fuel tank BMW 328i 1998 E36 User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: BMW, Model Year: 1998, Model line: 328i, Model: BMW 328i 1998 E36Pages: 759
Page 52 of 759
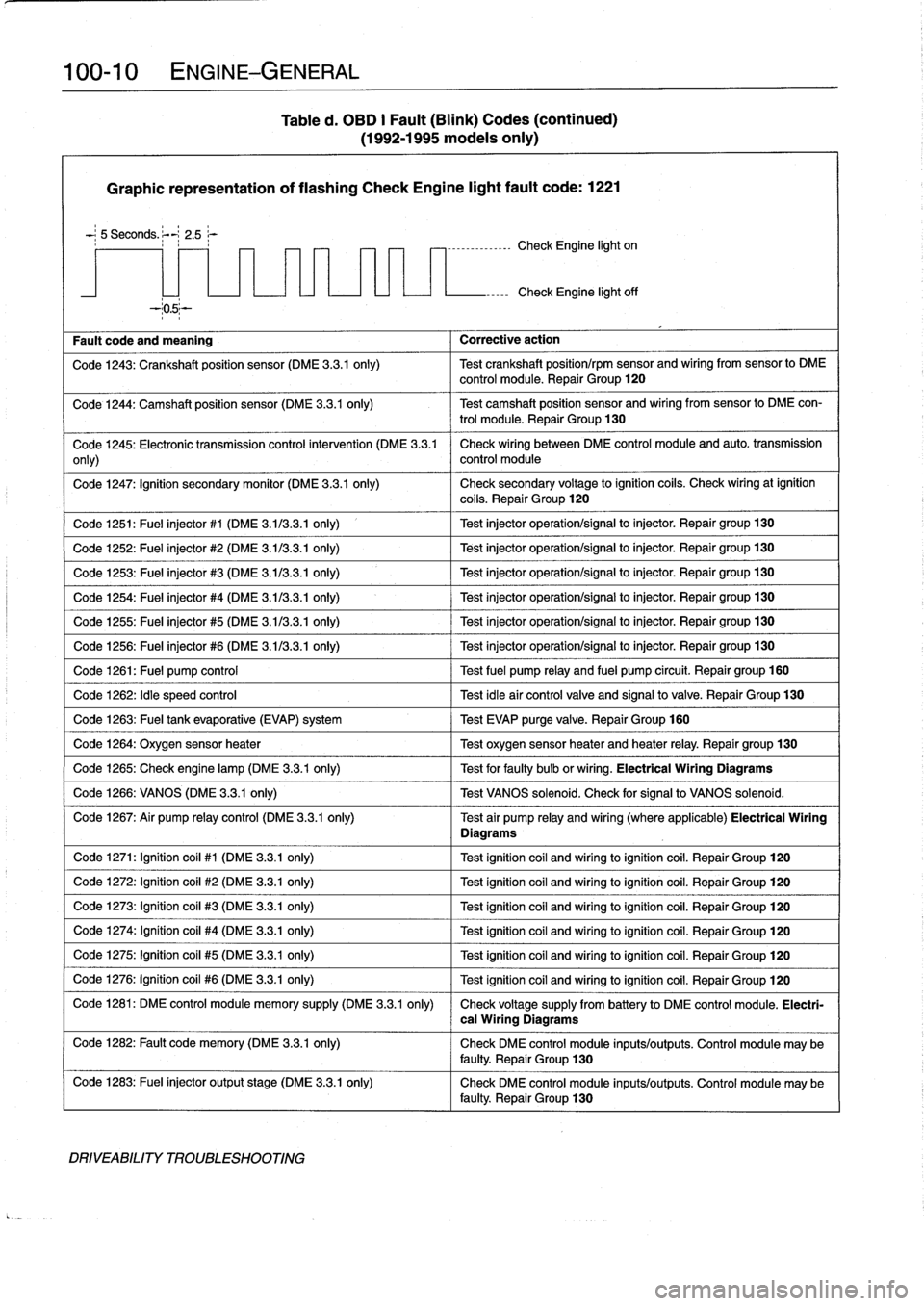
100-
1
0
ENGINE-GENERAL
Table
d
.
OBD
I
Fault
(Blink)
Codes
(continued)
(1992-1995
modeis
only)
Graphic
representation
of
flashing
Check
Engine
light
fault
code
:
1221
-
;
5
Seconds
.
;--~
2
.5
r
----------------
Check
Engine
light
on
Fault
code
and
meaning
Corrective
action
Check
Engine
light
off
Code
1243
:
Crankshaft
position
sensor
(DME
3
.3
.1
only)
Test
crankshaft
position/rpm
sensor
and
wiring
from
sensor
lo
DME
control
module
.
Repair
Group
120
Code
1244
:
Camshaft
position
sensor
(DME
3
.3
.1
only)
Test
camshaft
position
sensor
and
wiring
fromsensor
to
DME
con-
trol
module
.
Repair
Group
130
Code
1245
:
Electronic
transmission
control
intervention
(DME
3
.3
.1
Check
wiring
between
DME
control
module
and
auto
.
transmission
only)
control
module
Code
1247
:
Ignition
secondary
monitor
(DME
3
.3
.1
only)
Check
secondary
voltage
lo
ignition
coils
.
Check
wiringat
ignition
coils
.
Repair
Group
120
Code
1251
:
Fuel
injector
#1
(DME
3
.113
.3
.1
only)
1
Test
injector
operation/signal
lo
injector
.
Repair
group130
Code
1252
:
Fuel
injector
#2
(DME
3
.113
.3
.1
only)
Test
injector
operation/signal
lo
injector
.
Repair
group130
Code
1253
:
Fuel
injector
#3
(DME
3
.1/3
.3
.1
only)
Test
injector
operation/signal
to
injector
.
Repair
group130
Code
1254
:
Fuel
injector
#4
(DME
3
.1/3
.3
.1
only)
Test
injector
operation/signal
to
injector
.
Repair
group
130
Code
1255
:
Fuel
injector
#5
(DME
3
.1/3
.3
.1
only)
Test
injector
operation/signal
to
injector
.
Repair
group130
Code
1256
:
Fuel
injector
#6
(DME
3
.1/3
.3
.1
only)
Test
injector
operation/signal
lo
injector
.
Repair
group130
Code
1261
:
Fuel
pump
control
Test
fuel
pump
relay
and
fuel
pump
circuit
.
Repairgroup
160
Code
1262
:
Idle
speed
control
Test
idleair
controlvalve
and
signalto
valve
.
Repair
Group
130
Code
1263
:
Fuel
tank
evaporative
(EVAP)
system
Test
EVAP
purge
valve
.
Repair
Group
160
Code
1264
:
Oxygen
sensor
heater
1
Test
oxygen
sensorheater
and
heater
relay
.
Repair
group
130
Code
1265
:
Check
engine
lamp
(DME
3
.3.1
only)
1
Test
for
faulty
bulb
or
wiring
.
Electrical
Wiring
Diagrams
Code
1266
:
VANOS
(DME
3
.3
.1
only)
1
Test
VANOS
solenoid
.
Check
for
signal
to
VANOS
solenoid
.
Code
1267
:
Air
pump
relay
control
(DME
3
.3
.1
only)
Test
air
pump
relay
and
wiring
(where
applicable)
Electrical
Wiring
Diagrams
Code
1271
:
Ignition
coil
#1
(DME
3
.3.1
only)
Test
ignitioncoil
and
wiring
toignitioncoil
.
Repair
Group
120
Code
1272
:
Ignition
coil
#2
(DME
3
.3.1
only)
Test
ignitioncoil
and
wiring
loignitioncoil
.
Repair
Group
120
Code
1273
:
Ignition
coil
#3
(DME
3
.3.1
only)
Test
ignitioncoil
and
wiring
loignitioncoil
.
Repair
Group
120
Code
1274
:
Ignítion
coil
#4
(DME
3
.3.1
only)
Test
ignitioncoil
and
wiring
toignitioncoil
.
Repair
Group
120
Code
1275
:
Ignitioncoil
#5
(DME
3
.3.1
only)
Test
ignition
coil
and
wiring
loignitioncoil
.
Repair
Group
120
Code
1276
:
Ignition
coil
#6
(DME
3
.3.1
only)
Test
ignitioncoil
and
wiring
loignitioncoil
.
Repair
Group
120
Code
1281
:
DME
control
module
memory
supply
(DME
3
.3
.1
only)
Check
voltage
supply
from
battery
lo
DME
control
module
.
Electri-
Code
1282
:
Fault
code
memory
(DME
3
.3.1
only)
Check
DME
control
module
inputs/outputs
.
Control
module
may
be
faulty
.
Repair
Group
130
Code
1283
:
Fuel
injector
output
stage
(DME
3
.3
.1
only)
Check
DME
control
module
inputs/outputs
.
Control
module
may
be
faulty
.
Repair
Group
130
DRIVEABILITY
TROUBLESHOOTING
cal
Wiring
Diagrams
Page 53 of 759
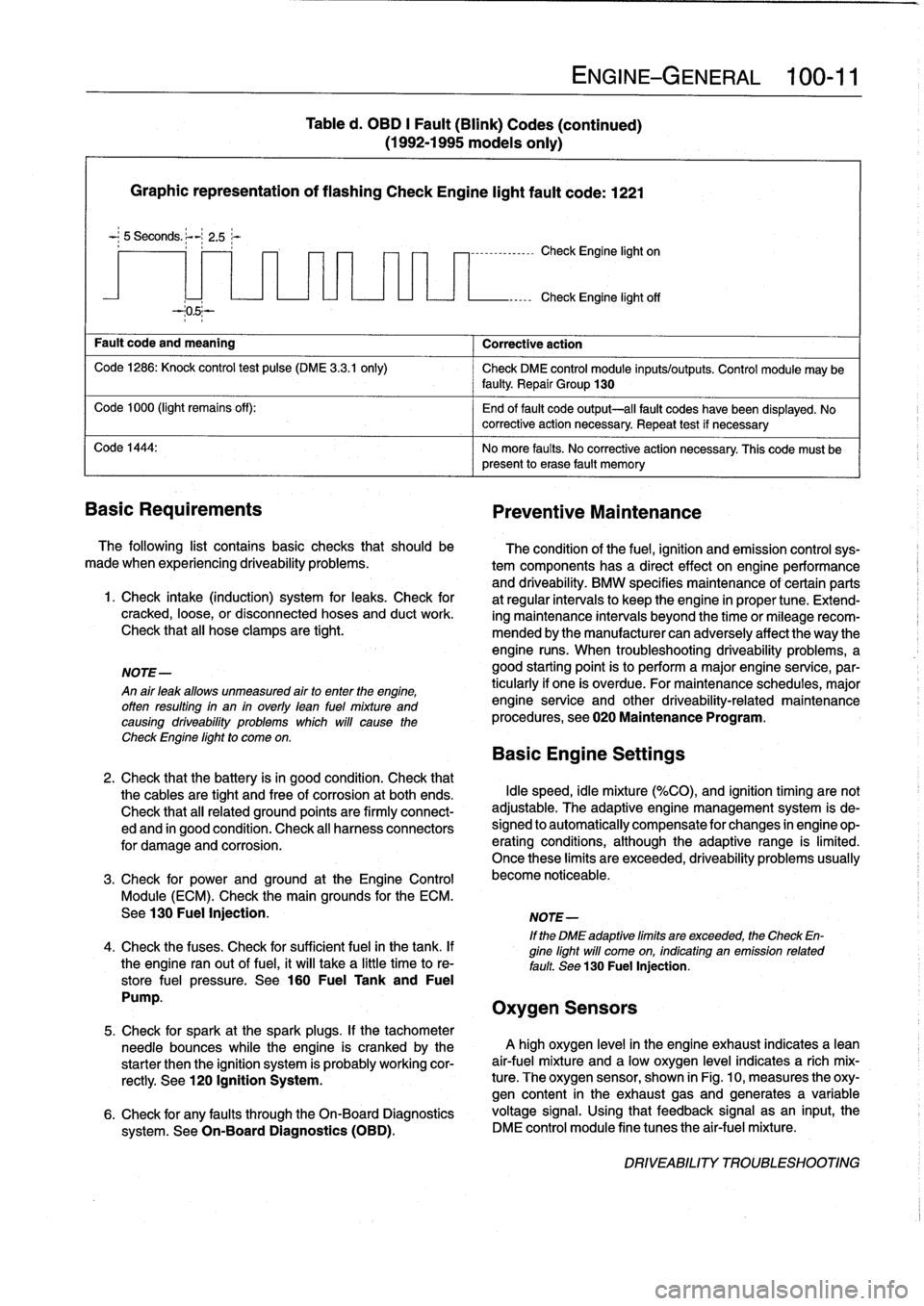
Graphic
representation
of
flashing
Check
Engine
light
fault
code
:
1221
-
;
5
Seconds
.
~-
2
.5;-
Fault
code
and
meaning
Corrective
action
Code
1286
:
Knock
control
test
pulse
(DME
3
.3
.1
only)
Check
DME
control
module
inputs/outputs
.
Control
module
may
be
faulty
Repair
Group
130
Code
1000
(light
remains
off)
:
End
of
fault
code
output-all
fault
codes
have
been
displayed
.
No
~
corrective
action
necessary
.
Repeat
test
if
necessary
Code
1444
:
No
more
faults
.
No
corrective
action
necessary
.
This
code
must
be
present
lo
erase
fault
memory
Basic
Requirements
Preventive
Maintenance
The
following
list
contains
basic
checks
that
should
be
made
when
experiencing
driveability
problems
.
1
.
Check
intake
(induction)
system
for
leaks
.
Check
for
cracked,
loose,
or
disconnected
hoses
and
duct
work
.
Check
that
all
hose
clamps
are
tight
.
NOTE-
An
air
leak
allows
unmeasured
airto
enter
the
engine,
offen
resulting
in
an
in
overly
lean
fuel
mixture
and
causing
driveability
problems
which
will
cause
the
Check
Engine
light
to
come
on
.
Table
d
.
OBD
I
Fault
(Blink)
Codes
(continued)
(1992-1995
models
only)
7
-
1
--------------
Check
Engine
light
on
ENGINE-GENERAL
100-
1
1
Check
Engine
light
off
The
condition
of
the
fuel,
ignition
and
emission
controlsys-
tem
components
has
a
directeffect
onengineperformance
and
driveability
.
BMW
specifies
maintenance
of
certain
parts
at
regular
intervals
lo
keep
the
engine
in
proper
tune
.
Extend-
ing
maintenance
intervals
beyond
the
time
or
mileagerecom-
mended
bythe
manufacturer
can
adversely
affect
the
way
the
engine
runs
.
When
troubleshooting
driveability
problems,
a
good
starting
point
is
to
perform
a
major
engine
service,par-
ticularly
if
one
is
overdue
.
For
maintenance
schedules,
major
engine
service
and
other
driveability-related
maintenance
procedures,
see020
Maintenance
Program
.
Basic
Engine
Settings
2
.
Check
that
the
battery
isin
good
condition
.
Check
that
the
cables
are
tight
and
free
of
corrosion
at
both
ends
.
Idle
speed,
idle
mixture
(%CO),
and
ignition
timing
are
not
Check
that
all
related
ground
points
are
firmly
connect-
adjustable
.
The
adaptive
engine
management
system
is
de-
ed
and
in
good
condition
.
Check
al¡
harness
connectors
signed
lo
automatically
compensate
for
changes
in
engine
op-
for
damage
and
corrosion
.
erating
conditions,
although
the
adaptive
range
is
limited
.
Once
these
limits
are
exceeded,
driveability
problems
usually
3
.
Check
for
prwer
and
ground
at
the
Engine
Control
become
noticeable
.
Module
(ECM)
.
Check
the
main
grounds
for
the
ECM
.
See130
Fuel
Injection
.
NOTE-
If
the
DME
adaptive
limits
are
exceeded,
the
Check
En-
4
.
Check
the
fuses
.
Check
for
sufficient
fuel
in
the
tank
.
If
gine
light
will
come
on,
indicating
an
emission
related
the
engine
ranout
of
fuel,
it
will
take
a
little
time
to
re-
fault
.
See
130
Fuel
Injection,
store
fuel
pressure
.
See
160
Fuel
Tank
and
Fuel
Pump
.
Oxygen
Sensors
5
.
Check
for
spark
at
the
spark
plugs
.
If
the
tachometer
needle
bounces
while
the
engine
is
crankedby
the
A
high
oxygen
level
in
the
engine
exhaust
indicates
a
lean
starter
then
the
ignition
system
is
probably
working
cor-
air-fuel
mixture
and
a
low
oxygen
level
indicates
a
rich
mix
rectly
.
See
120
Ignition
System
.
ture
.
The
oxygen
sensor,
shown
in
Fig
.
10,
measures
the
oxy-
gen
content
in
the
exhaust
gasand
generates
a
variable
6
.
Check
for
any
faults
through
the
On-Board
Diagnostics
voltage
signal
.
Using
that
feedback
signal
asan
input,
the
system
.
See
On-Board
Diagnostics
(OBD)
.
DME
control
module
fine
tunes
the
air-fuel
mixture
.
DRIVEABILITY
TROUBLESHOOTING
Page 56 of 759

100-
1
4
ENGINE-GENERAL
0013131
Fig
.
13
.
Main
chassis
ground
(arrow)
inleft
front
of
engine
compart-
ment
.
Fuel
Supply
For
the
engine
tostart
and
run
properly,
the
injection
sys-
tem
must
deliver
fuel
in
precise
proportion
to
the
amount
of
air
entering
the
engine
.
Todo
this,
the
injection
system
requires
an
unrestricted
supply
of
fuel
from
the
fuel
pump
.
If
the
fuel
pump
is
not
working,
the
engine
will
notrun
.
If
the
fuel
filter
or
a
fuel
line
is
restricted,
the
engine
may
run
poorly
.
If
the
restriction
is
severe
enough
the
engine
will
not
start
.
lf
fuel
delivery
problemsare
suspected,
perform
the
tests
de-
scribed
in
160
Fuel
Tank
and
Fuel
Pump
.
The
fuel
pressure
created
by
the
fuel
pump
is
controlled
by
a
pressure
regulator
thatreturns
excess
fuelto
the
tank
.
Any
change
in
fuel
pressure
will
cause
a
change
in
the
base
air-fuel
mixture
delivered
to
the
engine
.
If
the
fuel
pressure
is
too
low,
the
base
air-fuel
mixture
will
be
lean
.
lf
the
fuel
pressure
is
too
high,
the
base
mixture
will
be
rich
.
Fuel
pressure
tests
aredescribed
in
160
Fuel
Tank
and
Fuel
Pump
and130
Fuel
Injection
.
NOTE-
Fuel
pressure
tests
require
a
pressure
gauge
.
If
thistoolís
not
avaílable,
the
tests
can
be
performed
byan
authorized
BMW
dealer
or
other
qualified
shop
.
DRIVEABILITY
TROUBLESHOOTING
Properly
operating
fuel
injectors
play
amajor
role
in
fuel
de-
livery
.
The
DMEECM
switches
the
injectors
on
and
off
at
the
negative
(-)
or
ground
side
of
the
connectors
.
Posítíve
(+)
bat-
tery
voltage
is
always
present
at
the
connectors
when
theen-
gine
is
running
.
An
injector
that
fails
or
loses
power
will
not
open,
creating
a
lean
air-fuel
mixture
and
causing
the
engine
to
run
poorly
when
coldor
stumble
on
acceleration
.
An
injector
that
shorts
to
ground
will
remain
open
constantly
when
the
en-
gine
is
running,
creating
a
richair-fuel
mixture
that
can
dilute
engine
oil,
foul
the
spark
plugs,
cause
a
rough
idle,
and
damage
the
catalytic
converter
.
Table
e
lists
additional
symptoms
of
common
engine
drive-
ability
problems,
their
probable
causes,
and
the
suggested
corrective
actions
.
The
entries
in
boldtype
in
the
corrective
action
column
indicate
the
repair
groups
where
applicable
test
and
repair
procedures
can
befound
.
NOTE-
Most
of
the
symptoms
fisted
in
Table
e
will
also
cause
the
Check
Engine
light
to
come
on
.
If
the
light
is
on,
check
for
any
stored
faults
as
the
first
step
ín
trouble-
shooting
driveability
complaints
.
Page 60 of 759

110-2
ENGINE
REMOVAL
AND
INSTALLATION
8
.
Drain
engine
coolant
andremove
coolant
hoses
at-
10
.
Remove
radiator
cooling
fan
and
radiator
as
described
tached
to
cylinder
head
.
in
170
Radiator
and
Cooling
System
.
"
Drain
radiator
and
engine
block
.
See
170
Radiator
and
Cooling
System
.
NOTE-
"
Disconnect
hoses
from
thermostat
housing
at
front
of
Some
late
4-cylinder
modelsuse
an
electric
prímary
cylinder
head
.
cooling
fan
.
"
Disconnect
heater
hoses
at
rear
of
engine
.
See
Fig
.
2
.
CAUTION-
NOTE-
On
cars
with
viscous-type
cooling
fans,
the
radia-
"
The
block
drain
plug
is
located
on
the
exhaust
side
to-
tor
fan
has
left
hand
threads
.
wards
rear
of
engine
.
"
Remove
small
plastic
lock
clíp
to
pull
radiator
drain
11
.
Remove
upper
intake
manifold,
unfasten
cable
duct
plug
out
completely
.
from
lower
intake
manifold,
crankcase
vent
valve
hose
(M44
engine
only)
0012687
Fig
.
2
.
Coolant
hoses
at
heater
valve
and
heatercore
to
be
discon-
nected
(arrows)
.
9
.
Remove
air
shroud
from
top
of
radiator
.
See
Fig
.
3
.
ENGINE
REMOVAL
AND
INSTALLATION
12
.
Disconnect
fuel
supply
and
fuel
return
lines,
main
en-
gine
electrical
connectors,
and
lower
intake
manifold
as
described
in
113
Cylinder
HeadRemoval
and
Instal-
lation
.
See
Fig
.
4
.
0012504
Fig
.
4
.
Crankcase
ventvalve
(A)
on
top
of
lower
intake
manifoldof
M44
engine
.
Fueldelivery
and
retum
lines
shown
at
B
.
Engine
harness
and
sensor
connectors
shown
at
C
.
WARNING
-
"
Fuel
may
be
expelled
under
pressure
.
Do
not
smoke
orworknear
heaters
or
other
fire
haz-
ards
.
Keep
a
fire
extinguisher
handy
.
Before
dis-
connecting
fuel
hoses,
wrap
a
cloth
around
fuel
hoses
to
absorb
any
leaking
fuel
.
Plug
all
open
fuel
lines
.
"
Always
unscrew
the
fuel
tank
cap
to
release
pres-
sure
in
the
tank
before
working
on
the
tank
or
lines
.
CAUTION-
0013137
I
Stuff
clean
rags
into
the
open
intake
ports
topre-
Fig
.
3
.
Front
air
shroud
mounting
screws
(arrows)
.
vent
any
parts
from
falling
into
the
engine
intake
.
13
.
Disconnect
vacuum
hose
from
brake
booster
on
bulk-
head
.
Cover
bothhole
in
booster
and
plug
hose
end
.
Page 63 of 759

11
.
Draín
engine
coolant
and
Rmove
coolant
hoses
at-
tached
to
cylinder
head
.
"
Drain
engine
block
byremoving
block
drain
.
"
Disconnect
hoses
from
thermostat
housing
in
front
of
cylinder
head
.
"
Disconnect
heater
hoses
at
rear
of
engine
.
See
Fig
.
9
.
"
Drain
radiator
by
removingthreaded
plastic
plug
from
lower
left
comer
.
NOTE-
"
The
block
drain
plug
is
located
oh
the
exhaust
side
to-
wards
rear
ofengine
.
"
Remove
small
plastic
lock
clipto
pulíradiator
draín
plug
out
completely
.
NOTE-
CAUTION-
Radiatorfan
has
left
hand
threads
.
ENGINE
REMOVAL
AND
INSTALLATION
110-
5
Fig
.
9
.
Coolant
hoses
at
heater
valve
and
heater
core
to
be
discon-
nected
(arrows)
.
12
.
Remove
radiator
cooling
fan
and
radiator
as
described
in
170
Radiator
and
Cooling
System
.
13
.
Label
and
disconnectcoolant
hoses,
cables,
and
har-
ness
connectors
from
throttle
housing
.
See
Fig
.
10
.
14
.
Working
atrearof
intake
manifold,
label
and
then
re-
move
fuel
supply
and
fuel
retum
lines
.
Disconnect
fuel
lines
from
support
bracket
on
manifold
.
See
Fig
.
11
.
uu12ivu
Fig
.
10
.
Throttle
housing
assemblyon
M52
engine
.
Disconnect
hos-
es,
cables
and
harness
connectors
at
and
around
housing
.
0012699
Fig
.
11
.
Special
fuelline
fitting
at
fuel
rail
on
M52/S52US
engine
.
Use
BMW
special
tool
16
1
050
to
releaselocking
fittings
at
ends
offuel
lines
.
WARNING
-
"
Fuel
may
be
expelled
under
pressure
.
Do
not
smoke
or
work
near
heaters
or
other
fire
haz-ards
.
Keep
a
fire
extinguísher
handy
.
Before
dis-
connecting
fuel
hoses,
wrapa
cloth
around
fuel
hoses
to
absorb
any
leaking
fuel
.
Plug
all
oyen
fuel
fines
.
"
Always
unscrew
the
fuel
tank
cap
to
release
pres-
sure
ín
the
tank
before
working
on
the
tank
or
lines
.
OnM52
and
S52US
engines,
special
fittings
are
used
to
retain
the
fuel
lines
to
the
fuel
rail
.
Use
BMW
special
16
.
Remove
intake
manifold
from
engine
byremoving
sev-
tool
no
.
161050
to
compress
the
locking
clip
insidethe
en
mounting
nuts
from
above
andtwo
mounting
bracket
end
of
the
fuel
line
fittings
to
release
the
fine
.
boits
from
below
.
See
Fig
.
12
.
15
.
Unbolt
power
steering
fluid
reservoir
from
its
mounting
CAllTION-
bracket
.
Use
stiff
wire
to
hang
reservoir
to
one
side
.
Do
Stuff
clean
rags
into
the
open
intake
ports
to
pre-
not
disconnect
fluid
fines
.
vent
any
parts
from
falling
into
the
engine
intake
.
ENGINE
REMOVAL
AND
INSTALLATION
Page 69 of 759
11
.
Detach
wiring
harness
duct
at
rear
bulkhead
panel
and
pull
complete
duct
forward
and
up
to
allow
access
to
rear
of
cylinder
head
cover
.
12
.
Remove
spark
plugs
and
spark
plugwire
loom
.
"
Remove
plastic
cover
from
top
of
cylinder
head
.
"
Disconnect
spark
plug
wires
fromspark
plugs
and
re-
move
spark
plugs
.
"
Unbolt
spark
plug
cable
harness
and
heat
shield
from
right
side
of
cylinder
head
cover
and
set
aside
.
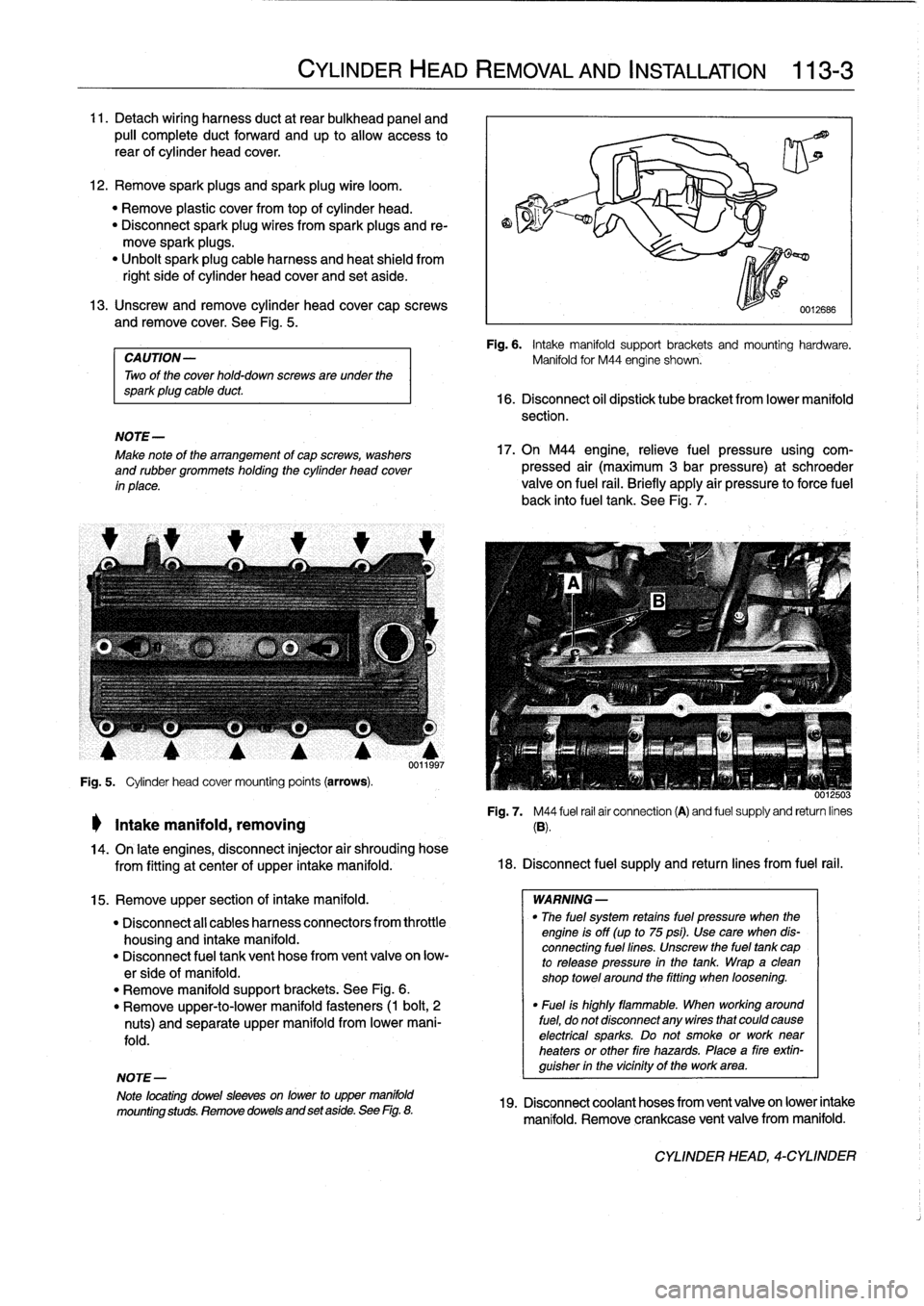
13
.
Unscrew
andremove
cylinder
head
cover
cap
screws
and
remove
cover
.
See
Fig
.
5
.
CAUTION-
Two
of
the
cover
hold-down
screws
are
under
the
spark
plug
cable
duct
.
NOTE-
Make
note
of
the
arrangement
of
cap
screws,
washers
and
rubber
grommets
holding
the
cylinder
head
cover
in
place
.
Fig
.
5
.
Cylinder
head
cover
mounting
points
(arrows)
.
Fig
.
7
.
M44
fuel
rail
air
connection
(A)
and
fuel
supply
and
return
lines
Intake
manifold,
removing
(B)
.
14
.
On
late
engines,
disconnect
injector
air
shrouding
hose
from
fitting
at
center
of
upper
intake
manifold
.
18
.
Disconnect
fuel
supply
and
return
lines
from
fuel
rail
.
15
.
Remove
upper
section
of
intake
manifold
.
"
Disconnect
ali
cables
harness
connectors
from
throttle
housing
and
intake
manifold
.
"
Disconnect
fuel
tank
vent
hose
fromvent
valve
on
low-
er
sitie
of
manifold
.
"
Remove
manifold
support
brackets
.
See
Fig
.
6
.
"
Remove
upper-to-lower
manifold
fasteners
(1
bolt,
2
nuts)
and
separate
upper
manifold
from
lowermani-
fold
.
Note
locating
dowei
sleeves
on
lower
to
upper
manifold
mounting
studs
.
Remove
dowels
and
set
aside
.
See
Fig
.
8
.
CYLINDER
HEAD
REMOVAL
AND
INSTALLATION
113-3
0012686
Fig
.
6
.
Intake
manifold
support
brackets
and
mountinghardware
.
Manifold
for
M44
engine
shows
.
16
.
Disconnect
oil
dipstick
tube
bracket
from
lower
manifold
section
.
17
.
On
M44
engine,
relieve
fuel
pressure
using
com-
pressed
air
(maximum
3
bar
pressure)
at
schroeder
valve
on
fuel
rail
.
Briefly
apply
air
pressure
to
force
fuel
back
intofuel
tank
.
See
Fig
.
7
.
WARNING
-
"
The
fuel
system
retains
fuel
pressure
when
the
engine
is
off
(up
to
75
psi)
.
Use
care
when
dis-
connecting
fuel
lines
.
Unscrew
the
fuel
tank
cap
to
retease
pressure
in
the
tank
.
Wrap
a
clean
shop
towel
around
the
fitting
when
loosening
.
"
Fuel
is
highly
flammable
.
When
working
around
fuel,
do
not
disconnect
any
wires
that
could
cause
electrical
sparks
.
Do
not
smoke
or
worknear
heaters
or
other
tire
hazards
.
Placea
tire
extin-
guisher
in
the
vicinity
of
the
work
area
.
19
.
Disconnect
coolant
hoses
from
vent
valve
on
lower
intake
manifold
.
Remove
crankcase
vent
valve
from
manifold
.
CYLINDER
HEAD,
4-CYLINDER
Page 78 of 759

113-12
CYLINDER
HEAD
REMOVAL
AND
INSTALLATION
18
.
Working
from
underside
of
intake
manifold,
disconnect
21
.
Detach
oil
dipstick
guide
tube
from
manifold
.
Disconharness
connectors,
vent
hoses,
and
air
bypass
nectvent
hose
at
base
of
dipstick
.
hoses)
.
22
.
Remove
intake
manifold
from
engine
byremoving
sev-19
.
Working
at
rear
of
intake
manifold,
label
and
disconnect
en
mounting
nuts
from
above
andtwo
support
bracket
fuel
supply
and
fuel
return
lines
.
Remove
fuelline
hold
bolts
from
below
.
See
Fig
.
32
.
down
bracket
to
free
lines
.
See
Fig
.
31
.
NOTE-
On
M52IS52US
engines,
a
special
fitting
is
used
to
re-tain
the
fuel
fines
to
the
fuel
rail
.
Use
BMW
special
tool
no
.
16
1
050
to
expand
the
locking
clip
inside
the
end
of
the
fuellíne
fittings
.
WARNING
-
"
The
fuel
system
is
desígned
to
retan
pressure
even
wheh
the
ignition
is
off
.
When
working
with
the
fuel
system,
loosen
the
fuel
lines
slowly
toal-
low
residual
fuel
pressure
to
dissipate
gradually
.
Avoid
spraying
fuel
.
"
Fuel
is
highly
flammable
.
When
working
around
fuel,
do
not
disconnect
any
wires
that
could
cause
electrfcal
sparks
.
Do
not
smoke
orwork
near
heaters
or
other
fire
hazards
.
"
Always
unscrew
the
fuel
tank
cap
to
release
pres-
sure
in
the
tank
before
working
on
the
tank
or
lines
.
20
.
Remove
mountingscrews
and
release
wiring
harness
duct
at
rear
bulkhead
and
move
aside
.
Remove
wiring
harness
brackets
frombulkhead
.
CYLINDER
HEAD,
6-CYLINDER
Fig
.
32
.
Intake
manifoldnuts
and
support
bracket
bolts
(arrows)
.
CAUTION-
Stuff
clean
rags
into
the
open
intake
ports
topre-
001269s
vent
any
ports
from
falfing
into
the
engine
.
Fig
.
31
.
Fuel
lines
at
intake
manifold
on
M52/S52
engine
.
Use
BMW
special
tool
16
1
050
to
release
locking
fittings
at
ends
of
fuel
enes
.
1
Timing
chains,
uncoupling
23
.
Remove
VANOS
unit
from
frontof
cylinder
head
.
See
VANOS
section
in
117
Camshaft
Timing
Chain
.
24
.
Setengine
to
approximate
TDC
by
rotating
in
normal
operating
direction
until
camshaft
lobes
at
cylinder
no
.
1
are
facing
each
other
.
Arrows
on
camshaft
sprockets
should
be
pointing
up
.
NOTE-
To
confirm
that
the
crankshaft
is
set
to
the
TDC
posi-
tion,
check
that
the
OIT
mark
(0°
TDC)on
the
front
low-
er
timing
chain
cover
ís
aligned
with
the
víbration
damperSee
Fig
.
33
.
25
.
Lock
crankshaft
at
TDC
.
"
Insert
BMW
special
tool
no
.
11
2
300
through
transmis-
sion
bellhousing
and
finto
hole
in
flywheelor
drive
plate
.
See
Fig
.
34
.
Page 148 of 759
130-2
FUEL
INJECTION
GENERAL
This
repair
group
covers
fuel
injection
system
component
testing
and
repair
.
Special
equipment
is
necessary
for
some
of
the
procedures
given
in
this
repair
group
.
If
you
do
not
have
the
equipment
required
to
do
the
job,
it
is
recommended
that
these
repairs
be
left
to
an
authorized
BMW
dealer
.
The
BMW
dealer
is
equipped
with
sophisticated
diagnostic
test
equip-
ment
that
is
capable
of
quicklypinpointing
hard-to-find
fuel
in-
jection
problems
.
NOTE-
"
Wiring
diagrams
for
the
engine
management
system,
can
be
found
at
the
rear
of
the
manual
under
Electri-
cal
Wiring
Diagrams
.
"
For
ignition
system
repairinformation,
see120
Igni-
tion
System
.
"
For
fuel
supply
system
testing
and
repair,
see160
The
engine
control
module
(ECM)
uses
electrical
signals
Fuel
Tank
and
Fuel
Pump
.
from
the
mass
air
flow
sensor,
the
air
and
coolant
temperature
sensors,
the
crankshaft
position/rpm
sensor,
the
knock
sen
Principies
Of
Operation
sors
and
the
oxygen
sensorsas
the
primary
inputs
to
electron-
ically
control
fuel
delivery
and
ignition
timing
.
There
are
five
versions
of
engine
management
systems
usedon
the
E36
cars
.
Each
has
the
same
basic
components
and
operating
principles
.
The
most
notable
difference
is
that
1996
and
later
cars
use
a
sophisticated
OBD
II-compliant
sys-
tem
.
See
Table
a
.
Table
a
.
Engine
Management
System
Variants
Engine
code/year
1
System
4-cy1inder
M42
(1
.8
I)
1992-1995
Bosch
DME
Ml
.7
M44
(1
.91)
1996-1998
~
Bosch
DME
M5
.2
(OBD
II)
6-cylinder
M50
1992
(2.5
I)
Bosch
DME
M3
.1
1993-1995
(2.5
I)
Bosch
DME
M3
.3.1
(VANOS)
M52
1996-1998
(3281-
2
.8
I)
Siemens
MS
41
.1
(OBD
II)
1998
(3231
-
2
.5
I)
Siemens
MS
41
.1
(OBD
II)
M-Power
S50US
(M3
-
3
.01)
1995
Bosch
DME
M3
.3
.1
S52US
(M3
-
3
.21)
1997-1998
Siemens
MS
41
.1
(0131)
11)
NOTE-
-
Descriptions
and
procedures
in
the
first
partof
this
re-
pairgroup
refer
to
all
the
various
engine
management
systems
.
"
Particulars
of
each
fuel
injection
system
are
treated
in
separate
sections
in
the
second
part
of
this
repair
group
.
GENERAL
Fig
.1
.
OBD
II
diagnostic
connector
locatíon
.
The
fuel
injection
system
is
completely
electronic
in
opera-
tion
.
Air
flow
is
measured
electronically
via
a
mass
air
flow
sensor
and
additional
sensors
supply
information
about
en-
gine
operating
conditions
.
The
ECM
calculates
the
amount
of
fuel
needed
for
the
correct
air-fuel
ratio
and
actuates
the
fuel
injectors
accordingly
.
The
amount
offuel
metered
to
theen-
gine
is
determined
by
how
long
the
injectors
are
open
.
Airintake
.
Air
entering
the
engine
passes
through
a
pleat-
ed
paper
air
filter
in
the
air
cleaner
.
Intake
air
volume
or
mass
is
then
measured
bya
mass
air
flow
(MAF)
sensor
.
In
al¡
ex-
cept
the
vane
type
sensor
(DME
M1
.7),
a
reference
current
is
used
to
heat
a
thin
wireor
film
in
the
sensor
when
the
engine
is
running
.
The
current
used
to
heat
the
wire/film
is
electroni-
cally
converted
into
a
voltage
measurement
corresponding
to
the
mass
of
the
intake
air
.
Table
b
.
Mass
Air
Flow
Sensor
Variants
System
Al
r
flow
sensor
type
Bosch
DME
M1
.7
Vane
(volume
sensor)
Bosch
DME
M3
.1
Hot
wire
(mass
sensor)
Bosch
DME
M3
.3
.1
Hot
film
(mass
sensor)
Bosch
DME
M5
.2
Hot
film
(mass
sensor)
Siemens
MS
41
.1
Hot
film
(mass
sensor)
"
The
16-pin
OBD
11
diagnostic
connector
is
located
on
NOTE-
the
lower
left
dashpanel
.
See
Fig
.
1
.
On
cars
equipped
wíth
tractioncontrol,
an
additional
throttle
valve
is
controlled
by
an
electronic
throttle
actu-
ator
(motor)
.
This
valve
is
used
for
engine
speed
inter
vention
.
Repair
information
forthis
system
is
notcovered
here
due
to
the
special
electrical
testing
equip-
ment
required
to
service
it
.
Page 153 of 759
ELECTRICAL
CHECKS
AND
COMPONENT
TESTING
Main
relay,
testing
The
main
relay
is
energized
via
the
engine
control
module
and
supplies
plus
(+)
power
to
the
many
of
the
engine
man-
agement
components
and
subsystems,
including
the
fuel
pump
relay
.
If
this
relay
is
faulty,
the
engine
will
not
start
.
1
.
With
ignition
off,
remove
main
relay
.
See
Fig
.
6
.
.
iommooommmoi
~
"""
Fuel
DME
sensor
CA
UTION-
Relay
positions
can
vary
.
Be
sure
to
confirm
relay
position
by
identífyíng
the
wiring
in
the
socket
us-
ingthe
wiring
diagramsfound
at
the
rearof
this
manual
.
0013034)
Fuel
pump
relay,
testing
FUEL
INJECTION
130-
7
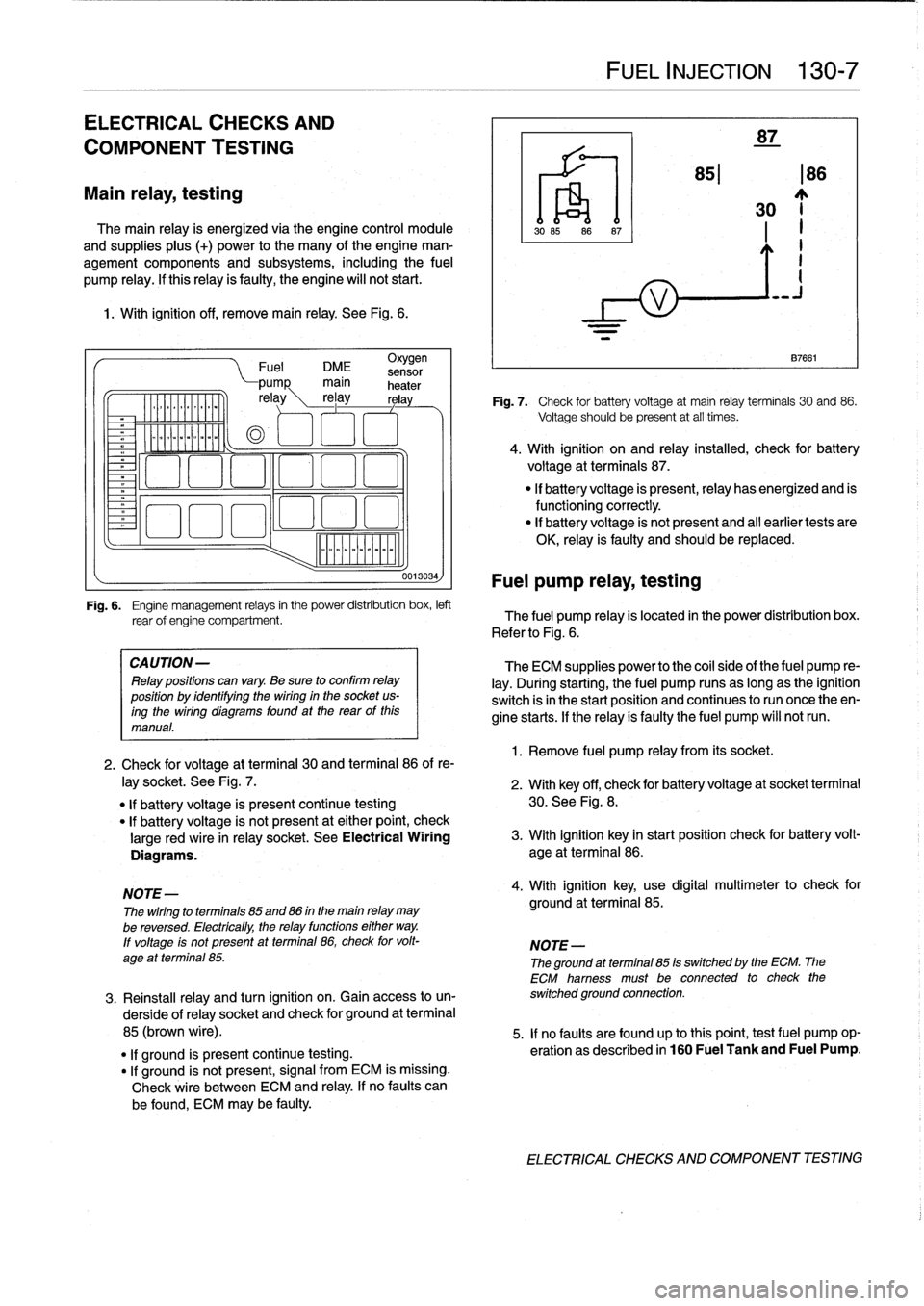
87
851186
30
~j
1
.
Remove
fuel
pump
relay
from
its
socket
.
87661
Fig
.
7
.
Check
for
battery
voltage
at
main
relay
terminals
30
and
86
.
Voltage
should
be
present
at
all
times
.
4
.
With
ignition
on
and
relay
installed,
check
for
battery
voltage
at
terminals
87
.
"
If
battery
voltage
is
present,relay
has
energized
and
is
functioningcorrectly
.
"
lf
battery
voltage
is
not
present
and
al¡
earlier
tests
are
OK,
relay
is
faulty
and
should
be
replaced
.
Fig
.
6
.
Engine
management
relays
in
the
power
distribution
box,
left
rear
of
engine
compartment
.
The
fuel
pump
relay
is
located
in
the
power
distribution
box
.
Refer
to
Fig
.
6
.
The
ECM
supplies
power
to
the
coil
side
of
the
fuel
pump
re-
lay
.
During
starting,
the
fuel
pump
runs
as
long
as
the
ignition
switch
isin
the
start
position
and
continues
to
run
once
theen-
gine
starts
.
If
the
relay
ís
faulty
the
fuel
pump
will
notrun
.
2
.
Check
for
voltage
at
terminal
30
and
terminal
86
of
re-
¡ay
socket
.
See
Fig
.
7
.
2
.
With
key
off,
check
for
batteryvoltage
at
socket
terminal
"
If
battery
voltage
is
present
continue
testing
30
.
See
Fig
.
8
.
"
lf
battery
voltage
is
not
present
at
either
point,
check
large
red
wire
in
relay
socket
.
See
Electrical
Wiring
3
.
With
ignition
key
in
start
position
check
for
battery
volt-
Diagrams
.
age
at
terminal
86
.
NOTE-
4
.
With
ignition
key,
use
digital
multimeter
to
check
for
The
wiring
to
terminals
85
and
86
in
the
main
relay
may
ground
at
terminal
85
.
be
reversed
.
Electrically,
the
relay
functions
either
way
.
lf
voltage
ís
not
present
at
terminal
86,
check
for
volt-
NOTE-
age
at
terminal
85
.
The
ground
atterminal
85
is
switched
by
the
ECM
.
The
ECM
hamess
must
be
connected
to
check
the
3
.
Reinstall
relay
and
turn
ignition
on
.
Gainaccess
to
un-
switched
ground
connection
.
derside
of
relay
socket
and
check
for
ground
at
terminal
85
(brown
wire)
.
5
.
If
no
faults
are
found
up
tothis
point,
testfuel
pump
op-
"
lf
ground
is
present
continue
testing
.
eration
as
described
in
160
Fuel
Tank
and
Fuel
Pump
.
"
If
ground
is
not
present,
signal
from
ECM
is
missing
.
Check
wire
between
ECM
and
relay
.
If
no
faults
can
be
found,
ECM
may
be
faulty
.
ELECTRICAL
CHECKS
AND
COMPONENT
TESTING
Page 155 of 759

Oxygen
Sensor
FUEL
DELIVERY
TESTS
FUEL
INJECTION
130-
9
"
Voltage
at
¡dle
..
.
..
..
....
0
.2
to
0
.8
VDC,
fluctuating
Checking
fuel
delivery
is
afundamental
part
of
trouble-
shooting
and
diagnosing
the
engine
management
system
.
Fuel
pressure
directly
influences
fuel
delivery
.
An
accurate
NOTE-
fuel
pressure
gauge
will
be
needed
to
make
the
tests
.
To
check
sensorresponse
to
lean
and
rich
mixtures,
createenairleak,
orpull
vacuumhoseofffue¡
pressure
There
are
three
significant
fuel
delivery
values
to
be
mea-
regulator
to
increase
fuel
pressure
.
sured
:
3
.
Separate
sensorharness
connector
from
sensor
.
Check
for
battery
voltage
between
terminals
3
and
4
(green
wire
and
brown
wire)
in
main
wiring
harness
side
of
con-
nector
with
engine
running
.
If
voltage
is
not
present,
check
oxygen
sensor
heater
relay
.
See610
Electrical
Component
Locations
.
4
.
Check
heater
element
resistance
between
terminals
3
and
4
in
sensor
side
of
connector
.
If
element
is
electri-
cally
open
(no
continuity),
replace
sensor
.
NOTE-
The
oxygen
sensor
heater
relay
is
mounted
in
the
main
power
distributfon
box
in
the
left
rear
of
the
engine
com-
partment
.
Refer
to
Fig
.
6
.
The
heater
relay
is
energized
wíth
positive
(+)
battery
voltage
from
the
main
relayanda
switched
ground
from
the
ECM
.
See
Electrical
Wir-
ing
Diagrams
.
"
Oxygen
sensor
to
exhaust
pipe
...
..
55
Nm
(41
ft-Ib)
"
System
pressure-created
by
the
fuel
pump
and
main-
tained
by
the
pressure
regulator
.
"
Fuel
delivery
volume-created
by
the
fuel
pump
and
af-
fected
by
restrictions,
suchasclogged
fuel
filter
.
"
Residual
pressure-the
pressure
maintained
in
the
closed
system
after
the
engine
and
fuel
pump
are
shut
off
.
Procedures
for
measuring
the
first
two
quantities
arede-
scribed
in
160
Fuel
Tank
and
Fuel
Pump
.
Residual
fuel
pres-
sure
is
checked
using
the
procedure
detailed
later
in
this
group
.
Operating
fuel
pump
fortests
To
operate
the
fuel
pump
for
testing
purposes
without
hav-
íng
to
runthe
engine,
the
fuel
pump
relay
can
be
bypassed
to
power
the
pump
directly
.
Fuel
pump
relay
location
is
shown
in
Fig
.
6
.
5
.
¡f
oxygen
sensor
doesn't
produce
a
fluctuating
voltage
To
runthe
fuel
pump,
remove
the
fuel
pump
relay
and
con-
and
preheater
circuit
is
OK,
replace
sensor
.
nect
the
socket
for
relayterminal
30
to
the
socket
for
relay
ter-
mina¡
87
with
a
fused
jumper
wire
.
After
completing
the
tests,
NOTE-
remove
the
jumper
wire
.
If
not
already
applied,
coat
the
oxygen
sensor
threads
with
an
anti-seize
compound
before
installation
.
Do
not
CAUTION-
getthe
compound
on
the
sensor
tip
.
"
Relay
locations
may
vary
.
Use
care
when
identi-
fying
relays
and
making
electrical
checks
at
the
fuselrelay
panel
.
See
610
Electrical
Compo
Tightening
Torque
nent
Locations
for
additional
relay
information
.
"
The
fuel
pump
relay
has
a
1
.5
mm2
red
wire
at
ter-
minal
30
in
the
relay
socket
.
Terminal
87
has
a
1
.5
mm
2
greenlviolet
wire
.
See
Electrical
Wiring
Di-
agrams
for
additional
wiring
information
.
NOTE-
Thejumper
wire
should
be
1.5
mm2
(14
ga
.)
and
in-
clude
an
in-line
tuse
holder
with
a15
amp
tuse
.
To
avoid
fuselrelay
panel
damage
from
repeated
connect-
ing
and
disconnecting,
also
include
a
toggle
switch
.
A
heavy-duty
jumper,
BMW
tool
no
.
61
3
050,
is
also
available
from
an
authorized
BMW
dealer
.
FUEL
DELIVERYTESTS