wheel bolts CHEVROLET HHR 2010 1.G Owners Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: CHEVROLET, Model Year: 2010, Model line: HHR, Model: CHEVROLET HHR 2010 1.GPages: 480, PDF Size: 5.25 MB
Page 378 of 480

Wheel Alignment and Tire Balance
The tires and wheels on your vehicle were aligned and
balanced carefully at the factory to give you the longest
tire life and best overall performance. Adjustments
to wheel alignment and tire balancing will not be
necessary on a regular basis. However, if you notice
unusual tire wear or your vehicle pulling to one side or
the other, the alignment might need to be checked.
If you notice your vehicle vibrating when driving on a
smooth road, the tires and wheels might need to be
rebalanced. See your dealer/retailer for proper
diagnosis.
Wheel Replacement
Replace any wheel that is bent, cracked, or badly
rusted or corroded. If wheel nuts keep coming loose,
the wheel, wheel bolts, and wheel nuts should be
replaced. If the wheel leaks air, replace it (except some
aluminum wheels, which can sometimes be repaired).
See your dealer/retailer if any of these conditions exist.
Your dealer/retailer will know the kind of wheel
you need.
Each new wheel should have the same load-carrying
capacity, diameter, width, offset, and be mounted the
same way as the one it replaces.If you need to replace any of your wheels, wheel bolts,
wheel nuts, or Tire Pressure Monitor System (TPMS)
sensors, replace them only with new GM original
equipment parts. This way, you will be sure to have the
right wheel, wheel bolts, wheel nuts, and TPMS sensors
for your vehicle.
{WARNING:
Using the wrong replacement wheels, wheel bolts,
or wheel nuts on your vehicle can be dangerous.
It could affect the braking and handling of your
vehicle, make your tires lose air and make you
lose control. You could have a collision in which
you or others could be injured. Always use the
correct wheel, wheel bolts, and wheel nuts for
replacement.
Notice: The wrong wheel can also cause problems
with bearing life, brake cooling, speedometer or
odometer calibration, headlamp aim, bumper height,
vehicle ground clearance, and tire or tire chain
clearance to the body and chassis.
See Changing a Flat Tire
on page 6‑88for more
information.
6-76
Page 397 of 480

6. Remove any rust or dirtfrom the wheel bolts,
mounting surfaces and
spare wheel.
7. Place the compact spare tire on the wheel-mounting surface.
{WARNING:
Never use oil or grease on bolts or nuts because
the nuts might come loose. The vehicle's wheel
could fall off, causing a crash. 8. Reinstall the wheel nuts with the rounded end of
the nuts toward the wheel. Tighten each nut by
hand until the wheel is held against the hub.9. Lower the vehicle by turning the jack handle
counterclockwise. Lower the jack completely.
6-95
Page 401 of 480

5. Remove all the wheelnuts and take off
the tire.
6. Install the compact spare tire.
{WARNING:
Rust or dirt on a wheel, or on the parts to which it
is fastened, can make wheel nuts become loose
after time. The wheel could come off and cause
an accident. When changing a wheel, remove any
rust or dirt from places where the wheel attaches (Continued)
WARNING: (Continued)
to the vehicle. In an emergency, use a cloth or a
paper towel to do this; but be sure to use a
scraper or wire brush later, if needed, to get all the
rust or dirt off. SeeChanging a Flat Tire
on
page 6‑88
.
7. Remove any rust or dirt from the wheel bolts,
mounting surfaces and
spare wheel.
8. Place the compact spare tire on the wheel-mounting surface.
6-99
Page 402 of 480

{WARNING:
Never use oil or grease on bolts or nuts because
the nuts might come loose. The vehicle's wheel
could fall off, causing a crash.
9. Reinstall the wheel nuts with the rounded end of the nuts toward the wheel. Tighten each nut by
hand until the wheel is held against the hub.
10. Lower the vehicle by turning the jack handle counterclockwise. Lower the jack completely.
{WARNING:
Wheel nuts that are improperly or incorrectly
tightened can cause the wheels to become loose
or come off. The wheel nuts should be tightened
with a torque wrench to the proper torque
specification after replacing. Follow the torque
specification supplied by the aftermarket
manufacturer when using accessory locking wheel
nuts. See Capacities and Specifications
on
page 6‑125
for original equipment wheel nut
torque specifications.
Notice: Improperly tightened wheel nuts can lead to
brake pulsation and rotor damage. To avoid
expensive brake repairs, evenly tighten the wheel
nuts in the proper sequence and to the proper
torque specification. See Capacities and
Specifications
on page 6‑125for the wheel nut torque
specification.
6-100
Page 406 of 480
{WARNING:
Rust or dirt on a wheel, or on the parts to which it
is fastened, can make wheel nuts become loose
after time. The wheel could come off and cause
an accident. When changing a wheel, remove any
rust or dirt from places where the wheel attaches
to the vehicle. In an emergency, use a cloth or a
paper towel to do this; but be sure to use a
scraper or wire brush later, if needed, to get all the
rust or dirt off. SeeChanging a Flat Tire
on
page 6‑88
.
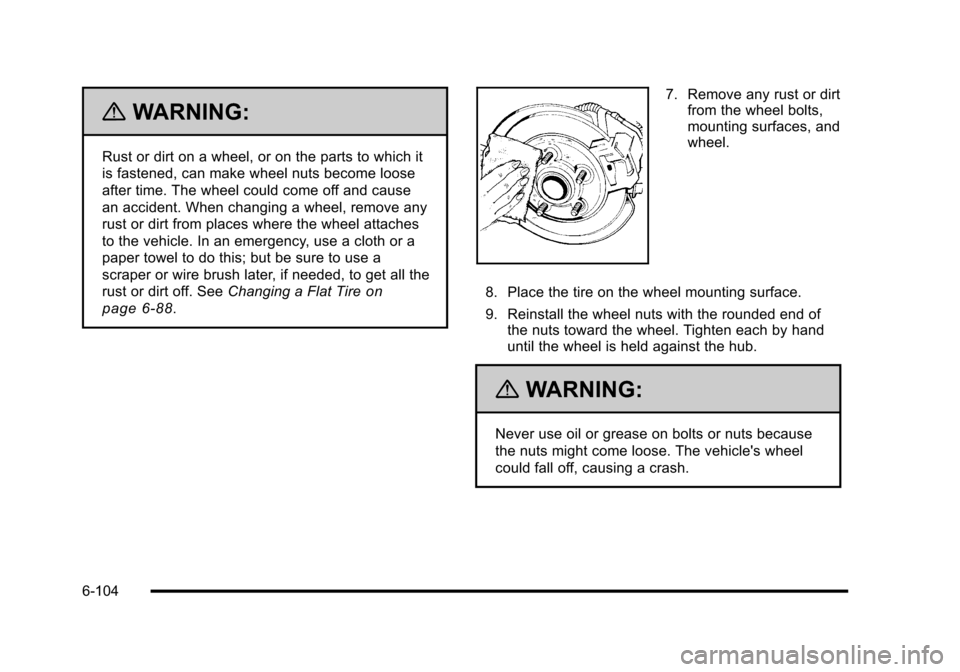
7. Remove any rust or dirt from the wheel bolts,
mounting surfaces, and
wheel.
8. Place the tire on the wheel mounting surface.
9. Reinstall the wheel nuts with the rounded end of the nuts toward the wheel. Tighten each by hand
until the wheel is held against the hub.
{WARNING:
Never use oil or grease on bolts or nuts because
the nuts might come loose. The vehicle's wheel
could fall off, causing a crash.
6-104