steering wheel BUICK REGAL 1998 User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: BUICK, Model Year: 1998, Model line: REGAL, Model: BUICK REGAL 1998Pages: 388, PDF Size: 20.19 MB
Page 108 of 388

TILT-WHEEL TM Adjustable
Steering Column
A tilt steering wheel allows
you to adjust the steering
wheel before
you drive. You
can also raise it to the
highest level to give your
legs more room when you
exit and enter the vehicle.
To tilt the wheel, hold the steering wheel and pull the
lever. Move the steering wheel to a comfortable level,
then release the lever to lock the wheel into place.
Turn SignaYMultifunction Lever
The lever on the left side of the steering column
includes your:
0 Turn Signal and Lane Change Indicator
Headlamp High/Low Beam Changer
0 Windshield Wipers
Windshield Washer
Cruise Control (Option)
0 Flash-to-Pass
2-34
ProCarManuals.com
Page 151 of 388
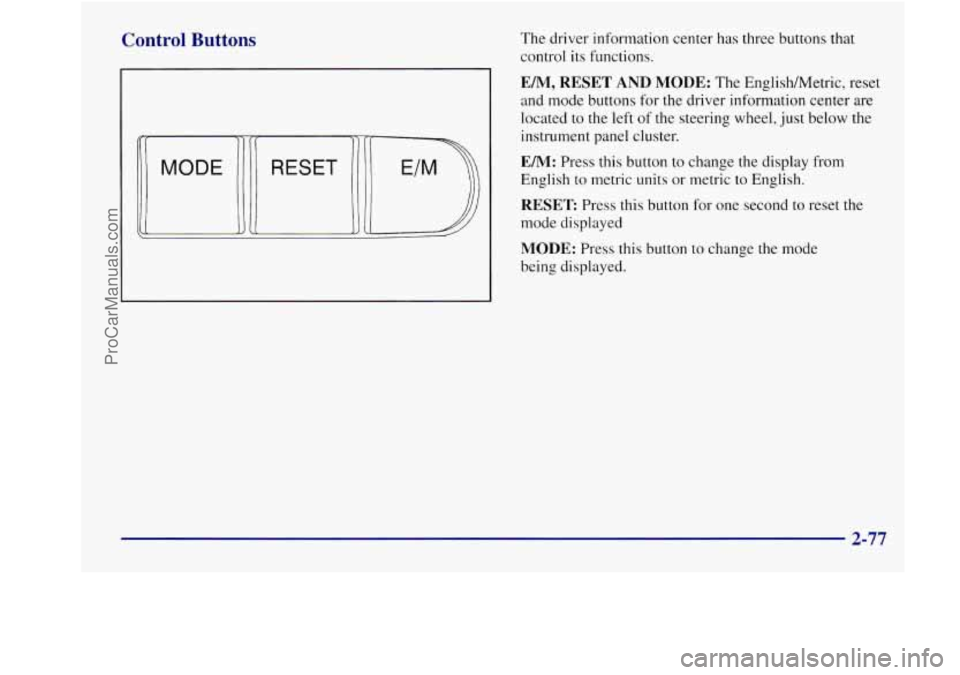
Control Buttons
I
RESET
The driver information center has three buttons that
control its functions.
EM, RESET AND MODE: The EnglishMetric, reset
and mode buttons
for the driver information center are
located
to the left of the steering wheel, just below the
instrument panel cluster.
EM: Press this button to change the display from
English to metric units
or metric to English.
RESET Press this button for one second to reset the
mode displayed
MODE: Press this button to change the mode
being displayed.
2-77
ProCarManuals.com
Page 153 of 388

Section 3 Comfort Controls and Audio Systems
In
this section, you’ll find out how to operate the comfort control and audio systems offered with your vehicle. Be
sure to read about the particular systems supplied with your vehicle.
3-2
3-2
3-4 3-7
3-10
3-11
3- 12 3- 12
3-13 3-16 Comfort Controls
Manual
Single Zone Climate Control
Dual ComforTemp Climate Control
(If Equipped)
Dual Automatic ComforTemp Climate Control (If Equipped)
Ventilation System
Rear Window Defogger
Audio Systems Setting the Clock
AM-FM Stereo with Cassette Tape Player
AM-FM Stereo with Cassette Tape Player and
Automatic Tone Control (If Equipped)
3-20
3-25
3-28
3-29
3-29
3-30
3-3 1
3-3 1
3-3 1
3-3 1 AM-FM Stereo
with Cassette Tape and
Compact Disc Player with Automatic Tone
Control (If Equipped)
Theft-Deterrent Feature (If Equipped)
Audio Steering Wheel Controls
(If Equipped)
Understanding Radio Reception
Tips About Your Audio System
Care
of Your Cassette Tape Player
Care of Your Compact Discs
Care
of Your Compact Disc Player
Fixed Mast Antenna
Backglass Antenna
(If Equipped)
3-1
ProCarManuals.com
Page 180 of 388

To unlock a secured radio see “Unlocking the
Theft-Deterrent Feature After a Power
Loss” earlier in
this section.
Audio Steering Wheel Controls
(If Equipped)
If your vehicle has this feature, you can control certain
radio functions using the buttons on your steering wheel.
SEEK: Press the up or
down arrow to tune to
the next or previous
radio station.
SCAN: Press the SCAN button and SCAN will appear
on the display. SCAN works as the PSCAN button on
your radio.
It will scan through each of the preset radio
stations. If a preset radio station has weak reception, the
radio will not stop at the preset station. Press SCAN
again to stop scanning.
AM-FM: Press this button to choose AM, FM1 or FM2.
If a cassette tape or compact disc is playing, press this
button to stop it and the radio will play.
SRCE: Press this button to
change to the cassette tape,
compact disc function or
return to playing the radio.
If a cassette tape or compact disc is playing, the player
will advance to the next
or previous selection. MUTE: Press this button to silence the audio system.
Press it again to turn on the sound.
VOL: Press the up or down arrow to increase or
decrease volume.
3-28
ProCarManuals.com
Page 196 of 388

To turn the system on or
off, press the TRACTION
button on the black panel located directly behind
your automatic transaxle
shift lever.
When
you turn the system off, the Enhanced Traction
System warning light will come on and stay on. If the
Enhanced Traction System is limiting wheel spin when
you press the button to turn the system off, the warning
light will come on
-- but the system won’t turn off right
away. It will wait until there’s no longer a current need
to limit wheel spin.
You can turn the system back on at any time by pressing
the button again. The Enhanced Traction System
warning light should go off.
Braking in Emergencies
With anti-lock, you can steer and brake at the same
time. In many emergencies, steering can help you more
than even
the very best braking.
Steering
Power Steering
If you lose power steering assist because the engine
stops or the system
is not functioning, you can steer but
it will take much more effort.
Magnetic Variable Effort Steering TM
This steering system provides lighter steering effort for
parking and when driving at low speeds. Steering effort
will increase at higher speeds for improved road feel.
Steering Tips
Driving on Curves
It’s important to take curves at a reasonable speed.
A lot of the “driver lost control’’ accidents mentioned on
the news happen on curves. Here’s why:
Experienced driver or beginner, each
of us is subject to
the same laws of physics when driving on curves. The
traction
of the tires against the road surface makes it
possible for the vehicle
to change its path when you turn
the front wheels.
If there’s no traction, inertia will keep
the vehicle going
in the same direction. If you’ve ever
tried to steer a vehicle on wet ice, you’ll understand this.
4-12
ProCarManuals.com
Page 197 of 388

The traction you can get in a curve depends on the
condition of your tires and the road surface, the angle at
which the curve is banked, and your speed.
While you’re
in a curve, speed is the one factor you can control.
Suppose you’re steering through a sharp curve. Then you
suddenly accelerate. Both control systems
-- steering and
acceleration
-- have to do their work where the tires meet
the road. Adding the sudden acceleration can demand too
much of those places. You can
lose control.
What should
you do if this ever happens? Ease up on the
accelerator pedal, steer the vehicle the way you want it
to go, and slow down.
Speed limit signs near curves warn that you should
adjust your speed. Of course, the posted speeds are
based on good weather and road conditions. Under less
favorable conditions you’ll want
to go slower.
Steering in Emergencies
There are times when steering can be more effective
than braking. For example, you come over a hill and
find a truck stopped
in your lane, or a car suddenly pulls
out from nowhere, or a child darts out from between
parked cars and stops right in front of you. You can
avoid these problems by braking
-- if you can stop in
time. But sometimes you can’t; there isn’t room.
That’s the time for evasive action
-- steering around
the problem.
Your vehicle can perform very well in emergencies like
these. First apply your brakes. (See “Braking
in
Emergencies” earlier in this section.) It is better to
remove as much speed as you can from a possible
collision. Then steer around the problem, to the left
or
right depending on the space available.
If you need to reduce your speed as you approach a
curve, do it before you enter the curve, while your front
wheels are straight ahead.
Try to adjust your speed so you can “drive” through the
curve. Maintain a reasonable, steady speed. Wait to
accelerate until you are out of the curve, and then
accelerate gently into the straightaway.
4-13
ProCarManuals.com
Page 198 of 388
An emergency like this requires close attention and a
quick decision. If you are holding the steering wheel at
the recommended
9 and 3 o’clock positions, you can
turn it a
full 180 degrees very quickly without removing
either hand. But you have to act fast, steer quickly, and
just as quickly straighten the wheel once you have
avoided the object.
The fact that such emergency situations are always
possible is
a good reason to practice defensive driving at
all times and wear safety belts properly.
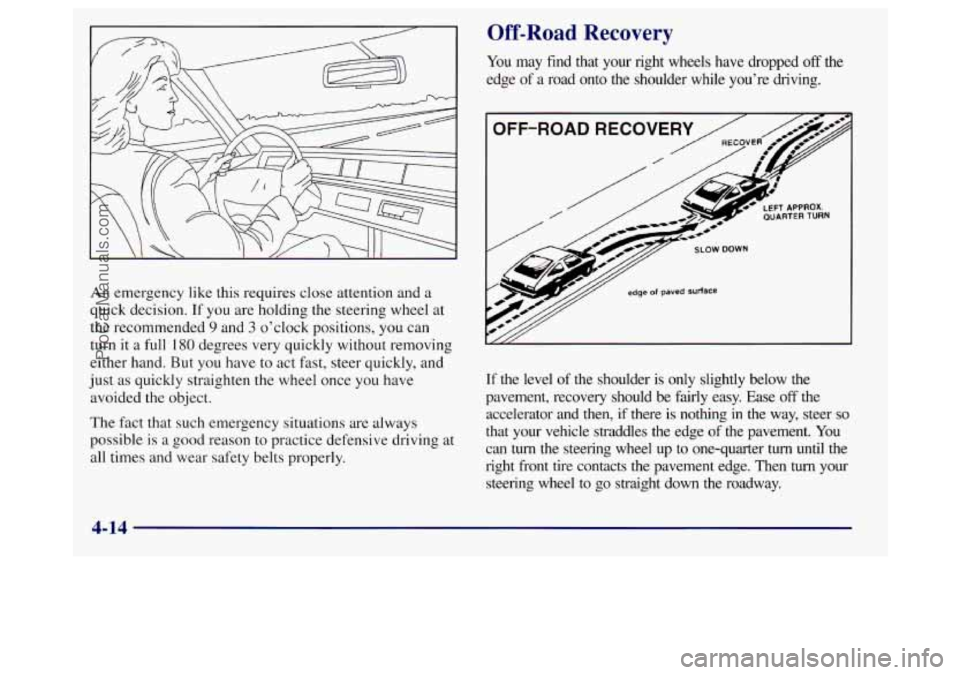
Off-Road Recovery
You may find that your right wheels have dropped off the
edge
of a road onto the shoulder while you’re driving.
If the level
of the shoulder is only slightly below the
pavement, recovery should be fairly easy. Ease
off the
accelerator and
then, if there is nothing in the way, steer so
that your vehicle straddles the edge of the pavement. You
can turn the steering wheel up to one-quarter turn until the
right front tire contacts the pavement edge. Then
turn your
steering wheel to
go straight down the roadway.
4-14
ProCarManuals.com
Page 200 of 388

0
0
0
0
Check your mirrors, glance over your shoulder, and start your left lane change signal before moving out
of the right lane
to pass. When you are far enough
ahead
of the passed vehicle to see its front in your
inside mirror, activate your right lane change signal
and move back into the right lane. (Remember that
your right outside mirror is convex. The vehicle you
just passed may seem to be farther away from you
than
it really is.)
Try not to pass more than one vehicle at a time
on two-lane roads. Reconsider before passing the
next vehicle.
Don’t overtake a slowly moving vehicle too rapidly.
Even though the brake lamps are not flashing, it may
be slowing down or starting to turn.
If you’re being passed, make
it easy for the
following driver to get ahead
of you. Perhaps you
can ease a little to the right.
Loss of Control
Let’s review what driving experts say about what
happens when the three control systems (brakes, steering
and acceleration) don’t have enough friction where the
tires meet the road to do what the driver has asked. In any emergency, don’t give up. Keep trying
to steer and
constantly seek an escape route or area of less danger.
Skidding
In a skid, a driver can lose control of the vehicle.
Defensive drivers avoid most skids by taking reasonable
care suited
to existing conditions, and by not “overdriving”
those conditions. But skids are always possible.
The three types of skids correspond to your vehicle’s
three control systems. In the braking skid, your wheels
aren’t rolling. In the steering or cornering skid, too
much speed or steering in a curve causes tires to slip and
lose cornering force. And in the acceleration skid, too
much throttle causes the driving wheels
to spin.
A cornering skid and an acceleration skid
are best
handled by easing your
foot off the accelerator pedal.
If your vehicle starts to slide, ease your foot off the
accelerator pedal and quickly steer the way you want the
vehicle to
go. If you start steering quickly enough, your
vehicle may straighten out. Always be ready for a
second skid if it occurs.
4-16
ProCarManuals.com
Page 222 of 388

Driving with a Trailer
Towing a trailer requires a certain amount of experience.
Before setting out for the open road, you’ll want to get
to know your rig. Acquaint yourself with the feel
of
handling and braking with the added weight of the
trailer. And always keep in mind that the vehicle you are
driving is now a good deal longer and not nearly as
responsive as your vehicle
is by itself.
Before you start, check the trailer hitch and platform
(and attachments), safety chains, electrical connector,
lamps, tires and mirror adjustment. If the trailer has
electric brakes, start your vehicle and trailer moving and
then apply the trailer brake controller by hand to be sure
the brakes are working. This lets you check your
electrical connection at the same time.
During your trip, check occasionally to be sure that the
load is secure, and that the lamps and any trailer brakes
are still working.
Following Distance
Stay at least twice as far behind the vehicle ahead as you
would when driving your vehicle without a trailer. This
can help you avoid situations that require heavy braking
and sudden turns.
Passing
You’ll need more passing distance up ahead when
you’re towing a trailer. And, because you’re a good deal
longer, you’ll need to go much farther beyond the
passed vehicle before you can return to your lane.
Backing Up
Hold the bottom of the steering wheel with one hand.
Then, to move the trailer
to the left, just move that hand
to
the left. To move the trailer to the right, move your
hand to the right. Always back up slowly and, if
possible, have someone guide
you.
4-38
ProCarManuals.com
Page 236 of 388

A vehicle can fall from a car carrier if it isn’t
adequately secured. This can cause
a collision,
serious personal injury and vehicle damage. The
vehicle should be tightly secured with chains or
steel cables before
it is transported,
Don’t use substitutes (ropes, leather straps,
canvas webbing, etc.) that can be cut by sharp
edges underneath the towed vehicle. Always use
T-hooks inserted in the T-hook slots. Never use
J-hooks. They will damage drivetrain and
suspension components.
When your vehicle is being towed, have the ignition key
in OFF. The steering wheel should be clamped in a
straight-ahead position, with a clamping device
designed for towing service.
Do not use the vehicle’s
steering column lock for this. The transaxle should be
in
NEUTRAL (N) and the parking brake released.
NOTICE:
Don’t have your vehicle towed on the drive
wheels, unless you must,
If the vehicle must be
towed on the drive wheels, do not tow the vehicle
more than
500 cumulative miles (800 km) or
exceed
50 mph (80 km/h). Cumulative miles are
defined
as total miles over the life of the vehicle.
For example, your vehicle cannot be towed
500 miles (800 km) each day of a trip totaling
3,000 miles (4800 km). If these limitations must
be exceeded, then the drive wheels have to be
supported on
a dolly.
5-10
ProCarManuals.com