tires CHEVROLET ASTRO 1996 Owners Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: CHEVROLET, Model Year: 1996, Model line: ASTRO, Model: CHEVROLET ASTRO 1996Pages: 372, PDF Size: 21.51 MB
Page 159 of 372

Control of a Vehicle
You have three systems that make your vehicle go where
you want it to go. They are the brakes, the steering and
the accelerator. All three systems have
to do their work
at the places where the tires meet the road.
Braking
Sometimes, as when you’re driving on snow or ice, it’s
easy to ask more of those control systems than the tires
and road can provide. That means you can lose control
of your vehicle. Braking action
involves
perception time and
reaction time.
First, you have to decide to push on the brake pedal.
That’s
perception time. Then you have to bring up
your
foot and do it. That’s reaction time.
Average reaction time is about 3/4 of a second. But
that’s
only an average. It might be less with one driver
and as long as two or three seconds or more with
another. Age, physical condition, alertness, coordination
and eyesight all play a part.
So do alcohol, drugs and
frustration. But even in
3/4 of a second, a vehicle
moving at
60 mph (1 00 km/h) travels 66 feet (20 m).
That could be a
lot of distance in an emergency, so
keeping enough space between your vehicle and others
is important.
And,
of course, actual stopping distances vary greatly
with the surface of the road (whether it’s pavement
or
gravel); the condition of the road (wet, dry, icy); tire
tread; and the condition of your brakes.
4-5
Page 162 of 372

Remember: Anti-lock doesn’t change the time you need
to get your foot up
to the brake pedal or always decrease
stopping distance. If you get too close
to the vehicle in
front
of you, you won’t have time to apply your brakes
if that vehicle suddenly slows or stops. Always leave
enough room up ahead
to stop, even though you have
anti-lock brakes.
Using Anti-Lock
Don’t pump the brakes. Just hold the brake pedal
down and let anti-lock work for you. You may feel
the brakes vibrate, or you
may notice some noise, but
this
is normal.
Braking in Emergencies
Use your anti-lock braking system when you need to.
With anti-lock, you can steer and brake at the same
time. In many emergencies, steering can help you more
than even the very best braking.
Steering
Power Steering
If you lose power steering assist because the engine
stops
or the system is not functioning, you can steer but
it will take much more effort,
Steering Tips
Driving on Curves
It’s important to take curves at a reasonable speed.
A lot of the “driver lost control’’ accidents mentioned on
the news happen on curves. Here’s why:
Experienced driver or beginner, each of us is subject to
the same laws of physics when driving
on curves. The
traction
of the tires against the road surface makes it
possible for the vehicle to change its path when
you turn
the front wheels.
If there’s no traction, inertia will keep
the vehicle going
in the same direction. If you’ve ever
tried to steer a vehicle
on wet ice, you’ll understand this.
The traction
you can get in a curve depends on the
condition of your tires and the road surface, the angle
at
which the curve is banked, and your speed. While you’re
in a curve, speed is the one factor
you can control.
Suppose you’re steering through a sharp curve. Then
you
suddenly accelerate. Both control systems -- steering and
acceleration
-- have to do their work where the tires meet
the road. Adding the sudden acceleration can demand too
much
of those places. You can lose control.
What should you do
if this ever happens? Ease up on the
accelerator
pedal, steer the vehicle the way you want it
to
go, and slow down.
4-8
Page 166 of 372

Loss of Control
Let’s review what driving experts say about what
happens when the three control systems (brakes, steering
and acceleration) don’t have enough friction where the
tires meet the road
to do what the driver has asked.
In
any emergency, don’t give up. Keep trying to
steer and constantly seek an escape route or area of
less danger.
Skidding
In a skid, a driver can lose control of the vehicle.
Defensive drivers avoid most skids by taking
reasonable care suited to existing conditions, and by
not “overdriving” those conditions. But skids are
always possible.
The three types
of skids correspond to your vehicle’s
three control systems. In the braking skid, your wheels
aren’t rolling. In
the steering or cornering skid, too
muchspeed or steering
in a curve causes tires to slip and
lose cornering force. And in the acceleration skid, too
much throttle causes the driving wheels
to spin.
A cornering skid and an acceleration skid are best
handled by easing your foot off the accelerator pedal.
If your vehicle starts to slide, ease your foot off the
accelerator pedal and quickly steer the way
you want the
vehicle
to go. If you start steering quickly enough, your
vehicle may straighten out. Always be ready for a
second skid
if it occurs.
Of course, traction is reduced when water, snow, ice,
gravel or other material is on the road. For safety,
you’ll
want to slow down and adjust your driving to these
conditions. It is important to slow down
on slippery
surfaces because stopping distance will be longer and
vehicle control more limited.
While driving on a surface with reduced traction, try
your best to avoid sudden steering, acceleration or
braking (including engine braking by shifting
to a lower
gear).
Any sudden changes could cause the tires to slide.
You may not realize the surface is slippery until your
vehicle is skidding. Learn to recognize warning clues
--
such as enough water, ice or packed snow on the road to
make a “mirrored surface”
-- and slow down when you
have any doubt.
Remember: Any anti-lock brake system (ABS) helps
avoid only
the braking skid.
4-12
Page 168 of 372

You can be temporarily blinded by approaching
headlamps. It can take a second or two, or even several
seconds, for your eyes
to readjust to the dark. When
you are faced with severe glare (as from a driver who
doesn’t lower the high beams,
or a vehicle with
misaimed headlamps), slow down a little. Avoid
staring directly into the approaching headlamps.
Keep your windshield and all the glass
on your vehicle
clean
-- inside and out. Glare at night is made much
worse by dirt
on the glass. Even the inside of the glass
can build up a film caused by dust. Dirty glass makes
lights dazzle and flash more than clean glass would,
making the pupils
of your eyes contract repeatedly.
Remember that your headlamps light up far less of a
roadway when you are in a turn or curve. Keep your
eyes moving; that way, it’s easier to pick out dimly
lighted objects. Just as your headlamps should be
checked regularly for proper aim,
so should your eyes
be examined regularly. Some drivers suffer from night
blindness
-- the inability to see in dim light -- and
aren’t
even aware of it.
Driving in Rain and on Wet Roads
L
Rain and wet roads can mean driving trouble. On a wet
road, you can’t stop, accelerate or turn as well because
your tire-to-road traction
isn’t as good as on dry roads.
And,
if your tires don’t have much tread left, you’ll get
even
less traction. It’s always wise to go slower and be
cautious
if rain starts to fall while you are driving. The
surface may get wet suddenly when your reflexes are
tuned for driving on dry pavement.
4-14
Page 170 of 372

Hydroplaning
Hydroplaning is dangerous. So much water can build up
under
your tires that they can actually ride on the water.
This can happen if the road
is wet enough and you’re
going fast enough. When your vehicle is hydroplaning,
it has little or no contact with the road.
Hydroplaning doesn’t happen often. But it can
if your
tires haven’t much tread or
if the pressure in one or
more is low. It can happen if a lot
of water is standing on
the road. If you can see reflections from trees, telephone
poles or other vehicles, and raindrops “dimple” the
water’s surface, there could be hydroplaning.
Hydroplaning usually happens at higher speeds. There
just isn’t a hard and fast rule about hydroplaning.
The best advice is to slow down when
it is raining.
Driving Through Deep Standing Water
NOTICE:
If you drive too quickly through deep puddles
or standing water, water can come in through
your engine’s air intake and badly damage your
engine. Never drive through water that is slightly
lower than the underbody
of your vehicle. If you
can’t avoid deep puddles or standing water, drive
through them very slowly.
Some Other Rainy Weather Tips
0 Besides slowing down, allow some extra following
distance. And be especially careful when you pass
another vehicle. Allow yourself more clear room
ahead, and be prepared
to have your view restricted
by road spray.
“Tires’’
in the Index.)
0 Have good tires with proper tread depth. (See
4-16
Page 173 of 372

Once you are moving on the freeway, make certain you
allow a reasonable following distance. Expect to move
slightly slower at night.
When you want
to leave the freeway, move to the proper
lane well
in advance. If you miss your exit, do not,
under any circumstances, stop and back up. Drive on to
the next exit.
The
exit ramp can be curved, sometimes quite sharply.
The exit speed is usually posted.
Reduce your speed according to
your speedometer, not
to your sense of motion. After driving for any distance
at higher speeds, you may tend
to think you are going
slower than
you actually are.
Before Leaving on a Long Trip
Make sure you’re ready. Try to be well rested. If you
must start when you’re
not fresh -- such as after a day’s
work
-- don’t plan to make too many miles that first part
of the journey. Wear comfortable clothing and shoes
you
can easily drive in.
Is your vehicle ready for a long trip? If you keep it
serviced and maintained, it’s ready to go. If it needs
service, have it done before starting
out. Of course,
you’ll find experienced and able service experts
in GM
dealers all across North America. They’ll be ready and
willing
to help if you need it.
Here are some things you can check before a trip:
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
Windshield WcrslTer Fluid: Is the reservoir full? Are
all windows clean inside and outside?
Wiper Blades: Are they in good shape?
Fuel, Engine Oil, Other Fluids: Have you checked
all levels?
Lamps: Are they all working? Are the lenses clean?
Tires: They are vitally important to a safe,
trouble-free trip. Is the tread good enough for
long-distance driving? Are the tires all inflated to the
recommended pressure?
Weather Forecasts: What’s the weather outlook
along your route? Should you delay your trip a short
time to avoid
a major storm system?
Maps: Do you have up-to-date maps?
4-19
Page 174 of 372

Highway Hypnosis
Is there actually such a condition as “highway hypnosis”?
Or
is it just plain falling asleep at the wheel? Call it
highway hypnosis, lack of awareness, or whatever.
There is something about an easy stretch of road with
the
same scenery, along with the hum of the tires on the road,
the drone
of the engine, and the rush of the wind against
the vehicle that can make
you sleepy. Don’t let it happen
to you! If it does, your vehicle can leave the road in Zess
than a secund, and you could crash and be injured.
What
can you do about highway hypnosis? First, be
aware
that it can happen.
Then here are
some tips:
0 Make sure your vehicle is well ventilated, with a
comfortably cool interior.
Hill and Mountain Roads
Keep your eyes moving. Scan the road ahead
and to the sides. Check your mirrors and your
instruments frequently. Driving on
steep hills or mountains is different from
driving
in flat or rolling terrain.
If you get sleepy, pull off the road into a rest, service
or parking area and take a nap, get some exercise, or
both. For safety, treat drowsiness
on the highway as
an emergency.
4-20
Page 175 of 372

If you drive regularly in steep country, or if you’re
planning to visit there, here are some tips that can make
your trips safer and more enjoyable.
0 Keep your vehicle in good shape. Check all fluid
. levels and also the brakes, tires, cooling system and
transmission. These parts can work hard
on
mountain roads.
0 Know how to go down hills. The most important
thing to know is this: let your engine do some
of the
slowing down. Shift to
a lower gear when you go
down a steep or long hill.
~~~
A CAUTION:
If you don’t shift down, your brakes could get
so hot that they wouldn’t work well. You would
then have poor braking
or even none going
down
a hill. You could crash. Shift down to let
your engine assist your brakes on
a steep
downhill slope. Coas ,g
downhill in
NEUTRAL (N) or with the
ignition
off is dangerous. Your brakes will have to
do
all the work of slowing down. They could get so
hot that they wouldn’t work well. You would then
have poor braking or even none going down
a hill.
You could crash. Always have your engine running
and your vehicle in gear when you go downhill.
0 Know how to go uphill. You may want to shift down
to a lower gear. The lower gears help cool your engine and transmission, and you can climb the hill better.
0 Stay in your own lane when driving on two-lane
roads
in hills or mountains. Don’t swing wide or cut
across the center
of the road. Drive at speeds that let
you stay
in your own lane.
0 As you go over the top of a hill, be alert. There could be
something in your lane, like a stalled car or an accident.
0 You may see highway signs on mountains that warn of
special problems. Examples are long grades, passing or
no-passing zones, a falling rocks area
or winding
roads. Be alert
to these and take appropriate action.
4-21
Page 177 of 372

What’s the worst time for this? “Wet ice.” Very cold
snow or
ice can be slick and hard to drive on. But wet
ice can be even more trouble because
it may offer the
least traction
of all. You can get wet ice when it’s about
freezing
(32°F; OOC) and freezing rain begins to fall.
Try
to avoid driving on wet ice until salt and sand crews
can get there. Whatever
the condition -- smooth ice,
packed, blowing
or loose snow
-- drive with caution.
Accelerate gently. Try
not to break the fragile traction. If
you accelerate too fast, the drive wheels will spin and
polish the surface under the tires even more.
Your anti-lock brakes improve your vehicle’s stability
when
you make a hard stop on a slippery road. Even
though
you have an anti-lock braking system, you’ll
want to begin stopping sooner than
you would on dry
pavement. See “Anti-Lock”
in the Index.
Allow greater following distance on any slippery road.
Watch for slippery spots. The road might be fine
until you hit a spot that’s covered with ice. On an
otherwise clear road, ice patches may appear
in
shaded areas where the sun can’t reach: around
clumps of trees, behind buildings or under bridges.
Sometimes the surface of a curve or an overpass may
remain icy when the surrounding roads are clear.
If
you see a patch of ice ahead of you, brake before you
are on
it. Try not to brake while you’re actually on
the ice, and avoid sudden steering maneuvers.
Page 180 of 372
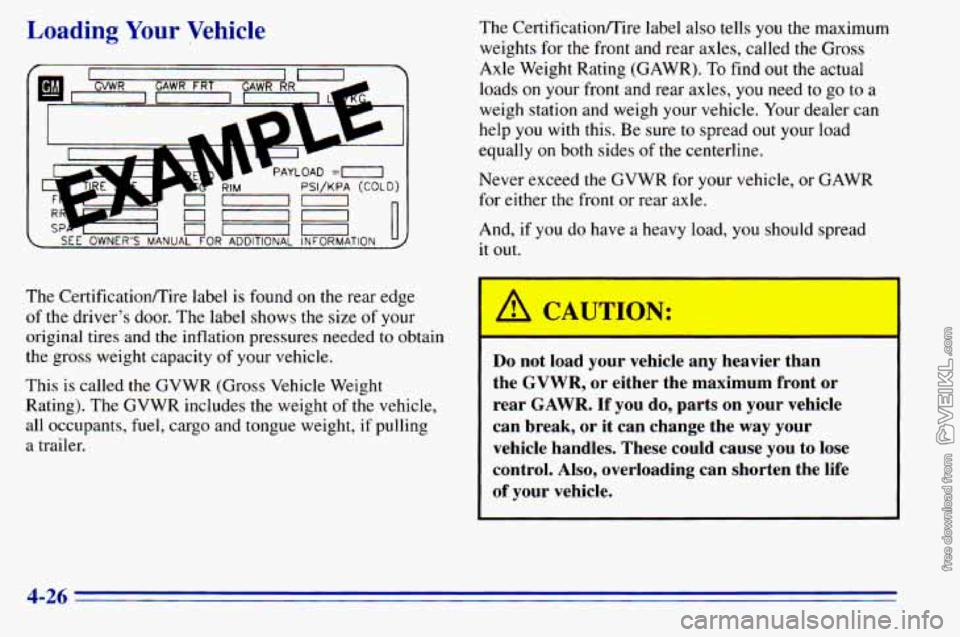
Loading Your Vehicle
7
_I r7 , 1 u-- SEE OWNER'S MANUAL FOR ADDITIONAL INFORMATION 1 U
The CertificatiodTire label is found on the rear edge
of the driver's door. The label shows the size of your
original tires and
the inflation pressures needed to obtain
the gross weight capacity
of your vehicle.
This
is called the GVWR (Gross Vehicle Weight
Rating). The GVWR includes
the weight of the vehicle,
all occupants,
fuel, cargo and tongue weight, if pulling
a trailer. The Certificationmire
label also tells you the maximum
weights for the front and rear axles, called the Gross
Axle Weight Rating (GAWR). To find out the actual
loads
on your front and rear axles, you need to go to a
weigh station and weigh your vehicle. Your dealer can
help
you with this. Be sure to spread out your load
equally
on both sides of the centerline.
Never exceed
the GVWR for your vehicle, or GAWR
for either
the front or rear axle.
And, if you do have a heavy load,
you should spread
it out.
I
A CAUTION: I
I---
Do not load your vehicle any Ldvier than
the
GVWR, or either the maximum front or
rear
GAWR. If you do, parts on your vehicle
can break, or it can change the way your
vehicle handles. These could cause you to lose
control.
Also, overloading can shorten the life
of your vehicle.
4-26