sensor BMW 318i 1998 E36 Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: BMW, Model Year: 1998, Model line: 318i, Model: BMW 318i 1998 E36Pages: 759
Page 148 of 759
130-2
FUEL
INJECTION
GENERAL
This
repair
group
covers
fuel
injection
system
component
testing
and
repair
.
Special
equipment
is
necessary
for
some
of
the
procedures
given
in
this
repair
group
.
If
you
do
not
have
the
equipment
required
to
do
the
job,
it
is
recommended
that
these
repairs
be
left
to
an
authorized
BMW
dealer
.
The
BMW
dealer
is
equipped
with
sophisticated
diagnostic
test
equip-
ment
that
is
capable
of
quicklypinpointing
hard-to-find
fuel
in-
jection
problems
.
NOTE-
"
Wiring
diagrams
for
the
engine
management
system,
can
be
found
at
the
rear
of
the
manual
under
Electri-
cal
Wiring
Diagrams
.
"
For
ignition
system
repairinformation,
see120
Igni-
tion
System
.
"
For
fuel
supply
system
testing
and
repair,
see160
The
engine
control
module
(ECM)
uses
electrical
signals
Fuel
Tank
and
Fuel
Pump
.
from
the
mass
air
flow
sensor,
the
air
and
coolant
temperature
sensors,
the
crankshaft
position/rpm
sensor,
the
knock
sen
Principies
Of
Operation
sors
and
the
oxygen
sensorsas
the
primary
inputs
to
electron-
ically
control
fuel
delivery
and
ignition
timing
.
There
are
five
versions
of
engine
management
systems
usedon
the
E36
cars
.
Each
has
the
same
basic
components
and
operating
principles
.
The
most
notable
difference
is
that
1996
and
later
cars
use
a
sophisticated
OBD
II-compliant
sys-
tem
.
See
Table
a
.
Table
a
.
Engine
Management
System
Variants
Engine
code/year
1
System
4-cy1inder
M42
(1
.8
I)
1992-1995
Bosch
DME
Ml
.7
M44
(1
.91)
1996-1998
~
Bosch
DME
M5
.2
(OBD
II)
6-cylinder
M50
1992
(2.5
I)
Bosch
DME
M3
.1
1993-1995
(2.5
I)
Bosch
DME
M3
.3.1
(VANOS)
M52
1996-1998
(3281-
2
.8
I)
Siemens
MS
41
.1
(OBD
II)
1998
(3231
-
2
.5
I)
Siemens
MS
41
.1
(OBD
II)
M-Power
S50US
(M3
-
3
.01)
1995
Bosch
DME
M3
.3
.1
S52US
(M3
-
3
.21)
1997-1998
Siemens
MS
41
.1
(0131)
11)
NOTE-
-
Descriptions
and
procedures
in
the
first
partof
this
re-
pairgroup
refer
to
all
the
various
engine
management
systems
.
"
Particulars
of
each
fuel
injection
system
are
treated
in
separate
sections
in
the
second
part
of
this
repair
group
.
GENERAL
Fig
.1
.
OBD
II
diagnostic
connector
locatíon
.
The
fuel
injection
system
is
completely
electronic
in
opera-
tion
.
Air
flow
is
measured
electronically
via
a
mass
air
flow
sensor
and
additional
sensors
supply
information
about
en-
gine
operating
conditions
.
The
ECM
calculates
the
amount
of
fuel
needed
for
the
correct
air-fuel
ratio
and
actuates
the
fuel
injectors
accordingly
.
The
amount
offuel
metered
to
theen-
gine
is
determined
by
how
long
the
injectors
are
open
.
Airintake
.
Air
entering
the
engine
passes
through
a
pleat-
ed
paper
air
filter
in
the
air
cleaner
.
Intake
air
volume
or
mass
is
then
measured
bya
mass
air
flow
(MAF)
sensor
.
In
al¡
ex-
cept
the
vane
type
sensor
(DME
M1
.7),
a
reference
current
is
used
to
heat
a
thin
wireor
film
in
the
sensor
when
the
engine
is
running
.
The
current
used
to
heat
the
wire/film
is
electroni-
cally
converted
into
a
voltage
measurement
corresponding
to
the
mass
of
the
intake
air
.
Table
b
.
Mass
Air
Flow
Sensor
Variants
System
Al
r
flow
sensor
type
Bosch
DME
M1
.7
Vane
(volume
sensor)
Bosch
DME
M3
.1
Hot
wire
(mass
sensor)
Bosch
DME
M3
.3
.1
Hot
film
(mass
sensor)
Bosch
DME
M5
.2
Hot
film
(mass
sensor)
Siemens
MS
41
.1
Hot
film
(mass
sensor)
"
The
16-pin
OBD
11
diagnostic
connector
is
located
on
NOTE-
the
lower
left
dashpanel
.
See
Fig
.
1
.
On
cars
equipped
wíth
tractioncontrol,
an
additional
throttle
valve
is
controlled
by
an
electronic
throttle
actu-
ator
(motor)
.
This
valve
is
used
for
engine
speed
inter
vention
.
Repair
information
forthis
system
is
notcovered
here
due
to
the
special
electrical
testing
equip-
ment
required
to
service
it
.
Page 149 of 759

FUEL
INJECTION
130-
3
Fuel
metering
.
The
ECM
meters
fuel
bychanging
the
The
engine
management
system
compensates
automatical-
opening
time
(pulsewidth)
of
the
fuel
injectors
.
To
ensure
that
ly
for
changes
in
the
engine
due
to
age,
minor
wear
or
small
injector
pulsewídth
is
the
only
factor
that
determines
fuel
me-
problems,
such
as
a
disconnected
vacuum
hose
.
Asa
result,
tering,fuel
pressure
is
maintained
bya
fuel
pressure
regula-
idle
speed
and
mixture
do
not
need
lo
be
adjustedas
partof
tor
.
The
injectors
are
mounted
lo
a
common
fuel
supply
called
routine
maintenance
.
the
fuel
rail
.
The
ECM
monitors
engine
speed
to
determine
the
duration
NOTE-
ofinjector
openings
.
Other
signals
to
the
ECM
help
determine
Poordriveabilitymaybe
encountered
when
the
batteryis
injector
pulse
time
for
different
operating
conditions
.
A
tem-
disconnected
and
reconnected
.
when
the
battery
is
dis-
connected,
the
adaptive
memory
is
lost
The
system
will
perature
sensor
signals
engine
temperature
for
mixture
adap-
readaptafterabout
ten
minutes
of
drfving
.
tion
.
A
throttle
position
sensor
signals
throttle
position
.
The
exhaust
oxygen
sensor(s)
signal
information
about
combus-
tion
efficiency
for
control
of
the
air-fuel
mixture
.
1992
to
1995
DISA
(Dual
Resonance
Intake
System)
engines
are
equipped
with
a
single
sensor
.
1996
and
later
(OBD
II)
engines
are
equipped
with
an
oxygen
sensor
before
TheE36
4-cylinder
engine
is
equipped
with
a
dual
intake
andone
after
each
catalytic
converter
.
Forexample,the
M52
runner
system,
termed
DISA
.
DISA
offers
the
advantages
of
engine
is
equipped
withfour
oxygen
sensors
.
both
short
and
long
intake
pipes
.
Long
intake
runners
are
most
useful
at
low
to
medium
engine
rpm
for
producing
good
Idle
speed
control
.
ldle
speed
is
electronically
controlled
torque
characteristics
.
Short
intake
runners
produce
hígherviathe
idle
speed
control
valve,
which
maintains
idle
speed
by
horsepower
at
hígher
engine
speeds
.
bypassing
varying
amounts
of
air
around
theclosed
throttle
valve
.
Idle
speed
is
not
adjustable
.
NOTE-
Knock
(detonation)
control
.
Knock
sensors
monitor
and
The
term
DISA
comes
from
the
German
words
Differen-
control
ignition
knock
through
the
ECM
.
The
knock
sensors
zierte
Sauganlage,
and
can
roughlybe
translated
as
"dif-
fering
intake
manifold
configuration
."
See
100
Engine-
function
like
microphones
and
are
able
to
convert
mechanical
General
foradditional
information
on
DISA
operation
.
vibration
(knock)
into
electrical
signals
.
The
ECM
is
pro-
grammed
to
react
to
frequencies
that
are
characteristic
of
en-
Manifold
construction
:
The
intake
manifold
is
a
two-piece
gine
knock
and
adapt
the
ignition
timing
point
accordingly
.
metal
construction,
with
a
pair
of
runners
in
thetop
section
See120
Ignition
System
for
further
details
.
and
four
runners
in
the
lower
section
.
A
butterfly
valve
is
in-
stalled
in
the
lower
section,
enabling
the
DISA
solenoid
toiso-
NOTE-
late
one
pair
of
runners
from
the
other
pair
.
See
Fig
.
2
.
The
1992
M50
engine
is
not
equipped
with
knock
sen-
Operation
.
With
the
DISA
butterfly
valve
closed,
the
pipes
sors
.
All
other
engines
are
equipped
with
two
knock
in
thetop
half
of
the
manifold
act
together
with
the
ram
air
sensors
.
pipes
in
the
lower
halfto
producea
single,
long
air
intake
pipe
for
each
cylinder
.
See
Fig
.
3
.
The
column
of
aír
oscíllating
in
Basic
Engine
Settings
this
combined
pipe
significantly
increases
engine
torque
in
the
medium
rpm
range
.
Idle
speed,
idle
mixture
(%CO),
and
ignition
timing
arenot
adjustable
.
The
adaptive
engine
management
system
is
de-
signed
to
automatically
compensate
for
changes
in
engine
op-
eratingconditions,
although
the
adaptive
range
is
limited
.
Once
these
limits
are
exceeded,
driveability
problems
usually
be-
come
noticeable
.
Above
approximately
4,800
rpm,
the
butterfly
valve
between
the
intake
air
pipes
for
the
two
cylinder
groups
is
opened
.
The
shorter
pipes
in
the
lower
manifold
section
now
become
the
main
suppliers
of
ram
air
to
the
cylinders,yielding
greater
pow-
er
at
the
upper
end
of
the
engine
rpm
range
.
See
Fig
.
4
.
Control
components
.
The
DISA
butterfly
valve
is
actuated
NOTE-
electro-pneumatically
via
the
engine
control
module
(ECM)
.
lf
the
system
adaptive
limits
are
exceeded,
the
Check
The
valve
begins
to
open
as
engine
speed
rises
aboye
4,840
Engine
light
will
most
likely
come
on,
indicating
an
rpmand
closes
below
4,760
rpm
.
The
action
of
the
valve
is
de-
emissions-
related
fault
For
Check
Engine
light
diag-
liberately
delayed
to
prevent
it
from
opening
and
closing
repeat-
nostics,
see100
Engine-General
.
edly
within
a
short
time
.
GENERAL
Page 152 of 759

130-
6
FUEL
INJECTION
Warnings
and
Cautions
For
personal
safety,
as
well
as
the
protection
of
sensitive
electronic
components,
the
following
warnings
and
cautions
should
be
adhered
to
when
working
on
the
engine
manage-
ment
system
.
GENERAL
WARNING
-
"
The
ignition
system
produces
high
voltages
that
can
be
fatal
.
Avoid
contact
with
exposed
termi-
nals
.
Use
extreme
caution
when
working
onacar
with
the
ignition
switched
on
or
the
engine
run-
ning
.
"
Do
not
touch
or
disconnect
any
high
voltage
ca-
bles
from
the
coils
or
spark
plugs
while
the
engine
is
running
or
beingcranked
by
the
starter
.
"
Connect
and
disconnect
the
DME
system
wiring
and
test
equipment
leads
only
when
the
ignition
is
switched
off
.
"
Gasoline
is
highly
flammable
and
fts
vaporsare
explosive
.
Do
not
smoke
or
work
on
a
car
near
heaters
or
other
fire
hazards
when
diagnosing
and
repalring
fuel
system
problems
.
Have
a
tire
extinguisher
avaílable
in
case
of
an
emergency
.
"
When
working
onan
open
fuel
system,
wear
suit-
able
hand
protection,
asprolonged
contact
wfth
fuel
can
cause
illnesses
and
skin
disorders
.
"
Renew
fuel
system
hoses,
clamps
and
O-rings
any
timethey
are
removed
.
"
Before
makingany
electrical
tests
that
require
the
engine
to
be
cranked
using
the
starter,
disable
the
ignition
system
as
described
in
120
Ignition
System
.
CAUTION-
"
Prior
to
disconnecting
the
battery,
read
the
bat-
tery
disconnectinn
cautions
given
at
the
front
of
this
manual
onpage
vifi
.
"
Do
not
connect
any
test
equipment
that
delivers
a
12-volt
power
supply
to
terminal
15
(+)
of
the
ig-
nitioncoil
.
The
current
flow
may
damage
the
ECM
.
In
general,
connect
test
equipment
only
as
speclfied
by
BMW,
this
manual,
or
the
equipment
maker
.
"
Only
use
a
digital
multlmeter
for
electrical
test
.
"
Only
use
an
LED
test
light
for
quick
tests
.
"
Disconnecting
the
battery
may
erase
fault
code(s)
stored
in
memory
.
Check
for
fault
codes
prior
to
disconnecting
the
battery
cables
.
ff
the
Check
Engine
light
ís
illuminated,
see100En-
gine-General
for
DME
fault
code
information
.
ff
any
other
system
faults
have
been
detected
(indi-
catedbyan
illuminated
warning
light),
see
an
au-
thorized
BMW
dealer
.
Additional
systems
with
self-diagnostic
capabilities
include,
ABS
(Anti-
lock
brakes),
SRS
(Airbags),
EML
and
ASC+T
and
AST
(Traction
Control)
.
"
Do
not
run
the
engine
wfth
any
of
the
spark
plug
wires
dlsconnected
.
Catalytic
converter
damage
may
result
.
"
Always
waitat
least
40
seconds
afterturning
off
the
ignition
before
removing
the
engine
control
module
(ECM)
connector
.
ff
the
connector
isre-
moved
before
this
time,
residual
power
in
the
sys-
tem
relay
may
damage
the
control
module
.
"
Cleanliness
is
essential
when
working
onan
open
fuel
system
.
Thoroughly
clean
fuel
line
con-
nections
and
surroundlng
areas
before
loosen-
ing
.
Avoid
moving
the
car
.
Only
fnstall
cleanparts
.
"
Fuel
system
cleaners
and
other
chemical
addi-
tives
other
than
those
specifically
recommended
by
BMW
may
damage
the
catalytic
converter,
the
oxygensensor
or
other
fuel
supply
components
.
Page 153 of 759
ELECTRICAL
CHECKS
AND
COMPONENT
TESTING
Main
relay,
testing
The
main
relay
is
energized
via
the
engine
control
module
and
supplies
plus
(+)
power
to
the
many
of
the
engine
man-
agement
components
and
subsystems,
including
the
fuel
pump
relay
.
If
this
relay
is
faulty,
the
engine
will
not
start
.
1
.
With
ignition
off,
remove
main
relay
.
See
Fig
.
6
.
.
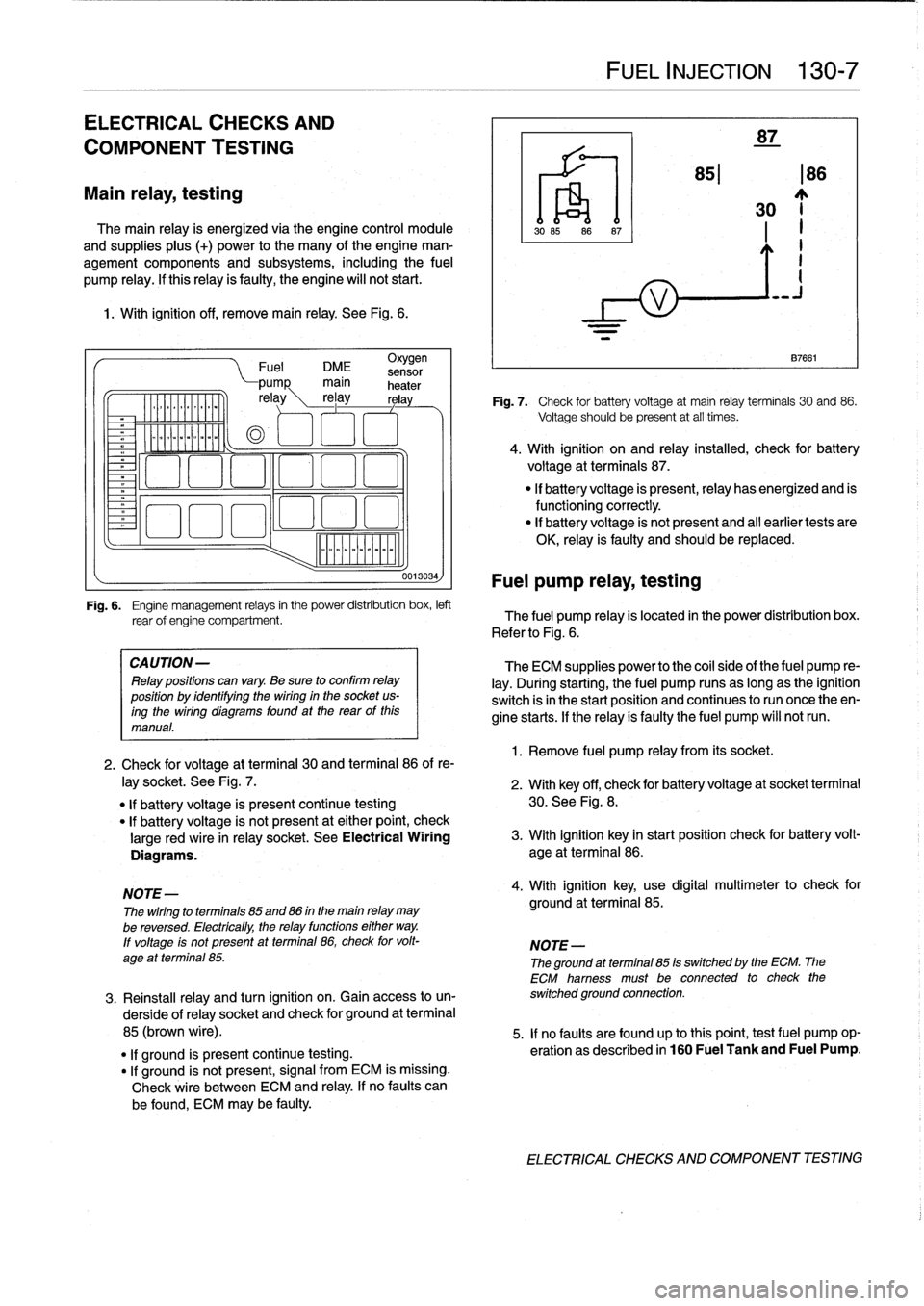
iommooommmoi
~
"""
Fuel
DME
sensor
CA
UTION-
Relay
positions
can
vary
.
Be
sure
to
confirm
relay
position
by
identífyíng
the
wiring
in
the
socket
us-
ingthe
wiring
diagramsfound
at
the
rearof
this
manual
.
0013034)
Fuel
pump
relay,
testing
FUEL
INJECTION
130-
7
87
851186
30
~j
1
.
Remove
fuel
pump
relay
from
its
socket
.
87661
Fig
.
7
.
Check
for
battery
voltage
at
main
relay
terminals
30
and
86
.
Voltage
should
be
present
at
all
times
.
4
.
With
ignition
on
and
relay
installed,
check
for
battery
voltage
at
terminals
87
.
"
If
battery
voltage
is
present,relay
has
energized
and
is
functioningcorrectly
.
"
lf
battery
voltage
is
not
present
and
al¡
earlier
tests
are
OK,
relay
is
faulty
and
should
be
replaced
.
Fig
.
6
.
Engine
management
relays
in
the
power
distribution
box,
left
rear
of
engine
compartment
.
The
fuel
pump
relay
is
located
in
the
power
distribution
box
.
Refer
to
Fig
.
6
.
The
ECM
supplies
power
to
the
coil
side
of
the
fuel
pump
re-
lay
.
During
starting,
the
fuel
pump
runs
as
long
as
the
ignition
switch
isin
the
start
position
and
continues
to
run
once
theen-
gine
starts
.
If
the
relay
ís
faulty
the
fuel
pump
will
notrun
.
2
.
Check
for
voltage
at
terminal
30
and
terminal
86
of
re-
¡ay
socket
.
See
Fig
.
7
.
2
.
With
key
off,
check
for
batteryvoltage
at
socket
terminal
"
If
battery
voltage
is
present
continue
testing
30
.
See
Fig
.
8
.
"
lf
battery
voltage
is
not
present
at
either
point,
check
large
red
wire
in
relay
socket
.
See
Electrical
Wiring
3
.
With
ignition
key
in
start
position
check
for
battery
volt-
Diagrams
.
age
at
terminal
86
.
NOTE-
4
.
With
ignition
key,
use
digital
multimeter
to
check
for
The
wiring
to
terminals
85
and
86
in
the
main
relay
may
ground
at
terminal
85
.
be
reversed
.
Electrically,
the
relay
functions
either
way
.
lf
voltage
ís
not
present
at
terminal
86,
check
for
volt-
NOTE-
age
at
terminal
85
.
The
ground
atterminal
85
is
switched
by
the
ECM
.
The
ECM
hamess
must
be
connected
to
check
the
3
.
Reinstall
relay
and
turn
ignition
on
.
Gainaccess
to
un-
switched
ground
connection
.
derside
of
relay
socket
and
check
for
ground
at
terminal
85
(brown
wire)
.
5
.
If
no
faults
are
found
up
tothis
point,
testfuel
pump
op-
"
lf
ground
is
present
continue
testing
.
eration
as
described
in
160
Fuel
Tank
and
Fuel
Pump
.
"
If
ground
is
not
present,
signal
from
ECM
is
missing
.
Check
wire
between
ECM
and
relay
.
If
no
faults
can
be
found,
ECM
may
be
faulty
.
ELECTRICAL
CHECKS
AND
COMPONENT
TESTING
Page 154 of 759

130-
8
FUEL
INJECTION
Fig
.
8
.
Fuel
pump
relayterminal
identification
.
1.
Peel
back
rubber
boot
on
oxygen
sensor
electrical
har-
ness
connector
(car
wiring
side)
.
With
connector
at-
Oxygen
sensor,
testing
tached
to
sensor,
connect
digital
voltmeter
to
pins
1
(BOSch
systems
only)
and
2
in
rear
of
connector
.
See
Fig
.
10
.
CAUTION-
"
The
information
inthis
sectionapplies
to
Bosch
engine
management
systems
only
.
"
The
Siemens
MS
41
.1
system
uses
resistive-type
oxygen
sensors
.
This
sensor
uses
a
5-volt
refer-
ence
signal
input
and
the
output
to
the
ECM
var-
ees
from
1-5
volts,
in
stepped
increments
based
on
oxygen
content
in
the
exhaust
.
NOTE-
"
On
pre-08D
11(1992-1995)
cars,
there
is
one
oxygen
sensor
mounted
upstream
of
the
catalytic
convert-
er(s)
in
the
exhaust
pipe
.
See
Fig
.
9
.
"
On
OBD
11
cars
(1996-1998)
cars,
there
is
one
oxygen
sensor
before
andone
after
each
catalytic
converter
.
"
OnM52
and
S52US
engines,
the
front
pairof
oxygen
sensors
are
installed
in
the
exhaust
manifolds
.
The
oxygen
sensor
providesan
input
voltage
signal
(0-1
VDC)
to
the
ECM
based
on
the
oxygen
content
in
the
exhaust
gas
.
TO
generate
voltage,
the
sensor
temperature
must
exceed
575°F
(300°C)
.
Therefore
it
ís
electrically
heated
.
NOTE-
"
The
test
given
below
is
not
a
conclusive
test
of
oxygen
sensor
efficiency
and
does
not
test
how
quickly
the
oxygensensor
can
react
to
changing
conditions
.
"
Pin
numbers
and
wirecolors
can
vary
.
Always
check
the
wiring
diagrams
to
conflrm
wire
color
and
pinas-
signment
.
ELECTRICAL
CHECKS
AND
COMPONENT
TESTING
0013135
Fig
.
9
.
Oxygen
sensor
location
(arrow)
ahead
of
catalytic
converter
.
3181
model
with
M42
engine
shown
.
1
.
Black
(ground)
2
.
Grey
(signal)
4
.
White
(heater
circuit)
3
.
White
(heater
circuit)
0013189
Fig
.
10
.
Oxygen
sensor
connector
terminal
identification
(sensor
sede)
.
Terminals
numbers
are
molded
into
connector
.
2
.
Start
engine
.
Oxygen
sensorshould
start
to
output
a
fluctuating
voltage
within
a
short
period
.
If
voltage
is
in-
correct,
turn
engine
off
and
check
preheater
circuit
as
described
below
.
WARNING
-
Exhaust
manifolds
and
pipes
can
be
hot
enough
to
cause
serious
burns
.
Wear
suitable
heavy
gloves
and
other
appropriate
protection
.
Page 155 of 759

Oxygen
Sensor
FUEL
DELIVERY
TESTS
FUEL
INJECTION
130-
9
"
Voltage
at
¡dle
..
.
..
..
....
0
.2
to
0
.8
VDC,
fluctuating
Checking
fuel
delivery
is
afundamental
part
of
trouble-
shooting
and
diagnosing
the
engine
management
system
.
Fuel
pressure
directly
influences
fuel
delivery
.
An
accurate
NOTE-
fuel
pressure
gauge
will
be
needed
to
make
the
tests
.
To
check
sensorresponse
to
lean
and
rich
mixtures,
createenairleak,
orpull
vacuumhoseofffue¡
pressure
There
are
three
significant
fuel
delivery
values
to
be
mea-
regulator
to
increase
fuel
pressure
.
sured
:
3
.
Separate
sensorharness
connector
from
sensor
.
Check
for
battery
voltage
between
terminals
3
and
4
(green
wire
and
brown
wire)
in
main
wiring
harness
side
of
con-
nector
with
engine
running
.
If
voltage
is
not
present,
check
oxygen
sensor
heater
relay
.
See610
Electrical
Component
Locations
.
4
.
Check
heater
element
resistance
between
terminals
3
and
4
in
sensor
side
of
connector
.
If
element
is
electri-
cally
open
(no
continuity),
replace
sensor
.
NOTE-
The
oxygen
sensor
heater
relay
is
mounted
in
the
main
power
distributfon
box
in
the
left
rear
of
the
engine
com-
partment
.
Refer
to
Fig
.
6
.
The
heater
relay
is
energized
wíth
positive
(+)
battery
voltage
from
the
main
relayanda
switched
ground
from
the
ECM
.
See
Electrical
Wir-
ing
Diagrams
.
"
Oxygen
sensor
to
exhaust
pipe
...
..
55
Nm
(41
ft-Ib)
"
System
pressure-created
by
the
fuel
pump
and
main-
tained
by
the
pressure
regulator
.
"
Fuel
delivery
volume-created
by
the
fuel
pump
and
af-
fected
by
restrictions,
suchasclogged
fuel
filter
.
"
Residual
pressure-the
pressure
maintained
in
the
closed
system
after
the
engine
and
fuel
pump
are
shut
off
.
Procedures
for
measuring
the
first
two
quantities
arede-
scribed
in
160
Fuel
Tank
and
Fuel
Pump
.
Residual
fuel
pres-
sure
is
checked
using
the
procedure
detailed
later
in
this
group
.
Operating
fuel
pump
fortests
To
operate
the
fuel
pump
for
testing
purposes
without
hav-
íng
to
runthe
engine,
the
fuel
pump
relay
can
be
bypassed
to
power
the
pump
directly
.
Fuel
pump
relay
location
is
shown
in
Fig
.
6
.
5
.
¡f
oxygen
sensor
doesn't
produce
a
fluctuating
voltage
To
runthe
fuel
pump,
remove
the
fuel
pump
relay
and
con-
and
preheater
circuit
is
OK,
replace
sensor
.
nect
the
socket
for
relayterminal
30
to
the
socket
for
relay
ter-
mina¡
87
with
a
fused
jumper
wire
.
After
completing
the
tests,
NOTE-
remove
the
jumper
wire
.
If
not
already
applied,
coat
the
oxygen
sensor
threads
with
an
anti-seize
compound
before
installation
.
Do
not
CAUTION-
getthe
compound
on
the
sensor
tip
.
"
Relay
locations
may
vary
.
Use
care
when
identi-
fying
relays
and
making
electrical
checks
at
the
fuselrelay
panel
.
See
610
Electrical
Compo
Tightening
Torque
nent
Locations
for
additional
relay
information
.
"
The
fuel
pump
relay
has
a
1
.5
mm2
red
wire
at
ter-
minal
30
in
the
relay
socket
.
Terminal
87
has
a
1
.5
mm
2
greenlviolet
wire
.
See
Electrical
Wiring
Di-
agrams
for
additional
wiring
information
.
NOTE-
Thejumper
wire
should
be
1.5
mm2
(14
ga
.)
and
in-
clude
an
in-line
tuse
holder
with
a15
amp
tuse
.
To
avoid
fuselrelay
panel
damage
from
repeated
connect-
ing
and
disconnecting,
also
include
a
toggle
switch
.
A
heavy-duty
jumper,
BMW
tool
no
.
61
3
050,
is
also
available
from
an
authorized
BMW
dealer
.
FUEL
DELIVERYTESTS
Page 160 of 759

130-
1
4
FUEL
INJECTION
NOTE-
Be
sure
to
retrieve
thrust
washer
behind
fuel
pressure
regulator
on
6-cylinder
engine
.
4
.
Installation
is
reverse
of
removal
.
Replace
O-rings
.
Fuel
pressure
regulator,
replacing
(under
car
mount)
WARNING
-
Fuel
will
be
discharged
.
Do
not
disconnect
any
wires
that
could
cause
electrical
sparks
.
Do
not
smoke
or
work
near
heaters
or
other
fire
hazards
.
Keep
an
approved
tire
extinguisher
handy
.
On
late
4-
and
6-cylinder
cars,
the
fuel
pressure
regulator
is
mounted
beneath
the
left
sideof
the
car,
under
a
protective
cover
.
See
Fig
.
20
.
0012726
Fig
.
20
.
Fuel
pressure
regulatorlocation
underneath
car
(arrow)
.
Vac-
uum
hose
to
regulator
is
shown
at
A
.
(Protective
cover
has
been
removed
.)
5
.
Installation
is
reverse
of
removal
.
Replace
O-rings
.
BOSCH
DME
Ml
.
7
COMPONENT
TESTS
AND
REPAIRS
BOSCH
DME
Ml
.7
COMPONENT
TESTS
AND
REPAIRS
CA
UTION-
Use
only
a
digital
multimeter
when
testing
compo-
nents
and
wiring
.
Use
of
an
analog
VOM
may
damage
the
engine
control
module
.
4-cylinder
cars
with
M42
engines(1992
to
1995)use
the
Bosch
DME
M1
.7
fuel
injection
system
.
Electrical
tests
of
the
main
and
fuel
pump
relays
and
the
DME
engine
control
module
(ECM)
are
covered
earlier
in
this
section
.
Fuel
pump
tests
arecovered
in
160
Fuel
Tank
and
Fuel
Pump
.
Air
flow
sensor,
testing
and
replacing
DME
M1
.7
fuel
injection
uses
a
volume
air
flow
type
sensor
with
integrated
intake
air
temperature
(IAT)
sensor
.
The
sen-
sor
provides
a
varyingvoltage
signal
to
the
ECM
based
on
the
position
of
the
air
vane
.
As
the
vane
doorswings
open
thepo-
tentiometer
increases
the
voltage
signal
to
the
ECM
.
The
IATsensor
adapts
theoutput
signal
to
the
ECM
based
on
intake
air
temperature
.
1
.
Check
ECM
reference
voltage
to
sensor
:
"
Peel
back
rubber
boot
from
air
flow
sensor
harness
connector
.
"
Turn
ignition
keyon
.
"
Check
for
5
volts
between
terminal
1
of
harness
con-
nector
and
ground
.
See
Fig
.
21
.
"
Turn
ignition
key
off
.
"
If
voltage
is
not
present
or
incorrect,
check
wring
from
ECM
and
check
air
flow
sensor
reference
voltage
out-
put
at
ECM
.
See
Table
h
.
1
.
Working
under
car
below
driver's
seat,
remove
protec-
tive
cover
from
below
fuel
pressure
regulator
.
"
Remove
intake
air
bootfrom
sensor
.
2
.
Remove
vacuum
hosefrom
fuel
pressure
regulator
.
"
Connect
a
digital
multimeter
(ohms)
across
terminais
1
and
2
.
Swing
air
flow
sensor
vane
through
its
travel
3
.
Remove
locking
clip
retaining
fuel
pressure
regulator
.
range
.
Resistance
should
change
steadily
without
in-
terruption
.
4
.
Wrap
a
shop
rag
around
regulator,
then
remove
regula-
"
If
any
faults
are
found,
the
air
flow
sensor
is
faulty
and
tor
from
213
way
valve
by
pullingstraight
out
.
should
be
replaced
.
2
.
Check
air
flow
sensor
potentiometer
:
3
.
Check
IAT
sensor
resistance
:
"
With
harness
connector
disconnected
at
air
flow
sen-
sor,
check
resistance
across
sensor
terminais
4
and
5
of
air
flow
sensor
.
Compare
tests
results
to
values
in
Table
d
given
later
.
If
any
faults
are
found,
the
air
flow
sensor
should
be
replaced
.
Page 161 of 759

u0
I
.[
Ia
Fig
.
21
.
Air
flow
sensor
harness
connector
terminal
identification
.
4
.
Replacing
air
flow
sensor
:
"
Remove
large
band
clamp
attaching
air
boot
to
sensor
.
"
Remove
airfiltertop
cover,
then
remove
airflow
sensor
mounting
nuts
inside
cover
.
"
Reconnect
air
boot
and
harness
connector
.
Engine
coolant
temperature
(ECT)
sensor,
testing
and
replacing
The
engine
coolant
temperature
(ECT)
sensor
sends
con-
tinuous
engine
coolant
temperature
information
to
the
ECM
.
As
temperature
increases,
sensor
resistance
decreases
.
"
With
harness
connector
disconnected,
check
resis-
tance
across
sensor
terminals
.
"
Compare
tests
results
to
values
in
Table
d
.
FUEL
INJECTION
130-
1
5
0011984
Fig
.
22
.
M42
engine
coolant
temperature
(ECG
sensor
(arrow)
.
Table
d
.
Engine
Coolant
Temperature
Sensoror
Intake
Air
TemperatureSensor
Test
Values
(DME
1
.7)
Test
temperatures
Resistance
(k
ohms)
',
14±2°F(-10t1°C)
7-11
.6
68±2°F
(20
t
1
°C)
2
.1
-2
.9
176
±
2°F
(80
t
V
C)
0
.27-0
.40
The
ECT
sensor
is
located
under
number
one
intake
run-
'
ner
.
See
Fig
.
22
.
NOTE-
1
.
Check
ECM
referente
voltage
to
sensor
:
The
test
values
listed
represent
only
three
test
points
from
a
continuous
resistance
NTC
sensor
.
Check
the
"
Disconnect
harness
connectorfrom
ECT
sensor
.
full
linear
response
to
increasing
temperature
as
the
"
Turn
ignition
key
on
.
engine
warms
up
.
"
Check
for
5
volts
between
supply
voltage
(brown/red)
wire
of
harness
connector
and
ground
.
3
.
If
ECT
sensor
fails
these
tests,
it
is
faulty
and
should
be
"
Turn
ignition
key
off
.
replaced
.
If
no
faults
are
found,
reconnect
electrical
"
If
voltage
is
not
present
or
incorrect,
check
wring
from
harness
.
ECM
and
check
ECT
sensor
reference
voltage
output
at
ECM
.
See
Table
h
.
NOTE-
2
.
Check
ECT
sensor
resistance
:
Use
a
new
copper
sealing
washer
when
installing
sen-
sor
.
Reptace
any
lost
coolant
.
WARNING
-
Do
not
replace
the
ECT
sensor
unlessthe
engine
is
cold
.
Hot
coolant
can
scald
.
Tightening
Torque
"
ECT
sensor
to
cylinder
head
.....
..
13
Nm
(10
ft-Ib)
BOSCH
DME
M1
.7
COMPONENT
TESTS
AND
REPAIRS
Page 162 of 759

130-
1
6
FUEL
INJECTION
Throttie
position
sensor
(TPS),
Idie
speed
control
valve,
testing
and
replacing
testing
and
replacing
The
throttie
position
sensor
(TPS)
is
mounted
on
the
side
of
¡die
speed
is
maintained
by
the
ECM
via
the
¡die
speed
con-
the
throttie
housing
and
is
directly
connected
to
the
throttie
trol
valve
.
See
Fig
.
24
.
¡die
speed
is
adaptive
through
the
valve
shaft
.
The
ECM
sends
a
voltage
signal
to
the
potentiom-
ECM
and
no
¡die
speed
adjustments
can
be
made
.
Before
eter-type
sensor
and
monitors
the
voltage
that
comes
back
.
testing
the
valve,
confirm
that
the
throttie
position
sensor(TPS)
is
working
correctly
.
Check
TPS
function
by
disconnecting
the
harnessconnec-
tor
and
checking
reference
voltage
and
sensor
resistance
.
See
Table
e
and
Fig
.
23
.
If
voltage
is
not
present,
check
the
output
voltage
signal
from
the
ECM
and
check
the
wiring
be-
tween
the
sensor
and
the
ECM
.
If
the
sensor
resistance
is
in-
correct,
replace
the
throttie
position
sensor
.
NOTE
-
The
throttie
position
sensor
is
not
adjustable
.
If
test
re-
sults
are
íncorrect,
the
sensor
should
be
replaced
.
Table
e
.
Throttle
Position
Sensor
Tests
(DME
1
.7)
Testconditions
1
Terminais
1
Test
value
Harness
connec-
(
1
and
ground
in
15
VDC
(approx
.)
tor
disconnected,
harness
connector
ignition
on
0013235
Fig
.
23
.
Throttieposition
sensor
terminal
identification
on
M42
engine
.
Harnessconnec-
I
1
and
3
at
sensor
(
4k
ohms
(approx
.)
tor
disconnected,
terminais
ignition
off
Connector
dis-
1
and
2
at
sensor
Continuously
vari-
connected,
igni-
terminais
able
from
1-4
k
tion
off
.
Throttle
ohms
(approx
.)
with
rotated
from
¡die
out
interruption
to
fui]
position
BOSCH
DME
Ml
.
7
COMPONENT
TESTS
AND
REPAIRS
Fig
.
24
.
¡die
speed
control
valve
(arrow)
on
M42
engine
.
NOTE
-
"
The
tests
given
below
are
electrical
checks
only
.
They
do
not
check
the
mechanical
operation
of
the
valve
or
if
the
valve
is
sticking
or
worn
.
If
the
valve
is
suspect,
substituting
a
known
good
valve
is
the
best
way
to
check
for
amechanical
fault
.
1
.
Check
battery
(+)
voltage
to
valve
:
0013226
"
Disconnect
harness
connector
from
valve
.
"
Check
for
battery
voltage
at
terminal
2
(red/white
wire)
.
"
If
voltage
is
not
present
check
wiring
between
valve
and
main
relay
(terminal
87)
.
2
.
Check
that
ECM
signal
is
reaching
valve
:
"
With
engine
running,
check
that
¡die
speed
control
valve
is
audibly
buzzing
.
"
If
valve
is
not
working,
disconnect
wiring
harness
con-
nector
.
"
Connect
12V
probe
light
across
connector
terminais
.
"
Turn
ignition
key
on
;
probe
should
light
.
lf
probe
does
nof
light,
check
the
wiring
from
the
ECM
(pin
29)
to
the
valve
.
See
Table
h
.
lf
probe
does
light
but
¡die
quality
is
poor,
the
valve
is
most
likely
sticking
and
or
worn
and
should
be
replaced
.
Page 163 of 759

BOSCH
DME
MM
AND
M33
.1
COMPONENT
TESTS
AND
REPAIRS
Consult
Table
a
for
engine
application
information
for
the
Bosch
DME
3
.1
and
3
.3.1
systems
.
The
DME
3
.1
and
DME
3
.3
.1
systems
are
similar
in
opera-
tion,
with
knock
control
and
VANOS
operation
being
the
key
differences
.
DME
3
.1
engines
arenot
equipped
with
VANOS
or
knock
detectors,
while
the
DM
E3
.3
.1
system
is
.
CA
UTION-
Use
onty
a
digital
multimeter
when
testing
wiring
.
Use
of
an
analog
VOM
may
damage
the
engine
control
module
.
Fig
.
25
.
Mass
air
flow
sensor
.
Hot
wire
sensor
usedon
carswith
DME
Electrical
tests
of
the
main
and
fuel
pump
relays
and
the
3
.1
(1992
6-cylinder
models)
.
DME
engine
control
module
(ECM)
are
covered
earlier
in
this
section
.
Fuel
pump
tests
are
covered
in
160
Fuel
Tank
and
CAUTION-
Fuel
Pump
.
Use
only
a
digital
multimeter
when
checking
the
mass
air
flow
sensor
.
An
analog
meter
can
dam-
Mass
Air
Flow
Sensor
age
theair
flow
sensor
.
There
are
two
types
of
mass
air
flow
sensors
used
onthe
1
.
Disconnect
air
flow
sensor
from
air
cleaner
only
.
Leave
cars
covered
by
this
section
.
Testing
procedures
vary
de-
it
connected
to
duct
leading
to
intake
manifold
and
pending
on
type
installed
.
The
airflow
sensor
is
not
adjustable
leave
wiring
harness
connected
.
and
must
only
be
tested
with
a
digital
multimeter
.
Mass
Air
FlowSensor
Variants
"
1992
M50
engine
DME
M3
.1
.
.
.
.
...
..
mass
air
flow
sensor-hot
wire
"
1993-1995
M50
and
S50US
DMEM33
.1)
.
...
...
.
mass
air
flow
sensor-hot
film
Mass
air
flow
sensor
(hot
wire),
testing
and
replacing
When
the
engine
is
running,
a
current
is
used
to
heat
a
thin
wire
in
the
center
of
the
sensor
.
See
Fig
.
25
.
The
current
in
the
wire
is
regulated
to
maintain
a
temperature
of
100°C
more
than
the
air
passing
over
it
.
The
current
used
to
heat
the
wire
is
electronically
conneced
into
a
voltage
measurement
corre-
sponding
to
the
mass
of
intake
a¡
r
.
To
keep
the
wire
clean,
it
is
heated
to
a
temperature
of
about
1,000°C
(1,830°F)
for
one
second
.
This
"burn-off"
cycle
takes
place
automatically,
four
seconds
after
the
engine
is
tumed
off
.
lf
thehot
wire
breaks
or
if
there
is
no
output
from
the
air
flow
sensor,
the
ECM
automatically
switches
to
a
"limp-home"
mode
and
tucos
on
the
Check
Engine
light
.
The
engine
can
usually
be
started
and
driven
.
The
air
flow
sensor
has
no
inter-
nal
moving
parts
and
cannot
be
serviced
.
FUEL
INJECTION
130-
1
7
2
.
Start
engine
and
run
it
to
normal
operating
temperature
.
3
.
Rev
engine
toat
least
2,500
rpm,then
shut
it
off
.
Look
through
meter
at
hot
wire
.
After
approximately
four
sec-
onds
wire
should
glow
brightly
for
about
one
second
.
NOTE
-
If
the
wire
glowsas
specified,
then
the
airflow
meter
and
ECM
are
probably
operating
correctly
.
lf
the
wire
does
not
glow,
continue
testing
.
4
.
lf
the
wire
does
not
glow,
remove
air
flow
sensor
and
look
through
it
to
see
if
wire
is
broken
.
lf
wire
is
broken,
meter
will
have
to
be
replaced
.
5
.
Reinstall
air
flow
sensor
and
harness
connector
.
Peel
back
rubber
bootfrom
harness
connector
.
Working
from
rear
of
connector,
connect
digital
voltmeter
across
terminals
1
and
4
.
See
Fig
.
26
.
6
.
Start
and
rev
engine
toat
least
2,500
rpm,thenshut
it
off
.
After
about
4
seconds,
voltage
should
riseto
about
4
volts
for
about
one
second
.
lf
voltage
is
present,
but
wire
does
not
glow,
air
flow
sensor
is
faulty
and
should
be
replaced
.
7
.
lf
voltage
is
not
present
in
step
6,
turn
ignition
key
on
and
check
for
voltage
and
ground
at
sensor
.
There
should
beground
at
pin
4
.
There
should
be
positive
(+)
battery
voltage
at
pin
2
.
BOSCH
DME
M3
.1
AND
M32
.1
COMPONENT
TESTS
AND
REPAIRS