power steering CHRYSLER CARAVAN 2005 Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: CHRYSLER, Model Year: 2005, Model line: CARAVAN, Model: CHRYSLER CARAVAN 2005Pages: 2339, PDF Size: 59.69 MB
Page 2171 of 2339
REMOVAL
WARNING: ON VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH AIR-
BAGS, DISABLE THE AIRBAG SYSTEM BEFORE
ATTEMPTING ANY STEERING WHEEL, STEERING
COLUMN, OR INSTRUMENT PANEL COMPONENT
DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. DISCONNECT AND ISO-
LATE THE BATTERY NEGATIVE (GROUND) CABLE,
THEN WAIT TWO MINUTES FOR THE AIRBAG SYS-
TEM CAPACITOR TO DISCHARGE BEFORE PER-
FORMING FURTHER DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. THIS
IS THE ONLY SURE WAY TO DISABLE THE AIRBAG
SYSTEM. FAILURE TO TAKE THE PROPER PRE-
CAUTIONS COULD RESULT IN ACCIDENTAL AIR-
BAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE PERSONAL
INJURY.
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Remove the center bezel from the instrument
panel (Refer to 23 - BODY/INSTRUMENT PANEL/
INSTRUMENT PANEL CENTER BEZEL -
REMOVAL).
(3) Place the instrument panel center bezel unit
face down on a suitable work surface. Take the
proper precautions to protect the center bezel from
cosmetic damage.
(4) If the vehicle is equipped with the optional
Automatic Temperature Control (ATC) system, dis-
connect the infrared sensor jumper harness connector
from the receptacle on the back of the A/C-heater
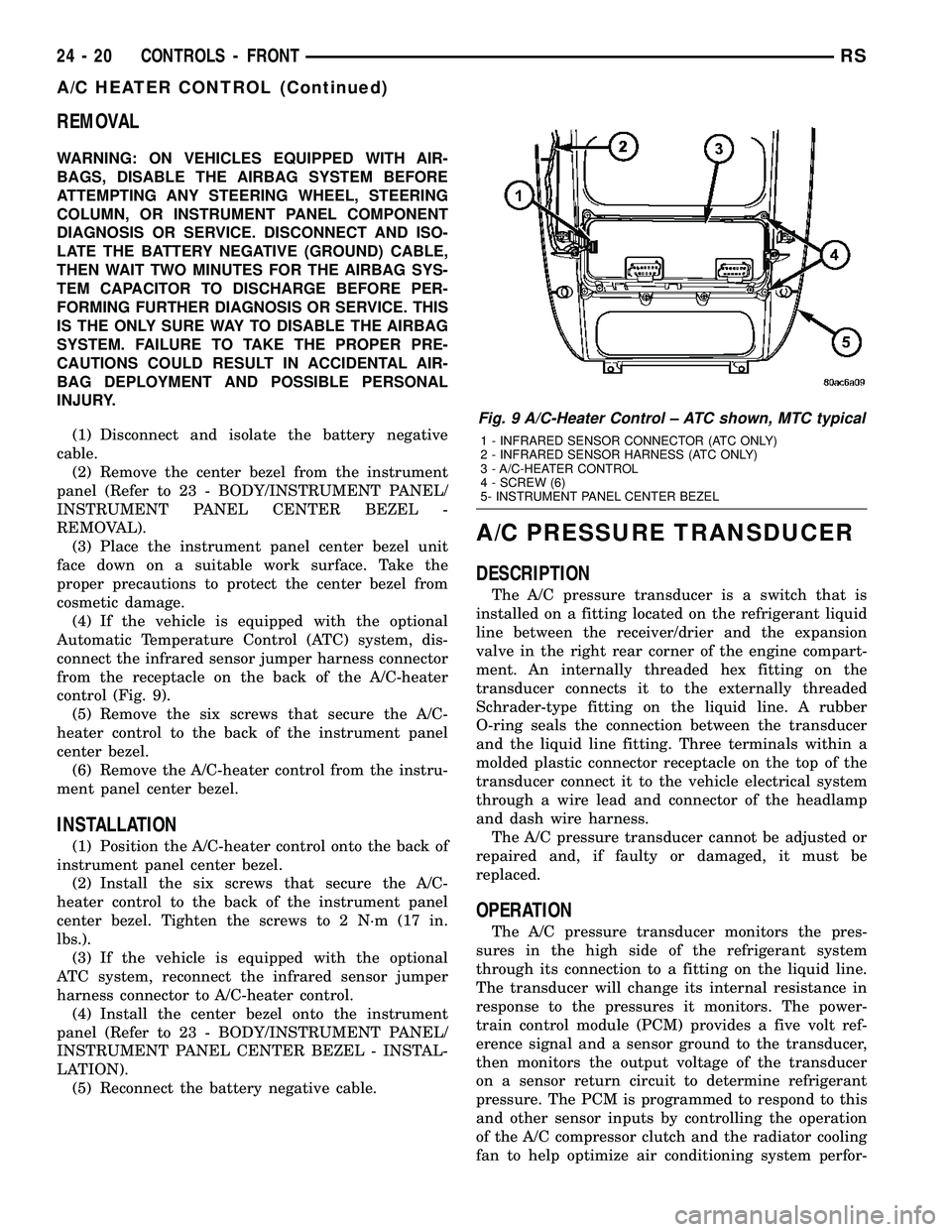
control (Fig. 9).
(5) Remove the six screws that secure the A/C-
heater control to the back of the instrument panel
center bezel.
(6) Remove the A/C-heater control from the instru-
ment panel center bezel.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position the A/C-heater control onto the back of
instrument panel center bezel.
(2) Install the six screws that secure the A/C-
heater control to the back of the instrument panel
center bezel. Tighten the screws to 2 N´m (17 in.
lbs.).
(3) If the vehicle is equipped with the optional
ATC system, reconnect the infrared sensor jumper
harness connector to A/C-heater control.
(4) Install the center bezel onto the instrument
panel (Refer to 23 - BODY/INSTRUMENT PANEL/
INSTRUMENT PANEL CENTER BEZEL - INSTAL-
LATION).
(5) Reconnect the battery negative cable.
A/C PRESSURE TRANSDUCER
DESCRIPTION
The A/C pressure transducer is a switch that is
installed on a fitting located on the refrigerant liquid
line between the receiver/drier and the expansion
valve in the right rear corner of the engine compart-
ment. An internally threaded hex fitting on the
transducer connects it to the externally threaded
Schrader-type fitting on the liquid line. A rubber
O-ring seals the connection between the transducer
and the liquid line fitting. Three terminals within a
molded plastic connector receptacle on the top of the
transducer connect it to the vehicle electrical system
through a wire lead and connector of the headlamp
and dash wire harness.
The A/C pressure transducer cannot be adjusted or
repaired and, if faulty or damaged, it must be
replaced.
OPERATION
The A/C pressure transducer monitors the pres-
sures in the high side of the refrigerant system
through its connection to a fitting on the liquid line.
The transducer will change its internal resistance in
response to the pressures it monitors. The power-
train control module (PCM) provides a five volt ref-
erence signal and a sensor ground to the transducer,
then monitors the output voltage of the transducer
on a sensor return circuit to determine refrigerant
pressure. The PCM is programmed to respond to this
and other sensor inputs by controlling the operation
of the A/C compressor clutch and the radiator cooling
fan to help optimize air conditioning system perfor-
Fig. 9 A/C-Heater Control ± ATC shown, MTC typical
1 - INFRARED SENSOR CONNECTOR (ATC ONLY)
2 - INFRARED SENSOR HARNESS (ATC ONLY)
3 - A/C-HEATER CONTROL
4 - SCREW (6)
5- INSTRUMENT PANEL CENTER BEZEL
24 - 20 CONTROLS - FRONTRS
A/C HEATER CONTROL (Continued)
Page 2181 of 2339

INSTALLATION
(1) Position the mode door actuator onto the HVAC
distribution housing. If necessary, rotate the actuator
slightly to align the splines on the actuator output
shaft with those in the mode door linkage.
(2) Install the two screws that secure the mode
door actuator to the distribution housing. Tighten the
screws to 2 N´m (17 in. lbs.).
(3) Connect the wire harness connector to the
mode door actuator.
(4) Install the silencer under the driver side end of
the instrument panel (Refer to 23 - BODY/INSTRU-
MENT PANEL/INSTRUMENT PANEL SILENCER -
INSTALLATION).
(5) Reconnect the negative battery cable.
(6) Perform the A/C-heater control calibration pro-
cedure (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITION-
ING/CONTROLS - FRONT/A/C-HEATER CONTROL
- STANDARD PROCEDURE - HEATER-A/C CON-
TROL CALIBRATION).
POWER MODULE - BLOWER
MOTOR
DESCRIPTION
A blower motor power module is used on this
model when it is equipped with the optional Auto-
matic Temperature Control (ATC) system. Models
equipped with the standard manual heater-A/C sys-
tem use a blower motor resistor block, instead of the
blower motor power module (Refer to 24 - HEATING
& AIR CONDITIONING/CONTROLS/BLOWER
MOTOR RESISTOR BLOCK - DESCRIPTION).
The blower motor power module is mounted to the
rear of the HVAC housing, directly behind the glove
box opening in the instrument panel. The module
consists of a molded plastic mounting plate with two
integral connector receptacles. Concealed behind the
mounting plate is the power module electronic cir-
cuitry and a large finned, heat sink. The blower
motor power module is accessed for service by remov-
ing the glove box from the instrument panel.
OPERATION
The blower motor power module is connected to the
vehicle electrical system through a dedicated lead
and connector from the instrument panel wire har-
ness. A second connector receptacle receives a wire
lead connector from the blower motor. The blower
motor power module allows the microprocessor-based
Automatic Temperature Control (ATC) heater-A/C
control module to calculate and provide infinitely
variable blower motor speeds based upon either man-
ual blower switch input or the ATC programming
using a Pulse Width Modulated (PWM) circuit strat-
egy. The PWM voltage is applied to a comparator cir-
cuit which compares the PWM signal voltage to the
blower motor feedback voltage. The resulting output
drives the power module circuitry, which adjusts the
voltage output received from the blower motor relay
to change or maintain the desired blower speed. The
blower motor power module is diagnosed using a
DRBIIItscan tool. Refer to Body Diagnostic Proce-
dures.
REMOVAL
WARNING: ON VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH AIR-
BAGS, DISABLE THE AIRBAG SYSTEM BEFORE
ATTEMPTING ANY STEERING WHEEL, STEERING
COLUMN, OR INSTRUMENT PANEL COMPONENT
DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. DISCONNECT AND ISO-
LATE THE BATTERY NEGATIVE (GROUND) CABLE,
THEN WAIT TWO MINUTES FOR THE AIRBAG SYS-
TEM CAPACITOR TO DISCHARGE BEFORE PER-
FORMING FURTHER DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. THIS
IS THE ONLY SURE WAY TO DISABLE THE AIRBAG
SYSTEM. FAILURE TO TAKE THE PROPER PRE-
CAUTIONS COULD RESULT IN ACCIDENTAL AIR-
BAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE PERSONAL
INJURY.
WARNING: THE HEAT SINK FOR THE BLOWER
MOTOR POWER MODULE MAY GET VERY HOT
DURING NORMAL OPERATION. IF THE BLOWER
MOTOR WAS TURNED ON PRIOR TO SERVICING
THE BLOWER MOTOR POWER MODULE, WAIT
FIVE MINUTES TO ALLOW THE HEAT SINK TO
COOL BEFORE PERFORMING DIAGNOSIS OR SER-
VICE. FAILURE TO TAKE THIS PRECAUTION CAN
RESULT IN PERSONAL INJURY.
24 - 30 CONTROLS - FRONTRS
MODE DOOR ACTUATOR (Continued)
Page 2197 of 2339

whenever the ignition switch is in the On position
and the A/C-heater control power is turned on.
The blower motor receives battery current when-
ever the front blower motor relay is energized. The
front blower motor relay output circuit is protected
by a fuse in the Integrated Power Module (IPM)
located in the engine compartment near the battery.
In the manual heater-A/C system, the blower motor
speed is controlled by regulating the path to ground
through the blower control switch and the blower
motor resistor. In the ATC system, the blower motor
speed is controlled by an electronic blower motor
power module, which uses a pulse width modulated
input from the ATC module and feedback from the
blower motor to regulate the blower motor ground
path it provides. The blower motor and wheel are
used to control the velocity of air moving through the
HVAC housing by spinning the blower wheel within
the housing at the selected speed or, in the ATC sys-
tem, at the selected or programmed speed.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
FRONT BLOWER MOTOR
BLOWER MOTOR INOPERATIVE
WARNING: ON VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH AIR-
BAGS, DISABLE THE AIRBAG SYSTEM BEFORE
ATTEMPTING ANY STEERING WHEEL, STEERING
COLUMN, OR INSTRUMENT PANEL COMPONENT
DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. DISCONNECT AND ISO-
LATE THE BATTERY NEGATIVE (GROUND) CABLE,
THEN WAIT TWO MINUTES FOR THE AIRBAG SYS-
TEM CAPACITOR TO DISCHARGE BEFORE PER-
FORMING FURTHER DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. THIS
IS THE ONLY SURE WAY TO DISABLE THE AIRBAG
SYSTEM. FAILURE TO TAKE THE PROPER PRE-
CAUTIONS COULD RESULT IN ACCIDENTAL AIR-
BAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE PERSONAL
INJURY.
For circuit descriptions and diagrams, refer to the
appropriate wiring information. The wiring informa-
tion includes wiring, diagrams, proper wire and con-
nector repair procedures, further details on wire
harness routing and retention, as well as pin-out and
location views for the various wire harness connec-
tors, splices and grounds.BLOWER MOTOR ELECTRICAL DIAGNOSIS
(1) Check the fuse (Fuse 10 - 40 ampere) in the
Integrated Power Module (IPM). If OK, go to Step 2.
If not OK, repair the shorted circuit or component as
required and replace the faulty fuse.
(2) Turn the ignition switch to the On position. Be
certain that the A/C-heater control power is turned
on. Check for battery voltage at the fuse (Fuse 10 -
40 ampere) in the IPM. If OK, go to Step 3. If not
OK, check the front blower motor relay.
(3) Turn the ignition switch to the Off position.
Disconnect and isolate the battery negative cable.
Disconnect the front HVAC wire harness connector
for the front blower motor resistor block (Manual
Temperature Control) or the front blower motor
power module (Automatic Temperature Control) from
the resistor or module connector receptacle. Recon-
nect the battery negative cable. Turn the ignition
switch to the On position. Be certain that the A/C-
heater control power is turned on. Check for battery
voltage at the fused front blower motor relay output
circuit cavity of the front HVAC wire harness connec-
tor for the front blower motor resistor block (MTC) or
the front blower motor power module (ATC). If OK,
go to Step 4. If not OK, repair the open fused front
blower motor relay output circuit to the IPM as
required.
(4) Turn the ignition switch to the Off position.
Disconnect and isolate the battery negative cable.
Disconnect the front blower motor pigtail wire con-
nector from the connector receptacle of the front
blower motor resistor block (MTC) or the front
blower motor power module (ATC). Use jumper wires
to connect a battery and ground feeds to the blower
motor pigtail wire connector. The blower motor
should operate. If OK with MTC, proceed to diagno-
sis of the front blower motor resistor block (Refer to
24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/CONTROLS
- FRONT/BLOWER MOTOR RESISTOR - DIAGNO-
SIS AND TESTING). If OK with ATC, use a DRBIII
scan tool to diagnose the front blower motor power
module. Refer to Body Diagnostic information. If not
OK with MTC or ATC, replace the faulty front blower
motor.
BLOWER MOTOR NOISE OR VIBRATION
Refer to the Blower Motor Noise/Vibration Diagno-
sis chart for basic checks of the blower motor when a
vibration or noise is present (Fig. 7).
24 - 46 DISTRIBUTION - FRONTRS
BLOWER MOTOR (Continued)
Page 2199 of 2339

REMOVAL
WARNING: ON VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH AIR-
BAGS, DISABLE THE AIRBAG SYSTEM BEFORE
ATTEMPTING ANY STEERING WHEEL, STEERING
COLUMN, OR INSTRUMENT PANEL COMPONENT
DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. DISCONNECT AND ISO-
LATE THE BATTERY NEGATIVE (GROUND) CABLE,
THEN WAIT TWO MINUTES FOR THE AIRBAG SYS-
TEM CAPACITOR TO DISCHARGE BEFORE PER-
FORMING FURTHER DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. THIS
IS THE ONLY SURE WAY TO DISABLE THE AIRBAG
SYSTEM. FAILURE TO TAKE THE PROPER PRE-
CAUTIONS COULD RESULT IN AN ACCIDENTAL
AIRBAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE PERSONAL
INJURY OR DEATH.
NOTE: The blower motor is located on the passen-
ger side of the vehicle under the instrument panel.
The blower motor can be removed from the vehicle
without having to remove the HVAC housing.
(1) Disconnect and isolate the negative battery
cable.
(2) Remove the passenger side cowl trim panel
(Refer to 23 - BODY/INTERIOR/COWL TRIM -
REMOVAL).
(3) Pull back the carpet to access the front upper
screw that secures the air inlet housing.
(4) Remove the recirculation door actuator (Refer
to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/CON-
TROLS - FRONT/RECIRCULATION DOOR ACTUA-
TOR - REMOVAL).
(5) Remove the recirculation door actuator wire
lead from the routing clip located on the lower air
inlet housing and position the wire lead aside.
(6) Disconnect the blower motor wire lead connec-
tor from the blower motor resistor block or power
module, depending on application.
(7) Remove the one screw (from the top) that
secures the lower air inlet housing to the upper air
inlet housing (Fig. 8).
(8) Remove the four screws (from the bottom) that
secure the lower air inlet housing to the upper air
inlet housing and the lower HVAC housing.
(9) Push the rubber blower motor wire lead grom-
met through the opening in the lower air inlet hous-
ing (Fig. 9).
(10) Feed the blower motor wire lead through the
opening in the lower air inlet housing and remove
the lower air inlet housing from the vehicle.(11) Position the recirculation-air door as neces-
sary to access and remove the three screws that
secure the blower motor to the lower half of the
HVAC housing.
Fig. 8 Lower Air Inlet Housing
1 - BLOWER MOTOR RESISTOR BLOCK/POWER MODULE
2 - BLOWER MOTOR WIRE LEAD
3 - LOWER HVAC HOUSING
4 - UPPER AIR INLET HOUSING
5 - UPPER SCREW (1)
6 - LOWER AIR INLET HOUSING
7 - RECIRCULATION DOOR ACTUATOR
8 - ACTUATOR WIRE LEAD
9 - LOWER SCREW (4)
Fig. 9 Blower Motor Wire Lead Grommet
1 - BLOWER MOTOR WIRE LEAD GROMMET
24 - 48 DISTRIBUTION - FRONTRS
BLOWER MOTOR (Continued)
Page 2200 of 2339
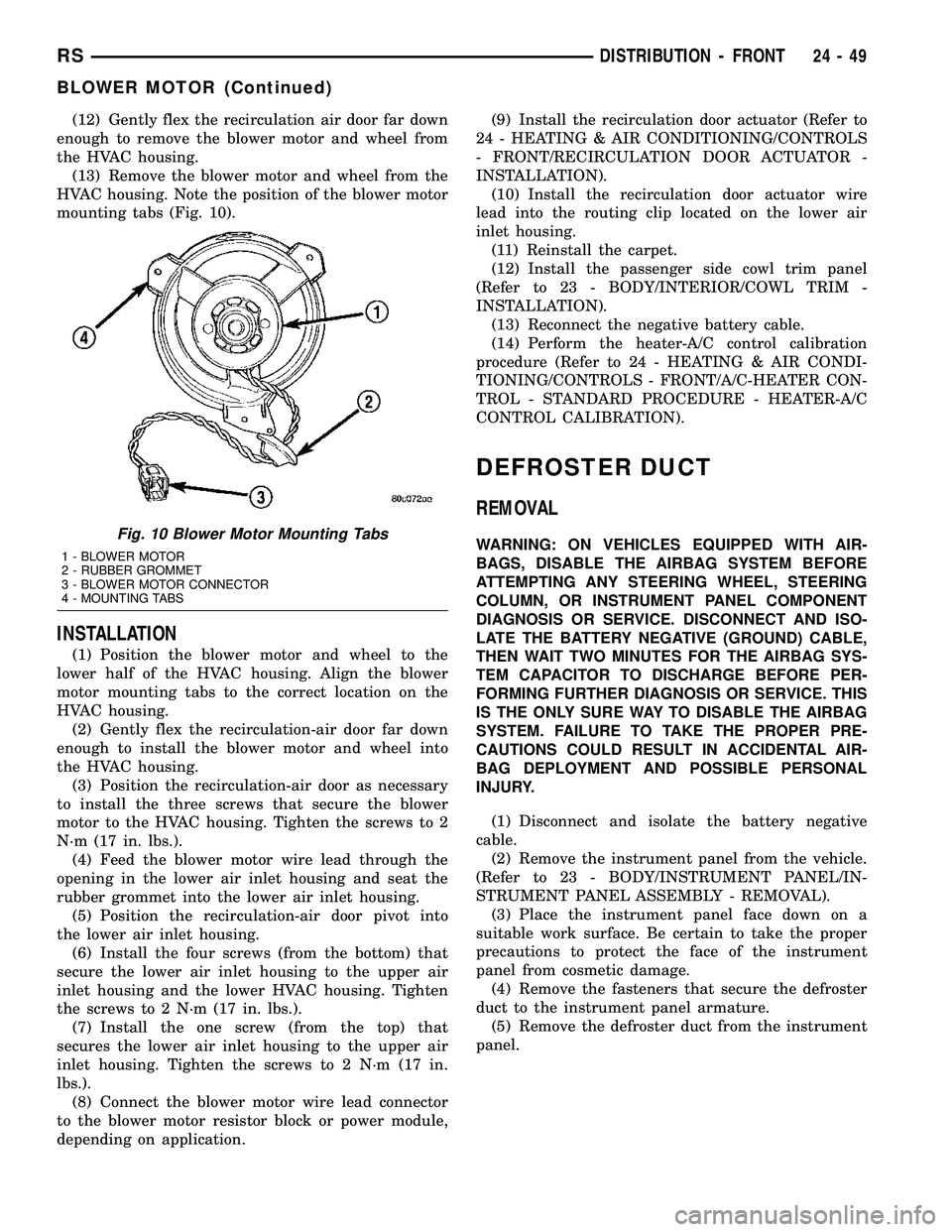
(12) Gently flex the recirculation air door far down
enough to remove the blower motor and wheel from
the HVAC housing.
(13) Remove the blower motor and wheel from the
HVAC housing. Note the position of the blower motor
mounting tabs (Fig. 10).
INSTALLATION
(1) Position the blower motor and wheel to the
lower half of the HVAC housing. Align the blower
motor mounting tabs to the correct location on the
HVAC housing.
(2) Gently flex the recirculation-air door far down
enough to install the blower motor and wheel into
the HVAC housing.
(3) Position the recirculation-air door as necessary
to install the three screws that secure the blower
motor to the HVAC housing. Tighten the screws to 2
N´m (17 in. lbs.).
(4) Feed the blower motor wire lead through the
opening in the lower air inlet housing and seat the
rubber grommet into the lower air inlet housing.
(5) Position the recirculation-air door pivot into
the lower air inlet housing.
(6) Install the four screws (from the bottom) that
secure the lower air inlet housing to the upper air
inlet housing and the lower HVAC housing. Tighten
the screws to 2 N´m (17 in. lbs.).
(7) Install the one screw (from the top) that
secures the lower air inlet housing to the upper air
inlet housing. Tighten the screws to 2 N´m (17 in.
lbs.).
(8) Connect the blower motor wire lead connector
to the blower motor resistor block or power module,
depending on application.(9) Install the recirculation door actuator (Refer to
24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/CONTROLS
- FRONT/RECIRCULATION DOOR ACTUATOR -
INSTALLATION).
(10) Install the recirculation door actuator wire
lead into the routing clip located on the lower air
inlet housing.
(11) Reinstall the carpet.
(12) Install the passenger side cowl trim panel
(Refer to 23 - BODY/INTERIOR/COWL TRIM -
INSTALLATION).
(13) Reconnect the negative battery cable.
(14) Perform the heater-A/C control calibration
procedure (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDI-
TIONING/CONTROLS - FRONT/A/C-HEATER CON-
TROL - STANDARD PROCEDURE - HEATER-A/C
CONTROL CALIBRATION).
DEFROSTER DUCT
REMOVAL
WARNING: ON VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH AIR-
BAGS, DISABLE THE AIRBAG SYSTEM BEFORE
ATTEMPTING ANY STEERING WHEEL, STEERING
COLUMN, OR INSTRUMENT PANEL COMPONENT
DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. DISCONNECT AND ISO-
LATE THE BATTERY NEGATIVE (GROUND) CABLE,
THEN WAIT TWO MINUTES FOR THE AIRBAG SYS-
TEM CAPACITOR TO DISCHARGE BEFORE PER-
FORMING FURTHER DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. THIS
IS THE ONLY SURE WAY TO DISABLE THE AIRBAG
SYSTEM. FAILURE TO TAKE THE PROPER PRE-
CAUTIONS COULD RESULT IN ACCIDENTAL AIR-
BAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE PERSONAL
INJURY.
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Remove the instrument panel from the vehicle.
(Refer to 23 - BODY/INSTRUMENT PANEL/IN-
STRUMENT PANEL ASSEMBLY - REMOVAL).
(3) Place the instrument panel face down on a
suitable work surface. Be certain to take the proper
precautions to protect the face of the instrument
panel from cosmetic damage.
(4) Remove the fasteners that secure the defroster
duct to the instrument panel armature.
(5) Remove the defroster duct from the instrument
panel.Fig. 10 Blower Motor Mounting Tabs
1 - BLOWER MOTOR
2 - RUBBER GROMMET
3 - BLOWER MOTOR CONNECTOR
4 - MOUNTING TABS
RSDISTRIBUTION - FRONT24-49
BLOWER MOTOR (Continued)
Page 2236 of 2339

FRONT HEATER CORE
WARNING: ON VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH AIR-
BAGS, DISABLE THE AIRBAG SYSTEM BEFORE
ATTEMPTING ANY STEERING WHEEL, STEERING
COLUMN, OR INSTRUMENT PANEL COMPONENT
DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. DISCONNECT AND ISO-
LATE THE BATTERY NEGATIVE (GROUND) CABLE,
THEN WAIT TWO MINUTES FOR THE AIRBAG SYS-
TEM CAPACITOR TO DISCHARGE BEFORE PER-
FORMING FURTHER DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. THIS
IS THE ONLY SURE WAY TO DISABLE THE AIRBAG
SYSTEM. FAILURE TO TAKE THE PROPER PRE-
CAUTIONS COULD RESULT IN ACCIDENTAL AIR-
BAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE PERSONAL
INJURY.
(1) Remove the silencer boot fasteners located
around the base of the lower steering shaft from the
dash panel so that it may be pushed aside.
(2) Remove the brake lamp switch from its mount-
ing bracket (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/LAMPS/
LIGHTING - EXTERIOR/BRAKE LAMP SWITCH -
REMOVAL).
(3) Disconnect the power brake booster input rod
(push rod) from the pin on the brake pedal arm
(Refer to 5 - BRAKES - ABS/HYDRAULIC/ME-
CHANICAL/POWER BRAKE BOOSTER -
REMOVAL).
(4) Remove the heater core tubes (Refer to 24 -
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING/
HEATER CORE - REMOVAL).
(5) Remove the two screws that secure the heater
core mounting plate to the distribution housing.
(6) While pulling the accelerator pedal upward
(Fig. 18) and pushing the brake pedal downward
(Fig. 19) far enough for clearance, pull the heater
core out of the distribution housing.
(7) Use absorbent toweling to mop up any engine
coolant spills from the preceding operation. Also, if
the heater core was leaking, use absorbent toweling
and reach into the heater core opening to mop up
any residual engine coolant within the distribution
housing.
INSTALLATION
FRONT HEATER CORE TUBES
(1) Remove the plugs or tape from both heater core
tube fittings and both heater core ports.
(2) Position the heater core tubes and sealing plate
as a unit beneath the instrument panel.
Fig. 18 Accelerator Pedal - LHD Shown, RHD Typical
1 - HEATER CORE
Fig. 19 Brake Pedal - LHD Shown, RHD Typical
1 - HEATER CORE
2 - BRAKE PEDAL
RSPLUMBING - FRONT24-85
HEATER CORE (Continued)
Page 2237 of 2339

(3) Align the engine compartment ends of both
heater core tubes with the openings in the dash
panel seal and push them simultaneously forward
through the seal far enough to engage the heater
core ends of the tubes with the heater core supply
and return ports.
(4) Position both heater core tubes and the sealing
plate simultaneously to the heater core supply and
return ports.
NOTE: The heater core tubes each have a slot that
must be indexed to a location tab within each of the
heater core ports. Adjust the position of the tubes
as required so that the sealing plate fits flush
against the heater core supply and return ports,
which indicates that the tubes are properly indexed.
(5) Index both heater core tubes to the heater core
ports.
(6) Install the screw that secures the heater core
tube sealing plate to the heater core supply and
return ports. Tighten the screw to 3 N´m (27 in. lbs.).
(7) Install the silencer under the driver side end of
the instrument panel.
(8) Connect the heater hoses to the heater hose
tubes (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITION-
ING/PLUMBING/HEATER INLET HOSE - INSTAL-
LATION) and(Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR
CONDITIONING/PLUMBING/HEATER RETURN
HOSE - INSTALLATION).
(9) Reconnect the battery negative cable.
(10) Refill the engine cooling system (Refer to 7 -
COOLING - STANDARD PROCEDURE - COOLING
SYSTEM REFILL).
FRONT HEATER CORE
(1) While pushing the brake pedal downward and
pulling the accelerator pedal upward far enough for
clearance, slide the heater core into the distribution
housing.
(2) Install the two screws that secure the heater
core mounting plate to the distribution housing.
Tighten the screws to 2 N´m (17 in. lbs.).(3) Install the heater core tubes (Refer to 24 -
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING/
HEATER CORE - INSTALLATION).
(4) Reconnect the power brake booster input rod
(push rod) to the pin on the brake pedal arm (Refer
to 5 - BRAKES/HYDRAULIC/MECHANICAL/
POWER BRAKE BOOSTER - INSTALLATION).
(5) Reinstall the brake lamp switch into its mount-
ing bracket (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/LAMPS/
LIGHTING - EXTERIOR/BRAKE LAMP SWITCH -
INSTALLATION).
(6) Reinstall the silencer boot around the base of
the lower steering shaft on the dash panel.
(7) Reconnect the battery negative cable.
(8) Refill the engine cooling system (Refer to 7 -
COOLING - STANDARD PROCEDURE - COOLING
SYSTEM REFILL).
(9) Operate system for two thermostat cycles to
assure the elimination of any air that may be
trapped within the cooling system.
HEATER INLET HOSE
REMOVAL
WARNING: REFER TO THE APPLICABLE WARN-
INGS AND CAUTIONS FOR THIS SYSTEM BEFORE
PERFORMING THE FOLLOWING OPERATION (Refer
to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING -
WARNING).
NOTE: The heater inlet hose is constructed from
formed steel tubing and rubber hoses. Depending
on application, the ends are secured to the heater
core, engine oil cooler or the engine by spring ten-
sion clamps.
(1) Drain the engine cooling system (Refer to 7 -
COOLING - STANDARD PROCEDURE - COOLING
SYSTEM DRAIN).
24 - 86 PLUMBING - FRONTRS
HEATER CORE (Continued)
Page 2275 of 2339

The following is a list of the monitored compo-
nents:
²Catalyst Monitor
²Comprehensive Components
²EGR (if equipped)
²Fuel Control (rich/lean)
²Oxygen Sensor Monitor
²Oxygen Sensor Heater Monitor
²Purge
²Misfire
²Natural Vacuum Leak Detection (NVLD)
COMPREHENSIVE COMPONENTS
Along with the major monitors, OBD II requires
that the diagnostic system monitor any component
that could affect emissions levels. In many cases,
these components were being tested under OBD I.
The OBD I requirements focused mainly on testing
emissions-related components for electrical opens and
shorts.
However, OBD II also requires that inputs from
powertrain components to the PCM be tested for
rationality, and that outputs to powertrain compo-
nents from the PCM be tested forfunctionality.
Methods for monitoring the various Comprehensive
Component monitoring include:
(1) Circuit Continuity
²Open
²Shorted high
²Shorted to ground
(2) Rationality or Proper Functioning
²Inputs tested for rationality
²Outputs tested for functionality
NOTE: Comprehensive component monitors are
continuous. Therefore, enabling conditions do not
apply. All will set a DTC and illuminate the MIL in 1-
trip.
Input RationalityÐWhile input signals to the
PCM are constantly being monitored for electrical
opens and shorts, they are also tested for rationality.
This means that the input signal is compared against
other inputs and information to see if it makes sense
under the current conditions.
PCM sensor inputs that are checked for rationality
include:
²Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Sensor
²Oxygen Sensor (O2S) (slow response)
²Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) Sensor
²Camshaft Position (CMP) Sensor
²Vehicle Speed Sensor
²Crankshaft Position (CKP) Sensor
²Intake Air Temperature (IAT) Sensor
²Throttle Position (TPS) Sensor
²Ambient/Battery Temperature Sensors
²Power Steering Switch²Oxygen Sensor Heater
²Engine Controller
²Brake Switch
²Natural Vacuum Leak Detection (NVLD)
²P/N Switch
²Trans Controls
Output FunctionalityÐPCM outputs are tested
for functionality in addition to testing for opens and
shorts. When the PCM provides a voltage to an out-
put component, it can verify that the command was
carried out by monitoring specific input signals for
expected changes. For example, when the PCM com-
mands the Idle Air Control (IAC) Motor to a specific
position under certain operating conditions, it expects
to see a specific (target) idle speed (RPM). If it does
not, it stores a DTC.
PCM outputs monitored for functionality include:
²Fuel Injectors
²Ignition Coils
²Torque Converter Clutch Solenoid
²Idle Air Control
²Purge Solenoid
²EGR Solenoid
²Radiator Fan Control
²Trans Controls
OXYGEN SENSOR (O2S) MONITOR
DESCRIPTIONÐEffective control of exhaust
emissions is achieved by an oxygen feedback system.
The most important element of the feedback system
is the O2S. The O2S is located in the exhaust path.
Once it reaches operating temperature 300É to 350ÉC
(572É to 662ÉF), the sensor generates a voltage that
is inversely proportional to the amount of oxygen in
the exhaust. When there is a large amount of oxygen
in the exhaust caused by a lean condition, misfire or
exhaust leak, the sensor produces a low voltage,
below 450 mV. When the oxygen content is lower,
caused by a rich condition, the sensor produces a
higher voltage, above 450mV.
The information obtained by the sensor is used to
calculate the fuel injector pulse width. The PCM is
programmed to maintain the optimum air/fuel ratio.
At this mixture ratio, the catalyst works best to
remove hydrocarbons (HC), carbon monoxide (CO)
and nitrous oxide (NOx) from the exhaust.
The O2S is also the main sensing element for the
EGR, Catalyst and Fuel Monitors, and purge.
The O2S may fail in any or all of the following
manners:
²Slow response rate (Big Slope)
²Reduced output voltage (Half Cycle)
²Heater Performance
Slow Response Rate (Big Slope)ÐResponse rate
is the time required for the sensor to switch from
lean to rich signal output once it is exposed to a
25 - 2 EMISSIONS CONTROLRS
EMISSIONS CONTROL (Continued)
Page 2276 of 2339

richer than optimum A/F mixture or vice versa. As
the PCM adjusts the air/fuel ratio, the sensor must
be able to rapidly detect the change. As the sensor
ages, it could take longer to detect the changes in the
oxygen content of the exhaust gas. The rate of
change that an oxygen sensor experiences is called
'Big Slope'. The PCM checks the oxygen sensor volt-
age in increments of a few milliseconds.
Reduced Output Voltage (Half Cycle)ÐThe
output voltage of the O2S ranges from 0 to 1 volt. A
good sensor can easily generate any output voltage in
this range as it is exposed to different concentrations
of oxygen. To detect a shift in the A/F mixture (lean
or rich), the output voltage has to change beyond a
threshold value. A malfunctioning sensor could have
difficulty changing beyond the threshold value. Many
times the condition is only temporey and the sensor
will recover. Under normal conditions the voltage sig-
nal surpasses the threshold, and a counter is incre-
mented by one. This is called the Half Cycle Counter.
Heater PerformanceÐThe heater is tested by a
separate monitor. Refer to the Oxygen Sensor Heater
Monitor.
OPERATIONÐAs the Oxygen Sensor signal
switches, the PCM monitors the half cycle and big
slope signals from the oxygen sensor. If during the
test neither counter reaches a predetermined value, a
malfunction is entered and a Freeze Frame is stored.
Only one counter reaching its predetermined value is
needed for the monitor to pass.
The Oxygen Sensor Signal Monitor is a two trip
monitor that is tested only once per trip. When the
Oxygen Sensor fails the test in two consecutive trips,
the MIL is illuminated and a DTC is set. The MIL is
extinguished when the Oxygen Sensor monitor
passes in three consecutive trips. The DTC is erased
from memory after 40 consecutive warm-up cycles
without test failure.
Enabling ConditionsÐThe following conditions
must typically be met for the PCM to run the oxygen
sensor monitor:
²Battery voltage
²Engine temperature
²Engine run time
²Engine run time at a predetermined speed
²Engine run time at a predetermined speed and
throttle opening
²Transmission in gear (automatic only)
²Fuel system in Closed Loop
²Long Term Adaptive (within parameters)
²Power Steering Switch in low PSI (no load)
²Engine at idle
²Fuel level above 15%
²Ambient air temperature
²Barometric pressure²Engine RPM within acceptable range of desired
idle
²Closed throttle speed
Pending ConditionsÐThe Task Manager typi-
cally does not run the Oxygen Sensor Signal Monitor
if overlapping monitors are running or the MIL is
illuminated for any of the following:
²Misfire Monitor
²Front Oxygen Sensor and Heater Monitor
²MAP Sensor
²Vehicle Speed Sensor
²Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor
²Throttle Position Sensor
²Engine Controller Self Test Faults
²Cam or Crank Sensor
²Injector and Coil
²Idle Air Control Motor
²EVAP Electrical
²EGR Solenoid Electrical
²Intake Air Temperature
²5 Volt Feed
ConflictÐThe Task Manager does not run the
Oxygen Sensor Monitor if any of the following condi-
tions are present:
²A/C ON (A/C clutch cycling temporarily sus-
pends monitor)
²Purge flow in progress
²Ethenal content learn is taking place and the
ethenal used once flag is set
SuspendÐThe Task Manager suspends maturing
a fault for the Oxygen Sensor Monitor if an of the fol-
lowing are present:
²Oxygen Sensor Heater Monitor, Priority 1
²Misfire Monitor, Priority 2
OXYGEN SENSOR HEATER MONITOR (NGC)
DESCRIPTIONÐIf the Oxygen sensor (O2S) DTC
as well as a O2S heater DTC is present, the O2S
Heater DTC MUST be repaired first. After the O2S
Heater is repaired, verify that the sensor circuit is
operating correctly.
The voltage reading taken from the O2S are very
temperature sensitive. The readings taken from the
O2S are not accurate below 300 degrees C. Heating
the O2S is done to allow the engine controller to shift
to closed loop control as soon as possible. The heating
element used to heat the O2S must be tested to
ensure that it is heating the sensor properly. Starting
with the introduction on the NGC module the strat-
egy for checking the heater circuit has changed. The
heater resistance is checked by the NGC almost
immediately after the engine is started. The same
O2S heater return pin used to read the heater resis-
tance is capable of detecting an open circuit, a
shorted high or shorted low condition.
RSEMISSIONS CONTROL25-3
EMISSIONS CONTROL (Continued)
Page 2304 of 2339

BACKLIGHT (EBL) SYSTEM, DIAGNOSISAND TESTING - ELECTRIC ..............8G-2
BACKSTOW STRAP - THIRD ROW - FOLD-IN-FLOOR - INSTALLATION, SEAT . . 23-158
BACKSTOW STRAP - THIRD ROW - FOLD-IN-FLOOR - REMOVAL, SEAT ......23-158
BAG RETAINER - INSTALLATION, PLASTIC GROCERY .................. 23-149
BAG RETAINER - REMOVAL, PLASTIC GROCERY ......................... 23-149
BALANCE - STANDARD PROCEDURE, TIRE AND WHEEL ..................... 22-5
BALANCE SHAFTS AND CARRIER ASSEMBLY - DESCRIPTION .............9-71
BALANCE SHAFTS AND CARRIER ASSEMBLY - INSTALLATION .............9-73
BALANCE SHAFTS AND CARRIER ASSEMBLY - OPERATION ...............9-71
BALANCE SHAFTS AND CARRIER ASSEMBLY - REMOVAL .................9-71
BALL JOINT - DESCRIPTION, LOWER ......2-10
BALL JOINT - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING, LOWER ............................. 2-10
BALL JOINT - OPERATION, LOWER .......2-10
BAR - DESCRIPTION, STABILIZER ....2-16,2-44
BAR - DESCRIPTION, TRACK ............2-45
BAR - INSPECTION, STABILIZER ..........2-17
BAR - INSTALLATION, STABILIZER ........2-17
BAR - INSTALLATION, TRACK ............2-46
BAR - OPERATION, STABILIZER ......2-16,2-44
BAR - OPERATION, TRACK ................2-46
BAR - REMOVAL, STABILIZER ...........2-17
BAR - REMOVAL, TRACK ...............2-46
BAR CUSHION - INSTALLATION, STABILIZER ...........................2-4
BAR CUSHION - REMOVAL, STABILIZER ....2-4
BASE BRAKE BLEEDING - STANDARD PROCEDURE ..........................5-8
BASE BRAKE SYSTEM - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING .............................5-4
BASE BRAKE SYSTEM, SPECIAL TOOLS ....5-10
BASE BRAKES - DESCRIPTION ............5-3
BASE BRAKES - OPERATION ..............5-3
BASE BRAKES (EXPORT) - DESCRIPTION . . . 5-3
BASE COAT/CLEARCOAT FINISH - DESCRIPTION ...................... 23-101
BASE RISER - SECOND ROW - FOLD-IN-FLOOR - INSTALLATION, SEAT . . 23-135
BASE RISER - SECOND ROW - FOLD-IN-FLOOR - REMOVAL, SEAT ......23-134
BASE TRAY - INSTALLATION, FLOOR CONSOLE ........................... 23-89
BASE TRAY - REMOVAL, FLOOR CONSOLE ........................... 23-89
BATTERY - DESCRIPTION ...............8F-7
BATTERY - OPERATION .................8F-9
BATTERY - REMOVAL .................8F-16
BATTERY - SPECIFICATIONS ............8N-24
BATTERY CABLES - DESCRIPTION .......8F-16
BATTERY CABLES - OPERATION .........8F-17
BATTERY CABLES, DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING ........................... 8F-17
BATTERY CHARGING, STANDARD PROCEDURE - CONVENTIONAL ..........8F-11
BATTERY CHARGING, STANDARD PROCEDURE - SPIRAL PLATE ...........8F-10
BATTERY, DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING ......8F-9
BATTERY ELECTROLYTE LEVEL, STANDARD PROCEDURE - CHECKING ....8F-14
BATTERY HOLDDOWN - INSTALLATION . . . 8F-16
BATTERY HOLDDOWN - REMOVAL .......8F-16
BATTERY REPLACEMENT - STANDARD PROCEDURE ........................ 8N-24
BATTERY, SPECIFICATIONS ..............8F-6
BATTERY SYSTEM - DESCRIPTION ........8F-1
BATTERY SYSTEM - OPERATION .........8F-2
BATTERY SYSTEM, DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING ............................ 8F-2
BATTERY SYSTEM SPECIAL TOOLS, SPECIAL TOOLS ...................... 8F-7
BATTERY TEMPERATURE SENSOR - DESCRIPTION ....................... 8F-24
BATTERY TEMPERATURE SENSOR - OPERATION ......................... 8F-24
BATTERY TEMPERATURE SENSOR - REMOVAL .......................... 8F-24
BATTERY TEMPERATURE SENSOR - SPECIFICATIONS ..................... 8F-23BATTERY TESTER, STANDARD
PROCEDURE - MICRO 420 .............8F-15
BATTERY TRAY - DESCRIPTION .........8F-19
BATTERY TRAY - INSTALLATION .........8F-20
BATTERY TRAY - REMOVAL ............8F-19
BEARING - DESCRIPTION, HUB .......2-30,2-5
BEARING - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING, HUB............................. 2-31,2-5
BEARING - INSTALLATION, HUB .......2-33,2-5
BEARING - OPERATION, HUB .........2-30,2-5
BEARING - REMOVAL, HUB ..........2-31,2-5
BEARING CLEARANCE - STANDARD PROCEDURE, MEASURING
CONNECTING ROD ................... 9-123
BEARING CLEARANCE USING PLASTIGAGE - STANDARD
PROCEDURE, MEASURING ..........9-12,9-86
BEARING FITTING - STANDARD PROCEDURE, MAIN ................... 9-125
BEARING PRELOAD - ADJUSTMENT, DIFFERENTIAL ...................... 21-228
BEARING PRELOAD MEASUREMENT AND ADJUSTMENT, ADJUSTMENTS -
DIFFERENTIAL ....................... 21-79
BEARINGS - INSTALLATION, CRANKSHAFT MAIN .................. 9-127
BEARINGS - REMOVAL, CRANKSHAFT MAIN .............................. 9-127
BEARINGS (IN BLOCK) - DESCRIPTION, CAMSHAFT ......................... 9-118
BEARINGS (IN BLOCK) - INSPECTION, CAMSHAFT ......................... 9-118
BEARINGS (IN BLOCK) - INSTALLATION, CAMSHAFT ......................... 9-118
BEARINGS (IN BLOCK) - OPERATION, CAMSHAFT ......................... 9-118
BEARINGS (IN BLOCK) - REMOVAL, CAMSHAFT ......................... 9-118
BELLCRANK - INSTALLATION ...........23-35
BELLCRANK - REMOVAL ...............23-35
BELT - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING, ACCESSORY DRIVE .....................7-7
BELT - FOLD-IN-FLOOR - INSTALLATION, SEAT BELT CENTER LAP ..............23-157
BELT - FOLD-IN-FLOOR - REMOVAL, SEAT BELT CENTER LAP ..............23-157
BELT - INSTALLATION, TIMING ...........9-67
BELT - REMOVAL, TIMING ..............9-65
BELT & RETRACTOR - FIRST ROW - OUTBOARD - INSTALLATION, SEAT ......8O-40
BELT & RETRACTOR - FIRST ROW - OUTBOARD - REMOVAL, SEAT ..........8O-39
BELT & RETRACTOR - OUTBOARD - FRONT - INSTALLATION, SEAT ..........8O-39
BELT & RETRACTOR - OUTBOARD - FRONT - REMOVAL, SEAT ..............8O-38
BELT & RETRACTOR - SECOND ROW - LEFT OUTBOARD - INSTALLATION,
SEAT .............................. 8O-42
BELT & RETRACTOR - SECOND ROW - LEFT OUTBOARD - REMOVAL, SEAT .....8O-42
BELT & RETRACTOR - SECOND ROW - RIGHT OUTBOARD - INSTALLATION,
SEAT .............................. 8O-40
BELT & RETRACTOR - SECOND ROW - RIGHT OUTBOARD - REMOVAL, SEAT ....8O-40
BELT & RETRACTOR - SECOND ROW - RIGHT OUTBOARD WITH REAR HVAC -
LWB - INSTALLATION, SEAT ............8O-41
BELT & RETRACTOR - SECOND ROW - RIGHT OUTBOARD WITH REAR HVAC -
LWB - REMOVAL, SEAT ...............8O-41
BELT BUCKLE - FIRST ROW - BENCH - INSTALLATION, SEAT .................8O-37
BELT BUCKLE - FIRST ROW - BENCH - REMOVAL, SEAT ..................... 8O-36
BELT BUCKLE - FIRST ROW INBOARD - QUAD BUCKET - INSTALLATION, SEAT ....8O-36
BELT BUCKLE - FIRST ROW INBOARD - QUAD BUCKET - REMOVAL, SEAT .......8O-35
BELT BUCKLE - FRONT INBOARD - INSTALLATION, SEAT .................8O-35
BELT BUCKLE - FRONT INBOARD - REMOVAL, SEAT ..................... 8O-35
BELT BUCKLE - SECOND ROW - THREE PASSENGER BENCH - INSTALLATION,
SEAT .............................. 8O-40BELT BUCKLE - SECOND ROW - THREE
PASSENGER BENCH - REMOVAL, SEAT . . . 8O-40
BELT BUCKLE - SECOND ROW INBOARD - 50/50 BENCH - INSTALLATION, SEAT . . . 8O-38
BELT BUCKLE - SECOND ROW INBOARD - 50/50 BENCH - REMOVAL, SEAT .......8O-37
BELT CENTER LAP BELT - FOLD-IN- FLOOR - INSTALLATION, SEAT .........23-157
BELT CENTER LAP BELT - FOLD-IN- FLOOR - REMOVAL, SEAT .............23-157
BELT COVER(S) - INSTALLATION, TIMING ............................. 9-64
BELT COVER(S) - REMOVAL, TIMING ......9-63
BELT HEIGHT ADJUSTE R-BOR
C-PILLAR - INSTALLATION, SEAT ........8O-38
BELT HEIGHT ADJUSTE R-BOR
C-PILLAR - REMOVAL, SEAT ...........8O-38
BELT HEIGHT ADJUSTER KNOB - INSTALLATION, SEAT .................8O-38
BELT HEIGHT ADJUSTER KNOB - REMOVAL, SEAT ..................... 8O-38
BELT MOLDING - INSTALLATION, FRONT DOOR INNER ....................... 23-168
BELT MOLDING - INSTALLATION, FRONT DOOR OUTER ...................... 23-167
BELT MOLDING - REMOVAL, FRONT DOOR INNER ....................... 23-168
BELT MOLDING - REMOVAL, FRONT DOOR OUTER ...................... 23-167
BELT TENSION - STANDARD PROCEDURE, CHECKING POWER
STEERING ............................7-8
BELT TENSION SENSOR - DESCRIPTION . . . 8O-8
BELT TENSION SENSOR - OPERATION .....8O-9
BELT TENSION, SPECIFICATIONS - ACCESSORY DRIVE .....................7-5
BELT TENSIONER - 2.4L - INSTALLATION . . 7-11
BELT TENSIONER - 2.4L - REMOVAL ......7-11
BELT TENSIONER - 3.3/3.8L - INSTALLATION ........................ 7-12
BELT TENSIONER - 3.3/3.8L - REMOVAL . . . 7-12
BELT TENSIONER - DESCRIPTION, SEAT . . 8O-43
BELT TENSIONER - OPERATION, SEAT ....8O-43
BELT TENSIONER & PULLEY - INSTALLATION, TIMING .................9-70
BELT TENSIONER & PULLEY - REMOVAL, TIMING .................... 9-69
BELTS - 2.4L - ADJUSTMENTS, DRIVE .....7-10
BELTS - 2.4L - INSTALLATION, DRIVE ......7-9
BELTS - 2.4L - REMOVAL, DRIVE ..........7-9
BELTS - 3.3/3.8L - INSTALLATION, DRIVE . . 7-12
BELTS - 3.3/3.8L - REMOVAL, DRIVE ......7-11
BELTS - CLEANING, DRIVE ...............7-8
BELTS - INSPECTION, DRIVE .............7-8
BENCH - INSTALLATION, SEAT BACK HINGE COVERS - QUAD BUCKET, 50/50
SPLIT ............................. 23-146
BENCH - INSTALLATION, SEAT BELT BUCKLE - FIRST ROW ................8O-37
BENCH - INSTALLATION, SEAT BELT BUCKLE - SECOND ROW - THREE
PASSENGER ........................ 8O-40
BENCH - INSTALLATION, SEAT BELT BUCKLE - SECOND ROW INBOARD -
50/50 .............................. 8O-38
BENCH - INSTALLATION, SEAT CUSHION COVER - QUAD BUCKET, 50/50 SPLIT . . . 23-144
BENCH - REMOVAL, SEAT BACK HINGE COVERS - QUAD BUCKET, 50/50 SPLIT . . 23-146
BENCH - REMOVAL, SEAT BELT BUCKLE - FIRST ROW ....................... 8O-36
BENCH - REMOVAL, SEAT BELT BUCKLE - SECOND ROW - THREE PASSENGER ....8O-40
BENCH - REMOVAL, SEAT BELT BUCKLE - SECOND ROW INBOARD - 50/50 .......8O-37
BENCH - REMOVAL, SEAT CUSHION COVER - QUAD BUCKET, 50/50 SPLIT . . . 23-144
BENCH SEAT - REMOVAL, CHILD SEAT MODULE .......................... 23-104
BENCH SEAT BACK - INSTALLATION .....23-147
BENCH SEAT BACK - REMOVAL ........23-147
BENCH SEAT BACK COVER - INSTALLATION ...................... 23-148
BENCH SEAT BACK COVER - REMOVAL . . 23-148
BENCH SEAT BACK HINGE - REMOVAL . . 23-146
BENCH SEAT BACK PANEL - INSTALLATION ...................... 23-144
BENCH SEAT BACK PANEL - REMOVAL . . 23-143
RS INDEX3
Description Group-Page Description Group-Page Description Group-Page