600 BMW 528i 2000 E39 Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: BMW, Model Year: 2000, Model line: 528i, Model: BMW 528i 2000 E39Pages: 1002
Page 3 of 1002

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine
YOU are now in Volume I
I
Foreword ................... .. ........................................................................\
.......... v
Index
........................ .. ................................................................ rear of manual
General, 001 General Warnings and Cautions 002 Vehicle Identification and VIN Decoder
Maintenance OiO 020 Maintenance
Engine
100 Engine-General 110 Engine Removal and Installation
113 Cylinder Head Removal and
Installation
116 Cyiinder Head and Valvetrain 117 Camshaft Timing Chain
119 Lubrication System
200 Transmission-General
2 Transmission 210 clutch 230 ManualTransmission
I20 Ignition System
121 Battery, Starter, Alternator
130 Fuel Injection
160 Fuel Tank and Fuel Pump 170 Radiator and Cooling System
180 Exhaust System
240 Automatic Transmission
250 Gearshift Linkage 260 Driveshaft
Suspension, 300 Suspension, Steering and 330 Rear Suspension
Brakes-General 331 Final Drive
Steering and No Front Suspension 340 Brakes
320 Steering and Wheel Alignment
400 Body-General
410 Fenders, Engine Hood 411 Doors
412 Trunk Lid, Tailgate
510 Exterior Trim, Bumpers 512 Door Windows
Equipment 513 Interior Trim
7
Equipment and 720 seat Belts
Accessories 721 Airbag System (SRS)
OBD On-Board Diagnostics
. ............ ..
515 Central Lociting and
Anti-Theft
520 Seats 540 Sunroof
.................................................................... Foreword .............................. .. v
Index ................... .. ................................................................ rear of manual
Electrical
6 system
600 Electrical System-General 620 Instruments
610 Electrical Comoonent Locations 630 Liohts
611 wipers and washers 612 Switches eati in^ and Air Conditioning
Radio
. ........... ........ .........................
Electrical Wiring Diagrams
Page 20 of 1002
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine
01 0-1 0
General
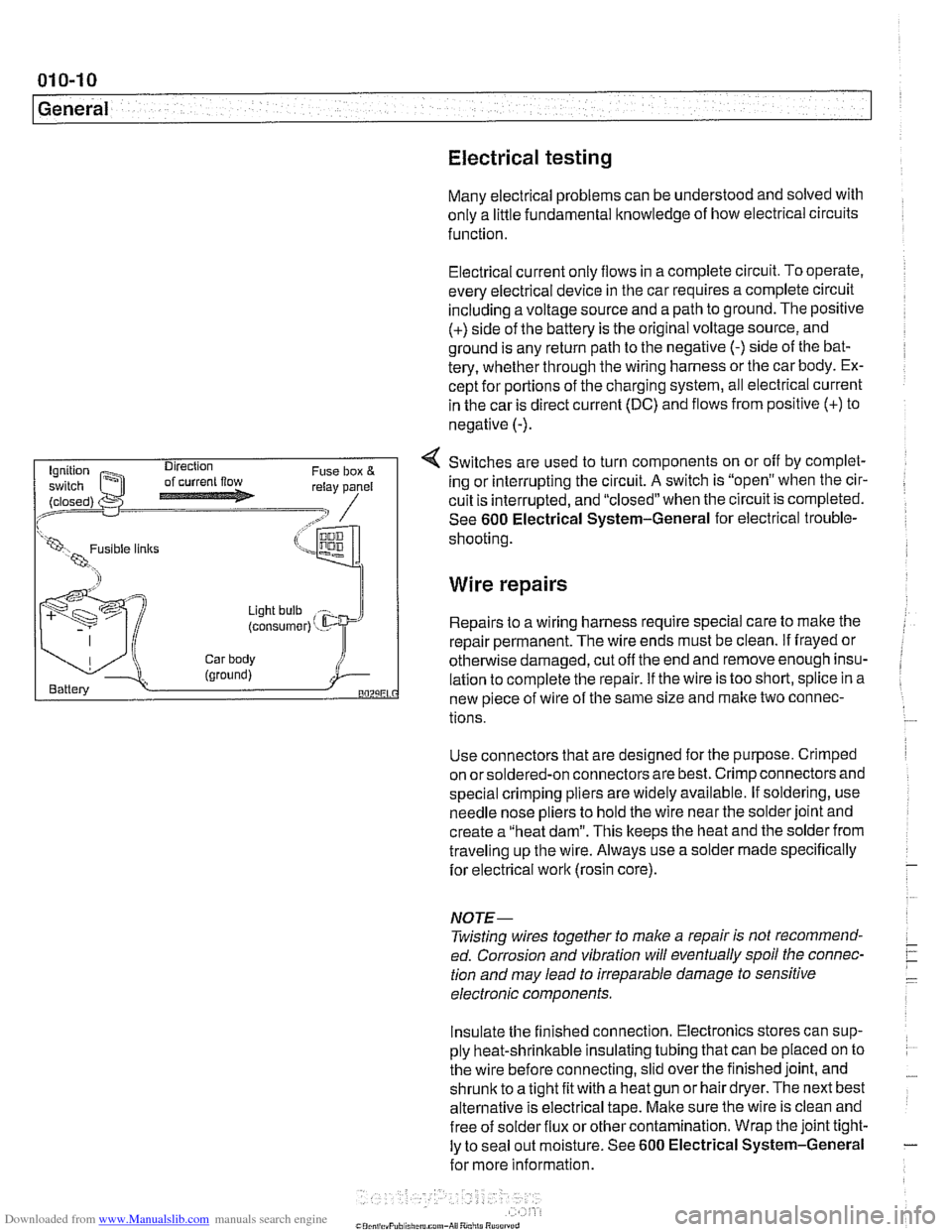
Electrical testing
Many electrical problems can be understood and solved with
only a little fundamental knowledge of how electrical circuits
function.
Electrical current
only flows in a complete circuit. To operate.
every electrical device in the car requires a complete circuit
including a voltage source and a path to ground. The positive
(+) side of the battery is the original voltage source, and
ground is any return path to the negative
(-) side of the bat-
tery, whether through the wiring harness or the car body. Ex-
cept for portions of the charging system, all electrical current
in the car is direct current (DC) and flows from positive
(+) to
negative
(-).
4 Switches are used to turn components on or off by complet-
ing or interrupting the circuit.
A switch is "open" when the cir-
cuit is interrupted, and "closed" when the circuit is completed.
See
600 Electrical System-General for electrical trouble-
(LW, 1 shooting
Wire repairs
Light bulb
(consumer) ' - Repairs to a wiring harness require special care to make the
repair permanent. The wire ends must be clean.
if frayed or
Car body otherwise damaged, cut off the end and remove enough insu- (ground) i Battery lation to complete the repair. if the wire is too short, splice in a BOZLiEL new piece of wire of the same size and make two connec-
tions.
Use connectors that are designed for the purpose. Crimped
on orsoldered-on connectors are best. Crimp connectors and
special crimping pliers are widely available. If soldering, use
needle nose pliers to hold the wire near the solder joint and
create a "heat dam". This keeps the heat and the solder from
traveling up the wire. Always use a solder made specifically
for electrical
work (rosin core).
NOJE-
Twisting wires together to make a repair is not recommend-
ed. Corrosion and vibration will eventually spoil the connec-
tion and may lead to irreparable damage to sensitive
electronic components.
Insulate the finished connection. Electronics stores can sup-
ply heat-shrinkable insulating tubing that can be placed on to
the wire before connecting, slid over the finished joint, and
shrunic to a tight fit with a heat gun or hair dryer. The next best
alternative is electrical tape. Make sure the wire is clean and
free of
solder flux or other contamination. Wrap the joint tight-
ly to seal out moisture. See
600 Electrical System-General
for more information.
Page 71 of 1002

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine
Two common causes of driveability problems are incorrect
system voltage and bad grounds.
System voltage
Digital motor electronics (DME) requires that the system (bat-
tery) voltage be maintained within a narrow range of DC volt-
age.
DC voltage levels beyond or below the operating range,
or any
AIC voltage in the electrical system can cause havoc.
When troubleshooting an illuminated MIL, make sure the bat-
tery is fully charged and capable of delivering all its power to
the electrical system. An undercharged battery can amplify
AIC alternator output ripple.
To
make a quick check of the battery charge, measure the
voltage across the battery terminals with all cables attached
and the ignition off.
Afully charged battery will measure 12.6
volts or slightly more, compared to 12.1 5 volts for a battery
with a 25% charge.
The DME system operates at low voltage and current levels,
making it sensitive to small increases in resistance. The elec-
trical system is routinely subjected to corrosion, vibration and
wear, so faults or corrosion in the wiring harness and connec-
tors are not uncommon. Check the battery terminals
forcorro-
sion or loose cable connections. See 121 Battery, Starter,
Alternator for additional information.
If a battery cable connection has no
v~sible faults but is still
suspect, measure the voltage drop across the connection. A
large drop indicates excessive resistance, meaning that the
connection is corroded, dirty, or damaged. Clean or repairthe
connection and retest.
NOTE-
For instructions on conducting a voltage drop test and other
general electrical troubleshooting information, see
600 Elec-
trical System-General.
Visually inspect all wiring, connectors, switches and fuses in
the system. Loose or damaged connectors can cause inter-
mittent problems, especially the small terminals in the ECM
connectors. Disconnect the wiring harness connectors to
check for corrosion, and use electrical cleaning spray to re-
move contaminants.
Main grounds
Good grounds are critical to proper DME operation. If a
ground connection has no visible faults but is still suspect.
measure the voltage drop across the connection. A large volt-
age drop means high resistance. Clean or repair the connec-
tion and retest.
LBuntr.yP~sbhnllcn.can#-AII A,~iltl Rcsrwsd
Page 368 of 1002

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine
- -
Battery, Starter, Alternator
This section covers the battery, alternator, starter and associ-
ated components of the electrical system.
Troubleshooting information
forthese components isfound in
Table a. Battery, alternator and starter troubleshooting.
For additional electrical troubleshooting information, see
600 Electrical System-General.
Special tools
4 Automotive digital multimeter
CAUTION-
Only use a digital multirneter when testing automotive electri- I) cal components.
4 Closed-circuit current measurement adaptor
(Tool No.
BMW 61 2 300)
Engine electrical system
The alternator and starter are wired directly to the battery. To
prevent accidental shorts that might blow a fuse or damage
wires and electrical components, always disconnect the
negative
(-) battery cable before working on the electrical
system.
Various versions of alternators, voltage regulators, starters,
and batteries are used in
E39 cars. Replace components ac-
cording to the original equipment specification.
Page 431 of 1002

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine
. -
Fuel Injection I
Working inside E-box, disconnect ECM harness connector
(arrow) by releasing fastener and pivoting connector up and
off ECM.
CA UTIOW
Be sure ignition is OFF before disconnecting or reconnecting
DME system components.
Remove ECM from retaining brackets and lift off holder.
Installation is reverse of removal
Before attempting to start engine, use
BMW service tester
DISplus, MoDiC, GTl or equivalent:
* Code replacement ECM with application information (i.e
engine code, transmission type, etc.).
Align ECM to EWS (electronic immobilizer).
Siemens MS 42.0 and MS 43.0
ECM pin assignments
ECM pin assignments are given in Table c. For engine man-
agement system schematics, see
ELE Electrical Wiring Di-
agrams.
/ CAUTIOW I
Al~ays wait at least one mfnule after turning off the ignition
before
remov;ng [he connecror irom rhe ECM. If the con-
nector is removed before this time, residual power
in the
system relay may damage the
ECM.
Always connect or disconnect the control module con-
nector and meter probes with the ignition off.
When making checks at the ECM itself, a
breakout box
should be used to allow tests to be made with the connector
attached to the ECM. This also prevents damage to the small
terminals in the connector. As an alternative, the harness
connector housing can be separated so that electrical checks
can be made from the back of the connector.
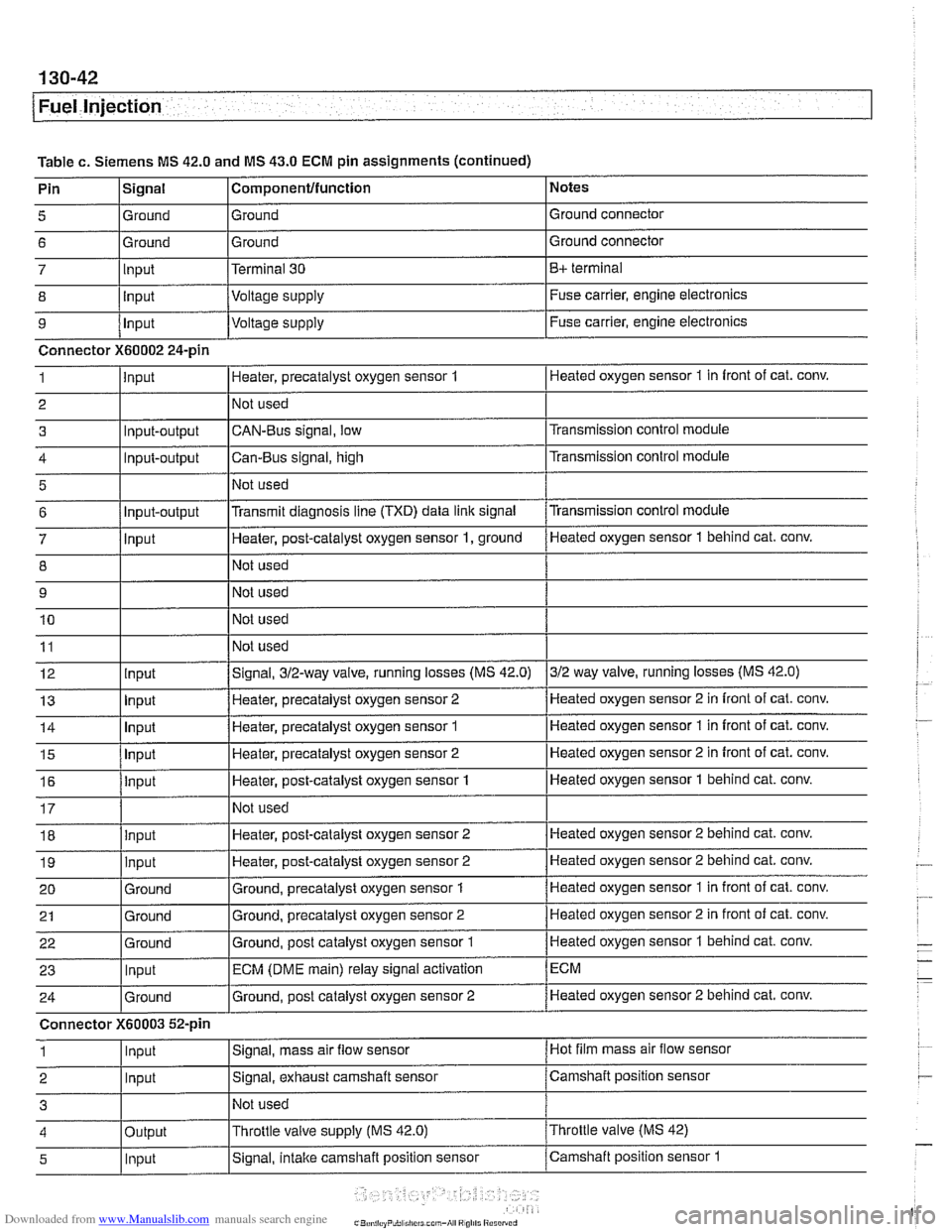
Table
c. Siemens MS 42.0 and MS 43.0 ECM pin assignments
Pin
lslgnal l~om~onentlfunction 1 Notes
Connector
X60001 9-pin black
1 loutput I~erminai 15 I Unloeder relay terminal 15
2 I 1 Not used I
3 Not used
4 Ground
Ground Ground
point
Page 432 of 1002
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine
.-
/Fuel Injection
I ' I - I
9 /ln~ut l~oltaqe supply I Fuse carrier, engine electronics
Table
c. Siemens MS 42.0 and MS 43.0 ECM pin assignments (continued) I ' I . I
Connector X60002 24-pin
1 linput IHeater, precatalyst oxygen sensor 1 I Heated oxygen sensor 1 in front of cat. conv.
I I I
18 llnout IHeater, post-catalyst oxygen sensor 2 ]Heated oxygen sensor 2 behind cat. conv.
Notes
Ground connector
Ground connector
B+ terminal
Fuse carrier, engine electronics
Pin
5
6
7
8
I I I
4 loutput l~hrottle valve supply (MS
42.0) I~hrottle valve (MS 42)
Signal
Ground
Ground Input
lnout
19
20 21
22
23
24
Connector
1
2
3
I I I
5 1 lnput ISignal, intake camshaft position sensor /camshaft position sensor 1
Componentlfunction
Ground
Ground
Terminal 30
Voltaae
SUDP~V
input
Ground
Ground
Ground
Input
Ground
X60003 52-pin
Input
Input
~ -
Heater, post-catalyst oxygen sensor 2
Ground, precatalyst oxygen sensor
1
Ground, precatalyst oxygen sensor 2
Ground, post catalyst oxygen sensor
1
ECM (DME main) relay signal activation
Ground, post catalyst oxygen sensor 2
Signal, mass air
flow sensor
Signal, exhaust camshaft sensor
Not used Heated
oxygen sensor 2 behind cat.
conv.
Heated oxygen sensor 1 in front of cat. conv.
Heated oxygen sensor 2 in front of cat. conv.
Heated oxygen sensor
1 behind cat. conv.
ECM
Heated oxygen sensor 2 behind cat. conv.
Hot film mass air flow sensor
Camshaft position sensor
Page 434 of 1002
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine
Fuel Injection
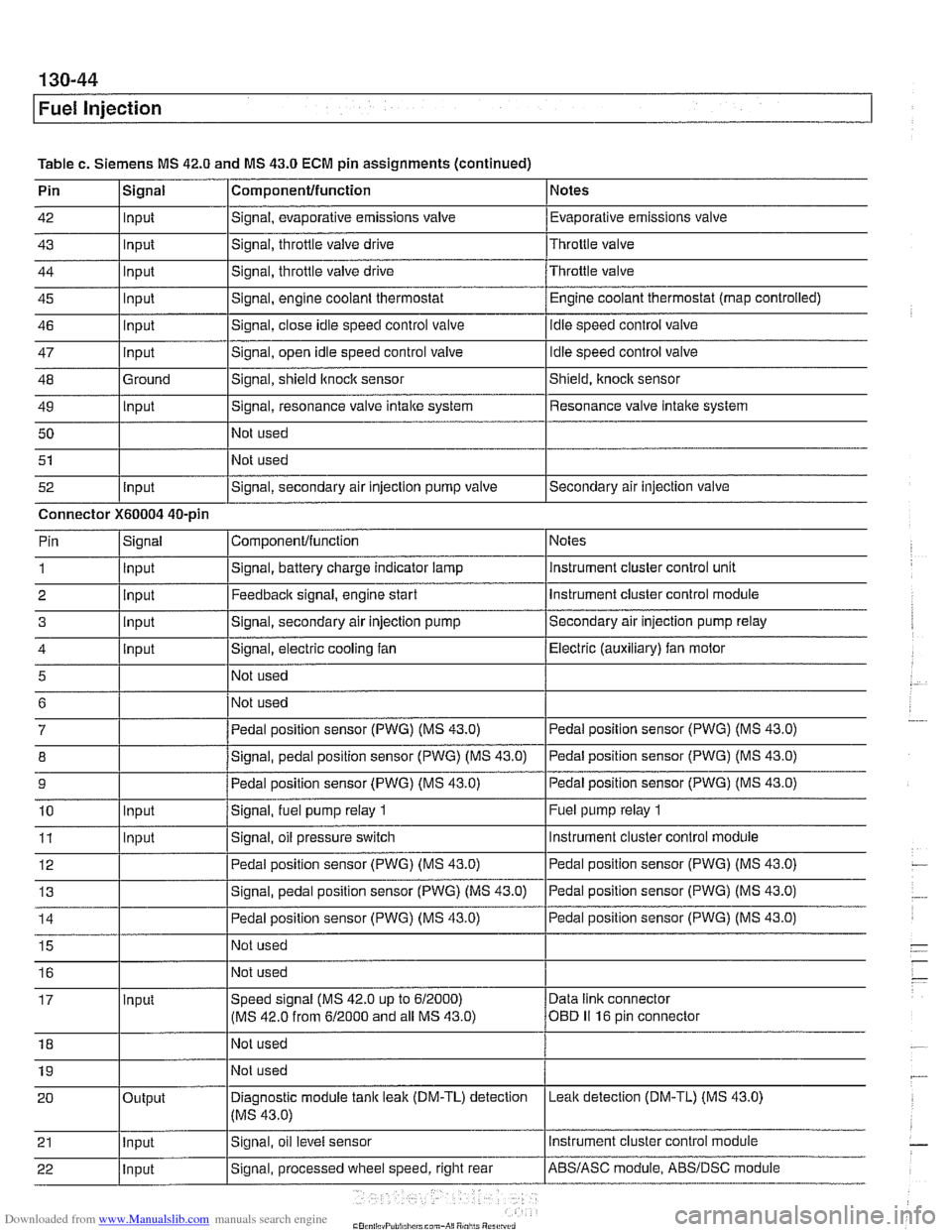
Table c. Siemens MS 42.0 and MS 43.0 ECM pin assignments (continued)
Pin
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49 50
51
52 Componentlfunction
Signal, evaporative emissions valve
Signal, throttle
valve drive
Signal, throttle valve drive
Signal, engine coolant thermostat
Signal, close idle speed control valve
Signal, open idle speed control valve
Signal, shield
ltnock sensor
Signal, resonance valve
intake system
Not used
Not used
Signal, secondary air injection pump valve
Signal
Input
Input
Input
Input
input
Input
Ground
Input
Input
Notes
Evaporative emissions valve
Throttle valve
Throttle valve Engine coolant thermostat (map controlled)
idle speed control valve
Idle speed control valve
Shield,
knock sensor
Resonance valve intake system
Secondary air injection valve
Connector
X60004 40-pin Notes
instrument cluster control unit
Instrument cluster control module
Secondary air injection pump relay
Electric (auxiliary) fan motor
Pedal position sensor (PWG) (MS 43.0)
Pedal position sensor (PWG) (MS 43.0)
Pedal position sensor (PWG) (MS 43.0)
Fuel pump relay
1
Instrument cluster control module
ComponenVfunction
Signal, battery charge indicator lamp
Feedback signal, engine start
Signal, secondary air injection pump
Signal, electric cooling fan
Not used
Not used
Pedal position sensor (PWG) (MS 43.0)
Signal, pedal position sensor (PWG) (MS 43.0)
Pedal position sensor (PWG) (MS 43.0)
Signal,
fuel pump relay 1
Signal, oil pressure switch
Pin
1
2 3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11 Signal
Input
Input
input
input
Input
Input
Page 435 of 1002
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine
Fuel Injection
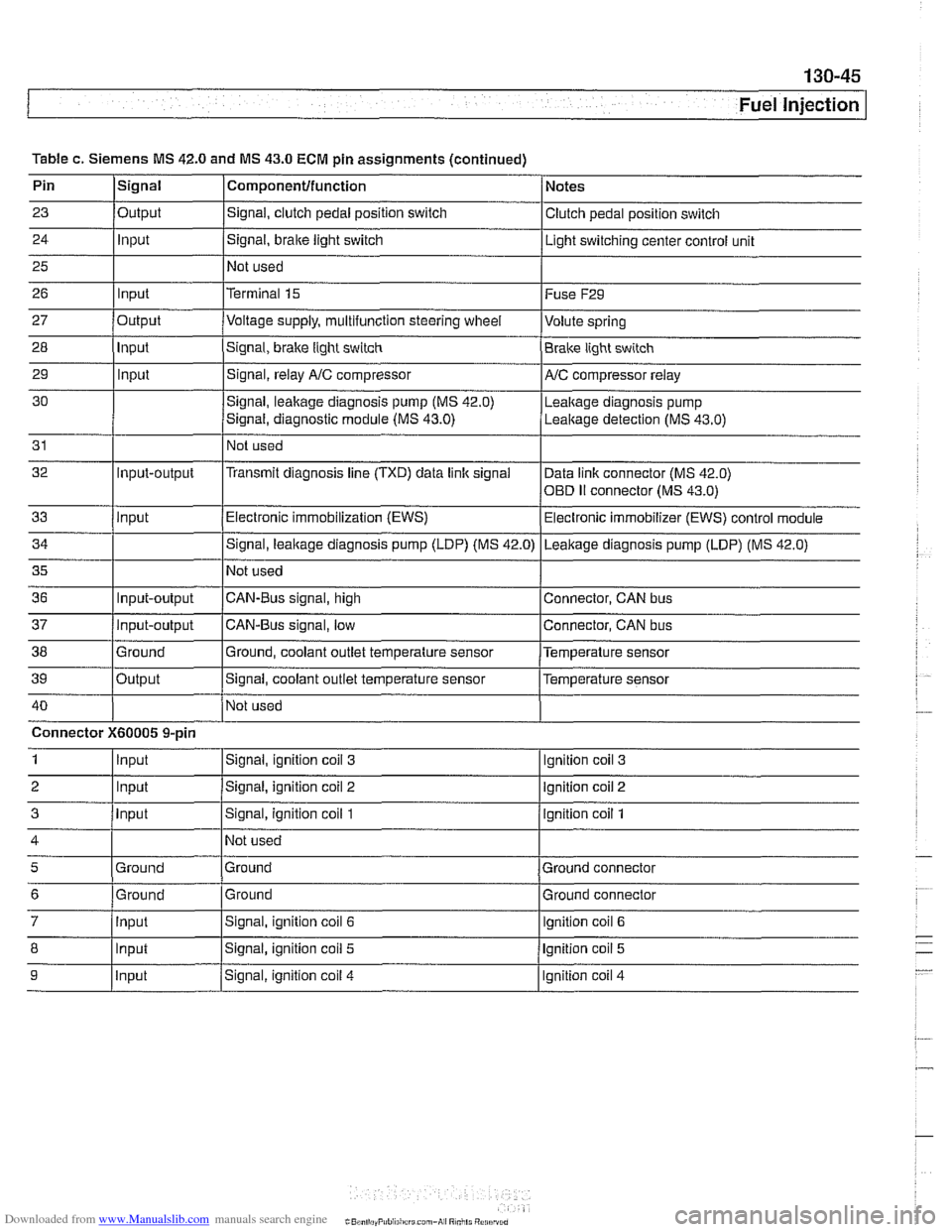
Table c. Siemens MS 42.0 and MS 43.0 ECM pin assignments (continued)
40
I I - . I -
9 llnput /signal, ignition coil 4 I Ignition coil 4
Not used
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
Connector X60005 9-pin
Input
Input
Input
Ground
Ground
Input
Input
Signal, ignition coil 3
Signal, ignition coil 2
Signal, ignition coil 1
Not used
Ground Ground
Signal, ignition coil
6
Signal, ignition coil 5
Ignition coil 3
Ignition coil 2
Ignition coil 1
Ground connector
Ground connector
Ignition coil
6
lqnition coil 5
Page 452 of 1002
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine
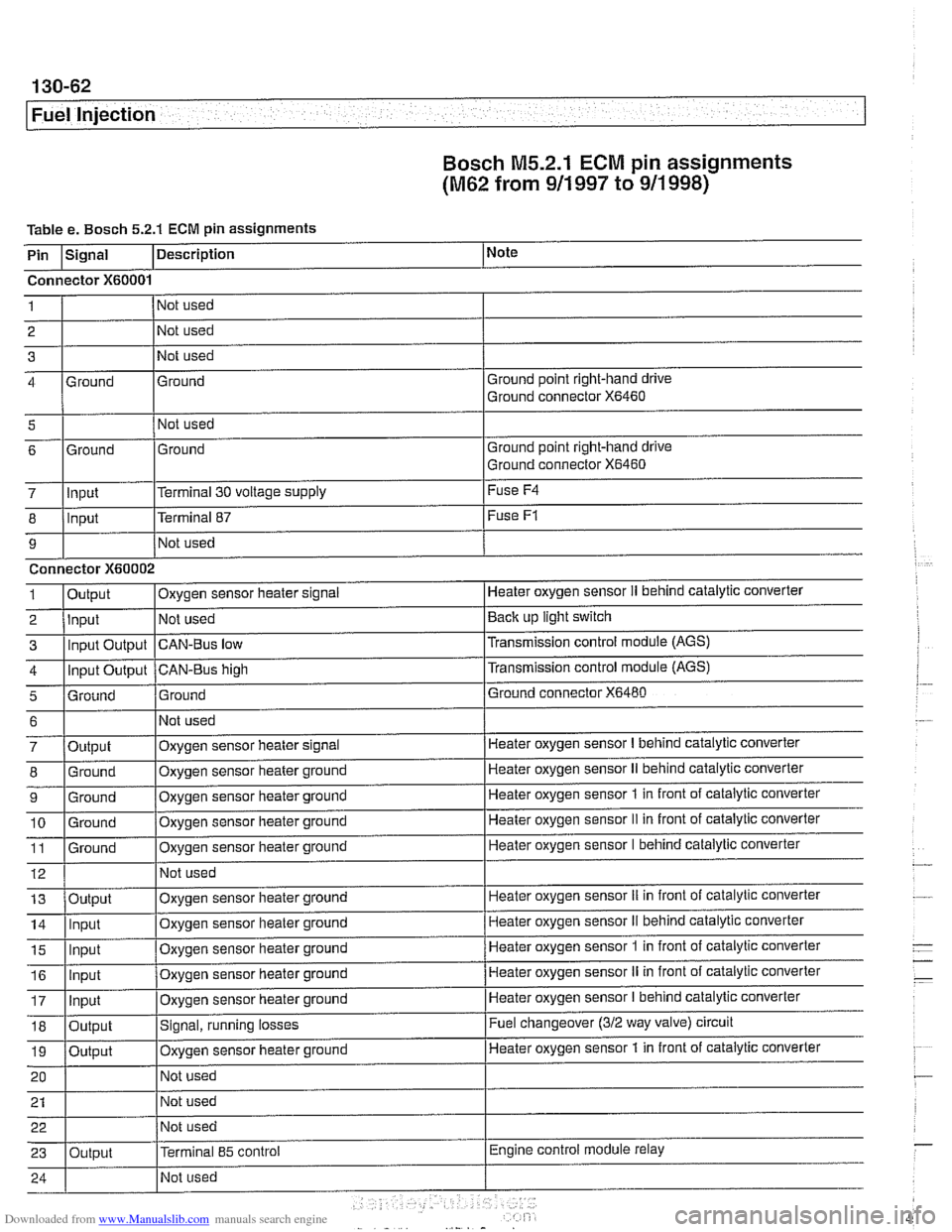
130-62
Fuel Injection
Bosch M5.2.1
ECM pin assignments
(M62 from 911 997 to 911 998)
Table e. Bosch 5.2.1 ECM pin assignments
i I I
5 1 I Not used
I
I I
Note
I I I
7 lln~ut l~erminal 30 voltage supply I Fuse
F4
Description
Pin
Ground point right-hand drive
Ground connector
X6460
I I I
Signal
Connector
X60001
Ground 4 1
2
3 Ground
Ground point right-hand drive
Ground connector
X6460 6
8
9 1
2
3
4
5
Not used
Not used
Not used
-
6
7
8
9
10 11
12
Ground
Input
Connector
X60002
Output Input Input Output
Input Output
Grniind
. -
13
14
15
Ground
- .- -
Output
Ground
Ground
Ground
Ground
16
17
18
19
20
21 22
23
.
Terminal 87
Not used
Oxygen sensor heater
slgnal
Not used
CAN-Bus low
CAN-BUS high
Ground
Output Input
ln~ut
Fuse F1
Heater oxygen sensor II behind cataiytic converter
Back up light switch
Transmission control module (AGS)
Transmission control module
(AGS)
Ground connector X6480
Not used
Oxygen sensor heater signal
Oxygen sensor heater ground
Oxygen sensor heater ground
Oxygen sensor heater ground
Oxygen sensor heater ground
Not used
Input
Input
Output
Output
Output Heater oxygen sensor
I behind catalytic converter
Heater oxygen sensor
II behind catalytic converter
Heater oxygen sensor
1 in front of catalytic converter
Heater oxygen sensor
II in front of catalytic converter
Heater oxygen sensor I behind catalytic converter
Oxygen sensor heater ground
Oxygen sensor heater ground
Oxvqen sensor heater ground Heater oxygen sensor
iI in front
of catalytic converter
Heater oxygen sensor
II behind catalytic converter
Heater oxygen sensor
1 in front of catalytic converter . -
Oxygen sensor heater ground
Oxygen sensor heater ground
Signal, running losses
Oxygen sensor iieater ground
Not used
Not used
Not used
Terminal
85 control
Heater oxygen sensor II in front of catalytic converter
Heater oxygen sensor
I behind catalytic converter
Fuel changeover
(312 way valve) circuit
Heater oxygen sensor 1 in front of catalytic converter
Engine control module relay
Page 453 of 1002
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine
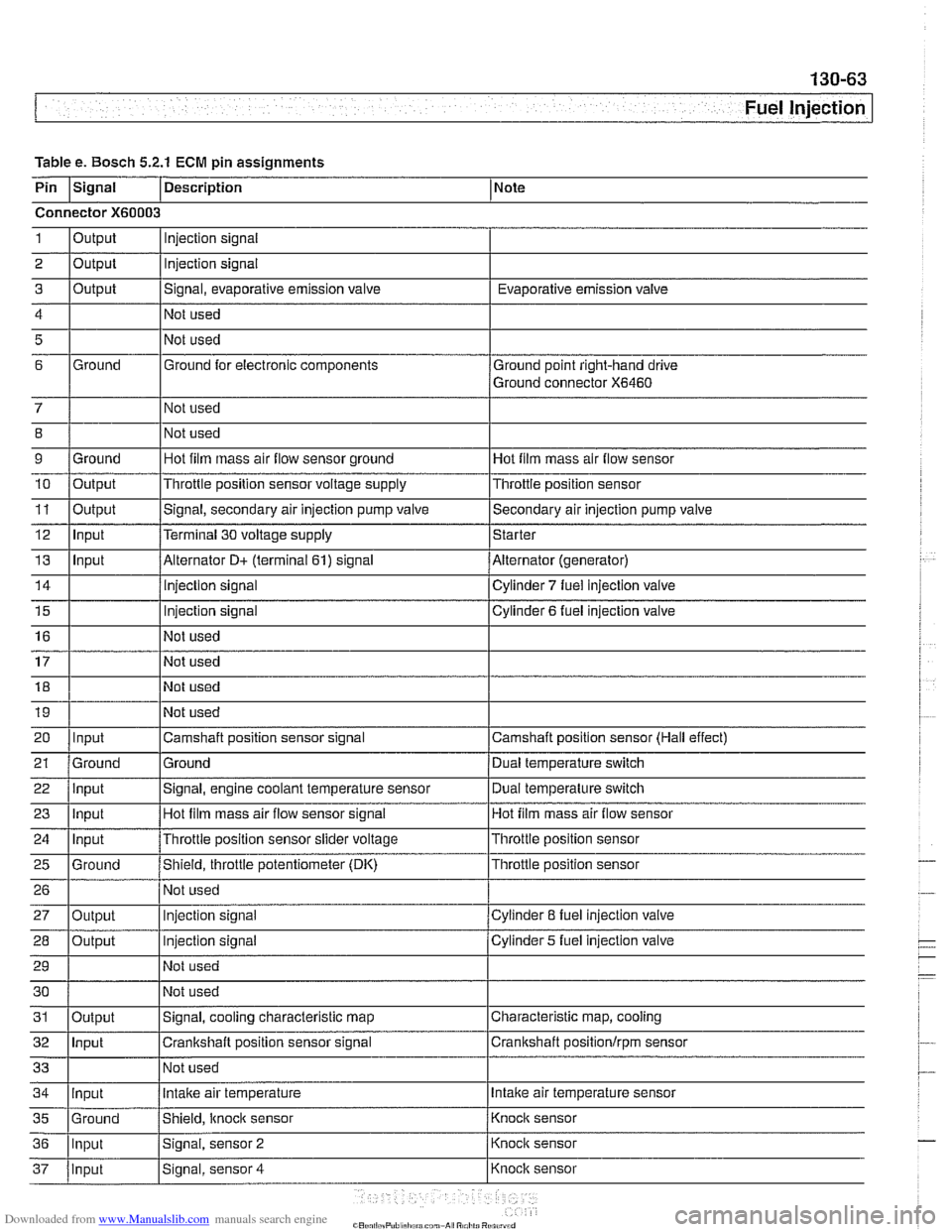
Fuel lnjection
Table e. Bosch 5.2.1 ECM pin assignments
Pin
Isignal 1 Description 1 Note
Connector
X60003
1
2
3
4
5
6
7 8
9 10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
ate alr empe
Output
Output
Output
Ground
Ground
Output
Output Input
Input
Input
Ground
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
Injection signal
Injection signal
Signal, evaporative emission valve
Not used
Not used
Ground for electronic components
Not used
Not used
Hot film mass air flow sensor ground
Throttle position sensor voltage supply
Signal, engine coolant temperature sensor
Hot
film mass air flow sensor signal
Throttle position sensor slider voltage
Shield, throttle potentiometer (DK) Not used
Injection signal
Injection signal
Not used
Not used
Input
Input
Input
Ground
Output
Output Evaporative emission
valve
Ground point right-hand drive
Ground connector
X6460
Hot film mass air flow sensor
Throttle position sensor
Signal, secondary air injection pump valve
Terminal
30 voltage supply
Alternator
D+ (terminal 61) signal
injection signal
Injection
signal
Not used
Not used
Not used
Not used
Camshaft position sensor signal
Ground Dual temperature switch
Hot film mass air flow sensor
Throttle position sensor
Throttle position sensor
Cylinder
8 fuel injection valve
Cylinder
5 fuel injection valve
Secondary air injection pump
valve
Starter
Alternator (generator)
Cylinder
7 fuel injection valve
Cylinder 6 fuel injection valve
Camshaft position sensor (Hall effect) Dual temperature
switch