clutch BMW 5 SERIES 1999 E39 Drive Away Protection Syst
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: BMW, Model Year: 1999, Model line: 5 SERIES, Model: BMW 5 SERIES 1999 E39Pages: 30, PDF Size: 0.7 MB
Page 15 of 30

15
EWS
Replacement Procedures
Keys
Up to 6 additional keys may be ordered as replacement keys. The EWS II control module
is codeable for only 10 keys (4 delivered with vehicle and 6 replacement).
EWS II Control Module
Replacement EWS II Control Modules must be ordered VIN specific. EWS II modules con-
tain the VIN and coding from the factory to recognize the key codes. Modules from other
vehicles will not recognize keys as being valid and not start the engine.
EWS II Control Modules store the Central Coding Key (ZCS) and the VIN. If the EWS II con-
trol module is replaced the system must be ZCS coded (SIB 61 02 96 and TRI 61 01 95).
The EWS II module must be synchronized with the DME (aligned). There is no limit to the
number of times the ISN may be changed in the EWS II module.
DME Control Module
The DME Control Module is not ordered VIN specific and must be programmed during
replacement. The ISN from the new DME must
be transferred to the EWS II module using the
DISplus or MoDic.
Key Activation
Keys that are lost or stolen may be deactivated
or made to not operate the starter functions.
The SERVICE FUNCTIONS of the DISplus or
MoDic for EWS II contains a “Bar/Release
Code” function that activates and deactivates
keys of the EWS II. Any key may be “Barred”
except the key in the ignition at the time of
deactivation. The lost or stolen key can be iden-
tified by the identification of the remaining keys.
There is no limit to the number of times a key
can be activated/deactivated.
EWS II Update
Beginning MY 1997 E31 and E36 vehicles with manual transmissions were updated to include a clutch
pedal position switch. The clutch switch signal is provided by a hall-effect sensor providing a high sig-
nal when the clutch is depressed.
Note: A “Barred” key will not start the engine, it
will still unlockthe vehicle.
Page 16 of 30

16
EWS
EWS III (3.2)
The 1997 Model Year E38is equipped with EWS III (3.2) drive away protection. E39vehi-
cles produced 3/97and later are also equipped with EWS III (3.2).
Purpose of the System
The major changes of the EWS III (3.2) system over the EWS II are a modified control mod-
ule, revised wiring and the addition of the clutch switch input.
Output functions, starter control and ISN signal, remain the same for EWS III (3.2).
Component changes are:
• EWS III (3.2) Control Module.
• Input From The K-Bus.
• Clutch Switch.
• Transmitter/Receiver Module Eliminated.
System Components
EWS III (3.2) Control Module
The EWS III (3.2) Control Module has a 13 pin connector. The transmitter/receiver module
is no longer a separate module of the system with the electronic functions for the data
transfer between the key transponder and the EWS control module being handled directly
by the EWS III (3.2) control module. The vehicle wiring harness has been changed to reflect
this modification and to route the wiring from the ring antenna directly to the EWS III (3.2)
control module.
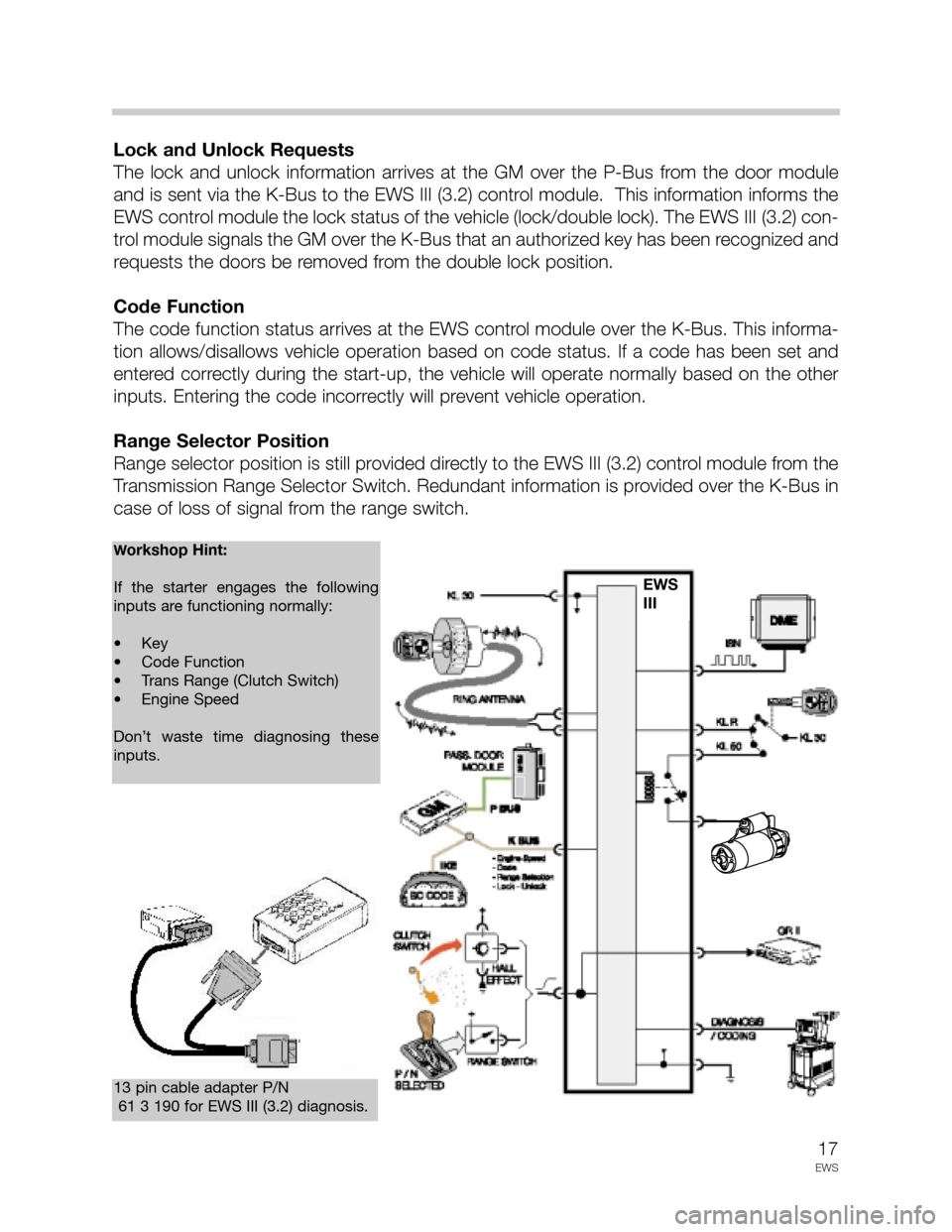
Input From The K-Bus
Reduction in wiring has also been accomplished with the use of the K-Bus for data com-
munication between the GM, Door Module, IKE and the EWS III (3.2) control module. This
data link provides the following signals to be communicated on one wire:
• Engine Speed.
• Lock and Unlock Requests.
• Code Function.
• Range Selector Position (Redundant Signal).
Engine Speed
The DME outputs the engine speed “TD” signal over the CAN Bus to the IKE. The IKE uses
the TD information as needed and passes it on to the EWS III (3.2) via the K-Bus.
Page 17 of 30
17
EWS
Lock and Unlock Requests
The lock and unlock information arrives at the GM over the P-Bus from the door module
and is sent via the K-Bus to the EWS III (3.2) control module. This information informs the
EWS control module the lock status of the vehicle (lock/double lock). The EWS III (3.2) con-
trol module signals the GM over the K-Bus that an authorized key has been recognized and
requests the doors be removed from the double lock position.
Code Function
The code function status arrives at the EWS control module over the K-Bus. This informa-
tion allows/disallows vehicle operation based on code status. If a code has been set and
entered correctly during the start-up, the vehicle will operate normally based on the other
inputs. Entering the code incorrectly will prevent vehicle operation.
Range Selector Position
Range selector position is still provided directly to the EWS III (3.2) control module from the
Transmission Range Selector Switch. Redundant information is provided over the K-Bus in
case of loss of signal from the range switch.
13 pin cable adapter P/N
61 3 190 for EWS III (3.2) diagnosis.
Workshop Hint:
If the starter engages the following
inputs are functioning normally:
• Key
• Code Function
• Trans Range (Clutch Switch)
• Engine Speed
Don’t waste time diagnosing these
inputs
.
EWS
III
Page 18 of 30

18
EWS
Clutch Switch
A Hall-Effect Switch is added to the clutch system to inform the EWS III (3.2) control mod-
ule of clutch status. Input from the switch replaces the signal from the Trans Range Selector
Switch on manual transmission equipped vehicles. High signal status indicates the clutch
is depressed and vehicle starting is allowed.
Principle of Operation
The starting sequence for the EWS III (3.2) is as follows:
• The key is inserted into the lock cylinder and switched “ON”. The EWS III control mod-
ule is powered through KL R and sends a 125kHz AM signal to the ring antenna. The
AM signal induces voltage in the key coil and powers up the transponder.
• Powered up, the key transponder sends the key identification code to the EWS III mod-
ule. The EWS III module verifies the key identification code and checks to see if the key
is enabled. If the key is correct and enabled, a password is sent to the transponder over
the 125kHz AM signal through the ring antenna.
• When the transponders accepts the password, it releases the changing code, which it
received from the EWS III module during the last start-up operation, to the EWS III mod-
ule via the ring antenna.
• The EWS III module compares the changing code received from the transponder with
the code stored in its memory and if they match the process is allowed to continue.
The EWS III module looks at the other inputs for correct status (e.g. Code function not
active, Transmission in P or N or clutch depressed, engine speed below specified RPM)
and energizes the the internal relay to begin starter operation.
• As the starter begins to operate, the EWS III module sends the ISN to the DME and if
verified as correct by the DME, drive away protection is cancelled and injection and igni-
tion is enabled. The EWS III module also sends a new changing code to the key
transponder through the ring antenna.
Replacement Procedures
Keys
Up to 6 additional keys may be ordered as replacement keys. The EWS III (3.2) module is
codeable for only 10 keys (4 delivered with vehicle and 6 replacement). The keys are
mechanically matched to the vehicle with the lock tumblers and electronically matched to
the EWS III (3.2) through unalterable coding.
Page 21 of 30

21
EWS
DME Control Module
The DME Control Module has changed in that it is not the source of the ISN but now only
stores the “Rolling Code”. It compares the “Codes” to those sent to it by the EWS III (3.3)
control module. The “Rolling Code Table” assigned to the DME must match the table in the
EWS III (3.3) module. The “Rolling Code Table is “burned” into the DME during the pro-
gramming of the DME and cannot be change once “burned”.
Transmission Range Selection Input
With the introduction of the SKE type connectors on Transmission Control Modules the
direct input from the Transmission Range Selector Switch is eliminated. The input for range
selection is now received from the AGS Control Module.
On manual transmission vehicles clutch status is input directly into the DME.
Principle of Operation
The starting sequence of the EWS III (3.3) is as follows:
(Same as EWS III (3.2)
• The key is inserted into the lock cylinder and switched “ON”. The EWS III (3.3) control
module is powered through KL R and sends a 125kHz AM signal to the ring antenna.
The AM signal induces voltage in the key coil and powers up the transponder.
• Powered up, the key transponder sends the key identification code to the EWS III (3.3)
module. The EWS III (3.3) module verifies the key identification code and checks to see
if the key is enabled. If the key is correct and enabled, a password is sent to the
transponder over the 125kHz AM signal through the ring antenna.
• When the transponders accepts the password, it releases the changing code which it
received from the EWS III (3.3) module during the last start-up operation to the EWS III
(3.3) module via the ring antenna.
• The EWS III (3.3) module compares the changing code received from the transponder
with the code stored in its memory and if they match the process is allowed to contin-
ue. The EWS III (3.3) module looks at the other inputs for correct status (e.g. Code func-
tion not active, Transmission in P or N or clutch depressed, engine speed below spec-
ified RPM) and energizes the the internal relay to begin starter operation.
Page 25 of 30
25
EWS
Under certain condition “Alignment” of the DME and EWS III D modules may still be nec-
essary. The alignment procedure only resets the code table to code #1 it does not change
the “Rolling Code Table”.
Key Activation
Keys that are lost or stolen may be deactivated or made to not operate the starter func-
tions. The SERVICE FUNCTIONS of the DISplus or MoDic for EWS III D contains a
“bar/release code” function that activates and deactivates keys of the EWS III D. Any key
may be “Barred” except the key in the ignition at the time of deactivation. The lost or stolen
key can be identified by the identification of the remaining keys.
There is no limit to the number of times a key can be activated/deactivated.
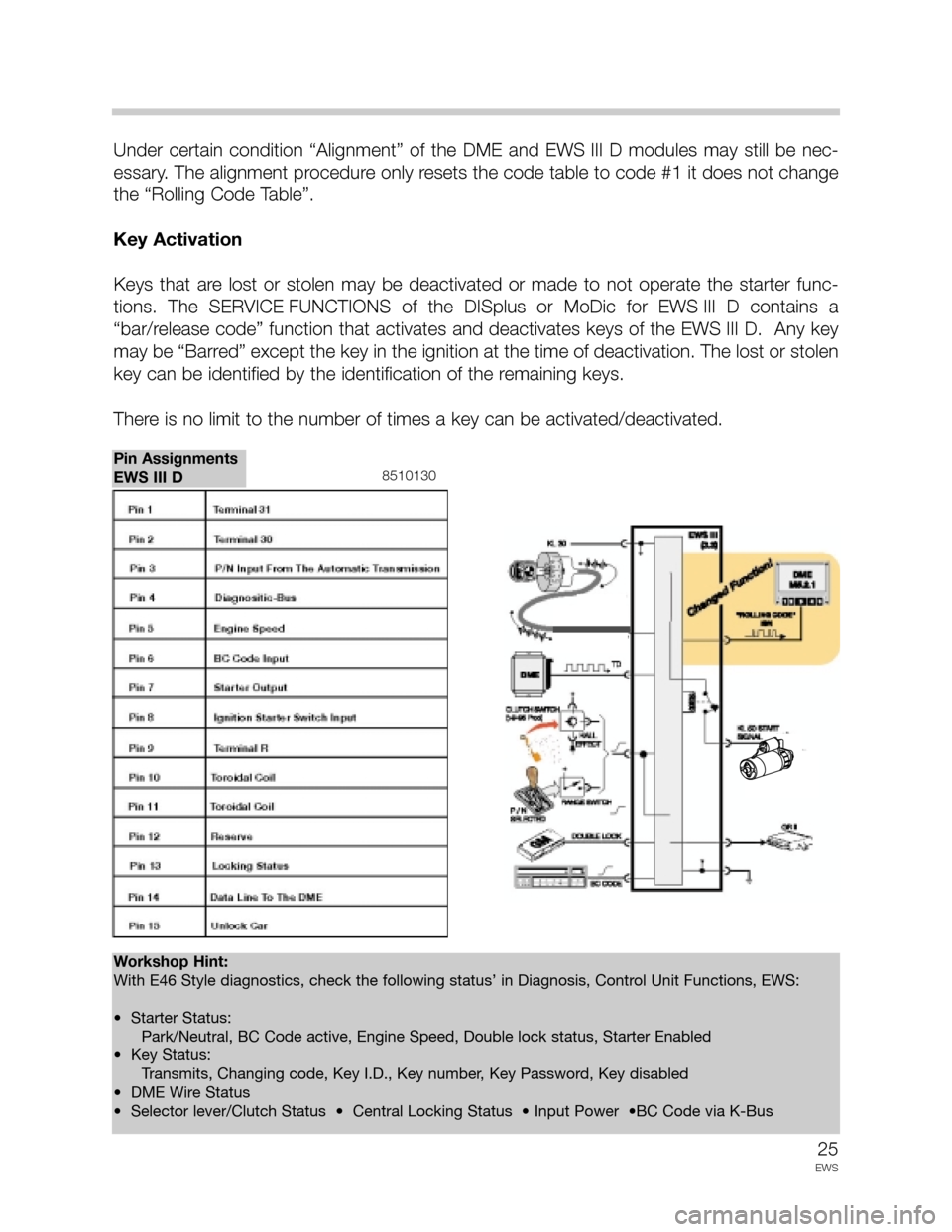
8510130
Pin Assignments
EWS III D
Workshop Hint:
With E46 Style diagnostics, check the following status’ in Diagnosis, Control Unit Functions, EWS:
• Starter Status:
Park/Neutral, BC Code active, Engine Speed, Double lock status, Starter Enabled
• Key Status:
Transmits, Changing code, Key I.D., Key number, Key Password, Key disabled
• DME Wire Status
• Selector lever/Clutch Status • Central Locking Status • Input Power •BC Code via K-Bus