BUICK LESABRE 2002 Service Manual
Manufacturer: BUICK, Model Year: 2002, Model line: LESABRE, Model: BUICK LESABRE 2002Pages: 398, PDF Size: 2.65 MB
Page 41 of 398

1-35
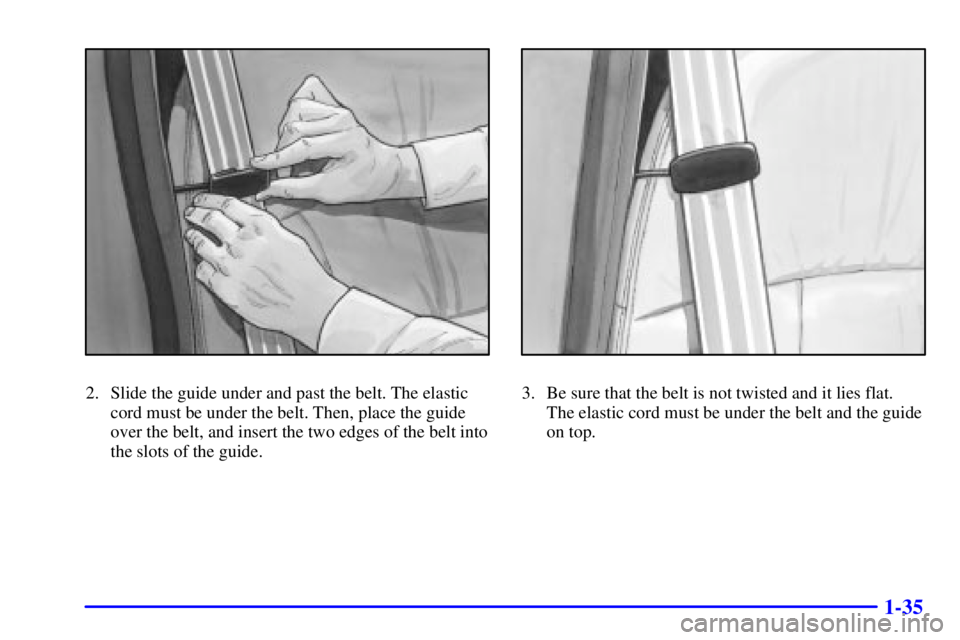
2. Slide the guide under and past the belt. The elastic
cord must be under the belt. Then, place the guide
over the belt, and insert the two edges of the belt into
the slots of the guide.3. Be sure that the belt is not twisted and it lies flat.
The elastic cord must be under the belt and the guide
on top.
Page 42 of 398

1-36
4. Buckle, position and release the safety belt as
described in ªRear Seat Passenger Positionsº earlier
in this section. Make sure that the shoulder belt
crosses the shoulder.
To remove and store the comfort guides, squeeze the
belt edges together so that you can take them out of the
guides. Slide the guide into its storage pocket on the side
of the seatback.
Children
Everyone in a vehicle needs protection! This includes
infants and all other children. Neither the distance
traveled nor the age and size of the traveler changes the
need, for everyone, to use safety restraints. In fact, the
law in every state in the United States and in every
Canadian province says children up to some age must be
restrained while in a vehicle.
Infants and Young Children
Every time infants and young children ride in vehicles,
they should have the protection provided by the
appropriate restraint. Young children should not use the
vehicle's safety belts, unless there is no other choice.
Page 43 of 398
1-37
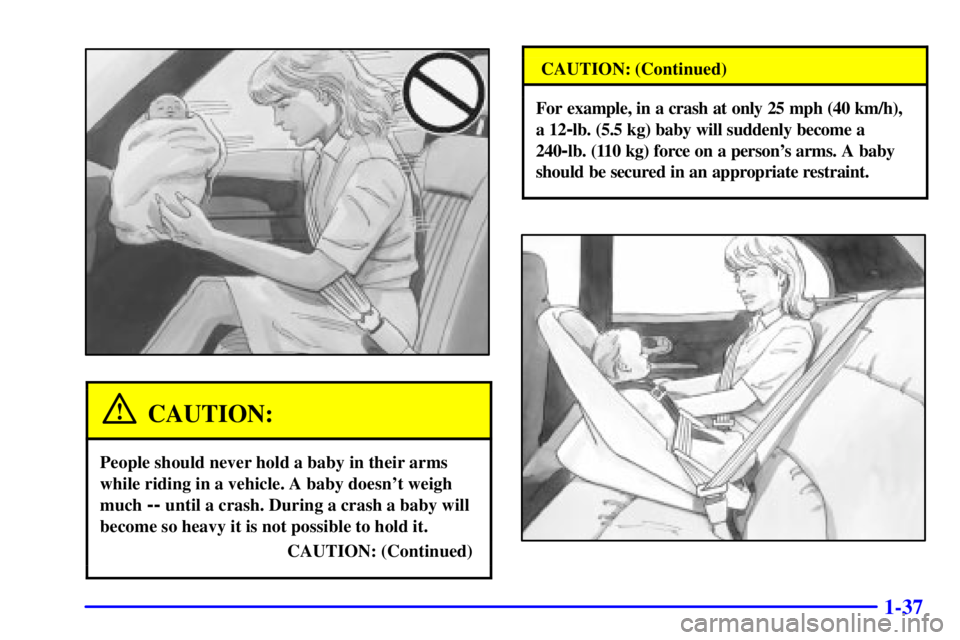
CAUTION:
People should never hold a baby in their arms
while riding in a vehicle. A baby doesn't weigh
much
-- until a crash. During a crash a baby will
become so heavy it is not possible to hold it.
CAUTION: (Continued)
CAUTION: (Continued)
For example, in a crash at only 25 mph (40 km/h),
a 12
-lb. (5.5 kg) baby will suddenly become a
240
-lb. (110 kg) force on a person's arms. A baby
should be secured in an appropriate restraint.
Page 44 of 398

1-38
CAUTION:
Children who are up against, or very close to, any
air bag when it inflates can be seriously injured
or killed. Air bags plus lap
-shoulder belts offer
outstanding protection for adults and older
children, but not for young children and infants.
Neither the vehicle's safety belt system nor its air
bag system is designed for them. Young children
and infants need the protection that a child
restraint system can provide.
Q:What are the different types of add-on
child restraints?
A:Add-on child restraints, which are purchased by the
vehicle's owner, are available in four basic types.
Selection of a particular restraint should take into
consideration not only the child's weight, height
and age but also whether or not the restraint will
be compatible with the motor vehicle in which it
will be used.
For most basic types of child restraints, there are
many different models available. When purchasing
a child restraint, be sure it is designed to be used
in a motor vehicle. If it is, the restraint will have
a label saying that it meets federal motor vehicle
safety standards.
The restraint manufacturer's instructions that
come with the restraint state the weight and
height limitations for a particular child restraint.
In addition, there are many kinds of restraints
available for children with special needs.
Page 45 of 398

1-39
CAUTION:
Newborn infants need complete support,
including support for the head and neck. This is
necessary because a newborn infant's neck is
weak and its head weighs so much compared with
the rest of its body. In a crash, an infant in a
rear
-facing seat settles into the restraint, so the
crash forces can be distributed across the
strongest part of an infant's body, the back and
shoulders. Infants always should be secured in
appropriate infant restraints.
CAUTION:
The body structure of a young child is quite
unlike that of an adult or older child, for whom
the safety belts are designed. A young child's hip
bones are still so small that the vehicle's regular
safety belt may not remain low on the hip bones,
as it should. Instead, it may settle up around the
child's abdomen. In a crash, the belt would apply
force on a body area that's unprotected by any
bony structure. This alone could cause serious or
fatal injuries. Young children always should be
secured in appropriate child restraints.
Page 46 of 398
1-40
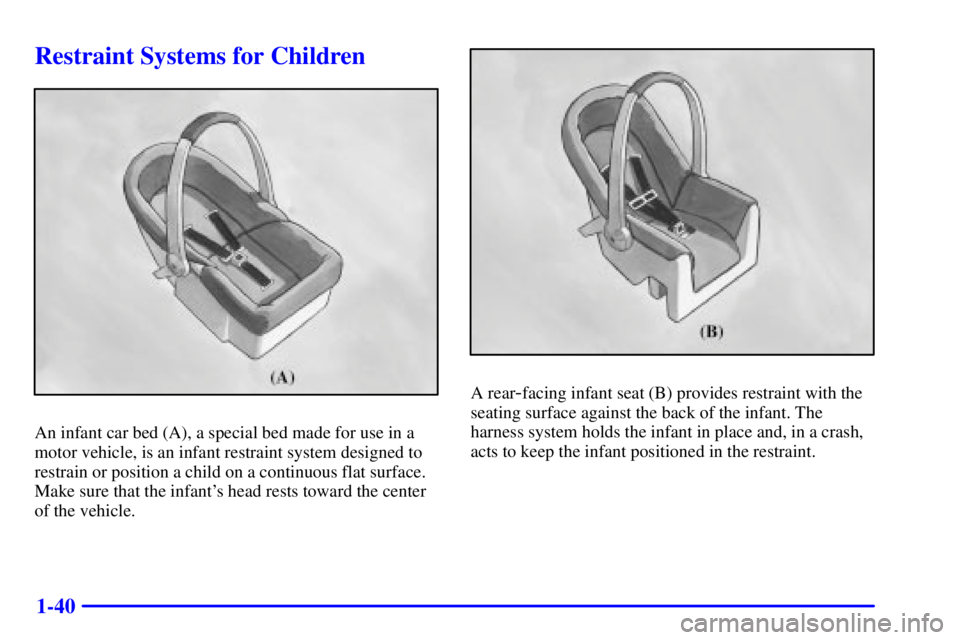
Restraint Systems for Children
An infant car bed (A), a special bed made for use in a
motor vehicle, is an infant restraint system designed to
restrain or position a child on a continuous flat surface.
Make sure that the infant's head rests toward the center
of the vehicle.
A rear-facing infant seat (B) provides restraint with the
seating surface against the back of the infant. The
harness system holds the infant in place and, in a crash,
acts to keep the infant positioned in the restraint.
Page 47 of 398
1-41
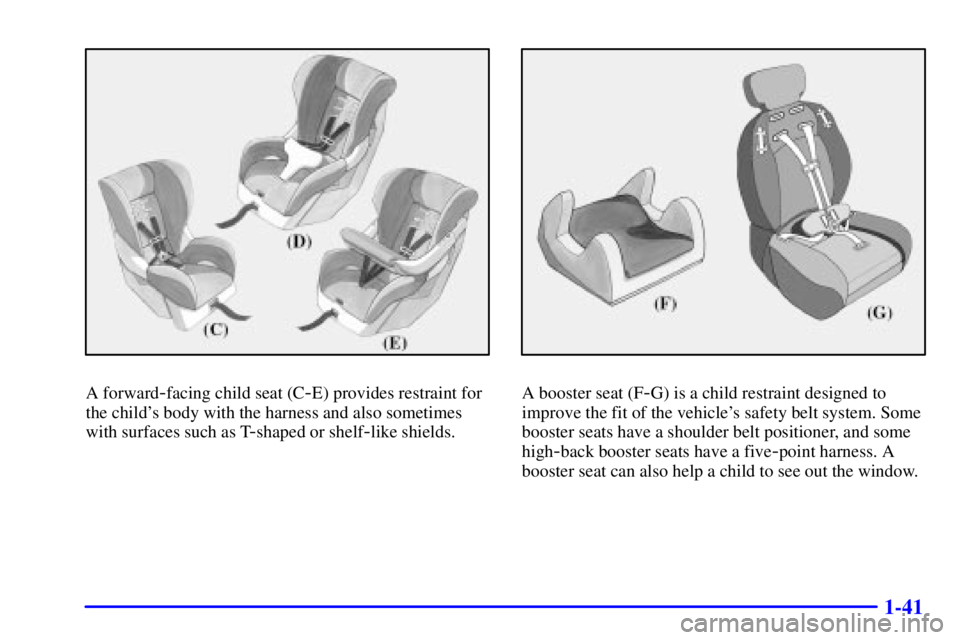
A forward-facing child seat (C-E) provides restraint for
the child's body with the harness and also sometimes
with surfaces such as T
-shaped or shelf-like shields.
A booster seat (F-G) is a child restraint designed to
improve the fit of the vehicle's safety belt system. Some
booster seats have a shoulder belt positioner, and some
high
-back booster seats have a five-point harness. A
booster seat can also help a child to see out the window.
Page 48 of 398

1-42
Q:How do child restraints work?
A:A child restraint system is any device designed for
use in a motor vehicle to restrain, seat, or position
children. A built
-in child restraint system is a
permanent part of the motor vehicle. An add
-on
child restraint system is a portable one, which is
purchased by the vehicle's owner.
For many years, add
-on child restraints have used
the adult belt system in the vehicle. To help reduce
the chance of injury, the child also has to be
secured within the restraint. The vehicle's belt
system secures the add
-on child restraint in the
vehicle, and the add
-on child restraint's harness
system holds the child in place within the restraint.
One system, the three
-point harness, has straps that
come down over each of the infant's shoulders and
buckle together at the crotch. The five
-point
harness system has two shoulder straps, two hip
straps and a crotch strap. A shield may take the
place of hip straps. A T
-shaped shield has shoulder
straps that are attached to a flat pad which rests low
against the child's body. A shelf
- or armrest-type
shield has straps that are attached to a wide,
shelf
-like shield that swings up or to the side.When choosing a child restraint, be sure the child
restraint is designed to be used in a vehicle. If it is,
it will have a label saying that it meets federal motor
vehicle safety standards.
Then follow the instructions for the restraint. You may
find these instructions on the restraint itself or in a
booklet, or both. These restraints use the belt system in
your vehicle, but the child also has to be secured within
the restraint to help reduce the chance of personal injury.
When securing an add
-on child restraint, refer to the
instructions that come with the restraint which may be
on the restraint itself or in a booklet, or both, and to this
manual. The child restraint instructions are important, so
if they are not available, obtain a replacement copy from
the manufacturer.
Page 49 of 398

1-43 Where to Put the Restraint
Accident statistics show that children are safer if they
are restrained in the rear rather than the front seat.
General Motors, therefore, recommends that child
restraints be secured in the rear seat including an infant
riding in a rear
-facing infant seat, a child riding in a
forward
-facing child seat and an older child riding in a
booster seat. Never put a rear
-facing child restraint in
the front passenger seat. Here's why:
CAUTION:
A child in a rear-facing child restraint can be
seriously injured or killed if the right front
passenger's air bag inflates. This is because the
back of the rear
-facing child restraint would be
very close to the inflating air bag. Always secure
a rear
-facing child restraint in a rear seat.
You may secure a forward-facing child restraint
in the right front seat, but before you do, always
move the front passenger seat as far back as it
will go. It's better to secure the child restraint in
a rear seat.
CAUTION:
A child in a child restraint in the center front seat
can be badly injured or killed by the right front
passenger air bag if it inflates. Never secure a
child restraint in the center front seat. It's always
better to secure a child restraint in the rear seat.
You may secure a forward
-facing child restraint
in the right front passenger seat, but before you
do, always move the front passenger seat as far
back as it will go. It's better to secure the child
restraint in a rear seat.
Wherever you install it, be sure to secure the child
restraint properly.
Keep in mind that an unsecured child restraint can move
around in a collision or sudden stop and injure people in
the vehicle. Be sure to properly secure any child
restraint in your vehicle
-- even when no child is in it.
Page 50 of 398
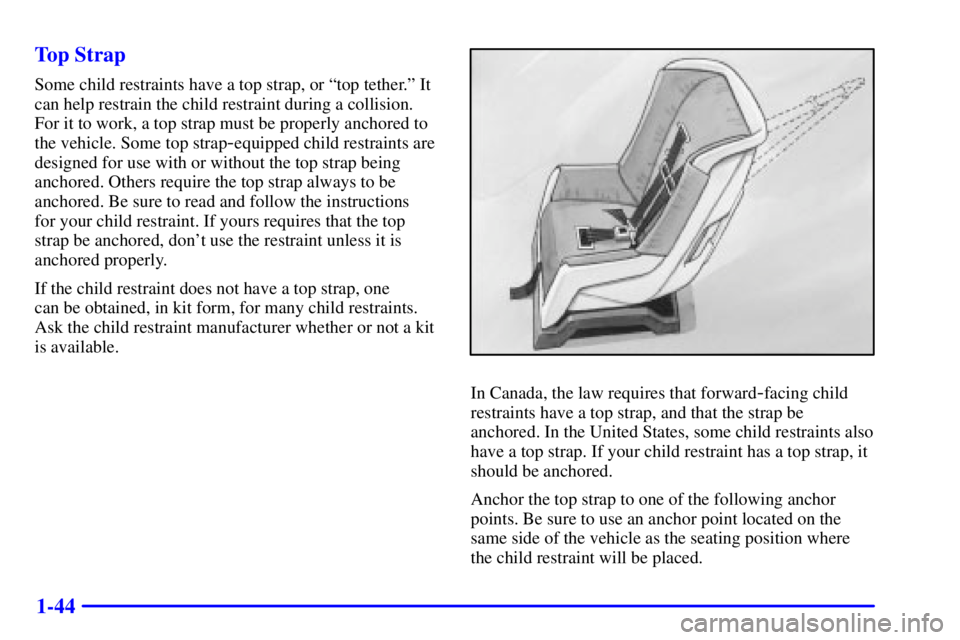

1-44 Top Strap
Some child restraints have a top strap, or ªtop tether.º It
can help restrain the child restraint during a collision.
For it to work, a top strap must be properly anchored to
the vehicle. Some top strap
-equipped child restraints are
designed for use with or without the top strap being
anchored. Others require the top strap always to be
anchored. Be sure to read and follow the instructions
for your child restraint. If yours requires that the top
strap be anchored, don't use the restraint unless it is
anchored properly.
If the child restraint does not have a top strap, one
can be obtained, in kit form, for many child restraints.
Ask the child restraint manufacturer whether or not a kit
is available.
In Canada, the law requires that forward-facing child
restraints have a top strap, and that the strap be
anchored. In the United States, some child restraints also
have a top strap. If your child restraint has a top strap, it
should be anchored.
Anchor the top strap to one of the following anchor
points. Be sure to use an anchor point located on the
same side of the vehicle as the seating position where
the child restraint will be placed.