navigation system BMW 7 SERIES LONG 2007 E66 MOST Bus Diagnosis Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: BMW, Model Year: 2007, Model line: 7 SERIES LONG, Model: BMW 7 SERIES LONG 2007 E66Pages: 20, PDF Size: 0.13 MB
Page 3 of 20
3
MOST Bus Diagnosis
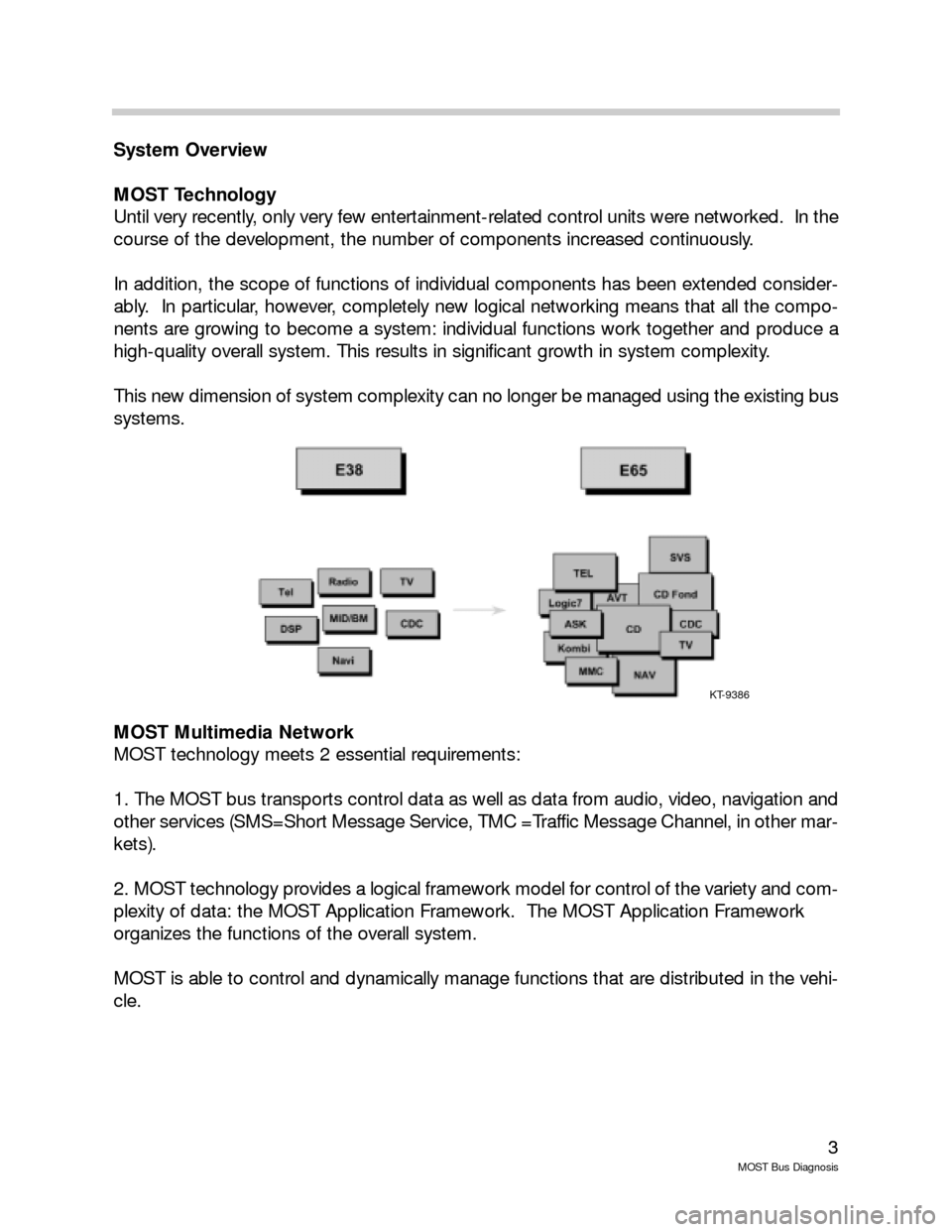
System Overview
MOST Technology
Until very recently, only very few entertainment-related control units were networked. In the
course of the development, the number of components increased continuously.
In addition, the scope of functions of individual components has been extended consider-
ably. In particular, however, completely new logical networking means that all the compo-
nents are growing to become a system: individual functions work together and produce a
high-quality overall system. This results in significant growth in system complexity.
This new dimension of system complexity can no longer be managed using the existing bus
systems.
MOST Multimedia Network
MOST technology meets 2 essential requirements:
1. The MOST bus transports control data as well as data from audio, video, navigation and
other services (SMS=Short Message Service, TMC =Traffic Message Channel, in other mar-
kets).
2. MOST technology provides a logical framework model for control of the variety and com-
plexity of data: the MOST Application Framework. The MOST Application Framework
organizes the functions of the overall system.
MOST is able to control and dynamically manage functions that are distributed in the vehi-
cle.
KT-9386
Page 5 of 20
5
MOST Bus Diagnosis
Functional Description
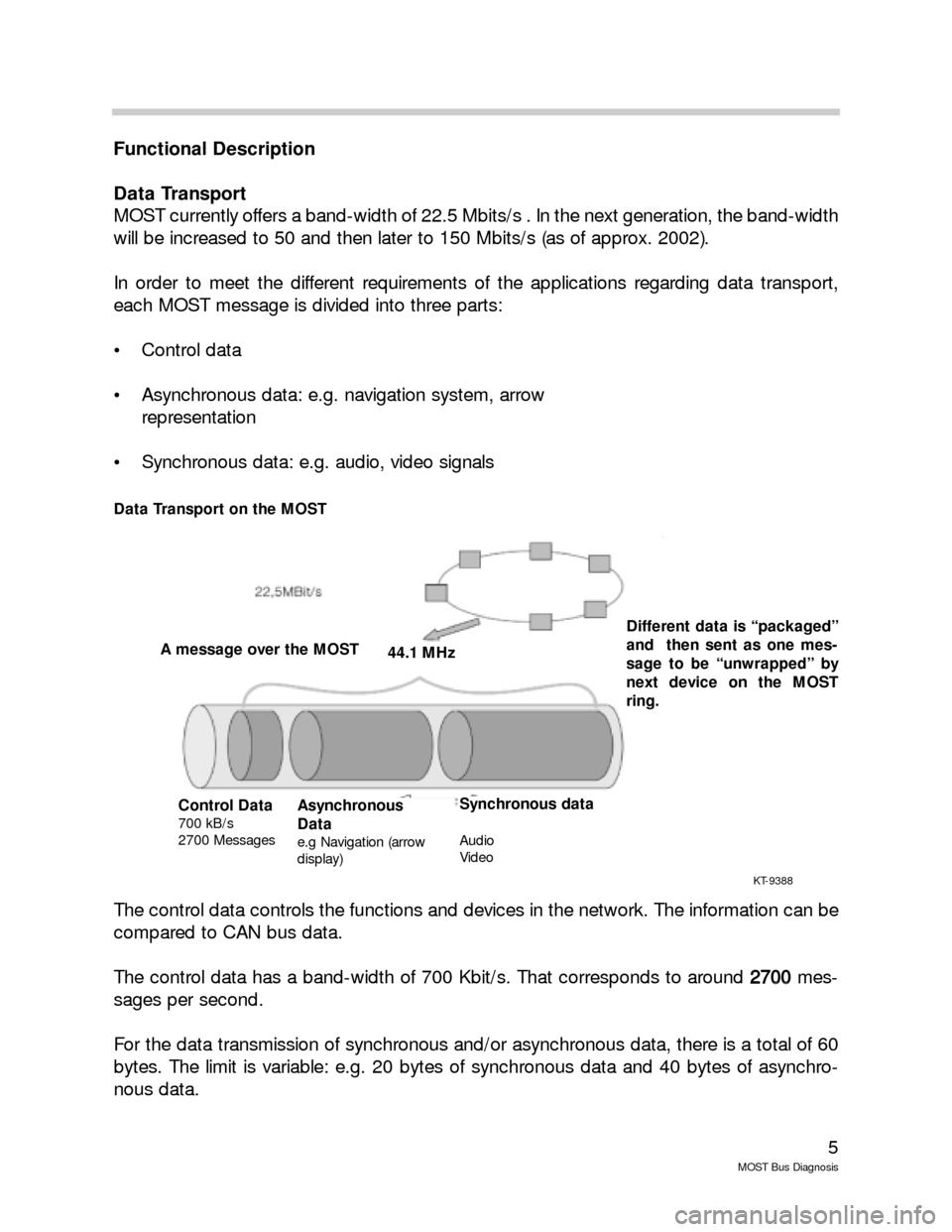
Data Transport
MOST currently offers a band-width of 22.5 Mbits/s . In the next generation, the band-width
will be increased to 50 and then later to 150 Mbits/s (as of approx. 2002).
In order to meet the different requirements of the applications regarding data transport,
each MOST message is divided into three parts:
Control data
Asynchronous data: e.g. navigation system, arrow
representation
Synchronous data: e.g. audio, video signals
The control data controls the functions and devices in the network. The information can be
compared to CAN bus data.
The control data has a band-width of 700 Kbit/s. That corresponds to around 2 27
70
00
0
mes-
sages per second.
For the data transmission of synchronous and/or asynchronous data, there is a total of 60
bytes. The limit is variable: e.g. 20 bytes of synchronous data and 40 bytes of asynchro-
nous data.
A message over the MOST
Control Data
700 kB/s
2700 Messages
Asynchronous
Data
e.g Navigation (arrow
display)
Synchronous data
Audio
Video
Data Transport on the MOST
Different data is “packaged”
and then sent as one mes-
sage to be “unwrapped” by
next device on the MOST
ring.
KT-9388
44.1 MHz
Page 9 of 20

9
MOST Bus Diagnosis
Audio Master
As audio master, the ASK has the task to collect and process all the audio signals of the
vehicle and to distribute them to their destinations.
The ASK controls all the acoustic requests from the Control Display. The changes in the
level of a signal is not sudden, but smooth, e.g. during suppression, insertion and fading
out or temporary suppression of the signal at the destination: Because of this, a high-qual-
ity acoustic sound is obtained.
The ASK also assumes the generation and preparation of different acoustic signals, e.g.
PDC signals and warnings. In the event of a request for a warning or caution signal from
a control unit, the ASK provides a clean acoustic change of the signals.
Audio data
All audio data from any control unit are converted by the ASK into digital audio AF
format at a sampling rate of 44.1 MHz.
Categorization of audio sources
All possible audio sources are divided into different groups according to priority. Warning
signals have priority over any other audio source. Mixing of lower priority audio signals
(e.g. navigation, radio) is possible.
Generation of acoustic gongs
These are acoustic alarm signals which help the driver perceive sounds according to a
system. The different sounds, requested by the different control units, (e.g. gongs, PDC,
etc.), must be generated only in association with a visual indication. These come from
the instrument cluster and the Control Display.
The following sounds can be generated in the ASK.
Beeping for the PDC.
Various Check Control and warning gongs.
Note:
A maximum of three sounds can be produced at once. Sounds are produced in order of
importance. Sounds requested exceeding three will be lost.
Connection Master
As connection master, the ASK must provide channels to the equipment connected to the
bus and distribute the audio signals on the outputs (loudspeakers).
The connection master also controls the basic Hi-Fi or the LOGIC 7 Hi-Fi amplifiers.
Page 10 of 20

10
MOST Bus Diagnosis
CD Changer Audio (CDC)
The CD changer is a slave control unit in the MOST framework.
Navigation System (NAV 01)
The control unit of the navigation system has controller tasks and slave functions in the
MOST framework.
Slave Control Units
The following control units are slave control units:
Kombi (control unit of the instrument cluster)
AVT
LOGIC7
SVS Speech processing system
Telephone
MMC
Component Locations
Located in the dashboard assembly:
Control Display
CD Changer
ASK
Kombi
OPPS Connector
Located in the luggage compartment, rear left:
Logic 7
SVS
NAV
MMC
Telephone
Located in the C pillar left side:
AVT
Page 11 of 20
11
MOST Bus Diagnosis
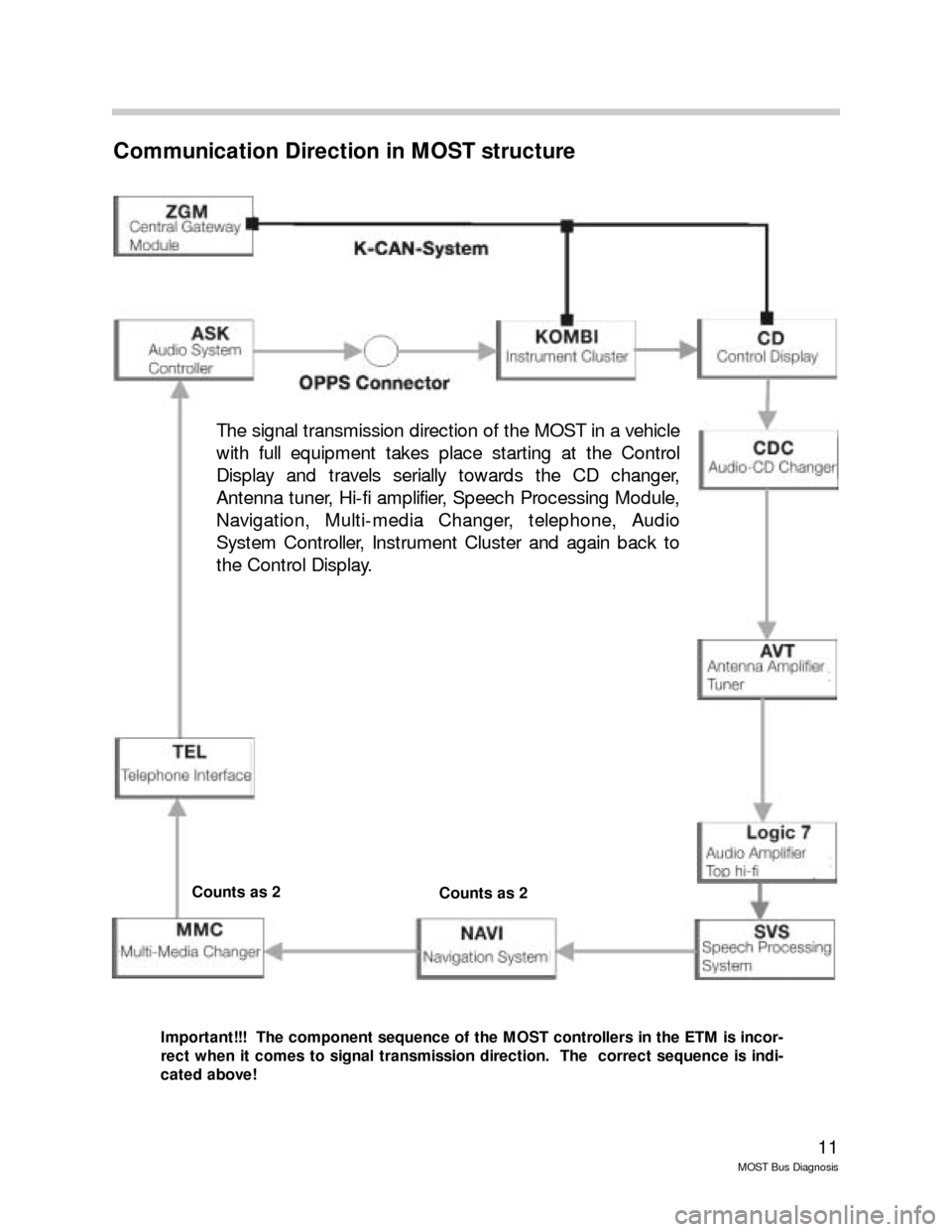
Communication Direction in MOST structure
Important!!! The component sequence of the MOST controllers in the ETM is incor-
rect when it comes to signal transmission direction. The correct sequence is indi-
cated above!
The signal transmission direction of the MOST in a vehicle
with full equipment takes place starting at the Control
Display and travels serially towards the CD changer,
Antenna tuner, Hi-fi amplifier, Speech Processing Module,
Navigation, Multi-media Changer, telephone, Audio
System Controller, Instrument Cluster and again back to
the Control Display.
Counts as 2Counts as 2