
drivebelt by hand to increase the tension, and
unscrew the pulley nuts or bolts.
5Loosen the power steering pump drivebelt
tensioner bolt, and remove the drivebelt (see
Chapter 1).
6Remove the mounting bolts (see
illustrations)and detach the power steering
pump.
Suspension and steering systems 10•15
21.10a This bolt (arrowed) secures the
steering box to the subframe
crossmember. The nut, not visible in this
photo, is accessed through a hole in the
crossmember (engine removed for clarity,
left-hand-drive shown)21.9 Disconnect the power steering
pressure line fitting (right arrow) and the
return line fitting (left arrow). Note that the
return line fitting banjo bolt is larger than
the bolt for the pressure line fitting (left-
hand-drive shown)21.7 Subframe crossmember bolts
(arrowed)
22.6a Typical 3-Series power steering
pump adjusting bolt (arrowed) . . .
21.10b This bolt (arrowed) attaches the
steering box to the body (the nut, not
visible in this photo, is on the front side of
the steering box)
10
Page 163 of 228

7 Hinges and locks-
maintenance
1
Every six months or so, the hinges and lock
assemblies on the doors, bonnet and the boot
lid/tailgate should be given a few drops of
light oil or lock lubricant. The door or tailgate
lock strikers should also be lubricated with a
thin coat of grease, to reduce wear and
ensure free movement.
8 Fixed glass- renewal
5
Renewal of the windscreen and fixed glass
requires the use of special fast-setting
adhesive materials, and some specialised
tools and techniques. These operations
should be left to a dealer service department
or windscreen specialist.
9 Radiator grille-
removal and refitting
1
3-Series
1Detach the clips along the top of the grille
(see illustration).2Remove the screws, and lift the centre and
side grilles out (see illustrations).
3Refitting is the reverse of removal.
5-Series
E28 (“old-shape”) models
6Remove the screws, and detach the centre
and side grille pieces.
7Refitting is the reverse of removal.
E34 (“new-shape”) models
Centre grille
8Remove the screws and detach the
headlight covers in the engine compartment
for access.
9Remove the screw, and lift out the plastic
cover behind the centre grille for access to the
clips.
10From the engine compartment, reach
under the headlight housings and detach the
clips retaining the centre grille valances, then
push the grille forwards (see illustration).
11Use a screwdriver to depress the clips,
detach the grille assembly and remove it by
pulling it straight out.
12Refit the centre grille by placing it in
position and pushing it straight back until it
clips into place.
Side grille
13Remove the centre grille.
14Remove the screws, and lift the side grille
assembly out (see illustration).
15Refitting is the reverse of removal.
10 Bonnet- removal, refitting and
adjustment
1
Note: The bonnet is heavy and somewhat
awkward to remove and refit - at least two
people should perform this procedure.
Removal and refitting
3-Series models
1Open the bonnet. Scribe or draw alignment
marks around the bolt heads to ensure proper
alignment on refitting (see illustration).
2Disconnect the earth cable and windscreen
washer hose from the bonnet.
3Detach the bonnet hinge rod clip and
11•4 Bodywork and fittings
10.3a Use needle-nose pliers to pull off
the hinge pin clip . . .
10.1 Use paint or a marking pen to mark
on the hinge plate around the bolt heads -
mark around the entire hinge plate, if
desired, before adjusting the bonnet
9.14 Remove the screws and pull the side
grille assembly straight out
9.10 Detach the centre grille valance by
reaching under each headlight and
pressing on the release lever
9.2b Side grille screw locations (arrowed)9.2a The centre grille is held in place by
two screws (arrowed)9.1 Open the bonnet and remove the grille
retaining clips (arrowed)
Page 169 of 228

12
Chapter 12 Body electrical systems
Bulb renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Central locking system - description and check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Cruise control system - description and check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Direction indicator/hazard warning flasher - check and renewal . . . 5
Electric windows - description and check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Electrical system fault finding - general information . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Fuses - general information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
General information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
Headlight housing - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Headlights - adjustment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Headlights - bulb renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12Heated rear window - check and repair . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Ignition switch - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Instrument cluster - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Radio - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Radio aerial - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Relays - general information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
Service Indicator (SI) board - general information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Steering column switches - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Supplemental Restraint System (SRS) - general information . . . . . . 18
Windscreen/tailgate wiper motor - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . 16
Wiring diagrams - general information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
12•1
Easy,suitable for
novice with little
experienceFairly easy,suitable
for beginner with
some experienceFairly difficult,
suitable for competent
DIY mechanic
Difficult,suitable for
experienced DIY
mechanicVery difficult,
suitable for expert
DIY or professional
Degrees of difficulty Contents
1 General information
The chassis electrical system of this vehicle
is of 12-volt, negative earth type. Power for
the lights and all electrical accessories is
supplied by a lead/acid-type battery, which is
charged by the alternator.
This Chapter covers repair and service
procedures for various chassis (non-engine
related) electrical components. For
information regarding the engine electrical
system components (battery, alternator,
distributor and starter motor), see Chapter 5.
Warning: To prevent electrical
short-circuits, fires and injury,
always disconnect the battery
negative terminal before
checking, repairing or renewing electrical
components.
Caution: If the radio in your
vehicle is equipped with an anti-
theft system, make sure you have
the correct activation code
before disconnecting the battery, Refer to
the information on page 0-7 at the front of
this manual before detaching the cable.
Note: If, after connecting the battery, the
wrong language appears on the instrument
panel display, refer to page 0-7 for the
language resetting procedure.
2 Electrical system fault
finding- general information
2
A typical electrical circuit consists of an
electrical component, any switches, relays,
motors, fuses, fusible links or circuit breakers,
etc related to that component, and the wiring
and connectors that link the components to
both the battery and the chassis. To help you
pinpoint an electrical circuit problem, wiring
diagrams are included at the end of this book.
Before tackling any troublesome electrical
circuit, first study the appropriate wiring
diagrams to get a complete understanding of
what makes up that individual circuit.
Troublespots, for instance, can often be
isolated by noting if other components related
to that circuit are routed through the same
fuse and earth connections.
Electrical problems usually stem from
simple causes such as loose or corroded
connectors, a blown fuse, a melted fusible
link, or a bad relay. Inspect all fuses, wires
and connectors in a problem circuit first.
The basic tools needed include a circuit
tester, a high-impedance digital voltmeter, a
continuity tester and a jumper wire with an in-
line circuit breaker for bypassing electrical
components. Before attempting to locate or
define a problem with electrical testinstruments, use the wiring diagrams to
decide where to make the necessary
connections.
Voltage checks
Perform a voltage check first when a circuit
is not functioning properly. Connect one lead
of a circuit tester to either the negative battery
terminal or a known good earth.
Connect the other lead to a connector in
the circuit being tested, preferably nearest to
the battery or fuse. If the bulb of the tester
lights up, voltage is present, which means that
the part of the circuit between the connector
and the battery is problem-free. Continue
checking the rest of the circuit in the same
fashion.
When you reach a point at which no voltage
is present, the problem lies between that point
and the last test point with voltage. Most of
the time, problems can be traced to a loose
connection.Note:Keep in mind that some
circuits receive voltage only when the ignition
key is turned to a certain position.
Electrical fault diagnosis is simple if you
keep in mind that all electrical circuits are
basically electricity running from the battery,
through the wires, switches, relays, fuses and
fusible links to each electrical component
(light bulb, motor, etc) and then to earth, from
where it is passed back to the battery. Any
electrical problem is an interruption in the flow
of electricity to and from the battery.
Page 170 of 228

Finding a short-circuit
One method of finding a short-circuit is to
remove the fuse and connect a test light or
voltmeter in its place. There should be no
voltage present in the circuit. Move the
electrical connectors from side-to-side while
watching the test light. If the bulb goes on,
there is a short to earth somewhere in that
area, probably where the insulation has been
rubbed through. The same test can be
performed on each component in a circuit,
even a switch.
Earth check
Perform a earth check to see whether a
component is properly earthed (passing
current back via the vehicle body). Disconnect
the battery, and connect one lead of a self-
powered test light (often known as a
continuity tester) to a known good earth.
Connect the other lead to the wire or earth
connection being tested. The bulb should
light, indicating a good earth connection. If
not, dismantle the connection, and clean all
relevant parts thoroughly. When re-making
the connection, use serrated (shakeproof)
washers if possible, and tighten all bolts, etc,
securely.
Caution: If the radio in your
vehicle is equipped with an anti-
theft system, make sure you have
the correct activation code
before disconnecting the battery, Refer to
the information on page 0-7 at the front of
this manual before detaching the cable.
Note: If, after connecting the battery, the
wrong language appears on the instrument
panel display, refer to page 0-7 for the
language resetting procedure.
Continuity check
A continuity check determines if there are
any breaks in a circuit - if it is conducting
electricity properly. With the circuit off (no
power in the circuit), a self-powered continuity
tester can be used to check the circuit.
Connect the test leads to both ends of the
circuit, and if the test light comes on, the
circuit is passing current properly. If the light
doesn’t come on, there is a break somewhere
in the circuit. The same procedure can be
used to test a switch, by connecting the
continuity tester to the power-in and power-
out sides of the switch. With the switch turned
on, the test light should come on.
Finding an open-circuit
When diagnosing for possible open-
circuits, it is often difficult to locate them by
sight, because oxidation or terminal
misalignment are hidden by the connectors.
Intermittent problems are often caused by
oxidised or loose connections. Merely
wiggling an electrical connector may correct
the open-circuit condition, albeit temporarily.
Dismantle the connector, and spray with a
water-dispersant aerosol. On simpler
connectors, it may be possible to carefullybend the connector pins inside, to improve
the metal-to-metal contact - don’t damage
the connector in the process, however.
3 Fuses- general information
1
The electrical circuits of the vehicle are
protected by a combination of fuses and
circuit breakers. The fusebox is located in the
left corner of the engine compartment (see
illustration). On some later models, it is
located under the rear seat cushion.
Each of the fuses is designed to protect a
specific circuit, and on some models, the
various circuits are identified on the fuse
panel itself.
Miniaturised fuses are employed in the
fuseboxes. These compact fuses, with blade
terminal design, allow fingertip removal and
renewal. If an electrical component fails,
always check the fuse first. A blown fuse is
easily identified through the clear plastic
body. Visually inspect the element for
evidence of damage. If a continuity check is
called for, the blade terminal tips are exposed
in the fuse body.
Be sure to renew blown fuses with the
correct type. Fuses of different ratings are
physically interchangeable, but only fuses of
the proper rating should be used. Replacing a
fuse with one of a higher or lower value than
specified is not recommended. Each electrical
circuit needs a specific amount of protection.
The amperage value of each fuse is moulded
into the fuse body.
If the new fuse immediately fails, don’t
renew it again until the cause of the problem
is isolated and corrected. In most cases, the
cause will be a short-circuit in the wiring
caused by a broken or deteriorated wire.
4 Relays- general information
1
Several electrical accessories in the vehicle
use relays to transmit the electrical signal to
the component. If the relay is defective, thatcomponent will not operate properly. Relays
are electrically-operated switches, which are
often used in circuits drawing high levels of
current, or where more complex switching
arrangements are required.
The various relays are grouped together for
convenience in several locations under the
dash and in the engine compartment (see
accompanying illustration and illus-
tration 3.1).
If a faulty relay is suspected, it can be
removed and tested by a dealer or qualified
automotive electrician. No overhaul is
possible. Like fuses, defective relays must be
replaced with the correct type; some relays
look identical, but perform very different
functions.
5 Direction indicator/hazard
warning flasher unit- check
and renewal
2
Warning: Some later models are
equipped with an airbag or
Supplemental Restraint System
(SRS). To avoid possible damage
to this system, the manufacturer
recommends that, on airbag-equipped
models, the following procedure should be
left to a dealer service department, or
other specialist, because of the special
tools and techniques required. There is a
risk of injury if the airbag is accidentally
triggered.
1The direction indicator/hazard flasher unit is
a small canister- or box-shaped unit located
in the wiring harness on or near the steering
column. Access is gained by removing the
steering column shrouds (see illustration).
2When the flasher unit is functioning
properly, a regular clicking noise can be heard
from it when the indicators or hazard flashers
are switched on. If the direction indicators fail
on one side or the other, and the flasher unit
does not make its characteristic clicking
sound, a faulty direction indicator bulb is
indicated.
3If both direction indicators fail to blink, the
problem may be due to a blown fuse, a faulty
flasher unit, a broken switch or a loose or open
connection. If a quick check of the fusebox
12•2 Body electrical systems
4.2 Engine compartment relays3.1 The fusebox is located in the engine
compartment under a cover - the box also
includes several relays