handbrake BMW 3 SERIES 1990 E30 User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: BMW, Model Year: 1990, Model line: 3 SERIES, Model: BMW 3 SERIES 1990 E30Pages: 228, PDF Size: 7.04 MB
Page 129 of 228

9
General
Brake fluid type . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 1
Disc brakes
Minimum brake pad thickness . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 1
Brake disc minimum permissible thickness (wear limit)*
Front
3-Series
Solid discs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10.7 mm
Ventilated discs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20.0 mm
5-Series
Solid discs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10.0 mm
Ventilated discs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20.0 mm
Rear . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8.0 mm
Brake disc minimum thickness after machining
Front
3-Series
Solid discs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11.1 mm
Ventilated discs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20.4 mm
5-Series
Solid discs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10.4 mm
Ventilated discs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20.4 mm
Rear . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8.4 mm
Parallelism (difference between any two measurements) . . . . . . . . . . . 0.02 mm
Maximum disc run-out . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.2 mm
*Refer to marks cast into the disc (they supersede information printed here)
Brake pedal adjustments
Brake pedal/servo pushrod adjustment (A) (3-Series) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 125 mm
Brake pedal height (pedal-to-bulkhead distance)
3-Series
Left-hand-drive . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 235 mm
Right-hand-drive . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 273 mm
5-Series . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 245 mm
Stop-light switch adjustment (dimension A - see text) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5.0 mm to 6.0 mm
Handbrake
Handbrake shoe lining minimum thickness . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1.5 mm
Handbrake lever travel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5 to 8 clicks
Chapter 9 Braking system
Anti-lock brake system (ABS) - general information . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Brake check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 1
Brake disc - inspection, removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Brake fluid level check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 1
Brake hoses and lines - inspection and renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Brake hydraulic system - bleeding . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Brake pedal - adjustment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Brake vacuum servo - check, removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Disc brake caliper - removal, overhaul and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4Disc brake pads - renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Drum brake shoes - renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
General information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
Handbrake assembly - check, removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Handbrake - adjustment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Handbrake cable(s) - renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Hydraulic brake servo - description, removal and refitting . . . . . . . . 9
Master cylinder - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Stop-light switch - check and adjustment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
9•1
Easy,suitable for
novice with little
experienceFairly easy,suitable
for beginner with
some experienceFairly difficult,
suitable for competent
DIY mechanic
Difficult,suitable for
experienced DIY
mechanicVery difficult,
suitable for expert
DIY or professional
Degrees of difficulty
Specifications Contents
Page 130 of 228

Torque wrench settingsNm
Front disc brake caliper
Caliper guide (mounting) bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30 to 35
Caliper bracket-to-strut housing bolts
3-Series, E30 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 123
5-Series, E28 (“old-shape”) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 123
5-Series, E34 (“new-shape”) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 110
Rear disc brake caliper
Caliper guide (mounting) bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30 to 35
Carrier-to-trailing arm bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67
Brake hose-to-caliper fitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14 to 17
Master cylinder-to-brake servo nuts
3-Series . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
5-Series . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25 to 29
Brake servo mounting nuts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22 to 24
Hydraulic line-to-hydraulic brake servo threaded
fittings - 5-Series, E28 (“old-shape”) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Wheel bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 1
9•2 Braking system
1 General information
All 3-Series models, and 5-Series E28 (“old-
shape”) models, are equipped with front disc
brakes and either rear drum or rear disc
brakes. 5-Series E34 (“new-shape”) models
have disc brakes front and rear. Front and
rear brakes are self-adjusting on all models.
Some later models are equipped with an Anti-
lock Braking System (ABS); this is described
in Section 2.
Hydraulic system
The hydraulic system consists of two
separate circuits. The master cylinder has
separate reservoirs for the two circuits; in the
event of a leak or failure in one hydraulic
circuit, the other circuit will remain operative.
Brake servo
The vacuum brake servo, utilising engine
manifold vacuum and atmospheric pressure
to provide assistance to the hydraulically
operated brakes, is mounted on the bulkhead
in the engine compartment.
A hydraulic brake servo system is used on
5-Series E28 models. This system uses
hydraulic pressure from the power steering
pump to assist braking.
Handbrake
The handbrake operates the rear brakes,
and is cable-operated via a lever mounted in
the centre console. The handbrake assembly
on rear drum brake models is part of the rear
drum brake assembly, and is self-adjusting.
On rear disc brake models, the handbrake
uses a pair of brake shoes located inside the
centre portion of the rear brake disc, and is
manually-adjusted.
Brake pad wear warning system
The brake pad wear warning system is
linked to a red warning light in the instrumentcluster, which comes on when the brake pads
have worn down to the point at which they
require renewal. DO NOT ignore this reminder.
If you don’t renew the pads shortly after the
brake pad wear warning light comes on, the
brake discs will be damaged.
On some models, the brake pad wear
warning system also includes an early
warning light that comes on only when the
brake pedal is depressed, letting you know in
advance that the pads need to be renewed.
The wear sensor is attached to the brake
pads. The sensor is located at the left front
wheel; on some models, there is another
sensor at the right rear wheel. The wear
sensor is part of a closed circuit. Once the
pads wear down to the point at which they’re
flush with the sensor, the disc grinds away the
side of the sensor facing the disc. Thus, the
wire inside the sensor is broken, and the red
light on the instrument panel comes on.
Always check the sensor(s) when renewing
the pads. If you change the pads before the
warning light comes on, the sensor(s) may still
be good; once the light has come on, renew
the sensor.
Service
After completing any operation involving
dismantling of any part of the brake system,
always test drive the vehicle to check for
proper braking performance before resuming
normal driving. When testing the brakes, try to
select a clean, dry, road with no camber (ie as
flat as possible) and with no other traffic.
Conditions other than these can lead to
inaccurate test results.
Test the brakes at various speeds with both
light and heavy pedal pressure. The vehicle
should stop evenly, without pulling to one side
or the other. Avoid locking the brakes,
because this slides the tyres and diminishes
braking efficiency and control of the vehicle.
Tyres, vehicle load and wheel alignment are
factors which also affect braking
performance.
2 Anti-lock Braking system
(ABS)- general information
The Anti-lock Braking System is designed
to maintain vehicle control, directional stability
and optimum deceleration under severe
braking conditions on most road surfaces. It
does so by monitoring the rotational speed of
each wheel and controlling the brake line
pressure to each wheel during braking. This
prevents the wheels from locking up.
The ABS system has three main
components - the wheel speed sensors, the
electronic control unit, and the hydraulic
control unit. The sensors - one at each wheel
since 1985, but at both front wheels and one
at the rear differential on earlier models - send
a variable voltage signal to the control unit,
which monitors these signals, compares them
to its program information, and determines
whether a wheel is about to lock up. When a
wheel is about to lock up, the control unit
signals the hydraulic unit to reduce hydraulic
pressure (or not increase it further) at that
wheel’s brake caliper. Pressure modulation is
handled by electrically-operated solenoid
valves.
If a problem develops within the system, an
“ABS” warning light will glow on the
dashboard. Sometimes, a visual inspection of
the ABS system can help you locate the
problem. Carefully inspect the ABS wiring
harness. Pay particularly close attention to the
harness and connections near each wheel.
Look for signs of chafing and other damage
caused by incorrectly-routed wires. If a wheel
sensor harness is damaged, the sensor
should be renewed (the harness and sensor
are integral).
Warning: DO NOT try to repair an
ABS wiring harness. The ABS
system is sensitive to even the
smallest changes in resistance. Repairing
the harness could alter resistance values
Page 134 of 228
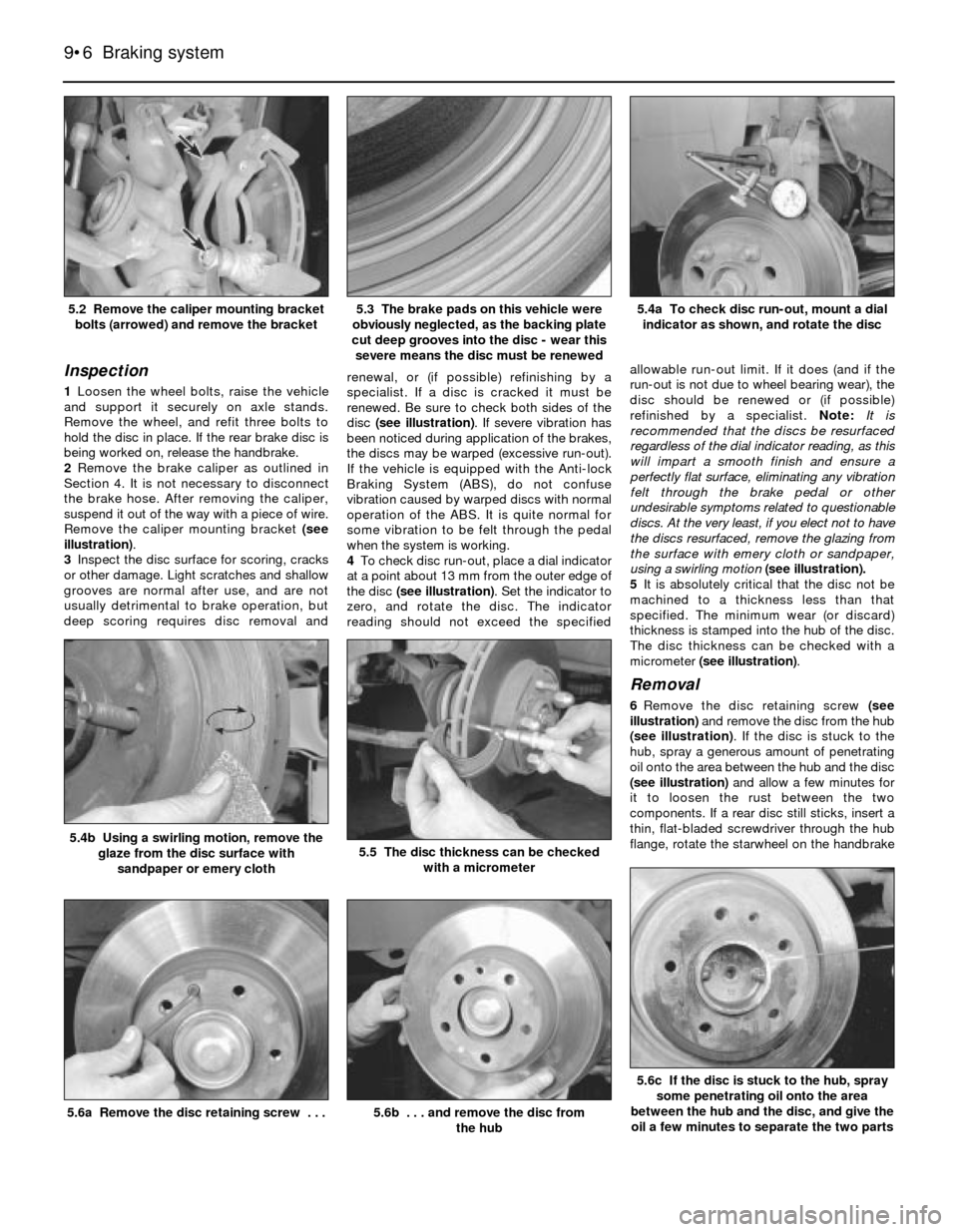
Inspection
1Loosen the wheel bolts, raise the vehicle
and support it securely on axle stands.
Remove the wheel, and refit three bolts to
hold the disc in place. If the rear brake disc is
being worked on, release the handbrake.
2Remove the brake caliper as outlined in
Section 4. It is not necessary to disconnect
the brake hose. After removing the caliper,
suspend it out of the way with a piece of wire.
Remove the caliper mounting bracket (see
illustration).
3Inspect the disc surface for scoring, cracks
or other damage. Light scratches and shallow
grooves are normal after use, and are not
usually detrimental to brake operation, but
deep scoring requires disc removal andrenewal, or (if possible) refinishing by a
specialist. If a disc is cracked it must be
renewed. Be sure to check both sides of the
disc (see illustration). If severe vibration has
been noticed during application of the brakes,
the discs may be warped (excessive run-out).
If the vehicle is equipped with the Anti-lock
Braking System (ABS), do not confuse
vibration caused by warped discs with normal
operation of the ABS. It is quite normal for
some vibration to be felt through the pedal
when the system is working.
4To check disc run-out, place a dial indicator
at a point about 13 mm from the outer edge of
the disc (see illustration). Set the indicator to
zero, and rotate the disc. The indicator
reading should not exceed the specifiedallowable run-out limit. If it does (and if the
run-out is not due to wheel bearing wear), the
disc should be renewed or (if possible)
refinished by a specialist. Note:It is
recommended that the discs be resurfaced
regardless of the dial indicator reading, as this
will impart a smooth finish and ensure a
perfectly flat surface, eliminating any vibration
felt through the brake pedal or other
undesirable symptoms related to questionable
discs. At the very least, if you elect not to have
the discs resurfaced, remove the glazing from
the surface with emery cloth or sandpaper,
using a swirling motion (see illustration).
5It is absolutely critical that the disc not be
machined to a thickness less than that
specified. The minimum wear (or discard)
thickness is stamped into the hub of the disc.
The disc thickness can be checked with a
micrometer (see illustration).
Removal
6Remove the disc retaining screw (see
illustration) and remove the disc from the hub
(see illustration). If the disc is stuck to the
hub, spray a generous amount of penetrating
oil onto the area between the hub and the disc
(see illustration)and allow a few minutes for
it to loosen the rust between the two
components. If a rear disc still sticks, insert a
thin, flat-bladed screwdriver through the hub
flange, rotate the starwheel on the handbrake
9•6 Braking system
5.6c If the disc is stuck to the hub, spray
some penetrating oil onto the area
between the hub and the disc, and give the
oil a few minutes to separate the two parts
5.6b . . . and remove the disc from
the hub5.6a Remove the disc retaining screw . . .
5.5 The disc thickness can be checked
with a micrometer5.4b Using a swirling motion, remove the
glaze from the disc surface with
sandpaper or emery cloth
5.4a To check disc run-out, mount a dial
indicator as shown, and rotate the disc5.3 The brake pads on this vehicle were
obviously neglected, as the backing plate
cut deep grooves into the disc - wear this
severe means the disc must be renewed5.2 Remove the caliper mounting bracket
bolts (arrowed) and remove the bracket
Page 135 of 228
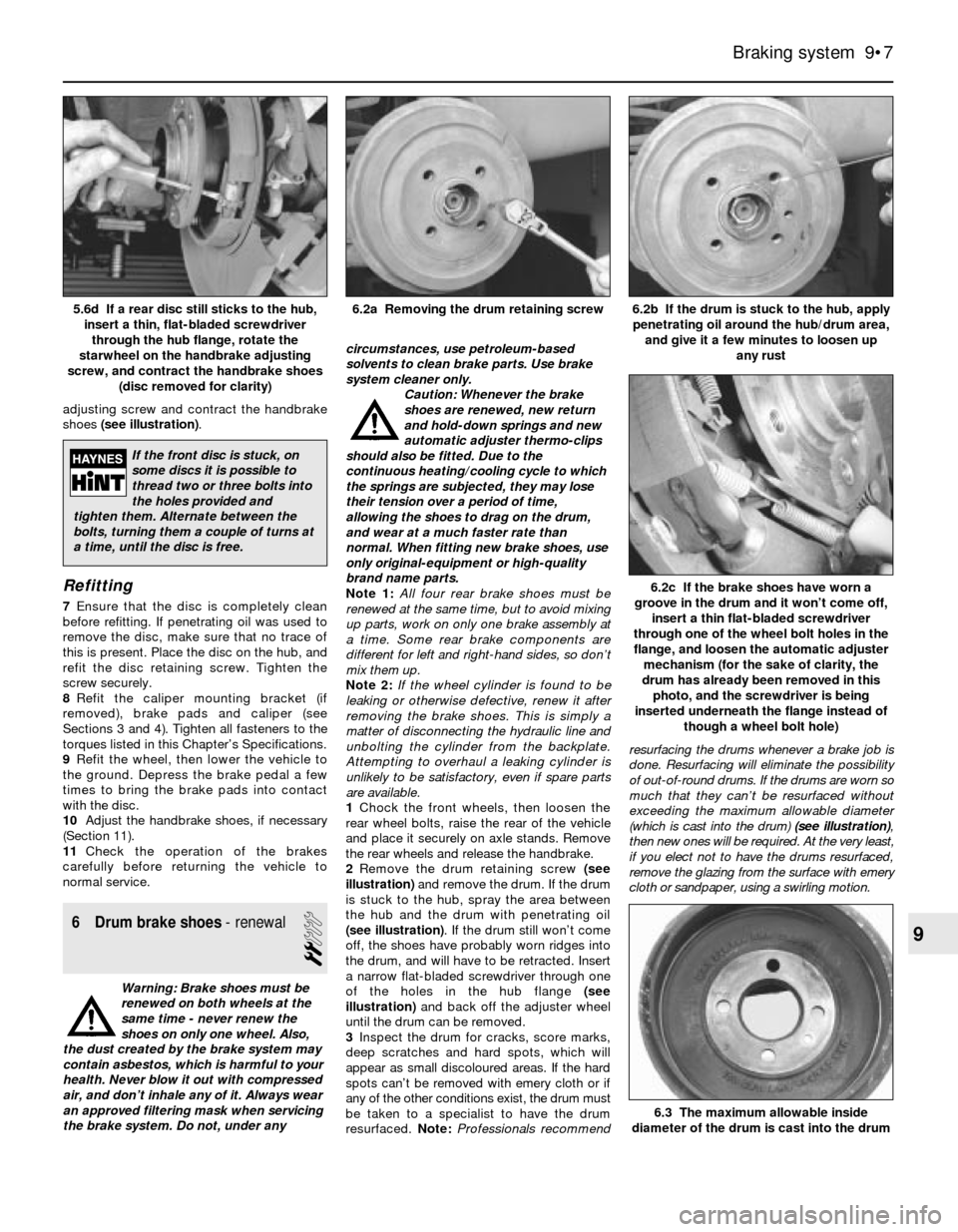
adjusting screw and contract the handbrake
shoes (see illustration).
Refitting
7Ensure that the disc is completely clean
before refitting. If penetrating oil was used to
remove the disc, make sure that no trace of
this is present. Place the disc on the hub, and
refit the disc retaining screw. Tighten the
screw securely.
8Refit the caliper mounting bracket (if
removed), brake pads and caliper (see
Sections 3 and 4). Tighten all fasteners to the
torques listed in this Chapter’s Specifications.
9Refit the wheel, then lower the vehicle to
the ground. Depress the brake pedal a few
times to bring the brake pads into contact
with the disc.
10Adjust the handbrake shoes, if necessary
(Section 11).
11Check the operation of the brakes
carefully before returning the vehicle to
normal service.
6 Drum brake shoes- renewal
2
Warning: Brake shoes must be
renewed on both wheels at the
same time - never renew the
shoes on only one wheel. Also,
the dust created by the brake system may
contain asbestos, which is harmful to your
health. Never blow it out with compressed
air, and don’t inhale any of it. Always wear
an approved filtering mask when servicing
the brake system. Do not, under anycircumstances, use petroleum-based
solvents to clean brake parts. Use brake
system cleaner only.
Caution: Whenever the brake
shoes are renewed, new return
and hold-down springs and new
automatic adjuster thermo-clips
should also be fitted. Due to the
continuous heating/cooling cycle to which
the springs are subjected, they may lose
their tension over a period of time,
allowing the shoes to drag on the drum,
and wear at a much faster rate than
normal. When fitting new brake shoes, use
only original-equipment or high-quality
brand name parts.
Note 1:All four rear brake shoes must be
renewed at the same time, but to avoid mixing
up parts, work on only one brake assembly at
a time. Some rear brake components are
different for left and right-hand sides, so don’t
mix them up.
Note 2:If the wheel cylinder is found to be
leaking or otherwise defective, renew it after
removing the brake shoes. This is simply a
matter of disconnecting the hydraulic line and
unbolting the cylinder from the backplate.
Attempting to overhaul a leaking cylinder is
unlikely to be satisfactory, even if spare parts
are available.
1Chock the front wheels, then loosen the
rear wheel bolts, raise the rear of the vehicle
and place it securely on axle stands. Remove
the rear wheels and release the handbrake.
2Remove the drum retaining screw (see
illustration)and remove the drum. If the drum
is stuck to the hub, spray the area between
the hub and the drum with penetrating oil
(see illustration). If the drum still won’t come
off, the shoes have probably worn ridges into
the drum, and will have to be retracted. Insert
a narrow flat-bladed screwdriver through one
of the holes in the hub flange (see
illustration)and back off the adjuster wheel
until the drum can be removed.
3Inspect the drum for cracks, score marks,
deep scratches and hard spots, which will
appear as small discoloured areas. If the hard
spots can’t be removed with emery cloth or if
any of the other conditions exist, the drum must
be taken to a specialist to have the drum
resurfaced. Note:Professionals recommendresurfacing the drums whenever a brake job is
done. Resurfacing will eliminate the possibility
of out-of-round drums. If the drums are worn so
much that they can’t be resurfaced without
exceeding the maximum allowable diameter
(which is cast into the drum) (see illustration),
then new ones will be required. At the very least,
if you elect not to have the drums resurfaced,
remove the glazing from the surface with emery
cloth or sandpaper, using a swirling motion.
Braking system 9•7
6.2b If the drum is stuck to the hub, apply
penetrating oil around the hub/drum area,
and give it a few minutes to loosen up
any rust6.2a Removing the drum retaining screw5.6d If a rear disc still sticks to the hub,
insert a thin, flat-bladed screwdriver
through the hub flange, rotate the
starwheel on the handbrake adjusting
screw, and contract the handbrake shoes
(disc removed for clarity)
6.3 The maximum allowable inside
diameter of the drum is cast into the drum
6.2c If the brake shoes have worn a
groove in the drum and it won’t come off,
insert a thin flat-bladed screwdriver
through one of the wheel bolt holes in the
flange, and loosen the automatic adjuster
mechanism (for the sake of clarity, the
drum has already been removed in this
photo, and the screwdriver is being
inserted underneath the flange instead of
though a wheel bolt hole)
9
If the front disc is stuck, on
some discs it is possible to
thread two or three bolts into
the holes provided and
tighten them. Alternate between the
bolts, turning them a couple of turns at
a time, until the disc is free.
Page 136 of 228
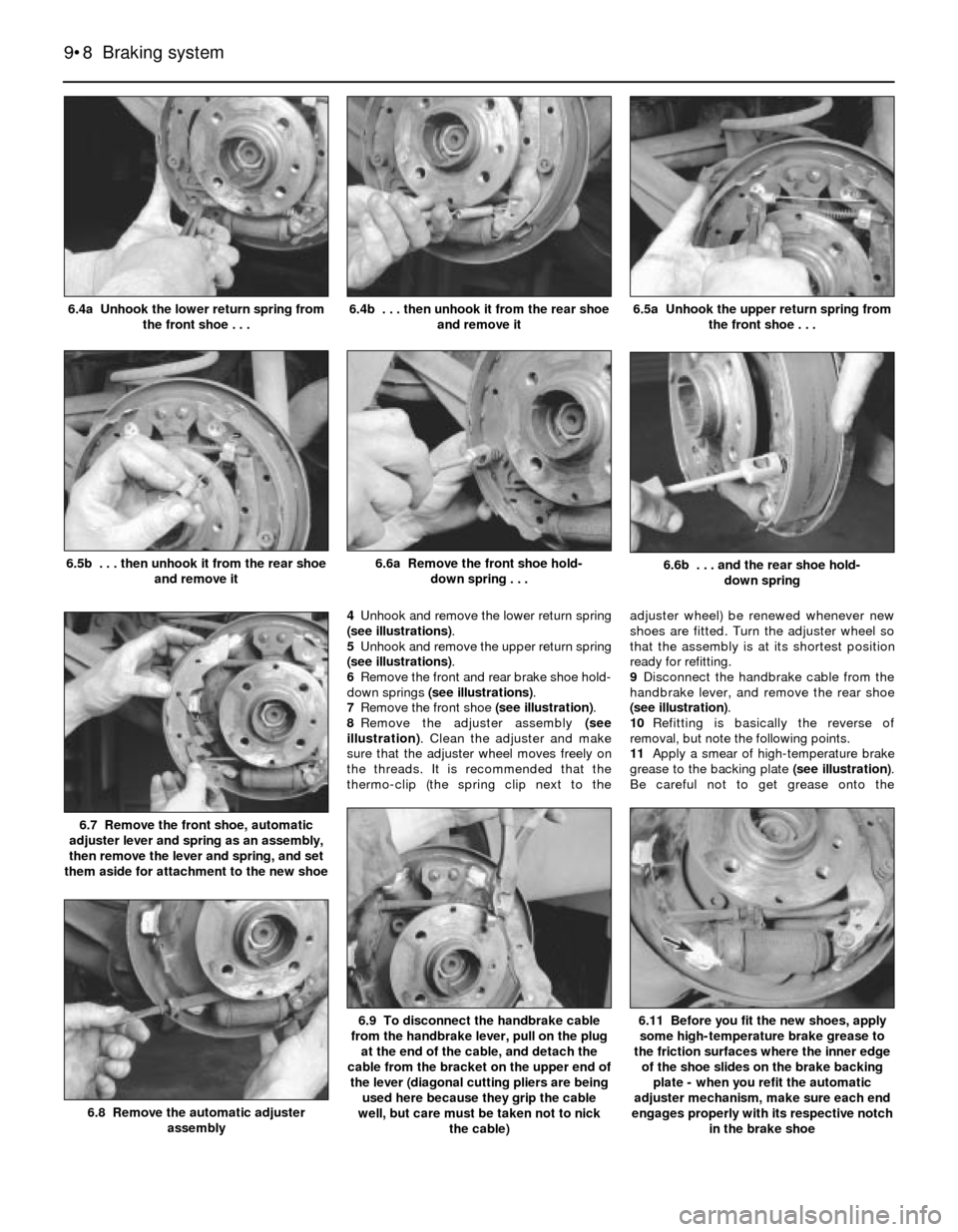
4Unhook and remove the lower return spring
(see illustrations).
5Unhook and remove the upper return spring
(see illustrations).
6Remove the front and rear brake shoe hold-
down springs (see illustrations).
7Remove the front shoe (see illustration).
8Remove the adjuster assembly (see
illustration). Clean the adjuster and make
sure that the adjuster wheel moves freely on
the threads. It is recommended that the
thermo-clip (the spring clip next to theadjuster wheel) be renewed whenever new
shoes are fitted. Turn the adjuster wheel so
that the assembly is at its shortest position
ready for refitting.
9Disconnect the handbrake cable from the
handbrake lever, and remove the rear shoe
(see illustration).
10Refitting is basically the reverse of
removal, but note the following points.
11Apply a smear of high-temperature brake
grease to the backing plate (see illustration).
Be careful not to get grease onto the
9•8 Braking system
6.11 Before you fit the new shoes, apply
some high-temperature brake grease to
the friction surfaces where the inner edge
of the shoe slides on the brake backing
plate - when you refit the automatic
adjuster mechanism, make sure each end
engages properly with its respective notch
in the brake shoe6.9 To disconnect the handbrake cable
from the handbrake lever, pull on the plug
at the end of the cable, and detach the
cable from the bracket on the upper end of
the lever (diagonal cutting pliers are being
used here because they grip the cable
well, but care must be taken not to nick
the cable)
6.8 Remove the automatic adjuster
assembly
6.7 Remove the front shoe, automatic
adjuster lever and spring as an assembly,
then remove the lever and spring, and set
them aside for attachment to the new shoe
6.6b . . . and the rear shoe hold-
down spring6.6a Remove the front shoe hold-
down spring . . .6.5b . . . then unhook it from the rear shoe
and remove it
6.5a Unhook the upper return spring from
the front shoe . . .6.4b . . . then unhook it from the rear shoe
and remove it6.4a Unhook the lower return spring from
the front shoe . . .
Page 137 of 228
friction surfaces of the brake shoes or
drums.
12Make sure the adjuster assembly is
properly engaged with its respective notch in
the handbrake lever.
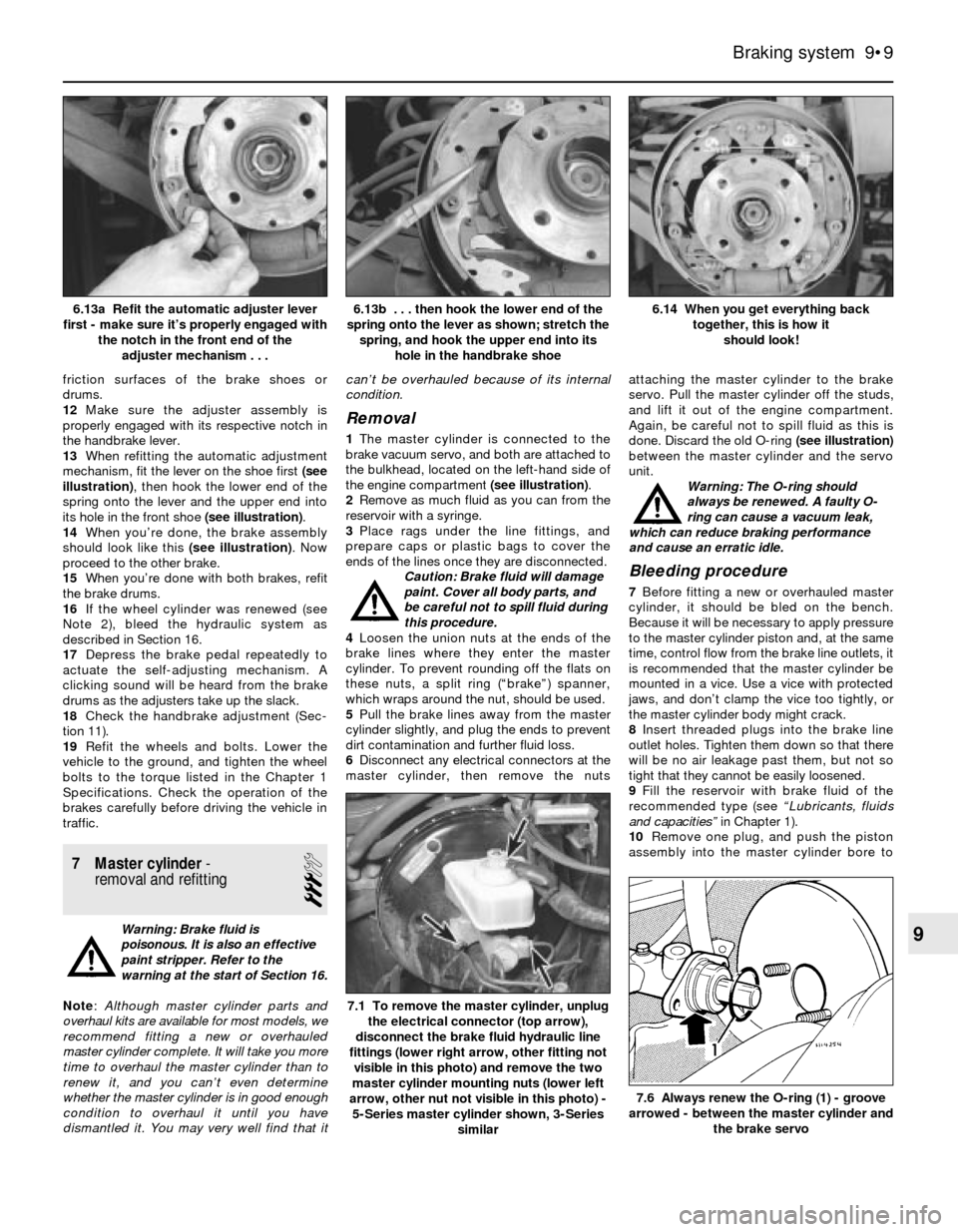
13When refitting the automatic adjustment
mechanism, fit the lever on the shoe first (see
illustration), then hook the lower end of the
spring onto the lever and the upper end into
its hole in the front shoe (see illustration).
14When you’re done, the brake assembly
should look like this (see illustration). Now
proceed to the other brake.
15When you’re done with both brakes, refit
the brake drums.
16If the wheel cylinder was renewed (see
Note 2), bleed the hydraulic system as
described in Section 16.
17Depress the brake pedal repeatedly to
actuate the self-adjusting mechanism. A
clicking sound will be heard from the brake
drums as the adjusters take up the slack.
18Check the handbrake adjustment (Sec-
tion 11).
19Refit the wheels and bolts. Lower the
vehicle to the ground, and tighten the wheel
bolts to the torque listed in the Chapter 1
Specifications. Check the operation of the
brakes carefully before driving the vehicle in
traffic.
7 Master cylinder-
removal and refitting
3
Warning: Brake fluid is
poisonous. It is also an effective
paint stripper. Refer to the
warning at the start of Section 16.
Note: Although master cylinder parts and
overhaul kits are available for most models, we
recommend fitting a new or overhauled
master cylinder complete. It will take you more
time to overhaul the master cylinder than to
renew it, and you can’t even determine
whether the master cylinder is in good enough
condition to overhaul it until you have
dismantled it. You may very well find that itcan’t be overhauled because of its internal
condition.
Removal
1The master cylinder is connected to the
brake vacuum servo, and both are attached to
the bulkhead, located on the left-hand side of
the engine compartment (see illustration).
2Remove as much fluid as you can from the
reservoir with a syringe.
3Place rags under the line fittings, and
prepare caps or plastic bags to cover the
ends of the lines once they are disconnected.
Caution: Brake fluid will damage
paint. Cover all body parts, and
be careful not to spill fluid during
this procedure.
4Loosen the union nuts at the ends of the
brake lines where they enter the master
cylinder. To prevent rounding off the flats on
these nuts, a split ring (“brake”) spanner,
which wraps around the nut, should be used.
5Pull the brake lines away from the master
cylinder slightly, and plug the ends to prevent
dirt contamination and further fluid loss.
6Disconnect any electrical connectors at the
master cylinder, then remove the nutsattaching the master cylinder to the brake
servo. Pull the master cylinder off the studs,
and lift it out of the engine compartment.
Again, be careful not to spill fluid as this is
done. Discard the old O-ring (see illustration)
between the master cylinder and the servo
unit.
Warning: The O-ring should
always be renewed. A faulty O-
ring can cause a vacuum leak,
which can reduce braking performance
and cause an erratic idle.
Bleeding procedure
7Before fitting a new or overhauled master
cylinder, it should be bled on the bench.
Because it will be necessary to apply pressure
to the master cylinder piston and, at the same
time, control flow from the brake line outlets, it
is recommended that the master cylinder be
mounted in a vice. Use a vice with protected
jaws, and don’t clamp the vice too tightly, or
the master cylinder body might crack.
8Insert threaded plugs into the brake line
outlet holes. Tighten them down so that there
will be no air leakage past them, but not so
tight that they cannot be easily loosened.
9Fill the reservoir with brake fluid of the
recommended type (see “Lubricants, fluids
and capacities” in Chapter 1).
10Remove one plug, and push the piston
assembly into the master cylinder bore to
Braking system 9•9
6.14 When you get everything back
together, this is how it
should look! 6.13b . . . then hook the lower end of the
spring onto the lever as shown; stretch the
spring, and hook the upper end into its
hole in the handbrake shoe6.13a Refit the automatic adjuster lever
first - make sure it’s properly engaged with
the notch in the front end of the
adjuster mechanism . . .
7.6 Always renew the O-ring (1) - groove
arrowed - between the master cylinder and
the brake servo
7.1 To remove the master cylinder, unplug
the electrical connector (top arrow),
disconnect the brake fluid hydraulic line
fittings (lower right arrow, other fitting not
visible in this photo) and remove the two
master cylinder mounting nuts (lower left
arrow, other nut not visible in this photo) -
5-Series master cylinder shown, 3-Series
similar
9
Page 139 of 228
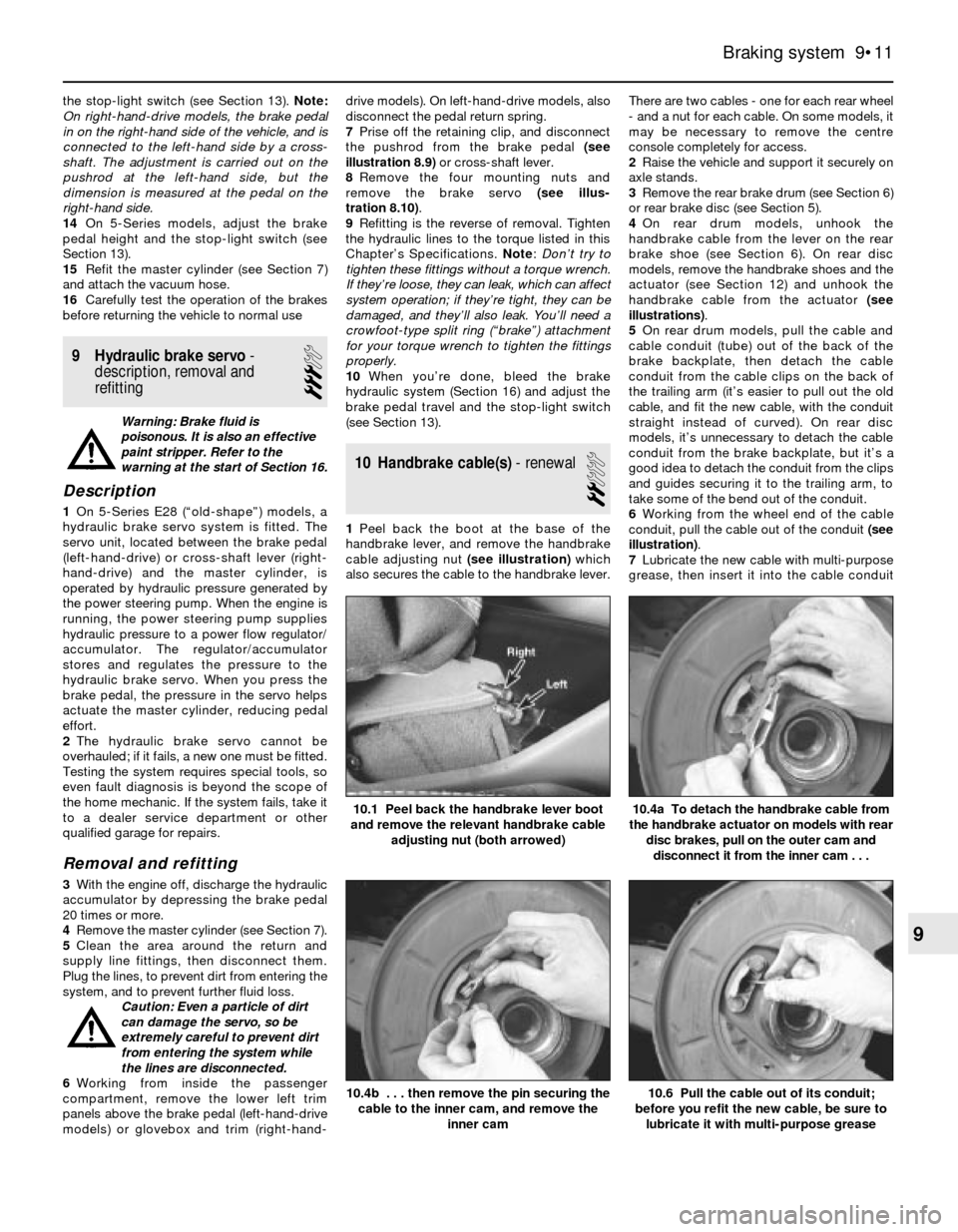
the stop-light switch (see Section 13). Note:
On right-hand-drive models, the brake pedal
in on the right-hand side of the vehicle, and is
connected to the left-hand side by a cross-
shaft. The adjustment is carried out on the
pushrod at the left-hand side, but the
dimension is measured at the pedal on the
right-hand side.
14On 5-Series models, adjust the brake
pedal height and the stop-light switch (see
Section 13).
15Refit the master cylinder (see Section 7)
and attach the vacuum hose.
16Carefully test the operation of the brakes
before returning the vehicle to normal use
9 Hydraulic brake servo-
description, removal and
refitting
3
Warning: Brake fluid is
poisonous. It is also an effective
paint stripper. Refer to the
warning at the start of Section 16.
Description
1On 5-Series E28 (“old-shape”) models, a
hydraulic brake servo system is fitted. The
servo unit, located between the brake pedal
(left-hand-drive) or cross-shaft lever (right-
hand-drive) and the master cylinder, is
operated by hydraulic pressure generated by
the power steering pump. When the engine is
running, the power steering pump supplies
hydraulic pressure to a power flow regulator/
accumulator. The regulator/accumulator
stores and regulates the pressure to the
hydraulic brake servo. When you press the
brake pedal, the pressure in the servo helps
actuate the master cylinder, reducing pedal
effort.
2The hydraulic brake servo cannot be
overhauled; if it fails, a new one must be fitted.
Testing the system requires special tools, so
even fault diagnosis is beyond the scope of
the home mechanic. If the system fails, take it
to a dealer service department or other
qualified garage for repairs.
Removal and refitting
3With the engine off, discharge the hydraulic
accumulator by depressing the brake pedal
20 times or more.
4Remove the master cylinder (see Section 7).
5Clean the area around the return and
supply line fittings, then disconnect them.
Plug the lines, to prevent dirt from entering the
system, and to prevent further fluid loss.
Caution: Even a particle of dirt
can damage the servo, so be
extremely careful to prevent dirt
from entering the system while
the lines are disconnected.
6Working from inside the passenger
compartment, remove the lower left trim
panels above the brake pedal (left-hand-drive
models) or glovebox and trim (right-hand-drive models). On left-hand-drive models, also
disconnect the pedal return spring.
7Prise off the retaining clip, and disconnect
the pushrod from the brake pedal (see
illustration 8.9) or cross-shaft lever.
8Remove the four mounting nuts and
remove the brake servo (see illus-
tration 8.10).
9Refitting is the reverse of removal. Tighten
the hydraulic lines to the torque listed in this
Chapter’s Specifications. Note:Don’t try to
tighten these fittings without a torque wrench.
If they’re loose, they can leak, which can affect
system operation; if they’re tight, they can be
damaged, and they’ll also leak. You’ll need a
crowfoot-type split ring (“brake”) attachment
for your torque wrench to tighten the fittings
properly.
10When you’re done, bleed the brake
hydraulic system (Section 16) and adjust the
brake pedal travel and the stop-light switch
(see Section 13).
10 Handbrake cable(s)- renewal
2
1Peel back the boot at the base of the
handbrake lever, and remove the handbrake
cable adjusting nut (see illustration)which
also secures the cable to the handbrake lever.There are two cables - one for each rear wheel
- and a nut for each cable. On some models, it
may be necessary to remove the centre
console completely for access.
2Raise the vehicle and support it securely on
axle stands.
3Remove the rear brake drum (see Section 6)
or rear brake disc (see Section 5).
4On rear drum models, unhook the
handbrake cable from the lever on the rear
brake shoe (see Section 6). On rear disc
models, remove the handbrake shoes and the
actuator (see Section 12) and unhook the
handbrake cable from the actuator (see
illustrations).
5On rear drum models, pull the cable and
cable conduit (tube) out of the back of the
brake backplate, then detach the cable
conduit from the cable clips on the back of
the trailing arm (it’s easier to pull out the old
cable, and fit the new cable, with the conduit
straight instead of curved). On rear disc
models, it’s unnecessary to detach the cable
conduit from the brake backplate, but it’s a
good idea to detach the conduit from the clips
and guides securing it to the trailing arm, to
take some of the bend out of the conduit.
6Working from the wheel end of the cable
conduit, pull the cable out of the conduit (see
illustration).
7Lubricate the new cable with multi-purpose
grease, then insert it into the cable conduit
Braking system 9•11
10.1 Peel back the handbrake lever boot
and remove the relevant handbrake cable
adjusting nut (both arrowed)
10.6 Pull the cable out of its conduit;
before you refit the new cable, be sure to
lubricate it with multi-purpose grease10.4b . . . then remove the pin securing the
cable to the inner cam, and remove the
inner cam
10.4a To detach the handbrake cable from
the handbrake actuator on models with rear
disc brakes, pull on the outer cam and
disconnect it from the inner cam . . .
9
Page 140 of 228

and push it through until the forward end
comes out at the handbrake lever.
8Insert the cable conduit through the
backplate, and attach the rear end of the
cable to the handbrake lever (rear drum
models) or the actuator (rear disc models).
Make sure you don’t kink the cable while
connecting it.
9Refit the cable conduit to the clips on the
back of the trailing arm.
10On rear drum models, refit the brake
shoes and drum (see Section 6). On rear disc
models, refit the handbrake shoes and
actuator (see Section 12) and the rear brake
disc (see Section 5).
11Lower the vehicle, and refit the adjusting
nut at the handbrake lever. Adjust the
handbrake cable (see Section 11) and refit the
handbrake lever boot.
11 Handbrake- adjustment
2
Rear drum brake models
Note:Adjustment of the handbrake cable(s)
on models with rear drum brakes should only
be necessary when you renew a cable or
detach if from the rear brake assembly for
some reason. Failure of the handbrake system
to hold the vehicle usually indicates worn
brake shoes or a faulty self-adjusting
mechanism.
1Raise the rear of the vehicle, and place it
securely on axle stands.
2Fully release the handbrake lever, then
apply the brakes firmly several times with the
footbrake pedal.
3Pull the handbrake lever up five clicks.
4Tighten or loosen the adjusting nuts by
equal amounts until the rear brake shoes just
begin to drag on the brake drum. You should
feel the same amount of resistance at both
wheels when you rotate them.
5Release the handbrake lever, and verify that
the wheels rotate freely. If they don’t, re-
adjust them.
Rear disc brake models
Note: The handbrake system is not self-
adjusting on models with rear disc brakes. The
handbrake therefore requires periodic
adjustment to compensate for wear. It should
also be adjusted anytime either cable, brake
disc or handbrake assembly is renewed or
removed for some reason.
6Slowly apply the handbrake, and count the
number of clicks at the lever. If the lever can
be pulled up further than the eighth click,
adjust the handbrake cable as follows.
7Peel back the handbrake lever boot, and
loosen the cable adjusting nut (see
illustration 10.1). On some models, it may be
necessary to remove the centre console
completely for access.
8Loosen a single bolt in each rear wheel.Raise the vehicle and place it securely on axle
stands.
9Remove the bolt you loosened in each rear
wheel. Turn the wheel until, using a torch, you
can see the adjuster starwheel through the
bolt hole.
10Turn the adjuster - clockwise to expand
the shoes, anti-clockwise to retract them -
until the brake shoes just contact the brake
drum (see illustration 5.6d). Back off the
brake shoes so the wheel spins freely (three to
four teeth on the adjuster). Note:If the
adjuster starwheel is hard to turn, remove the
wheel and brake disc, lubricate the adjuster
wheel, and try again.
11With the disc fitted, apply the handbrake
three times to stretch and seat the cables,
then slowly pull up on the handbrake lever to
the fifth click. Tighten the cable adjusting nuts
by equal amounts until the rear brake shoes
just touch the brake drum. Verify that both
wheels have the same amount of resistance.
12Release the handbrake, and verify that
both rear wheels rotate freely.
13Tighten the wheel bolts to the torque
listed in Chapter 1 Specifications.
12 Handbrake assembly-
check, removal and refitting
2
Warning: The handbrake linings
on rear disc brake models may
be manufactured of asbestos-
based material. Refer to the
warning at the start of Section 6. When
servicing these components, do not create
dust by grinding or sanding the linings.
1The handbrake system should be checked
regularly. With the vehicle parked on a hill,
apply the handbrake, select neutral, and
check that the handbrake alone will hold the
vehicle when the footbrake is released (be
sure to stay in the vehicle during this check).
However, every 2 years (or whenever a fault is
suspected), the assembly itself should be
inspected.
2With the vehicle raised and supported onaxle stands, remove the rear wheels.
3On rear brake drum models, refer to
Chapter 1; checking the thickness of the
brake shoes is a routine maintenance
procedure.
4On rear disc brake models, remove the rear
discs as outlined in Section 5. Support the
caliper assemblies with a coat hanger or
heavy wire; do not disconnect the brake line
from the caliper.
5With the disc removed, the handbrake
components are visible, and can be inspected
for wear and damage. The linings should last
the life of the vehicle. However, they can wear
down if the handbrake system has been
improperly adjusted, or if the handbrake is
regularly used to stop the vehicle. There is no
minimum thickness specification for the
handbrake shoes, but as a rule of thumb, if
the shoe material is less than 1.5 mm thick,
you should renew them. Also check the
springs and adjuster mechanism and inspect
the drum for deep scratches and other
damage.
Removal and refitting
Note:The following procedure applies only to
models with rear disc brakes. The handbrake
system on models with rear drum brakes is an
integral part of the rear brake assembly (see
Section 6).
6Loosen the rear wheel bolts, raise the rear
of the vehicle and place it securely on axle
stands. Remove the rear wheels. Remove the
brake discs (see Section 5). Work on only one
side at a time, so you can use the other side
as a reference during reassembly, and to
avoid mixing up parts.
7Remove the shoe return and hold-down
springs (see illustrations).
8Remove the shoes (see illustration).
9Refitting is the reverse of removal. When
you’re done, the actuator should be properly
seated between the two shoes as shown (see
illustration).
10After refitting the brake disc, adjust the
handbrake shoes. Temporarily refit two wheel
bolts, turn the adjuster (see illustration 5.6d)
and expand the shoes until the disc locks,
9•12 Braking system
12.7b Remove the upper shoe
return spring12.7a Remove the lower shoe return
spring (diagonal cutting pliers are being
used here because they grip the spring
well, but care must be taken not to cut or
nick the spring)
Page 152 of 228

4Inspect and, if necessary, renew any worn
or defective bolts, washers, bushes or links.
Refitting
5Refitting is the reverse of removal. Tighten
all fasteners securely.
13 Rear trailing arms (3-Series)
- removal and refitting
3
Removal
1Loosen the wheel bolts, then chock the
front wheels. Raise the rear of the vehicle, and
support it securely on axle stands. Remove
the wheel(s).
2Remove the driveshaft (see Chapter 8), or
disconnect it from the final drive output
flange.
3Disconnect the rear brake hose from the
metal brake line at the bracket on the trailing
arm (see illustration). Note: For information
on disconnecting brake hose-to-metal line
connections, see Chapter 9. Plug the line and
hose, to prevent dirt ingress and loss of brake
fluid.
4Disconnect the handbrake cable (see
Chapter 9).
5Disconnect the lower end of the shockabsorber from the trailing arm (see Section 9),
and lower the trailing arm.
6Remove the trailing arm pivot bolts (see
illustration)and remove the trailing arm.
7Inspect the pivot bolt bushes. If they’re
cracked, dried out or torn, take the trailing
arm to an engineering works and have them
new ones fitted. Each bush has a larger
diameter shoulder on one end. Make sure this
larger diameter shoulder on each bush faces
away from the trailing arm, ie the inner bush
shoulder faces the centre of the vehicle, and
the outer bush shoulder faces away from the
vehicle.Refitting
8Refitting is the reverse of removal. Support
the trailing arm with a trolley jack, and raise it
to simulate normal ride height, then tighten
the nuts and bolts to the torque listed in this
Chapter’s Specifications. Be sure to bleed the
brakes as described in Chapter 9.
14 Rear trailing arms (5-Series)
- removal and refitting
3
Removal
1Loosen the wheel bolts, then chock the
front wheels. Raise the rear of the vehicle and
support it securely on axle stands. Remove
the wheel(s).2Remove the driveshaft (see Chapter 8).
3Disconnect the rear brake hose from the
metal brake line at the bracket on the trailing
arm (see illustration). Note: For information
on disconnecting brake hose-to-metal line
connections, see Chapter 9. Plug the line and
hose, to prevent dirt ingress and loss of brake
fluid.
4Disconnect the handbrake cable from the
handbrake actuator, and unclip the handbrake
cable from the trailing arm (see Chapter 9).
5Remove the ABS wheel sensor (if
applicable) from the trailing arm, and unclip
the sensor wire harness from the arm.
Position the sensor aside so it won’t be
damaged during removal of the trailing arm.
6If you’re removing the right trailing arm,
unplug the connector for the brake pad wear
sensor, if applicable.
7Disconnect the rear anti-roll bar from the
trailing arm (see Section 12).
8On 1983 and later models, remove one of
the rear axle carrier bolts (see illustration).
9Disconnect the shock absorber lower
mounting bolt (see Section 11).
10Remove the two trailing arm pivot bolts
and nuts, and remove the trailing arm from the
vehicle.
11Inspect the pivot bolt bushes. If they’re
cracked, dried out or torn, take the trailing
arm to an engineering works, and have new
ones fitted. The bush inner sleeve is longer on
one side. Make sure the bushes are fitted with
10•10 Suspension and steering systems
14.3 Disconnect the brake hose (left
arrow) from the fitting on the metal brake
line (right arrow) at this bracket13.6 Nut (arrowed) for the outer pivot bolt
13.3 Disconnect the rear brake hose
(middle arrow) from the metal brake line
fitting (right arrow) at this bracket on the
trailing arm, then plug the line and hose
immediately; the other arrow points to the
nut for the inner pivot bolt
12.3b Bolt (arrowed) connecting rear anti-
roll bar link to trailing arm (5-Series)12.3a A nut and bolt (arrowed) connect
each rear anti-roll bar link to the rear
trailing arms (3-Series)12.2 Rear anti-roll bar bracket bolt
(arrowed) (3-Series)
Page 202 of 228

REF•1
REF
MOT Test Checks
This is a guide to getting your vehicle through the MOT test.
Obviously it will not be possible to examine the vehicle to the same
standard as the professional MOT tester. However, working through
the following checks will enable you to identify any problem areas
before submitting the vehicle for the test.
Where a testable component is in borderline condition, the tester
has discretion in deciding whether to pass or fail it. The basis of such
discretion is whether the tester would be happy for a close relative or
friend to use the vehicle with the component in that condition. If the
vehicle presented is clean and evidently well cared for, the tester may
be more inclined to pass a borderline component than if the vehicle is
scruffy and apparently neglected.
It has only been possible to summarise the test requirements here,
based on the regulations in force at the time of printing. Test standards
are becoming increasingly stringent, although there are some
exemptions for older vehicles. For full details obtain a copy of the Haynes
publication Pass the MOT! (available from stockists of Haynes manuals).
An assistant will be needed to help carry out some of these checks.
The checks have been sub-divided into four categories, as follows:
HandbrakeMTest the operation of the handbrake.
Excessive travel (too many clicks) indicates
incorrect brake or cable adjustment.
MCheck that the handbrake cannot be
released by tapping the lever sideways. Check
the security of the lever mountings.
Footbrake
MDepress the brake pedal and check that it
does not creep down to the floor, indicating a
master cylinder fault. Release the pedal, wait
a few seconds, then depress it again. If the
pedal travels nearly to the floor before firm
resistance is felt, brake adjustment or repair is
necessary. If the pedal feels spongy, there is
air in the hydraulic system which must be
removed by bleeding.MCheck that the brake pedal is secure and in
good condition. Check also for signs of fluid
leaks on the pedal, floor or carpets, which
would indicate failed seals in the brake master
cylinder.
MCheck the servo unit (when applicable) by
operating the brake pedal several times, then
keeping the pedal depressed and starting the
engine. As the engine starts, the pedal will
move down slightly. If not, the vacuum hose or
the servo itself may be faulty.
Steering wheel and column
MExamine the steering wheel for fractures or
looseness of the hub, spokes or rim.
MMove the steering wheel from side to side
and then up and down. Check that the
steering wheel is not loose on the column,
indicating wear or a loose retaining nut.
Continue moving the steering wheel as before,
but also turn it slightly from left to right.
MCheck that the steering wheel is not loose
on the column, and that there is no abnormalmovement of the steering wheel, indicating
wear in the column support bearings or
couplings.
Windscreen and mirrors
MThe windscreen must be free of cracks or
other significant damage within the driver’s
field of view. (Small stone chips are
acceptable.) Rear view mirrors must be
secure, intact, and capable of being adjusted.
1Checks carried out
FROM THE DRIVER’S SEAT
1Checks carried out
FROM THE DRIVER’S
SEAT2Checks carried out
WITH THE VEHICLE
ON THE GROUND3Checks carried out
WITH THE VEHICLE
RAISED AND THE
WHEELS FREE TO
TURN4Checks carried out on
YOUR VEHICLE’S
EXHAUST EMISSION
SYSTEM