Fuel system CHRYSLER TOWN AND COUNTRY 2002 User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: CHRYSLER, Model Year: 2002, Model line: TOWN AND COUNTRY, Model: CHRYSLER TOWN AND COUNTRY 2002Pages: 2399, PDF Size: 57.96 MB
Page 329 of 2399

(9) Disconnect the wire connectors from the back
of the radio.
INSTALLATION
(1) Connect wire harness to back of radio.
(2) Install bolt holding ground strap to the radio (if
equipped).
(3) Connect antenna cable to back of radio.
(4) Position radio into instrument panel.
(5) Install screws holding radio to instrument
panel.
(6) Install center instrument panel trim.
(7) Install trim panel above cupholder.
(8) Install cupholder.
(9) Connect battery negative cable.
RADIO NOISE SUPPRESSION
COMPONENTS
DESCRIPTION
Radio noise suppression devices are factory-in-
stalled standard equipment on this vehicle. Radio
Frequency Interference (RFI) and ElectroMagnetic
Interference (EMI) can be produced by any on-board
or external source of electromagnetic energy. These
electromagnetic energy sources can radiate electro-
magnetic signals through the air, or conduct them
through the vehicle electrical system.
When the audio system converts RFI or EMI to an
audible acoustic wave form, it is referred to as radionoise. This undesirable radio noise is generally man-
ifested in the form of ªbuzzing,º ªhissing,º ªpopping,º
ªclicking,º ªcrackling,º and/or ªwhirringº sounds. In
most cases, RFI and EMI radio noise can be sup-
pressed using a combination of vehicle and compo-
nent grounding, filtering and shielding techniques.
This vehicle is equipped with factory-installed radio
noise suppression devices that were designed to min-
imize exposure to typical sources of RFI and EMI;
thereby, minimizing radio noise complaints.
Factory-installed radio noise suppression is accom-
plished primarily through circuitry or devices that
are integral to the factory-installed radios, audio
power amplifiers and other on-board electrical com-
ponents such as generators, wiper motors, blower
motors, and fuel pumps that have been found to be
potential sources of RFI or EMI.
OPERATION
There are two common strategies that can be used
to suppress Radio Frequency Interference (RFI) and
ElectroMagnetic Interference (EMI) radio noise. The
first suppression strategy involves preventing the
production of RFI and EMI electromagnetic signals
at their sources. The second suppression strategy
involves preventing the reception of RFI and EMI
electromagnetic signals by the audio system compo-
nents.
The use of braided ground straps in key locations
is part of the RFI and EMI prevention strategy.
These ground straps ensure adequate ground paths,
particularly for high current components such as
many of those found in the starting, charging, igni-
tion, engine control and transmission control sys-
tems. An insufficient ground path for any of these
high current components may result in radio noise
caused by induced voltages created as the high cur-
rent seeks alternative ground paths through compo-
nents or circuits intended for use by, or in close
proximity to the audio system components or circuits.
Preventing the reception of RFI and EMI is accom-
plished by ensuring that the audio system compo-
nents are correctly installed in the vehicle. Loose,
corroded or improperly soldered wire harness connec-
tions, improperly routed wiring and inadequate audio
system component grounding can all contribute to
the reception of RFI and EMI. A properly grounded
antenna body and radio chassis, as well as a shielded
antenna coaxial cable with clean and tight connec-
tions will each help reduce the potential for reception
of RFI and EMI.
Fig. 9 ANTENNA TO RADIO
1 - RADIO
2 - LOCKING ANTENNA CONNECTOR
3 - INSTRUMENT PANEL ANTENNA CABLE
8A - 10 AUDIORS
RADIO (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 349 of 2399

²Ignition sense
²Intake Air Temperature Sensor
²Knock Sensor
²Leak Detection Pump Feedback
²Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Sensor
²Park/Neutral (from transmission control module)
²PCI Bus
²Power Steering Pressure Switch
²Proportional Purge Sense
²SCI Receive
²Speed Control
²Throttle Position Sensor
²Torque Management Input (From TCM)
²Transaxle Control Module (TCM)
²Transaxle Gear Engagement (From TCM)
²Vehicle Speed (from transmission control mod-
ule)
NOTE: PCM Outputs:
²Air Conditioning Clutch Relay
²Automatic Shut Down (ASD) and Fuel Pump
Relays
²Data Link Connector (PCI and SCI Transmit)
²Double Start Override
²EGR Solenoid
²Fuel Injectors
²Generator Field
²High Speed Fan Relay
²Idle Air Control Motor
²Ignition Coils
²Leak Detection Pump
²Low Speed Fan Relay
²MTV Actuator
²Proportional Purge Solenoid
²SRV Valve
²Speed Control Relay
²Speed Control Vent Relay
²Speed Control Vacuum Relay
²8 Volt Output
²5 Volt Output
Based on inputs it receives, the powertrain control
module (PCM) adjusts fuel injector pulse width, idle
speed, ignition timing, and canister purge operation.
The PCM regulates the cooling fans, air conditioning
and speed control systems. The PCM changes gener-
ator charge rate by adjusting the generator field.
The PCM adjusts injector pulse width (air-fuel
ratio) based on the following inputs.
²Battery Voltage
²Intake Air Temperature Sensor
²Engine Coolant Temperature
²Engine Speed (crankshaft position sensor)²Exhaust Gas Oxygen Content (heated oxygen
sensors)
²Manifold Absolute Pressure
²Throttle Position
The PCM adjusts engine idle speed through the
idle air control motor based on the following inputs.
²Brake Switch
²Engine Coolant Temperature
²Engine Speed (crankshaft position sensor)
²Park/Neutral (transmission gear selection)
²Transaxle Gear Engagement
²Throttle Position
²Vehicle Speed (from Transmission Control Mod-
ule)
The PCM adjusts ignition timing based on the fol-
lowing inputs.
²Intake Air Temperature
²Engine Coolant Temperature
²Engine Speed (crankshaft position sensor)
²Knock Sensor
²Manifold Absolute Pressure
²Park/Neutral (transmission gear selection)
²Transaxle Gear Engagement
²Throttle Position
The automatic shut down (ASD) and fuel pump
relays are mounted externally, but turned on and off
by the powertrain control module through the same
circuit.
The camshaft and crankshaft signals are sent to
the powertrain control module. If the PCM does not
receive both signals within approximately one second
of engine cranking, it deactivates the ASD and fuel
pump relays. When these relays are deactivated,
power is shut off to the fuel injectors, ignition coils,
fuel pump and the heating element in each oxygen
sensor.
The PCM contains a voltage converter that
changes battery voltage to a regulated 8.0 volts. The
8.0 volts power the camshaft position sensor, crank-
shaft position sensor and vehicle speed sensor. The
PCM also provides a 5.0 volts supply for the engine
coolant temperature sensor, intake air temperature
sensor, manifold absolute pressure sensor and throt-
tle position sensor.
The PCM engine control strategy prevents reduced
idle speeds until after the engine operates for 320 km
(200 miles). If the PCM is replaced after 320 km (200
miles) of usage, update the mileage in new PCM. Use
the DRB scan tool to change the mileage in the PCM.
Refer to the appropriate Powertrain Diagnostic Man-
ual and the DRB scan tool.
8E - 12 ELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULESRS
POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 352 of 2399
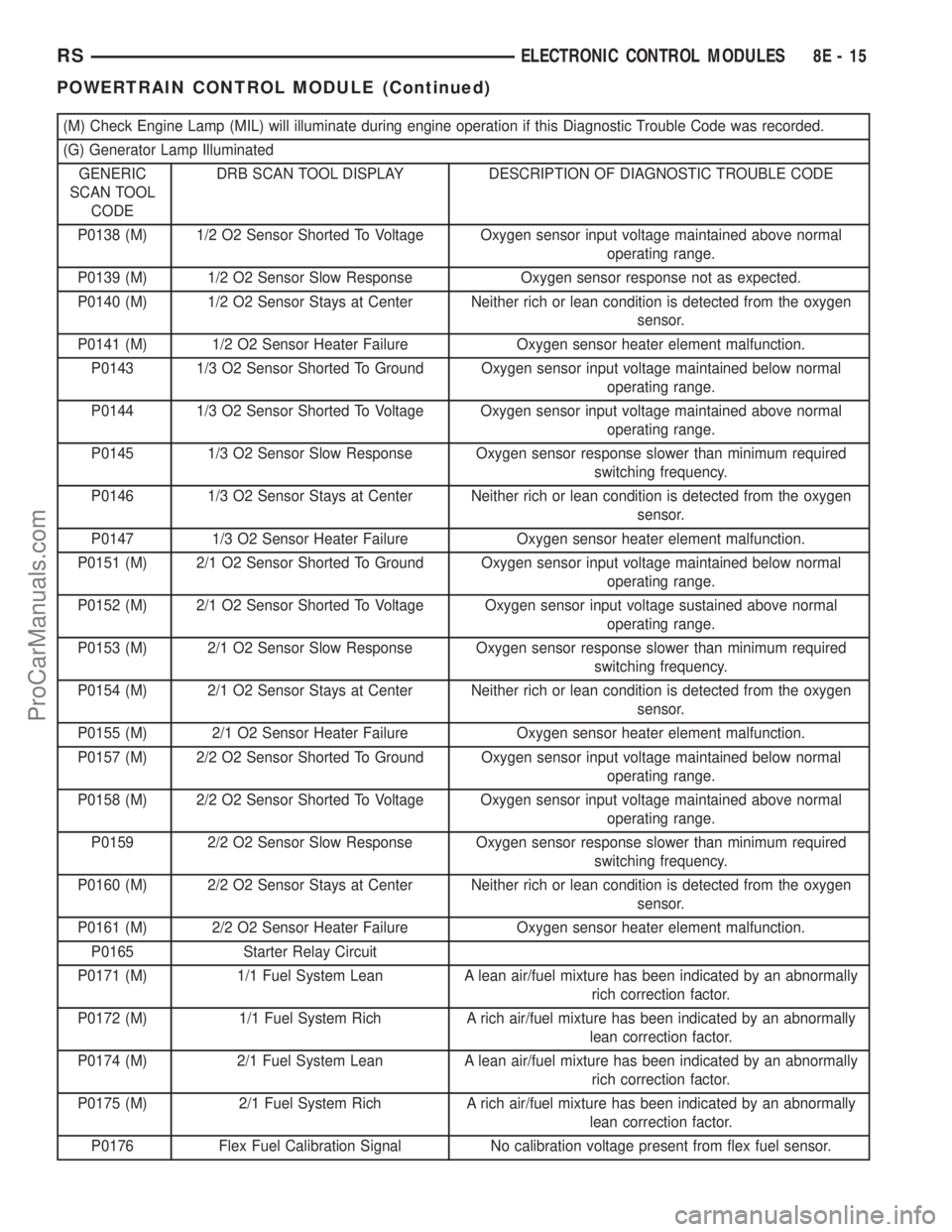
(M) Check Engine Lamp (MIL) will illuminate during engine operation if this Diagnostic Trouble Code was recorded.
(G) Generator Lamp Illuminated
GENERIC
SCAN TOOL
CODEDRB SCAN TOOL DISPLAY DESCRIPTION OF DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE
P0138 (M) 1/2 O2 Sensor Shorted To Voltage Oxygen sensor input voltage maintained above normal
operating range.
P0139 (M) 1/2 O2 Sensor Slow Response Oxygen sensor response not as expected.
P0140 (M) 1/2 O2 Sensor Stays at Center Neither rich or lean condition is detected from the oxygen
sensor.
P0141 (M) 1/2 O2 Sensor Heater Failure Oxygen sensor heater element malfunction.
P0143 1/3 O2 Sensor Shorted To Ground Oxygen sensor input voltage maintained below normal
operating range.
P0144 1/3 O2 Sensor Shorted To Voltage Oxygen sensor input voltage maintained above normal
operating range.
P0145 1/3 O2 Sensor Slow Response Oxygen sensor response slower than minimum required
switching frequency.
P0146 1/3 O2 Sensor Stays at Center Neither rich or lean condition is detected from the oxygen
sensor.
P0147 1/3 O2 Sensor Heater Failure Oxygen sensor heater element malfunction.
P0151 (M) 2/1 O2 Sensor Shorted To Ground Oxygen sensor input voltage maintained below normal
operating range.
P0152 (M) 2/1 O2 Sensor Shorted To Voltage Oxygen sensor input voltage sustained above normal
operating range.
P0153 (M) 2/1 O2 Sensor Slow Response Oxygen sensor response slower than minimum required
switching frequency.
P0154 (M) 2/1 O2 Sensor Stays at Center Neither rich or lean condition is detected from the oxygen
sensor.
P0155 (M) 2/1 O2 Sensor Heater Failure Oxygen sensor heater element malfunction.
P0157 (M) 2/2 O2 Sensor Shorted To Ground Oxygen sensor input voltage maintained below normal
operating range.
P0158 (M) 2/2 O2 Sensor Shorted To Voltage Oxygen sensor input voltage maintained above normal
operating range.
P0159 2/2 O2 Sensor Slow Response Oxygen sensor response slower than minimum required
switching frequency.
P0160 (M) 2/2 O2 Sensor Stays at Center Neither rich or lean condition is detected from the oxygen
sensor.
P0161 (M) 2/2 O2 Sensor Heater Failure Oxygen sensor heater element malfunction.
P0165 Starter Relay Circuit
P0171 (M) 1/1 Fuel System Lean A lean air/fuel mixture has been indicated by an abnormally
rich correction factor.
P0172 (M) 1/1 Fuel System Rich A rich air/fuel mixture has been indicated by an abnormally
lean correction factor.
P0174 (M) 2/1 Fuel System Lean A lean air/fuel mixture has been indicated by an abnormally
rich correction factor.
P0175 (M) 2/1 Fuel System Rich A rich air/fuel mixture has been indicated by an abnormally
lean correction factor.
P0176 Flex Fuel Calibration Signal No calibration voltage present from flex fuel sensor.
RSELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULES8E-15
POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 354 of 2399

(M) Check Engine Lamp (MIL) will illuminate during engine operation if this Diagnostic Trouble Code was recorded.
(G) Generator Lamp Illuminated
GENERIC
SCAN TOOL
CODEDRB SCAN TOOL DISPLAY DESCRIPTION OF DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE
P0330 Knock Sensor #2 Circuit Knock sensor (#2) signal above or below minimum
acceptable threshold voltage at particular engine speeds.
P0335 Crankshaft Position Sensor Circuit A rationality error has been detected for loss of crankshaft
position sensor.
P0339 Crankshaft Position Sensor Circuit
IntermittentA rationality error has been detected for intermittent loss of
crankshaft position sensor.
P0340 (M) Camshaft Position Sensor Circuit A rationality error has been detected for loss of camshaft
position sensor.
P0344 Camshaft Position Sensor Circuit
IntermittentA rationality error has been detected for intermittent loss of
camshaft position sensor.
P0350 Ignition Coil Draws Too Much Current A coil (1-5) is drawing too much current.
P0351 (M) Ignition Coil Primary # 1 Circuit Peak primary circuit current not achieved with maximum
dwell time.
P0352 (M) Ignition Coil Primary # 2 Circuit Peak primary circuit current not achieved with maximum
dwell time.
P0353 (M) Ignition Coil Primary # 3 Circuit Peak primary circuit current not achieved with maximum
dwell time.
P0354 (M) Ignition Coil Primary# 4 Circuit Peak primary circuit current not achieved with maximum
dwell time (High Impedance).
P0355 (M) Ignition Coil Primary # 5 Circuit Peak primary circuit current not achieved with maximum
dwell time (High Impedance).
P0356 (M) Ignition Coil Primary # 6 Circuit Peak primary circuit current not achieved with maximum
dwell time (high impedance).
P0357 Ignition Coil Primary # 7 Circuit Peak primary circuit current not achieved with maximum
dwell time (high impedance).
P0358 Ignition Coil Primary # 8 Circuit Peak primary circuit current not achieved with maximum
dwell time (high impedance).
P0400 Diesel EGR System Failure
P0401 (M) EGR System Failure Required change in air/fuel ration not detected during
diagnostic test.
P0403 (M) EGR Solenoid Circuit An open or shorted condition detected in the EGR solenoid
control circuit.
P0404 (M) EGR Position Sensor Rationality EGR position sensor signal does not correlate to EGR duty
cycle.
P0405 (M) EGR Position Sensor Volts Too Low EGR position sensor input below the acceptable voltage
range.
P0406 (M) EGR Position Sensor Volts Too High EGR position sensor input above the acceptable voltage
range.
P0412 Secondary Air Solenoid Circuit An open or shorted condition detected in the secondary air
(air switching/aspirator) solenoid control circuit.
P0420 (M) 1/1 Catalytic Converter Efficiency Catalyst 1/1 efficiency below required level.
P0432 (M) 1/2 Catalytic Converter Efficiency Catalyst 2/1 efficiency below required level.
P0440 General EVAP System Failure General system failure.
RSELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULES8E-17
POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 355 of 2399

(M) Check Engine Lamp (MIL) will illuminate during engine operation if this Diagnostic Trouble Code was recorded.
(G) Generator Lamp Illuminated
GENERIC
SCAN TOOL
CODEDRB SCAN TOOL DISPLAY DESCRIPTION OF DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE
P0441 (M) Evap Purge Flow Monitor Insufficient or excessive vapor flow detected during
evaporative emission system operation.
P0442 (M) Evap Leak Monitor 0.040 Leak
DetectedA 0.040 leak has been detected in the evaporative system.
P0443 (M) Evap Purge Solenoid Circuit An open or shorted condition detected in the EVAP purge
solenoid control circuit.
P0452 NVLD Pressure Switch Stuck Closed NVLD pressure switch stuck closed.
P0453 NVLD Pressure Switch Stuck Open NVLD pressure switch stuck open.
P0455 (M) Evap Leak Monitor Large Leak
DetectedA large leak has been detected in the evaporative system.
P0456 (M) Evap Leak Monitor 0.020 Leak
DetectedA 0.020 leak has been detected in the evaporative system.
P0460 Fuel Level Unit No Change Over Miles No movement of fuel level sender detected.
P0461 Fuel Level Unit No Changeover Time No level of fuel level sender detected.
P0462 Fuel Level Sending Unit Volts Too Low Fuel level sensor input below acceptable voltage.
P0463 Fuel Level Sending Unit Volts Too
HighFuel level sensor input above acceptable voltage.
P0480 Low Speed Fan Relay Control Circuit An open or shorted condition detected in the low speed rad.
fan relay control circuit.
P0481 High Speed Fan Relay Control Circuit An open or shorted condition detected in the high speed rad.
fan relay control circuit.
P0498 NVLD Canister Vent Valve Solenoid
Circuit LowA shorted low condition detected in NVLD solenoid circuit.
P0499 NVLD Canister Vent Valve Solenoid
Circuit HighA shorted high condition detected in NVLD solenoid circuit.
P0500 (M) No Vehicle Speed Sensor Signal No vehicle speed sensor signal detected during road load
conditions.
P0501 Vehicle Speed Sensor #1 Performance A rationality error has been detected for no vehicle speed
sensor signal detected during road load conditions.
P0505 (M) Idle Air Control Motor Circuits Replace idle air control motor.
P0508 (M) Idle Air Control Motor Circuit Low Idle Air Control Motor Circuit input below acceptable current
P0509 (M) Idle Air Control Motor Circuit High Idle Air Control Motor Circuit input above acceptable current
P0511 Idle Air Control Valve Solenoid Circuit An open or shorted condition detected in the IAC control
circuit.
P0513 Invalid SKIM Key The engine controller has received an invalid key from the
Smart Key Immobilizer Module.
P0516 Battery Temperature Sensor Low Battery Temp. sensor input below minimum acceptable
voltage.
P0517 Battery Temperature Sensor High Battery Temp. sensor input above maximum acceptable
voltage.
P0519 Idle Speed Performance A rationality error has been detected for target RPM not met
during drive idle condition. Possible Vacuum leak or IAC lost
steps.
8E - 18 ELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULESRS
POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 358 of 2399
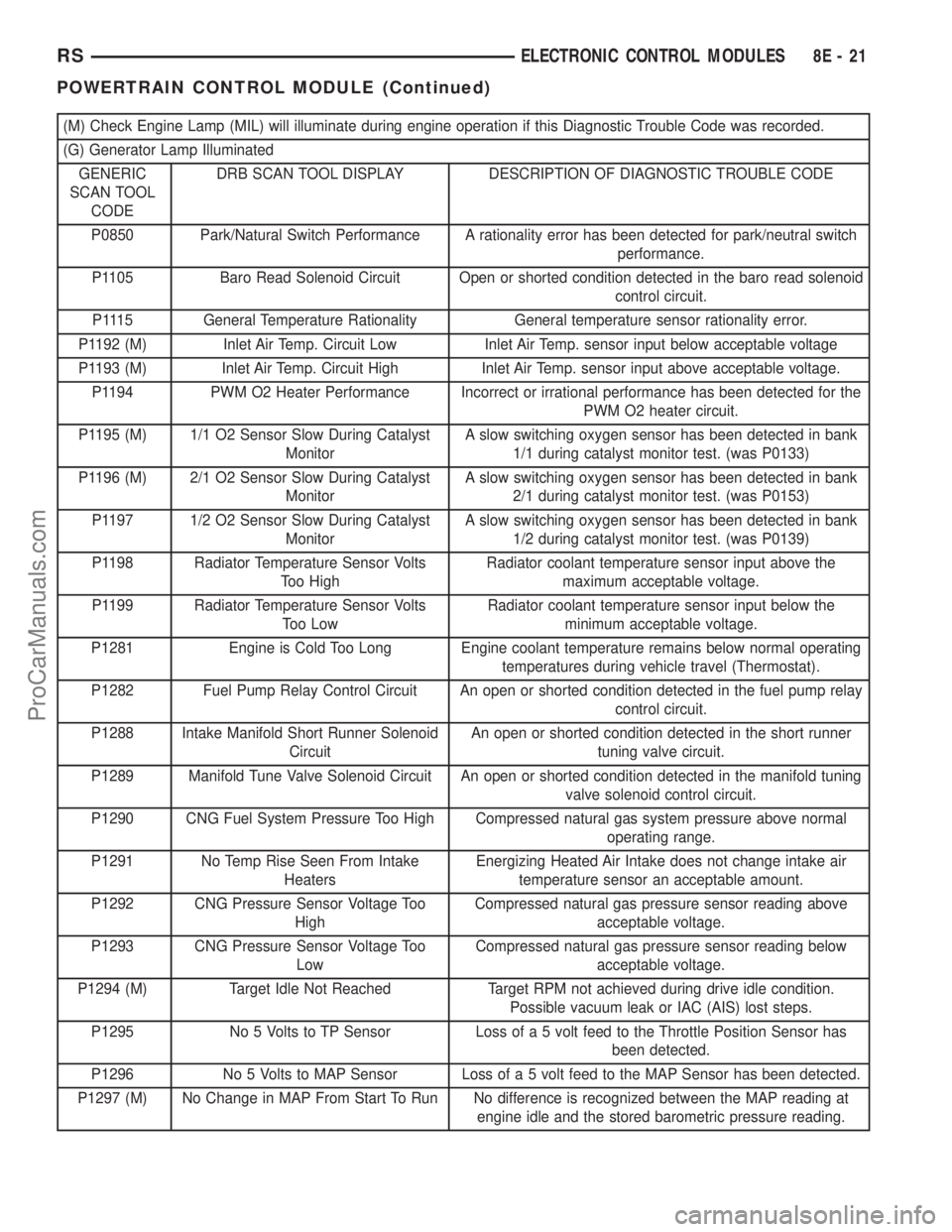
(M) Check Engine Lamp (MIL) will illuminate during engine operation if this Diagnostic Trouble Code was recorded.
(G) Generator Lamp Illuminated
GENERIC
SCAN TOOL
CODEDRB SCAN TOOL DISPLAY DESCRIPTION OF DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE
P0850 Park/Natural Switch Performance A rationality error has been detected for park/neutral switch
performance.
P1105 Baro Read Solenoid Circuit Open or shorted condition detected in the baro read solenoid
control circuit.
P1115 General Temperature Rationality General temperature sensor rationality error.
P1192 (M) Inlet Air Temp. Circuit Low Inlet Air Temp. sensor input below acceptable voltage
P1193 (M) Inlet Air Temp. Circuit High Inlet Air Temp. sensor input above acceptable voltage.
P1194 PWM O2 Heater Performance Incorrect or irrational performance has been detected for the
PWM O2 heater circuit.
P1195 (M) 1/1 O2 Sensor Slow During Catalyst
MonitorA slow switching oxygen sensor has been detected in bank
1/1 during catalyst monitor test. (was P0133)
P1196 (M) 2/1 O2 Sensor Slow During Catalyst
MonitorA slow switching oxygen sensor has been detected in bank
2/1 during catalyst monitor test. (was P0153)
P1197 1/2 O2 Sensor Slow During Catalyst
MonitorA slow switching oxygen sensor has been detected in bank
1/2 during catalyst monitor test. (was P0139)
P1198 Radiator Temperature Sensor Volts
Too HighRadiator coolant temperature sensor input above the
maximum acceptable voltage.
P1199 Radiator Temperature Sensor Volts
Too LowRadiator coolant temperature sensor input below the
minimum acceptable voltage.
P1281 Engine is Cold Too Long Engine coolant temperature remains below normal operating
temperatures during vehicle travel (Thermostat).
P1282 Fuel Pump Relay Control Circuit An open or shorted condition detected in the fuel pump relay
control circuit.
P1288 Intake Manifold Short Runner Solenoid
CircuitAn open or shorted condition detected in the short runner
tuning valve circuit.
P1289 Manifold Tune Valve Solenoid Circuit An open or shorted condition detected in the manifold tuning
valve solenoid control circuit.
P1290 CNG Fuel System Pressure Too High Compressed natural gas system pressure above normal
operating range.
P1291 No Temp Rise Seen From Intake
HeatersEnergizing Heated Air Intake does not change intake air
temperature sensor an acceptable amount.
P1292 CNG Pressure Sensor Voltage Too
HighCompressed natural gas pressure sensor reading above
acceptable voltage.
P1293 CNG Pressure Sensor Voltage Too
LowCompressed natural gas pressure sensor reading below
acceptable voltage.
P1294 (M) Target Idle Not Reached Target RPM not achieved during drive idle condition.
Possible vacuum leak or IAC (AIS) lost steps.
P1295 No 5 Volts to TP Sensor Loss of a 5 volt feed to the Throttle Position Sensor has
been detected.
P1296 No 5 Volts to MAP Sensor Loss of a 5 volt feed to the MAP Sensor has been detected.
P1297 (M) No Change in MAP From Start To Run No difference is recognized between the MAP reading at
engine idle and the stored barometric pressure reading.
RSELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULES8E-21
POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 372 of 2399

ELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULES
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
ENGINE CONTROL MODULE
DESCRIPTION..........................1
OPERATION............................1
STANDARD PROCEDURE - PCM/ECM/SKIM
PROGRAMMING - DIESEL...............2REMOVAL.............................4
INSTALLATION..........................4
ENGINE CONTROL MODULE
DESCRIPTION
The ECM is located in the left front corner of the
engine compartment attached to the radiator support
(Fig. 1).
OPERATION
The ECM has been programmed to monitor differ-
ent circuits of the diesel fuel injection system. Thismonitoring is called on-board diagnostics. Certain cri-
teria must be met for a diagnostic trouble code to be
entered into the ECM memory. The criteria may be a
range of: engine rpm, engine temperature, time or
other input signals to the ECM. If all of the criteria
for monitoring a system or circuit are met, and a
problem is sensed, then a DTC will be stored in the
ECM memory. It is possible that a DTC for a moni-
tored circuit may not be entered into the ECM mem-
ory, even though a malfunction has occurred. This
may happen when the monitoring criteria have not
been met. The ECM compares input signal voltages
from each input device with specifications (the estab-
lished high and low limits of the input range) that
are programmed into it for that device. If the input
voltage is not within the specifications and other
trouble code criteria are met, a DTC will be stored in
the ECM memory.
ECM OPERATING MODES
As input signals to the ECM change, the ECM
adjusts its response to the output devices. For exam-
ple, the ECM must calculate a different fuel quantity
and fuel timing for engine idle condition than it
would for a wide open throttle condition. There are
several different modes of operation that determine
how the ECM responds to the various input signals.
Ignition Switch On (Engine Off)
When the ignition is turned on, the ECM activates
the glow plug relay for a time period that is deter-
mined by engine coolant temperature, atmospheric
temperature and battery voltage.
Engine Start-Up Mode
The ECM uses the engine temperature sensor and
the crankshaft position sensor (engine speed) inputs
to determine fuel injection quantity.
Normal Driving Modes
Engine idle, warm-up, acceleration, deceleration
and wide open throttle modes are controlled based on
all of the sensor inputs to the ECM. The ECM uses
Fig. 1 ENGINE CONTROL MODULE LOCATION-
TYPICAL
1 - BATTERY
2 - IPM (INTEGRATED POWER MODULE)
3 - ECM (ENGINE CONTROL MODULE)
4 - RETAINING BOLT
5 - RADIATOR SUPPORT
6 - CLUTCH CABLE BRACKET (LHD)
7 - CLUTCH CABLE BRACKET RETAINING BOLT (LHD)
RGELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULES8Ea-1
ProCarManuals.com
Page 373 of 2399

these sensor inputs to adjust fuel quantity and fuel
injector timing.
Limp-In Mode
If there is a fault detected with the accelerator
pedal position sensor, the ECM will set the engine
speed at 1100 RPM.
Overspeed Detection Mode
If the ECM detects engine RPM that exceeds 5200
RPM, the ECM will set a DTC in memory and illu-
minate the MIL until the DTC is cleared.
After-Run Mode
The ECM transfers RAM information to ROM and
performs an Input/Output state check.
MONITORED CIRCUITS
The ECM is able to monitor and identify most
driveability related trouble conditions. Some circuits
are directly monitored through ECM feedback cir-
cuitry. In addition, the ECM monitors the voltage
state of some circuits and compares those states with
expected values. Other systems are monitored indi-
rectly when the ECM conducts a rationality test to
identify problems. Although most subsytems of the
engine control module are either directly or indirectly
monitored, there may be occasions when diagnostic
trouble codes are not immediately identified. For a
trouble code to set, a specific set of conditions must
occur and unless these conditions occur, a DTC will
not set.
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES
Each diagnostic trouble code (DTC) is diagnosed by
following a specific procedure. The diagnostic test
procedure contains step-by-step instruction for deter-
mining the cause of the DTC as well as no trouble
code problems. Refer to the appropriate Diesel Pow-
ertrain Diagnostic Manual for more information.
HARD CODE
A DTC that comes back within one cycle of the
ignition key is a hard code. This means that the
problem is current every time the ECM/SKIM checks
that circuit or function. Procedures in this manual
verify if the DTC is a hard code at the beginning of
each test. When the fault is not a hard code, an
intermittent test must be performed. NOTE: If the
DRBIIItdisplays faults for multiple components (i.e.
ECT, VSS, IAT sensors) identify and check the
shared circuits for possible problems before continu-
ing (i.e. sensor grounds or 5-volt supply circuits).
Refer to the appropriate schematic to identify shared
circuits. Refer to the appropriate Diesel Powertrain
Diagnostic Manual for more information.INTERMITTENT CODE
A DTC that is not current every time the ECM/
SKIM checks the circuit or function is an intermit-
tent code. Most intermittent DTCs are caused by
wiring or connector problems. Problems that come
and go like this are the most difficult to diagnose;
they must be looked for under specific conditions that
cause them.NOTE: Electromagnetic (radio)
interference can cause an intermittent system
malfunction.This interference can interrupt com-
munication between the ignition key transponder and
the SKIM. The following checks may assist you in
identifying a possible intermittent problem:
²Visually inspect the related wire harness connec-
tors. Look for broken, bent, pushed out or corroded
terminals.
²Visually inspect the related wire harness. Look
for chafed, pierced or partially broken wire.
²Refer to hotlines or technical service bulletins
that may apply. Refer to the appropriate Diesel Pow-
ertrain Diagnostic Manual for more information.
ECM DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES
IMPORTANT NOTE: Before replacing the ECM for
a failed driver, control circuit or ground circuit, be
sure to check the related component/circuit integrity
for failures not detected due to a double fault in the
circuit. Most ECM driver/control circuit failures are
caused by internal failures to components (i.e. relays
and solenoids) and shorted circuits (i.e. sensor pull-
ups, drivers and ground circuits). These faults are
difficult to detect when a double fault has occurred
and only one DTC has set. If the DRBIIItdisplays
faults for multiple components (i.e.VSS, ECT, Batt
Temp, etc.) identify and check the shared circuits for
possible problems before continuing (i.e. sensor
grounds or 5-volt supply circuits). Refer to the appro-
priate wiring diagrams to identify shared circuits.
Refer to the appropriate Diesel Powertrain Diagnos-
tic Manual for more information.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - PCM/ECM/SKIM
PROGRAMMING - DIESEL
NOTE: Before replacing the PCM/ECM for a failed
driver, control circuit or ground circuit, be sure to
check the related component/circuit integrity for
failures not detected due to a double fault in the cir-
cuit. Most PCM/ECM driver/control circuit failures
are caused by internal component failures (i.e. relay
and solenoids) and shorted circuits (i.e. pull-ups,
drivers and switched circuits). These failures are
difficult to detect when a double fault has occurred
and only one DTC has set.
8Ea - 2 ELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULESRG
ENGINE CONTROL MODULE (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 406 of 2399

CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
STARTER
ENGAGES,
SPINS OUT
BEFORE
ENGINE
STARTS.1. BROKEN TEETH ON
STARTER RING GEAR.1. REMOVE STARTER. INSPECT RING GEAR AND REPLACE
IF NECESSARY.
2. STARTER ASSEMBLY
FAULTY.2. IF ALL OTHER STARTING SYSTEM COMPONENTS AND
CIRCUITS CHECK OK, REPLACE STARTER ASSEMBLY.
STARTER DOES
NOT
DISENGAGE.1. STARTER
IMPROPERLY
INSTALLED.1. INSTALL STARTER. TIGHTEN STARTER MOUNTING
HARDWARE TO CORRECT TORQUE SPECIFICATIONS.
2. STARTER RELAY
FAULTY.2. REFER TO RELAY TEST, IN THIS SECTION. REPLACE
RELAY, IF NECESSARY.
3. IGNITION SWITCH
FAULTY.3. REFER TO IGNITION SWITCH TEST, IN THE STEERING
SECTION. REPLACE SWITCH, IF NECESSARY.
4. STARTER ASSEMBLY
FAULTY.4. IF ALL OTHER STARTING SYSTEM COMPONENTS AND
CIRCUITS CHECK OK, REPLACE STARTER ASSEMBLY.
5. FAULTY TEETH ON
RING GEAR.5. ROTATE FLYWHEEL 360É, AND INSPECT TEETH AND RING
GEAR REPLACED IF DAMAGED.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CONTROL
CIRCUIT TEST
The starter control circuit has:
²Starter motor with integral solenoid
²Starter relay
²Transmission range sensor, or Park/Neutral
Position switch with automatic transmissions
²Ignition switch
²Battery
²All related wiring and connections
²Powertrain Control Module (PCM)
CAUTION: Before performing any starter tests, the
ignition and fuel systems must be disabled.
²To disable ignition and fuel systems, disconnect
the Automatic Shutdown Relay (ASD). The ASD relay
is located in the Power Distribution Center (PDC).
Refer to the PDC cover for the proper relay location.
STARTER SOLENOID
WARNING: CHECK TO ENSURE THAT THE TRANS-
MISSION IS IN THE PARK POSITION WITH THE
PARKING BRAKE APPLIED.
(1) Verify battery condition. Battery must be in
good condition with a full charge before performing
any starter tests. Refer to Battery Tests.
(2) Perform Starter Solenoid test BEFORE per-
forming the starter relay test.(3) Perform a visual inspection of the starter/
starter solenoid for corrosion, loose connections or
faulty wiring.
(4) Locate and remove the starter relay from the
Power Distribution Center (PDC). Refer to the PDC
label for relay identification and location.
(5) Connect a remote starter switch or a jumper
wire between the remote battery positive post and
terminal 87 of the starter relay connector.
(a) If engine cranks, starter/starter solenoid is
good. Go to the Starter Relay Test.
(b) If engine does not crank or solenoid chatters,
check wiring and connectors from starter relay to
starter solenoid for loose or corroded connections.
Particularly at starter terminals.
(c) Repeat test. If engine still fails to crank prop-
erly, trouble is within starter or starter mounted
solenoid, and replace starter. Inspect the ring gear
teeth.
STARTER RELAY
WARNING: CHECK TO ENSURE THAT THE TRANS-
MISSION IS IN THE PARK/NEUTRAL POSITION
WITH THE PARKING BRAKE APPLIED.
RELAY TEST
The starter relay is located in the Power Distribu-
tion Center (PDC) in the engine compartment. Refer
to the PDC label for relay identification and location.
RSSTARTING8F-31
STARTING (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 408 of 2399

tion. If that checks OK check for continuity between
PCM and the terminal 85. Repair open circuit as
required. If OK, the PCM may be defective.
SAFETY SWITCHES
For diagnostics of the Transmission Range Sensor,
refer to the Transaxle section for more information.
If equipped with Clutch Interlock/Upstop Switch,
refer to Diagnosis and Testing in the Clutch section.
IGNITION SWITCH
After testing starter solenoid and relay, test igni-
tion switch and wiring. Refer to the Ignition Section
or Wiring Diagrams for more information. Check all
wiring for opens or shorts, and all connectors for
being loose or corroded.
BATTERY
For battery diagnosis and testing, refer to the Bat-
tery section for procedures.
ALL RELATED WIRING AND CONNECTORS
Refer to Wiring Diagrams for more information.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - FEED CIRCUIT
RESISTANCE TEST
Before proceeding with this operation, review Diag-
nostic Preparation and Starter Feed Circuit Tests.
The following operation will require a voltmeter,
accurate to 1/10 of a volt.
CAUTION: Ignition and Fuel systems must be dis-
abled to prevent engine start while performing the
following tests.
(1) To disable the Ignition and Fuel systems, dis-
connect the Automatic Shutdown Relay (ASD). The
ASD relay is located in the Power Distribution Cen-
ter (PDC). Refer to the PDC cover for proper relay
location.
(2) Gain access to battery terminals.
(3) With all wiring harnesses and components
properly connected, perform the following:
(a) Connect the negative lead of the voltmeter to
the battery negative post, and positive lead to the
battery negative cable clamp. Rotate and hold the
ignition switch in the START position. Observe the
voltmeter. If voltage is detected, correct poor con-
tact between cable clamp and post.
(b) Connect positive lead of the voltmeter to the
battery positive post, and negative lead to the bat-
tery positive cable clamp. Rotate and hold the igni-
tion switch key in the START position. Observe the
voltmeter. If voltage is detected, correct poor con-
tact between the cable clamp and post.(c) Connect negative lead of voltmeter to battery
negative terminal, and positive lead to engine
block near the battery cable attaching point.
Rotate and hold the ignition switch in the START
position. If voltage reads above 0.2 volt, correct
poor contact at ground cable attaching point. If
voltage reading is still above 0.2 volt after correct-
ing poor contacts, replace ground cable.
(4) Connect positive voltmeter lead to the starter
motor housing and the negative lead to the battery
negative terminal. Hold the ignition switch key in
the START position. If voltage reads above 0.2 volt,
correct poor starter to engine ground.
(a) Connect the positive voltmeter lead to the
battery positive terminal, and negative lead to bat-
tery cable terminal on starter solenoid. Rotate and
hold the ignition switch in the START position. If
voltage reads above 0.2 volt, correct poor contact at
battery cable to solenoid connection. If reading is
still above 0.2 volt after correcting poor contacts,
replace battery positive cable.
(b) If resistance tests do not detect feed circuit
failures, replace the starter motor.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - FEED CIRCUIT
TEST
NOTE: The following results are based upon the
vehicle being at room temperature.
The following procedure will require a suitable
volt-ampere tester (Fig. 3).
CAUTION: Before performing any starter tests, the
ignition and fuel systems must be disabled.
(1) Check battery before performing this test. Bat-
tery must be fully charged.
(2) Connect a volt-ampere tester to the battery ter-
minals. Refer to the operating instructions provided
with the tester being used.
Fig. 3 Volt Ampere Tester
RSSTARTING8F-33
STARTING (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com