belt CHEVROLET CORVETTE 2003 5.G Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: CHEVROLET, Model Year: 2003, Model line: CORVETTE, Model: CHEVROLET CORVETTE 2003 5.GPages: 368, PDF Size: 2.55 MB
Page 34 of 368
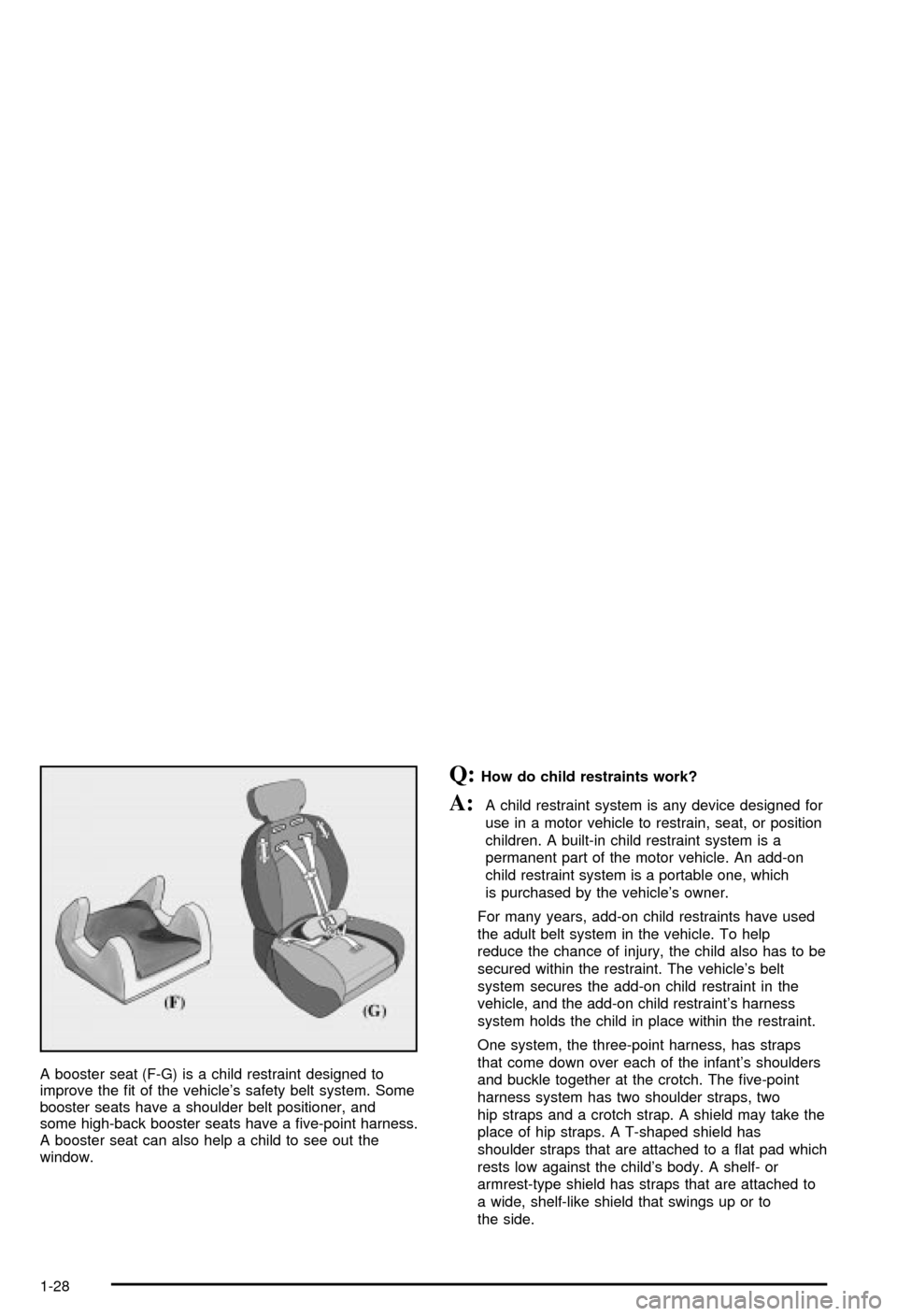
A booster seat (F-G) is a child restraint designed to
improve the ®t of the vehicle's safety belt system. Some
booster seats have a shoulder belt positioner, and
some high-back booster seats have a ®ve-point harness.
A booster seat can also help a child to see out the
window.
Q:How do child restraints work?
A:A child restraint system is any device designed for
use in a motor vehicle to restrain, seat, or position
children. A built-in child restraint system is a
permanent part of the motor vehicle. An add-on
child restraint system is a portable one, which
is purchased by the vehicle's owner.
For many years, add-on child restraints have used
the adult belt system in the vehicle. To help
reduce the chance of injury, the child also has to be
secured within the restraint. The vehicle's belt
system secures the add-on child restraint in the
vehicle, and the add-on child restraint's harness
system holds the child in place within the restraint.
One system, the three-point harness, has straps
that come down over each of the infant's shoulders
and buckle together at the crotch. The ®ve-point
harness system has two shoulder straps, two
hip straps and a crotch strap. A shield may take the
place of hip straps. A T-shaped shield has
shoulder straps that are attached to a ¯at pad which
rests low against the child's body. A shelf- or
armrest-type shield has straps that are attached to
a wide, shelf-like shield that swings up or to
the side.
1-28
Page 35 of 368

When choosing a child restraint, be sure the child
restraint is designed to be used in a vehicle. If it is, it
will have a label saying that it meets federal motor
vehicle safety standards.
Then follow the instructions for the restraint. You may
®nd these instructions on the restraint itself or in a
booklet, or both. These restraints use the belt system in
your vehicle, but the child also has to be secured
within the restraint to help reduce the chance of personal
injury. When securing an add-on child restraint, refer
to the instructions that come with the restraint which may
be on the restraint itself or in a booklet, or both, and
to this manual. The child restraint instructions are
important, so if they are not available, obtain a
replacement copy from the manufacturer.
The child restraint must be secured properly in the
passenger seat. If you want to secure a rear-facing child
restraint in the passenger's seat, turn off the passenger's
air bag. See
Air Bag Off Switch on page 1-44andSecuring a Child Restraint in the Passenger Seat
Position on page 1-34for more on this, including
important safety information.
{CAUTION:
A child in a rear-facing child restraint can be
seriously injured or killed if the passenger's air
bag in¯ates. This is because the back of the
rear-facing child restraint would be very close
to the in¯ating air bag. Be sure to turn off the
air bag before using a rear-facing child
restraint in the passenger seat position.
Keep in mind that an unsecured child restraint can
move around in a collision or sudden stop and injure
people in the vehicle. Be sure to properly secure
any child restraint in your vehicle ┬▒ even when no child
is in it.
1-29
Page 38 of 368
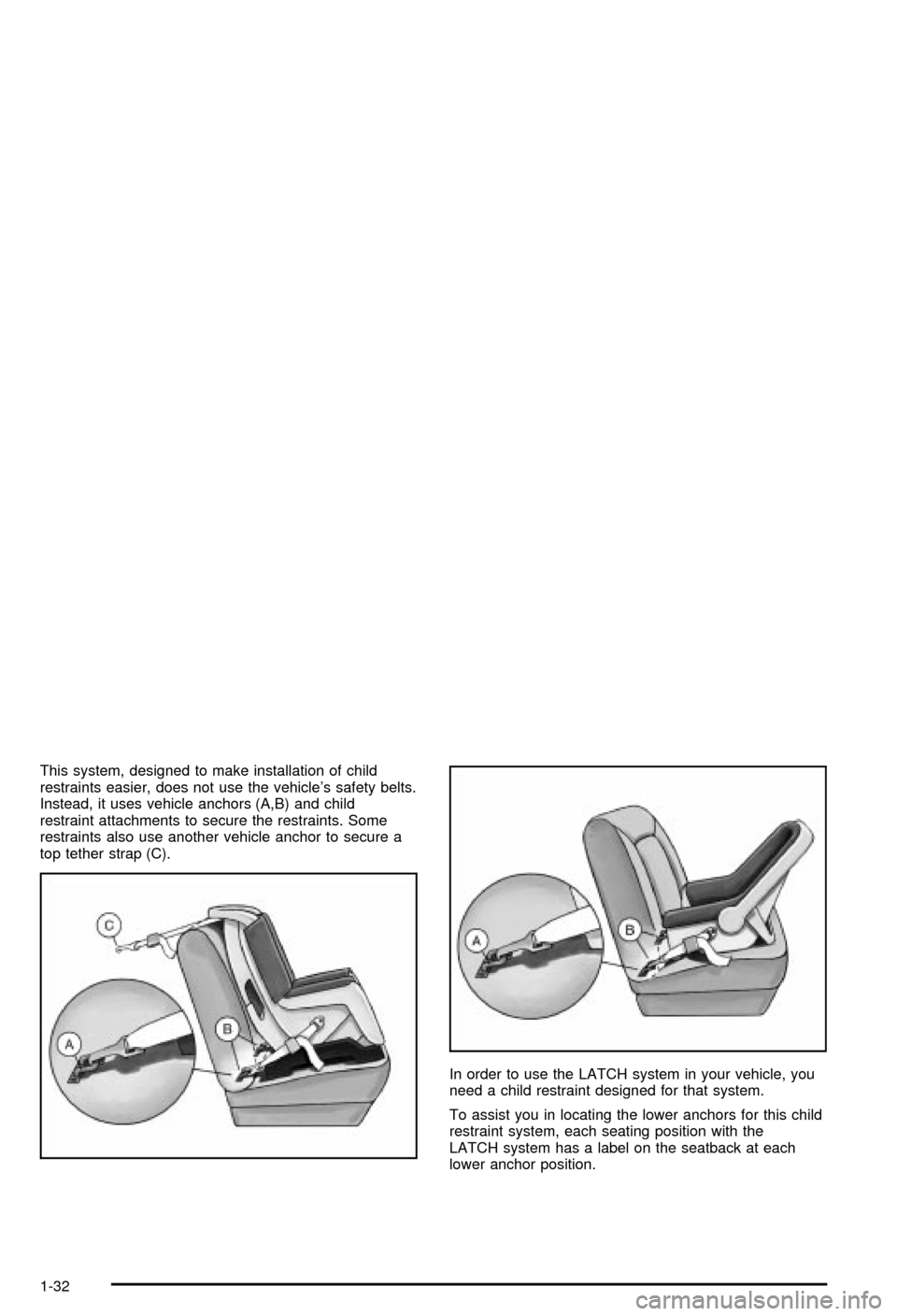

This system, designed to make installation of child
restraints easier, does not use the vehicle's safety belts.
Instead, it uses vehicle anchors (A,B) and child
restraint attachments to secure the restraints. Some
restraints also use another vehicle anchor to secure a
top tether strap (C).
In order to use the LATCH system in your vehicle, you
need a child restraint designed for that system.
To assist you in locating the lower anchors for this child
restraint system, each seating position with the
LATCH system has a label on the seatback at each
lower anchor position.
1-32
Page 39 of 368

The labels are located
near the base of the
passenger seat.
{CAUTION:
If a LATCH-type child restraint isn't attached to
its anchorage points, the restraint won't be
able to protect the child correctly. In a crash,
the child could be seriously injured or killed.
Make sure that a LATCH-type child restraint is
properly installed using the anchorage points,
or use the vehicle's safety belts to secure the
restraint. See ªSecuring a Child Restraint
Designed for the LATCH Systemº or ªSecuring
a Child Restraint in the Passenger Seat
Position┬║ in the Index for information on how
to secure a child restraint in your vehicle.
Securing a Child Restraint Designed
for the LATCH System
1. Find the anchors in the passenger seat. SeeLower
Anchorages and Top Tethers for Children (LATCH
System) on page 1-31
.
2. Put the child restraint on the seat.
3. Attach the anchor points on the child restraint to the
anchors in the vehicle. The child restraint
instructions will show you how.
4. If the child restraint is forward-facing, attach the top
strap to the top strap anchor if your vehicle has
one. See
Top Strap on page 1-30. Tighten the top
strap according to the child restraint instructions.
5. Push and pull the child restraint in different
directions to be sure it is secure.
To remove the child restraint, simply unhook the top
strap from the top tether anchor and then disconnect the
anchor points.
1-33
Page 42 of 368
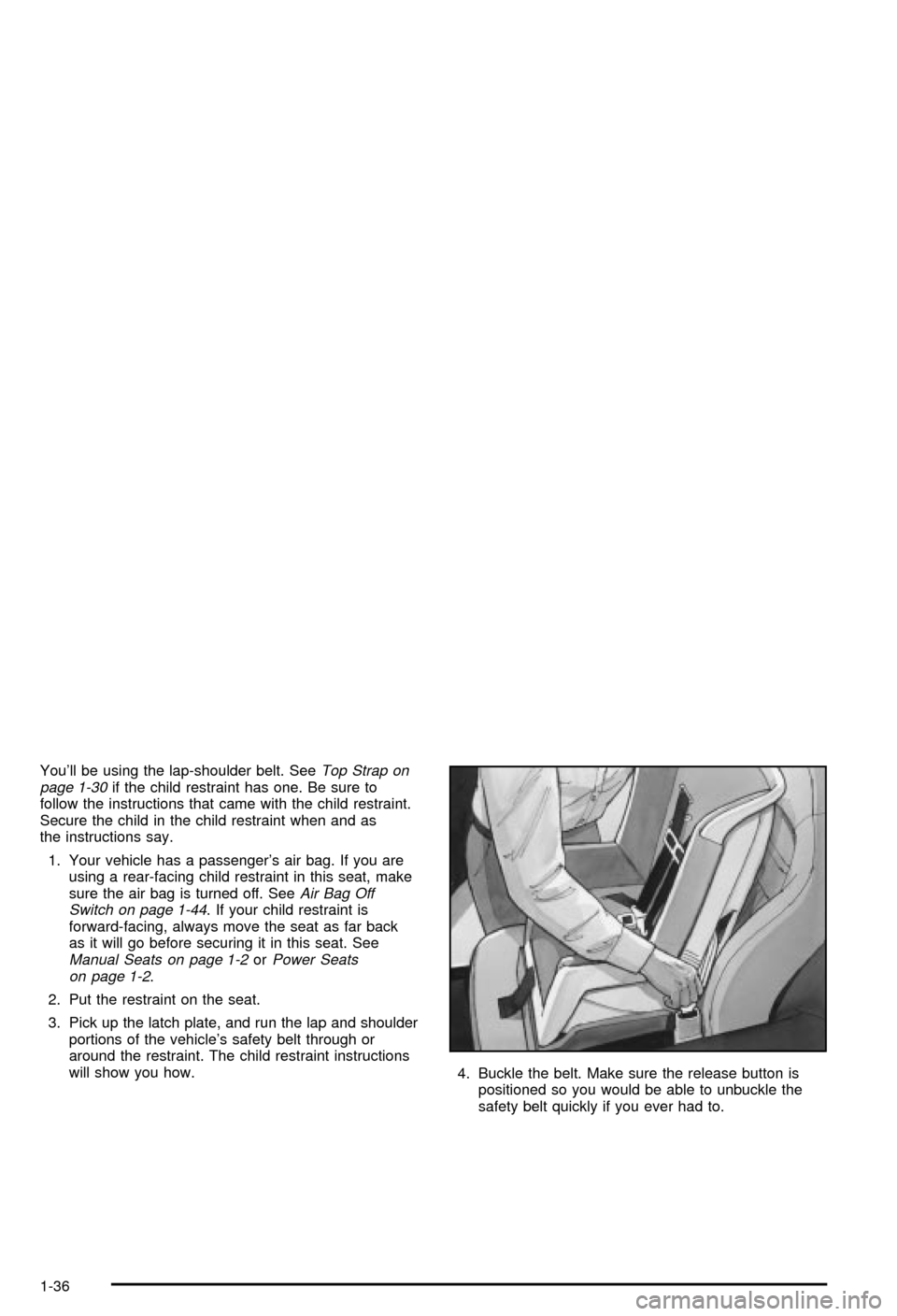

You'll be using the lap-shoulder belt. SeeTop Strap on
page 1-30if the child restraint has one. Be sure to
follow the instructions that came with the child restraint.
Secure the child in the child restraint when and as
the instructions say.
1. Your vehicle has a passenger's air bag. If you are
using a rear-facing child restraint in this seat, make
sure the air bag is turned off. See
Air Bag Off
Switch on page 1-44. If your child restraint is
forward-facing, always move the seat as far back
as it will go before securing it in this seat. See
Manual Seats on page 1-2orPower Seats
on page 1-2.
2. Put the restraint on the seat.
3. Pick up the latch plate, and run the lap and shoulder
portions of the vehicle's safety belt through or
around the restraint. The child restraint instructions
will show you how.
4. Buckle the belt. Make sure the release button is
positioned so you would be able to unbuckle the
safety belt quickly if you ever had to.
1-36
Page 43 of 368
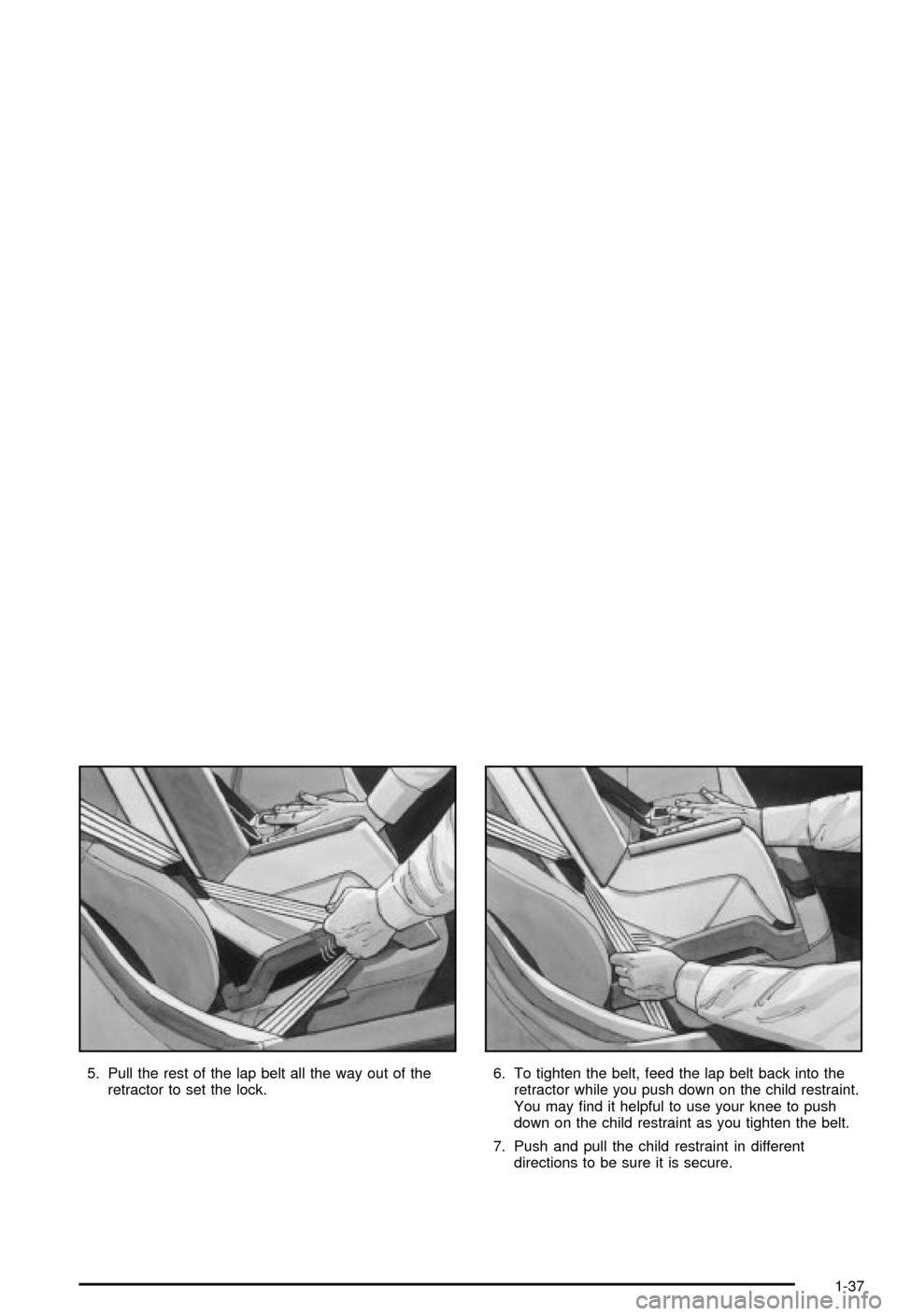

5. Pull the rest of the lap belt all the way out of the
retractor to set the lock.6. To tighten the belt, feed the lap belt back into the
retractor while you push down on the child restraint.
You may ®nd it helpful to use your knee to push
down on the child restraint as you tighten the belt.
7. Push and pull the child restraint in different
directions to be sure it is secure.
1-37
Page 44 of 368

To remove the child restraint, just unbuckle the vehicle's
safety belt and let it go back all the way. The safety
belt will move freely again and be ready to work for an
adult or larger child passenger.
If you were using a rear-facing child restraint, turn on
the passenger's air bag when you remove the
rear-facing child restraint from the vehicle unless the
person who will be sitting there is a member of a
passenger air bag risk group. See
Air Bag Off Switch on
page 1-44.
{CAUTION:
If the passenger's air bag is turned off for a
person who isn't in a risk group identi®ed by
the national government, that person won't
have the extra protection of an air bag. In a
crash, the air bag wouldn't be able to in¯ate
and help protect the person sitting there. Don't
turn off the passenger's air bag unless the
person sitting there is in a risk group. See ªAir
Bag Off Switch┬║ in the Index for more on this,
including important safety information.
1-38
Page 45 of 368
Air Bag System
This part explains the air bag system.
Your vehicle has air bags ┬▒ one air bag for the driver
and another air bag for the passenger.
Frontal air bags are designed to help reduce the risk of
injury from the force of an in¯ating air bag. But these
air bags must in¯ate very quickly to do their job
and comply with federal regulations.
Here are the most important things to know about the
air bag system:
{CAUTION:
You can be severely injured or killed in a crash
if you aren't wearing your safety belt Ð even if
you have air bags. Wearing your safety belt
during a crash helps reduce your chance of
hitting things inside the vehicle or being
ejected from it. Air bags are designed to work
with safety belts, but don't replace them. Air
bags are designed to deploy only in moderate
to severe frontal and near frontal crashes.
CAUTION: (Continued)
CAUTION: (Continued)
They aren't designed to in¯ate at all in rollover,
rear or low-speed frontal crashes, or in many
side crashes. And, for some unrestrained
occupants, air bags may provide less
protection in frontal crashes than more
forceful air bags have provided in the past.
Everyone in your vehicle should wear a safety
belt properly Ð whether or not there's an air
bag for that person.
{CAUTION:
Air bags in¯ate with great force, faster than the
blink of an eye. If you're too close to an
in¯ating air bag, as you would be if you were
leaning forward, it could seriously injure you.
Safety belts help keep you in position before
and during a crash. Always wear your safety
belt, even with air bags. The driver should sit
as far back as possible while still maintaining
control of the vehicle.
1-39
Page 46 of 368
{CAUTION:
Anyone who is up against, or very close to,
any air bag when it in¯ates can be seriously
injured or killed. Air bags plus lap-shoulder
belts offer the best protection for adults, but
not for young children and infants. Neither the
vehicle's safety belt system nor its air bag
system is designed for them. Young children
and infants need the protection that a child
restraint system can provide. Always secure
children properly in your vehicle. To read how,
see
Older Children on page 1-21andInfants
and Young Children on page 1-23
.
There is a air bag
readiness light on the
instrument panel, which
shows the air bag symbol.The system checks the air bag electrical system for
malfunctions. The light tells you if there is an electrical
problem. See
Air Bag Readiness Light on page 3-32for more information.
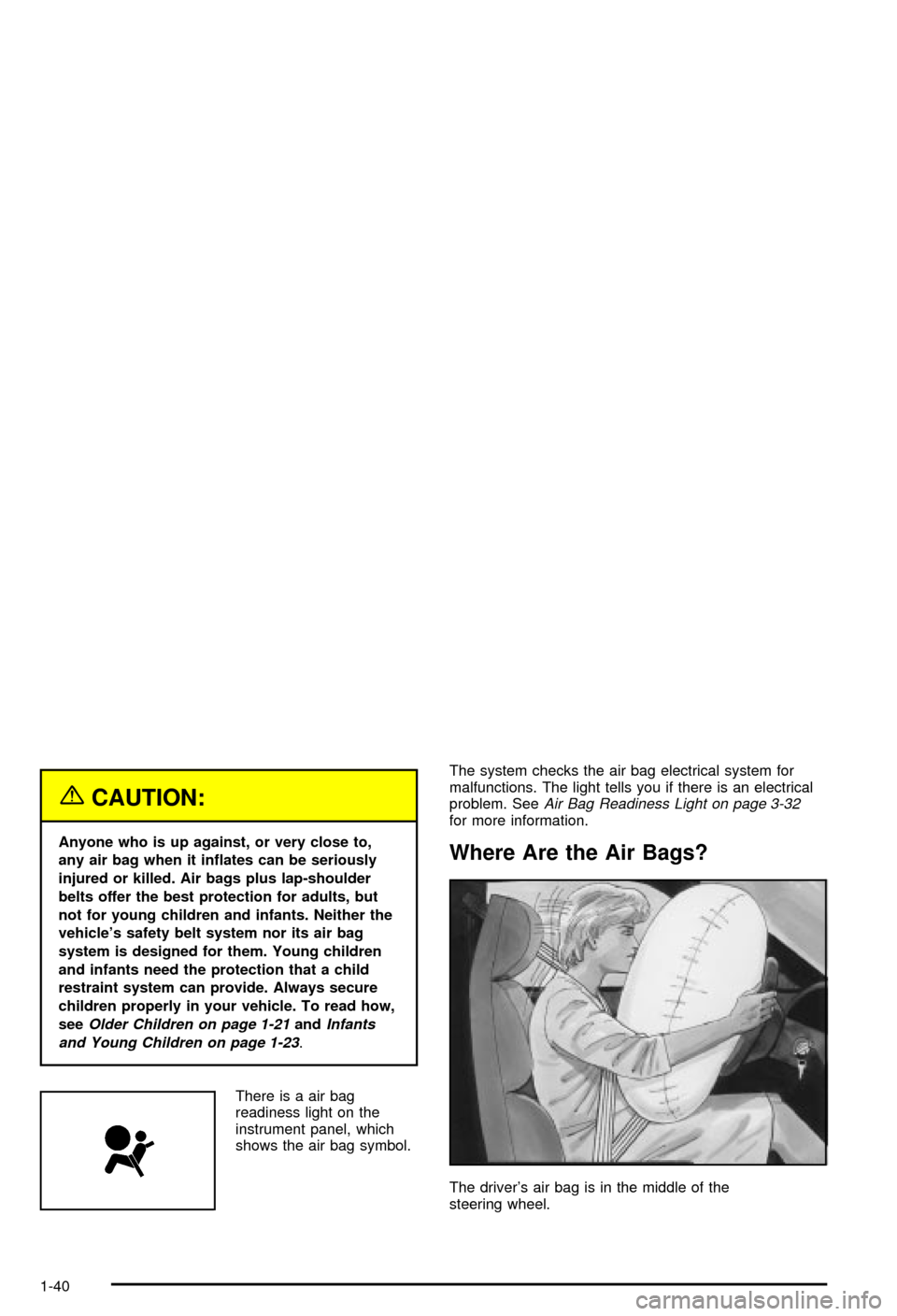
Where Are the Air Bags?
The driver's air bag is in the middle of the
steering wheel.
1-40
Page 48 of 368

When Should an Air Bag In¯ate?
An air bag is designed to in¯ate in a moderate to severe
frontal, or near-frontal crash. The air bag will in¯ate
only if the impact speed is above the system's designed
ªthreshold level.º If your vehicle goes straight into a
wall that does not move or deform, the threshold level is
about 9 to 15 mph (14 to 24 km/h). The threshold
level can vary, however, with speci®c vehicle design, so
that it can be somewhat above or below this range. If
your vehicle strikes something that will move or deform,
such as a parked car, the threshold level will be
higher. The air bag is not designed to in¯ate in rollovers,
rear impacts, or in many side impacts because in¯ation
would not help the occupant.
In any particular crash, no one can say whether an air
bag should have in¯ated simply because of the damage
to a vehicle or because of what the repair costs were.
In¯ation is determined by the angle of the impact
and how quickly the vehicle slows down in frontal or
near-frontal impacts.
What Makes an Air Bag In¯ate?
In an impact of sufficient severity, the air bag sensing
system detects that the vehicle is in a crash. The
sensing system triggers a release of gas from the
in¯ator, which in¯ates the air bag. The in¯ator, air bag
and related hardware are all part of the air bag modules
inside the steering wheel and in the instrument panel
in front of the passenger.
How Does an Air Bag Restrain?
In moderate to severe frontal or near-frontal collisions,
even belted occupants can contact the steering wheel or
the instrument panel. Air bags supplement the
protection provided by safety belts. Air bags distribute
the force of the impact more evenly over the occupant's
upper body, stopping the occupant more gradually.
But air bags would not help you in many types of
collisions, including rollovers, rear impacts and many
side impacts, primarily because an occupant's motion is
not toward those air bags. Air bags should never be
regarded as anything more than a supplement to safety
belts, and then only in moderate to severe frontal or
near-frontal collisions.
1-42