sensor BMW X5 2002 E53 M54 Engine Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: BMW, Model Year: 2002, Model line: X5, Model: BMW X5 2002 E53Pages: 48, PDF Size: 2.52 MB
Page 1 of 48

Initial Print Date: 02/2000Revision Date: 6/2000
Subject Page
M54 Engine
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Mechanical changes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
Performance Charts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Review Questions. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Siemen’s MS 43.0 System
• Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
• I - P - O . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
MS 43.0 New functions
• Electronic throttle Control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10
• Accelerator Pedal Sensor (PWG) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11
• Electronic Throttle Valve (EDK) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13
• Main Relay Monitor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15
• Engine Optimized Ignition Key OFF . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .16
• Diagnosis Module Tank Leakage (DM-TL) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .17
• DM-TL Function . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .18
• DM-TL Test Procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .20
Carry Over Functions
Inputs
• Oxygen Sensor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .25
• Camshaft Sensors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .26
• Crankshaft Sensor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .27
• Misfire Detection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .28
• OBD Fault Codes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .30
• Mass Air Meter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .31
Outputs
• VANOS Control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .33
• Electric Fan . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .36
• Secondary Air Injection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .37
• Engine Speed Limit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .39
• RZV Ignition . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .40
• Resonance - Turbulence Manifold . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .42
• Idle Speed control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .45
• Cruise Control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .46
• Purge Control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .47
Table of Contents
Page 8 of 48

8
M54engMS43/ST036/6/2000
SIEMENS ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM
Models: E53 X5
SOP: 3 liter - 4/00
Objectives of the Module:
At the end of this section of the handout you will be able to:
• Identify the changes that have occurred to the MS 43 system compared to the MS 42
• Describe the operation of the new inputs
• Describe the operation of the new outputs
• Discuss which new components/subsystems relate directly to ULEV compliancy
This new generation Siemens system is designated as
MS 43.0.
Siemens MS 43.0 is a newly developed engine management system to meet the needs of
Ultra Low Emission Vehicle (ULEV) compliancy and continuing with present systems is also
OBD II compliant. This system also includes control of the Motor-driven Throttle Valve
(EDK).
The ECM uses a pc-board dual-processor control unit in the SKE housing configuration.
The MS 43.0 ECM is flash programmable as seen with previous systems.
ECM hardware includes:
Modular plug connectors featuring 5 connectors in the SKE housing with 134 pins.
• Connector 1 = Supply voltages and grounds
• Connector 2 = Peripheral signals (oxygen
sensors, CAN, etc.)
• Connector 3 = Engine signals
• Connector 4 = Vehicle signals
• Connector 5 = Ignition signals
Special features:
• Flash EPROM which is adaptable to several M52 LEV engines and has the capability to
be programmed up to 13 times
• Once a control unit is installed and coded to a vehicle it cannot be swapped with anoth-
er vehicle for diagnosing or replacement (because of EWS 3.3).
Page 10 of 48
10
M54engMS43/ST036/6/2000
MS 43 NEW FUNCTIONS
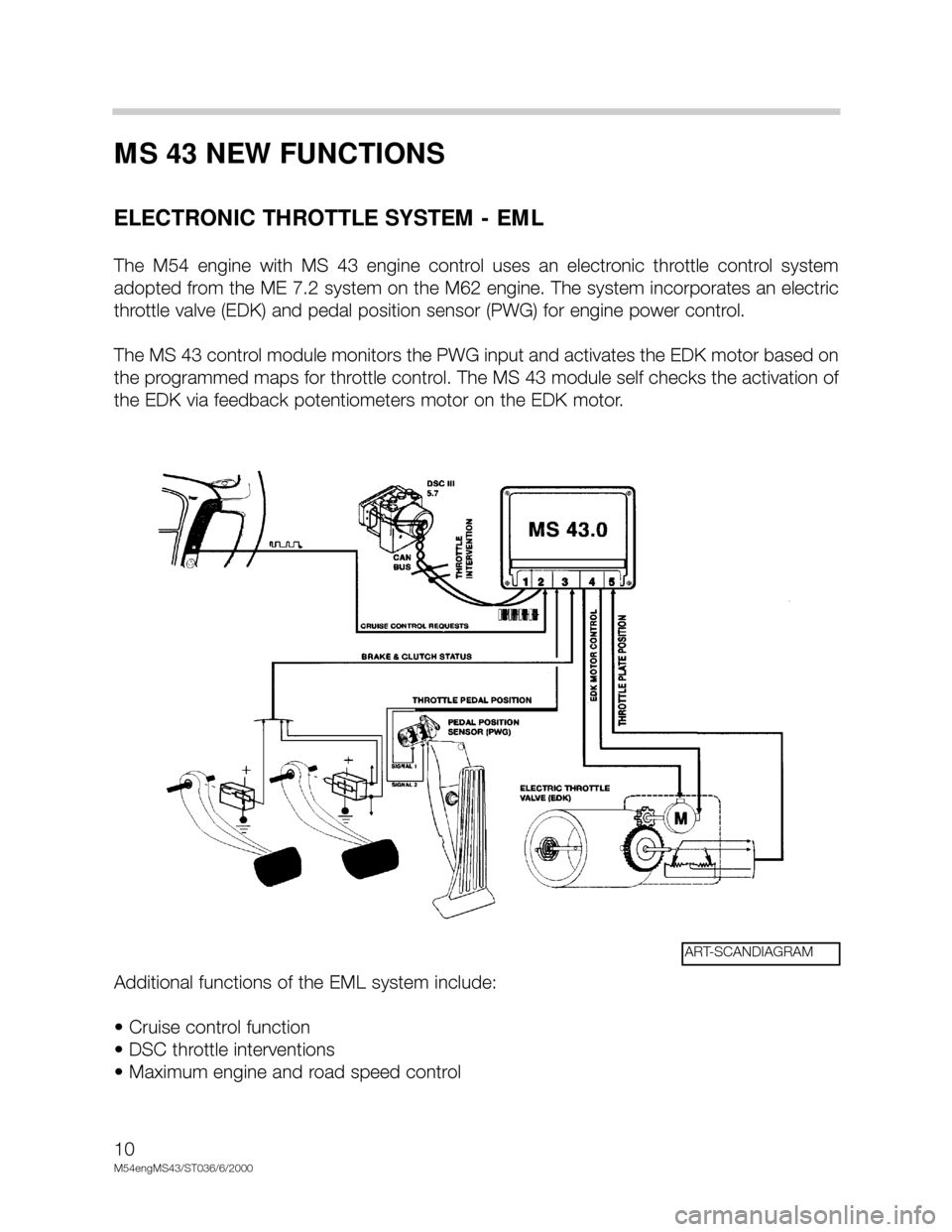
ELECTRONIC THROTTLE SYSTEM - EML
The M54 engine with MS 43 engine control uses an electronic throttle control system
adopted from the ME 7.2 system on the M62 engine. The system incorporates an electric
throttle valve (EDK) and pedal position sensor (PWG) for engine power control.
The MS 43 control module monitors the PWG input and activates the EDK motor based on
the programmed maps for throttle control. The MS 43 module self checks the activation of
the EDK via feedback potentiometers motor on the EDK motor.
Additional functions of the EML system include:
• Cruise control function
• DSC throttle interventions
• Maximum engine and road speed control
ART-SCANDIAGRAM
Page 11 of 48
11
M54engMS43/ST036/6/20000
MS 43 NEW FUNCTIONS
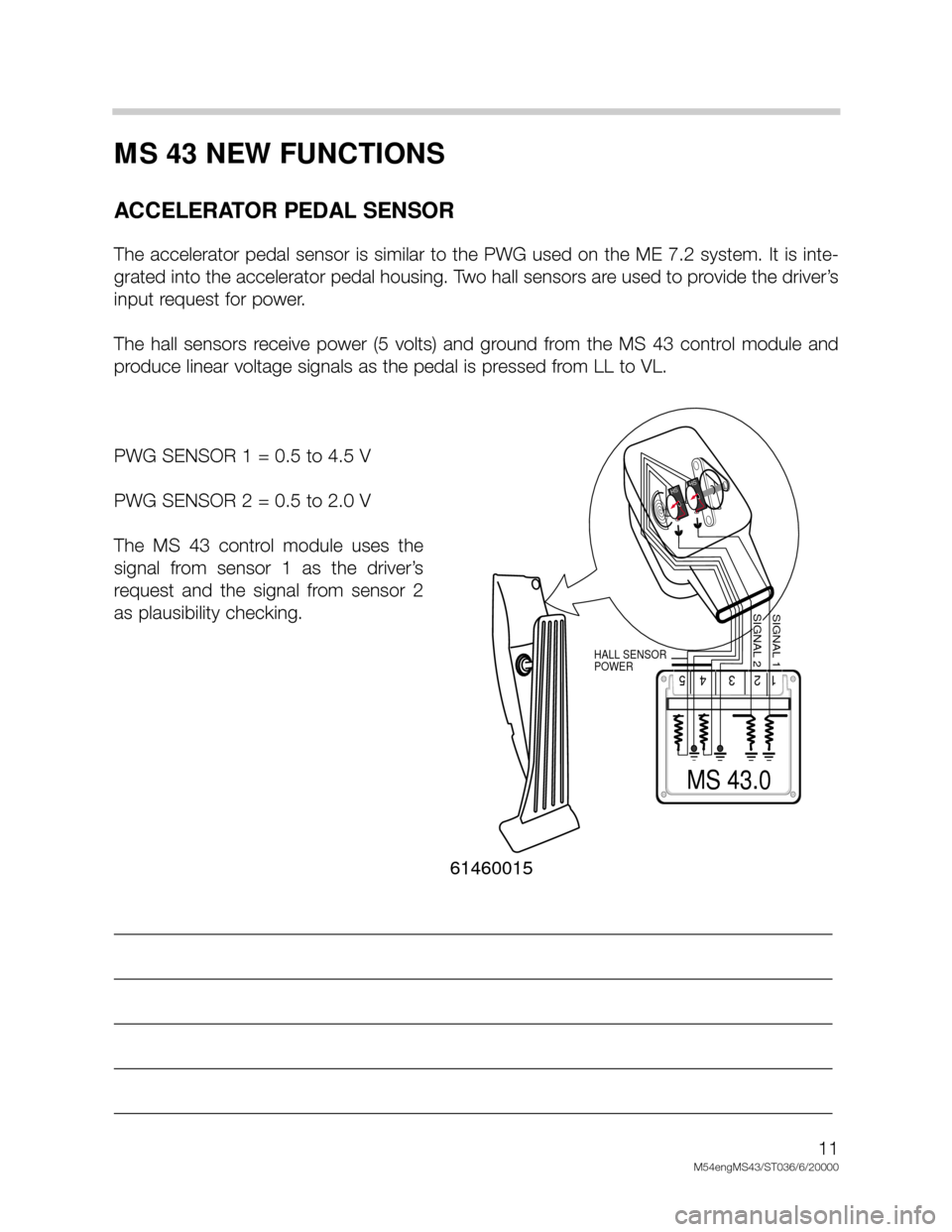
ACCELERATOR PEDAL SENSOR
The accelerator pedal sensor is similar to the PWG used on the ME 7.2 system. It is inte-
grated into the accelerator pedal housing. Two hall sensors are used to provide the driver’s
input request for power.
The hall sensors receive power (5 volts) and ground from the MS 43 control module and
produce linear voltage signals as the pedal is pressed from LL to VL.
PWG SENSOR 1 = 0.5 to 4.5 V
PWG SENSOR 2 = 0.5 to 2.0 V
The MS 43 control module uses the
signal from sensor 1 as the driver’s
request and the signal from sensor 2
as plausibility checking.
_____________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________
HS
12 3 4 5
MS 43.0
HS
SIGNAL 1
SIGNAL 2
HALL SENSOR
POWER
61460015
Page 12 of 48
12
M54engMS43/ST036/6/2000
MS 43 NEW FUNCTIONS
ACCELERATOR PEDAL SENSOR
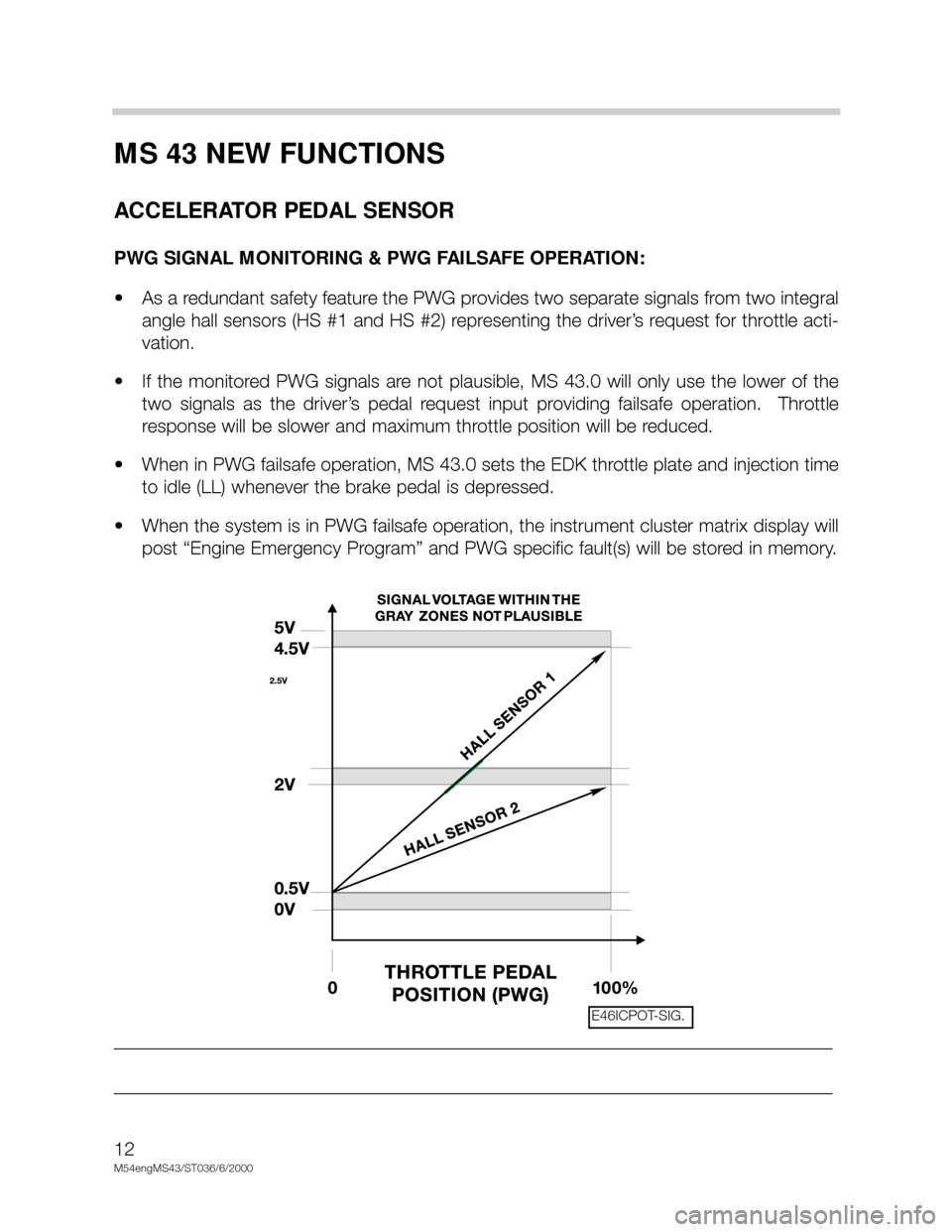
PWG SIGNAL MONITORING & PWG FAILSAFE OPERATION:
• As a redundant safety feature the PWG provides two separate signals from two integral
angle hall sensors (HS #1 and HS #2) representing the driver’s request for throttle acti-
vation.
• If the monitored PWG signals are not plausible, MS 43.0 will only use the lower of the
two signals as the driver’s pedal request input providing failsafe operation. Throttle
response will be slower and maximum throttle position will be reduced.
• When in PWG failsafe operation, MS 43.0 sets the EDK throttle plate and injection time
to idle (LL) whenever the brake pedal is depressed.
• When the system is in PWG failsafe operation, the instrument cluster matrix display will
post “Engine Emergency Program” and PWG specific fault(s) will be stored in memory.
_____________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________
E46ICPOT-SIG.
Page 24 of 48
24
M54engMS43/ST036/6/2000
MS 43 CARRY OVER FUNCTIONS
INPUT FUNCTIONS
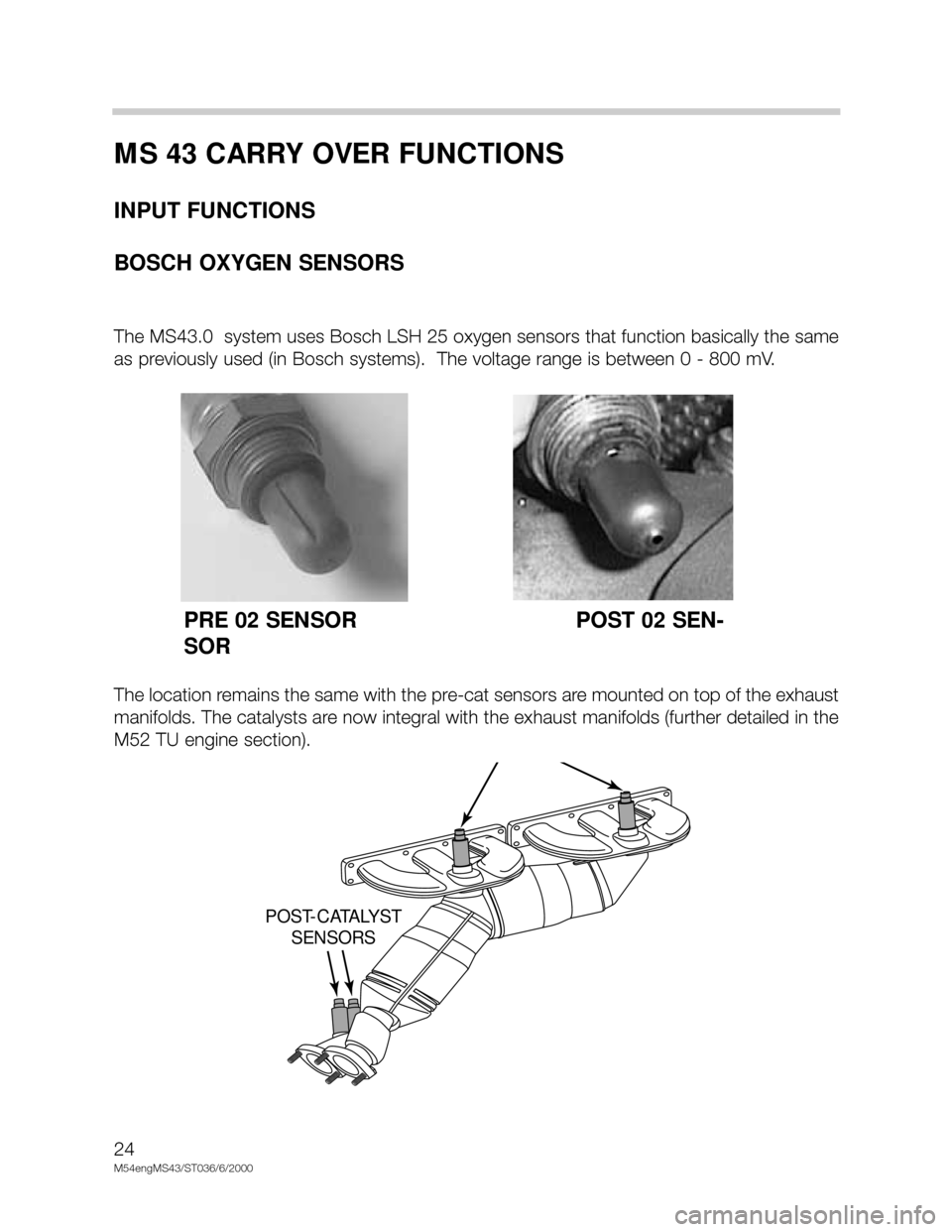
BOSCH OXYGEN SENSORS
The MS43.0 system uses Bosch LSH 25 oxygen sensors that function basically the same
as previously used (in Bosch systems). The voltage range is between 0 - 800 mV.
The location remains the same with the pre-cat sensors are mounted on top of the exhaust
manifolds. The catalysts are now integral with the exhaust manifolds (further detailed in the
M52 TU engine section).
PRE 02 SENSOR POST 02 SEN-
SOR
POST-CATALYST
SENSORS
Page 25 of 48

25
M54engMS43/ST036/6/20000
OXYGEN SENSOR SIGNAL INFLUENCE ON INJECTOR “OPEN” TIME
The ECM monitors the:
• Amplitude of the signal (highest voltage or range sensor is producing)
• Switching time of the signal (how fast from lean to rich)
• Frequency of complete cycles (how many within a period of time)
These characteristics provide info to the ECM that reflect the overall condition of the sen-
sor.
POST CATALYTIC CONVERTER SENSOR SIGNAL
The post catalyst O2 sensors monitor the efficiency of the catalyst as a requirement of OBD
II. This signal also provides feedback of the pre-catalyst sensors efficiency and can cause
the ECM to “trim” the ms injection time to correct for slight deviations.
• If the catalyst is operating efficiently, most of the remaining oxygen in the exhaust gas
is burned (lack of O2 - “constant lean signal”).
The sensor signal fluctuates slightly in the higher end of the voltage scale.
• If the post sensor shows excessive fluctuations
(which echo the scope pattern of the pre
sensor), this indicates that the catalytic converter is not functioning correctly and cannot
consume the O2 (fault set).
• If the post sensor fluctuations move out of the normal voltage “window”, this indicates
that the pre sensor is not performing properly due toslight
deterioration. These systems
can also “trim” the ms injection time to compensate for this.
The constantly changing oxygen sensor input to the ECM is needed to correct the ms
injection time to ensure that the ideal air/fuel ratio is maintained.
Page 26 of 48
26
M54engMS43/ST036/6/2000
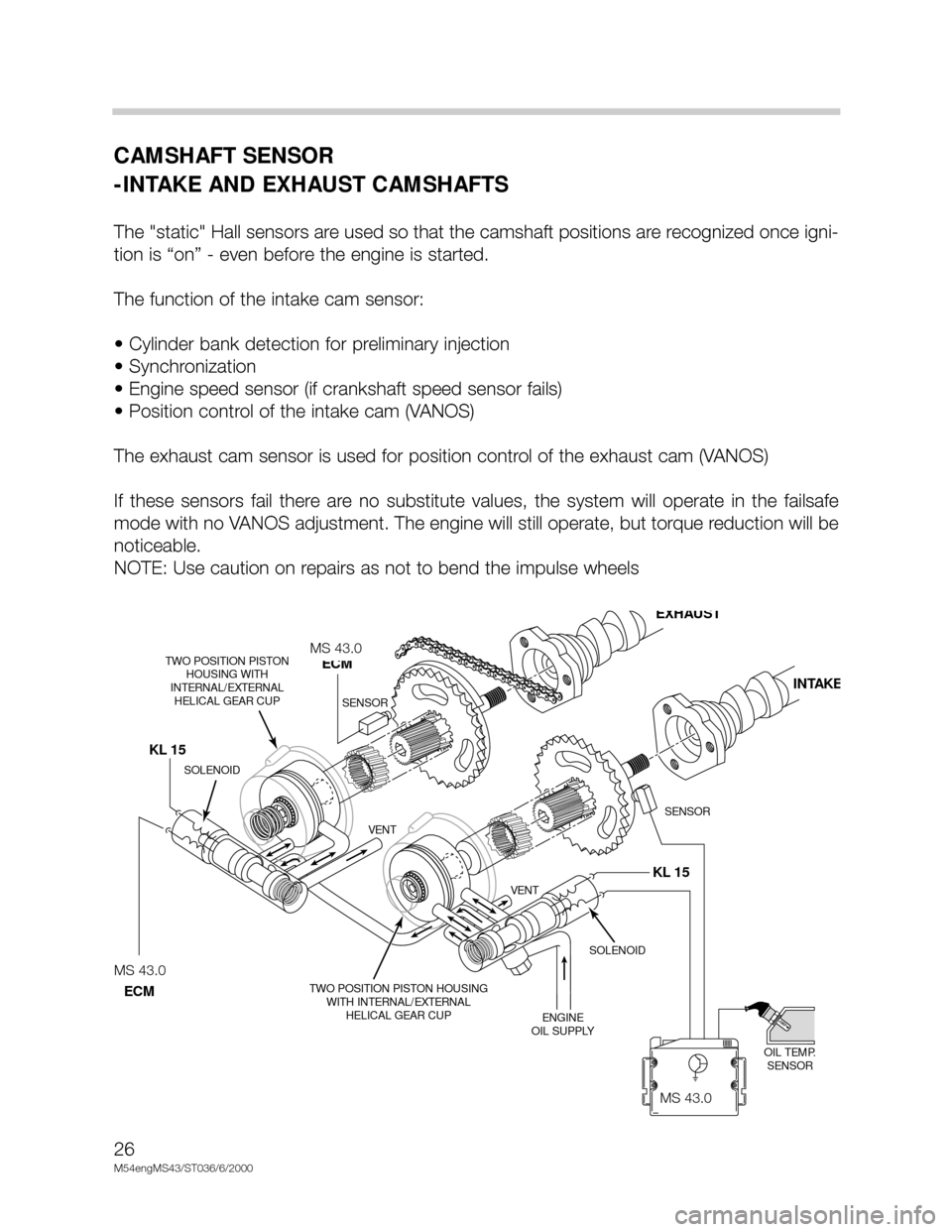
CAMSHAFT SENSOR
-INTAKE AND EXHAUST CAMSHAFTS
The "static" Hall sensors are used so that the camshaft positions are recognized once igni-
tion is “on” - even before the engine is started.
The function of the intake cam sensor:
• Cylinder bank detection for preliminary injection
• Synchronization
• Engine speed sensor (if crankshaft speed sensor fails)
• Position control of the intake cam (VANOS)
The exhaust cam sensor is used for position control of the exhaust cam (VANOS)
If these sensors fail there are no substitute values, the system will operate in the failsafe
mode with no VANOS adjustment. The engine will still operate, but torque reduction will be
noticeable.
NOTE: Use caution on repairs as not to bend the impulse wheels
KL 15 KL 15
MS42.0
SOLENOID
OIL TEMP.
SENSOR TWO POSITION PISTON HOUSING
WITH INTERNAL/EXTERNAL
HELICAL GEAR CUP TWO POSITION PISTON
HOUSING WITH
INTERNAL/EXTERNAL
HELICAL GEAR CUP
ENGINE
OIL SUPPLY VENT VENT
SOLENOID
SENSOR SENSOR
MS42
ECM
EXHAUST
INTAKE
MS42.0
ECM
MS 43.0
MS 43.0
MS 43.0
Page 27 of 48
27
M54engMS43/ST036/6/20000
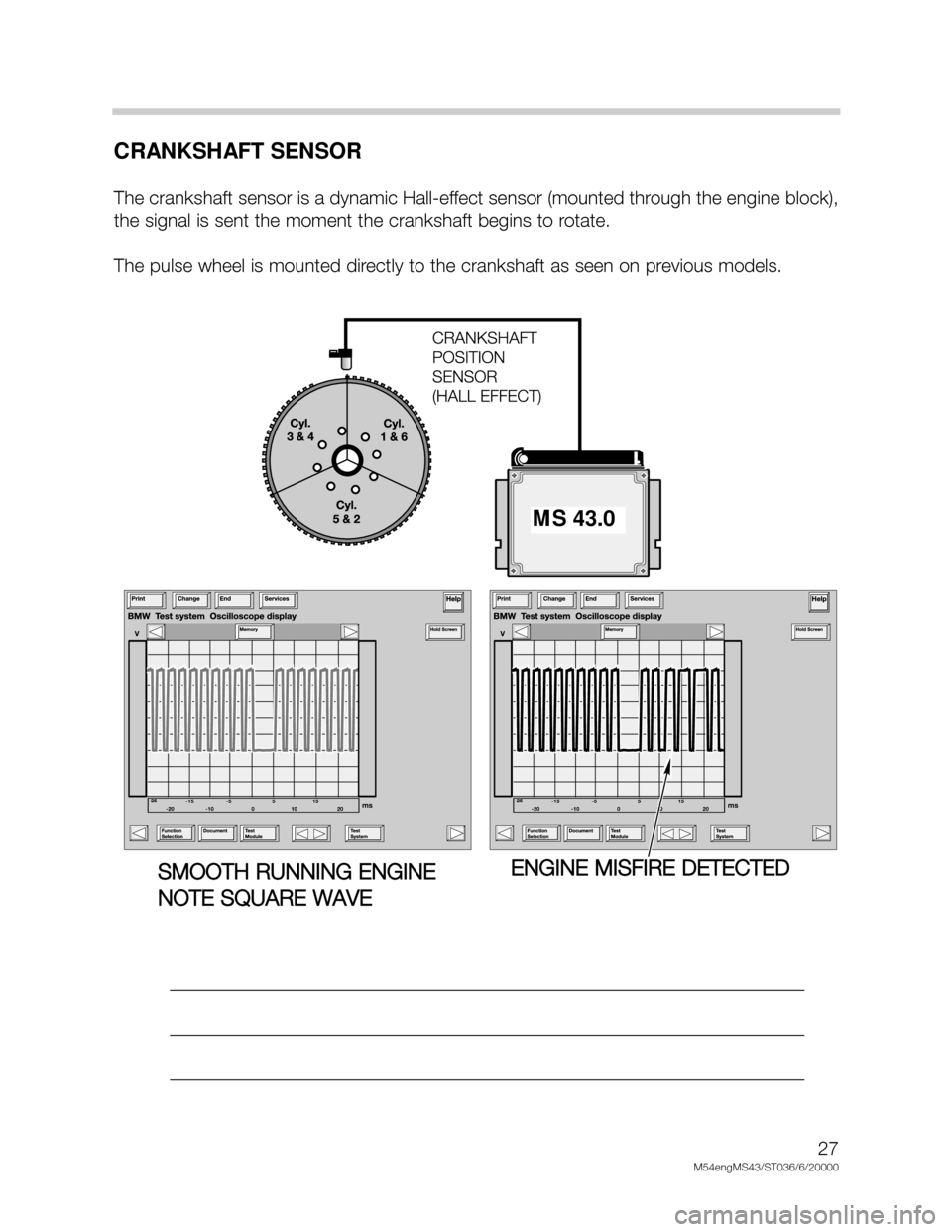
CRANKSHAFT SENSOR
The crankshaft sensor is a dynamic Hall-effect sensor (mounted through the engine block),
the signal is sent the moment the crankshaft begins to rotate.
The pulse wheel is mounted directly to the crankshaft as seen on previous models.
____________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________
MS 43.0
SMOOTH RUNNING ENGINE
NOTE SQUARE WAVEENGINE MISFIRE DETECTED
Page 29 of 48

29
M54engMS43/ST036/6/20000
EMISSIONS RELEVANT:
During an interval of 1000 crankshaft revolutions
the misfire events of all cylinders are
added and if the sum is greater than a predetermined value a fault will be set identifying the
particular cylinder(s). The “Service Engine Soon” light will be illuminated during and after
the second cycle if the fault is again present.
CATALYST DAMAGING:
During an interval of 200 crankshaft revolutions
the misfire events of all cylinders are added
and if the sum is greater than a predetermined value a fault will be set identifying the par-
ticular cylinders(s). The “Service Engine Soon” lamp:
• On vehicles with a Siemens Control Module (M54 engines) - the lamp will immediately go
to a steady illumination since fuel to the injector(s) is removed. Fuel cut-off to the cylin-
der will resume after several (
>>7) periods of decel if crankshaft sensor adaptation is suc-
cessfully completed or the engine is shut-off and restarted.
In each case the number of misfire events permitted is dependent on engine speed, load
and temperature map.
The process of misfire detection continues well after the diagnostic drive cycle requirements
have been completed. Misfire detection is an on-going monitoring process
that is only dis-
continued under certain conditions.
Misfire detection is only disabled under the following conditions:
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
REQUIREMENTSSTATUS/CONDITION
Engine Speed< 512 RPM
Engine LoadVarying/Unstable
Throttle AngleVarying/Unstable
TimingTiming retard request active (i.e. knock
control - ASC, AGS)
Engine Start-upUp to 5 seconds after start-up
A/CUp to 0.5 seconds after A/C activation
Decel fuel cut-offActive
Rough road recognitionActive
ASC ControlActive