fuel pressure BMW 3 SERIES 1990 E30 Owner's Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: BMW, Model Year: 1990, Model line: 3 SERIES, Model: BMW 3 SERIES 1990 E30Pages: 228, PDF Size: 7.04 MB
Page 124 of 228

4 Information sensors
2
Note:Refer to Chapters 4 and 5 for additional
information on the location and diagnosis of
the information sensors that are not covered in
this Section.
Coolant temperature sensor
General description
1The coolant temperature sensor (see
illustration)is a thermistor (a resistor which
varies its resistance value in accordance with
temperature changes). The change in the
resistance value regulates the amount of
voltage that can pass through the sensor. At
low temperatures, the sensor’s resistance is
high. As the sensor temperature increases, its
resistance will decrease. Any failure in this
sensor circuit will in most cases be due to a
loose or shorted-out wire; if no wiring
problems are evident, check the sensor as
described below.
Check
2To check the sensor, first check its
resistance (see illustration)when it is
completely cold (typically 2100 to 2900 ohms).
Next, start the engine and warm it up until it
reaches operating temperature. The resistance
should be lower (typically 270 to 400 ohms).
Note: If restricted access to the coolant
temperature sensor makes it difficult to attach
electrical probes to the terminals, remove the
sensor as described below, and perform the
tests in a container of heated water to simulate
the conditions.
Warning: Wait until the engine is
completely cool before beginning
this procedure.
Renewal
3To remove the sensor, depress the spring
lock, unplug the electrical connector, then
carefully unscrew the sensor. Be prepared for
some coolant spillage; to reduce this, have
the new sensor ready for fitting as quickly as
possible.Caution: Handle the coolant
sensor with care. Damage to this
sensor will affect the operation of
the entire fuel injection system.
Note: It may be necessary to drain a small
amount of coolant from the radiator before
removing the sensor.
4Before the sensor is fitted, ensure its
threads are clean, and apply a little sealant to
them.
5Refitting is the reverse of removal.
Oxygen sensor
General description
Note:Oxygen sensors are normally only fitted
to those vehicles equipped with a catalytic
converter. Most oxygen sensors are located in
the exhaust pipe, downstream from the
exhaust manifold. On 535 models, the oxygen
sensor is mounted in the catalytic converter.
The sensor’s electrical connector is located
near the bulkhead (left side) for easy access.
6The oxygen sensor, which is located in the
exhaust system (see illustration), monitors
the oxygen content of the exhaust gas. The
oxygen content in the exhaust reacts with the
oxygen sensor, to produce a voltage output
which varies from 0.1 volts (high oxygen, lean
mixture) to 0.9 volts (low oxygen, rich
mixture). The ECU constantly monitors this
variable voltage output to determine the ratio
of oxygen to fuel in the mixture. The ECU
alters the air/fuel mixture ratio by controlling
the pulse width (open time) of the fuel
injectors. A mixture ratio of 14.7 parts air to 1
part fuel is the ideal mixture ratio for
minimising exhaust emissions, thus allowing
the catalytic converter to operate at maximum
efficiency. It is this ratio of 14.7 to 1 which the
ECU and the oxygen sensor attempt to
maintain at all times.
7The oxygen sensor produces no voltage
when it is below its normal operating
temperature of about 320º C. During this initial
period before warm-up, the ECU operates in
“open-loop” mode (ie without the information
from the sensor).
8If the engine reaches normal operating
temperature and/or has been running for two
or more minutes, and if the oxygen sensor is
producing a steady signal voltage below 0.45 volts at 1500 rpm or greater, the ECU
fault code memory will be activated.
9When there is a problem with the oxygen
sensor or its circuit, the ECU operates in the
“open-loop” mode - that is, it controls fuel
delivery in accordance with a programmed
default value instead of with feedback
information from the oxygen sensor.
10The proper operation of the oxygen
sensor depends on four conditions:
a) Electrical - The low voltages generated by
the sensor depend upon good, clean
connections, which should be checked
whenever a malfunction of the sensor is
suspected or indicated.
b) Outside air supply - The sensor is
designed to allow air circulation to the
internal portion of the sensor. Whenever
the sensor is disturbed, make sure the air
passages are not restricted.
c) Proper operating temperature - The ECU
will not react to the sensor signal until the
sensor reaches approximately 320º C.
This factor must be taken into
consideration when evaluating the
performance of the sensor.
d) Unleaded fuel - The use of unleaded fuel
is essential for proper operation of the
sensor. Make sure the fuel you are using
is of this type.
11In addition to observing the above
conditions, special care must be taken
whenever the sensor is serviced.
a) The oxygen sensor has a permanently-
attached pigtail and electrical connector,
which should not be removed from the
sensor. Damage or removal of the pigtail
or electrical connector can adversely
affect operation of the sensor.
b) Grease, dirt and other contaminants
should be kept away from the electrical
connector and the louvered end of the
sensor.
c) Do not use cleaning solvents of any kind
on the oxygen sensor.
d) Do not drop or roughly handle the sensor.
e) The silicone boot must be fitted in the
correct position, to prevent the boot from
being melted and to allow the sensor to
operate properly.
6•2 Engine management and emission control systems
4.6 The oxygen sensor (arrowed) is usually
located in the exhaust pipe, downstream
from the exhaust manifold4.2 Check the resistance of the coolant
temperature sensor at different
temperatures4.1 The coolant temperature sensor
(arrowed) is usually located next to the
temperature sender unit, near the fuel
pressure regulator
Page 126 of 228
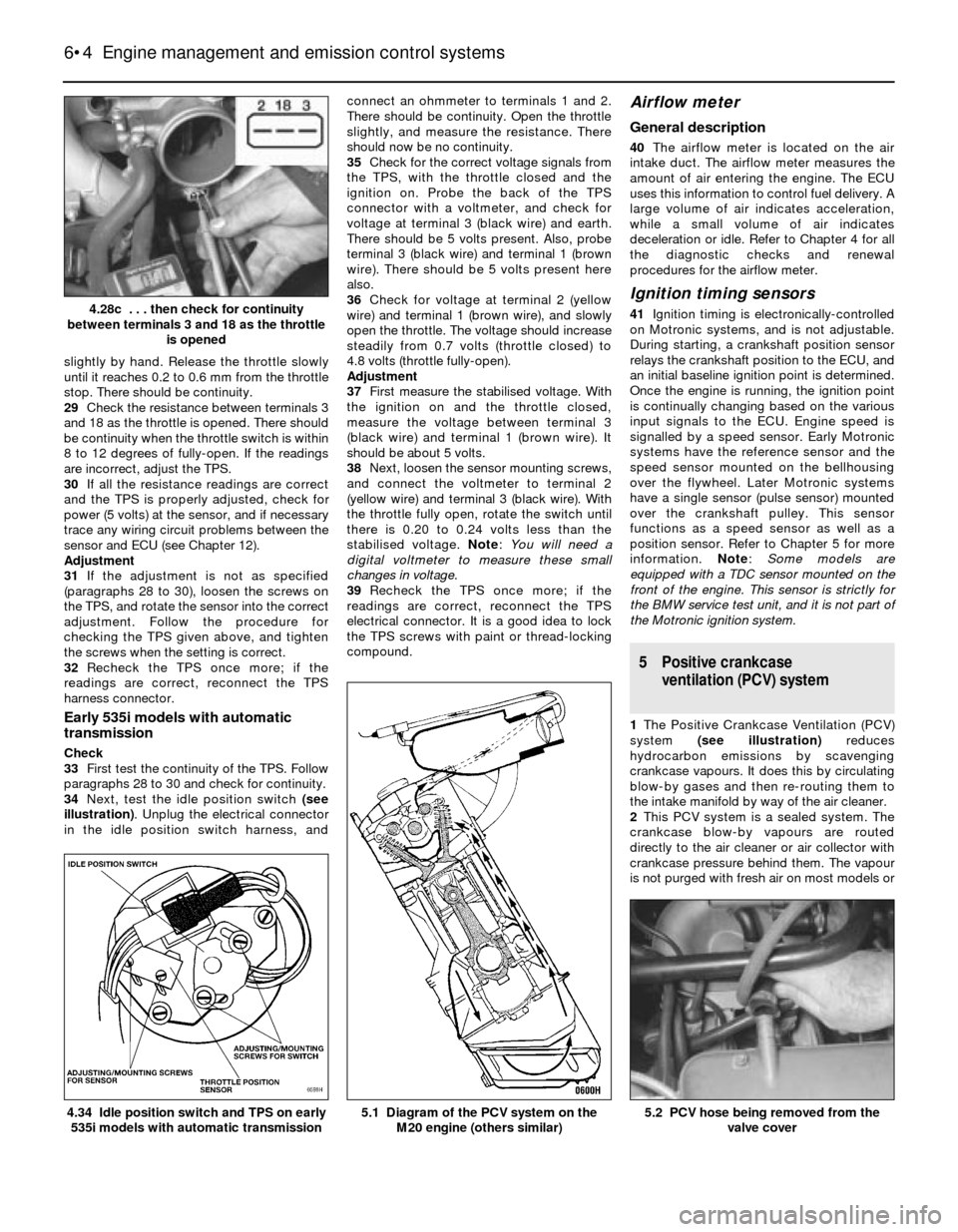
slightly by hand. Release the throttle slowly
until it reaches 0.2 to 0.6 mm from the throttle
stop. There should be continuity.
29Check the resistance between terminals 3
and 18 as the throttle is opened. There should
be continuity when the throttle switch is within
8 to 12 degrees of fully-open. If the readings
are incorrect, adjust the TPS.
30If all the resistance readings are correct
and the TPS is properly adjusted, check for
power (5 volts) at the sensor, and if necessary
trace any wiring circuit problems between the
sensor and ECU (see Chapter 12).
Adjustment
31If the adjustment is not as specified
(paragraphs 28 to 30), loosen the screws on
the TPS, and rotate the sensor into the correct
adjustment. Follow the procedure for
checking the TPS given above, and tighten
the screws when the setting is correct.
32Recheck the TPS once more; if the
readings are correct, reconnect the TPS
harness connector.
Early 535i models with automatic
transmission
Check
33First test the continuity of the TPS. Follow
paragraphs 28 to 30 and check for continuity.
34Next, test the idle position switch (see
illustration). Unplug the electrical connector
in the idle position switch harness, andconnect an ohmmeter to terminals 1 and 2.
There should be continuity. Open the throttle
slightly, and measure the resistance. There
should now be no continuity.
35Check for the correct voltage signals from
the TPS, with the throttle closed and the
ignition on. Probe the back of the TPS
connector with a voltmeter, and check for
voltage at terminal 3 (black wire) and earth.
There should be 5 volts present. Also, probe
terminal 3 (black wire) and terminal 1 (brown
wire). There should be 5 volts present here
also.
36Check for voltage at terminal 2 (yellow
wire) and terminal 1 (brown wire), and slowly
open the throttle. The voltage should increase
steadily from 0.7 volts (throttle closed) to
4.8 volts (throttle fully-open).
Adjustment
37First measure the stabilised voltage. With
the ignition on and the throttle closed,
measure the voltage between terminal 3
(black wire) and terminal 1 (brown wire). It
should be about 5 volts.
38Next, loosen the sensor mounting screws,
and connect the voltmeter to terminal 2
(yellow wire) and terminal 3 (black wire). With
the throttle fully open, rotate the switch until
there is 0.20 to 0.24 volts less than the
stabilised voltage. Note: You will need a
digital voltmeter to measure these small
changes in voltage.
39Recheck the TPS once more; if the
readings are correct, reconnect the TPS
electrical connector. It is a good idea to lock
the TPS screws with paint or thread-locking
compound.
Airflow meter
General description
40The airflow meter is located on the air
intake duct. The airflow meter measures the
amount of air entering the engine. The ECU
uses this information to control fuel delivery. A
large volume of air indicates acceleration,
while a small volume of air indicates
deceleration or idle. Refer to Chapter 4 for all
the diagnostic checks and renewal
procedures for the airflow meter.
Ignition timing sensors
41Ignition timing is electronically-controlled
on Motronic systems, and is not adjustable.
During starting, a crankshaft position sensor
relays the crankshaft position to the ECU, and
an initial baseline ignition point is determined.
Once the engine is running, the ignition point
is continually changing based on the various
input signals to the ECU. Engine speed is
signalled by a speed sensor. Early Motronic
systems have the reference sensor and the
speed sensor mounted on the bellhousing
over the flywheel. Later Motronic systems
have a single sensor (pulse sensor) mounted
over the crankshaft pulley. This sensor
functions as a speed sensor as well as a
position sensor. Refer to Chapter 5 for more
information. Note: Some models are
equipped with a TDC sensor mounted on the
front of the engine. This sensor is strictly for
the BMW service test unit, and it is not part of
the Motronic ignition system.
5 Positive crankcase
ventilation (PCV) system
1The Positive Crankcase Ventilation (PCV)
system (see illustration)reduces
hydrocarbon emissions by scavenging
crankcase vapours. It does this by circulating
blow-by gases and then re-routing them to
the intake manifold by way of the air cleaner.
2This PCV system is a sealed system. The
crankcase blow-by vapours are routed
directly to the air cleaner or air collector with
crankcase pressure behind them. The vapour
is not purged with fresh air on most models or
6•4 Engine management and emission control systems
5.2 PCV hose being removed from the
valve cover5.1 Diagram of the PCV system on the
M20 engine (others similar)4.34 Idle position switch and TPS on early
535i models with automatic transmission
4.28c . . . then check for continuity
between terminals 3 and 18 as the throttle
is opened
Page 127 of 228
filtered with a flame trap like most
conventional systems. There are no
conventional PCV valves fitted on these
systems - just a hose (see illustration).
3The main components of the PCV system
are the hoses that connect the valve cover to
the throttle body or air cleaner. If abnormal
operating conditions (such as piston ring
problems) arise, the system is designed to
allow excessive amounts of blow-by gases to
flow back through the crankcase vent tube
into the intake system, to be consumed by
normal combustion. Note: Since these
models don’t use a filtering element, it’s a
good idea to check the PCV system
passageways for clogging from sludge and
combustion residue(see illustration).
6 Evaporative emissions
control (EVAP) system
2
General description
Note:This system is normally only fitted to
those vehicles equipped with a catalytic
converter.
1When the engine isn’t running, the fuel in the
fuel tank evaporates to some extent, creating
fuel vapour. The evaporative emissions control
system (see illustration)stores these fuel
vapours in a charcoal canister. When the
engine is cruising, the purge control valve is
opened slightly, and a small amount of fuel
vapour is drawn into the intake manifold and
burned. When the engine is starting cold or
idling, the purge valve prevents any vapours
from entering the intake manifold and causing
excessively-rich fuel mixture.
2Two types of purge valve are used;
electrically-operated or vacuum-operated. To
find out which type is on your vehicle, follow
the hose from the charcoal canister until you
locate the purge valve. Some are located on
the intake manifold, and others near the
charcoal canister. Look for either an electrical
connector, or vacuum lines, to the purge
valve.3A faulty EVAP system will only affect engine
driveability when the engine is warm. The
EVAP system is not usually the cause of
difficult cold starting or any other cold-running
problems.
Check
Vacuum-operated purge valve
4Remove the vacuum lines from the purge
valve, and blow into the larger valve port. It
should be closed, and not pass any air. Note:
Some models have a thermo-vacuum valve
that delays canister purging until the coolant
temperature reaches approximately 46º C.
Check this valve to make sure that vacuum is
controlled at the proper temperatures. The
valve is usually located in the intake manifold,
near the thermo-time switch and the coolant
temperature sensor.
5Disconnect the small vacuum hose from the
purge valve, and apply vacuum with a hand-
held vacuum pump. The purge valve should
be open, and air should be able to pass
through.6If the test results are unsatisfactory, renew
the purge valve.
Electrically-operated purge valve
7Disconnect any lines from the purge valve,
and (without disconnecting the electrical
connector) place it in a convenient spot for
testing.
8Check that the valve makes a “click” sound
as the ignition is switched on (see
illustration).
9If the valve does not “click”, disconnect the
valve connector, and check for power to the
valve using a test light or a voltmeter (see
illustration).
10If battery voltage is present, but the valve
does not work, renew it. If there is no voltage
present, check the Motronic control unit and
the wiring.
Canister
11Mark all the hoses for position, then
detach them from the canister.
12Slide the canister out of its mounting clip.
Engine management and emission control systems 6•5
6.1 Diagram of the EVAP system on the M10 engine (others similar)
6.9 Check for battery voltage at the
electrical connector to the purge valve6.8 When the ignition is switched on, there
should be a distinct “click” from the purge
valve
6
5.3 It’s a good idea to check for excess
residue from the crankcase vapours
circulating in the hoses and ports - this
can eventually clog the system, and cause
a pressure increase in the engine block
Page 205 of 228

REF•4MOT Test Checks
MExamine the handbrake mechanism,
checking for frayed or broken cables,
excessive corrosion, or wear or insecurity of
the linkage. Check that the mechanism works
on each relevant wheel, and releases fully,
without binding.
MIt is not possible to test brake efficiency
without special equipment, but a road test can
be carried out later to check that the vehicle
pulls up in a straight line.
Fuel and exhaust systems
MInspect the fuel tank (including the filler
cap), fuel pipes, hoses and unions. All
components must be secure and free from
leaks.
MExamine the exhaust system over its entire
length, checking for any damaged, broken or
missing mountings, security of the retaining
clamps and rust or corrosion.
Wheels and tyres
MExamine the sidewalls and tread area of
each tyre in turn. Check for cuts, tears, lumps,
bulges, separation of the tread, and exposure
of the ply or cord due to wear or damage.
Check that the tyre bead is correctly seated
on the wheel rim, that the valve is sound andproperly seated, and that the wheel is not
distorted or damaged.
MCheck that the tyres are of the correct size
for the vehicle, that they are of the same size
and type on each axle, and that the pressures
are correct.
MCheck the tyre tread depth. The legal
minimum at the time of writing is 1.6 mm over
at least three-quarters of the tread width.
Abnormal tread wear may indicate incorrect
front wheel alignment.
Body corrosion
MCheck the condition of the entire vehicle
structure for signs of corrosion in load-bearing
areas. (These include chassis box sections,
side sills, cross-members, pillars, and all
suspension, steering, braking system and
seat belt mountings and anchorages.) Any
corrosion which has seriously reduced the
thickness of a load-bearing area is likely to
cause the vehicle to fail. In this case
professional repairs are likely to be needed.
MDamage or corrosion which causes sharp
or otherwise dangerous edges to be exposed
will also cause the vehicle to fail.
Petrol models
MHave the engine at normal operating
temperature, and make sure that it is in good
tune (ignition system in good order, air filter
element clean, etc).
MBefore any measurements are carried out,
raise the engine speed to around 2500 rpm,
and hold it at this speed for 20 seconds. Allowthe engine speed to return to idle, and watch
for smoke emissions from the exhaust
tailpipe. If the idle speed is obviously much
too high, or if dense blue or clearly-visible
black smoke comes from the tailpipe for more
than 5 seconds, the vehicle will fail. As a rule
of thumb, blue smoke signifies oil being burnt
(engine wear) while black smoke signifies
unburnt fuel (dirty air cleaner element, or other
carburettor or fuel system fault).
MAn exhaust gas analyser capable of
measuring carbon monoxide (CO) and
hydrocarbons (HC) is now needed. If such an
instrument cannot be hired or borrowed, a
local garage may agree to perform the check
for a small fee.
CO emissions (mixture)
MAt the time of writing, the maximum CO
level at idle is 3.5% for vehicles first used after
August 1986 and 4.5% for older vehicles.
From January 1996 a much tighter limit
(around 0.5%) applies to catalyst-equipped
vehicles first used from August 1992. If the
CO level cannot be reduced far enough to
pass the test (and the fuel and ignition
systems are otherwise in good condition) then
the carburettor is badly worn, or there is some
problem in the fuel injection system or
catalytic converter (as applicable).
HC emissionsMWith the CO emissions within limits, HC
emissions must be no more than 1200 ppm
(parts per million). If the vehicle fails this test
at idle, it can be re-tested at around 2000 rpm;
if the HC level is then 1200 ppm or less, this
counts as a pass.
MExcessive HC emissions can be caused by
oil being burnt, but they are more likely to be
due to unburnt fuel.
Diesel models
MThe only emission test applicable to Diesel
engines is the measuring of exhaust smoke
density. The test involves accelerating the
engine several times to its maximum
unloaded speed.
Note: It is of the utmost importance that the
engine timing belt is in good condition before
the test is carried out.
M
Excessive smoke can be caused by a dirty
air cleaner element. Otherwise, professional
advice may be needed to find the cause.
4Checks carried out on
YOUR VEHICLE’S EXHAUST
EMISSION SYSTEM
Page 210 of 228

REF•9
REF
Fault Finding
Engine
m mEngine will not rotate when attempting to start
m mEngine rotates, but will not start
m mEngine hard to start when cold
m mEngine hard to start when hot
m mStarter motor noisy or excessively-rough in engagement
m mEngine starts, but stops immediately
m mOil puddle under engine
m mEngine idles erratically
m mEngine misses at idle speed
m mEngine misses throughout driving speed range
m mEngine misfires on acceleration
m mEngine surges while holding accelerator steady
m mEngine stalls
m mEngine lacks power
m mEngine backfires
m mPinking or knocking engine sounds when accelerating
or driving uphill
m mEngine runs with oil pressure light on
m mEngine runs-on after switching off
Engine electrical system
m
mBattery will not hold charge
m mIgnition (no-charge) warning light fails to go out
m mIgnition (no-charge) warning light fails to come on
when key is turned
Fuel system
m mExcessive fuel consumption
m mFuel leakage and/or fuel odour
Cooling system
m
mOverheating
m mOvercooling
m mExternal coolant leakage
m mInternal coolant leakage
m mCoolant loss
m mPoor coolant circulation
Clutch
m
mPedal travels to floor - no pressure or very little resistance
m mFluid in area of master cylinder dust cover and on pedal
m mFluid on slave cylinder
m mPedal feels “spongy” when depressed
m mUnable to select gears
m mClutch slips (engine speed increases with no increase in
vehicle speed)
m mGrabbing (chattering) as clutch is engaged
m mNoise in clutch area
m mClutch pedal stays on floor
m mHigh pedal effort
Manual transmission
m
mVibration
m mNoisy in neutral with engine running
m mNoisy in one particular gear
m mNoisy in all gears
m mSlips out of gear
m mLeaks lubricant
Automatic transmission
m
mFluid leakage
m mTransmission fluid brown, or has a burned smell
m mGeneral shift mechanism problems
m mTransmission will not kickdown with accelerator pedal
pressed to the floor
m mEngine will start in gears other than Park or Neutral
m mTransmission slips, shifts roughly, is noisy, or has no drive
in forward or reverse gears
Brakes
m mVehicle pulls to one side during braking
m mNoise (high-pitched squeal) when the brakes are applied
m mBrake vibration (pedal pulsates)
m mExcessive pedal effort required to stop vehicle
m mExcessive brake pedal travel
m mDragging brakes
m mGrabbing or uneven braking action
m mBrake pedal feels “spongy” when depressed
m mBrake pedal travels to the floor with little resistance
m mHandbrake does not hold
Suspension and steering
m
mVehicle pulls to one side
m mAbnormal or excessive tyre wear
m mWheel makes a “thumping” noise
m mShimmy, shake or vibration
m mHigh steering effort
m mPoor steering self-centring
m mAbnormal noise at the front end
m mWandering or poor steering stability
m mErratic steering when braking
m mExcessive pitching and/or rolling around corners or
during braking
m mSuspension bottoms
m mUnevenly-worn tyres
m mExcessive tyre wear on outside edge
m mExcessive tyre wear on inside edge
m mTyre tread worn in one place
m mExcessive play or looseness in steering system
m mRattling or clicking noise in steering gear
Page 211 of 228

REF•10Fault Finding
Engine will not rotate when attempting to start
m mBattery terminal connections loose or corroded (Chapter 1).
m mBattery discharged or faulty (Chapter 1).
m mAutomatic transmission not completely engaged in Park (Chap-
ter 7B) or (on models with a clutch switch) clutch not completely
depressed (Chapter 8).
m mBroken, loose or disconnected wiring in the starting circuit
(Chapters 5 and 12).
m mStarter motor pinion jammed in flywheel ring gear (Chapter 5).
m mStarter solenoid faulty (Chapter 5).
m mStarter motor faulty (Chapter 5).
m mIgnition switch faulty (Chapter 12).
m mStarter pinion or flywheel teeth worn or broken (Chapter 5).
m mEngine internal problem (Chapter 2B).
Engine rotates, but will not start
m
mFuel tank empty.
m mBattery discharged (engine rotates slowly) (Chapter 5).
m mBattery terminal connections loose or corroded (Chapter 1).
m mLeaking fuel injector(s), faulty fuel pump, pressure regulator, etc
(Chapter 4).
m mFuel not reaching fuel injection system or carburettor (Chapter 4).
m mIgnition components damp or damaged (Chapter 5).
m mFuel injector stuck open (Chapter 4).
m mWorn, faulty or incorrectly-gapped spark plugs (Chapter 1).
m mBroken, loose or disconnected wiring in the starting circuit
(Chapter 5).
m mLoose distributor mounting bolts causing ignition timing to wander
(Chapters 1 and 5).
m mBroken, loose or disconnected wires at the ignition coil, or faulty
coil (Chapter 5).
Engine hard to start when cold
m mBattery discharged (Chapter 1).
m mFuel system malfunctioning (Chapter 4).
m mInjector(s) leaking or carburettor automatic choke faulty (Chap-
ter 4).
m mDistributor rotor carbon-tracked (Chapter 5).
Engine hard to start when hot
m
mAir filter element clogged (Chapter 1).
m mFuel not reaching the fuel injection system or carburettor (Chap-
ter 4).
m mCorroded battery connections, especially earth (negative)
connection (Chapter 1).
Starter motor noisy or excessively-rough in
engagement
m mPinion or flywheel gear teeth worn or broken (Chapter 5).
m mStarter motor mounting bolts loose or missing (Chapter 5).
Engine starts, but stops immediately
m
mLoose or faulty electrical connections at distributor, coil or
alternator (Chapter 5).
m mInsufficient fuel reaching the fuel injector(s) or carburettor
(Chapters 1 and 4).
m mDamaged fuel injection system speed sensors (Chapter 5).
m mFaulty fuel injection relays (Chapter 5).
Oil puddle under engine
m
mOil sump gasket and/or sump drain plug seal leaking (Chapter 2).
m mOil pressure sender unit leaking (Chapter 2).
m mValve cover gaskets leaking (Chapter 2).
m mEngine oil seals leaking (Chapter 2).
Engine idles erratically
m
mVacuum leakage (Chapter 4).
m mAir filter element clogged (Chapter 1).
m mFuel pump not delivering sufficient fuel to the fuel injection system
or carburettor (Chapter 4).
m mLeaking head gasket (Chapter 2).
m mTiming belt/chain and/or sprockets worn (Chapter 2).
m mCamshaft lobes worn (Chapter 2).
m mFaulty charcoal canister, where fitted (Chapter 6). This Section provides an easy-reference guide to the more
common problems which may occur during the operation of your
vehicle. These problems and their possible causes are grouped under
headings denoting various components or systems, such as Engine,
Cooling system, etc. They also refer you to the Chapter and/or
Section which deals with the problem.
Remember that successful fault diagnosis is not a mysterious
black art practised only by professional mechanics. It is simply the
result of the right knowledge combined with an intelligent, systematic
approach to the problem. Always work by a process of elimination,
starting with the simplest solution and working through to the mostcomplex - and never overlook the obvious. Anyone can run the fuel
tank dry or leave the lights on overnight, so don’t assume that you are
exempt from such oversights.
Finally, always establish a clear idea of why a problem has
occurred, and take steps to ensure that it doesn’t happen again. If the
electrical system fails because of a poor connection, check all other
connections in the system to make sure that they don’t fail as well. If a
particular fuse continues to blow, find out why - don’t just renew one
fuse after another. Remember, failure of a small component can often
be indicative of potential failure or incorrect functioning of a more
important component or system.
Engine
Page 212 of 228

REF•11
REF
Fault Finding
Engine misses at idle speed
m mSpark plugs worn or incorrectly-gapped (Chapter 1).
m mFaulty spark plug HT leads (Chapter 1).
m mVacuum leaks (Chapter 1).
m mIncorrect ignition timing (Chapter 5).
m mUneven or low compression (Chapter 2).
m mFaulty charcoal canister, where fitted (Chapter 6).
Engine misses throughout driving speed range
m
mFuel filter clogged and/or impurities in the fuel system (Chapter 1).
m mLow fuel output at the injectors, or partially-blocked carburettor
jets (Chapter 4).
m mFaulty or incorrectly-gapped spark plugs (Chapter 1).
m mIncorrect ignition timing (Chapter 5).
m mCracked distributor cap, disconnected distributor HT leads, or
damaged distributor components (Chapter 1).
m mFaulty spark plug HT leads (Chapter 1).
m mFaulty emission system components (Chapter 6).
m mLow or uneven cylinder compression pressures (Chapter 2).
m mWeak or faulty ignition system (Chapter 5).
m mVacuum leak in fuel injection system, intake manifold or vacuum
hoses (Chapter 4).
Engine misfires on acceleration
m mSpark plugs fouled (Chapter 1).
m mFuel injection system or carburettor malfunctioning (Chapter 4).
m mFuel filter clogged (Chapters 1 and 4).
m mIncorrect ignition timing (Chapter 5).
m mIntake manifold air leak (Chapter 4).
Engine surges while holding accelerator steady
m
mIntake air leak (Chapter 4).
m mFuel pump faulty (Chapter 4).
m mLoose fuel injector harness connections (Chapters 4 and 6).
m mDefective ECU (Chapter 5).
Engine lacks power
m
mIncorrect ignition timing (Chapter 5).
m mExcessive play in distributor shaft (Chapter 5).
m mWorn rotor, distributor cap or HT leads (Chapters 1 and 5).
m mFaulty or incorrectly-gapped spark plugs (Chapter 1).
m mFuel injection system or carburettor malfunctioning (Chapter 4).
m mFaulty coil (Chapter 5).
m mBrakes binding (Chapter 1).
m mAutomatic transmission fluid level incorrect (Chapter 1).
m mClutch slipping (Chapter 8).
m mFuel filter clogged and/or impurities in the fuel system (Chapter 1).
m mEmission control system not functioning properly (Chapter 6).
m mLow or uneven cylinder compression pressures (Chapter 2).
Engine stalls
m
mIdle speed incorrect (Chapter 1).
m mFuel filter clogged and/or water and impurities in the fuel system
(Chapter 1).
m mDistributor components damp or damaged (Chapter 5).
m mFaulty emissions system components (Chapter 6).
m mFaulty or incorrectly-gapped spark plugs (Chapter 1).
m mFaulty spark plug HT leads (Chapter 1).
m mVacuum leak in the fuel injection system, intake manifold or
vacuum hoses (Chapter 4).
Engine backfires
m mEmissions system not functioning properly (Chapter 6).
m mIgnition timing incorrect (Chapter 5).
m mFaulty secondary ignition system (cracked spark plug insulator,
faulty plug HT leads, distributor cap and/or rotor) (Chapters 1 and 5).
m mFuel injection system or carburettor malfunctioning (Chapter 4).
m mVacuum leak at fuel injector(s), intake manifold or vacuum hoses
(Chapter 4).
m mValve clearances incorrect (Chapter 1), or valve(s) sticking or
damaged (Chapter 2).
Pinking or knocking engine sounds when
accelerating or driving uphill
m mIncorrect grade of fuel.
m mIgnition timing incorrect (Chapter 5).
m mFuel injection system or carburettor in need of adjustment (Chap-
ter 4).
m mDamaged spark plugs or HT leads, or incorrect type fitted (Chapter 1).
m mWorn or damaged distributor components (Chapter 5).
m mFaulty emission system (Chapter 6).
m mVacuum leak (Chapter 4).
Engine runs with oil pressure light on
Caution: Stop the engine immediately if the oil
pressure light comes on and establish the cause.
Running the engine while the oil pressure is low can
cause severe damage.
m mLow oil level (Chapter 1).
m mIdle speed too low (Chapter 1).
m mShort-circuit in wiring (Chapter 12).
m mFaulty oil pressure sender unit (Chapter 2).
m mWorn engine bearings and/or oil pump (Chapter 2).
Engine runs-on after switching off
m
mIdle speed too high (Chapter 1).
m mExcessive engine operating temperature (Chapter 3).
m mIncorrect fuel octane grade.
m mSpark plugs defective or incorrect grade (Chapter 1).
Engine electrical system
Battery will not hold charge
m
mAlternator drivebelt defective or not adjusted properly (Chapter 1).
m mElectrolyte level low (Chapter 1).
m mBattery terminals loose or corroded (Chapter 1).
m mAlternator not charging properly (Chapter 5).
m mLoose, broken or faulty wiring in the charging circuit (Chapter 5).
m mShort in vehicle wiring (Chapters 5 and 12).
m mInternally-defective battery (Chapters 1 and 5).
m mIgnition (no-charge) warning light bulb blown - on some early
models (Chapter 5)
Ignition (no-charge) warning light fails to go out
m mFaulty alternator or charging circuit (Chapter 5).
m mAlternator drivebelt defective or out of adjustment (Chapter 1).
m mAlternator voltage regulator inoperative (Chapter 5).
Ignition (no-charge) warning light fails to come on
when key is turned
m mWarning light bulb defective (Chapter 12).
m mFault in the printed circuit, wiring or bulbholder (Chapter 12).
Page 213 of 228

REF•12Fault Finding
Fuel system
Excessive fuel consumption
m mDirty or clogged air filter element (Chapter 1).
m mIgnition timing incorrect (Chapter 5).
m mEmissions system not functioning properly (Chapter 6).
m mFuel injection internal parts or carburettor jets excessively worn or
damaged (Chapter 4).
m mLow tyre pressure or incorrect tyre size (Chapter 1).
m mUnsympathetic driving style, or unfavourable conditions.
Fuel leakage and/or fuel odour
Warning: Don’t drive the vehicle if a fuel leak is
suspected. Leaking fuel in the engine compartment
could catch fire.
m mLeak in a fuel feed or vent line (Chapter 4).
m mTank overfilled.
m mFuel injector or carburettor parts excessively worn, or fuel system
gaskets leaking (Chapter 4).
Cooling system
Overheating
m mInsufficient coolant in system (Chapter 1).
m mWater pump drivebelt defective or out of adjustment (Chapter 1).
m mRadiator matrix blocked, or grille restricted (Chapter 3).
m mThermostat faulty (Chapter 3).
m mRadiator cap not maintaining proper pressure (Chapter 3).
m mIgnition timing incorrect (Chapter 5).
Overcooling
m
mFaulty thermostat (Chapter 3).
External coolant leakage
m
mDeteriorated/damaged hoses; loose clamps (Chapters 1 and 3).
m mWater pump seal defective (Chapters 1 and 3).
m mLeakage from radiator matrix, heater matrix or header tank
(Chapter 3).
m mRadiator/engine block drain plugs or water jacket core plugs
leaking (Chapters 2 and 3).
Internal coolant leakage
m mLeaking cylinder head gasket (Chapter 2).
m mCracked cylinder bore or cylinder head (Chapter 2).
Coolant loss
m
mToo much coolant in system (Chapter 1).
m mCoolant boiling away because of overheating (see above).
m mInternal or external leakage (see above).
m mFaulty radiator cap (Chapter 3).
Poor coolant circulation
m
mInoperative water pump (Chapter 3).
m mRestriction in cooling system (Chapters 1 and 3).
m mWater pump drivebelt defective/out of adjustment (Chapter 1).
m mThermostat sticking (Chapter 3).
Clutch
Pedal travels to floor - no pressure or very little
resistance
m mMaster or slave cylinder faulty (Chapter 8).
m mFluid line burst or leaking (Chapter 8).
m mConnections leaking (Chapter 8).
m mNo fluid in reservoir (Chapter 1).
m mIf fluid is present in master cylinder dust cover, master cylinder rear
seal has failed (Chapter 8).
m mBroken release bearing or fork (Chapter 8).
Fluid in area of master cylinder dust cover, and on
pedal
m mRear seal failure in master cylinder (Chapter 8).
Fluid on slave cylinder
m
mSlave cylinder plunger seal faulty (Chapter 8).
Pedal feels “spongy” when depressed
m
mAir in system (Chapter 8).
Unable to select gears
m
mFaulty transmission (Chapter 7).
m mFaulty clutch plate (Chapter 8).
m mFork and bearing not assembled properly (Chapter 8).
m mFaulty pressure plate (Chapter 8).
m mPressure plate-to-flywheel bolts loose (Chapter 8).
Clutch slips (engine speed increases with no
increase in vehicle speed)
m mClutch plate worn (Chapter 8).
m mClutch plate is oil-soaked by leaking rear main seal (Chapter 8).
m mWarped pressure plate or flywheel (Chapter 8).
m mWeak diaphragm spring (Chapter 8).
m mClutch plate overheated.
Grabbing (chattering) as clutch is engaged
m
mOil on clutch plate lining, burned or glazed facings (Chapter 8).
m mWorn or loose engine or transmission mountings (Chapters 2
and 7A).
m mWorn splines on clutch plate hub (Chapter 8).
m mWarped pressure plate or flywheel (Chapter 8).
Noise in clutch area
m
mFork improperly fitted (Chapter 8).
m mFaulty release bearing (Chapter 8).
Clutch pedal stays on floor
m
mFork binding in housing (Chapter 8).
m mBroken release bearing or fork (Chapter 8).
High pedal effort
m
mFork binding in housing (Chapter 8).
m mPressure plate faulty (Chapter 8).
m mIncorrect-size master or slave cylinder fitted (Chapter 8).
Page 217 of 228

REF•17
REF
Conversion Factors
Length (distance)Inches (in) 25.4 = Millimetres (mm) x 0.0394 = Inches (in)
Feet (ft) 0.305 = Metres (m) x 3.281 = Feet (ft)
Miles 1.609 = Kilometres (km) x 0.621 = Miles
Volume (capacity)Cubic inches (cu in; in3) x 16.387 = Cubic centimetres (cc; cm3) x 0.061 = Cubic inches (cu in; in3)
Imperial pints (Imp pt) x 0.568 = Litres (l) x 1.76 = Imperial pints (Imp pt)
Imperial quarts (Imp qt) x 1.137 = Litres (l) x 0.88 = Imperial quarts (Imp qt)
Imperial quarts (Imp qt) x 1.201 = US quarts (US qt) x 0.833 = Imperial quarts (Imp qt)
US quarts (US qt) x 0.946 = Litres (l) x 1.057 = US quarts (US qt)
Imperial gallons (Imp gal) x 4.546 = Litres (l) x 0.22 = Imperial gallons (Imp gal)
Imperial gallons (Imp gal) x 1.201 = US gallons (US gal) x 0.833 = Imperial gallons (Imp gal)
US gallons (US gal) x 3.785 = Litres (l) x 0.264 = US gallons (US gal)
Mass (weight)Ounces (oz) x 28.35 = Grams (g) x 0.035 = Ounces (oz)
Pounds (lb) x 0.454 = Kilograms (kg) x 2.205 = Pounds (lb)
ForceOunces-force (ozf; oz) x 0.278 = Newtons (N) x 3.6 = Ounces-force (ozf; oz)
Pounds-force (lbf; lb) x 4.448 = Newtons (N) x 0.225 = Pounds-force (lbf; lb)
Newtons (N) x 0.1 = Kilograms-force (kgf; kg) x 9.81 = Newtons (N)
PressurePounds-force per square inch x 0.070 = Kilograms-force per square x 14.223 = Pounds-force per square inch
(psi; lbf/in2; lb/in2) centimetre (kgf/cm2; kg/cm2) (psi; lbf/in2; lb/in2)
Pounds-force per square inch x 0.068 = Atmospheres (atm) x 14.696 = Pounds-force per square inch
(psi; lbf/in
2; lb/in2)(psi; lbf/in2; lb/in2)
Pounds-force per square inch x 0.069 = Bars x 14.5 = Pounds-force per square inch
(psi; lbf/in
2; lb/in2)(psi; lbf/in2; lb/in2)
Pounds-force per square inch x 6.895 = Kilopascals (kPa) x 0.145 = Pounds-force per square inch
(psi; lbf/in
2; lb/in2)(psi; lbf/in2; lb/in2)
Kilopascals (kPa) x 0.01 = Kilograms-force per square x 98.1 = Kilopascals (kPa)
centimetre (kgf/cm
2; kg/cm2)
Millibar (mbar) x 100 = Pascals (Pa) x 0.01 = Millibar (mbar)
Millibar (mbar) x 0.0145 = Pounds-force per square inch x 68.947 = Millibar (mbar)
(psi; lbf/in
2; lb/in2)
Millibar (mbar) x 0.75 = Millimetres of mercury (mmHg) x 1.333 = Millibar (mbar)
Millibar (mbar) x 0.401 = Inches of water (inH
2O) x 2.491 = Millibar (mbar)
Millimetres of mercury (mmHg) x 0.535 = Inches of water (inH
2O) x 1.868 = Millimetres of mercury (mmHg)
Inches of water (inH
2O) x 0.036 = Pounds-force per square inch x 27.68 = Inches of water (inH2O)
(psi; lbf/in2; lb/in2)
Torque (moment of force)Pounds-force inches (lbf in; lb in) x 1.152 = Kilograms-force centimetre x 0.868 = Pounds-force inches (lbf in; lb in)
(kgf cm; kg cm)
Pounds-force inches (lbf in; lb in) x 0.113 = Newton metres (Nm) x 8.85 = Pounds-force inches (lbf in; lb in)
Pounds-force inches (lbf in; lb in) x 0.083 = Pounds-force feet (lbf ft; lb ft) x 12 = Pounds-force inches (lbf in; lb in)
Pounds-force feet (lbf ft; lb ft) x 0.138 = Kilograms-force metres (kgf m; kg m) x 7.233 = Pounds-force feet (lbf ft; lb ft)
Pounds-force feet (lbf ft; lb ft) x 1.356 = Newton metres (Nm) x 0.738 = Pounds-force feet (lbf ft; lb ft)
Newton metres (Nm) x 0.102 = Kilograms-force metres (kgf m; kg m) x 9.804 = Newton metres (Nm)
PowerHorsepower (hp) x 745.7 = Watts (W) x 0.0013 = Horsepower (hp)
Velocity (speed)Miles per hour (miles/hr; mph) x 1.609 = Kilometres per hour (km/hr; kph) x 0.621 = Miles per hour (miles/hr; mph)
Fuel consumption*Miles per gallon (mpg) x 0.354 = Kilometres per litre (km/l) x 2.825 = Miles per gallon (mpg)
* It is common practice to convert from miles per gallon (mpg) to litres/100 kilometres (l/100km), where mpg x l/100 km = 282
TemperatureDegrees Fahrenheit = (°C x 1.8) + 32 Degrees Celsius (Degrees Centigrade; °C) = (°F - 32) x 0.56
Page 218 of 228

REF•18Automotive chemicals and lubricants
A number of automotive chemicals and
lubricants are available for use during vehicle
maintenance and repair. They include a wide
variety of products ranging from cleaning
solvents and degreasers to lubricants and
protective sprays for rubber, plastic and
vinyl.
Cleaners
Carburettor cleaner and choke cleaner
is a strong solvent for gum, varnish and
carbon. Most carburettor cleaners leave a
dry-type lubricant film which will not harden or
gum up. Because of this film, it is not
recommended for use on electrical
components.
Brake system cleaneris used to remove
grease and brake fluid from the brake system,
where clean surfaces are absolutely
necessary. It leaves no residue, and often
eliminates brake squeal caused by
contaminants.
Electrical cleaner removes oxidation,
corrosion and carbon deposits from electrical
contacts, restoring full current flow. It can also
be used to clean spark plugs, carburettor jets,
voltage regulators and other parts where an
oil-free surface is desired.
Moisture dispersantsremove water and
moisture from electrical components such as
alternators, voltage regulators, electrical
connectors and fuse blocks. They are non-
conductive and non-corrosive.
Degreasersare heavy-duty solvents used
to remove grease from the outside of the
engine and from chassis components. They
can be sprayed or brushed on, and are usually
rinsed off with water.
Lubricants
Engine oilis the lubricant formulated for
use in engines. It normally contains a wide
variety of additives to prevent corrosion and
reduce foaming and wear. Engine oil comes in
various weights (viscosity ratings) from 5 to
60. The recommended weight of the oil
depends on the season, temperature and the
demands on the engine. Light oil is used in
cold climates and under light load conditions.
Heavy oil is used in hot climates, and where
high loads are encountered. Multi-viscosity
(multigrade) oils are designed to have
characteristics of both light and heavy oils,
and are available in a number of weights from
5W-20 to 20W-50.
Gear oilis designed to be used in
differentials, manual transmissions and other
areas where high-temperature lubrication is
required.
Chassis and wheel bearing greaseis a
heavy grease used where increased loads and
friction are encountered, such as for wheel
bearings, balljoints, tie-rod ends and universal
joints.High-temperature wheel bearing grease
is designed to withstand the extreme
temperatures encountered by wheel bearings
in disc brake-equipped vehicles. It usually
contains molybdenum disulphide (moly),
which is a dry-type lubricant.
White greaseis a heavy grease for metal-
to-metal applications where water is a
problem. White grease stays soft at both low
and high temperatures, and will not wash off
or dilute in the presence of water.
Assembly lubeis a special extreme-
pressure lubricant, usually containing moly,
used to lubricate high-load parts (such as
main and rod bearings and cam lobes) for
initial start-up of a new engine. The assembly
lube lubricates the parts without being
squeezed out or washed away until the engine
oiling system begins to function.
Silicone lubricants are used to protect
rubber, plastic, vinyl and nylon parts.
Graphite lubricantsare used where oils
cannot be used due to contamination
problems, such as in locks. The dry graphite
will lubricate metal parts while remaining
uncontaminated by dirt, water, oil or acids. It
is electrically conductive, and will not foul
electrical contacts in locks such as the
ignition switch.
Penetrating oilsloosen and lubricate
frozen, rusted and corroded fasteners and
prevent future rusting or freezing.
Heat-sink greaseis a special electrically
non-conductive grease that is used for
mounting electronic ignition modules where it
is essential that heat is transferred away from
the module.
Sealants
RTV sealantis one of the most widely-
used gasket compounds. Made from silicone,
RTV is air-curing; it seals, bonds, waterproofs,
fills surface irregularities, remains flexible,
doesn’t shrink, is relatively easy to remove,
and is used as a supplementary sealer with
almost all low- and medium-temperature
gaskets.
Anaerobic sealantis much like RTV in that
it can be used either to seal gaskets or to form
gaskets by itself. It remains flexible, is solvent-
resistant, and fills surface imperfections. The
difference between an anaerobic sealant and
an RTV-type sealant is in the curing. RTV
cures when exposed to air, while an anaerobic
sealant cures only in the absence of air. This
means that an anaerobic sealant cures only
after the assembly of parts, sealing them
together.
Thread and pipe sealant is used for
sealing hydraulic and pneumatic fittings and
vacuum lines. It is usually made from a Teflon
compound, and comes in a spray, a paint-on
liquid and as a wrap-around tape.
Chemicals
Anti-seize compoundprevents seizing,
chafing, cold welding, rust and corrosion in
fasteners. High-temperature anti-seize,
usually made with copper and graphite
lubricants, is used for exhaust system and
exhaust manifold bolts.
Anaerobic locking compoundsare used
to keep fasteners from vibrating or working
loose, and cure only after installation, in the
absence of air. Medium-strength locking
compound is used for small nuts, bolts and
screws that may be removed later. High-
strength locking compound is for large nuts,
bolts and studs which aren’t removed on a
regular basis.
Oil additivesrange from viscosity index
improvers to chemical treatments that claim
to reduce internal engine friction. It should be
noted that most oil manufacturers caution
against using additives with their oils.
Fuel additivesperform several functions,
depending on their chemical make-up. They
usually contain solvents that help dissolve
gum and varnish that build up on carburettor,
fuel injection and intake parts. They also serve
to break down carbon deposits that form on
the inside surfaces of the combustion
chambers. Some additives contain upper
cylinder lubricants for valves and piston rings,
and others contain chemicals to remove
condensation from the fuel tank.
Miscellaneous
Brake fluidis specially-formulated
hydraulic fluid that can withstand the heat and
pressure encountered in brake systems. It is
poisonous and inflammable. Care must be
taken so this fluid does not come in contact
with painted surfaces or plastics. An opened
container should always be resealed, to
prevent contamination by water or dirt. Brake
fluid absorbs moisture from the air, if left in an
unsealed container.
Weatherstrip adhesiveis used to bond
weatherstripping around doors, windows and
boot lids. It is sometimes used to attach trim
pieces.
Undersealis a petroleum-based, tar-like
substance that is designed to protect metal
surfaces on the underside of the vehicle from
corrosion. It also acts as a sound-deadening
agent by insulating the bottom of the vehicle.
Waxes and polishesare used to help
protect painted and plated surfaces from the
weather. Different types of paint may require
the use of different types of wax and polish.
Some polishes utilise a chemical or abrasive
cleaner to help remove the top layer of
oxidised (dull) paint on older vehicles. In
recent years, many non-wax polishes
containing a wide variety of chemicals such as
polymers and silicones have been introduced.
These non-wax polishes are usually easier to
apply, and last longer than conventional
waxes and polishes.