Rear seat BMW 3 SERIES 1989 E30 User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: BMW, Model Year: 1989, Model line: 3 SERIES, Model: BMW 3 SERIES 1989 E30Pages: 228, PDF Size: 7.04 MB
Page 160 of 228

11
1 General information
These models feature an all-steel welded
construction, where the floorpan and body
components are welded together and
attached to separate front and rear subframe
assemblies. Certain components are
particularly vulnerable to accident damage,
and can be unbolted and repaired or renewed.
Among these parts are the body mouldings,
bumpers, bonnet, doors, tailgate, and all
glass.
Only general body maintenance procedures
and body panel repair procedures within the
scope of the do-it-yourselfer are included in
this Chapter.
2 Bodywork and underframe-
maintenance
1
The general condition of a vehicle’s
bodywork is the one thing that significantly
affects its value. Maintenance is easy, but
needs to be regular. Neglect, particularly after
minor damage, can lead quickly to further
deterioration and costly repair bills. It is
important also to keep watch on those parts
of the vehicle not immediately visible, for
instance the underside, inside all the wheelarches, and the lower part of the engine
compartment.
The basic maintenance routine for the
bodywork is washing - preferably with a lot of
water, from a hose. This will remove all the
loose solids which may have stuck to the
vehicle. It is important to flush these off in
such a way as to prevent grit from scratching
the finish. The wheel arches and underframe
need washing in the same way, to remove any
accumulated mud, which will retain moisture
and tend to encourage rust. Paradoxically
enough, the best time to clean the underframe
and wheel arches is in wet weather, when the
mud is thoroughly wet and soft. In very wet
weather, the underframe is usually cleaned of
large accumulations automatically, and this is
a good time for inspection.
Periodically, except on vehicles with a wax-
based underbody protective coating, it is a
good idea to have the whole of the
underframe of the vehicle steam-cleaned,
engine compartment included, so that a
thorough inspection can be carried out to see
what minor repairs and renovations are
necessary. Steam-cleaning is available at
many garages, and is necessary for the
removal of the accumulation of oily grime,
which sometimes is allowed to become thick
in certain areas. If steam-cleaning facilities are
not available, there are some excellent grease
solvents available which can be brush-
applied; the dirt can then be simply hosed off.
Note that these methods should not be usedon vehicles with wax-based underbody
protective coating, or the coating will be
removed. Such vehicles should be inspected
annually, preferably just prior to Winter, when
the underbody should be washed down, and
any damage to the wax coating repaired.
Ideally, a completely fresh coat should be
applied. It would also be worth considering
the use of such wax-based protection for
injection into door panels, sills, box sections,
etc, as an additional safeguard against rust
damage, where such protection is not
provided by the vehicle manufacturer.
After washing paintwork, wipe off with a
chamois leather to give an unspotted clear
finish. A coat of clear protective wax polish will
give added protection against chemical
pollutants in the air. If the paintwork sheen has
dulled or oxidised, use a cleaner/polisher
combination to restore the brilliance of the
shine. This requires a little effort, but such
dulling is usually caused because regular
washing has been neglected. Care needs to be
taken with metallic paintwork, as special non-
abrasive cleaner/polisher is required to avoid
damage to the finish. Always check that the
door and ventilator opening drain holes and
pipes are completely clear, so that water can
be drained out. Brightwork should be treated in
the same way as paintwork. Windscreens and
windows can be kept clear of the smeary film
which often appears, by the use of proprietary
glass cleaner. Never use any form of wax or
other body or chromium polish on glass.
Chapter 11 Bodywork and fittings
Bodywork and underframe - maintenance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Bodywork repair - major damage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Bodywork repair - minor damage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Bonnet - removal, refitting and adjustment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Boot lid/tailgate - removal, refitting and adjustment . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Bumpers - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Door - removal, refitting and adjustment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Door trim panel - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Door window glass - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Door window regulator - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Exterior mirror - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18Fixed glass - renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
General information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
Hinges and locks - maintenance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Interior trim - maintenance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Latch, lock cylinder and handles - removal, refitting and
adjustment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Radiator grille - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Seat belt check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Seats - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Steering column shrouds - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Upholstery and carpets - maintenance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
11•1
Easy,suitable for
novice with little
experienceFairly easy,suitable
for beginner with
some experienceFairly difficult,
suitable for competent
DIY mechanic
Difficult,suitable for
experienced DIY
mechanicVery difficult,
suitable for expert
DIY or professional
Degrees of difficulty Contents
Page 168 of 228
19 Steering column shrouds -
removal and refitting
1
Caution: If the radio in your
vehicle is equipped with an anti-
theft system, make sure you have
the correct activation code
before disconnecting the battery, Refer to
the information on page 0-7 at the front of
this manual before detaching the cable.
Note: If, after connecting the battery, the
wrong language appears on the instrument
panel display, refer to page 0-7 for the
language resetting procedure.
Removal
1Disconnect the battery negative cable.
2Remove the steering wheel (Chapter 10).
3Remove the upper shroud screws (see
illustration).
4Remove the two screws from the underside
of the column (see illustration).
5Detach the lower shroud, then lift the upper
half off the column (see illustrations).
Refitting
6Refitting is the reverse of removal.
20 Seats- removal and refitting
1
Front seat
1Remove the four bolts securing the seat
track to the floorpan, and lift the seat from the
vehicle (see illustration). On some models, it
will be necessary to disconnect the seat
heating wiring; it may also be necessary to
detach the seat belt from the seat.2Refitting is the reverse of removal. Tighten
the retaining bolts securely.
Rear seat cushion
3If applicable, first remove the two retaining
bolts. Grasp the front of the cushion
(Saloon/Convertible models) or the rear of the
cushion (Touring/Estate models) securely, and
pull up sharply (see illustration).
4Refitting is the reverse of the removal.
21 Seat belt check
1
1Check the seat belts, buckles, lock plates
and guide loops for obvious damage and
signs of wear.
2Where applicable, check that the seat belt
reminder light comes on when the ignition key
is turned to the Run or Start position.
3The seat belts are designed to lock up
during a sudden stop or impact, yet allow free
movement during normal driving. Check thatthe retractors return the belt against your
chest while driving and rewind the belt fully
when the buckle is unlocked.
4If any of the above checks reveal problems
with the seat belt system, renew parts as
necessary.
5Belts which have been subject to impact
loads must be renewed.
Bodywork and fittings 11•9
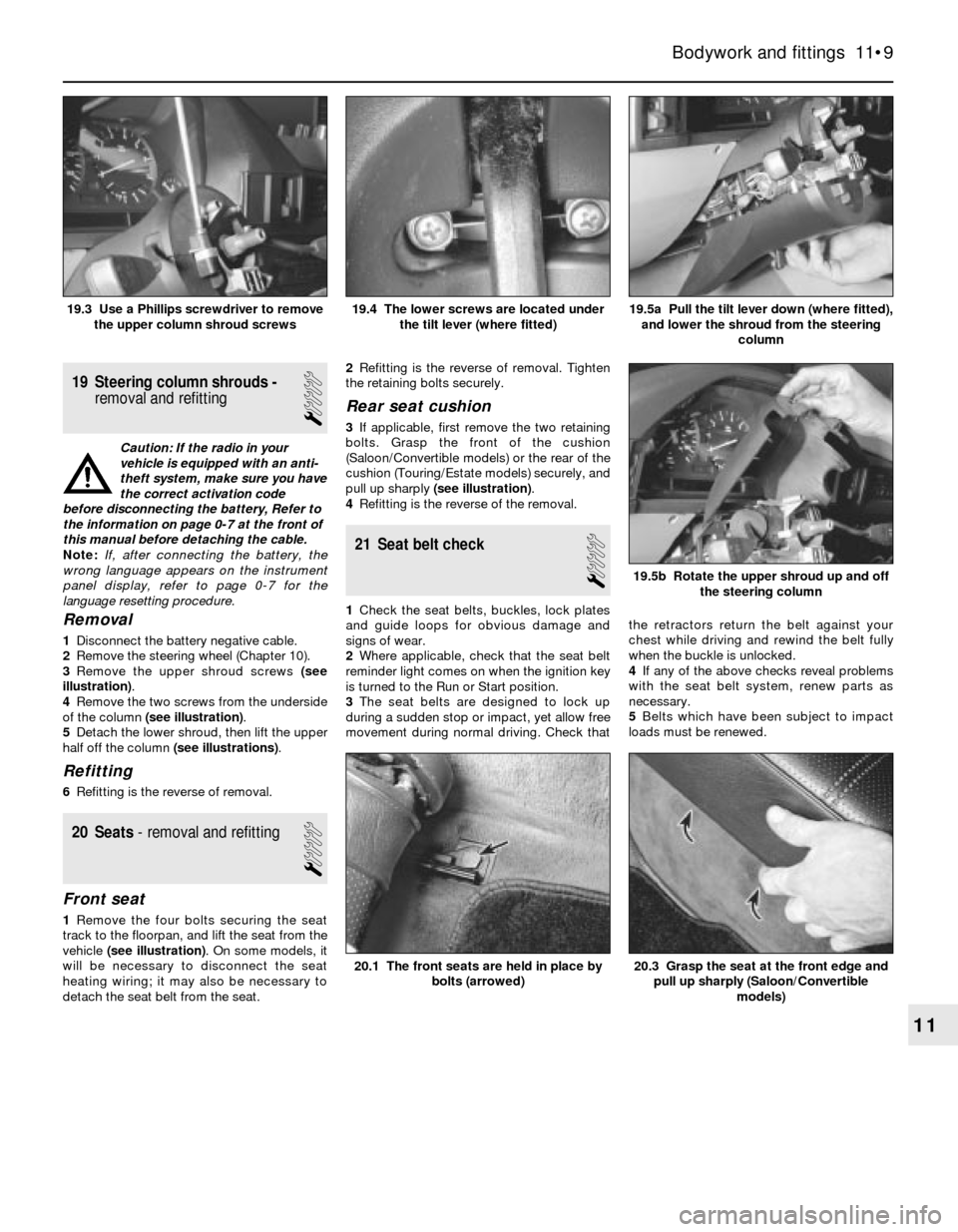
19.5a Pull the tilt lever down (where fitted),
and lower the shroud from the steering
column19.4 The lower screws are located under
the tilt lever (where fitted)19.3 Use a Phillips screwdriver to remove
the upper column shroud screws
20.3 Grasp the seat at the front edge and
pull up sharply (Saloon/Convertible
models)20.1 The front seats are held in place by
bolts (arrowed)
19.5b Rotate the upper shroud up and off
the steering column
11
Page 170 of 228

Finding a short-circuit
One method of finding a short-circuit is to
remove the fuse and connect a test light or
voltmeter in its place. There should be no
voltage present in the circuit. Move the
electrical connectors from side-to-side while
watching the test light. If the bulb goes on,
there is a short to earth somewhere in that
area, probably where the insulation has been
rubbed through. The same test can be
performed on each component in a circuit,
even a switch.
Earth check
Perform a earth check to see whether a
component is properly earthed (passing
current back via the vehicle body). Disconnect
the battery, and connect one lead of a self-
powered test light (often known as a
continuity tester) to a known good earth.
Connect the other lead to the wire or earth
connection being tested. The bulb should
light, indicating a good earth connection. If
not, dismantle the connection, and clean all
relevant parts thoroughly. When re-making
the connection, use serrated (shakeproof)
washers if possible, and tighten all bolts, etc,
securely.
Caution: If the radio in your
vehicle is equipped with an anti-
theft system, make sure you have
the correct activation code
before disconnecting the battery, Refer to
the information on page 0-7 at the front of
this manual before detaching the cable.
Note: If, after connecting the battery, the
wrong language appears on the instrument
panel display, refer to page 0-7 for the
language resetting procedure.
Continuity check
A continuity check determines if there are
any breaks in a circuit - if it is conducting
electricity properly. With the circuit off (no
power in the circuit), a self-powered continuity
tester can be used to check the circuit.
Connect the test leads to both ends of the
circuit, and if the test light comes on, the
circuit is passing current properly. If the light
doesn’t come on, there is a break somewhere
in the circuit. The same procedure can be
used to test a switch, by connecting the
continuity tester to the power-in and power-
out sides of the switch. With the switch turned
on, the test light should come on.
Finding an open-circuit
When diagnosing for possible open-
circuits, it is often difficult to locate them by
sight, because oxidation or terminal
misalignment are hidden by the connectors.
Intermittent problems are often caused by
oxidised or loose connections. Merely
wiggling an electrical connector may correct
the open-circuit condition, albeit temporarily.
Dismantle the connector, and spray with a
water-dispersant aerosol. On simpler
connectors, it may be possible to carefullybend the connector pins inside, to improve
the metal-to-metal contact - don’t damage
the connector in the process, however.
3 Fuses- general information
1
The electrical circuits of the vehicle are
protected by a combination of fuses and
circuit breakers. The fusebox is located in the
left corner of the engine compartment (see
illustration). On some later models, it is
located under the rear seat cushion.
Each of the fuses is designed to protect a
specific circuit, and on some models, the
various circuits are identified on the fuse
panel itself.
Miniaturised fuses are employed in the
fuseboxes. These compact fuses, with blade
terminal design, allow fingertip removal and
renewal. If an electrical component fails,
always check the fuse first. A blown fuse is
easily identified through the clear plastic
body. Visually inspect the element for
evidence of damage. If a continuity check is
called for, the blade terminal tips are exposed
in the fuse body.
Be sure to renew blown fuses with the
correct type. Fuses of different ratings are
physically interchangeable, but only fuses of
the proper rating should be used. Replacing a
fuse with one of a higher or lower value than
specified is not recommended. Each electrical
circuit needs a specific amount of protection.
The amperage value of each fuse is moulded
into the fuse body.
If the new fuse immediately fails, don’t
renew it again until the cause of the problem
is isolated and corrected. In most cases, the
cause will be a short-circuit in the wiring
caused by a broken or deteriorated wire.
4 Relays- general information
1
Several electrical accessories in the vehicle
use relays to transmit the electrical signal to
the component. If the relay is defective, thatcomponent will not operate properly. Relays
are electrically-operated switches, which are
often used in circuits drawing high levels of
current, or where more complex switching
arrangements are required.
The various relays are grouped together for
convenience in several locations under the
dash and in the engine compartment (see
accompanying illustration and illus-
tration 3.1).
If a faulty relay is suspected, it can be
removed and tested by a dealer or qualified
automotive electrician. No overhaul is
possible. Like fuses, defective relays must be
replaced with the correct type; some relays
look identical, but perform very different
functions.
5 Direction indicator/hazard
warning flasher unit- check
and renewal
2
Warning: Some later models are
equipped with an airbag or
Supplemental Restraint System
(SRS). To avoid possible damage
to this system, the manufacturer
recommends that, on airbag-equipped
models, the following procedure should be
left to a dealer service department, or
other specialist, because of the special
tools and techniques required. There is a
risk of injury if the airbag is accidentally
triggered.
1The direction indicator/hazard flasher unit is
a small canister- or box-shaped unit located
in the wiring harness on or near the steering
column. Access is gained by removing the
steering column shrouds (see illustration).
2When the flasher unit is functioning
properly, a regular clicking noise can be heard
from it when the indicators or hazard flashers
are switched on. If the direction indicators fail
on one side or the other, and the flasher unit
does not make its characteristic clicking
sound, a faulty direction indicator bulb is
indicated.
3If both direction indicators fail to blink, the
problem may be due to a blown fuse, a faulty
flasher unit, a broken switch or a loose or open
connection. If a quick check of the fusebox
12•2 Body electrical systems
4.2 Engine compartment relays3.1 The fusebox is located in the engine
compartment under a cover - the box also
includes several relays
Page 202 of 228

REF•1
REF
MOT Test Checks
This is a guide to getting your vehicle through the MOT test.
Obviously it will not be possible to examine the vehicle to the same
standard as the professional MOT tester. However, working through
the following checks will enable you to identify any problem areas
before submitting the vehicle for the test.
Where a testable component is in borderline condition, the tester
has discretion in deciding whether to pass or fail it. The basis of such
discretion is whether the tester would be happy for a close relative or
friend to use the vehicle with the component in that condition. If the
vehicle presented is clean and evidently well cared for, the tester may
be more inclined to pass a borderline component than if the vehicle is
scruffy and apparently neglected.
It has only been possible to summarise the test requirements here,
based on the regulations in force at the time of printing. Test standards
are becoming increasingly stringent, although there are some
exemptions for older vehicles. For full details obtain a copy of the Haynes
publication Pass the MOT! (available from stockists of Haynes manuals).
An assistant will be needed to help carry out some of these checks.
The checks have been sub-divided into four categories, as follows:
HandbrakeMTest the operation of the handbrake.
Excessive travel (too many clicks) indicates
incorrect brake or cable adjustment.
MCheck that the handbrake cannot be
released by tapping the lever sideways. Check
the security of the lever mountings.
Footbrake
MDepress the brake pedal and check that it
does not creep down to the floor, indicating a
master cylinder fault. Release the pedal, wait
a few seconds, then depress it again. If the
pedal travels nearly to the floor before firm
resistance is felt, brake adjustment or repair is
necessary. If the pedal feels spongy, there is
air in the hydraulic system which must be
removed by bleeding.MCheck that the brake pedal is secure and in
good condition. Check also for signs of fluid
leaks on the pedal, floor or carpets, which
would indicate failed seals in the brake master
cylinder.
MCheck the servo unit (when applicable) by
operating the brake pedal several times, then
keeping the pedal depressed and starting the
engine. As the engine starts, the pedal will
move down slightly. If not, the vacuum hose or
the servo itself may be faulty.
Steering wheel and column
MExamine the steering wheel for fractures or
looseness of the hub, spokes or rim.
MMove the steering wheel from side to side
and then up and down. Check that the
steering wheel is not loose on the column,
indicating wear or a loose retaining nut.
Continue moving the steering wheel as before,
but also turn it slightly from left to right.
MCheck that the steering wheel is not loose
on the column, and that there is no abnormalmovement of the steering wheel, indicating
wear in the column support bearings or
couplings.
Windscreen and mirrors
MThe windscreen must be free of cracks or
other significant damage within the driver’s
field of view. (Small stone chips are
acceptable.) Rear view mirrors must be
secure, intact, and capable of being adjusted.
1Checks carried out
FROM THE DRIVER’S SEAT
1Checks carried out
FROM THE DRIVER’S
SEAT2Checks carried out
WITH THE VEHICLE
ON THE GROUND3Checks carried out
WITH THE VEHICLE
RAISED AND THE
WHEELS FREE TO
TURN4Checks carried out on
YOUR VEHICLE’S
EXHAUST EMISSION
SYSTEM
Page 203 of 228
REF•2MOT Test Checks
Seat belts and seats
Note: The following checks are applicable to
all seat belts, front and rear.
MExamine the webbing of all the belts
(including rear belts if fitted) for cuts, serious
fraying or deterioration. Fasten and unfasten
each belt to check the buckles. If applicable,
check the retracting mechanism. Check the
security of all seat belt mountings accessible
from inside the vehicle.
MThe front seats themselves must be
securely attached and the backrests must
lock in the upright position.
Doors
MBoth front doors must be able to be opened
and closed from outside and inside, and must
latch securely when closed.
Vehicle identification
MNumber plates must be in good condition,
secure and legible, with letters and numbers
correctly spaced – spacing at (A) should be
twice that at (B).
MThe VIN plate and/or homologation plate
must be legible.
Electrical equipment
MSwitch on the ignition and check the
operation of the horn.
MCheck the windscreen washers and wipers,
examining the wiper blades; renew damaged
or perished blades. Also check the operation
of the stop-lights.
MCheck the operation of the sidelights and
number plate lights. The lenses and reflectors
must be secure, clean and undamaged.
MCheck the operation and alignment of the
headlights. The headlight reflectors must not
be tarnished and the lenses must be
undamaged.
MSwitch on the ignition and check the
operation of the direction indicators (including
the instrument panel tell-tale) and the hazard
warning lights. Operation of the sidelights and
stop-lights must not affect the indicators - if it
does, the cause is usually a bad earth at the
rear light cluster.
MCheck the operation of the rear foglight(s),
including the warning light on the instrument
panel or in the switch.
Footbrake
MExamine the master cylinder, brake pipes
and servo unit for leaks, loose mountings,
corrosion or other damage.
MThe fluid reservoir must be secure and the
fluid level must be between the upper (A) and
lower (B) markings.MInspect both front brake flexible hoses for
cracks or deterioration of the rubber. Turn the
steering from lock to lock, and ensure that the
hoses do not contact the wheel, tyre, or any
part of the steering or suspension mechanism.
With the brake pedal firmly depressed, check
the hoses for bulges or leaks under pressure.
Steering and suspension
MHave your assistant turn the steering wheel
from side to side slightly, up to the point where
the steering gear just begins to transmit this
movement to the roadwheels. Check for
excessive free play between the steering
wheel and the steering gear, indicating wear or
insecurity of the steering column joints, the
column-to-steering gear coupling, or the
steering gear itself.
MHave your assistant turn the steering wheel
more vigorously in each direction, so that the
roadwheels just begin to turn. As this is done,
examine all the steering joints, linkages,
fittings and attachments. Renew any
component that shows signs of wear or
damage. On vehicles with power steering,
check the security and condition of the
steering pump, drivebelt and hoses.
MCheck that the vehicle is standing level,
and at approximately the correct ride height.
Shock absorbers
MDepress each corner of the vehicle in turn,
then release it. The vehicle should rise and
then settle in its normal position. If the vehicle
continues to rise and fall, the shock absorber
is defective. A shock absorber which has
seized will also cause the vehicle to fail.
2Checks carried out
WITH THE VEHICLE ON THE
GROUND
Page 204 of 228
REF•3
REF
MOT Test Checks
Exhaust system
MStart the engine. With your assistant
holding a rag over the tailpipe, check the
entire system for leaks. Repair or renew
leaking sections.
Jack up the front and rear of the vehicle,
and securely support it on axle stands.
Position the stands clear of the suspension
assemblies. Ensure that the wheels are
clear of the ground and that the steering
can be turned from lock to lock.
Steering mechanism
MHave your assistant turn the steering from
lock to lock. Check that the steering turns
smoothly, and that no part of the steering
mechanism, including a wheel or tyre, fouls
any brake hose or pipe or any part of the body
structure.
MExamine the steering rack rubber gaiters
for damage or insecurity of the retaining clips.
If power steering is fitted, check for signs of
damage or leakage of the fluid hoses, pipes or
connections. Also check for excessive
stiffness or binding of the steering, a missing
split pin or locking device, or severe corrosion
of the body structure within 30 cm of any
steering component attachment point.
Front and rear suspension and
wheel bearings
MStarting at the front right-hand side, grasp
the roadwheel at the 3 o’clock and 9 o’clock
positions and shake it vigorously. Check for
free play or insecurity at the wheel bearings,
suspension balljoints, or suspension mount-
ings, pivots and attachments.
MNow grasp the wheel at the 12 o’clock and
6 o’clock positions and repeat the previous
inspection. Spin the wheel, and check for
roughness or tightness of the front wheel
bearing.
MIf excess free play is suspected at a
component pivot point, this can be confirmed
by using a large screwdriver or similar tool and
levering between the mounting and the
component attachment. This will confirm
whether the wear is in the pivot bush, its
retaining bolt, or in the mounting itself (the bolt
holes can often become elongated).
MCarry out all the above checks at the other
front wheel, and then at both rear wheels.
Springs and shock absorbers
MExamine the suspension struts (when
applicable) for serious fluid leakage, corrosion,
or damage to the casing. Also check the
security of the mounting points.
MIf coil springs are fitted, check that the
spring ends locate in their seats, and that the
spring is not corroded, cracked or broken.
MIf leaf springs are fitted, check that all
leaves are intact, that the axle is securely
attached to each spring, and that there is no
deterioration of the spring eye mountings,
bushes, and shackles.MThe same general checks apply to vehicles
fitted with other suspension types, such as
torsion bars, hydraulic displacer units, etc.
Ensure that all mountings and attachments are
secure, that there are no signs of excessive
wear, corrosion or damage, and (on hydraulic
types) that there are no fluid leaks or damaged
pipes.
MInspect the shock absorbers for signs of
serious fluid leakage. Check for wear of the
mounting bushes or attachments, or damage
to the body of the unit.
Driveshafts
(fwd vehicles only)
MRotate each front wheel in turn and inspect
the constant velocity joint gaiters for splits or
damage. Also check that each driveshaft is
straight and undamaged.
Braking system
MIf possible without dismantling, check
brake pad wear and disc condition. Ensure
that the friction lining material has not worn
excessively, (A) and that the discs are not
fractured, pitted, scored or badly worn (B).
MExamine all the rigid brake pipes
underneath the vehicle, and the flexible
hose(s) at the rear. Look for corrosion, chafing
or insecurity of the pipes, and for signs of
bulging under pressure, chafing, splits or
deterioration of the flexible hoses.
MLook for signs of fluid leaks at the brake
calipers or on the brake backplates. Repair or
renew leaking components.
MSlowly spin each wheel, while your
assistant depresses and releases the
footbrake. Ensure that each brake is operating
and does not bind when the pedal is released.
3Checks carried out
WITH THE VEHICLE RAISED
AND THE WHEELS FREE TO
TURN
Page 215 of 228

REF•14Fault Finding
Brakes
Note:Before assuming that a brake problem exists, make sure that:
a) The tyres are in good condition and properly inflated (Chapter 1).
b) The wheel alignment (tracking) is correct (Chapter 10).
c) The vehicle is not loaded with weight in an unequal manner.
Vehicle pulls to one side during braking
m mIncorrect tyre pressures (Chapter 1).
m mWheel alignment (tracking) incorrect (Chapter 10)
m mUnmatched tyres on same axle.
m mRestricted brake lines or hoses (Chapter 9).
m mMalfunctioning caliper assembly (Chapter 9).
m mLoose suspension parts (Chapter 10).
m mLoose calipers (Chapter 9).
Noise (high-pitched squeal) when the brakes are
applied
m mFront and/or rear disc brake pads worn out. The noise comes from
the wear sensor rubbing against the disc. Renew the pads
immediately (Chapter 9).
Brake vibration (pedal pulsates)
Note:If the vehicle has ABS, it is normal for the brake pedal to pulsate
when the system is working.
m mExcessive lateral disc run-out (Chapter 9).
m mParallelism not within specifications (Chapter 9).
m mUneven pad wear - caused by caliper not sliding, due to improper
clearance or dirt (Chapter 9).
m mDefective disc (Chapter 9).
Excessive brake pedal travel
m
mPartial brake system failure (Chapter 9).
m mInsufficient fluid in master cylinder (Chapters 1 and 9).
m mAir trapped in system (Chapters 1 and 9).
Excessive pedal effort required to stop vehicle
m
mMalfunctioning brake servo unit (Chapter 9).
m mPartial system failure (Chapter 9).
m mExcessively-worn pads or shoes (Chapter 9).
m mCaliper piston stuck or sluggish (Chapter 9).
m mBrake pads contaminated with oil or grease (Chapter 9).
m mNew pads fitted and not yet seated. It will take a while for the new
material to seat against the disc.
Dragging brakes
m mMaster cylinder pistons not returning correctly (Chapter 9).
m mRestricted brakes lines or hoses (Chapters 1 and 9).
m mIncorrect handbrake adjustment (Chapter 9).
m mRear drum brake self-adjuster mechanism faulty (when applicable)
(Chapter 9).
Grabbing or uneven braking action
m mMalfunction of brake servo unit (Chapter 9).
m mBinding brake pedal mechanism (Chapter 9).
Brake pedal feels “spongy” when depressed
m
mAir in hydraulic lines (Chapter 9).
m mMaster cylinder mounting bolts loose (Chapter 9).
m mMaster cylinder defective (Chapter 9).
Brake pedal travels to the floor with little resistance
m
mLittle or no fluid in the master cylinder reservoir, caused by leaking
caliper piston(s), loose, damaged or disconnected brake lines
(Chapter 9).
Handbrake does not hold
m mHandbrake linkage incorrectly adjusted (Chapter 9).
m mHandbrake shoe linings worn out or contaminated (Chapter 9).