engines BMW 5 SERIES 1989 E34 Owner's Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: BMW, Model Year: 1989, Model line: 5 SERIES, Model: BMW 5 SERIES 1989 E34Pages: 228, PDF Size: 7.04 MB
Page 62 of 228
detach them. Pieces of masking tape with
numbers or letters written on them work well
(see illustration).
6Label and detach all coolant hoses from the
engine (see Chapter 3).
7Remove the cooling fan, shroud and
radiator (see Chapter 3). Note:On the M40
engine, it is only necessary to remove the
cooling fan and shroud; however, prevent
damage to the radiator by covering it with a
piece of wood or cardboard.
8Remove the drivebelts (see Chapter 1).
9Disconnect the fuel lines from the fuel rail
(see Chapter 4).
Warning: Fuel is extremely
flammable, so take extra
precautions when you work on
any part of the fuel system. Don’t
smoke, or allow open flames or bare light
bulbs, near the work area, and don’t work
in a garage where a natural gas-type
appliance (such as a water heater or
clothes dryer) with a pilot light is present.
If you spill any fuel on your skin, rinse it off
immediately with soap and water. When
you perform any kind of work on the fuel
system, wear safety glasses, and have a
fire extinguisher on hand.
10Disconnect the accelerator cable (see
Chapter 4) and kickdown linkage/speed
control cable (see Chapter 7B), if applicable,
from the engine.
11Where fitted, unbolt the power steering
pump (see Chapter 10). Leave the lines/hoses
attached, and make sure the pump is kept in
an upright position in the engine compartment
(use wire or rope to restrain it out of the way).
12On air-conditioned models, unbolt the
compressor (see Chapter 3) and set it aside,
or tie it up out of the way. Do not disconnect
the hoses.
13Drain the engine oil (see Chapter 1) and
remove the filter. Remove the engine splash
guard from under the engine.
14Remove the starter motor (see Chapter 5).15Remove the alternator (see Chapter 5).
This is not essential on all models, but it is a
good idea in any case to avoid accidental
damage.
16Unbolt the exhaust system from the
engine (see Chapter 4).
17If you’re working on a vehicle with an
automatic transmission, remove the torque
converter-to-driveplate fasteners (see
Chapter 7B). On the M40 engine, unbolt the
automatic transmission fluid coolant pipes
from the sump.
18Support the transmission with a jack.
Position a block of wood between them, to
prevent damage to the transmission. Special
transmission jacks with safety chains are
available - use one if possible.
19Attach an engine sling or a length of chain
to the lifting brackets on the engine. If the
brackets have been removed, the chain can
be bolted directly to the intake manifold studs,
but place a flat washer between the chain and
the nut, and tighten the nut all the way up to
the chain, to avoid the possibility of the studs
bending.
20Roll the hoist into position and connect
the sling to it. Take up the slack in the sling or
chain, but don’t lift the engine.
Warning: DO NOT place any part
of your body under the engine
when it’s supported only by a
hoist or other lifting device.
21On M10, M20 and M30 engines, remove
the transmission rear crossmember, and
slightly lower the rear of the transmission.
22Remove the transmission-to-engine block
bolts using a Torx socket. Note:The bolts
holding the bellhousing to the engine block
will require a swivel at the socket, and a very
long extension going back towards the
transmission.
23Remove the engine mounting-to-frame
bracket nuts. On the M40 engine, unbolt the
dampers from the mountings.
24Recheck to be sure nothing is still
connecting the engine to the transmission or
vehicle. Disconnect anything still remaining.
25Raise the engine slightly. Carefully work it
forwards to separate it from the transmission.
If you’re working on a vehicle with an
automatic transmission, you may find the
torque converter comes forward with theengine. If it stays with the transmission, leave
it, but you may find it easier to let it come
forward until it can be grasped easier and be
pulled from the crankshaft. Note:When
refitting the torque converter to the
transmission before the engine is refitted, be
sure to renew the transmission front pump
seal, which will probably be damaged when
the converter comes out with the engine.
Either method is acceptable, but be prepared
for some fluid to leak from the torque
converter if it comes out of the transmission. If
you’re working on a vehicle with a manual
transmission, draw the engine forwards until
the input shaft is completely disengaged from
the clutch. Slowly raise the engine out of the
engine compartment. Check carefully to make
sure everything is disconnected.
26Remove the flywheel/driveplate (and
where applicable, the engine rear plate), and
mount the engine on an engine stand (see
illustration). Do not turn the M40 engine
upside-down (see Cautionin Section 4).
Refitting
27Check the engine and transmission
mountings. If they’re worn or damaged, renew
them.
28Refit the flywheel or driveplate (see
Chapter 2A). If you’re working on a manual
transmission vehicle, refit the clutch and
pressure plate (see Chapter 7A). Now is a
good time to fit a new clutch.
29If the torque converter came out with the
engine during removal, carefully refit the
converter into the transmission before the
engine is lowered into the vehicle.
30Carefully lower the engine into the engine
compartment - make sure the engine
mountings line up.
31If you’re working on an automatic
transmission vehicle, guide the torque
converter onto the crankshaft following the
procedure outlined in Chapter 7B.
32If you’re working on a manual
transmission vehicle, apply a dab of high-
melting-point grease to the input shaft, and
guide it into the clutch and crankshaft pilot
bearing until the bellhousing is flush with the
engine block.. Do not allow the weight of the
engine to hang on the input shaft.
33Refit the transmission-to-engine bolts,
and tighten them securely.
Caution: DO NOT use the bolts to
force the transmission and
engine together.
34Refit the remaining components in the
reverse order of removal.
35Add coolant, oil, power steering and
transmission fluid as needed.
2B•6 General engine overhaul procedures
5.26 Removing the engine rear plate -
M40 engine5.5 Label each wire before unplugging the
connector
If there’s any possibility of
confusion, make a sketch of
the engine compartment and
clearly label the lines, hoses
and wires.
It may be necessary to rock
the engine slightly, or to turn
the crankshaft, to allow the
input shaft splines to mate
with the clutch plate
Page 63 of 228
36Run the engine and check for leaks and
proper operation of all accessories, then refit
the bonnet and test drive the vehicle.
37Where necessary, have the air
conditioning system recharged and leak-
tested.
6 Engine overhaul- alternatives
The do-it-yourselfer is faced with a number
of options when performing an engine
overhaul. The decision to renew the engine
block, piston/connecting rod assemblies and
crankshaft depends on a number of factors,
with the number one consideration being the
condition of the block. Other considerations
are cost, access to machine shop facilities,
parts availability, time required to complete
the project, and the extent of prior mechanical
experience on the part of the do-it-yourselfer.
Some of the alternatives include:
Individual parts - If the inspection
procedures reveal that the engine block and
most engine components are in re-usable
condition, purchasing individual parts may be
the most economical alternative. The block,
crankshaft and piston/connecting rod
assemblies should all be inspected carefully.
Even if the block shows little wear, the
cylinder bores should be surface-honed.
Crankshaft kit- A crankshaft kit (where
available) consists of a reground crankshaft
with matched undersize new main and
connecting big-end bearings. Sometimes,
reconditioned connecting rods and new
pistons and rings are included with the kit
(such a kit is sometimes called an “engine
kit”). If the block is in good condition, but the
crankshaft journals are scored or worn, a
crankshaft kit and other individual parts may
be the most economical alternative.
Short block- A short block consists of an
engine block with a crankshaft and
piston/connecting rod assemblies already
fitted. New bearings are fitted, and all
clearances will be correct. The existing
camshaft, valve train components, cylinder
head and external parts can be bolted to the
short block with little or no machine shop
work necessary.
Full block - A “full” or “complete” block
consists of a short block plus an oil pump,
sump, cylinder head, valve cover, camshaft
and valve train components, timing sprockets
and chain (or belt) and timing cover. All
components are fitted with new bearings,
seals and gaskets used throughout. The
refitting of manifolds and external parts is all
that’s necessary.
Give careful thought to which alternative is
best for you, and discuss the situation with
local machine shops, parts dealers and
experienced rebuilders before ordering or
purchasing new parts.
7 Engine overhaul-
dismantling sequence
1It’s much easier to dismantle and work on
the engine if it’s mounted on a portable
engine stand. A stand can often be hired quite
cheaply from a tool hire shop. Before the
engine is mounted on a stand, the
flywheel/driveplate should be removed from
the engine.
2If a stand isn’t available, it’s possible to
dismantle the engine with it blocked up on the
floor. Be extra-careful not to tip or drop the
engine when working without a stand.
3If you’re going to obtain a rebuilt engine, all
the external components listed below must
come off first, to be transferred to the new
engine if applicable. This is also the case if
you’re doing a complete engine overhaul
yourself. Note:When removing the external
components from the engine, pay close
attention to details that may be helpful or
important during refitting. Note the fitted
position of gaskets, seals, spacers, pins,
brackets, washers, bolts and other small items.
Alternator and brackets
Emissions control components
Distributor, HT leads and spark plugs
Thermostat and housing cover
Water pump
Fuel injection/carburettor and fuel system
components
Intake and exhaust manifolds
Oil filter and oil pressure sending unit
Engine mounting brackets (see illustration)
Clutch and flywheel/driveplate
Engine rear plate (where applicable)
4If you’re obtaining a short block, which
consists of the engine block, crankshaft,
pistons and connecting rods all assembled,
then the cylinder head, sump and oil pump
will have to be removed as well. See Section 6
for additional information regarding the
different possibilities to be considered.
5If you’re planning a complete overhaul, the
engine must be dismantled and the internal
components removed in the following general
order:
Valve cover
Intake and exhaust manifolds
Timing belt or chain covers
Timing chain/belt
Water pump
Cylinder head
Sump
Oil pump
Piston/connecting rod assemblies
Crankshaft and main bearings
Camshaft
Rocker shafts and rocker arms (M10, M20
and M30 engines)
Cam followers and hydraulic tappets
(M40 engine)
Valve spring retainers and springs
Valves
6Before beginning the dismantling andoverhaul procedures, make sure the following
items are available. Also, refer to Section 21
for a list of tools and materials needed for
engine reassembly.
Common hand tools
Small cardboard boxes or plastic bags for
storing parts
Compartment-type metal box for storing
the hydraulic tappets (M40 engine)
Gasket scraper
Ridge reamer
Vibration damper puller
Micrometers
Telescoping gauges
Dial indicator set
Valve spring compressor
Cylinder surfacing hone
Piston ring groove cleaning tool
Electric drill motor
Tap and die set
Wire brushes
Oil gallery brushes
Cleaning solvent
8 Cylinder head- dismantling
4
1Remove the cylinder head (see Chapter 2A).
2Remove the oil supply tube from its
mounting on top of the cylinder head (see
illustrations). Note:It’s important to renew
the seals under the tube mounting bolts.
General engine overhaul procedures 2B•7
7.3 Engine left-hand mounting bracket -
M40 engine
8.2a Remove the oil tube from the top of
the cylinder head (M10 engine). Be sure to
note the location of all gaskets and
washers for reassembly
2B
Page 64 of 228
M10, M20 and M30 engines
3Adjust all valves to their maximum clearance
by rotating the eccentric on the valve end of
the rocker arm towards the centre of the head
(see Chapter 1, if necessary).
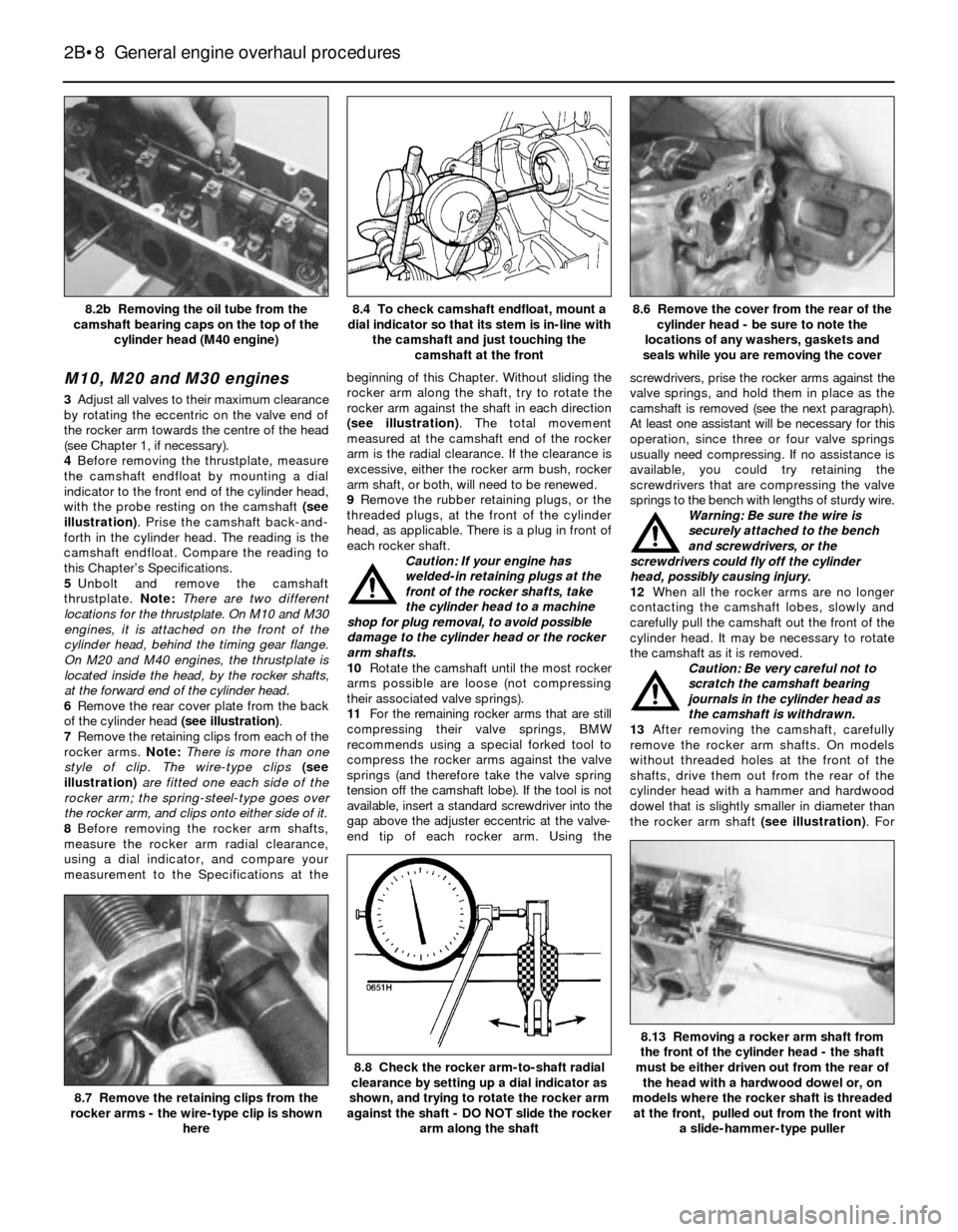
4Before removing the thrustplate, measure
the camshaft endfloat by mounting a dial
indicator to the front end of the cylinder head,
with the probe resting on the camshaft (see
illustration). Prise the camshaft back-and-
forth in the cylinder head. The reading is the
camshaft endfloat. Compare the reading to
this Chapter’s Specifications.
5Unbolt and remove the camshaft
thrustplate. Note:There are two different
locations for the thrustplate. On M10 and M30
engines, it is attached on the front of the
cylinder head, behind the timing gear flange.
On M20 and M40 engines, the thrustplate is
located inside the head, by the rocker shafts,
at the forward end of the cylinder head.
6Remove the rear cover plate from the back
of the cylinder head (see illustration).
7Remove the retaining clips from each of the
rocker arms. Note:There is more than one
style of clip. The wire-type clips (see
illustration)are fitted one each side of the
rocker arm; the spring-steel-type goes over
the rocker arm, and clips onto either side of it.
8Before removing the rocker arm shafts,
measure the rocker arm radial clearance,
using a dial indicator, and compare your
measurement to the Specifications at thebeginning of this Chapter. Without sliding the
rocker arm along the shaft, try to rotate the
rocker arm against the shaft in each direction
(see illustration). The total movement
measured at the camshaft end of the rocker
arm is the radial clearance. If the clearance is
excessive, either the rocker arm bush, rocker
arm shaft, or both, will need to be renewed.
9Remove the rubber retaining plugs, or the
threaded plugs, at the front of the cylinder
head, as applicable. There is a plug in front of
each rocker shaft.
Caution: If your engine has
welded-in retaining plugs at the
front of the rocker shafts, take
the cylinder head to a machine
shop for plug removal, to avoid possible
damage to the cylinder head or the rocker
arm shafts.
10Rotate the camshaft until the most rocker
arms possible are loose (not compressing
their associated valve springs).
11For the remaining rocker arms that are still
compressing their valve springs, BMW
recommends using a special forked tool to
compress the rocker arms against the valve
springs (and therefore take the valve spring
tension off the camshaft lobe). If the tool is not
available, insert a standard screwdriver into the
gap above the adjuster eccentric at the valve-
end tip of each rocker arm. Using thescrewdrivers, prise the rocker arms against the
valve springs, and hold them in place as the
camshaft is removed (see the next paragraph).
At least one assistant will be necessary for this
operation, since three or four valve springs
usually need compressing. If no assistance is
available, you could try retaining the
screwdrivers that are compressing the valve
springs to the bench with lengths of sturdy wire.
Warning: Be sure the wire is
securely attached to the bench
and screwdrivers, or the
screwdrivers could fly off the cylinder
head, possibly causing injury.
12When all the rocker arms are no longer
contacting the camshaft lobes, slowly and
carefully pull the camshaft out the front of the
cylinder head. It may be necessary to rotate
the camshaft as it is removed.
Caution: Be very careful not to
scratch the camshaft bearing
journals in the cylinder head as
the camshaft is withdrawn.
13After removing the camshaft, carefully
remove the rocker arm shafts. On models
without threaded holes at the front of the
shafts, drive them out from the rear of the
cylinder head with a hammer and hardwood
dowel that is slightly smaller in diameter than
the rocker arm shaft (see illustration). For
2B•8 General engine overhaul procedures
8.13 Removing a rocker arm shaft from
the front of the cylinder head - the shaft
must be either driven out from the rear of
the head with a hardwood dowel or, on
models where the rocker shaft is threaded
at the front, pulled out from the front with
a slide-hammer-type puller
8.8 Check the rocker arm-to-shaft radial
clearance by setting up a dial indicator as
shown, and trying to rotate the rocker arm
against the shaft - DO NOT slide the rocker
arm along the shaft
8.7 Remove the retaining clips from the
rocker arms - the wire-type clip is shown
here
8.6 Remove the cover from the rear of the
cylinder head - be sure to note the
locations of any washers, gaskets and
seals while you are removing the cover8.4 To check camshaft endfloat, mount a
dial indicator so that its stem is in-line with
the camshaft and just touching the
camshaft at the front8.2b Removing the oil tube from the
camshaft bearing caps on the top of the
cylinder head (M40 engine)
Page 65 of 228

rocker shafts with a threaded front hole,
screw in a slide hammer to pull the shaft from
the head.
14As each rocker arm shaft is slid out of the
cylinder head, the rocker arms will be
released, one by one.
15Drop each rocker arm into a labelled bag,
so they can be returned to their original
locations on reassembly. While you’re
removing the rocker arm shafts, note their
orientation. The guide plate notches and the
small oil holes face in; the large oil holes face
down, toward the valve guides. Also, label the
rocker shafts so they can be returned to their
original locations in the cylinder head.
M40 engines
Caution: Keep the cylinder head
upright until all of the hydraulic
tappets have been removed. If
this precaution is not taken, the
oil may drain out of the tappets and render
them unserviceable.
16Check that the camshaft bearing caps are
numbered or identified for location.
17Progressively unscrew and remove the
camshaft bearing cap retaining bolts, then
remove the caps (see illustrations).
18Lift the camshaft from the top of the
cylinder head, and remove the oil seal from
the timing end.
19Have ready a compartmentalised box
filled with engine oil to receive the hydraulic
tappets so that they are kept identified for
their correct location (see illustration). Also
have a further box ready to receive the cam
followers.20Remove the cam followers and thrust
discs, then lift out the hydraulic tappets from
their bores in the cylinder head (see
illustrations).
All engines
21Before the valves are removed, arrange to
label and store them, along with their related
components, so they can be kept separate
and reinstalled in the same valve guides from
which they’re removed (see illustration).
22Compress the springs on the first valve
with a spring compressor, and remove the
collets (see illustration). Carefully release the
valve spring compressor, and remove the
retainer, the spring and the spring seat (if
used).
23Pull the valve out of the head, then
remove the oil seal from the guide.
General engine overhaul procedures 2B•9
8.19 Compartmentalised box to hold the
hydraulic tappets (M40 engine)8.17b . . . and camshaft - M40 engine8.17a Removing the camshaft bearing
caps . . .
8.22 Using a valve spring compressor to
compress a valve spring
8.21 A small plastic bag, with an
appropriate label, can be used to store the
valve components so they can be kept
together and refitted in the original position
8.20b . . . and thrust discs . . .8.20a Remove the cam followers . . .
8.20c . . . then lift out the hydraulic tappets
2B
If the valve binds in the guide (won’t
pull through), push it back into the
head, and deburr the area around the
collet groove with a fine file or
whetstone.
Page 67 of 228

that they’re suitable for use in a rebuilt engine
(take the springs to a machine shop for this
check).
16Stand each spring on a flat surface, and
check it for squareness (see illustration). If
any of the springs are distorted or sagged, or
possibly have a broken coil, fit new parts.
17Check the spring retainers and keepers
for obvious wear and cracks. Any
questionable parts should be renewed, as
extensive damage will occur if they fail during
engine operation.
Rocker arms (M10, M20 and
M30 engines)
Note:The rocker arms for the exhaust valves
are the most subject to wear, and should be
checked with particular care.
18Inspect all the rocker arms for excessive
wear on the tips that contact the valve stem
and camshaft (see illustration).
19Check the rocker arm radial clearance
(see Section 8). If it’s excessive, either the
rocker arm bush or the shaft (or both) is
excessively worn. To determine which is more
worn, slide the rocker arm onto an unworn
portion of the rocker arm shaft, and check the
radial clearance again. If it’s now within speci-
fications, the shaft is probably the most-worn
component. If it’s not within specifications,
the rocker arm bushes should be renewed.
Rocker arm shafts (M10, M20 and
M30 engines)
20Check the shafts for scoring, excessive
wear and other damage. The areas where therocker arms contact the shafts should be
smooth. If there is a visible ridge at the edge
of where the rocker arm rides, the shaft is
probably worn excessively.
Cam followers and hydraulic tappets
(M40 engines)
21Check the cam followers where they
contact the valve stems and pivot posts for
wear, scoring and pitting. If there is excessive
wear on both the followers and camshaft,
then a new camshaft, complete with cam
followers, must be obtained.
22Similarly check the hydraulic tappets where
they contact the bores in the cylinder head for
wear, scoring and pitting. Occasionally, a
hydraulic tappet may be noisy and require
renewal, and this will have been noticed when
the engine was running. It is not easy to check a
tappet for internal damage or wear once it has
been removed; if there is any doubt, a complete
set of new tappets should be fitted.
Camshaft
23Inspect the camshaft journals (the round
bearing areas) and lobes for scoring, pitting,
flaking and excessive wear. Using a
micrometer, measure the height of each
exhaust and intake lobe. Compare the heights
of all the exhaust lobes and intake lobes. If the
readings among the exhaust valve lobes or
intake valve lobes vary more than about
0.08 mm, or if the camshaft is exhibiting any
signs of wear, renew the camshaft.
24Inspect the camshaft bearing surfaces in
the cylinder head for scoring and other
damage. If the bearing surfaces are scored or
damaged, you’ll normally have to renew the
cylinder head, since the bearings are simply a
machined surface in the cylinder head. Note:
A machine shop (particularly one that
specialises in BMWs) or dealer service
department may be able to provide an
alternative to fitting a new cylinder head, if the
only problem with the head is mildly-scored
camshaft bearing surfaces.
25Using a micrometer, measure the journals
on the camshaft, and record the
measurements (see illustration). Using a
telescoping gauge or inside micrometer,measure the camshaft bearing diameters in the
cylinder head (on the M40 engine, refit the
bearing caps first). Subtract the camshaft
journal measurement from its corresponding
bearing inside diameter to obtain the oil
clearance. Compare the oil clearance to what’s
listed in this Chapter’s Specifications. If it’s not
within tolerance, a new camshaft and/or
cylinder head will be required. Note:Before
fitting a new cylinder head, check with a
machine shop (particularly one that specialises
in BMWs). They may be able to repair the head.
10 Valves- servicing
4
1Examine the valves as described in Sec-
tion 9, paragraphs 13 and 14. Renew any
valve that shows signs of wear or damage.
2If the valve appears satisfactory at this
stage, measure the valve stem diameter at
several points using a micrometer (see
illustration 9.13). Any significant difference in
the readings obtained indicates wear of the
valve stem. Should any of these conditions be
apparent, the valve(s) must be renewed.
3If the valves are in satisfactory condition they
should be ground (lapped) into their respective
seats to ensure a gas-tight seal. If the seat is
only lightly pitted, or if it has been re-cut, fine
grinding compound should be used to produce
the required finish. Coarse valve-grinding
compound should not normally be used,
unless a seat is badly burned or deeply pitted.
If this is the case, the cylinder head and valves
should be inspected by an expert, to decide
whether seat re-cutting or even the renewal of
the valve or seat insert is required.
4Valve grinding is carried out as follows.
Place the cylinder head upside-down on a
bench, with a block of wood at each end to
give clearance for the valve stems.
5Smear a trace of the appropriate grade of
valve-grinding compound on the seat face,
and press a suction grinding tool onto the
valve head. With a semi-rotary action, grind
the valve head to its seat, lifting the valve
occasionally to redistribute the grinding
compound (see illustration).
General engine overhaul procedures 2B•11
9.25 Measure each camshaft bearing
journal and its corresponding bearing
diameter in the cylinder head, then subtract
the journal diameter from the bearing
inside diameter to obtain the oil clearance9.18 Look for signs of pitting, discoloration
or excessive wear on the ends of the
rocker arms where they contact the
camshaft and the valve stem tip10.5 Grinding-in a valve - do not grind-in
the valves any more than absolutely
necessary, or their seats will be
prematurely sunk into the cylinder head
2B
9.16 Check each valve spring for
squareness
Page 68 of 228
6If coarse grinding compound is being used,
work only until a dull, matt even surface is
produced on both the valve seat and the
valve, then wipe off the used compound and
repeat the process with fine compound. When
a smooth, unbroken ring of light grey matt
finish is produced on both the valve and seat,
the grinding operation is complete. Do not
grind in the valves any further than absolutely
necessary.
7When all the valves have been ground-in,
carefully wash off all traces of grinding
compound using paraffin or a suitable solvent
before reassembly of the cylinder head.
11 Cylinder head- reassembly
5
1Make sure the cylinder head is spotlessly-
clean before beginning reassembly.
2If the head was sent out for valve servicing,
the valves and related components will
already be in place. Begin the reassembly
procedure with paragraph 8.
3Starting at one end of the head, applymolybdenum disulphide (“moly”) grease or
clean engine oil to each valve stem, and refit
the first valve.
4Lubricate the lip of the valve guide seal,
carefully slide it over the tip of the valve, then
slide it all the way down the stem to the guide.
Using a hammer and a deep socket or seal-
fitting tool, gently tap the seal into place until
it’s completely seated on the guide (see
illustrations). Don’t twist or distort a seal
during fitting, or it won’t seal properly against
the valve stem. Note:On some engines, the
seals for intake and exhaust valves are
different - don’t mix them up.
5Drop the spring seat or shim(s) over the
valve guide, and set the valve spring and
retainer in place.
6Compress the spring with a valve spring
compressor and carefully refit the collets in
the upper groove, then slowly release the
compressor and make sure the collets seat
properly (see illustration).
7Repeat paragraphs 3 to 6 for each of the
valves. Be sure to return the components to
their original locations - don’t mix them up!
M10, M20 and M30 engines
8Refit the rocker arms and shafts by
reversing the dismantling sequence. Be sure
to refit the rocker shafts in the correct
orientation. The guide plate notches and the
small oil holes face inwards; the large oil holes
face down, toward the valve guides.
9Lubricate the camshaft journals and lobes(see illustration), then carefully insert it into
the cylinder head, rotating it as you go so the
camshaft lobes will clear the rocker arms. It
will also be necessary to compress the rocker
arms against the valve springs, as described
in Section 8, so they’ll clear the camshaft
lobes. Be very careful not to scratch or gouge
the camshaft bearing surfaces in the cylinder
head.
M40 engines
10Lubricate the bores for the hydraulic
tappets in the cylinder head, then insert the
tappets in their original positions.
11Locate the thrust discs and cam followers
on the valves and pivot posts in their original
positions.
12Lubricate the bearing surfaces of the
camshaft in the cylinder head.
13Locate the camshaft in the cylinder head
so that the valves of No 1 cylinder are both
open, and the valves of No 4 cylinder are
“rocking” (exhaust closing and inlet opening).
No 1 cylinder is at the timing belt end.
14Lubricate the bearing surfaces in the
bearing caps, then locate them in their correct
positions and insert the retaining bolts.
Progressively tighten the bolts to the specified
torque.
15Fit a new oil seal to the camshaft front
bearing cap (see Chapter 2A, Section 11).
All engines
16Refit the oil supply tube to the top of the
cylinder head together with new seals, then
tighten the bolts to the specified torque.
17The cylinder head may now be refitted
(see Chapter 2A).
12 Pistons/connecting rods-
removal
5
Note:Before removing the piston/connecting
rod assemblies, remove the cylinder head and
the sump. On M10, M20 and M30 engines
only, remove the oil pump. Refer to the
appropriate Sections in Chapter 2A.
1Use your fingernail to feel if a ridge has
formed at the upper limit of ring travel (about
6 mm down from the top of each cylinder). If
2B•12 General engine overhaul procedures
11.9 Lubricate the camshaft bearing
journals and lobes with engine assembly
paste or molybdenum disulphide (“moly”)
grease
11.6 With the retainer fitted, compress the
valve spring and refit the collets as shown 11.4b . . .then lightly drive on the seal with
a socket or piece of tubing11.4a Lubricate the valve guide seal, and
place it on the guide (the valve should be
in place too) . . .
A light spring placed under
the valve head will greatly
ease the valve grinding
operation.
Apply a small dab of grease to each
collet to hold it in place, if necessary.
Page 76 of 228

positions (don’t mix them up) with the arrows
pointing towards the front of the engine. Don’t
disturb the Plastigage.
13Starting with the centre main bearing and
working out toward the ends, progressively
tighten the main bearing cap bolts to the
torque listed in this Chapter’s Specifications.
On M10, M20 and M30 engines, tighten the
bolts in three stages. On the M40 engine,
tighten all the bolts initially to the Stage 1
torque, then angle-tighten them by the angle
given in the Specifications. Carry out the
angle-tightening on each bolt in one
controlled movement. Don’t rotate the
crankshaft at any time during the tightening
operation.
14Remove the bolts and carefully lift off the
main bearing caps. Keep them in order. Don’t
disturb the Plastigage or rotate the
crankshaft. If any of the main bearing caps are
difficult to remove, tap them gently from side-
to-side with a soft-face hammer to loosen
them.
15Compare the width of the crushed
Plastigage on each journal to the scale printed
on the Plastigage envelope to obtain the main
bearing oil clearance (see illustration). Check
the Specifications to make sure it’s correct.
16If the clearance is not as specified, thebearing shells may be the wrong size (which
means different ones will be required). Before
deciding that different shells are needed,
make sure that no dirt or oil was between the
bearing shells and the caps or block when the
clearance was measured. If the Plastigage
was wider at one end than the other, the
journal may be tapered (see Section 19).
17Carefully scrape all traces of the
Plastigage material off the main bearing
journals and/or the bearing faces. Use your
fingernail or the edge of a credit card - don’t
nick or scratch the bearing faces.
Final crankshaft refitting
18Carefully lift the crankshaft out of the
engine.
19Clean the bearing faces in the block, then
apply a thin, uniform layer of molybdenum
disulphide (“moly”) grease or engine oil to
each of the bearing surfaces. Be sure to coat
the thrust faces as well as the journal face of
the thrust bearing.
20Make sure the crankshaft journals are
clean, then lay the crankshaft back in place in
the block.
21Clean the faces of the bearings in the
caps, then apply engine oil to them.
22Refit the caps in their respective
positions, with the arrows pointing towards
the front of the engine.
23Refit the bolts finger-tight.
24Lightly tap the ends of the crankshaft
forward and backward with a lead or brass
hammer, to line up the main bearing and
crankshaft thrust surfaces.
25Tighten the bearing cap bolts to the
specified torque, working from the centre
outwards. On M10, M20 and M30 engines,
tighten the bolts in three stages to the final
torque, leaving out the thrust bearing cap
bolts at this stage. On M40 engines, tighten all
of the bolts in the two stages given in the
Specifications.
26On M10, M20 and M30 engines, tighten
the thrust bearing cap bolts to the torque
listed in this Chapter’s Specifications.
27On manual transmission models, fit a new
pilot bearing in the end of the crankshaft (see
Chapter 8).28Rotate the crankshaft a number of times
by hand to check for any obvious binding.
29The final step is to check the crankshaft
endfloat with a feeler gauge or a dial indicator
as described in Section 13. The endfloat
should be correct, providing the crankshaft
thrust faces aren’t worn or damaged, and new
bearings have been fitted.
30Fit the new seal, then bolt the housing to
the block (see Section 25).
25 Crankshaft rear oil seal-
refitting
3
1The crankshaft must be fitted first, and the
main bearing caps bolted in place. The new
seal should then be fitted in the retainer, and
the retainer bolted to the block.
2Before refitting the crankshaft, check the
seal contact surface very carefully for
scratches and nicks that could damage the
new seal lip and cause oil leaks. If the
crankshaft is damaged, the only alternative is
a new or different crankshaft, unless a
machine shop can suggest a means of repair.
3The old seal can be removed from the
housing with a hammer and punch by driving
it out from the back side (see illustration). Be
sure to note how far it’s recessed into the
housing bore before removing it; the new seal
will have to be recessed an equal amount. Be
very careful not to scratch or otherwise
damage the bore in the housing, or oil leaks
could develop.
4Make sure the retainer is clean, then apply
a thin coat of engine oil to the outer edge of
the new seal. The seal must be pressed
squarely into the housing bore, so hammering
it into place is not recommended. At the very
least, use a block of wood as shown, or a
section of large-diameter pipe (see
illustration). If you don’t have access to a
press, sandwich the housing and seal
between two smooth pieces of wood, and
press the seal into place with the jaws of a
large vice. The pieces of wood must be thick
enough to distribute the force evenly around
the entire circumference of the seal. Work
2B•20 General engine overhaul procedures
25.5 Lubricate the lip of the seal, and bolt
the retainer to the rear of the engine block25.4 Drive the new seal into the retainer
with a wooden block or a section of pipe, if
you have one large enough - make sure
the seal enters the retainer bore squarely25.3 After removing the retainer from the
block, support it on two wooden blocks,
and drive out the old seal with a punch and
hammer
24.15 Compare the width of the crushed
Plastigage to the scale on the envelope to
determine the main bearing oil clearance
(always take the measurement at the
widest point of the Plastigage); be sure to
use the correct scale - standard and
metric ones are included
Page 77 of 228
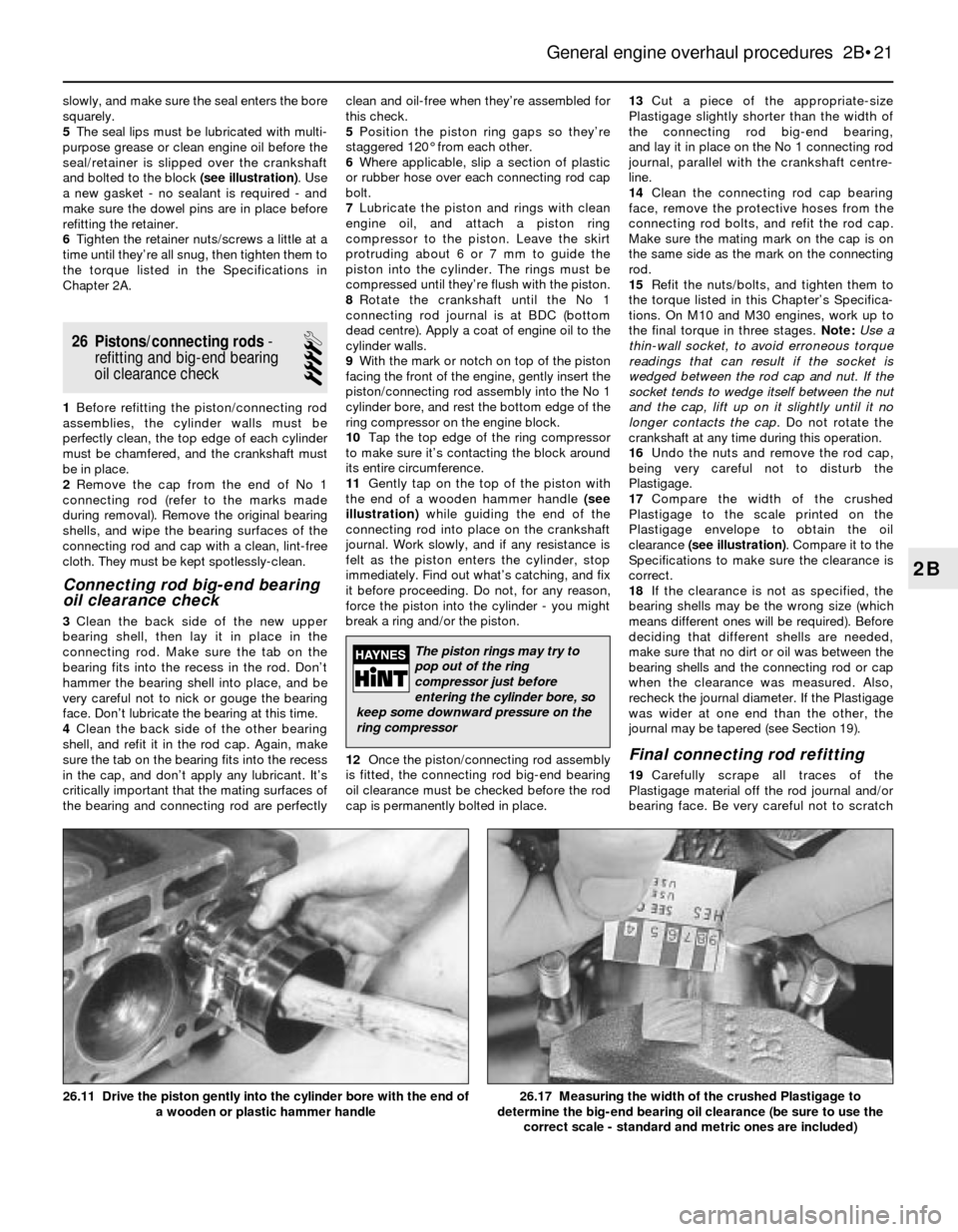
slowly, and make sure the seal enters the bore
squarely.
5The seal lips must be lubricated with multi-
purpose grease or clean engine oil before the
seal/retainer is slipped over the crankshaft
and bolted to the block (see illustration). Use
a new gasket - no sealant is required - and
make sure the dowel pins are in place before
refitting the retainer.
6Tighten the retainer nuts/screws a little at a
time until they’re all snug, then tighten them to
the torque listed in the Specifications in
Chapter 2A.
26 Pistons/connecting rods-
refitting and big-end bearing
oil clearance check
4
1Before refitting the piston/connecting rod
assemblies, the cylinder walls must be
perfectly clean, the top edge of each cylinder
must be chamfered, and the crankshaft must
be in place.
2Remove the cap from the end of No 1
connecting rod (refer to the marks made
during removal). Remove the original bearing
shells, and wipe the bearing surfaces of the
connecting rod and cap with a clean, lint-free
cloth. They must be kept spotlessly-clean.
Connecting rod big-end bearing
oil clearance check
3Clean the back side of the new upper
bearing shell, then lay it in place in the
connecting rod. Make sure the tab on the
bearing fits into the recess in the rod. Don’t
hammer the bearing shell into place, and be
very careful not to nick or gouge the bearing
face. Don’t lubricate the bearing at this time.
4Clean the back side of the other bearing
shell, and refit it in the rod cap. Again, make
sure the tab on the bearing fits into the recess
in the cap, and don’t apply any lubricant. It’s
critically important that the mating surfaces of
the bearing and connecting rod are perfectlyclean and oil-free when they’re assembled for
this check.
5Position the piston ring gaps so they’re
staggered 120° from each other.
6Where applicable, slip a section of plastic
or rubber hose over each connecting rod cap
bolt.
7Lubricate the piston and rings with clean
engine oil, and attach a piston ring
compressor to the piston. Leave the skirt
protruding about 6 or 7 mm to guide the
piston into the cylinder. The rings must be
compressed until they’re flush with the piston.
8Rotate the crankshaft until the No 1
connecting rod journal is at BDC (bottom
dead centre). Apply a coat of engine oil to the
cylinder walls.
9With the mark or notch on top of the piston
facing the front of the engine, gently insert the
piston/connecting rod assembly into the No 1
cylinder bore, and rest the bottom edge of the
ring compressor on the engine block.
10Tap the top edge of the ring compressor
to make sure it’s contacting the block around
its entire circumference.
11Gently tap on the top of the piston with
the end of a wooden hammer handle (see
illustration)while guiding the end of the
connecting rod into place on the crankshaft
journal. Work slowly, and if any resistance is
felt as the piston enters the cylinder, stop
immediately. Find out what’s catching, and fix
it before proceeding. Do not, for any reason,
force the piston into the cylinder - you might
break a ring and/or the piston.
12Once the piston/connecting rod assembly
is fitted, the connecting rod big-end bearing
oil clearance must be checked before the rod
cap is permanently bolted in place.13Cut a piece of the appropriate-size
Plastigage slightly shorter than the width of
the connecting rod big-end bearing,
and lay it in place on the No 1 connecting rod
journal, parallel with the crankshaft centre-
line.
14Clean the connecting rod cap bearing
face, remove the protective hoses from the
connecting rod bolts, and refit the rod cap.
Make sure the mating mark on the cap is on
the same side as the mark on the connecting
rod.
15Refit the nuts/bolts, and tighten them to
the torque listed in this Chapter’s Specifica-
tions. On M10 and M30 engines, work up to
the final torque in three stages. Note:Use a
thin-wall socket, to avoid erroneous torque
readings that can result if the socket is
wedged between the rod cap and nut. If the
socket tends to wedge itself between the nut
and the cap, lift up on it slightly until it no
longer contacts the cap. Do not rotate the
crankshaft at any time during this operation.
16Undo the nuts and remove the rod cap,
being very careful not to disturb the
Plastigage.
17Compare the width of the crushed
Plastigage to the scale printed on the
Plastigage envelope to obtain the oil
clearance (see illustration). Compare it to the
Specifications to make sure the clearance is
correct.
18If the clearance is not as specified, the
bearing shells may be the wrong size (which
means different ones will be required). Before
deciding that different shells are needed,
make sure that no dirt or oil was between the
bearing shells and the connecting rod or cap
when the clearance was measured. Also,
recheck the journal diameter. If the Plastigage
was wider at one end than the other, the
journal may be tapered (see Section 19).
Final connecting rod refitting
19Carefully scrape all traces of the
Plastigage material off the rod journal and/or
bearing face. Be very careful not to scratch
General engine overhaul procedures 2B•21
26.17 Measuring the width of the crushed Plastigage to
determine the big-end bearing oil clearance (be sure to use the
correct scale - standard and metric ones are included)26.11 Drive the piston gently into the cylinder bore with the end of
a wooden or plastic hammer handle
2B
The piston rings may try to
pop out of the ring
compressor just before
entering the cylinder bore, so
keep some downward pressure on the
ring compressor
Page 79 of 228

3General
Coolant capacity . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 1
Thermostat rating
Opening temperature . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 80°C (176°F)
Fully open at . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 100°C (212°F)
Cooling fan thermo-switch - switching temperatures
Low-speed . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 91°C (196°F)
High-speed . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 99°C (210°F)
Torque wrench settingsNm
Mechanical cooling fan clutch-to-water pump securing
nut (left-hand thread) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
Mechanical cooling fan-to-clutch bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Water pump bolts
Small bolts (M6) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Large bolts (M8) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Thermostat housing bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Chapter 3
Cooling, heating and air conditioning systems
Air conditioner receiver-drier - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Air conditioning blower motor (E28/”old-shape” 5-series
models) - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Air conditioning compressor - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Air conditioning condenser - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Air conditioning system - precautions and maintenance . . . . . . . . . 12
Antifreeze - general information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Coolant level check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 1
Coolant temperature sender unit - check and renewal . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Cooling system check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 1
Cooling system servicing (draining, flushing and refilling)See Chapter 1Engine cooling fan(s) and clutch - check, removal and refitting . . . . 5
Evaporator matrix - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
General information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
Heater and air conditioner control assembly - removal and refitting 10
Heater and air conditioning blower motor - removal,testing and
refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Heater matrix - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Radiator - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
Thermostat - check and renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Water pump - check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Water pump - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
3•1
Easy,suitable for
novice with little
experienceFairly easy,suitable
for beginner with
some experienceFairly difficult,
suitable for competent
DIY mechanic
Difficult,suitable for
experienced DIY
mechanicVery difficult,
suitable for expert
DIY or professional
Degrees of difficulty
Specifications Contents
1 General information
Engine cooling system
All vehicles covered by this manual employ
a pressurised engine cooling system, with
thermostatically-controlled coolant circulation.
An impeller-type water pump mounted on
the front of the block pumps coolant through
the engine. The coolant flows around each
cylinder, and towards the rear of the engine.
Cast-in coolant passages direct coolantaround the intake and exhaust ports, near the
spark plug areas, and in close proximity to the
exhaust valve guides.
A wax-pellet-type thermostat is located in-
line in the bottom hose on M10 engines, in a
housing near the front of the engine on M20
and M30 engines, or behind an elbow under
the timing belt upper cover (on the front of the
cylinder head) on M40 engines. During warm-
up, the closed thermostat prevents coolant
from circulating through the radiator. As the
engine nears normal operating temperature,
the thermostat opens and allows hot coolant
to travel through the radiator, where it’s
cooled before returning to the engine.The pressure in the system raises the
boiling point of the coolant, and increases the
cooling efficiency of the radiator. The cooling
system is sealed by a pressure-type cap. If
the system pressure exceeds the cap
pressure relief value, the excess pressure in
the system forces the spring-loaded valve
inside the cap off its seat, and allows the
coolant to escape through the overflow tube.
The pressure cap on four-cylinder models is
on the top of the radiator; on six-cylinder models,
it’s on top of a translucent plastic expansion
tank. The cap pressure rating is moulded into the
top of the cap. The pressure rating is either
1.0 bar (14 psi) or 1.2 bars (17 psi).
Page 80 of 228

Warning: Do not remove the
pressure cap from the radiator or
expansion tank until the engine
has cooled completely and
there’s no pressure remaining in the
cooling system. Removing the cap from a
hot engine risks personal injury by
scalding.
Heating system
The heating system consists of a blower fan
and heater matrix located in the heater box,
with hoses connecting the heater matrix to the
engine cooling system, and the heater/air
conditioning control head on the dashboard.
Hot engine coolant is circulated through the
heater matrix passages all the time the engine
is running. Switching the heater on opens a
flap door to direct air through the heater
matrix, and the warmed air enters the
passenger compartment. A fan switch on the
control head activates the blower motor,
which forces more air through the heater
matrix, giving additional heater output for
demisting, etc.
Air conditioning system
The air conditioning system consists of a
condenser mounted in front of the radiator, an
evaporator mounted adjacent to the heater
matrix, a compressor mounted on the engine,
a filter-drier (receiver-drier) which contains a
high-pressure relief valve, and the plumbing
connecting all of the above components.
A blower fan forces the warmer air of the
passenger compartment through the
evaporator matrix (a radiator-in-reverse),
transferring the heat from the air to the
refrigerant. The liquid refrigerant boils off into
low-pressure vapour, taking the heat with it
when it leaves the evaporator.
Note: Refer to the precautions at the start
of Section 12 concerning the potential
dangers associated with the air conditioning
system.
2 Antifreeze-
general information
Warning: Do not allow antifreeze
to come in contact with your skin
or painted surfaces of the
vehicle. Rinse off spills
immediately with plenty of water. If
consumed, antifreeze can be fatal;
children and pets are attracted by its
sweet taste, so wipe up garage floor and
drip pan coolant spills immediately. Keep
antifreeze containers covered, and repair
leaks in your cooling system as soon as
they are noticed.
The cooling system should be filled with a
60/40% water/ethylene-glycol-based anti-
freeze solution, which will prevent freezing
down to approximately -27°C (-17°F). The
antifreeze also raises the boiling point of thecoolant, and (if of good quality) provides
protection against corrosion.
The cooling system should be drained,
flushed and refilled at the specified intervals
(see Chapter 1). Old or contaminated
antifreeze solutions are likely to cause
damage, and encourage the formation of rust
and scale in the system. Use distilled water
with the antifreeze, if available, or clean
rainwater. Tap water will do, but not if the
water in your area is at all “hard”.
Before adding antifreeze, check all hose
connections, because antifreeze tends to
search out and leak through very minute
openings. Engines don’t normally consume
coolant, so if the level goes down, find the
cause and correct it.
The antifreeze mixture should be
maintained at its correct proportions; adding
too much antifreeze reduces the efficiency of
the cooling system. If necessary, consult the
mixture ratio chart on the antifreeze container
before adding coolant. Hydrometers are
available at most car accessory shops to test
the coolant. Use antifreeze which meets the
vehicle manufacturer’s specifications.
3 Thermostat-
check and renewal
1
Warning: Do not remove the
radiator cap, drain the coolant, or
renew the thermostat until the
engine has cooled completely.
Check
1Before assuming the thermostat is to blame
for a cooling system problem, check the
coolant level, drivebelt tension (see Chapter 1)
and temperature gauge (or warning light)
operation.
2If the engine seems to be taking a long time
to warm up (based on heater output or
temperature gauge operation), the thermostat
is probably stuck open. Renew the
thermostat.
3If the engine runs hot, use your hand to
check the temperature of the upper radiator
hose. If the hose isn’t hot, but the engine is,
the thermostat is probably stuck closed,preventing the coolant inside the engine from
circulating to the radiator. Renew the
thermostat.
Caution: Don’t drive the vehicle
without a thermostat. The engine
will be very slow to warm-up in
cold conditions, resulting in poor
fuel economy and driveability. A new
thermostat is normally an inexpensive
component anyway.
4If the upper radiator hose is hot, it means
that the coolant is flowing and the thermostat
is at least partly open. Consult the “Fault
finding” Section at the rear of this manual for
cooling system diagnosis.
Renewal
All models
5Disconnect the negative cable from the
battery.
Caution: If the radio in your
vehicle is equipped with an anti-
theft system, make sure you
have the correct activation code
before disconnecting the battery.
Note: If, after connecting the battery, the
wrong language appears on the instrument
panel display, refer to page 0-7 for the
language resetting procedure.
6Drain the cooling system (see Chapter 1). If
the coolant is relatively new or in good
condition, save it and re-use it.
M10 engines
7The thermostat is located in the bottom
hose. First remove the cooling fan.
8Note the fitted position of the thermostat,
then unscrew the hose clamps and withdraw
the thermostat from the hose connections
(see illustration).
9Refit the thermostat-to-hose connections,
and tighten the hose clamps.
10Refit the cooling fan.
M20 and M30 engines
11Loosen the hose clamp (see illustration),
then detach the hose(s) from the thermostat
cover.
3•2 Cooling, heating and air conditioning systems
3.11 On M20 and M30 engine models,
loosen the hose clamp (A) and disconnect
the hose from the thermostat housing
cover - note that the coolant temperature
sender unit (barely visible behind the fuel
pressure regulator) is located at the top of
the thermostat housing (B)
3.8 On the M10 (four-cylinder) engine, the
thermostat (arrowed) is connected in-line
in the radiator hose