relay BMW 3 SERIES 1998 E46 Drive Away Protection Syst
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: BMW, Model Year: 1998, Model line: 3 SERIES, Model: BMW 3 SERIES 1998 E46Pages: 30, PDF Size: 0.7 MB
Page 5 of 30

5
EWS
EWS I
EWS I was installed on vehicles beginning production 1/94, replacing the original Drive
Away Protection System.
Purpose of the System
The next level of compliancy with the European Insurance Commission required additional
changes from the previous system. An additional component was added called the Starter
Immobilization Relay. This relay module provides added theft prevention and safety fea-
tures.
At the time of introduction the system was referred to as Electronic Drive Away
Protectionwhich in German is E
lectronische Wegfahrsperreor EWS.
The EWS I system consisted of the following components:
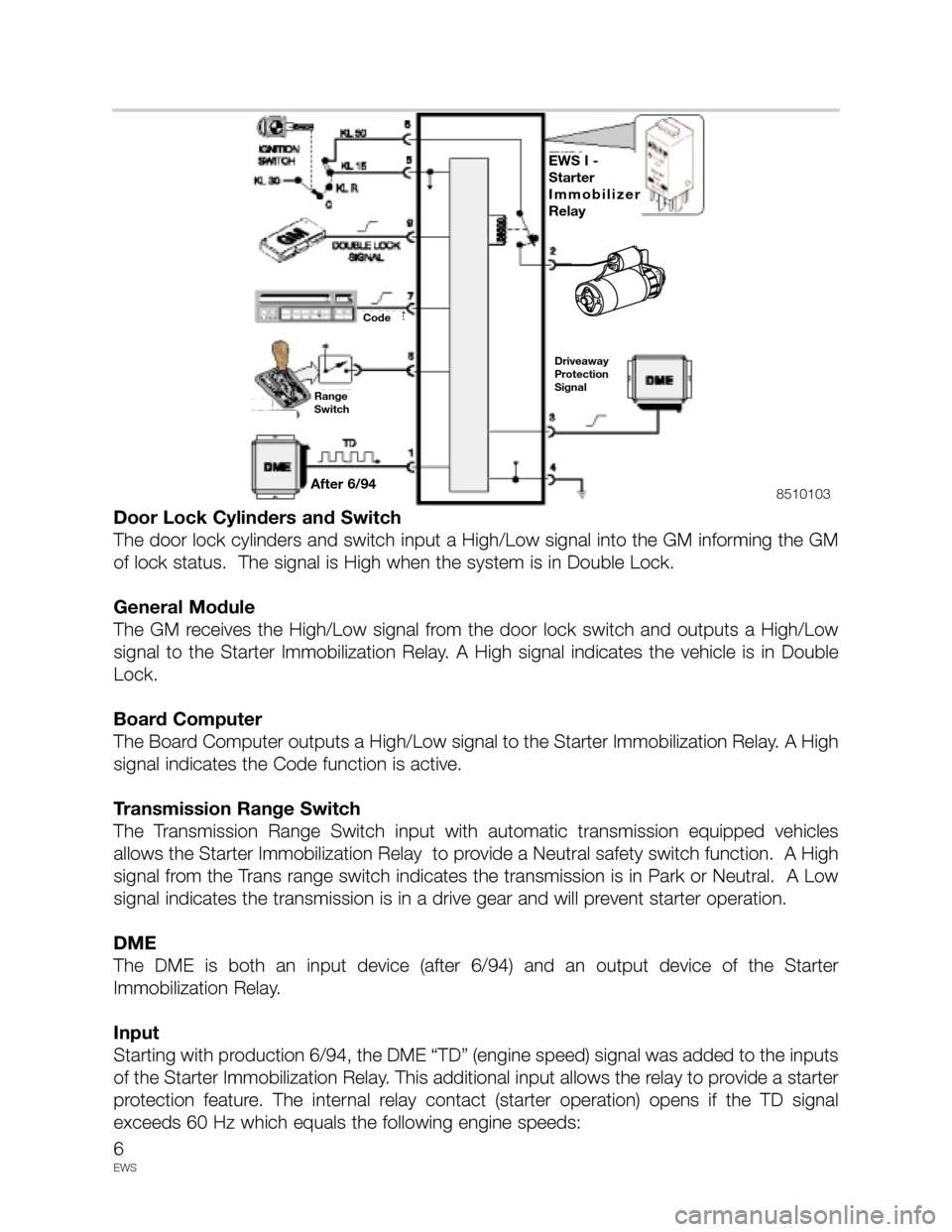
• Starter Immobilization Relay
• Door Lock Cylinders and Switch
• General Module
• Board Computer (if equipped)
• Transmission Range Switch
• DME Engine Speed Signal (Beginning 6/94 Production)
• DWA (E31)
System Components
Starter Immobilization Relay
The Starter Immobilization Relay was installed on E31, E34 and E36 vehicles.
It was in the following location:
E36 -In the relay carrier to the left of the steering column.
E31/E34-In the “A” pillar above the footwell kick panel speaker.
The Starter Immobilization Relay functions as a “Smart Relay”, a relay which receives inputs
from various sources looking at the proper combination of input signals before activating a
component, in this case the starter.
The Starter Immobilization Relay receives input from:
• Ignition Switch • General Module • Board Computer
• Trans Range Switch • DME (>6/94)
And processes output to:
• Starter • DME8510104
Page 6 of 30
6
EWS
Door Lock Cylinders and Switch
The door lock cylinders and switch input a High/Low signal into the GM informing the GM
of lock status. The signal is High when the system is in Double Lock.
General Module
The GM receives the High/Low signal from the door lock switch and outputs a High/Low
signal to the Starter Immobilization Relay. A High signal indicates the vehicle is in Double
Lock.
Board Computer
The Board Computer outputs a High/Low signal to the Starter Immobilization Relay. A High
signal indicates the Code function is active.
Transmission Range Switch
The Transmission Range Switch input with automatic transmission equipped vehicles
allows the Starter Immobilization Relay to provide a Neutral safety switch function. A High
signal from the Trans range switch indicates the transmission is in Park or Neutral. A Low
signal indicates the transmission is in a drive gear and will prevent starter operation.
DME
The DME is both an input device (after 6/94) and an output device of the Starter
Immobilization Relay.
Input
Starting with production 6/94, the DME “TD” (engine speed) signal was added to the inputs
of the Starter Immobilization Relay. This additional input allows the relay to provide a starter
protection feature. The internal relay contact (starter operation) opens if the TD signal
exceeds 60 Hz which equals the following engine speeds:
8510103
EWS I -
Starter
Immobilizer
Relay
After 6/94
Driveaway
Protection
Signal
Range
Switch
Code
Page 7 of 30

7
EWS
• 4 cylinder =1800 RPM
• 6 or 12 cylinder =1200 RPM
• 8 cylinder =900 RPM
The relay contacts will close when the exceeded Hz value drops to 5Hz below the maxi-
mum value. This is intended as a safety feature to prevent starter motor activation when the
engine is running above these speeds.
Output
The DME receives a High/Low signal from the Starter Immobilization Relay. When the sig-
nal is High, the DME does not activate injector or ignition operation.
DWA (E31)
The DWA outputs a High/Low signal to the Starter Immobilization Relay indicating the con-
dition of the alarm system. A High signal indicates the alarm is armed, preventing vehicle
starting.
Principle of Operation
The EWS Starter Immobilization Relay receives it’s inputs from the Ignition switch, GM (or
DWA), BC, Trans Range Switch and the DME (after 6/94). The relay will prevent engine
starting if:
• The vehicle is locked from the outside. The GM receives the High signal from the
door lock switch and sends a High signal to the EWS.
• The BC Code function is set.
• A DWA High signal is received. (E31only)
• A Low signal is received from the Trans Range Switch.
• The engine speed signal from the DME exceeds 60Hz. (after 6/94)
The Ignition and injection functions of the DME are disabled and the KL50 start signal to
the starter is opened to prevent starter operation.
Workshop Hints:
Starter Immobilization Relays are different for manual and automatic vehicles, check to ensure correct
relay is installed.
The Starter Immobilization Relay is not on the Diagnostic Link. Conventional troubleshooting techniques
using the DISplus, a DVOM and the correct ETM are necessary.
Loss of input from the GM or BC will allow the engine to start.
Loss of input from the Trans Range Switch will NOTallow the engine to start.
Page 11 of 30

11
EWS
EWS II Control Module
The EWS II Control Module is linked to the BC, GM, DME, Trans Range switch and the
starter for drive away protection operation. The module incorporates an integral starter relay
and stores data and codes for communication with the transponder chip.
The function of the EWS II module is to provide improved drive away protection for the vehi-
cle and it incorporates many features of previous systems:
• Lock out of the starter when the code function of the BC is set.
• Disable injection and ignition through the DME.
• Prevent starter engagement with engine running.
• Recognition of Park/Neutral position with automatic transmission.
New features that have been added:
• Disable injection, ignition and starter operation until a correct key is recognized.
• EWS and DME synchronization through the use of the ISN.
• Release of double lock when a correctly coded key is switched on.
The EWS II control module stores the following data
for the key transponder inter-link:
• Key identification code- up to 10 keys.
• Key password.
• Changing code- up to 10 keys.
Workshop Hint:
On E31, E36, E38 and E39 models the
EWS II control module is located behind
the glove box in the electrical carrier.
On E34 models the module is located on
the drivers side of the vehicle behind the
knee bolster.
8510106
Typical component locations
E36 shown
Page 14 of 30
14
EWS
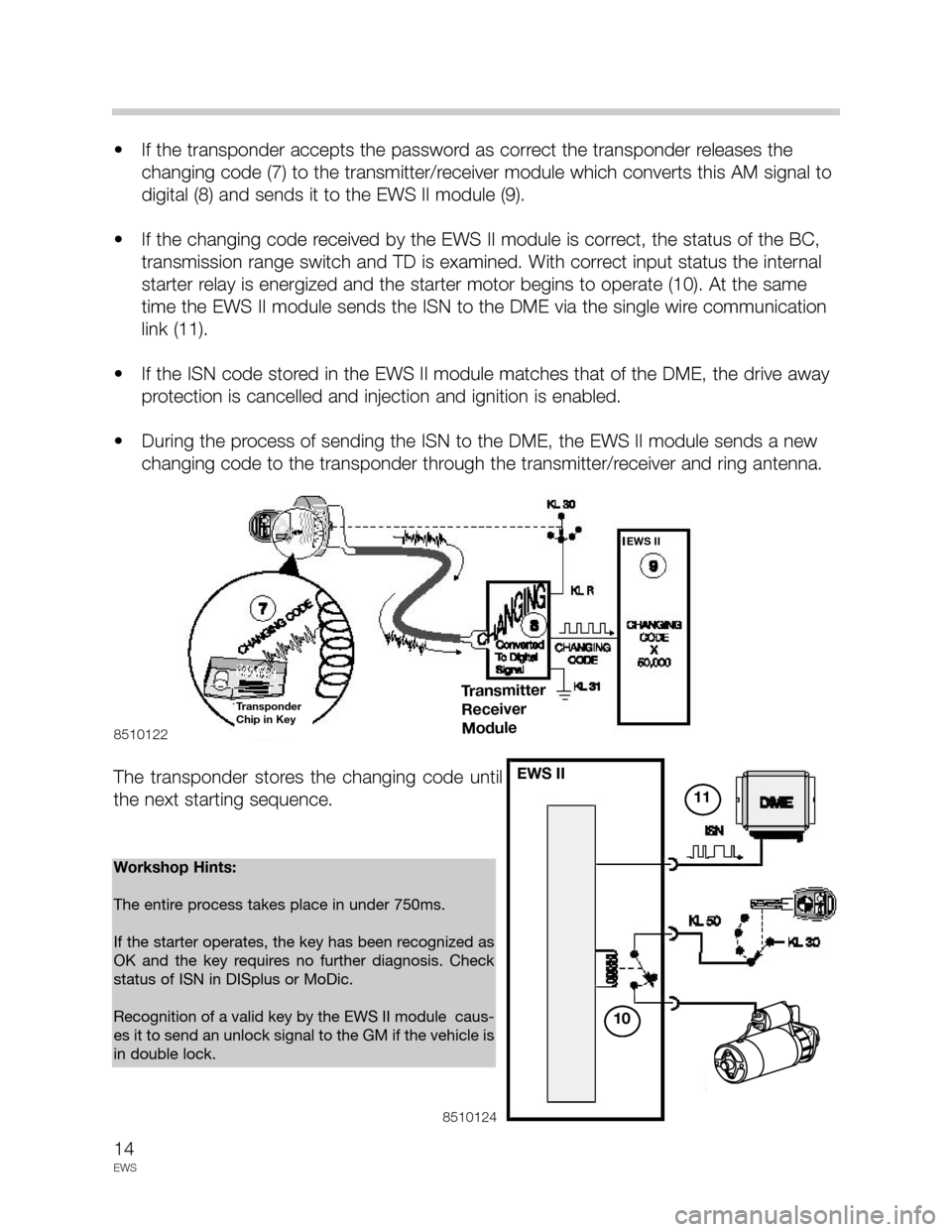
• If the transponder accepts the password as correct the transponder releases the
changing code (7) to the transmitter/receiver module which converts this AM signal to
digital (8) and sends it to the EWS II module (9).
• If the changing code received by the EWS II module is correct, the status of the BC,
transmission range switch and TD is examined. With correct input status the internal
starter relay is energized and the starter motor begins to operate (10). At the same
time the EWS II module sends the ISN to the DME via the single wire communication
link (11).
• If the ISN code stored in the EWS II module matches that of the DME, the drive away
protection is cancelled and injection and ignition is enabled.
• During the process of sending the ISN to the DME, the EWS II module sends a new
changing code to the transponder through the transmitter/receiver and ring antenna.
The transponder stores the changing code until
the next starting sequence.
8510122
8510124
10
11
Workshop Hints:
The entire process takes place in under 750ms.
If the starter operates, the key has been recognized as
OK and the key requires no further diagnosis. Check
status of ISN in DISplus or MoDic.
Recognition of a valid key by the EWS II module caus-
es it to send an unlock signal to the GM if the vehicle is
in double lock.
Transponder
Chip in KeyTransmitter
Receiver
Module
EWS II
EWS II
Page 18 of 30

18
EWS
Clutch Switch
A Hall-Effect Switch is added to the clutch system to inform the EWS III (3.2) control mod-
ule of clutch status. Input from the switch replaces the signal from the Trans Range Selector
Switch on manual transmission equipped vehicles. High signal status indicates the clutch
is depressed and vehicle starting is allowed.
Principle of Operation
The starting sequence for the EWS III (3.2) is as follows:
• The key is inserted into the lock cylinder and switched “ON”. The EWS III control mod-
ule is powered through KL R and sends a 125kHz AM signal to the ring antenna. The
AM signal induces voltage in the key coil and powers up the transponder.
• Powered up, the key transponder sends the key identification code to the EWS III mod-
ule. The EWS III module verifies the key identification code and checks to see if the key
is enabled. If the key is correct and enabled, a password is sent to the transponder over
the 125kHz AM signal through the ring antenna.
• When the transponders accepts the password, it releases the changing code, which it
received from the EWS III module during the last start-up operation, to the EWS III mod-
ule via the ring antenna.
• The EWS III module compares the changing code received from the transponder with
the code stored in its memory and if they match the process is allowed to continue.
The EWS III module looks at the other inputs for correct status (e.g. Code function not
active, Transmission in P or N or clutch depressed, engine speed below specified RPM)
and energizes the the internal relay to begin starter operation.
• As the starter begins to operate, the EWS III module sends the ISN to the DME and if
verified as correct by the DME, drive away protection is cancelled and injection and igni-
tion is enabled. The EWS III module also sends a new changing code to the key
transponder through the ring antenna.
Replacement Procedures
Keys
Up to 6 additional keys may be ordered as replacement keys. The EWS III (3.2) module is
codeable for only 10 keys (4 delivered with vehicle and 6 replacement). The keys are
mechanically matched to the vehicle with the lock tumblers and electronically matched to
the EWS III (3.2) through unalterable coding.
Page 21 of 30

21
EWS
DME Control Module
The DME Control Module has changed in that it is not the source of the ISN but now only
stores the “Rolling Code”. It compares the “Codes” to those sent to it by the EWS III (3.3)
control module. The “Rolling Code Table” assigned to the DME must match the table in the
EWS III (3.3) module. The “Rolling Code Table is “burned” into the DME during the pro-
gramming of the DME and cannot be change once “burned”.
Transmission Range Selection Input
With the introduction of the SKE type connectors on Transmission Control Modules the
direct input from the Transmission Range Selector Switch is eliminated. The input for range
selection is now received from the AGS Control Module.
On manual transmission vehicles clutch status is input directly into the DME.
Principle of Operation
The starting sequence of the EWS III (3.3) is as follows:
(Same as EWS III (3.2)
• The key is inserted into the lock cylinder and switched “ON”. The EWS III (3.3) control
module is powered through KL R and sends a 125kHz AM signal to the ring antenna.
The AM signal induces voltage in the key coil and powers up the transponder.
• Powered up, the key transponder sends the key identification code to the EWS III (3.3)
module. The EWS III (3.3) module verifies the key identification code and checks to see
if the key is enabled. If the key is correct and enabled, a password is sent to the
transponder over the 125kHz AM signal through the ring antenna.
• When the transponders accepts the password, it releases the changing code which it
received from the EWS III (3.3) module during the last start-up operation to the EWS III
(3.3) module via the ring antenna.
• The EWS III (3.3) module compares the changing code received from the transponder
with the code stored in its memory and if they match the process is allowed to contin-
ue. The EWS III (3.3) module looks at the other inputs for correct status (e.g. Code func-
tion not active, Transmission in P or N or clutch depressed, engine speed below spec-
ified RPM) and energizes the the internal relay to begin starter operation.
Page 22 of 30
22
EWS
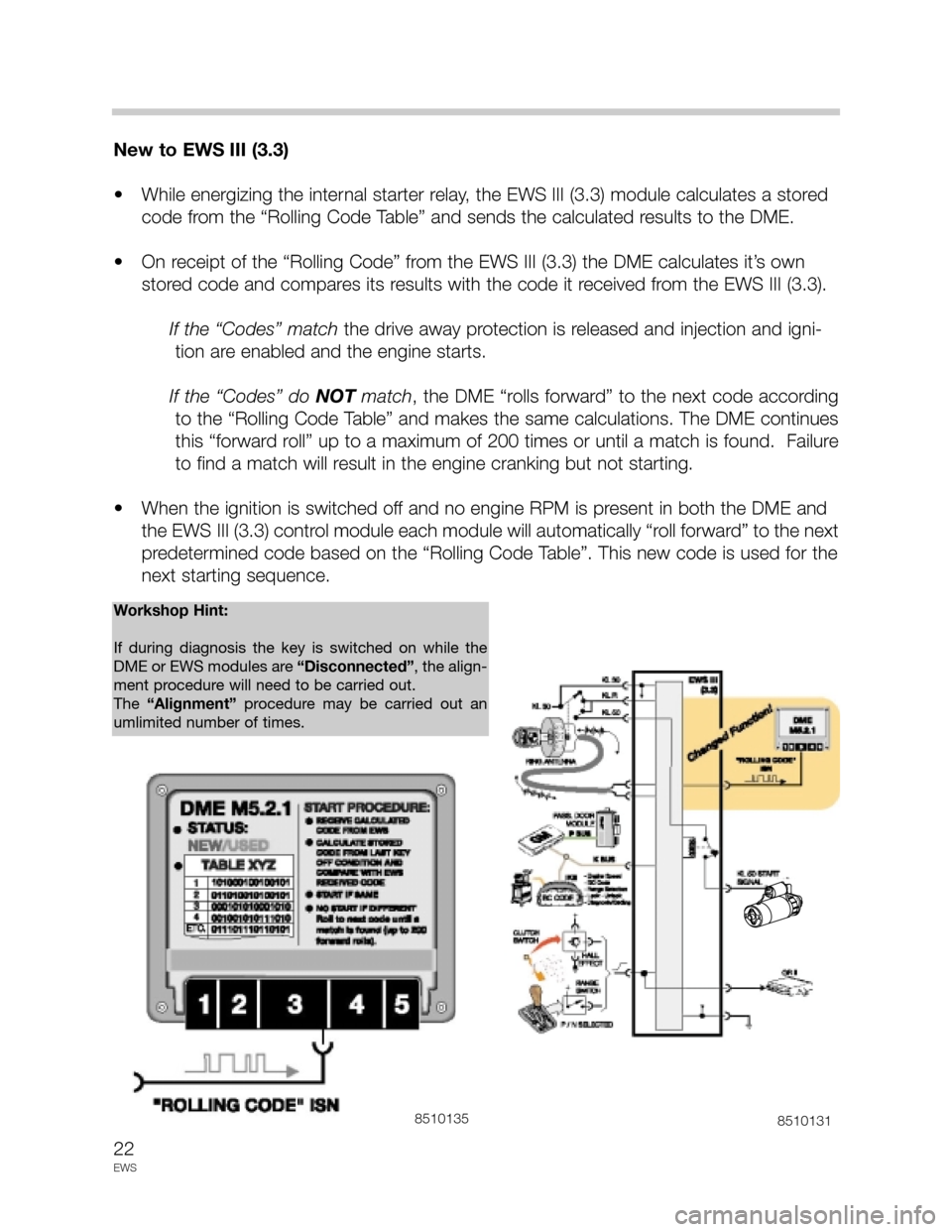
New to EWS III (3.3)
• While energizing the internal starter relay, the EWS III (3.3) module calculates a stored
code from the “Rolling Code Table” and sends the calculated results to the DME.
• On receipt of the “Rolling Code” from the EWS III (3.3) the DME calculates it’s own
stored code and compares its results with the code it received from the EWS III (3.3).
If the “Codes” matchthe drive away protection is released and injection and igni-
tion are enabled and the engine starts.
If the “Codes” do NOTmatch, the DME “rolls forward” to the next code according
to the “Rolling Code Table” and makes the same calculations. The DME continues
this “forward roll” up to a maximum of 200 times or until a match is found. Failure
to find a match will result in the engine cranking but not starting.
• When the ignition is switched off and no engine RPM is present in both the DME and
the EWS III (3.3) control module each module will automatically “roll forward” to the next
predetermined code based on the “Rolling Code Table”. This new code is used for the
next starting sequence.
85101318510135
Workshop Hint:
If during diagnosis the key is switched on while the
DME or EWS modules are “Disconnected”, the align-
ment procedure will need to be carried out.
The“Alignment”procedure may be carried out an
umlimited number of times.