equipment BMW 328i 1997 E36 Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: BMW, Model Year: 1997, Model line: 328i, Model: BMW 328i 1997 E36Pages: 759
Page 116 of 759

119-2
LUBRICATION
SYSTEM
NOTE-
Component
Location
If
the
light
does
not
go
out,
thewiring
to
theswitch
is"
Oil
pressure
switch
most
likely
grounded
somewhere
between
the
switch
all
engines
.......
...
.
..
......
ora
oil
filter
housing
terminal
and
the
warning
light
.
Sea
Electrical
Wiring
Diagrams
atrearof
manual
for
electrical
schematics
.
CAUTION-
Some
oil
may
drain
out
as
the
oil
pressure
switch
is
removed
.
Use
a
rag
to
soak
up
any
spills
.
2
.
Install
pressure
gauge
in
place
of
switch
.
3
.
With
gauge
instalied,
start
engine
and
allow
to
reach
operating
temperature
.
Check
oil
pressureboth
cold
and
hot
.
NOTE-
For
the
most
accurate
test
results,
the
engine
oil
(and
filter)
shouldbe
newand
of
the
correct
grade
.
Oil
Pressure
"
¡dle
(mínimum)
..
.
.
..............
.
.
0
.5
bar
(7psi)
"
Regulated
pressure
(elevated
engine
speed)
4-cylinder
engines
..
......
4
.3
±
0
.2
bar
(63
t3
psi)
6-cylinder
engines
.
.
.............
.
4
.0
bar
(59
psi)
4
.
Remove
pressure
gauge
and
reinstall
pressure
switch
.
If
testing
shows
low
oil
pressure,
one
or
more
of
the
follow-
ing
conditions
may
be
indicated
:
OIL
PAN
"
Worn
or
faulty
oii
pump
.
"
Worn
or
faulty
engine
bearings
The
oil
pancan
be
removed
with
the
engine
instalied,
al-
Severe
engine
wear
.
though
specíal
enginesupport
equipment
will
be
needed
.
Al¡
of
these
conditionsindicate
the
need
for
major
repairs
.
Oil
pressure
warning
system,
testing
When
the
ignition
is
tumed
ora,
the
oil
pressure
warning
light
comes
ora
.
When
the
engine
ís
started
and
the
oil
pressure
ris-
es
slightly,
the
oil
pressure
switch
opens
and
thewarning
light
goes
out
.
Make
sure
the
oil
leve¡
is
correct
before
making
tests
.
1
.
Turra
ignition
switch
ora
.
"
Warning
light
ora
instrument
panel
must
light
up
.
2
.
Remove
connector
from
oil
pressure
switch
.
"
Warning
light
ora
instrument
panel
must
go
out
.
OIL
PAN
3
.
If
warning
light
does
not
light
when
ignition
is
ora,
re-
move
connector
from
oil
pressure
switch
anduse
a
jumper
wire
to
ground
connector
terminal
to
a
clean
metal
surface
.
NOTE
-
If
the
warning
light
comes
ora,
check
the
switch
as
de-
scríbed
in
the
nextstep
.
If
the
warning
light
does
not
come
ora,
thewiring
to
the
instrument
cluster
or
to
the
light
itself
isfaulty
.
4
.
To
test
switch,
connect
ara
ohmmeter
between
terminal
in
switch
body
and
ground
.
With
engine
off,
these
should
be
continuity
.
With
engine
running,
oil
pressure
should
opera
switch
and
there
should
beno
continuity
Replace
a
faulty
switch
.
WARNING
-
Keep
in
mind
that
low
oil
pressure
may
be
prevent-
ing
the
switch
from
tuming
the
light
out
.
If
the
light
remains
ora
while
the
engine
is
running,
check
the
oil
pressure
asdescribed
earlier
.
Do
not
drive
the
car
until
the
problem
is
corrected
.
Theengine
may
be
severely
damaged
.
Oil
pan,
removing
and
installing
(4-cylinder
engines)
1
.
Raise
car
arad
place
securely
ora
jackstands
.
2
.
Remove
splash
shíeld(s)
from
under
engine,
where
ap-
plicable
.
3
.
Drain
engine
oil
as
described
in
020
Maintenance
Pro-
gram
.
4
.
Disconnect
vacuum
hose
adapter
from
vacuum
brake
booster
at
rear
of
engine
compartment
.
5
.
Remove
oil
dipstick
guide
tube
mounting
nut
and
pull
guide
tube
from
oil
pan
.
See
Fig
.
2
.
Page 117 of 759

NOTE
-
The
guide
tube
is
sealed
in
the
pan
with
an
O-ring
.
Check
that
theO-ring
comes
out
with
the
tube
.
Use
a
new
O-ring
when
installing
the
tube
.
Fig
.
2
.
Oil
dipstick
guide
tube
mounting
nut
(arrow)
on
M44
engine
.
Use
new
O-ring
at
base
of
tube
during
installatidn
.
6
.
Install
engine
lifting
equipment
at
front
engine
lifting
point
and
raise
engine
approximately
5
mm
(
1
/4
inch)
until
engineweight
is
supported
.
7
.
Workingbeneath
car,
separate
steering
column
shaft
from
steeringrack
at
universal
joint
.
"
Point
wheels
straight
ahead
before
disconnecting
shaft
from
rack
.
Mark
steering
column
shaft
joint
to
steering
rackspíndle
.
See
320
Steering
and
Wheel
Align-
ment
.
CAUTION
-
In
order
to
avoíd
the
need
for
front-end
realign-
ment,
do
notunbolt
power
steering
rack
from
sus-
pension
crossmember
.
8
.
Supportsuspension
crossmember
(subframe)
from
be-
low
usingappropriate
jacking
equipment
.
9
.
At
left
and
right
sides,
unbolt
control
arm
bushing
carri-
ers
from
body
.
Disconnect
stabilizer
bar
links
fromcon-
trol
arms
.
See
Fig
.
3
.
LUBRICATION
SYSTEM
119-
3
0011960
Fig
.
3
.
Stabilizer
bar
link
nut
(A)
and
control
arm
bushing
carrier
bolts
(B)
.
Right
side
shows
.
10
.
Remove
bolts
from
left
and
right
sides
of
suspension
crossmember
.
RemoveM10
nuts
from
bottom
of
left
and
right
engine
mounts
.
Lower
crossmember
as
far
as
possible
.
See
Fig
.
4
.
uu1ibb4
Fig
.
4
.
Suspension
crossmember
bolts
(A)
and
lower
engine
mount-
ing
nut
(B)
.
Right
side
shows
.
11
.
Remove
clamping
brackets
holding
fuel
lines
to
oil
pan
.
12
.
On
cars
with
automatic
transmission,
remove
ATF
cool-
er
line
brackets
from
oil
pan
.
13
.
Remove
engine
drive
belt
from
power
steering
pump
.
See020
Maintenance
Program
.
14
.
Unbolt
power
steering
pumpbracket
andremove
bracket
with
pump
.
Hang
pump
from
chassis
using
wire
.
OIL
PAN
Page 119 of 759

8
.
Remove
air
plenum
from
rear
of
engine
compartment
.
See
640
Heating
and
Air
Conditioning
.
9
.
Release
drive
belt
tension
and
remove
alternator
drive
belt
.
Remove
A/C
compressor
drive
belt
.
See
Fig
.
6
.
B11143
Fig
.
6
.
To
remove
poly-ribbed
drive
belt,
pry
cover
from
front
of
ten-
sioner
.
Then
using
8
mm
hex
key,
turntensioner
clockwise
(arrow)
torelease
tension
and
slip
belt
off
pulleys
.
10
.
Unbolt
power
steering
reservoir
and
pull
reservoir
off
engine
mount
bracket
.
11
.
Without
disconnecting
fluid
lines,
remove
power
steer-
ing
bracket
(with
pump)
from
oil
panand
engine
block
.
See
Fig
.
7
.
Disconnect
fluid
lines
from
bracket
on
en-
gine
mount
.
Hang
pump
from
chassis
using
wire
.
12
.
Without
disconnecting
refrigerant
lines,
remove
A/C
compressor
from
engine
block
.
Hang
compressor
from
chassis
using
wire
.
See
640
Heating
and
Air
Condi-
tioning
.
13
.
Remove
oil
dipstick
guide
tube
mounting
bolt
and
re-
move
tube
.
See
Fig
.
8
.
NOTE-
The
guide
tube
is
sealed
in
the
oil
pan
with
an
O-ring
.
Check
that
the
O-ring
comes
out
with
the
tube
.
Use
anew
O-ring
when
installing
the
tube
.
14
.
On
cars
with
automatic
transmission,
remove
brackets
holding
ATF
cooler
linesto
oil
pan
and
cylinder
block
.
LUBRICATION
SYSTEM
119-
5
Fig
.
7
.
Power
steering
pump
mounting
bolts
(arrows)
.
Fig
.
8
.
Oil
dipstick
guide
tube
being
removed
.
Usea
new
O-ring
(arrow)
during
installation
.
15
.
Insta¡¡
engine
lifting
equipment
at
front
engine
lifting
point
and
raise
engine
just
until
its
weight
is
supported
.
16
.
Remove
nuts
at
bottom
of
left
and
right
engine
mounts
.
Remove
ground
wire
from
right
engine
mount
.
1-oosen
nuts
at
top
of
left
and
right
engine
mounts
(do
not
re-
move)
.
OIL
PAN
Page 121 of 759

5
.
Remove
air
filter
housingcomplete
with
mass
air
flow
sensor
.
See113
Cylinder
HeadRemoval
and
Instal-
lation
.
6
.
Remove
oil
dipstick
guide
tube
mounting
bolt
.
Discon-
nect
oil
separator
hose
frombase
of
guide
tube
and
re-
move
tubefrom
oil
pan
(where
applicable)
.
See
Fig
.
10
.
NOTE-
The
guide
tube
is
sealed
in
the
blockusing
an
O-ring
.
Check
that
the
O-ring
comes
out
with
the
tube
.
Use
a
new
O-ring
when
installing
the
tube
.
Fig
.
10
.
Oil
dipstick
guide
tube
being
removed
.
Use
new
O-ring
(ar-
row)
during
installation
.
7
.
M50/S50US
engine
:
Using
a
clean
syringe,
remove
power
steering
fluid
from
fluid
reservoir
.
Disconnect
power
steering
fluid
lines
from
steering
rack
.
See
320
Steering
and
Wheel
Alignment
.
8
.
M52/S52US
engine
:
Unbolt
power
steering
reservoir
from
engíne,
then
tie
to
chassis
with
wire
.
9
.
Insta¡¡
engine
lifting
equipment
atfront
engine
lifting
point
and
raise
engine
approximately
5
mm
('/a
inch)
until
engineweight
is
supported
.
See
Fig
.
11
.
10
.
Workingbeneath
car,
separate
steering
column
shaft
from
steeringrack
at
universal
joint
.
"
Mark
steering
column
shaft
jointto
steering
rack
spin-
dle
.
Point
wheels
straight
ahead
before
disconnecting
shaft
from
rack
.
See
320
Steering
and
Wheel
Align-
ment
.
LUBRICATION
SYSTEM
119
Fig
.
11
.
Engine
lifting
equipment
shown
installed
acrossengíne
.
CA
UTION-
In
order
to
avoid
the
need
for
front-end
realign-
ment,
donot
unbolt
power
steering
rack
from
sus-
pension
crossmember
.
11
.
Support
suspension
crossmember
from
below
using
appropriate
jacking
equipment
.
12
.
Loosen
nuts
at
top
of
left
and
right
side
engine
mounts
.
Remove
nuts
from
bottom
of
left
and
right
side
engine
mounts
.
13
.
At
left
and
right
sides,
unbolt
control
arm
bushíng
carri-
ers
from
body
.
Disconnect
stabilizer
bar
links
fromcon-
trol
arms
.
Refer
to
Fig
.
3
.
14
.
Remove
bolts
from
left
and
right
sides
of
suspension
crossmember
and
lower
front
axle
as
far
as
possible
.
15
.
Remove
fuelline
clamping
brackets
from
oil
pan
.
On
cars
with
automatic
transmission,
remove
ATF
cooler
line
brackets
from
oil
pan
.
16
.
Remove
oil
pan
screws
.
Lower
and
remove
oil
pan
for-
ward
to
remove
.
CA
UTION-
If
the
oil
pan
does
not
separate
easily
from
the
en-
gine
cylinder
block,
a
few
taps
with
a
rubber
mallet
shouldbreak
it
free
.
Do
notpry
the
oil
pan
loose
.
OIL
PAN
Page 126 of 759

120-2
IGNITION
SYSTEM
Fig
.1
.
Ignition
characteristic
map
.
Disabling
Ignition
System
WARNING
-
The
ignition
system
is
a
high-energy
system
operat-
ing
in
a
dangerous
voltage
range
that
couldprove
to
be
fatal
if
exposed
terminals
or
live
parts
are
con-
tacted
.
Use
extreme
caution
when
working
on
a
car
with
the
ignition
on
or
the
engine
running
.
The
ignition
system
operates
in
a
lethal
voltage
range
and
should
therefore
be
disabied
any
time
senrice
or
repair
work
is
being
doneon
the
engine
that
requires
the
ignition
to
be
switched
on
.
The
engine
management
system
can
be
disabled
byremov-
ingthe
main
relay
.
The
relay
is
located
in
the
power
distribution
box
in
the
left
rear
of
the
engine
compartment
.
See
Fig
.
2
.
0013134
Fig
.
2
.
Maínsystem
relay
(arrow)
in
power
distribution
box
(left
rear
of
engine
compartment)
.
GENERAL
WARNING
-
"
Do
not
touch
or
disconnect
any
of
the
high
ten-
sion
cables
at
the
cotls
orspark
plugs
while
the
engine
ts
running
orbeingcranked
by
the
starter
.
Fatalvoltages
are
present
.
"
Before
operating
the
starter
without
starting
the
engine
(for
example
when
making
a
compression
test)
always
disable
the
ignition
.
CAUTION-
"
Prior
to
disconnecting
the
battery,
read
the
bat-tery
disconnection
cautions
gtven
at
the
front
of
thts
manual
on
page
viti
.
"
Do
not
attempt
to
disable
the
ignition
by
either
re-
moving
the
cotl
from
the
spark
plugs
(6-cylinder
engines)
or
disconnecting
the
coll
wires
from
the
plugs
(4-cylinder
engines)
.
"
Connect
or
disconnect
ignition
system
wires,
multiple
connectors,
and
ignition
test
equipment
leads
only
while
the
ignitionis
off
.
Switch
multtm-
eter
functions
or
measurement
ranges
onty
with
the
test
probes
disconnected
.
"
Do
not
disconnect
the
battery
while
the
engine
ts
running
.
"
Many
of
the
tests
of
ignition
system
components
require
the
use
of
high-impedance
test
equip-
ment
to
prevent
damage
to
the
electrical
compo-
nents
.
A
high
impedance
digital
multimeter
should
be
used
for
all
voltage
and
resistance
tests
.
AnLED
test
light
shouldbe
used
in
place
of
an
incandescent-type
test
lamp
.
"In
general,
make
test
connections
only
as
speci-fied
by
BMW,
as
described
inthis
manual,
or
as
described
by
the
instrumenta
manufacturer
.
Page 127 of 759

IGNITION
SYSTEM
DIAGNOSTICS
IGNITION
SYSTEM
SERVICE
Poor
driveability
may
have
a
variety
of
causes
.
The
fault
On
4-cylinder
engines,
an
ignition
coil
pack
is
mounted
to
may
lie
with
the
ignition
system,
the
fuel
system,
parts
of
the
the
passenger
side
strut
tower
in
the
engine
compartment
.
emission
control
system,
or
a
combination
of
the
three
.
Be-
The
coil
pack
integrates
4
individual
coils
.
cause
of
these
interrelated
functions
and
their
effects
oneach
other,
it
is
often
difficult
to
know
where
to
begin
looking
for
On
6-cylinder
engines,
an
ignition
coil
is
located
directly
problems
.
above
each
spark
plug
.
For
this
reason,
effective
troubleshooting
should
alwaysbe-
gin
with
an
interrogation
of
the
On-Board
Diagnostic
(OBD)
system
.
The
OBD
system
detects
certain
emissions-related
engine
management
malfunctions
.
When
faults
are
detected,
the
OBD
system
stores
a
Diagnostic
Trouble
Code
(DTC)
in
the
system
ECM
.
In
addition,
the
Check
Enginewarning
light
will
come
on
if
an
emissions-related
fault
is
detected
.
Two
generations
of
OBD
areusedon
the
cars
coveredby
this
manual
.
See
100
Engine-General
for
OBD
information
.
On-Board
Diagnostics
"
1992-1995
models
............
...
.
..
...
OBD
I
"
1996
and
later
models
.........
.......
..
OBD
II
NOTE-
"
On
carswith
OBD
ti,
specialized
OBD
11
scan
tool
equipment
mustbeused
to
access
DTCs,
either
using
the
BMW
special
tool
or
a
`generic"
OBD
11
scan
tool
.
"
The
OBD
11
fault
memory
(including
an
illuminated
Check
Engine
light)
can
only
be
reset
using
the
spe-
cial
scan
tool
.
Removing
the
connector
from
the
ECM
or
dísconnecting
the
battery
will
not
erase
the
fault
memory
.
Basic
Troubleshooting
Principies
An
engine
that
starts
and
runs
indicates
the
ignition
system
is
fundamentally
working-delivering
voltage
toat
least
some
of
the
sparkplugs
.
A
hard-starting
or
poor-running
engine,
however,
may
indicate
ignition
coil
problems,
cracked
or
dete-
riorated
spark
plug
wires
(4-cylinder
engines
only),
and
worn
or
fouled
spark
plugs
.
WARNING
-
Inefficient
combustion
(richair/fuel
mixture)
can
cause
the
catalytic
converter
to
overheat
and
plug
.
An
overheated
catalytic
converter
can
also
bea
tire
hazard
.
Checking
for
Spark
IGNITION
SYSTEM
120-
3
WARNING
-
If
a
spark
test
is
done
incorrectly,
damage
to
theen-
gine
control
module
(ECM)
or
the
ignitioncoil(s)
may
result
.
Checking
for
spark
is
difficult
onengines
with
distributorless
ignition
systems
.
Try
Rmovng
the
plugs
and
inspecting
for
differences
be-
tween
them
.
A
poor-firing
plug
may
be
wet
with
fuel
and/or
black
and
sooty,
butnot
always
.
If
a
coil
is
not
operating,
the
engine
management
system
will
electrically
disable
the
fuel
injectorto
that
cylinder
.
The
key
is
to
look
for
differences
be-
tween
cylinders
.
Ignition
coil,
testing
and
replacing
(4-cylinder
engine)
1.
Disconnect
mainharness
connector
from
coils
:
"
On
M42
engine,
remove
plastic
covering
from
coils
and
disconnect
individual
harness
connectors
.
"
On
M44
engine,
disconnect
main
harness
connectorat
end
of
coil
pack
.
See
Fig
.
3
.
Fig
.
3
.
Ignition
coil
pack
for
M44
engine
(arrow)
.
Coil
harness
con-
nector
shown
at1
.
IGNITION
SYSTEM
SERVICE
Page 137 of 759

CHARGING
SYSTEM
TROUBLESHOOTING
.............
.
.
.
.
.121-2
Charging
System
Quick-Check
...
.
..
.
...
.
121-2
Static
current
draw,
checking
........
.
...
.
121-2
BATTERY
SERVICE
....................
121-3
Battery
Testing
.
.
.
.
.
.........
.
........
.
121-3
Hydrometer
Testing
.
...
.
.
.
...
.
.........
121-3
Battery
Open-Circuit
Voltage
Test
....
.
....
121-4
Battery
Load
Voltage
Test
.
.
.
.
.
.
.........
121-4
Battery
Charging
.
.
.
.
...
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.........
121-4
ALTERNATOR
SERVICE
.
.
.
.
.
.
.....
.
...
121-4
Chargingsystem,checking
.
.
.
.
.
.........
121-4
Alternator,
removingand
installing
(4-cylinder
engine)
....
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.........
121-5
Alternator,
removingand
installing
(6-cylinder
engine)
..
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.........
121-6
GENERAL
The
charging
system
consists
of
a
belt-driven
alternator
with
integral
voltage
regulator
and
a
battery
mounted
in
the
luggage
compartment
.
Various
versions
of
alternators,
voltage
regulators,
starters,
and
batteries
are
used
in
the
E36
cars
.
It
is
important
to
re-
place
components
according
tothe
original
equipment
speci-
fication
.
Check
with
an
authorized
BMW
dealer
for
specific
application
and
parts
information
.
WARNING
-
"
Weargoggles,
rubbergloves,
and
a
rubberapron
when
working
around
batteries
and
battery
acid
(electrolyte)
.
"
Battery
acid
contains
sulfuric
acid
and
can
cause
skin
irritation
and
burning
.
ff
acid
is
spilled
onyour
skin
or
clothing,
flush
the
area
at
once
with
large
quantities
of
water
.
lf
electrolyte
gets
into
your
eyes,flush
them
with
largequantities
of
clean
wa-
terfor
several
minutes
and
call
a
physician
.
"
Batteries
that
are
being
charged
or
are
fully
charged
give
off
explosive
hydrogen
gas
.
Keep
sparks
and
open
flames
away
.
Do
not
smoke
.
BATTERY,
STARTER,
ALTERNATOR
121-1
121
Battery,
Starter,
Alternator
GENERAL
..
.
...
.
........
.
...
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
121-1
Voltage
regulator,
removing
and
ínstalling
.
.
.
121-6
Alternator
brushes,
inspecting
and
replacing
.121-7
STARTER
SERVICE
....
.
.
.
.
.
..........
.121-7
Starter
Troubleshootíng
121-7
15
..
.
.
.
.
.
........
.
.
.
Starter,
removing
and
installing
(4-cylinder
engine)
....
.
.
.
............
.
121-8
Starter,
removing
and
installing
(6-cylinder
engine
with
manual
transmission)
..
.
...........
.
...
121-8
Starter,
removing
and
installing
(6-cylinder
engine
with
automatic
transmission)
................
121-9
Solenoid
switch,
removingand
installing
....
121-10
TABLES
a
.
Battery,
Starter
and
Charging
System
Troubleshooting
............
.
.
.
.
:...
........
121-2
b
.
Specific
Gravity
of
Battery
Electrolyte
at
80°F
(27°C)
...............
.
.
..
..........
121-3
c
.
Open-Circuit
Voltage
and
Battery
Charge
........
121-4
d
.
Battery
Load
Test-Minimum
Voltage
.
..........
121-4
CAUTION
-
"
Prior
to
disconnectiog
the
battery,
read
the
bat-tery
disconnection
cautions
given
at
the
front
of
this
manual
on
page
viii
.
"
Disconnecting
the
battery
cables
may
erase
fault
codes
stored
in
control
unit
memory
.
"
Always
disconnect
the
negative
()
battery
cable
first
and
reconnect
it
last
.
Cover
the
battery
post
with
an
insulating
material
whenever
the
cable
is
removed
.
"
After
reconnecting
the
battery,
the
power
window
motors
must
be
reinitialized
.
See
511
Door
Win-
dows
.
"
Never
reverse
the
battery
cables
.
Even
a
momen-
tary
wrong
connection
can
damage
the
alternatoror
other
electrical
components
.
"
Battery
cables
may
be
the
same
color
.
Label
ca-blebefore
removing
.
GENERAL
Page 138 of 759
121-2
BATTERY,
STARTER,
ALTERNATOR
CHARGING
SYSTEM
TROUBLESHOOTING
Static
currentdraw,
checking
Charging
system
diagnostics
requires
special
test
equip-
ment
.
If
the
test
equipment
is
not
available,
charging
system
fault
diagnosis
can
be
performedby
an
authorized
BMW
deal-
eror
other
qualified
repair
shop
.
A
general
troubleshooting
guide
is
given
in
Table
a
.
Charging
System
Quick-Check
As
a
quick-check,
use
a
digital
multimeter
lo
measure
volt-
2
.
Disconnect
battery
negative
(-)
cable
.
age
across
the
battery
terminals
with
the
key
off
and
then
again
with
the
engine
running
.
The
battery
voltage
should
be
CAUTION-
about12
.6
volts
with
key
off
and
approximately
14
.0
volts
with
Prior
to
disconnecting
the
battery,
read
the
battery
the
engine
running
.
If
the
voltage
does
not
increase
when
the
disconnection
cautions
given
at
the
front
of
this
engine
is
running,there
is
a
fault
in
the
charging
system
.
manual
onpaga
viii
.
NOTE
-
The
regulated
voltage
(engine
running)
should
be
be-
tween
13
.5
and
14
.5,
depending
on
temperatura
and
operating
conditions
.
If
the
voltage
is
higher
than
14
.8,
the
voltage
regulator
is
most
Mely
faulty
.
Check
for
clean
and
tight
battery
cables
.
Check
the
ground
cable
running
from
the
negative
(-)
battery
terminal
lo
the
chassis
and
the
ground
cable
running
from
the
engine
lo
the
chassis
.
Check
the
alternator
drive
belt
condition
and
tension
.
If
the
battery
discharges
over
time,
there
may
be
a
constant
drain
or
current
draw
on
the
battery
.
A
small
static
drain
on
the
battery
is
normal,
but
a
largedrain
will
cause
the
battery
lo
quickly
discharge
.
Make
a
static
current
draw
test
asthe
first
step
when
experiencing
battery
discharge
.
1
.
Make
sure
ignition
and
al¡
electrical
accessories
are
switched
off
.
3
.
Connect
a
digital
ammeter
between
negative
battery
post
and
negative
battery
cable
lo
measure
current
.
See
Fig
.
1
.
Wait
at
least
one
minuta
lo
get
an
accurate
reading
.
A
range
of
about
0
lo
100
milliamps
is
normal,
dependingon
the
number
of
accessories
that
need
constant
power
.
A
current
of
400
milliamps
(0.4
amp)
or
more
may
indicate
a
problem
.
Table
a
.
Battery,
Starter
and
Charging
System
Troubleshooting
Symptom
1
Probable
Cause
1
Correctiva
Action
1
.
Engine
cranks
slowlyor
not
a
.
Battery
cables
loose,
dirty
orcor-
a
.
Clean
or
replace
cables
.
See020
Maintenance
Program
.
a
tall,
solenoíd
clicks
when
roded
.
starter
is
operated
.
b
.
Battery
discharged
.
b
.
Charge
battery,
test
and
replace
if
necessary
.
c
.
Body
ground
straploose,
dirty
or
c
.
Inspect
ground
strap,
clean,
tighten
or
replace
if
necessary
.
corroded
.
d
.
Poor
connection
at
starter
motor
d
.
Check
connections,
test
for
voltage
at
starter
.
Test
for
voltage
at
terminal
30
.
neutral
safety
or
clutch
interlock
switch
.
e
.
Starter
motor
or
solenoid
faulty
.
e
.
Test
starter
.
2
.
Battery
will
not
stay
a
.
Short
circuit
draining
the
battery
.
a
.
Test
for
excessive
current
drainwith
everything
electrical
in
the
charged
more
than
a
few
vehicle
off
.
days
.
b
.
Short
driving
trips
and
high
elec-
b
.
Evaluate
driving
style
.
Where
possible,
reduce
electrical
con
trical
drain
on
charging
system
sumption
when
making
short
trips
.
does
not
allow
battery
to
re-
charge
.
c
.
Drive
belt(s)
worn
or
damaged
.
c
.
Inspect
or
replace
multi-ribbed
belt(s)
.
See
020
Maintenance
Program
.
d
.
Battery
faulty
.
d
.
Test
battery
and
replace
íf
necessary
.
e
.
Battery
cables
loose,
dirty
orcor-
e
.
Clean
or
replace
cables
.
See
020
Maintenance
Program
.
rodad
.
f
.
Alternatoror
voltage
regulator
f
.
Test
alternator
and
voltage
regulator
.
faulty
.
3
.
Battery
losing
water
.
1
a
.
Battery
overcharging
.
1
a
.
Test
voltage
regulator
for
proper
operation
.
4
.
Lights
dim,
light
intensity
a
.
Drive
belt(s)
worn
or
damaged
.
a
.
Inspect
or
replace
multi-ribbed
belt(s)
.
See
020
Maintenance
varies
with
engine
speed
.
Program
.
b
.
Alternatoror
voltage
regulator
b
.
Test
alternator
and
voltage
regulator
.
faulty
.
c
.
Body
ground
straps
loose,
dirty
or
c
.
Inspect
ground
straps,
clean,
tighten
or
replace
as
necessary
.
corroded
.
CHARGING
SYSTEM
TROUBLESHOOTING
Page 148 of 759
130-2
FUEL
INJECTION
GENERAL
This
repair
group
covers
fuel
injection
system
component
testing
and
repair
.
Special
equipment
is
necessary
for
some
of
the
procedures
given
in
this
repair
group
.
If
you
do
not
have
the
equipment
required
to
do
the
job,
it
is
recommended
that
these
repairs
be
left
to
an
authorized
BMW
dealer
.
The
BMW
dealer
is
equipped
with
sophisticated
diagnostic
test
equip-
ment
that
is
capable
of
quicklypinpointing
hard-to-find
fuel
in-
jection
problems
.
NOTE-
"
Wiring
diagrams
for
the
engine
management
system,
can
be
found
at
the
rear
of
the
manual
under
Electri-
cal
Wiring
Diagrams
.
"
For
ignition
system
repairinformation,
see120
Igni-
tion
System
.
"
For
fuel
supply
system
testing
and
repair,
see160
The
engine
control
module
(ECM)
uses
electrical
signals
Fuel
Tank
and
Fuel
Pump
.
from
the
mass
air
flow
sensor,
the
air
and
coolant
temperature
sensors,
the
crankshaft
position/rpm
sensor,
the
knock
sen
Principies
Of
Operation
sors
and
the
oxygen
sensorsas
the
primary
inputs
to
electron-
ically
control
fuel
delivery
and
ignition
timing
.
There
are
five
versions
of
engine
management
systems
usedon
the
E36
cars
.
Each
has
the
same
basic
components
and
operating
principles
.
The
most
notable
difference
is
that
1996
and
later
cars
use
a
sophisticated
OBD
II-compliant
sys-
tem
.
See
Table
a
.
Table
a
.
Engine
Management
System
Variants
Engine
code/year
1
System
4-cy1inder
M42
(1
.8
I)
1992-1995
Bosch
DME
Ml
.7
M44
(1
.91)
1996-1998
~
Bosch
DME
M5
.2
(OBD
II)
6-cylinder
M50
1992
(2.5
I)
Bosch
DME
M3
.1
1993-1995
(2.5
I)
Bosch
DME
M3
.3.1
(VANOS)
M52
1996-1998
(3281-
2
.8
I)
Siemens
MS
41
.1
(OBD
II)
1998
(3231
-
2
.5
I)
Siemens
MS
41
.1
(OBD
II)
M-Power
S50US
(M3
-
3
.01)
1995
Bosch
DME
M3
.3
.1
S52US
(M3
-
3
.21)
1997-1998
Siemens
MS
41
.1
(0131)
11)
NOTE-
-
Descriptions
and
procedures
in
the
first
partof
this
re-
pairgroup
refer
to
all
the
various
engine
management
systems
.
"
Particulars
of
each
fuel
injection
system
are
treated
in
separate
sections
in
the
second
part
of
this
repair
group
.
GENERAL
Fig
.1
.
OBD
II
diagnostic
connector
locatíon
.
The
fuel
injection
system
is
completely
electronic
in
opera-
tion
.
Air
flow
is
measured
electronically
via
a
mass
air
flow
sensor
and
additional
sensors
supply
information
about
en-
gine
operating
conditions
.
The
ECM
calculates
the
amount
of
fuel
needed
for
the
correct
air-fuel
ratio
and
actuates
the
fuel
injectors
accordingly
.
The
amount
offuel
metered
to
theen-
gine
is
determined
by
how
long
the
injectors
are
open
.
Airintake
.
Air
entering
the
engine
passes
through
a
pleat-
ed
paper
air
filter
in
the
air
cleaner
.
Intake
air
volume
or
mass
is
then
measured
bya
mass
air
flow
(MAF)
sensor
.
In
al¡
ex-
cept
the
vane
type
sensor
(DME
M1
.7),
a
reference
current
is
used
to
heat
a
thin
wireor
film
in
the
sensor
when
the
engine
is
running
.
The
current
used
to
heat
the
wire/film
is
electroni-
cally
converted
into
a
voltage
measurement
corresponding
to
the
mass
of
the
intake
air
.
Table
b
.
Mass
Air
Flow
Sensor
Variants
System
Al
r
flow
sensor
type
Bosch
DME
M1
.7
Vane
(volume
sensor)
Bosch
DME
M3
.1
Hot
wire
(mass
sensor)
Bosch
DME
M3
.3
.1
Hot
film
(mass
sensor)
Bosch
DME
M5
.2
Hot
film
(mass
sensor)
Siemens
MS
41
.1
Hot
film
(mass
sensor)
"
The
16-pin
OBD
11
diagnostic
connector
is
located
on
NOTE-
the
lower
left
dashpanel
.
See
Fig
.
1
.
On
cars
equipped
wíth
tractioncontrol,
an
additional
throttle
valve
is
controlled
by
an
electronic
throttle
actu-
ator
(motor)
.
This
valve
is
used
for
engine
speed
inter
vention
.
Repair
information
forthis
system
is
notcovered
here
due
to
the
special
electrical
testing
equip-
ment
required
to
service
it
.
Page 151 of 759
The
fuel
injection
systems
used
on
the
1996
and
later
cars
covered
bythis
manual
are
OBD
II
compliant
.
This
system
is
in-
corporated
into
both
the
Bosch
M5
.2
(M44
engine)
and
the
Si-
emens
MS
41
.1
(M52/S52US
engine)
engine
management
systems
.
OBD
II
systems
use
sophisticateddiagnostic
soft-
ware
capable
of
recognizing
and
electronically
storing
hun-
dreds
of
DTCs
in
the
system
ECM
.
DTCs
can
only
be
accessed
using
special
scan
tooltest
equipment
.
The
BMW
dealer
is
equipped
with
the
specialized
OBD
II
scan
toolto
quickly
and
efficiently
locate
engine
management
problems
.
Alternately,
a
"generic"
scan
tool
can
be
used
to
access
OBD
II
fault
informa-
tion
.
NOTE-
"
At
the
time
this
manual
went
to
press,
generic
scan
tools
were
notwidely
available
for
BMW
vehicles
.
The
generic
sean
tool
is
a
specialized
toolthat
plugs
into
a
standardized
OBD
11
connector
on
1996
and
later
pas-senger
vehícles
built
for
sale
in
the
US
.
"
The
OBD
11
fault
memory
(including
an
illuminated
Check
Engine
light)
can
only
be
reset
using
the
spe-
cial
scan
tool
.
Removing
the
connector
trom
the
ECM
or
disconnecting
the
battery
will
not
erase
the
fault
memory
.
"
The
16-pin
OBD
11
diagnostic
connector
is
located
on
the
lower
left
dash
panel
.
Refer
to
Fig
.
1
.
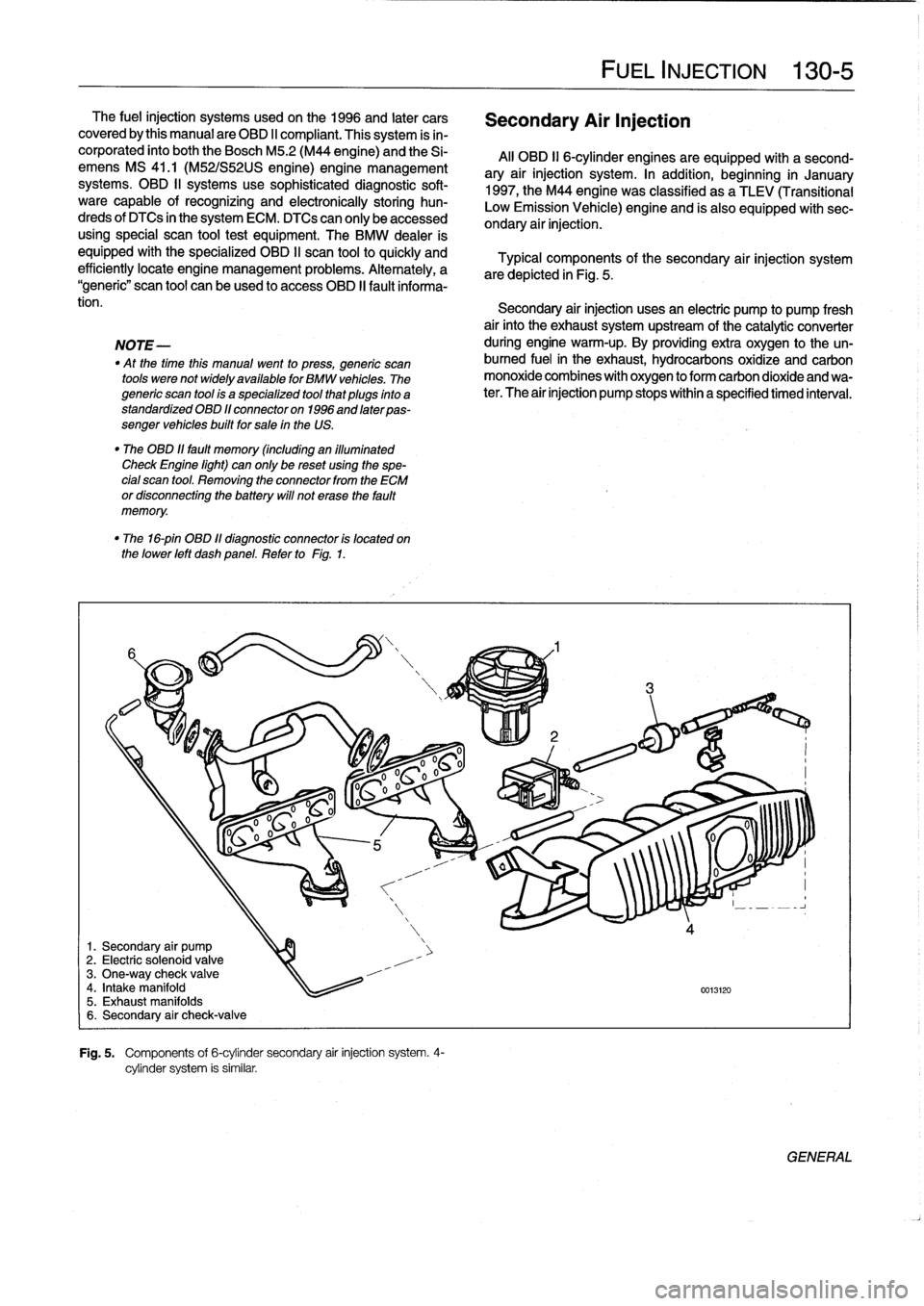
6
1
.
Secondary
air
pump
2
.
Electric
solenoid
valve
3
.
One-way
check
valve
4
.
Intake
manifold
5
.
Exhaust
manifolds
6
.
Secondary
air
check-valve
®
G~
i
o
o
0
0
G
0000
o
,-
00
~
1111111
in
,,
0
1--
a
Fig
.
5
.
Components
of
6-cylinder
secondary
air
injection
system
.
4-
cylinder
system
is
similar
.
Secondary
AirInjection
FUEL
INJECTION
130-
5
All
OBD
II
6-cylinder
engines
are
equípped
with
asecond-
ary
air
injection
system
.
In
addition,
beginning
in
January
1997,
the
M44
engine
was
classified
as
a
TLEV
(Transitional
Low
Emission
Vehicle)
engine
and
is
also
equipped
with
sec-
ondary
air
injection
.
Typical
components
of
the
secondary
air
injection
system
are
depicted
in
Fig
.
5
.
Secondary
air
injection
usesan
electric
pump
to
pump
fresh
air
finto
the
exhaust
systemupstream
of
the
catalytic
converter
during
engine
warm-up
.
By
providing
extra
oxygen
to
the
un-
burned
fuel
in
the
exhaust,
hydrocarbons
oxidize
and
carbon
monoxide
combines
with
oxygen
to
form
carbon
dioxide
andwa-
ter
.
The
air
injection
pump
stops
within
a
specified
timed
intenral
.
4
0013120
GENERAL