wheel BMW Z8 2002 User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: BMW, Model Year: 2002, Model line: Z8, Model: BMW Z8 2002Pages: 174, PDF Size: 2.37 MB
Page 52 of 174
52n
AirbagsSitting correctly with airbags
Comply with the following instruc-
tions for the airbags, otherwise,
the airbags may not be able to provide
their maximum protection, with
resulting risks to personal safety. All
passengers in the vehicle should be
aware of and comply with this informa-
tion:
The airbag is a supplemental restraint
device; it is not a substitute or replace-
ment for your safety belt, which you
should continue to wear at all times.
When adjusting your seat, assume a
comfortable driving posture allowing
comfortable and secure access to all of
the vehicle's controls. Avoid sitting too
close to the steering wheel.
Always hold the steering wheel by the
rim Ð hands in the "9 o'clock" and
"3 o'clock" positions Ð otherwise, your
hands or arms could be injured if the
airbag is triggered.
Never allow any other passengers,
animals or objects to intrude into the
area between the airbag and the driver
or front passenger.
Do not use the cover panel above the
front passenger airbag as a storage
area.
Do not apply adhesive materials to the
cover panels of the airbags, or cover or
modify them in any other way.
Do not use a rear-facing child seat in
the front passenger seat. If you use a
child-restraint system, carefully read
and comply with the instructions on
page 53.
Be sure that child seats are installed
correctly and with the greatest possible
distance between them and the side
airbag. Do not allow children to lean out
of the child's seat in the direction of the
side trim panels. If they do so, serious
injuries can occur if the airbag is trig-
gered.<
Even when all these guidelines are
observed, there is still a small residual
risk of injury to the face, hands and
arms occurring from airbag deployment
in isolated instances.
The ignition and inflation noise may
cause a mild temporary hearing loss in
extremely sensitive individuals.
You will find the proper airbag safety
precautions on both sun visors and on
the instrument cluster (US models).
For additional information concerning
the airbag system, refer to pages 123
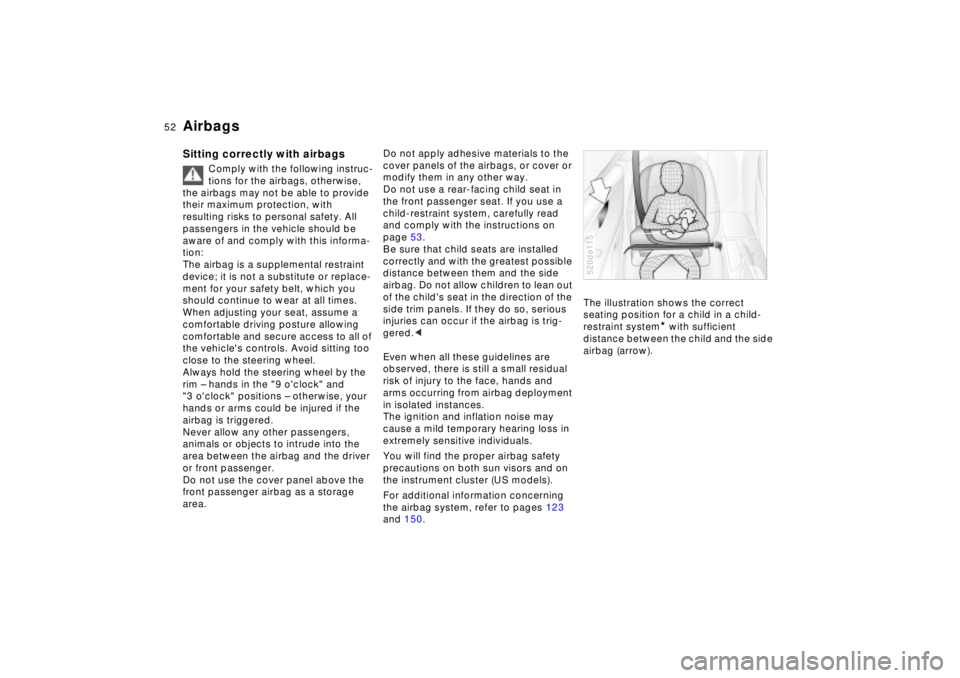
and 150.The illustration shows the correct
seating position for a child in a child-
restraint system
* with sufficient
distance between the child and the side
airbag (arrow).
520de115
Page 55 of 174
55n
IndexDataTechnologyRepairsCar careControlsOverview
Your vehicle is equipped with an elec-
trically powered steering lock mecha-
nism.To activate the electrical power
supply and release the steering>Insert key at position 1. The steering
detent can be heard disengaging. If
you encounter any resistance when
turning the key to the right this indi-
cates that the detent is still engaged:
turn the steering wheel slightly to free
the mechanism and turn the key.
The vehicle immobilizer is deacti-
vated
>The sound system and other elec-
trical accessories are available for
use when the ignition key is in posi-
tion 1 520de023
>Turning the key to position 2 provides
electrical power to the ignition and all
remaining electrical systems.
Removing the key The key is removed in position 0. Turn
the steering wheel to engage the
steering lock and activate the electronic
vehicle immobilizer.
With a discharged or discon-
nected battery, the steering
column will not be locked or unlocked.
Leaving the key in the ignition uses up a
minimal amount of power. In order to
avoid discharging the battery, remove
the key if the vehicle is to be parked for
an extended period of time.<
If the steering is locked and the
battery discharged or discon-
nected, do not tow the vehicle, as it will
not be possible to turn the steering
wheel.<
Ignition and steering lock
Page 57 of 174
57n
IndexDataTechnologyRepairsCar careControlsOverview
Switching off the engine Parking brake Turn ignition key to position 1 or 0.
Never remove the ignition key
while the vehicle is rolling. If you
do so, the ignition lock would engage
when the steering wheel is turned.
When you leave the vehicle, always
remove the ignition key and engage the
steering lock.
Always engage the parking brake when
parking on hills and inclined surfaces,
as first gear or reverse may not provide
adequate resistance to rolling.<
The parking brake is primarily designed
to prevent the vehicle from rolling while
parked. It operates on the rear wheels. To engage The lock engages automatically when
you lift the lever, and the indicator lamp
in the instrument cluster comes on
when the ignition key is in position 2.
Refer to page 21.To releasePull up slightly on the lever, press the
button and lower the lever. 520de024
If, in rare circumstances, it should
be necessary to engage the
parking brake while the vehicle is in
motion, do not pull hard on the lever.
Keep your thumb pressed against the
release button while carefully pulling
the lever up to apply moderate pres-
sure.
Excessive pressure can lead to over-
braking and loss of traction (fishtailing)
at the rear axle.
The brake lamps do not come on when
the parking brake is engaged.
Always engage the parking brake when
parking on hills and inclined surfaces,
as selecting first gear or reverse may
not provide adequate resistance to
rolling.<
To avoid corrosion and one-sided
braking, apply the parking brake lightly
from time to time when coasting to a
standstill (at a traffic signal, for
instance), provided that it is safe to do
so.
Page 65 of 174
65n
IndexDataTechnologyRepairsCar careControlsOverview
The conceptDSC maintains vehicle stability even in
critical driving situations.
DSC maintains optimal, predictable
response while maximizing traction
when you accelerate from a standing
start or speed up while already
underway. The system recognizes any
tendency for the vehicle to assume an
instable attitude such as oversteer and
understeer, and counteracts this
tendency with a combination of gradu-
ated reductions in engine torque and
braking intervention at individually
selected wheels. DSC provides optimal
stability Ð within the limits defined by
the laws of physics.
The system automatically assumes
operational status each time the engine
is started.
Indicator lamp
The indicator lamp in the instru-
ment cluster goes out shortly
after you switch on the ignition.
Refer to page 22.
The indicator lamp flashes:
The system is actively regulating drive
torque and braking force.
The indicator lamp does not go out
after the engine is started, or it comes
on during normal driving and stays on:
There is a system malfunction or the
system was deactivated with the
button. You can continue to drive the
vehicle normally, but without DSC.
Please respond to any suspected
defects by referring the problem to your
BMW center.
To deactivate the systemPress the button, the indicator lamp
comes on and stays on.
When DSC is deactivated, you are
operating the vehicle in the conven-
tional drive mode.
In the following rare circumstances, it
may be effective to deactivate the DSC
for a short period of time:
>When rocking the vehicle or starting
off in deep snow or on loose
surfaces.
To maintain vehicle stability,
always drive with the system
switched on when possible.<520de035
Dynamic Stability Control (DSC)
Page 67 of 174
67n
IndexDataTechnologyRepairsCar careControlsOverview
Dynamic Performance Flat Tire MonitorSport mode recognitionActivating:
In ignition position 2, press the button.
The indicator lamp will come on.
Deactivating:
Whenever the indicator lamp is on, it
will go out if you press the button again.
The conceptThe Flat Tire Monitor keeps track of the
inflation pressures in all four wheels as
you drive. The system provides an alert
whenever the inflation pressure has
dropped significantly in one of the tires.
To initialize the Flat Tire Monitor with
the correct inflation pressures, start by
ensuring that all of the vehicle's tires
are inflated to the pressures specified
in the inflation pressure table on
page 27. Now you can activate the
system.
The indicator lamp within the
instrument cluster flashes to
alert you to substantial pres-
sure loss in any of the tires.
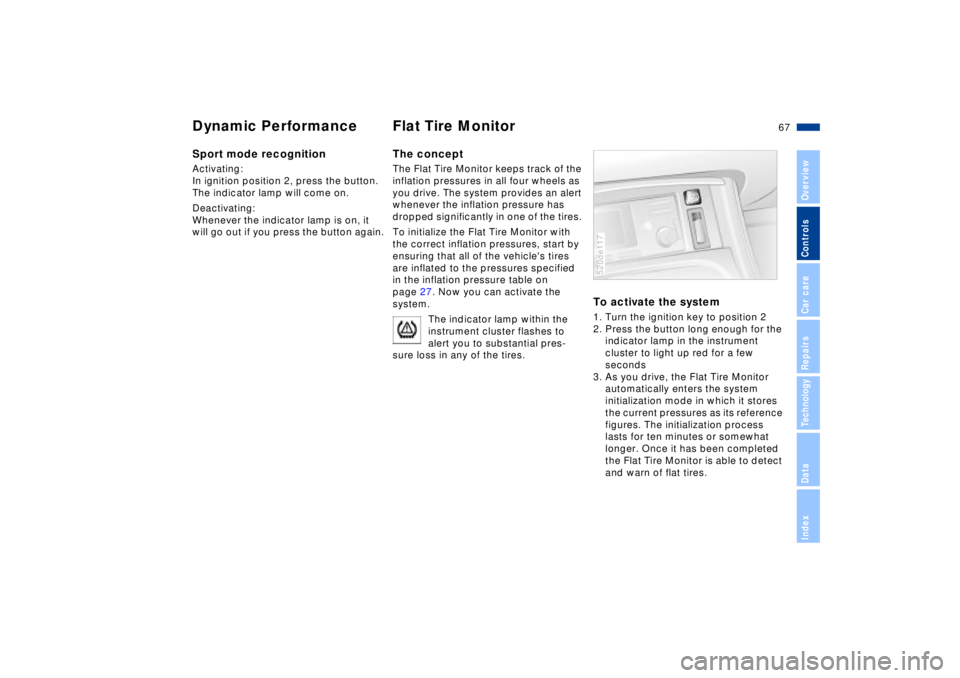
To activate the system1. Turn the ignition key to position 2
2. Press the button long enough for the
indicator lamp in the instrument
cluster to light up red for a few
seconds
3. As you drive, the Flat Tire Monitor
automatically enters the system
initialization mode in which it stores
the current pressures as its reference
figures. The initialization process
lasts for ten minutes or somewhat
longer. Once it has been completed
the Flat Tire Monitor is able to detect
and warn of flat tires.520de117
Page 68 of 174

68n
Flat Tire MonitorRepeat this process after any changes
in tire inflation pressure, tire rotation or
replacement.
Do not reactivate the system after peri-
odic corrections of inflation pressures
to maintain them at the levels stored
during an earlier initialization process. In the event of a flat tireThe red indicator lamp will flash in the
event of a flat tire.
A supplementary gong is also heard.
Carefully reduce speed to less than
50 mph (80 km/h), avoiding any hard
braking or steering maneuvers while
doing so.
For additional details, refer to
page 137.
The Flat Tire Monitor cannot alert
you to severe and sudden tire
damage caused by external factors.
Another factor which the Flat Tire
Monitor does not recognize is the
balanced and very gradual pressure
loss that takes place in all tires over an
extended period of time.<
Check tire pressure on a regular
basis and correct it as required.
Refer to page 26.
Do not activate the system when driving
on snow chains or when operating the
vehicle on a closed racing circuit. False
alarms and undetected pressure loss
are both possible under these condi-
tions.
In certain circumstances, there could
be a delayed detection of any loss in
inflation pressure while driving on
snow-covered or slippery road
surfaces.
Performance-oriented driving (slip at
the drive wheels, high levels of lateral
acceleration) can also delay the
appearance of status reports in the Flat
Tire Monitor's display panel.<
System interferenceThe red indicator lamp in the instrument
cluster will stay on for as long as there
is a malfunction.
The indicator lamp will come on if the
system malfunctions.
Please contact your BMW center for
additional information.
Page 85 of 174
Overview
Controls and features
Operation, care
and maintenance
Owner service procedures
Technical data
Index Advanced technology
85n
IndexDataTechnologyRepairsCar careControlsOverview
Car care Special operating instructions:
Break-in procedures86
Driving notes87
Catalytic converter87
Antilock Brake System (ABS)88
Dynamic Brake Control
(DBC)90
Disc brakes90
Brake system92
Winter operation92
Power steering94
Cellular phone94
Car radio reception95
Wind deflector95
Hardtop96
Wheels and tires:
Tire inflation pressure99
Tire condition99
Tire replacement100
Tire rotation101
Wheel and tire
combinations102
Special features of winter
tires103
Snow chains103
Approved wheel and tire
specifications104Under the hood:
Hood105
Engine compartment108
Washer fluids110
Washer nozzles110
Engine oil111
Coolant113
Brake fluid114
Vehicle Identification
Number115
Maintenance and care:
The BMW Maintenance
System116
Caring for your vehicle117
Airbags123
Vehicle storage124
Laws and regulations:
Technical modifications125
California Proposition 65
Warning125
OBD interface socket126
Page 88 of 174

88n
Antilock Brake System (ABS)The concept ABS enhances active safety by helping
to prevent the wheels from locking
under braking. Why is this important?
When front wheels lock up and cease
to turn, the tires break into a slide.
Result: the driver loses the ability to
steer the vehicle. Traction loss at the
rear wheels can cause the back end of
the vehicle to slip sideways and break
away in uncontrolled oversteer.
With ABS, you will achieve the shortest-
possible braking distances under all
given conditions (braking while driving
straight ahead or in curves, different
road surfaces).
ABS is designed to meet two essential
requirements during every brake appli-
cation:
>To help provide vehicle stability
>To help retain steering and maneu-
vering capability on all types of road
surfaces (asphalt, concrete, dirt, wet
surfaces, snow and ice).
Braking with ABSThe system is operative once the
vehicle exceeds a speed of approx.
6 mph (10 km/h). The ABS is deacti-
vated whenver the vehicle's speed
drops back below approx. 4 mph
(6 km/h). This means that the wheels
can lock only in the final phase of a
panic stop Ð a factor of no substantive
significance in actual use.
The ABS system works best in situa-
tions requiring maximum pressure on
the pedal (full braking). Since the
vehicle maintains steering responsive-
ness, you can nevertheless avoid
possible obstacles with a minimum of
steering effort.
The ABS system's closed-loop control
circuit cycles in fractions of a second.
A pulsing of the brake pedal, combined
with the sounds associated with the
hydraulic controls, tells you that the
brake system is within its maximum
limit range and reminds you that you
should adapt your vehicle's speed to
road conditions. On road surfaces that have a loose
surface layer on a firm base with good
traction (on gravel, deep sand or snow,
for example), braking distances may be
longer than with locked wheels. This
also applies to driving with snow
chains. However, ABS continues to
provide enhanced vehicle stability and
steering response under these condi-
tions.
Page 91 of 174

91n
IndexDataTechnologyRepairsCar careControlsOverview
Disc brakesDriving notesWhen driving in heavy rain and on wet
roads it is advisable to apply light pres-
sure to the brake pedal every few miles.
Monitor traffic conditions to ensure that
this maneuver does not pose a hazard
to you or to other road users. The heat
generated in this braking process helps
dry the pads and rotors
Maximum braking force is obtained
while the wheels are not locked, but
rather when they are still barely turning
immediately prior to locking. ABS main-
tains this state automatically. If the ABS
fails, you should revert to the staggered
braking technique (refer to page 93).
When descending steep hills and
extended grades, downshift to a gear
that will allow you to continue safely
with only a minimal amount of braking.
By minimizing the loads placed on the
brake system, this strategy helps
ensure that optimal brake system
response will remain available at all
times.
You can enhance the engine's braking
effect by downshifting, into first gear, if
necessary. Even if engine braking fails to slow the
vehicle sufficiently, you should still
make every effort to avoid prolonged
braking with continuous application of
low to moderate pressure at the pedal.
It is better to decelerate the vehicle by
applying a higher level of force at the
pedal (watch following traffic!) and then
subsequently pausing to allow the
brakes to cool briefly before starting on
your next braking cycle. By protecting
brake system components against
overheating, the cooling phases
afforded by this staggered, or intermit-
tent braking technique help maintain
consistent availability of optimal braking
response when it is needed.
Do not coast with the clutch pedal
depressed, the gear-shift lever in
neutral, or, above all, with the engine
off; otherwise, the engine will provide
no braking effect if the transmission is
in neutral, and there is no braking or
steering power assist if the engine is
not running. Never allow floor mats,
carpets or any other objects to obstruct
the accelerator, clutch or brake pedals
and pose a safety hazard by reducing
their available travel range.<
Page 93 of 174

93n
IndexDataTechnologyRepairsCar careControlsOverview
Winter operationRubber seals and componentsTo prevent the weather-stripping from
freezing, apply a spray-on rubber treat-
ment or silicone spray to the door, hood
and luggage compartment lid seals.
A full range of car-care products is
available from your BMW center.
on rear tires, complying with the manu-
facturer's safety precautions. Do not
exceed a maximum speed of 30 mph
(50 km/h) while the snow chains are
mounted and refrain from activating the
Flat Tire Monitor, as the snow chains
could trigger false alarms and/or
prevent the system from detecting
actual pressure loss.
Starting off When starting off in deep snow or when
"rocking" the vehicle to free it, it may be
advisable to temporarily deactivate the
DSC. Refer to page 65.
To maintain vehicle stability,
always drive with the system
switched on whenever possible.<
Driving on low-traction road
surfaces Do not activate the Sport mode (refer to
page 66). Use smooth, gentle pressure
to control the accelerator pedal. Avoid
excessive engine speeds and upshift
early. Downshift well in advance when
approaching uphill or downhill grades.
Maintain an adequate distance
between yourself and the vehicle
ahead. BrakesWinter road conditions substantially
reduce the amount of traction available
between the tires and the road surface.
The resulting increases in braking
distance are considerable and should
be kept in mind at all times.
ABS is intended to prevent the wheels
from locking during brake applications,
thus helping to maintain vehicle stability
and steering response. If the ABS does not respond in a critical
braking situation and the wheels lock,
reduce the pressure on the brake pedal
until the wheels just start to roll again
while still maintaining enough force to
continue braking.
Then increase the pressure, reduce the
pressure when the wheels lock, reapply
pressure etc.
This staggered braking procedure will
reduce braking distances while helping
you maintain steering control.
You can always then attempt to steer
around hazards after you have reduced
pressure on the brake pedal.
Never downshift to exploit engine
braking when driving on slippery
road surfaces, as this could lead to a
loss of traction at the rear wheels,
impairing your ability to control the
vehicle.<
Depress the clutch during hard
braking on road surfaces that
provide only poor or uneven traction.<