tire pressure CHEVROLET MONTE CARLO 1995 5.G Owners Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: CHEVROLET, Model Year: 1995, Model line: MONTE CARLO, Model: CHEVROLET MONTE CARLO 1995 5.GPages: 324, PDF Size: 16.74 MB
Page 135 of 324

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine The anti-lock system can change the brake pressure faster
than any driver could. The computer is programmed to
make the
most of available tire and road conditions.
Here’s how anti-lock works. Let’s say the road is wet.
You’re driving safely. Suddenly an animal jumps out
in
front of you.
You slam on the brakes. Here’s what happens with
ABS.
A computer senses that wheels are slowing down. If one
of the wheels
is about to stop rolling, the computer will
separately work the brakes at each front wheel and at the
rear wheels.
You can steer around the obstacle while braking hard.
As you brake, your computer keeps receiving updates on
wheel speed and controls braking pressure accordingly.
4-7
Page 136 of 324

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Remember: Anti-lock doesn’t change the time you need
to get your foot up to the brake pedal. If you get too
close to the vehicle in front of you, you won’t have time
to apply your brakes if that vehicle suddenly slows or
stops. Always leave enough room up ahead
to stop, even
though
you have anti-lock brakes.
To Use Anti-Lock
Don’t pump the brakes. Just hold the brake pedal down
and let anti-lock work for you.
You may feel the system
worhng, or you may notice some noise, but this is
normal. When your anti-lock system
is adjusting brake
pressure to help avoid a braking skid, the
LOW TRAC
light will come on. See “Anti-Lock Brake System
Active Light” in the Index.
Braking in Emergencies
Use your anti-lock braking system when you need to.
With anti-lock, you can steer and brake at the same
time.
In many emergencies, steering can help you more
than even the
very best braking.
Steering
Power Steering
If you lose power steering assist because the engine
stops or the system is not functioning, you can steer but
it will take much more effort.
Steering Tips
Driving on Curves
It’s important to take curves at a reasonable speed.
A
lot of the “driver lost control” accidents mentioned on
the news happen on curves. Here’s why:
Experienced driver
or beginner, each of us is subject to
the same laws of physics when driving on curves. The
traction of the tires against the road surface makes
it
possible for the vehicle to change its path when you turn
the front wheels. If there’s no traction, inertia will keep
the vehicle going in the same direction. If you’ve ever
tried to steer
a vehicle on wet ice, you’ll understand this.
Page 144 of 324

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Driving too fast through large water puddles or even
going through some car washes can cause problems, too.
The water may affect your brakes. Try to avoid puddles.
But if
you can’t, try to slow down before YOU hit them.
Hydroplaning
Hydroplaning is dangerous. So much water can build up
under your tires that they can actually ride on the water.
This can happen
if the road is wet enough and you’re
going fast enough. When your vehicle is hydroplaning,
it has little or no contact with the road. Hydroplaning
doesn’t happen often. But it
can if your
tires haven’t much tread or if the pressure
in one or
more is low. It can happen
if a lot of water is standing on
the road. If
you can see reflections from trees, telephone
poles, or other vehicles, and raindrops “dimple” the
water’s surface, there could be hydroplaning.
Hydroplaning usually happens at higher speeds. There
just isn’t a hard and fast rule about hydroplaning. The
best advice is to slow down when
it is raining.
Some Other Rainy Weather Tips
Turn on your low-beam headlamps -- not just your
parking lamps
-- to help make you more visible to
others.
Besides slowing down, allow some extra following
distance. And be especially careful when you pass
another vehicle. Allow yourself more clear room
ahead, and be prepared to have your view restricted
by road spray.
Have good tires with proper tread depth. (See
“Tires”
in the Index.)
4-16
Page 147 of 324

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Once you are moving on the freeway, make certain you
allow
a reasonable following distance. Expect to move
slightly slower at night.
When you want
to leave the fremy, move to the proper
lane well
in advance. If you miss your exit do not, under
any circumstances, stop and back up. Drive on to
the
next exit.
The exit ramp can be curved, sometimes quite sharply.
The exit speed is usually posted.
Reduce your speed according
to your speedometer, not
to your sense of motion. After driving for any distance
at higher speeds, you may tend to think you are going
slower than you actually are.
Before Leaving on a Long Trip
Make sure you’re ready. Try to be well rested. If you
must start when you’re not fresh
-- such as after a day’s
work
-- don’t plan to make too many miles that first part
of the journey. Wear comfortable clothing and shoes you
can easily drive
in.
Is your vehicle ready for a long trip? If you keep it
serviced and maintained, it’s ready to go.
If it needs
service, have it done before starting out.
Of course,
you’ll find experienced and able service experts in
Chevrolet dealers all across North America. They’ll be
ready and willing
to help if you need it.
Here are some things you can check before
a trip:
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
Windshield Washer Fluid: Is the reservoir full? Are
all windows clean inside and outside?
Wiper Blades: Are they in good shape?
Fuel, Engine Oil, Other Fluids: Have you checked
all levels?
knzps: Are they all working? Are the lenses clean?
Tires: They are vitally important to a safe,
trouble-free trip.
Is the tread good enough for
long-distance driving? Are
the tires all inflated to the
recommended pressure?
Weather Forecasts: What’s the weather outlook
along your route? Should you delay your trip
a short
time
to avoid a major storm system?
Maps: Do you have up-to-date maps?
4-19
Page 154 of 324

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Loading Your Vehicle
r
OCCUPANTS VEHICLE CAP. WT.
TIRE-LOADING INFORMATION
FRT. CTR.
RR. TOTAL LBS. KG
MAX. LOADING & GVWR SAME AS VEHICLE
CAPACITY WEIGHT
XXX COLD TIRE
TIRE
SIZE SPEED PRESSURE
RTG PSIiKPa
FRT.
RR.
SPA.
IF TIRES ARE HOT, ADD 4PSIi28KPa
SEE OWNER’S MANUAL
FOR ADDITIONAL
INFORMATION
Two labels on your vehicle show how much weight it
may properly carry. The Tire-Loading Information label
is inside the trunk lid. The label tells you the proper size,
speed rating and recommended inflation pressures for
the tires on your vehicle.
It also gives you important
information about the number of people that can be in
your vehicle and the total weight
you can carry. This
includes the weight
of all occupants, cargo and all
nonfactory-installed options.
MFD BY GENERAL MOTORS CORP
DATE
GVWR GAWR FRT GAWR RR
THIS VEHICLE CONFORMS TO ALL APPLI-
CABLE U.S. FEDERAL MOTOR VEHICLE
SAFETY, BUMPER,
AND THEFT PREVENTION
STANDARDS
IN EFFECT ON THE DATE OF
MANUFACTURE SHOWN ABOVE.
The other label is the Certification label, found on the
rear edge of
the driver’s door. It tells you the gross
weight capacity of your vehicle, called the GVWR
(Gross Vehicle Weight Rating). The GVWR includes the
weight of the vehicle, all occupants, fuel and cargo.
Never exceed the GVWR for your vehicle or the Gross
Axle Weight Rating (GAWR) for either the front or rear
axle.
If you do have a heavy load, spread it out. Don’t carry
more than
167 pounds (75 kg) in your trunk.
4-26
Page 158 of 324
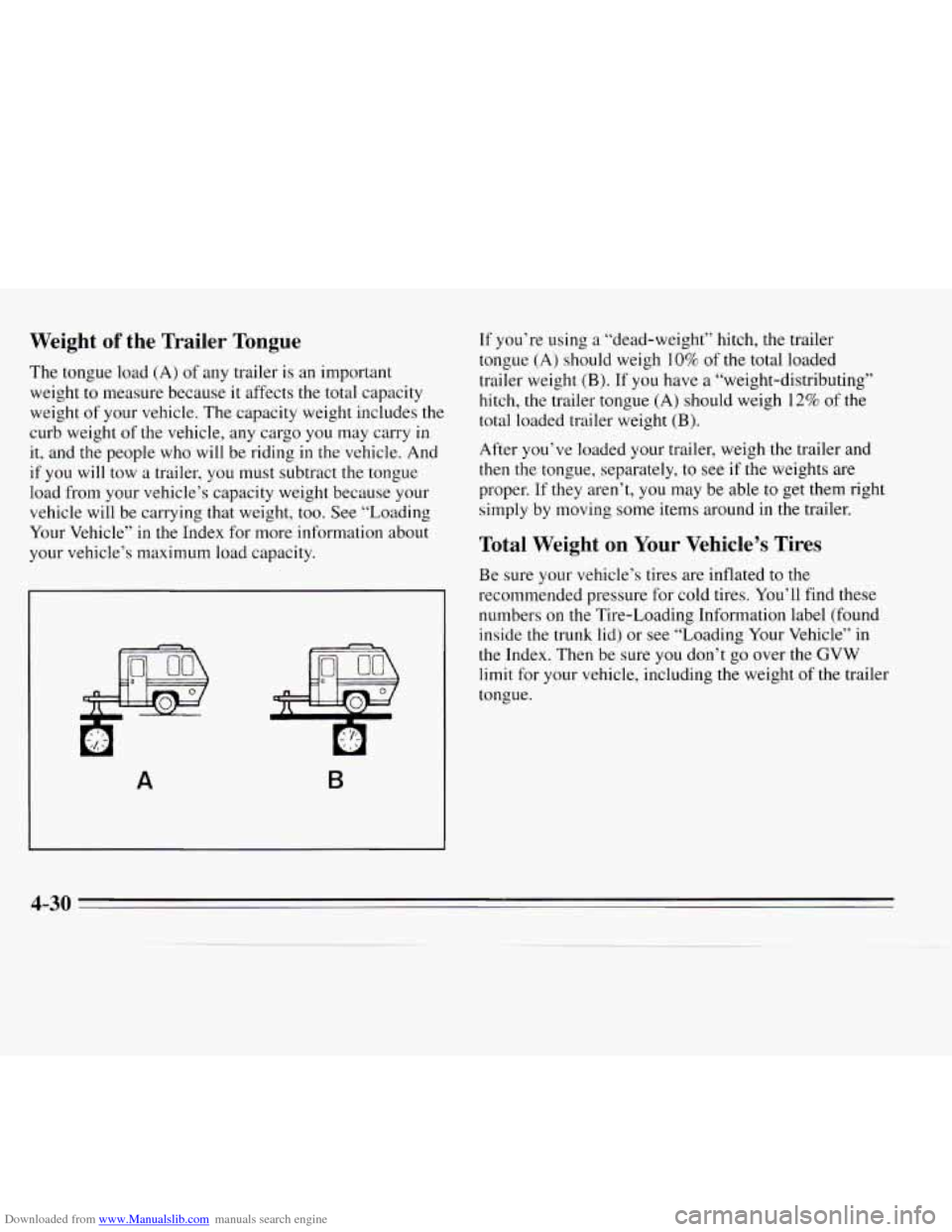
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Weight of the Trailer Tongue
The tongue load (A) of any trailer is an important
weight to measure because
it affects the total capacity
weight of your vehicle.
The capacity weight includes the
curb weight of the vehicle, any cargo you may carry in
it, and the people who will be riding in
the vehicle. And
if you will tow a trailer, you must subtract the tongue
load from your vehicle’s capacity weight because your vehicle will be carrying that weight, too. See “Loading
Your Vehicle”
in the Index for more information about
your vehicle’s maximum load capacity.
A B
If you’re using a “dead-weight” hitch, the trailer
tongue
(A) should weigh 10% of the total loaded
trailer weight
(B). If you have a “weight-distributing’’
hitch, the trailer tongue
(A) should weigh 12% of the
total loaded trailer weight
(B).
After you’ve loaded your trailer, weigh the trailer and
then the tongue, separately,
to see if the weights are
proper. If they aren’t, you may be able to get them right
simply by moving some items around in the trailer.
Total Weight on Your Vehicle’s Tires
Be sure your vehicle’s tires are inflated to the
recommended pressure for cold tires. You’ll find these
numbers on the Tire-Loading Information label (found
inside the trunk lid) or see “Loading Your Vehicle” in
the Index. Then be sure
you don’t go over the GVW
limit for your vehicle, including the weight of the trailer
tongue.
4-30
Page 193 of 324
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Compact Spare Tire
Although the compact spare was fully inflated when
your vehicle was new, it can lose air after a time. Check
the inflation pressure regularly. It should be
60 psi
(420 Wa). After installing the compact spare on your
vehicle, you should stop as soon as possible and make
sure your spare tire is correctly inflated. The compact
spare is made to perform well at posted speed limits for
distances up to
3,000 miles (5 000 km), so you can
finish your trip and have your full-size tire repaired or
replaced where you want. Of course, it’s best to replace
your spare with a full-size tire as soon as you can. Your
spare will last longer and be
in good shape in case you
need it again.
NOTICE:
Don’t take your compact spare through an
automatic car wash with guide rails. The
compact spare can get caught on the rails. That
can damage the tire and wheel, and maybe other
parts
of your vehicle.
Don’t use your compact spare on some other vehicle.
And don’t mix your compact spare or wheel with other
wheels or tires. They won’t fit. Keep your spare and its
wheel together.
NOTICE:
Tire chains won’t fit your compact spare. Using
them will damage your vehicle and destroy the
chains too. Don’t use tire chains on your compact
spare.
3-3 1
Page 231 of 324

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Inflation - Tire Pressure
The Tire-Loading Information label which is on the
inside of the
trunk lid shows the correct inflation
pressures for your tires, when they’re cold. “Cold”
means your vehicle has been sitting for at least three
hours
or driven no more than a mile.
NOTICE:
Don’t let anyone tell you that underinflation or
overinflation
is all right. It’s not. If your tires don’t
have enough
air (underinflation) you can get:
Too much flexing
Too much heat
0 Tire overloading
Bad wear
Bad handling
Bad fuel economy.
If your tires have too much
air (over
you can get:
Unusual wear
Bad handling
Rough ride inflation),
0 Needless
damage from road hazards. When
to Check
Check your tires once a month or more.
Don’t forget your compact spare tire. It should be at
60 psi (420 kPa).
How to Check
Use a good quality pocket-type gage to check tire
pressure. Simply looking at the tires will not tell you the
pressure, especially
if you have radial tires -- which
may look properly inflated even
if they’re underinflated.
If your tires have valve caps, be sure to put them back
on. They help prevent leaks by keeping out dirt and
moisture.
Tire Inspection and Rotation
Tires should be inspected every 6,000 to 8,000 miles
(10
000 to 13 000 km) for any signs of unusual wear. If
unusual wear is present, rotate your tires as soon as
possible and check wheel alignment. Also check for
damaged tires or wheels. See “When It’s Time for New
Tires” and “Wheel Replacement” later in this section for
more information.
6-37
Page 232 of 324
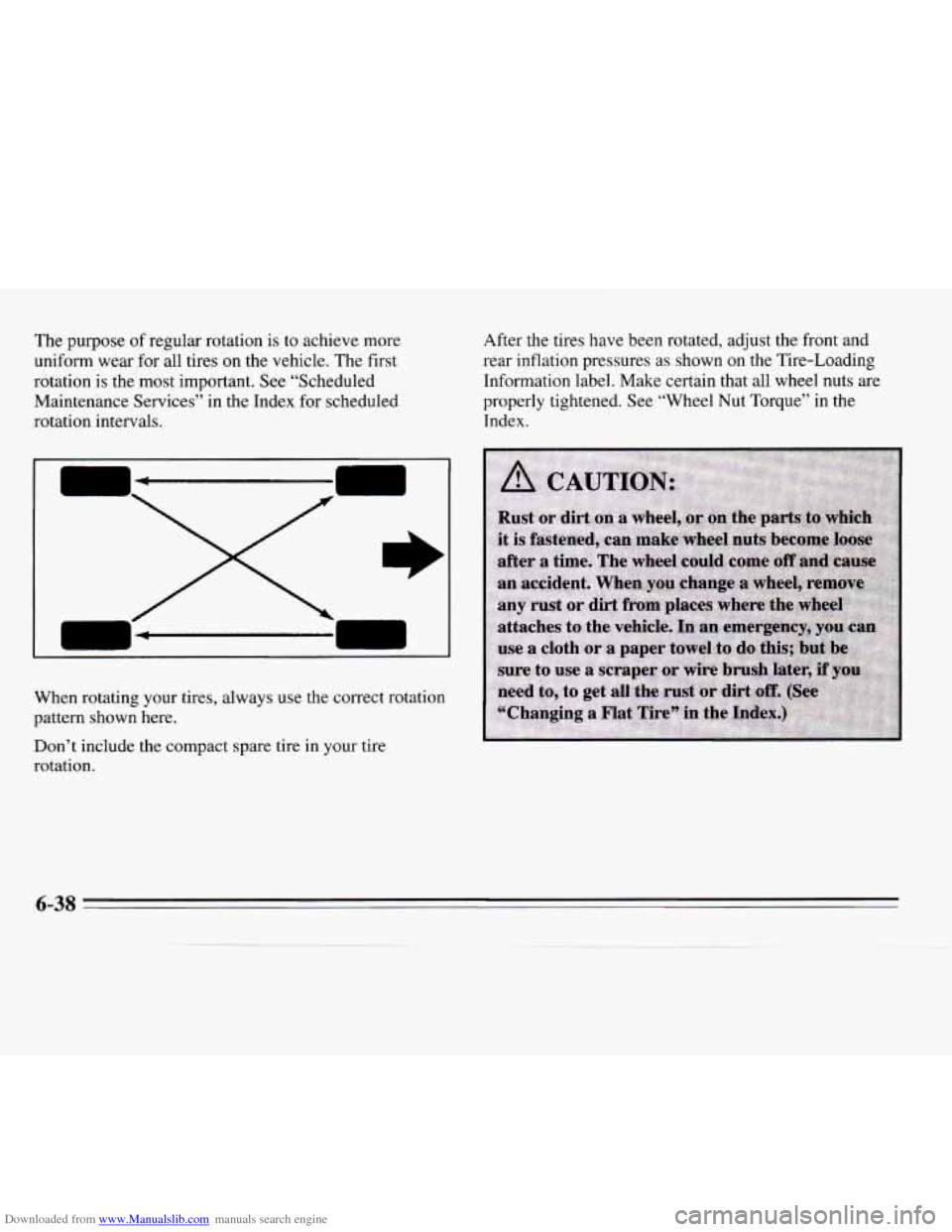
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine The purpose of regular rotation is to achieve more
uniform wear for all tires on the vehicle. The first
rotation is the most important. See “Scheduled
Maintenance Services” in the Index for scheduled
rotation intervals. After the tires have been rotated, adjust
the front and
rear inflation pressures as shown
on the Tire-Loading
Information label. Make certain that all wheel nuts are
properly tightened. See “Wheel Nut Torque” in the
Index.
When rotating your tires, always use the correct rotation
pattern shown here.
Don’t include the compact spare tire in your tire
rotation.
6-38
Page 269 of 324

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Maintenance Schedule I
30,000 Miles (50 000 km)
0 Change engine oil and filter (or every
3 months, whichever occurs first).
An Emission Control Service.
0 Lubricate the shift linkage, parking brake cable
guides, underbody contact
points and linkage
(or every
6 months, whichever occurs first).
every 24 months, whichever occurs first).
0 Drain, flush and refill cooling system (or
every 24 months, whichever occurs first).
See “Engine Coolant’’ in the Index for what
to use. Inspect hoses. Clean radiator,
condenser, pressure cap and neck. Pressure
test the cooling system and pressure cap.
0 Inspect engine accessory drive belt (or
An Emission Control Service.
An Emission Control Service.
0 Replace spark plugs. An Emission Control
Service.
17 Replace air cleaner filter. Replace filter
more often under dusty conditions.
An Emission Control Service.
0 Inspect fuel tank, cap and lines for damage
or leaks. Inspect fuel cap gasket for any
damage. Replace parts as needed.
An Emission Control Service. i-
0 Rotate tires. See “Tire Inspection and
Rotation’’ in the Index for proper rotation
pattern and additional information.
7-11