Light fuse BMW 3 SERIES 1991 E30 User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: BMW, Model Year: 1991, Model line: 3 SERIES, Model: BMW 3 SERIES 1991 E30Pages: 228, PDF Size: 7.04 MB
Page 134 of 228
Inspection
1Loosen the wheel bolts, raise the vehicle
and support it securely on axle stands.
Remove the wheel, and refit three bolts to
hold the disc in place. If the rear brake disc is
being worked on, release the handbrake.
2Remove the brake caliper as outlined in
Section 4. It is not necessary to disconnect
the brake hose. After removing the caliper,
suspend it out of the way with a piece of wire.
Remove the caliper mounting bracket (see
illustration).
3Inspect the disc surface for scoring, cracks
or other damage. Light scratches and shallow
grooves are normal after use, and are not
usually detrimental to brake operation, but
deep scoring requires disc removal andrenewal, or (if possible) refinishing by a
specialist. If a disc is cracked it must be
renewed. Be sure to check both sides of the
disc (see illustration). If severe vibration has
been noticed during application of the brakes,
the discs may be warped (excessive run-out).
If the vehicle is equipped with the Anti-lock
Braking System (ABS), do not confuse
vibration caused by warped discs with normal
operation of the ABS. It is quite normal for
some vibration to be felt through the pedal
when the system is working.
4To check disc run-out, place a dial indicator
at a point about 13 mm from the outer edge of
the disc (see illustration). Set the indicator to
zero, and rotate the disc. The indicator
reading should not exceed the specifiedallowable run-out limit. If it does (and if the
run-out is not due to wheel bearing wear), the
disc should be renewed or (if possible)
refinished by a specialist. Note:It is
recommended that the discs be resurfaced
regardless of the dial indicator reading, as this
will impart a smooth finish and ensure a
perfectly flat surface, eliminating any vibration
felt through the brake pedal or other
undesirable symptoms related to questionable
discs. At the very least, if you elect not to have
the discs resurfaced, remove the glazing from
the surface with emery cloth or sandpaper,
using a swirling motion (see illustration).
5It is absolutely critical that the disc not be
machined to a thickness less than that
specified. The minimum wear (or discard)
thickness is stamped into the hub of the disc.
The disc thickness can be checked with a
micrometer (see illustration).
Removal
6Remove the disc retaining screw (see
illustration) and remove the disc from the hub
(see illustration). If the disc is stuck to the
hub, spray a generous amount of penetrating
oil onto the area between the hub and the disc
(see illustration)and allow a few minutes for
it to loosen the rust between the two
components. If a rear disc still sticks, insert a
thin, flat-bladed screwdriver through the hub
flange, rotate the starwheel on the handbrake
9•6 Braking system
5.6c If the disc is stuck to the hub, spray
some penetrating oil onto the area
between the hub and the disc, and give the
oil a few minutes to separate the two parts
5.6b . . . and remove the disc from
the hub5.6a Remove the disc retaining screw . . .
5.5 The disc thickness can be checked
with a micrometer5.4b Using a swirling motion, remove the
glaze from the disc surface with
sandpaper or emery cloth
5.4a To check disc run-out, mount a dial
indicator as shown, and rotate the disc5.3 The brake pads on this vehicle were
obviously neglected, as the backing plate
cut deep grooves into the disc - wear this
severe means the disc must be renewed5.2 Remove the caliper mounting bracket
bolts (arrowed) and remove the bracket
Page 162 of 228

it to the approximate size and shape required,
then pull off the backing paper (if used) and
stick the tape over the hole; it can be
overlapped if the thickness of one piece is
insufficient. Burnish down the edges of the
tape with the handle of a screwdriver or
similar, to ensure that the tape is securely
attached to the metal underneath.
Bodywork repairs - filling and
respraying
Before using this Section, see the Sections
on dent, deep scratch, rust holes and gash
repairs.
Many types of bodyfiller are available, but
generally speaking, those proprietary kits
which contain a tin of filler paste and a tube of
resin hardener are best for this type of repair. A
wide, flexible plastic or nylon applicator will be
found invaluable for imparting a smooth and
well-contoured finish to the surface of the filler.
Mix up a little filler on a clean piece of card
or board - measure the hardener carefully
(follow the maker’s instructions on the pack),
otherwise the filler will set too rapidly or too
slowly. Using the applicator, apply the filler
paste to the prepared area; draw the
applicator across the surface of the filler to
achieve the correct contour and to level the
surface. As soon as a contour that
approximates to the correct one is achieved,
stop working the paste - if you carry on too
long, the paste will become sticky and begin
to “pick-up” on the applicator. Continue to
add thin layers of filler paste at 20-minute
intervals, until the level of the filler is just
proud of the surrounding bodywork.
Once the filler has hardened, the excess
can be removed using a metal plane or file.
From then on, progressively-finer grades of
abrasive paper should be used, starting with a
40-grade production paper, and finishing with
a 400-grade wet-and-dry paper. Always wrap
the abrasive paper around a flat rubber, cork,
or wooden block - otherwise the surface of
the filler will not be completely flat. During the
smoothing of the filler surface, the wet-and-
dry paper should be periodically rinsed in
water. This will ensure that a very smooth
finish is imparted to the filler at the final stage.
At this stage, the “dent” should be
surrounded by a ring of bare metal, which in
turn should be encircled by the finely
“feathered” edge of the good paintwork.
Rinse the repair area with clean water, until all
of the dust produced by the rubbing-down
operation has gone.
Spray the whole area with a light coat of
primer - this will show up any imperfections in
the surface of the filler. Repair these
imperfections with fresh filler paste or
bodystopper, and once more smooth the
surface with abrasive paper. Repeat this
spray-and-repair procedure until you are
satisfied that the surface of the filler, and the
feathered edge of the paintwork, are perfect.
Clean the repair area with clean water, and
allow to dry fully.The repair area is now ready for final
spraying. Paint spraying must be carried out
in a warm, dry, windless and dust-free
atmosphere. This condition can be created
artificially if you have access to a large indoor
working area, but if you are forced to work in
the open, you will have to pick your day very
carefully. If you are working indoors, dousing
the floor in the work area with water will help
to settle the dust which would otherwise be in
the atmosphere. If the repair area is confined
to one body panel, mask off the surrounding
panels; this will help to minimise the effects of
a slight mis-match in paint colours. Bodywork
fittings (eg chrome strips, door handles etc)
will also need to be masked off. Use genuine
masking tape, and several thicknesses of
newspaper, for the masking operations.
Before commencing to spray, agitate the
aerosol can thoroughly, then spray a test area
(an old tin, or similar) until the technique is
mastered. Cover the repair area with a thick
coat of primer; the thickness should be built
up using several thin layers of paint, rather
than one thick one. Using 400-grade wet-and-
dry paper, rub down the surface of the primer
until it is really smooth. While doing this, the
work area should be thoroughly doused with
water, and the wet-and-dry paper periodically
rinsed in water. Allow to dry before spraying
on more paint.
Spray on the top coat, again building up the
thickness by using several thin layers of paint.
Start spraying at one edge of the repair area,
and then, using a side-to-side motion, work
until the whole repair area and about 2 inches
of the surrounding original paintwork is
covered. Remove all masking material 10 to
15 minutes after spraying on the final coat of
paint.
Allow the new paint at least two weeks to
harden, then, using a paintwork renovator, or
a very fine cutting paste, blend the edges of
the paint into the existing paintwork. Finally,
apply wax polish.
Plastic components
With the use of more and more plastic body
components by the vehicle manufacturers (eg
bumpers. spoilers, and in some cases major
body panels), rectification of more serious
damage to such items has become a matter
of either entrusting repair work to a specialist
in this field, or renewing complete
components. Repair of such damage by the
DIY owner is not really feasible, owing to the
cost of the equipment and materials required
for effecting such repairs. The basic technique
involves making a groove along the line of the
crack in the plastic, using a rotary burr in a
power drill. The damaged part is then weldedback together, using a hot-air gun to heat up
and fuse a plastic filler rod into the groove.
Any excess plastic is then removed, and the
area rubbed down to a smooth finish. It is
important that a filler rod of the correct plastic
is used, as body components can be made of
a variety of different types (eg polycarbonate,
ABS, polypropylene).
Damage of a less serious nature (abrasions,
minor cracks etc) can be repaired by the DIY
owner using a two-part epoxy filler repair
material. Once mixed in equal proportions,
this is used in similar fashion to the bodywork
filler used on metal panels. The filler is usually
cured in twenty to thirty minutes, ready for
sanding and painting.
If the owner is renewing a complete
component himself, or if he has repaired it
with epoxy filler, he will be left with the
problem of finding a suitable paint for finishing
which is compatible with the type of plastic
used. At one time, the use of a universal paint
was not possible, owing to the complex range
of plastics encountered in body component
applications. Standard paints, generally
speaking, will not bond to plastic or rubber
satisfactorily. However, it is now possible to
obtain a plastic body parts finishing kit which
consists of a pre-primer treatment, a primer
and coloured top coat. Full instructions are
normally supplied with a kit, but basically, the
method of use is to first apply the pre-primer
to the component concerned, and allow it to
dry for up to 30 minutes. Then the primer is
applied, and left to dry for about an hour
before finally applying the special-coloured
top coat. The result is a correctly-coloured
component, where the paint will flex with the
plastic or rubber, a property that standard
paint does not normally possess.
6 Bodywork repair-
major damage
5
1Major damage must be repaired by a
qualified bodywork repair specialist, or
preferably by a BMW dealer. Specialised
equipment is required to do the job properly.
2If the damage is extensive, the bodyshell
must be checked for proper alignment, or the
vehicle’s handling characteristics may be
adversely affected and other components
may wear at an accelerated rate.
3Due to the fact that all of the major body
components (bonnet, wings, etc.) are
separate units, any seriously damaged
components should be replaced with new
ones rather than repaired.
Bodywork and fittings 11•3
11
If bodystopper is used, it can
be mixed with cellulose
thinners to form a really thin
paste which is ideal for filling
small holes
Sometimes bodywork
components can be found in
a scrapyard that specialises
in used vehicle components,
often at a considerable saving over the
cost of new parts.
Page 169 of 228

12
Chapter 12 Body electrical systems
Bulb renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Central locking system - description and check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Cruise control system - description and check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Direction indicator/hazard warning flasher - check and renewal . . . 5
Electric windows - description and check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Electrical system fault finding - general information . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Fuses - general information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
General information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
Headlight housing - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Headlights - adjustment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Headlights - bulb renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12Heated rear window - check and repair . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Ignition switch - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Instrument cluster - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Radio - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Radio aerial - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Relays - general information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
Service Indicator (SI) board - general information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Steering column switches - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Supplemental Restraint System (SRS) - general information . . . . . . 18
Windscreen/tailgate wiper motor - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . 16
Wiring diagrams - general information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
12•1
Easy,suitable for
novice with little
experienceFairly easy,suitable
for beginner with
some experienceFairly difficult,
suitable for competent
DIY mechanic
Difficult,suitable for
experienced DIY
mechanicVery difficult,
suitable for expert
DIY or professional
Degrees of difficulty Contents
1 General information
The chassis electrical system of this vehicle
is of 12-volt, negative earth type. Power for
the lights and all electrical accessories is
supplied by a lead/acid-type battery, which is
charged by the alternator.
This Chapter covers repair and service
procedures for various chassis (non-engine
related) electrical components. For
information regarding the engine electrical
system components (battery, alternator,
distributor and starter motor), see Chapter 5.
Warning: To prevent electrical
short-circuits, fires and injury,
always disconnect the battery
negative terminal before
checking, repairing or renewing electrical
components.
Caution: If the radio in your
vehicle is equipped with an anti-
theft system, make sure you have
the correct activation code
before disconnecting the battery, Refer to
the information on page 0-7 at the front of
this manual before detaching the cable.
Note: If, after connecting the battery, the
wrong language appears on the instrument
panel display, refer to page 0-7 for the
language resetting procedure.
2 Electrical system fault
finding- general information
2
A typical electrical circuit consists of an
electrical component, any switches, relays,
motors, fuses, fusible links or circuit breakers,
etc related to that component, and the wiring
and connectors that link the components to
both the battery and the chassis. To help you
pinpoint an electrical circuit problem, wiring
diagrams are included at the end of this book.
Before tackling any troublesome electrical
circuit, first study the appropriate wiring
diagrams to get a complete understanding of
what makes up that individual circuit.
Troublespots, for instance, can often be
isolated by noting if other components related
to that circuit are routed through the same
fuse and earth connections.
Electrical problems usually stem from
simple causes such as loose or corroded
connectors, a blown fuse, a melted fusible
link, or a bad relay. Inspect all fuses, wires
and connectors in a problem circuit first.
The basic tools needed include a circuit
tester, a high-impedance digital voltmeter, a
continuity tester and a jumper wire with an in-
line circuit breaker for bypassing electrical
components. Before attempting to locate or
define a problem with electrical testinstruments, use the wiring diagrams to
decide where to make the necessary
connections.
Voltage checks
Perform a voltage check first when a circuit
is not functioning properly. Connect one lead
of a circuit tester to either the negative battery
terminal or a known good earth.
Connect the other lead to a connector in
the circuit being tested, preferably nearest to
the battery or fuse. If the bulb of the tester
lights up, voltage is present, which means that
the part of the circuit between the connector
and the battery is problem-free. Continue
checking the rest of the circuit in the same
fashion.
When you reach a point at which no voltage
is present, the problem lies between that point
and the last test point with voltage. Most of
the time, problems can be traced to a loose
connection.Note:Keep in mind that some
circuits receive voltage only when the ignition
key is turned to a certain position.
Electrical fault diagnosis is simple if you
keep in mind that all electrical circuits are
basically electricity running from the battery,
through the wires, switches, relays, fuses and
fusible links to each electrical component
(light bulb, motor, etc) and then to earth, from
where it is passed back to the battery. Any
electrical problem is an interruption in the flow
of electricity to and from the battery.
Page 170 of 228

Finding a short-circuit
One method of finding a short-circuit is to
remove the fuse and connect a test light or
voltmeter in its place. There should be no
voltage present in the circuit. Move the
electrical connectors from side-to-side while
watching the test light. If the bulb goes on,
there is a short to earth somewhere in that
area, probably where the insulation has been
rubbed through. The same test can be
performed on each component in a circuit,
even a switch.
Earth check
Perform a earth check to see whether a
component is properly earthed (passing
current back via the vehicle body). Disconnect
the battery, and connect one lead of a self-
powered test light (often known as a
continuity tester) to a known good earth.
Connect the other lead to the wire or earth
connection being tested. The bulb should
light, indicating a good earth connection. If
not, dismantle the connection, and clean all
relevant parts thoroughly. When re-making
the connection, use serrated (shakeproof)
washers if possible, and tighten all bolts, etc,
securely.
Caution: If the radio in your
vehicle is equipped with an anti-
theft system, make sure you have
the correct activation code
before disconnecting the battery, Refer to
the information on page 0-7 at the front of
this manual before detaching the cable.
Note: If, after connecting the battery, the
wrong language appears on the instrument
panel display, refer to page 0-7 for the
language resetting procedure.
Continuity check
A continuity check determines if there are
any breaks in a circuit - if it is conducting
electricity properly. With the circuit off (no
power in the circuit), a self-powered continuity
tester can be used to check the circuit.
Connect the test leads to both ends of the
circuit, and if the test light comes on, the
circuit is passing current properly. If the light
doesn’t come on, there is a break somewhere
in the circuit. The same procedure can be
used to test a switch, by connecting the
continuity tester to the power-in and power-
out sides of the switch. With the switch turned
on, the test light should come on.
Finding an open-circuit
When diagnosing for possible open-
circuits, it is often difficult to locate them by
sight, because oxidation or terminal
misalignment are hidden by the connectors.
Intermittent problems are often caused by
oxidised or loose connections. Merely
wiggling an electrical connector may correct
the open-circuit condition, albeit temporarily.
Dismantle the connector, and spray with a
water-dispersant aerosol. On simpler
connectors, it may be possible to carefullybend the connector pins inside, to improve
the metal-to-metal contact - don’t damage
the connector in the process, however.
3 Fuses- general information
1
The electrical circuits of the vehicle are
protected by a combination of fuses and
circuit breakers. The fusebox is located in the
left corner of the engine compartment (see
illustration). On some later models, it is
located under the rear seat cushion.
Each of the fuses is designed to protect a
specific circuit, and on some models, the
various circuits are identified on the fuse
panel itself.
Miniaturised fuses are employed in the
fuseboxes. These compact fuses, with blade
terminal design, allow fingertip removal and
renewal. If an electrical component fails,
always check the fuse first. A blown fuse is
easily identified through the clear plastic
body. Visually inspect the element for
evidence of damage. If a continuity check is
called for, the blade terminal tips are exposed
in the fuse body.
Be sure to renew blown fuses with the
correct type. Fuses of different ratings are
physically interchangeable, but only fuses of
the proper rating should be used. Replacing a
fuse with one of a higher or lower value than
specified is not recommended. Each electrical
circuit needs a specific amount of protection.
The amperage value of each fuse is moulded
into the fuse body.
If the new fuse immediately fails, don’t
renew it again until the cause of the problem
is isolated and corrected. In most cases, the
cause will be a short-circuit in the wiring
caused by a broken or deteriorated wire.
4 Relays- general information
1
Several electrical accessories in the vehicle
use relays to transmit the electrical signal to
the component. If the relay is defective, thatcomponent will not operate properly. Relays
are electrically-operated switches, which are
often used in circuits drawing high levels of
current, or where more complex switching
arrangements are required.
The various relays are grouped together for
convenience in several locations under the
dash and in the engine compartment (see
accompanying illustration and illus-
tration 3.1).
If a faulty relay is suspected, it can be
removed and tested by a dealer or qualified
automotive electrician. No overhaul is
possible. Like fuses, defective relays must be
replaced with the correct type; some relays
look identical, but perform very different
functions.
5 Direction indicator/hazard
warning flasher unit- check
and renewal
2
Warning: Some later models are
equipped with an airbag or
Supplemental Restraint System
(SRS). To avoid possible damage
to this system, the manufacturer
recommends that, on airbag-equipped
models, the following procedure should be
left to a dealer service department, or
other specialist, because of the special
tools and techniques required. There is a
risk of injury if the airbag is accidentally
triggered.
1The direction indicator/hazard flasher unit is
a small canister- or box-shaped unit located
in the wiring harness on or near the steering
column. Access is gained by removing the
steering column shrouds (see illustration).
2When the flasher unit is functioning
properly, a regular clicking noise can be heard
from it when the indicators or hazard flashers
are switched on. If the direction indicators fail
on one side or the other, and the flasher unit
does not make its characteristic clicking
sound, a faulty direction indicator bulb is
indicated.
3If both direction indicators fail to blink, the
problem may be due to a blown fuse, a faulty
flasher unit, a broken switch or a loose or open
connection. If a quick check of the fusebox
12•2 Body electrical systems
4.2 Engine compartment relays3.1 The fusebox is located in the engine
compartment under a cover - the box also
includes several relays
Page 171 of 228

indicates that the direction indicator and/or
hazard fuse has blown, check the wiring for a
short-circuit before fitting a new fuse.
4Make sure that the new unit is identical to
the original. Compare the old one to the new
one before fitting it.
5Refitting is the reverse of removal.
6 Steering column switches-
removal and refitting
1
Warning: Some later models are
equipped with an airbag or
Supplemental Restraint System
(SRS). To avoid possible damage
to this system, the manufacturer
recommends that, on airbag-equipped
models, the following procedure should be
left to a dealer service department, or
other specialist, because of the special
tools and techniques required. There is a
risk of injury if the airbag is accidentally
triggered.
Caution: If the radio in your
vehicle is equipped with an anti-
theft system, make sure you have
the correct activation code
before disconnecting the battery, Refer to
the information on page 0-7 at the front of
this manual before detaching the cable.
Note: If, after connecting the battery, the
wrong language appears on the instrument
panel display, refer to page 0-7 for the
language resetting procedure.
1Disconnect the battery negative cable,
remove the steering wheel (see Chapter 10)
and steering column shrouds (see Chapter 11).
Direction indicator/headlight
switch
2Where necessary, remove the switch
mounting screws. Depress the tabs and pull
the switch out of the steering column
mounting (see illustration).
3Trace the switch wires down the steering
column to the electrical connector, and
unplug them (see illustration).
4Refitting is the reverse of removal.
Wiper/washer switch
5Where necessary, remove the switch
mounting screws.
6Depress the release clip, and detach the
switch from the steering column mounting
(see illustration). Trace the switch wiring
down the steering column to the electrical
connector, and unplug it.
7Refitting is the reverse of removal.
Cruise control switch
8Remove the wiper/washer switch.
9Where necessary, remove the switch
mounting screw. Squeeze the release tabs,
and withdraw the switch from the mounting
(see illustration).
10Disconnect the switch electrical
connector from the harness at the base of the
steering column.
11Refitting is the reverse of removal.
7 Ignition switch-
removal and refitting
1
Warning: Some later models are
equipped with an airbag or
Supplemental Restraint System
(SRS). To avoid possible damage
to this system, the manufacturer
recommends that, on airbag-equipped
models, the following procedure should be
left to a dealer service department, or
other specialist, because of the specialtools and techniques required. There is a
risk of injury if the airbag is accidentally
triggered.
Caution: If the radio in your
vehicle is equipped with an anti-
theft system, make sure you have
the correct activation code
before disconnecting the battery, Refer to
the information on page 0-7 at the front of
this manual before detaching the cable.
Note: If, after connecting the battery, the
wrong language appears on the instrument
panel display, refer to page 0-7 for the
language resetting procedure.
Removal
1Disconnect the battery negative cable.
2Remove the steering wheel (see Chap-
ter 10).
3Remove the steering column shrouds (see
Chapter 11).
4Where necessary, remove the direction
indicator/headlight control switch (see Sec-
tion 6).
5Detach the clips by inserting a small
screwdriver into the openings on the sides
while pulling out on the switch (see
illustration).
6Unplug the electrical connector from the
harness at the base of the steering column,
and remove the switch.
Refitting
7Refitting is the reverse of removal.
Body electrical systems 12•3
6.3 Follow the wiring down the steering
column to the connector6.2 Squeeze the tabs to release the switch
from the mounting
6.9 Cruise control switch removal6.6 Squeeze the wiper/washer switch tabs
and pull it directly out of the mounting
12
5.1 The direction indicator/hazard warning
flasher unit is located on the steering
column on most models - squeeze the
tabs to detach it
Page 173 of 228
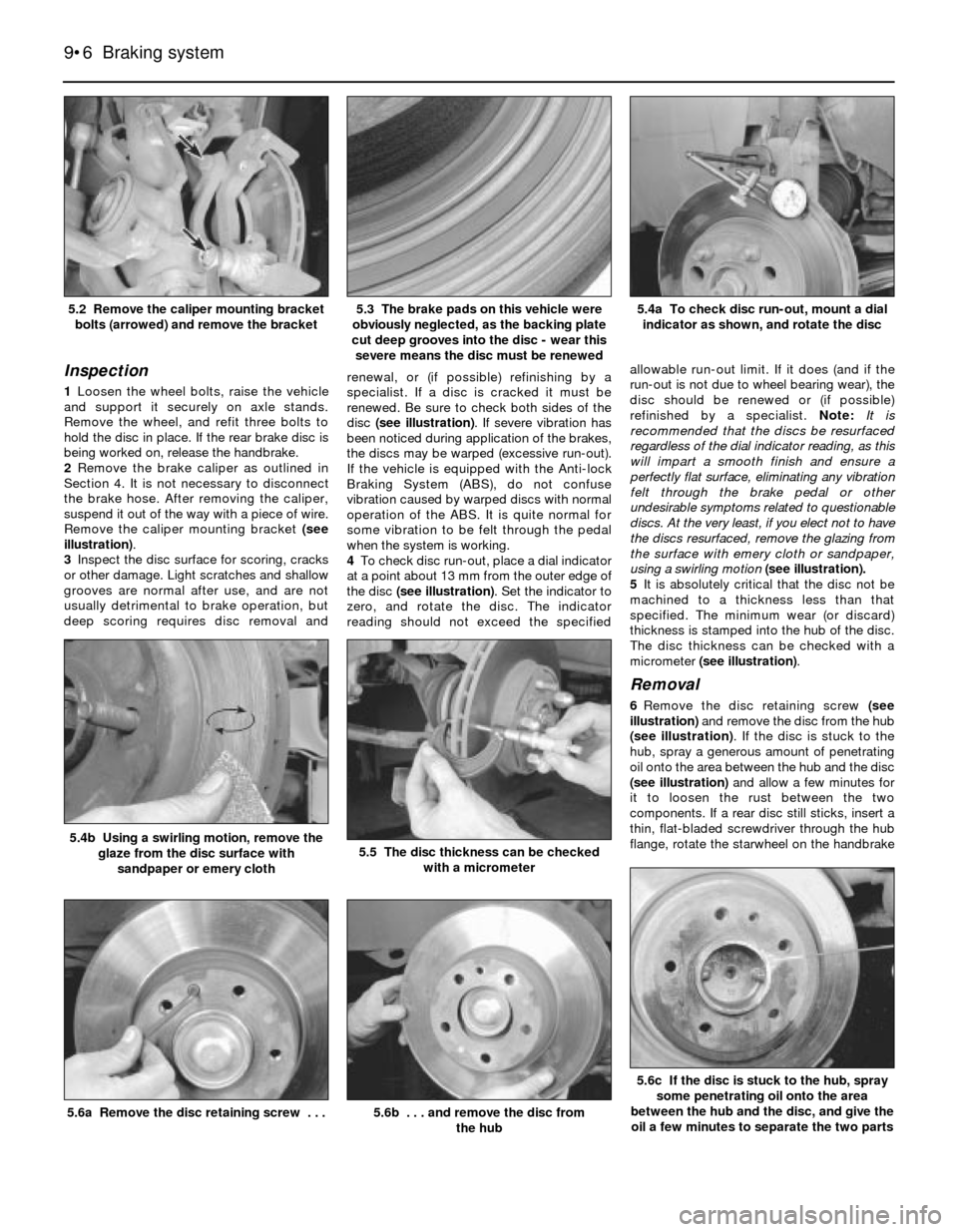
SI board is a self-contained computer which
includes a chip and batteries.
The rechargeable SI board nickel cadmium
(nicad) batteries maintain power to the
computer memory in the event of a power
drop (such as during starting) or complete
power loss (such as a dead or disconnected
battery) (see illustration). This assures power
so the computer can continue to keep track of
mileage and turn the lights on at the proper
interval.
The batteries have a life of approximately
six years, at which time they must be replaced
with new ones. Also, since they are recharged
by the engine charging system, they can run
down prematurely if power is cut off for some
reason (such as a blown fuse, a fault in the
wiring, or extended storage of the vehicle).
Excessive heat or cold can also shorten
battery life, with heat the greatest enemy.
Extreme heat can cause the batteries to
actually split open, allowing acid to drip into
the instrument cluster.
Several instruments controlled by the SI
board can be affected by low or discharged
batteries. Symptoms of low or dead SI board
batteries can include inconsistent tachometer
and temperature gauge readings, background
radio noise, and the inability to turn the
service lights off with the special tool.
Although only complete SI boards are
available from the manufacturer, batteries are
available separately from aftermarket sources.
While it is possible for the home mechanic to
renew the batteries, they are soldered to the
board, so unless you are skilled at this and
have the proper tools, this job should be left
to an experienced electronics technician.
Considerable savings can be realised by
removing the instrument cluster (see
Section 10) and taking it to an electronics
specialist.
Caution: the instrument cluster
and components are very
susceptible to damage from
static electricity. Make sure you
are earthed and have discharged any
static electricity (by touching an object
such as a metal water pipe) before
touching the cluster components.12 Headlights- bulb renewal
1
Caution: If the radio in your
vehicle is equipped with an anti-
theft system, make sure you have
the correct activation code
before disconnecting the battery, Refer to
the information on page 0-7 at the front of
this manual before detaching the cable.
Note: If, after connecting the battery, the
wrong language appears on the instrument
panel display, refer to page 0-7 for the
language resetting procedure.
1Disconnect the battery negative cable.
Sealed-beam type
2Remove the grille (see Chapter 11).
3Remove the headlight retainer screws,
taking care not to disturb the adjustment
screws.
4Remove the retainer and pull the headlight
out enough to allow the connector to be
unplugged.
5Remove the headlight.
6To refit the headlight, plug the connector in,
place the headlight in position, and refit the
retainer and screws. Tighten the screws
securely.7Refit the grille. Connect the battery negative
cable.
Halogen bulb type
Warning: Halogen gas-filled bulbs
are under pressure, and may
shatter if the surface is scratched
or the bulb is dropped. Wear eye
protection, and handle the bulbs carefully,
grasping only the base whenever possible.
Do not touch the surface of the bulb with
your fingers, because the oil from your
skin could cause it to overheat and fail
prematurely.
8From behind the headlight assembly,
remove the outer cover (see illustration).
9Twist and release the inner cover from the
rear of the headlight (see illustration).
10Disconnect the wire from the rear of the
headlight bulb (see illustration).
11Release the clips, and withdraw the bulb
from the headlight unit (see illustration).
12Fit the new bulb using a reversal of the
removal procedure. Make sure that the clips
engage the bulb correctly.
13Connect the battery negative cable.
Body electrical systems 12•5
12.9 Twist and release the headlight inner
cover12.8 Removing the headlight rear outer
cover (3-Series shown)11.2 These batteries (arrowed) power the
Service Indicator (SI) board
12.11 Removing the headlight bulb (do not
touch the surface of the bulb with your
fingers)12.10 Disconnecting the wire from the rear
of the headlight bulb
12
If you do touch the headlamp
bulb surface, clean it with
methylated spirit.
Page 176 of 228
12Refitting is a reversal of removal. When
fitting the motor, if necessary plug in the
connector and run the motor briefly until it is
in the “neutral” (wiper parked) position.
17 Heated rear window-
check and repair
2
1The heated rear window consists of a
number of horizontal elements on the glass
surface.
2Small breaks in the element can be repaired
without removing the rear window.
Check
3Switch on the ignition and the heated rear
window.
4Place the positive lead of a voltmeter to the
heater element nearest to the incoming power
source.
5Wrap a piece of aluminium foil around the
negative lead of the voltmeter on the positive
side of the suspected broken element, and
slide it slowly towards the negative side.
Watch the voltmeter needle - when it moves
from zero, you have located the break.
Repair
6Repair the break in the line using a repair kit
recommended specifically for this purpose,
such as BMW repair kit No. 81 22 9 (or
equivalent). Included in this kit is plastic
conductive epoxy. The following paragraphs
give general instructions for this type of repair;
follow the instructions supplied with the repair
kit if they are different.
7Prior to repairing a break, switch off the
circuit and allow it to cool down for a few
minutes.
8Lightly buff the element area with fine steel
wool, then clean it thoroughly.
9Use masking tape to mask off the area of
repair, leaving a slit to which the epoxy can be
applied.
10Mix the epoxy thoroughly, according to
the instructions on the package.
11Apply the epoxy material to the slit in the
masking tape, overlapping the undamaged
area about 20 mm on each end.12Allow the repair to cure for 24 hours
before removing the tape and using the
heated rear window.
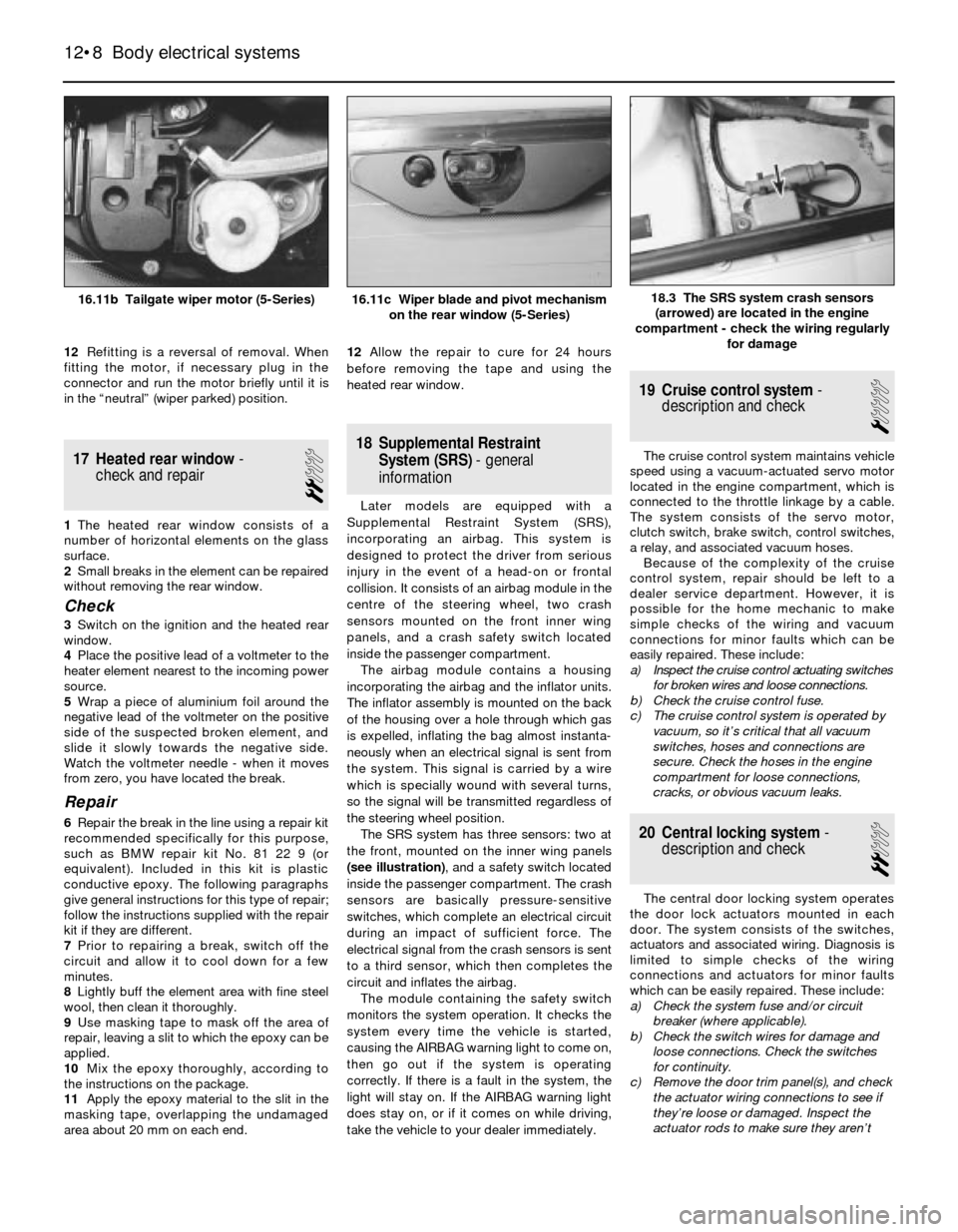
18 Supplemental Restraint
System (SRS)- general
information
Later models are equipped with a
Supplemental Restraint System (SRS),
incorporating an airbag. This system is
designed to protect the driver from serious
injury in the event of a head-on or frontal
collision. It consists of an airbag module in the
centre of the steering wheel, two crash
sensors mounted on the front inner wing
panels, and a crash safety switch located
inside the passenger compartment.
The airbag module contains a housing
incorporating the airbag and the inflator units.
The inflator assembly is mounted on the back
of the housing over a hole through which gas
is expelled, inflating the bag almost instanta-
neously when an electrical signal is sent from
the system. This signal is carried by a wire
which is specially wound with several turns,
so the signal will be transmitted regardless of
the steering wheel position.
The SRS system has three sensors: two at
the front, mounted on the inner wing panels
(see illustration), and a safety switch located
inside the passenger compartment. The crash
sensors are basically pressure-sensitive
switches, which complete an electrical circuit
during an impact of sufficient force. The
electrical signal from the crash sensors is sent
to a third sensor, which then completes the
circuit and inflates the airbag.
The module containing the safety switch
monitors the system operation. It checks the
system every time the vehicle is started,
causing the AIRBAG warning light to come on,
then go out if the system is operating
correctly. If there is a fault in the system, the
light will stay on. If the AIRBAG warning light
does stay on, or if it comes on while driving,
take the vehicle to your dealer immediately.
19 Cruise control system-
description and check
1
The cruise control system maintains vehicle
speed using a vacuum-actuated servo motor
located in the engine compartment, which is
connected to the throttle linkage by a cable.
The system consists of the servo motor,
clutch switch, brake switch, control switches,
a relay, and associated vacuum hoses.
Because of the complexity of the cruise
control system, repair should be left to a
dealer service department. However, it is
possible for the home mechanic to make
simple checks of the wiring and vacuum
connections for minor faults which can be
easily repaired. These include:
a) Inspect the cruise control actuating switches
for broken wires and loose connections.
b) Check the cruise control fuse.
c) The cruise control system is operated by
vacuum, so it’s critical that all vacuum
switches, hoses and connections are
secure. Check the hoses in the engine
compartment for loose connections,
cracks, or obvious vacuum leaks.
20 Central locking system-
description and check
2
The central door locking system operates
the door lock actuators mounted in each
door. The system consists of the switches,
actuators and associated wiring. Diagnosis is
limited to simple checks of the wiring
connections and actuators for minor faults
which can be easily repaired. These include:
a) Check the system fuse and/or circuit
breaker (where applicable).
b) Check the switch wires for damage and
loose connections. Check the switches
for continuity.
c) Remove the door trim panel(s), and check
the actuator wiring connections to see if
they’re loose or damaged. Inspect the
actuator rods to make sure they aren’t
12•8 Body electrical systems
18.3 The SRS system crash sensors
(arrowed) are located in the engine
compartment - check the wiring regularly
for damage16.11b Tailgate wiper motor (5-Series)16.11c Wiper blade and pivot mechanism
on the rear window (5-Series)
Page 209 of 228

REF•8General Repair Procedures
Whenever servicing, repair or overhaul work
is carried out on the car or its components,
observe the following procedures and
instructions. This will assist in carrying out the
operation efficiently and to a professional
standard of workmanship.
Joint mating faces and gaskets
When separating components at their
mating faces, never insert screwdrivers or
similar implements into the joint between the
faces in order to prise them apart. This can
cause severe damage which results in oil
leaks, coolant leaks, etc upon reassembly.
Separation is usually achieved by tapping
along the joint with a soft-faced hammer in
order to break the seal. However, note that
this method may not be suitable where
dowels are used for component location.
Where a gasket is used between the mating
faces of two components, a new one must be
fitted on reassembly; fit it dry unless otherwise
stated in the repair procedure. Make sure that
the mating faces are clean and dry, with all
traces of old gasket removed. When cleaning a
joint face, use a tool which is unlikely to score
or damage the face, and remove any burrs or
nicks with an oilstone or fine file.
Make sure that tapped holes are cleaned
with a pipe cleaner, and keep them free of
jointing compound, if this is being used,
unless specifically instructed otherwise.
Ensure that all orifices, channels or pipes
are clear, and blow through them, preferably
using compressed air.
Oil seals
Oil seals can be removed by levering them
out with a wide flat-bladed screwdriver or
similar implement. Alternatively, a number of
self-tapping screws may be screwed into the
seal, and these used as a purchase for pliers or
some similar device in order to pull the seal free.
Whenever an oil seal is removed from its
working location, either individually or as part
of an assembly, it should be renewed.
The very fine sealing lip of the seal is easily
damaged, and will not seal if the surface it
contacts is not completely clean and free from
scratches, nicks or grooves. If the original
sealing surface of the component cannot be
restored, and the manufacturer has not made
provision for slight relocation of the seal
relative to the sealing surface, the component
should be renewed.
Protect the lips of the seal from any surface
which may damage them in the course of
fitting. Use tape or a conical sleeve where
possible. Lubricate the seal lips with oil before
fitting and, on dual-lipped seals, fill the space
between the lips with grease.
Unless otherwise stated, oil seals must be
fitted with their sealing lips toward the
lubricant to be sealed.
Use a tubular drift or block of wood of the
appropriate size to install the seal and, if the
seal housing is shouldered, drive the seal
down to the shoulder. If the seal housing isunshouldered, the seal should be fitted with
its face flush with the housing top face (unless
otherwise instructed).
Screw threads and fastenings
Seized nuts, bolts and screws are quite a
common occurrence where corrosion has set
in, and the use of penetrating oil or releasing
fluid will often overcome this problem if the
offending item is soaked for a while before
attempting to release it. The use of an impact
driver may also provide a means of releasing
such stubborn fastening devices, when used
in conjunction with the appropriate
screwdriver bit or socket. If none of these
methods works, it may be necessary to resort
to the careful application of heat, or the use of
a hacksaw or nut splitter device.
Studs are usually removed by locking two
nuts together on the threaded part, and then
using a spanner on the lower nut to unscrew
the stud. Studs or bolts which have broken off
below the surface of the component in which
they are mounted can sometimes be removed
using a stud extractor. Always ensure that a
blind tapped hole is completely free from oil,
grease, water or other fluid before installing
the bolt or stud. Failure to do this could cause
the housing to crack due to the hydraulic
action of the bolt or stud as it is screwed in.
When tightening a castellated nut to accept
a split pin, tighten the nut to the specified
torque, where applicable, and then tighten
further to the next split pin hole. Never slacken
the nut to align the split pin hole, unless stated
in the repair procedure.
When checking or retightening a nut or bolt
to a specified torque setting, slacken the nut
or bolt by a quarter of a turn, and then
retighten to the specified setting. However,
this should not be attempted where angular
tightening has been used.
For some screw fastenings, notably
cylinder head bolts or nuts, torque wrench
settings are no longer specified for the latter
stages of tightening, “angle-tightening” being
called up instead. Typically, a fairly low torque
wrench setting will be applied to the
bolts/nuts in the correct sequence, followed
by one or more stages of tightening through
specified angles.
Locknuts, locktabs and washers
Any fastening which will rotate against a
component or housing during tightening
should always have a washer between it and
the relevant component or housing.
Spring or split washers should always be
renewed when they are used to lock a critical
component such as a big-end bearing
retaining bolt or nut. Locktabs which are
folded over to retain a nut or bolt should
always be renewed.
Self-locking nuts can be re-used in non-
critical areas, providing resistance can be felt
when the locking portion passes over the bolt
or stud thread. However, it should be noted
that self-locking stiffnuts tend to lose theireffectiveness after long periods of use, and
should then be renewed as a matter of course.
Split pins must always be replaced with
new ones of the correct size for the hole.
When thread-locking compound is found
on the threads of a fastener which is to be re-
used, it should be cleaned off with a wire
brush and solvent, and fresh compound
applied on reassembly.
Special tools
Some repair procedures in this manual
entail the use of special tools such as a press,
two or three-legged pullers, spring com-
pressors, etc. Wherever possible, suitable
readily-available alternatives to the manu-
facturer’s special tools are described, and are
shown in use. In some instances, where no
alternative is possible, it has been necessary
to resort to the use of a manufacturer’s tool,
and this has been done for reasons of safety
as well as the efficient completion of the repair
operation. Unless you are highly-skilled and
have a thorough understanding of the
procedures described, never attempt to
bypass the use of any special tool when the
procedure described specifies its use. Not
only is there a very great risk of personal
injury, but expensive damage could be
caused to the components involved.
Environmental considerations
When disposing of used engine oil, brake
fluid, antifreeze, etc, give due consideration to
any detrimental environmental effects. Do not,
for instance, pour any of the above liquids
down drains into the general sewage system,
or onto the ground to soak away. Many local
council refuse tips provide a facility for waste
oil disposal, as do some garages. If none of
these facilities are available, consult your local
Environmental Health Department, or the
National Rivers Authority, for further advice.
With the universal tightening-up of legis-
lation regarding the emission of environmen-
tally-harmful substances from motor vehicles,
most vehicles have tamperproof devices fitted
to the main adjustment points of the fuel
system. These devices are primarily designed
to prevent unqualified persons from adjusting
the fuel/air mixture, with the chance of a
consequent increase in toxic emissions. If
such devices are found during servicing or
overhaul, they should, wherever possible, be
renewed or refitted in accordance with the
manufacturer’s requirements or current
legislation.
Note: It is
antisocial and
illegal to dump
oil down the
drain. To find
the location of
your local oil
recycling
bank, call this
number free.
Page 211 of 228

REF•10Fault Finding
Engine will not rotate when attempting to start
m mBattery terminal connections loose or corroded (Chapter 1).
m mBattery discharged or faulty (Chapter 1).
m mAutomatic transmission not completely engaged in Park (Chap-
ter 7B) or (on models with a clutch switch) clutch not completely
depressed (Chapter 8).
m mBroken, loose or disconnected wiring in the starting circuit
(Chapters 5 and 12).
m mStarter motor pinion jammed in flywheel ring gear (Chapter 5).
m mStarter solenoid faulty (Chapter 5).
m mStarter motor faulty (Chapter 5).
m mIgnition switch faulty (Chapter 12).
m mStarter pinion or flywheel teeth worn or broken (Chapter 5).
m mEngine internal problem (Chapter 2B).
Engine rotates, but will not start
m
mFuel tank empty.
m mBattery discharged (engine rotates slowly) (Chapter 5).
m mBattery terminal connections loose or corroded (Chapter 1).
m mLeaking fuel injector(s), faulty fuel pump, pressure regulator, etc
(Chapter 4).
m mFuel not reaching fuel injection system or carburettor (Chapter 4).
m mIgnition components damp or damaged (Chapter 5).
m mFuel injector stuck open (Chapter 4).
m mWorn, faulty or incorrectly-gapped spark plugs (Chapter 1).
m mBroken, loose or disconnected wiring in the starting circuit
(Chapter 5).
m mLoose distributor mounting bolts causing ignition timing to wander
(Chapters 1 and 5).
m mBroken, loose or disconnected wires at the ignition coil, or faulty
coil (Chapter 5).
Engine hard to start when cold
m mBattery discharged (Chapter 1).
m mFuel system malfunctioning (Chapter 4).
m mInjector(s) leaking or carburettor automatic choke faulty (Chap-
ter 4).
m mDistributor rotor carbon-tracked (Chapter 5).
Engine hard to start when hot
m
mAir filter element clogged (Chapter 1).
m mFuel not reaching the fuel injection system or carburettor (Chap-
ter 4).
m mCorroded battery connections, especially earth (negative)
connection (Chapter 1).
Starter motor noisy or excessively-rough in
engagement
m mPinion or flywheel gear teeth worn or broken (Chapter 5).
m mStarter motor mounting bolts loose or missing (Chapter 5).
Engine starts, but stops immediately
m
mLoose or faulty electrical connections at distributor, coil or
alternator (Chapter 5).
m mInsufficient fuel reaching the fuel injector(s) or carburettor
(Chapters 1 and 4).
m mDamaged fuel injection system speed sensors (Chapter 5).
m mFaulty fuel injection relays (Chapter 5).
Oil puddle under engine
m
mOil sump gasket and/or sump drain plug seal leaking (Chapter 2).
m mOil pressure sender unit leaking (Chapter 2).
m mValve cover gaskets leaking (Chapter 2).
m mEngine oil seals leaking (Chapter 2).
Engine idles erratically
m
mVacuum leakage (Chapter 4).
m mAir filter element clogged (Chapter 1).
m mFuel pump not delivering sufficient fuel to the fuel injection system
or carburettor (Chapter 4).
m mLeaking head gasket (Chapter 2).
m mTiming belt/chain and/or sprockets worn (Chapter 2).
m mCamshaft lobes worn (Chapter 2).
m mFaulty charcoal canister, where fitted (Chapter 6). This Section provides an easy-reference guide to the more
common problems which may occur during the operation of your
vehicle. These problems and their possible causes are grouped under
headings denoting various components or systems, such as Engine,
Cooling system, etc. They also refer you to the Chapter and/or
Section which deals with the problem.
Remember that successful fault diagnosis is not a mysterious
black art practised only by professional mechanics. It is simply the
result of the right knowledge combined with an intelligent, systematic
approach to the problem. Always work by a process of elimination,
starting with the simplest solution and working through to the mostcomplex - and never overlook the obvious. Anyone can run the fuel
tank dry or leave the lights on overnight, so don’t assume that you are
exempt from such oversights.
Finally, always establish a clear idea of why a problem has
occurred, and take steps to ensure that it doesn’t happen again. If the
electrical system fails because of a poor connection, check all other
connections in the system to make sure that they don’t fail as well. If a
particular fuse continues to blow, find out why - don’t just renew one
fuse after another. Remember, failure of a small component can often
be indicative of potential failure or incorrect functioning of a more
important component or system.
Engine
Page 218 of 228

REF•18Automotive chemicals and lubricants
A number of automotive chemicals and
lubricants are available for use during vehicle
maintenance and repair. They include a wide
variety of products ranging from cleaning
solvents and degreasers to lubricants and
protective sprays for rubber, plastic and
vinyl.
Cleaners
Carburettor cleaner and choke cleaner
is a strong solvent for gum, varnish and
carbon. Most carburettor cleaners leave a
dry-type lubricant film which will not harden or
gum up. Because of this film, it is not
recommended for use on electrical
components.
Brake system cleaneris used to remove
grease and brake fluid from the brake system,
where clean surfaces are absolutely
necessary. It leaves no residue, and often
eliminates brake squeal caused by
contaminants.
Electrical cleaner removes oxidation,
corrosion and carbon deposits from electrical
contacts, restoring full current flow. It can also
be used to clean spark plugs, carburettor jets,
voltage regulators and other parts where an
oil-free surface is desired.
Moisture dispersantsremove water and
moisture from electrical components such as
alternators, voltage regulators, electrical
connectors and fuse blocks. They are non-
conductive and non-corrosive.
Degreasersare heavy-duty solvents used
to remove grease from the outside of the
engine and from chassis components. They
can be sprayed or brushed on, and are usually
rinsed off with water.
Lubricants
Engine oilis the lubricant formulated for
use in engines. It normally contains a wide
variety of additives to prevent corrosion and
reduce foaming and wear. Engine oil comes in
various weights (viscosity ratings) from 5 to
60. The recommended weight of the oil
depends on the season, temperature and the
demands on the engine. Light oil is used in
cold climates and under light load conditions.
Heavy oil is used in hot climates, and where
high loads are encountered. Multi-viscosity
(multigrade) oils are designed to have
characteristics of both light and heavy oils,
and are available in a number of weights from
5W-20 to 20W-50.
Gear oilis designed to be used in
differentials, manual transmissions and other
areas where high-temperature lubrication is
required.
Chassis and wheel bearing greaseis a
heavy grease used where increased loads and
friction are encountered, such as for wheel
bearings, balljoints, tie-rod ends and universal
joints.High-temperature wheel bearing grease
is designed to withstand the extreme
temperatures encountered by wheel bearings
in disc brake-equipped vehicles. It usually
contains molybdenum disulphide (moly),
which is a dry-type lubricant.
White greaseis a heavy grease for metal-
to-metal applications where water is a
problem. White grease stays soft at both low
and high temperatures, and will not wash off
or dilute in the presence of water.
Assembly lubeis a special extreme-
pressure lubricant, usually containing moly,
used to lubricate high-load parts (such as
main and rod bearings and cam lobes) for
initial start-up of a new engine. The assembly
lube lubricates the parts without being
squeezed out or washed away until the engine
oiling system begins to function.
Silicone lubricants are used to protect
rubber, plastic, vinyl and nylon parts.
Graphite lubricantsare used where oils
cannot be used due to contamination
problems, such as in locks. The dry graphite
will lubricate metal parts while remaining
uncontaminated by dirt, water, oil or acids. It
is electrically conductive, and will not foul
electrical contacts in locks such as the
ignition switch.
Penetrating oilsloosen and lubricate
frozen, rusted and corroded fasteners and
prevent future rusting or freezing.
Heat-sink greaseis a special electrically
non-conductive grease that is used for
mounting electronic ignition modules where it
is essential that heat is transferred away from
the module.
Sealants
RTV sealantis one of the most widely-
used gasket compounds. Made from silicone,
RTV is air-curing; it seals, bonds, waterproofs,
fills surface irregularities, remains flexible,
doesn’t shrink, is relatively easy to remove,
and is used as a supplementary sealer with
almost all low- and medium-temperature
gaskets.
Anaerobic sealantis much like RTV in that
it can be used either to seal gaskets or to form
gaskets by itself. It remains flexible, is solvent-
resistant, and fills surface imperfections. The
difference between an anaerobic sealant and
an RTV-type sealant is in the curing. RTV
cures when exposed to air, while an anaerobic
sealant cures only in the absence of air. This
means that an anaerobic sealant cures only
after the assembly of parts, sealing them
together.
Thread and pipe sealant is used for
sealing hydraulic and pneumatic fittings and
vacuum lines. It is usually made from a Teflon
compound, and comes in a spray, a paint-on
liquid and as a wrap-around tape.
Chemicals
Anti-seize compoundprevents seizing,
chafing, cold welding, rust and corrosion in
fasteners. High-temperature anti-seize,
usually made with copper and graphite
lubricants, is used for exhaust system and
exhaust manifold bolts.
Anaerobic locking compoundsare used
to keep fasteners from vibrating or working
loose, and cure only after installation, in the
absence of air. Medium-strength locking
compound is used for small nuts, bolts and
screws that may be removed later. High-
strength locking compound is for large nuts,
bolts and studs which aren’t removed on a
regular basis.
Oil additivesrange from viscosity index
improvers to chemical treatments that claim
to reduce internal engine friction. It should be
noted that most oil manufacturers caution
against using additives with their oils.
Fuel additivesperform several functions,
depending on their chemical make-up. They
usually contain solvents that help dissolve
gum and varnish that build up on carburettor,
fuel injection and intake parts. They also serve
to break down carbon deposits that form on
the inside surfaces of the combustion
chambers. Some additives contain upper
cylinder lubricants for valves and piston rings,
and others contain chemicals to remove
condensation from the fuel tank.
Miscellaneous
Brake fluidis specially-formulated
hydraulic fluid that can withstand the heat and
pressure encountered in brake systems. It is
poisonous and inflammable. Care must be
taken so this fluid does not come in contact
with painted surfaces or plastics. An opened
container should always be resealed, to
prevent contamination by water or dirt. Brake
fluid absorbs moisture from the air, if left in an
unsealed container.
Weatherstrip adhesiveis used to bond
weatherstripping around doors, windows and
boot lids. It is sometimes used to attach trim
pieces.
Undersealis a petroleum-based, tar-like
substance that is designed to protect metal
surfaces on the underside of the vehicle from
corrosion. It also acts as a sound-deadening
agent by insulating the bottom of the vehicle.
Waxes and polishesare used to help
protect painted and plated surfaces from the
weather. Different types of paint may require
the use of different types of wax and polish.
Some polishes utilise a chemical or abrasive
cleaner to help remove the top layer of
oxidised (dull) paint on older vehicles. In
recent years, many non-wax polishes
containing a wide variety of chemicals such as
polymers and silicones have been introduced.
These non-wax polishes are usually easier to
apply, and last longer than conventional
waxes and polishes.