check engine BMW X5 2001 E53 M62TU Engine Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: BMW, Model Year: 2001, Model line: X5, Model: BMW X5 2001 E53Pages: 37, PDF Size: 3.87 MB
Page 7 of 37
7
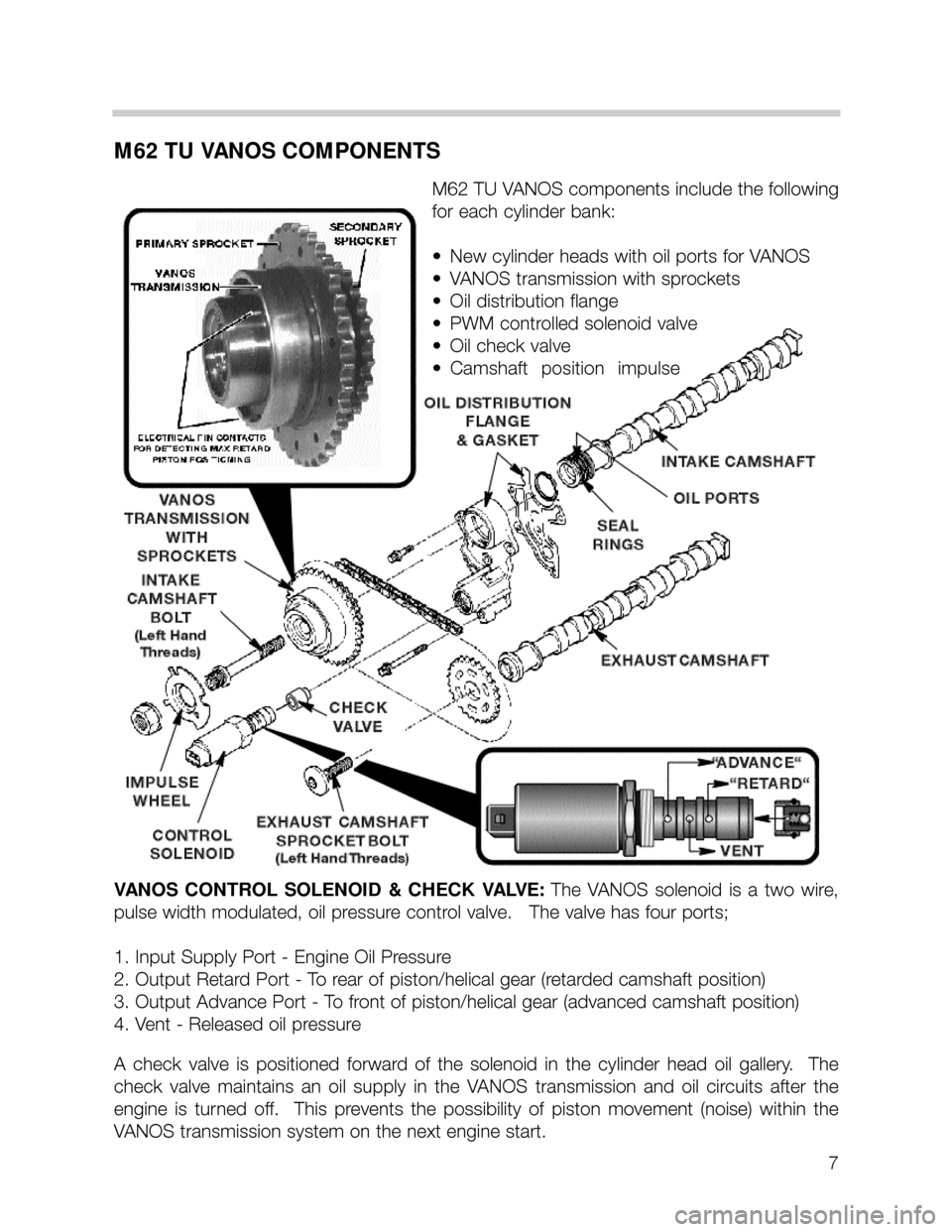
M62 TU VANOS COMPONENTS
M62 TU VANOS components include the following
for each cylinder bank:
•New cylinder heads with oil ports for VANOS
•VANOS transmission with sprockets
•Oil distribution flange
•PWM controlled solenoid valve
•Oil check valve
•Camshaft position impulse
VANOS CONTROL SOLENOID & CHECK VALVE:The VANOS solenoid is a two wire,
pulse width modulated, oil pressure control valve. The valve has four ports;
1. Input Supply Port - Engine Oil Pressure
2. Output Retard Port - To rear of piston/helical gear (retarded camshaft position)
3. Output Advance Port - To front of piston/helical gear (advanced camshaft position)
4. Vent - Released oil pressure
A check valve is positioned forward of the solenoid in the cylinder head oil gallery. The
check valve maintains an oil supply in the VANOS transmission and oil circuits after the
engine is turned off. This prevents the possibility of piston movement (noise) within the
VANOS transmission system on the next engine start.
Page 17 of 37
17
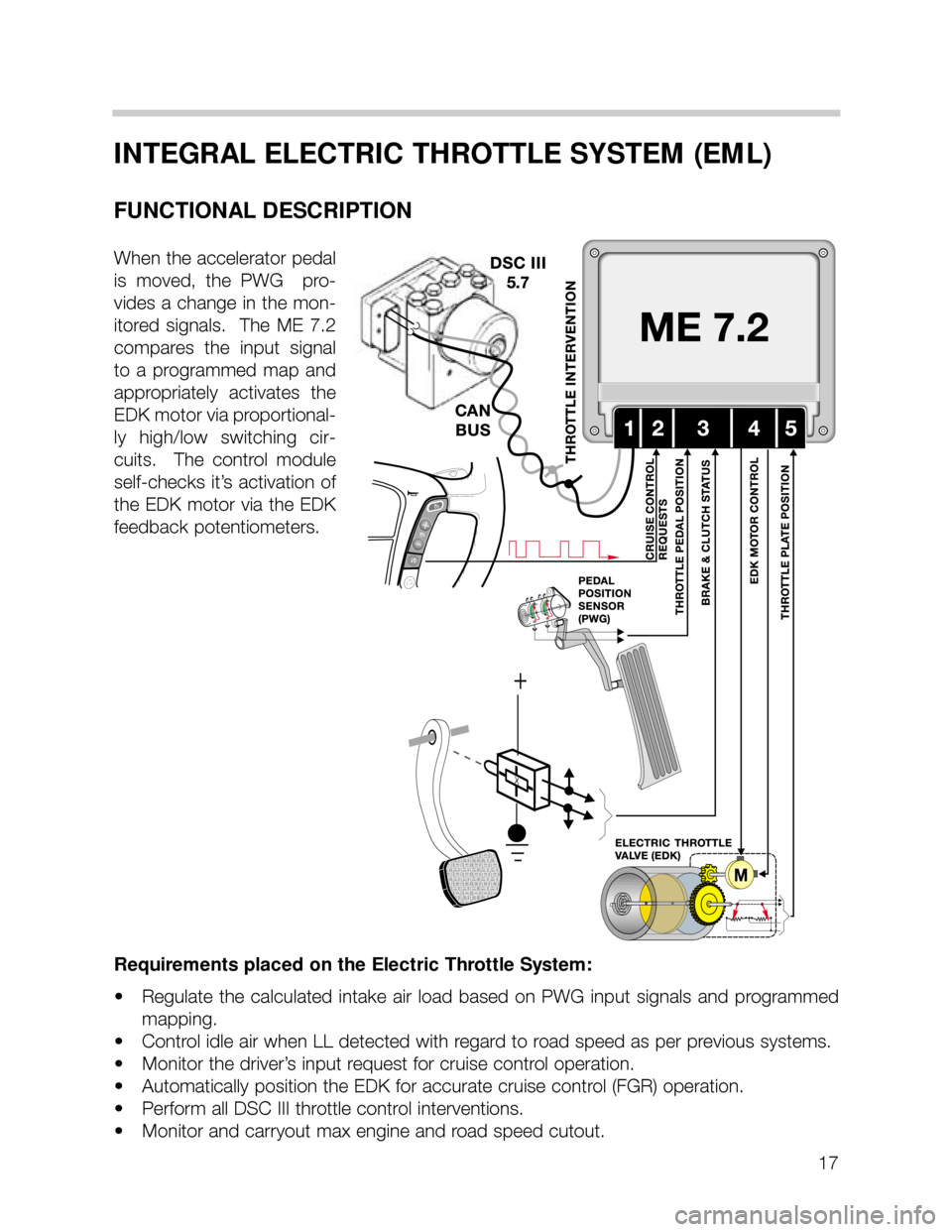
INTEGRAL ELECTRIC THROTTLE SYSTEM (EML)
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
When the accelerator pedal
is moved, the PWG pro-
vides a change in the mon-
itored signals. The ME 7.2
compares the input signal
to a programmed map and
appropriately activates the
EDK motor via proportional-
ly high/low switching cir-
cuits. The control module
self-checks it’s activation of
the EDK motor via the EDK
feedback potentiometers.
Requirements placed on the Electric Throttle System:
• Regulate the calculated intake air load based on PWG input signals and programmed
mapping.
• Control idle air when LL detected with regard to road speed as per previous systems.
• Monitor the driver’s input request for cruise control operation.
• Automatically position the EDK for accurate cruise control (FGR) operation.
• Perform all DSC III throttle control interventions.
• Monitor and carryout max engine and road speed cutout.
Page 18 of 37

18
PWG SIGNAL MONITORING & PWG FAILSAFE OPERATION:
• As a redundant safety feature the PWG provides two separate signals from two integral
potentiometers (Pot 1 and Pot 2) representing the driver’s request for throttle activation.
• If the monitored PWG potentiometer signals are not plausible, ME 7.2 will only use the
lower of the two signals as the driver’s pedal request input providing failsafe operation.
Throttle response will be slower and maximum throttle position will be reduced.
• When in PWG failsafe operation, ME 7.2 sets the EDK throttle plate and injection time
to idle (LL) whenever the brake pedal is depressed.
• When the system is in PWG failsafe operation, the instrument cluster matrix display will
post “Engine Emergency Program” and PWG specific fault(s) will be stored in memory.
EDK FEEDBACK SIGNAL MONITORING & EDK FAILSAFE OPERATION:
• The EDK provides two separate signals from two integral potentiometers (Pot 1 and Pot
2) representing the exact position of the throttle plate.
• EDK Pot 1 provides the primary throttle plate position feedback. As a redundant safe-
ty feature, Pot 2 is continuously cross checked with Pot 1 for signal plausibility.
• If plausibility errors are detected between Pot 1 and Pot 2, ME 7.2 will calculate the
inducted engine air mass (from HFM signal) and only utilize the potentiometer signal that
closely matches the detected intake air mass.
- The ME 7.2 uses the air mass signalling as a “virtual potentiometer” (pot 3) for a
comparative source to provide failsafe operation.
- If ME 7.2 cannot calculate a plausible conclusion from the monitored pots (1 or 2
and virtual 3) the EDK motor is switched off and fuel injection cut out is activated
(no failsafe operation possible).
• The EDK is continuously monitored during all phases of engine operation. It is also
briefly activated when KL 15 is initially switched on as a “pre-flight check” to verify it’s
mechanical integrity (no binding, appropriate return spring tension, etc). This is accom-
plished by monitoring both the motor control amperage and the reaction speed of the
EDK feedback potentiometers. If faults are detected the EDK motor is switched off and
fuel injection cut off is activated (no failsafe operation possible). The engine does how-
ever continue to run extremely rough at idle speed.
• When a replacement EDK is installed, the ME 7.2 adapts to the new component
(required amperage draw for motor control, feedback pot tolerance differences, etc).
This occurs immediately after the next cycle of KL 15 for approximately 30 seconds.
During this period of adaptation, the maximum opening of the throttle plate is 25%.
Page 24 of 37
24
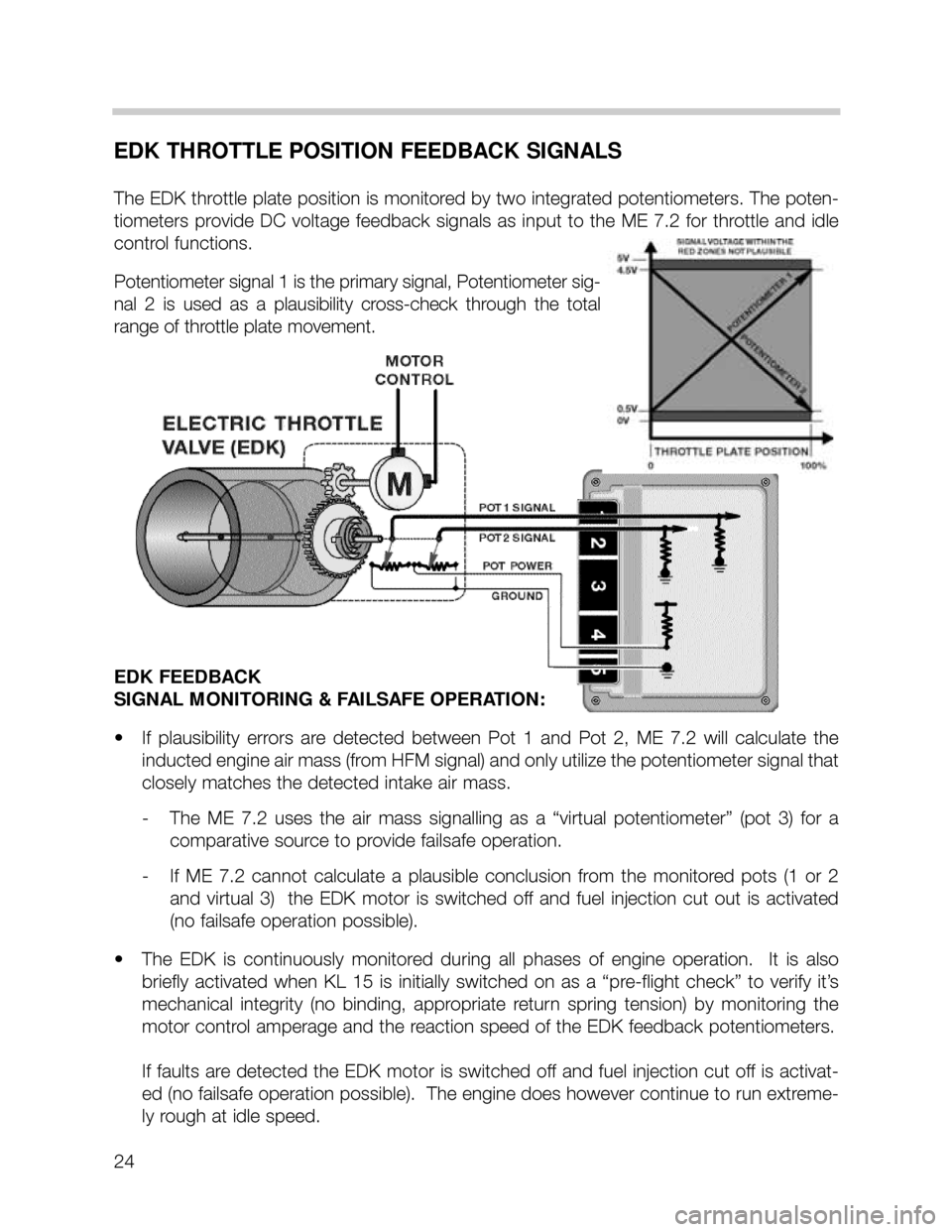
EDK THROTTLE POSITION FEEDBACK SIGNALS
The EDK throttle plate position is monitored by two integrated potentiometers. The poten-
tiometers provide DC voltage feedback signals as input to the ME 7.2 for throttle and idle
control functions.
Potentiometer signal 1 is the primary signal, Potentiometer sig-
nal 2 is used as a plausibility cross-check through the total
range of throttle plate movement.
EDK FEEDBACK
SIGNAL MONITORING & FAILSAFE OPERATION:
• If plausibility errors are detected between Pot 1 and Pot 2, ME 7.2 will calculate the
inducted engine air mass (from HFM signal) and only utilize the potentiometer signal that
closely matches the detected intake air mass.
- The ME 7.2 uses the air mass signalling as a “virtual potentiometer” (pot 3) for a
comparative source to provide failsafe operation.
- If ME 7.2 cannot calculate a plausible conclusion from the monitored pots (1 or 2
and virtual 3) the EDK motor is switched off and fuel injection cut out is activated
(no failsafe operation possible).
• The EDK is continuously monitored during all phases of engine operation. It is also
briefly activated when KL 15 is initially switched on as a “pre-flight check” to verify it’s
mechanical integrity (no binding, appropriate return spring tension) by monitoring the
motor control amperage and the reaction speed of the EDK feedback potentiometers.
If faults are detected the EDK motor is switched off and fuel injection cut off is activat-
ed (no failsafe operation possible). The engine does however continue to run extreme-
ly rough at idle speed.