Cylinder BMW 325i 1993 E36 Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: BMW, Model Year: 1993, Model line: 325i, Model: BMW 325i 1993 E36Pages: 759
Page 218 of 759
210-
4
CLUTCH
Clutch,
removing
1
.
Remove
transmission
fromengine
.
See230
Manual
Transmission
.
2
.
Remove
release
bearing
from
transmission
inputshaft
.
3
.
Remove
clutch
release
lever
by
sliding
it
out
from
under
spring
clip
.
See
Fig
.
5
.
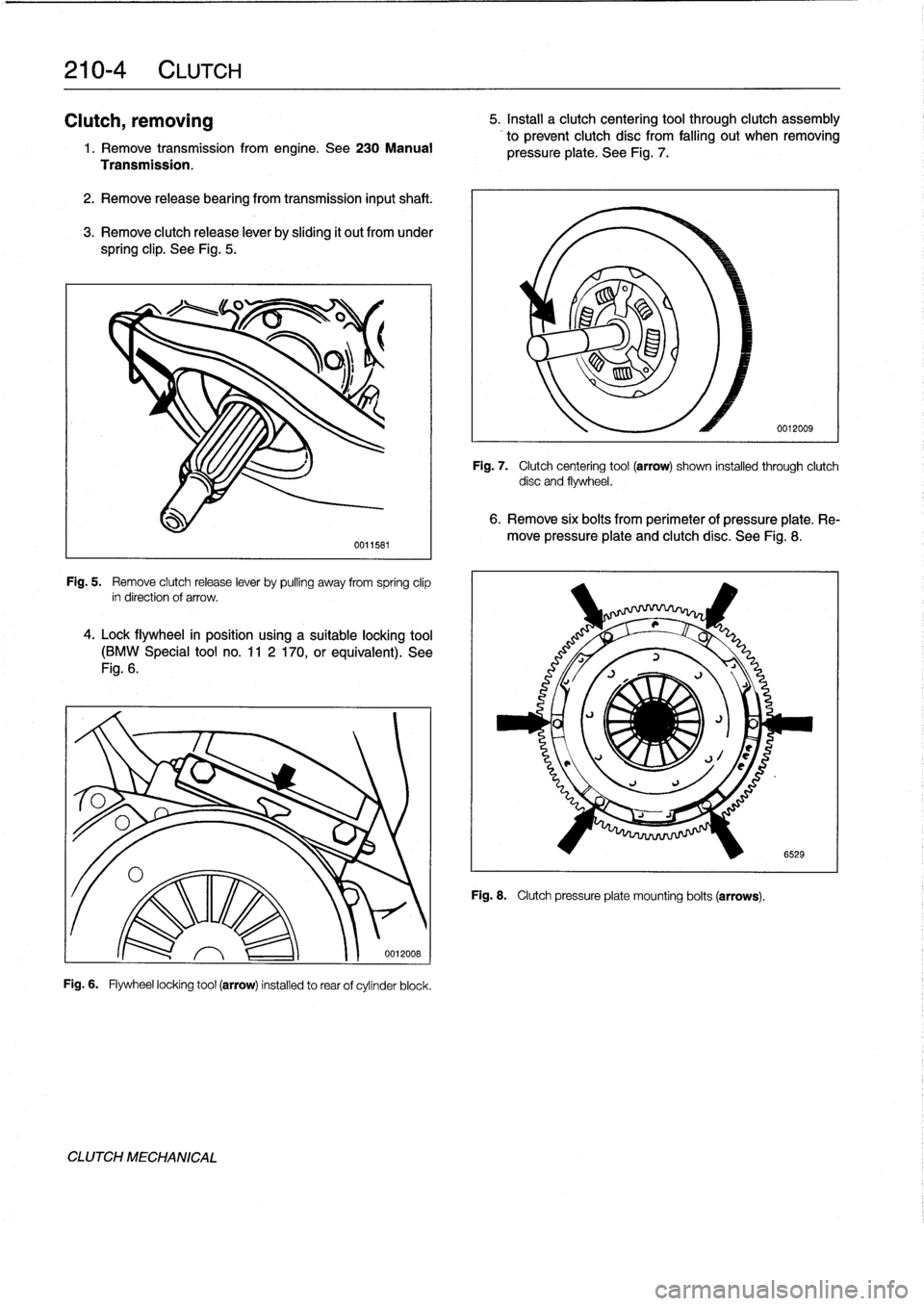
Fig
.
5
.
Remove
clutch
release
lever
by
pulling
away
from
spring
clip
in
direction
of
arrow
.
4
.
Lock
flywheel
in
posítion
using
a
suitable
locking
tool
(BMW
Special
tool
no
.
11
2
170,or
equivalent)
.
See
Fig
.
6
.
Fig
.
6
.
Flywheel
locking
tool
(arrow)
installed
to
rear
of
cylinder
block
.
CLUTCH
MECHANICAL
0011581
0012008
5
.
Install
a
clutch
centering
tool
through
clutch
assembly
to
prevent
clutch
disc
from
falling
out
when
removing
pressure
plate
.
See
Fig
.
7
.
Fig
.
7
.
Clutch
centering
tool
(arrow)
shown
installed
through
clutch
disc
and
flywheel
.
6
.
Remove
six
bolts
from
perimeter
of
pressure
plate
.
Re-
move
pressure
plate
and
clutch
disc
.
See
Fig
.
8
.
Fig
.
8
.
Clutch
pressure
plate
mounting
bolts
(arrows)
.
0012009
6529
Page 226 of 759

230-
6
MANUAL
TRANSMISSION
Transmission,
removing
and
installing
1
.
Disconnect
negative
(-)
cable
from
battery
.
CAUTION-
Prior
to
disconnecting
the
battery,
read
the
battery
disconnection
cautions
given
at
the
front
of
this
manual
onpage
viii
.
2
.
Insta¡¡
enginesupportacrossengine
bay
.
Raise
engine
so
that
weight
of
engine
ís
supported
.
See
Fig
.
10
.
Fig
.
10
.
Engine
support
equipment
used
to
support
engine
from
above
before
removing
transmission
.
3
.
Raise
vehicle
to
gain
access
to
underside
of
car
.
4
.
Support
transmission
with
transmission
jack
.
lf
applica-
ble,
remove
reinforcing
cross
brace
from
belowen-
gine/transmission
.
5
.
Disconnect
harnesscon
nector
from
reverse
light
switch
on
transmission
.
6
.
Remove
completeexhaustsystem
and
heat
shield
.
See
180
Exhaust
System
.
NOTE-
Disconnect
oxygensensor
hamess
connector(s)be-
fore
lowering
exhaust
system
.
7
.
Remove
driveshaft
.
See260
Driveshaft
.
8
.
Disconnect
shift
rod
from
transmission
selectorshaft
.
See
Fig
.
11
.
9
.
Disconnect
shift
console
fromtop
of
transmission
.
See
250
Gearshift
Linkage
.
TRANSMISSION
REMOVAL
AND
INSTALLATION
Washers
Shift
Shift
rod
rod
retaining
clip
0
0
,
Fig
.
11
.
Shift
lever
to
transmission
connection
.
Shift
console
0012024
10
.
Unbolt
clutch
slave
cylinder
from
sideof
transmission
.
Do
not
disconnect
fluid
hose
.
Suspend
slavecylinder
from
chassis
using
stiff
wire
.
CAUTION-
Do
not
operate
clutch
pedal
with
slave
cylinder
re-
moved
from
transmission
.
11
.
Support
transmission
from
below
with
jack
.
Remove
rear
support
crossmember
from
transmission
.
See
Fig
.
12
.
Fig
.
12
.
Rear
transmission
crossmember
(arrow)
.
12
.
Lower
transmission/engine
assembly
until
it
rests
on
front
suspension
crossmember
.
CAUTION-
Tilting
the
engine
to
lower
thetransmission
can
lead
to
damage
to
various
componente
due
to
lackof
clearance
at
rear
of
engine
-On
cars
with
AST
remove
throttle
body
before
tilt-
ing
engine
.
-Remove
brace
fluid
reservoir
if
necessary
.
0013135
Page 227 of 759
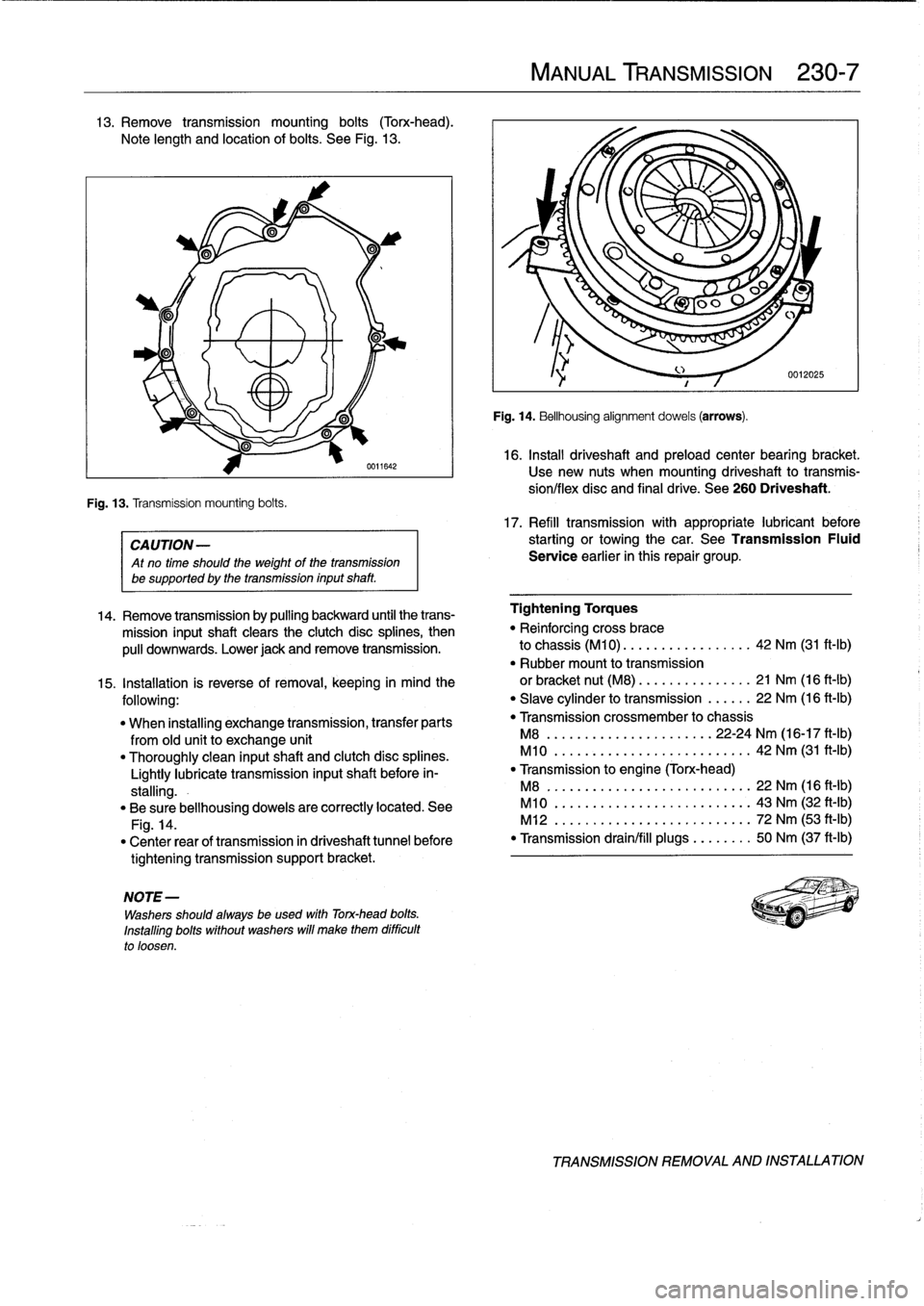
13
.
Remove
transmission
mounting
bolts
(Torx-head)
.
Note
length
and
location
of
bolts
.
See
Fig
.
13
.
Fig
.
13
.
Transmission
mounting
bolts
.
0611642
CA
UTION-
Atno
time
should
the
weight
of
thetransmission
be
supported
by
the
transmission
inputshaft
.
NOTE
-
Washers
should
always
be
used
with
Torx-head
bolts
.
Installing
bolts
without
washers
will
make
them
difficult
to
loosen
.
MANUAL
TRANSMISSION
230-
7
Fig
.
14
.
Bellhousing
alignment
dowels
(arrows)
.
16
.
Install
driveshaft
and
preload
center
bearing
bracket
.
Usenew
nuts
when
mounting
driveshaft
to
transmis-
síon/flex
disc
and
final
drive
.
See
260
Driveshaft
.
17
.
Refill
transmission
with
appropriate
lubricant
before
starting
or
towingthe
car
.
See
Transmission
Fluid
Service
earlier
in
this
repair
group
.
14
.
Remove
transmission
by
pulling
backward
until
the
trans-
Tightening
Torques
mission
inputshaft
clears
the
clutch
disc
splines,
then
"
Reinforcing
cross
brace
pulí
downwards
.
Lower
jack
andremove
transmission
.
to
chassis
(M10)
.
...
.............
42
Nm
(31
ft-Ib)
"
Rubber
mount
to
transmission
15
.
Installation
is
reverse
of
removal,
keeping
in
mind
the
or
bracket
nut
(M8)
.
...
.
...
.......
21
Nm
(16
ft-Ib)
following
:
"
Slave
cylinder
to
transmission
......
22
Nm
(16
ft-Ib)
"
When
installing
exchange
transmission,
transfer
parts
"
Transmission
crossmember
to
chassis
from
old
unit
to
exchange
unit
M8
...............
.
.
...
..
22-24
Nm
(16-17
ft-Ib)
"
Thoroughly
clean
inputshaft
and
clutch
disc
splines
.
M10
..............
.
..
..
.......
42
Nm
(31
ft-Ib)
Lightly
lubrícate
transmission
inputshaft
before
in-
"
Transmission
to
engine
(Torx-head)
stalling
.-
M8
..
..................
..
.
..
..
22
Nm
(16
ft-Ib)
"
Be
sure
bellhousing
dowels
are
correctly
located
.
See
M10
.
.................
...
.
..
..
43
Nm
(32
ft-Ib)
Fig
.
14
.
M12
.
..................
..
.
..
..
72
Nm
(53
ft-Ib)
"
Center
rear
of
transmission
in
driveshaft
tunnel
before
"
Transmission
drain/fill
plugs
.
..
.
..
..
50
Nm
(37
ft-Ib)
tightening
transmission
support
bracket
.
TRANSMISSION
REMOVAL
AND
INSTALLATION
Page 250 of 759

300-2
SUSPENSION,
STEERING
AND
BRAKES-GENERAL
Steering
INTEGRATED
SYSTEMS
The
steering
linkage
connects
the
rack-and-pinion
unit
through
tie
rodsto
the
steering
arms
.
The
tie
rod
ends
allow
the
wheels
to
pivot
and
react
to
suspension
travel
.
Rear
Suspension
The
rear
axle
carrier
is
the
main
mounting
point
for
the
final
drive
housing
and
the
rear
suspension
components
.
Trailing
arms
locatethe
rear
wheels
and
anchorthe
springs,
shocks
and
stabilizer
bar
.
Driveaxies
with
constant-velocity
(CV)
joints
at
both
ends
transfer
power
from
the
differential
to
the
road
wheels
.
The
differential
is
mounted
to
the
rearaxle
carrier
through
rubber
mountsand
bushings
to
hele
isolate
drivetrain
noise
and
vibration
.
Brakes
E36
cars
areequipped
with
power
disc
brakes
with
an
inte-
gral
antilock
brakes
(ABS)
.
The
parking
brake
is
a
dual-drum
system
integrated
with
the
rear
brake
rotors
.
See
Fig
.
3
.
Power
assist
is
provided
by
a
vacuum
booster
when
the
en-
gine
is
running
.
The
brakepedal
pushrod
is
connected
directly
to
the
master
cylinder,
so
failure
of
the
vacuum
booster
does
not
normally
result
in
total
brake
failure
.
0012124
Each
disc
brakeuses
a
caliper
with
a
single
hydraulic
cylin-
Fig
.
2
.
Front
suspension
control
arm
(arrow)
.
der
.
Brake
pads
in
the
left
front
and
right
rear
contain
wear
sensors
.
When
the
padsneed
replacement,the
sensors
illu-
The
front
suspension
is
designed
with
minimum
positive
minate
a
light
on
the
dashboard
.
steering
offset
.
This
geometry
contributes
to
stability
when
traction
is
unequalfrom
side
to
side
.
Suspension
travel
is
lim-
Tires
and
Wheels
ited
by
rubber
bump
stops
.
The
three
point
mounting
of
each
L-shaped
control
arm
ere-
Tiresize
is
critica¡
to
the
proper
operatíon
of
the
E36
ABS
or
cisely
controls
the
front-to-rear
and
side-to-side
position
of
the
ABS/AST
system
.
Severa¡
different
styles
of
wheels,
in
15,16
strut,
while
the
flexibility
of
the
joints
and
mounts
alsoallows
and
17
inch
diameters,
are
available
from
an
authorized
BMW
the
movement
necessary
for
suspension
travel
.
The
control
dealer
.
arm
mounting
points
are
designed
with
anti-dive
geometry
.
The
suspension
reduces
the
normaltendency
for
the
front
of
NOTE-
the
vehicle
to
dive
under
hard
braking
.
Aftermarket
wheelsshould
be
selected
wlth
care
.
Im-
properly
fitted
wheels
can
contact
anddamage
sus
Control
arm
position
is
fixed,
with
no
adjustment
provisions
pension,
brakeorbodycomponentsandmayadversely
on
the
control
arms
for
alter¡ng
front
wheel
al
ignment
.
A
stabi-
affect
vehicle
stability
.
lizer
bar
mounted
to
both
control
arms
heles
to
reduce
body
rol¡
whencomering
.
INTEGRATED
SYSTEMS
Antilock
Brake
System
(ABS)
is
standard
on
all
E36
cars
.
The
variable-assist
power
steering
system
consists
of
an
Standard
on
some
models
and
installed
as
optional
equipment
on
engine-driven
hydraulic
pump,
a
rack-and-pinion
type
steer-
others,
is
All
Season
Traction
(AST)
.
ing
gear,
and
connecting
linkage
to
the
road
wheels
.
TheE36
utilizes
an
engine-speed
dependent
variable
effort
steering
Antilock
Brake
System
(ABS)
system
.
At
low
speeds,
maximum
power
assist
is
provided
to
ease
parking
and
city
driving
.
Athigh
speeds,
assist
is
re-
The
electronically-controlled
ABS
maintains
vehícle
stabili
duced
to
ensure
stability
.
ty
and
control
during
emergency
braking
by
preventing
wheel
lock-up
.
ABS
provides
optimum
deceleration
and
stability
dur-
Page 251 of 759
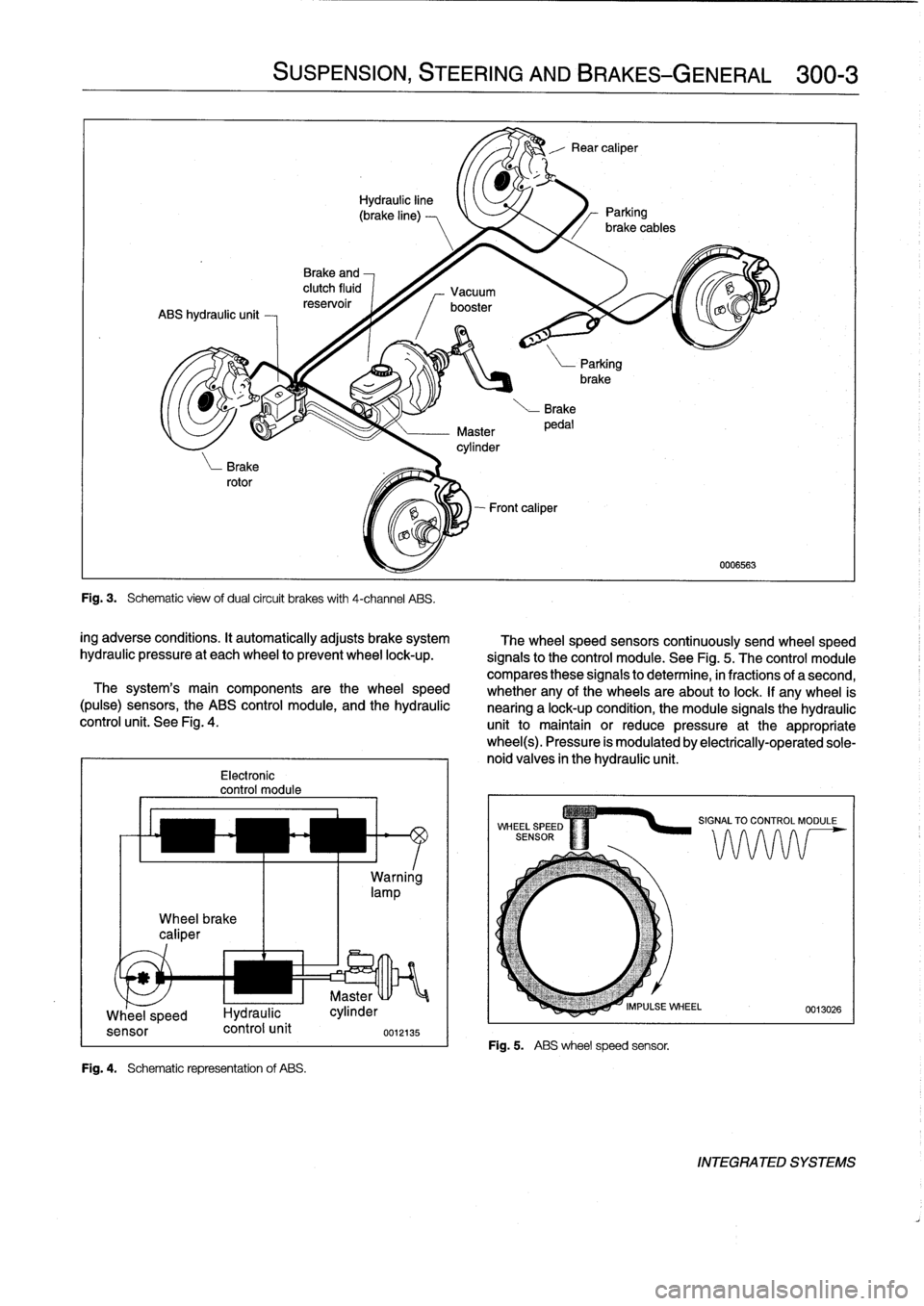
Wheel
brake
caliper
Electronic
control
module
Fig
.
4
.
Schematic
representation
of
ABS
.
SUSPENSION,
STEERING
ANDBRAKES-GENERAL
300-3
Fig
.
3
.
Schematic
view
ofdual
circuit
brakes
with
4-channel
ABS
.
ing
adverse
conditions
.
It
automatically
adjusts
brake
system
hydraulic
pressure
at
each
wheel
to
prevent
wheel
lock-up
.
The
system's
main
components
arethe
wheel
speed
(pulse)
sensors,
the
ABS
control
module,
and
the
hydraulic
control
unit
.
See
Fig
.
4
.
Warning
lamp
u
Master
Whee
_
l
speed
I-lydraulic
cylinder
sensor
control
unit
0012135
UNI
The
wheel
speed
sensors
continuously
send
wheel
speed
signals
to
the
control
module
.
See
Fig
.
5
.
The
control
module
compares
these
signals
to
determine,
in
fractions
of
a
second,
whether
any
of
the
wheels
areabout
to
lock
.
If
any
wheel
is
nearing
a
lock-up
condition,
the
module
signals
the
hydraulic
unit
to
maintain
or
reduce
pressure
at
the
appropriatewheel(s)
.
Pressure
is
modulated
by
electrically-operated
sole-
noid
valves
in
the
hydraulic
unit
.
Fig
.
5
.
ABS
wheelspeed
sensor
.
0006563
INTEGRATED
SYSTEMS
Page 287 of 759

GENERAL
......
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.....
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
331-1
Final
Drive
Oil
Seals
.
.
...
.
.
.
.......
.
.
.
.
.
331-1
Finaldrive
flange
oil
sea¡,
replacing
....
.
.
.
..
331-2
FINAL
DRIVE
SERVICE
.
.....
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
331-1
Finaldrive
inputshaft
oil
seal,
replacing
.
.
.
.
.
331-3
Final
drive
oí¡,
draining
and
filling
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
331-1
Finaldrive
unit,
removíng
and
installing
.
.
.
.
.
.
331-3
GENERAL
This
repa¡r
group
covers
repair
operations
that
do
not
re-
quire
complicated
disassembly
of
the
final
drive
.
Internal
re-
pairs
and
final
drive
disassembly
are
not
covered
in
this
manual
.
FINAL
DRIVE
SERVICE
Al¡
final
drive
work
requires
some
method
of
raising
thecar
and
supporting
it
securely
while
the
work
is
performed
.
Jack
stands
and
a
floor
jack
can
easily
be
used,
but
use
extreme
caution
when
working
beneath
the
car
.
See010
Fundamen-
tais
for
the
Do-It-Yourself
Owner
.
NOTE-
Removal
of
final
drive
carrier
is
covered
in
330
Rear
Suspension
.
Final
drive
oil,
draining
and
filling
1
.
Drive
car
to
warm
final
drive
fluid
.
2
.
Raise
car
and
support
safely
.
WARNING
-
Make
sure
that
thecar
is
firmly
supported
on
jack
standsdesigned
for
the
purpose
.
Place
the
jack
standsbeneatha
structural
chassis
point
.
Do
not
place
jack
stands
under
suspension
parts
.
5
.
Fill
final
drive
with
appropriate
type
and
quantity
of
lu-
bricant
.
Insta¡¡
and
tighten
fill
plug
.
331
Final
Drive
0
Fig
.
1
.
Final
drivedrain
plug
(A)
and
fill
plug
(B)
.
D
NOTE-
The
final
drive
fluid
level
is
correct
when
the
fluid
begins
to
spill
from
the
fill
plug
.
Final
Drive
Oil
Seals
FINAL
DRIVE
331-1
0013113
Final
DriveDrain
and
Fill
"
Oil
specifications
w/o
limited
slip
.
.......
BMW
SAF-XO
Synthetic
Oil
with
limited
slip
.
......
BMW
SAF-XIS
Synthetic
Oil
"
Final
drive
oil
capacity
4-cylinder
.
.
.
...
................
1
.1
liters
(1
.2
qt)
6-cylinder
.
.
.
...
................
1
.7liters(1.8
qt)
3
.
Place
a
drain
pail
below
final
drive
andremove
drain
and
fill
plugfrom
final
drive
.
See
Fig
.
1
.
Low
oil
level
caused
by
faulty
oil
seals
may
be
the
cause
of
noisy
final
drive
operation
or
limited-slip
chatter
.
The
drive
NOTE-
flange
(side)
and
inputshaft
(front)
oil
seals
can
be
replaced
"
Use
a14
mm
alíen
bit
socket
to
remove
the
drain
plug
.
while
the
final
drive
is
installed
.
Alternatively,
cut
approximately
30
mm
(1
.2
in)
from
an
alíen
key
and
usea
box
end
wrenchon
the
key
NOTE-
stub
.
Do
not
mistake
leaking
CV
joints
for
flangeseal
leaks
.
4
.
Install
and
tighten
drain
plug
.
It
may
be
helpful
to
degrease
the
final
drive
to
pinpoint
the
source
of
the
leak
prior
to
replacing
seals
.
FINAL
DRIVE
SERVICE
Page 291 of 759

Brake
rotor,
removing
and
installing
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
340-7
MASTER
CYLINDER
............
.
.
.
.
.
.
.340-7
Master
cylinder,
removing
and
installing
.
...
.
340-7
GENERAL
TROUBLESHOOTING
WARNING
-
"
Although
semi-metallic
and
metallic
Brake
friction
materials
in
Brake
pads
or
shoes
no
longer
con-
tain
asbestos,
they
produce
dangerous
dust
.
"
Brake
fluid
is
poisonous,
highly
corrosive
and
dangerous
to
the
environment
Wear
safety
glasses
and
rubber
gloves
when
working
with
Brake
fluid
.
Do
not
siphonBrake
fluid
with
your
mouth
.
Immediately
clean
away
any
fluid
spilled
on
painted
surfaces
and
wash
with
water,
asBrake
fluid
will
remove
paint
.
"
Always
use
new
Brake
fluid
froma
fresh,
un-
opened
container
.
Brake
fluid
will
absorb
mois-
ture
from
the
air
.
This
canlead
to
corrosion
problems
in
the
brakingsystem,
and
will
also
low-
er
the
Brake
fluid's
boiling
point
.
Dispose
of
Brake
fluid
properly
.
"
Do
notreuse
self-locking
nuts,bolts
or
fasteners
.
They
are
designed
to
be
used
only
once
and
may
failif
reused
.
Always
replace
them
with
new
self-
locking
fasteners
.
BMW
E36
models
areequipped
with
vacuum
power-assist-
ed
four-wheel
disc
brakes
with
an
integral
Antilock
Brake
Sys-
tem
(ABS)
.
Single-pistoncalipers
act
on
solid
or
vented
front
rotors
and
solid
rear
rotors
.
A
brake
pad
wear
sensor
for
each
axle
indicates
when
brake
padsneed
replacement
.
The
dual
drum-type
parking
brakesystem
is
integrated
with
the
rear
brake
rotors
.
NOTE-
M3
models
havevented
directional
Brake
rotors
on
the
rearaxle
as
well
ason
the
front
.
340
Brakes
BRAKES
340-1
GENERAL
.
.
.
.
.
.
.........
.
.
.
..........
340-1
BRAKE
BOOSTER
.........
.
.
.
.
.
...
.
.
.
.
340-8
TROUBLESHOOTING
.......
.
......
.
...
340-1
Brake
booster,
removing
and
installing
....
.
.
340-8
PARKING
BRAKE
.
.....
.
...
.
.
.
.....
.
.
.
340-10
BLEEDING
BRAKES
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
..........
340-3
Parking
brake,adjusting
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.....
.
340-10
Pressure
bleeding
brakes
Parking
brake
shoes,
removing
and
installing
.
340-11(except
cars
with
AST)
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
...
.
.
.
.
.340-3
Parking
Brake
cable,
replacing
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
340-11
BRAKE
PADS,
CALIPERS,
ANTILOCK
BRAKE
SYSTEM
(ABS)
.
.
.
.340-11
AND
ROTORS
..........
.
.......
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
340-3
ABS
System
Inspection
.
...
.
.......
.
.
.
..
340-12
Brake
pads,
replacing
............
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
340-4
ABS
wheel
speed
sensors,
replacing
.
.
.
.
..
340-12
Brake
caliper,
removing
and
installing
.
..
..
.
340-6
TABLES
a
.
Brake
System
Troubleshooting
.....
...
.
.
.....
.340-2
b
.
Brake
Rotor
Reconditioning
Specifications
.
.....
.340-7
Brakeperformance
is
mainly
affected
by
three
things
:
the
leve¡
and
condition
of
the
brake
fluid,
the
system's
abilíty
to
create
and
maintain
hydraulic
pressure,
and
the
condition
of
the
friction
components
.
Air
in
the
Brake
fluid
will
make
the
Brake
pedal
feel
spongy
during
braking
or
will
increase
the
Brake
pedalforce
required
to
stop
.
Fluid
contaminated
by
moisture
or
dirt
can
corrode
the
system
.
Inspect
the
Brake
fluid
inside
the
reservoir
.
Ifit
is
dirty
or
murky,
or
is
over
a
year
old,
the
fluid
should
be
replaced
.
Visually
check
the
hydraulic
system
startingat
the
master
cylinder
.
To
check
the
function
of
the
master
cylinder
hold
the
brake
pedal
down
hard
with
the
engine
running
.
The
pedal
should
feelsolid
and
stay
solid
.
If
the
pedal
slowly
falls
to
the
floor,
either
the
master
cylinder
is
leaking
internally,
or
fluid
is
leaking
externally
.
If
no
leaks
canbe
found,
the
master
cylin-
der
is
faulty
and
should
be
replaced
.
Check
all
Brake
fluid
lines
and
couplings
for
leaks,
kinks,
chafing
and
corrosion
.
Check
the
Brake
booster
by
pumping
the
Brake
pedal
ap-
proximately
10
times
with
the
engine
off
.
Hold
the
pedal
down
and
start
the
engine
.
The
pedal
should
fa¡¡
slightly
.
If
not,
check
for
any
visiblefaults
before
suspecting
a
faulty
brake
booster
.
Check
for
strong
vacuum
at
the
vacuum
hose
fitting
at
the
booster,
and
check
the
non-retum
valve
for
one-way
flow
.
Worn
or
contaminated
brake
pads
will
cause
poor
braking
performance
.
Oil-contaminated
or
glazed
pads
will
cause
stopping
distances
to
increase
.
Inspect
the
rotors
for
glazing,
discoloration
and
scoring
.
Steering
wheel
vibration
while
braking
at
speed
is
often
caused
by
warped
rotors,
but
can
also
be
caused
byworn
suspension
components
.
TROUBLESHOOTING
Page 292 of 759
340-2
BRAKES
When
troubleshooting,
keep
in
mind
that
tire
inflation,
wear
and
temperature
can
affect
braking
and
suspension
.
See310
Front
Suspension
for
more
information
on
front
suspension
parts
inspection
.
Table
a
lists
symptoms
of
brake
problems,
their
probable
causes,
and
suggested
corrective
actions
.
Table
a
.
Brake
System
Troubleshooting
Symptom
1
Probable
cause
1
Repairs
Brake
squeal
a
.
Incorrectly
installed
brake
pads
or
a
.
Check
component
installation
.
parking
brake
shoes
b
.
Brakepad
carriers
dirty
or
corroded
b
.
Remove
brake
pads
and
clean
calipers
.
c
.
Brake
pad
anti-rattle
springs
faulty
or
c
.
Install/replace
anti-rattle
springs
.
missing
d
.
Brakepads
heat-glazed
or
oil-soaked
d
.
Replace
brake
pads
.
Clean
rotors
.
Replace
leaking
calipers
as
required
.
e
.
Wheel
bearings
worn
(noise
most
e
.
Replace
worn
bearings
.
See310
Front
Suspension
pronounced
when
turning)
or
330
Rear
Suspension
.
Pedal
goes
to
f
loor
when
braking
a
.
Brake
fluid
leve¡
low
due
to
system
a
.
Check
fluidlevel
and
inspect
hydraulic
system
for
leaks
signs
of
leakage
.
Fill
and
bleed
system
.
b
.
Master
cylinder
faulty
I
b
.
Replacemaster
cylinder
.
Low
pedal
after
system
bleeding
1
a
.
Master
cylinder
faulty
1
a
.
Replace
master
cylinder
.
Pedal
spongy
or
brakes
work
only
a
.
Air
in
brake
fluid
a
.
Bleedsystem
.
when
pedal
is
pumped
b
.
Master
cylinder
faulty
(interna¡
return
b
.
Replacemaster
cylinder
.
spring
weak)
c
.
Leaking
line
or
hose
unions
c
.
Repair
or
replace
lines
and
hoses
.
Bleed
system
.
Excessive
braking
effort
a
.
Brake
pads
wet
a
.
Use
light
pedal
pressure
to
dry
pads
while
driving
.
b
.
Brake
pads
heat-glazed
oroil-soaked
b
.
Replace
brake
pads
.
Clean
rotors
.
Replace
leaking
calipers
.
c
.
Vacuum
booster
or
vacuum
hose
con-
c
.
Inspect
vacuum
lines
.
Test
vacuum
booster
and
re
nections
to
booster
faulty
place
as
required
.
Test
vacuum
non-return
valve
for
one-way
air
flow
.
Brakes
pulsate,
chatter
or
grab
a
.
Warped
brake
rotors
a
.
Resurface
or
replace
rotors
.
b
.
Brake
padsworn
b
.
Replace
brake
pads
.
c
.
Brake
pads
heat-glazed
or
oil-soaked
c
.
Replace
brake
pads
.
Clean
rotors
.
Replace
leaking
calipers
.
Uneven
braking,
car
pulís
to
one
a
.
Incorrect
tire
pressures
or
worn
tires
a
.
Inspect
tire
condition
.
Check
and
correct
tire
pres-
side,
rear
brakes
lock
sures
.
b
.
Brake
pads
on
one
side
of
car
heat-
b
.
Replace
brake
pads
.
Clean
rotors
.
Replace
leaking
glazed
or
oil-soaked
calipers
.
c
.
Caliper
or
brake
pads
binding
c
.
Clean
and
recondition
brakes
.
d
.
Worn
suspension
components
d
.
Inspect
for
worn
or
damaged
suspension
compo-
nents
.
See
310
Front
Suspension
or
330
Rear
Sus-
pension
.
Brakes
drag,
bind
or
overheat
a
.
Brake
caliper
or
brake
pads
binding
a
.
Clean
or
replace
caliper
.(
b
.
Master
cylinder
faulty
b
.
Replacemaster
cylinder
.
WARNING
-
On
cars
with
All
Season
Traction
(AST),
special
BMW
service
equipment
is
required
to
properly
bleed
the
ABS/AST
system
.
For
safety
reasons,
the
brake
system
on
carswith
ABS/AST
must
not
be
bled
using
the
procedures
described
inthis
repair
group
.
BLEEDING
BRAKES
Brake
bleeding
is
usually
done
for
one
of
two
reasons
:
Ei-
ther
to
replace
oíd
brake
fluid
as
part
of
routine
maintenance
or
to
expel
trapped
air
in
the
system
that
resulted
from
open-
ingthe
brake
hydraulic
system
during
repairs
.
BLEEDING
BRAKES
Alwaysuse
new
brake
fluid
from
an
unopened
container
.It
is
important
to
bleed
the
entire
system
when
any
part
of
the
hydraulic
system
has
been
opened
.
On
cars
not
equipped
with
traction
control
(AST),
brake
system
bleeding
should
be
done
with
a
pressure
bleeder
.
On
cars
with
AST,
brake
bleed-
ing
should
be
done
by
an
authorized
BMW
dealer
.
WARNING
-
On
cars
with
All
Season
Traction
(AST),
special
BMW
service
equipment
is
requíred
to
properly
bleed
the
ABS/AST
system
.
For
safetyreasons,
the
brake
system
on
carswith
ABS/AST
must
not
be
bled
using
the
procedures
described
inthís
repair
group
.
Page 293 of 759

When
bleeding
the
brakes,
startat
the
wheel
farthest
from
4
.
Close
bleeder
screw
and
release
brake
pedal
.
Refill
the
master
cylinder
and
progress
in
the
following
order
:
brake
fluid
reservoir
and
proceed
to
rear
left
wheel
.
"
right
rear
brake
5
.
Proceed
with
the
remaining
wheels
using
the
order
list-
"
left
rear
brake
ed
earlier
.
"
rightfront
brake
"
left
front
brake
Pressure
bleeding
brakes
(except
carswith
AST)
1
.
Top
off
brake
fluid
in
reservoir
and
connect
pressure
bleeder
to
reservoir
.
Connect
bleeder
hose
and
bottle
to
right
rearcaliper
bleeder
screw
.
Pressurize
system
to
approximately
1
bar
(14
.5
psi)
.
BRAKES
340-
3
Tightening
Torques
"
Bleeder
screws
:
7
mm
screw
..........
..
.
.
.
.
......
5
Nm
(4
ft-Ib)
9
mm
screw
..........
..
.
..
.......
6
Nm
(5
ft-Ib)
BRAKE
PADS,
CALIPERS,
AND
ROTORS
CAUTION-
TheE36
front
brake
caliper
is
shown
in
Fig
.
2
.
The
rear
Do
not
exceed
a
pressure
of
2
bar
(29
psi)
when
brake
caliper
is
shown
in
Fig
.
7
.
pressure
bleeding
the
brake
system
.
Excessive
pressure
will
damage
the
brake
fluid
reservoir
.
Brake
pads
canbe
replaced
without
disconnecting
the
brake
fluid
hose
from
the
caliper
or
having
to
bleed
the
brakes
.
2
.
Have
a
helperhold
brake
pedal
down
.
The
rotors
can
be
replaced
without
disassembling
the
wheel
huband
bearing
.
Always
machine
or
replace
rotors
in
parts
.
3
.
Open
bleeder
screw
.
See
Fig
1
.
Have
helper
slowly
,
Replace
pads
in
sets
.
pump
brakes
about10
times
with
bleeder
screw
open,
holding
pedal
down
on
the
last
pump
.
When
escaping
WARNING-
fluid
is
free
of
air
bubbles,
close
bleeder
screw
.
"
Althoughsemi-metallicandmetallicbrake
friction
materials
in
brake
pads
or
shoes
no
longer
con
CAUTION-
tain
asbestos,
they
produce
dangerous
dust
.
Bleeder
hose
must
alwaysremain
submersed
in
"
Treat
all
brake
dust
asa
hazardous
material
.
the
clean
brake
fluid
whenever
the
bleeder
valve
is
open
.
"
Do
not
create
dust
by
grinding,
sanding,
orclean-
ing
brake
friction
surfaces
with
compressed
air
.
"
Breathing
any
brake
dust
can
cause
serious
dis-
eases
such
as
cancer,
and
may
result
in
death
.
Brake
pads,
replacing
This
procedure
is
applicable
lo
both
front
and
rear
brakes
.
Front
and
rear
brake
assemblies
are
basically
the
same,
ex-
cept
that
the
rear
brake
rotors
house
the
parking
brake
mech-
anism
1
.
Raise
car
andremove
wheels
.
WARNING
-
Make
sure
thecar
is
firmly
supported
onjack
stands
designed
for
the
purpose
.
Place
the
jack
stands
be-
neath
a
structural
chassis
point
.
Do
not
place
jack
stands
undersuspension
parts
.
2
.
Remove
plastic
caps
from
guide
bolts
and
then
remove
guide
bolts
.
See
Fig
.
3
.
0012113
3
.
If
applicable,
disconnect
brake
pad
wear
sensor
con-
Fig
.
1
.
Brake
caliper
bleeder
screw
(arrow)
.
nector
and
remove
wiring
from
its
holder
.
4
.
Remove
anti-rattle
clip
from
caliper
.
See
Fig
.
4
.
BRAKE
PADS,
CALIPERS,
AND
ROTORS
Page 297 of 759

Brake
rotor,
removing
and
installing
Brake
rotors
shouldalways
be
replaced
in
pairs
.
Fig
.
9
.
Brake
rotor
mounting
screw
(arrow)
.
3
.
Inspect
rotor
for
excessive
grooving,
cracks,
and
warp-
ing
.
Check
rotor
thickness
.
See
Table
b
.
4
.
Installation
is
reverse
of
removal
.
"
Clean
rotor
with
brakecleaner
before
installing
.
"
If
brake
fluid
hose
veas
removed
or
loosened,
brake
systemmustbe
bled
as
described
aboveunder
Bleeding
Brakes
.
BRAKES
340-
7
5
.
Once
brake
assembly
is
instalind,
depress
brakepedal
several
times
to
adjust
caliper
and
pads
.
"
Pedal
should
feel
firm
and
be
at
proper
height
.
"
Check
fluid
leve¡
.
Top
up
if
necessary
.
NOTE-
M3
models
use
directional
brake
rotors
and
mustbe
in-
NOTE-
stalled
on
the
proper
side
.
Part
numbes
are
cast
finto
When
installing
new
rear
brake
rotors,
the
parking
therotors
.
A
part
that
ends
in
an
odd
number
is
a
left
brakeshouldbe
adjusted
.
See
Parking
Brake
.
rotor
.
One
that
ends
in
an
even
number
is
a
right
rotor
.
1.
Remove
caliper
as
described-above
and
hang
from
Tightening
Torques
chassis
using
stiff
wire
.
"
Brake
rotor
to
wheel
hub
..........
16
Nm
(12
ft-Ib)
"
Front
brake
caliper
to
steering
arm
...
110
Nm
(81
ft-Ib)
NOTE-
"
Rear
brake
caliper
to
traíling
arm
....
67
Nm
(50
ft-Ib)
Do
notloosen
caliper
brake
hose
.
"
Road
wheel
to
hub
...
..
.
100
±
10
Nm
(74
t
7
ft-Ib)
2
.
Remove
mountingscrew
holding
rotor
to
wheel
hub
.
,
See
Fig
.
9
.
Table
b
.
Brake
Rotor
Reconditioning
Specificati*M`
Front
Rear
Vented
rotor
wear
limit
(min
.
thickness)
20
.4
mm
(0
.803
in.)
Solid
rotor
wear
limit
(min
.
thickness)
8
.4
mm
(0.331
in
.)
M3
models
wear
limit
(min
.
thickness)
26
.4mm
(0
.977
in
.)
18
.4
mm
(0
.723
in
.)
Axial
runout
(max
.)
rotor
removed
0
.05
mm
(0
.002
in
.)
0
.05
mm
(0
.002
in
.)
rotor
installed
0
.20
mm
(0
.008
in
.)
0
.20
mm
(0
.008
in
.)
CAUTION-
M3
brake
rotors
must
not
be
machined
.
MASTER
CYLINDER
The
brake
master
cylinder
is
mounted
to
the
front
of
the
vac-
uum
booster
on
the
driver
side
bulkhead
.
Master
cylinder,
removing
and
installing
1
.
Using
a
clean
syringe,
empty
brake
fluid
reservoir
.
WARNING
-
Brake
fluid
is
highly
corrosive
and
dangerous
to
the
environment
.
Dispose
of
it
properly
.
NOTE-
On
original
equipment
rotors,
the
mínimum
allowable
2
.
Disconnect
brake
fluid
leve¡
sender
connector
from
fluid
thickness
is
stamped
on
the
rotor
hub
.
Measure
the
rotor
reservoi
r
cap
.
brakingsurface
with
a
micrometer
at
eight
to
ten
different
points
and
use
the
smallest
measurement
recorded
.
3
.
Disconnect
brake
fluid
lines
frommaster
cylinder
.
See
Fig
.
10
.
Disconnect
hydraulic
clutch
system
supply
line
.
4
.
Unscrew
mounting
nuts
and
remove
master
cylinder
from
brake
booster
.
5
.
Make
sure
all
nuts,
fluid
couplings,
thread
bores,
and
mating
surfaces
are
clean
.
MASTER
CYLINDER